Cu-Sn Electrocatalyst Prepared with Chemical Foaming and Electroreduction for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
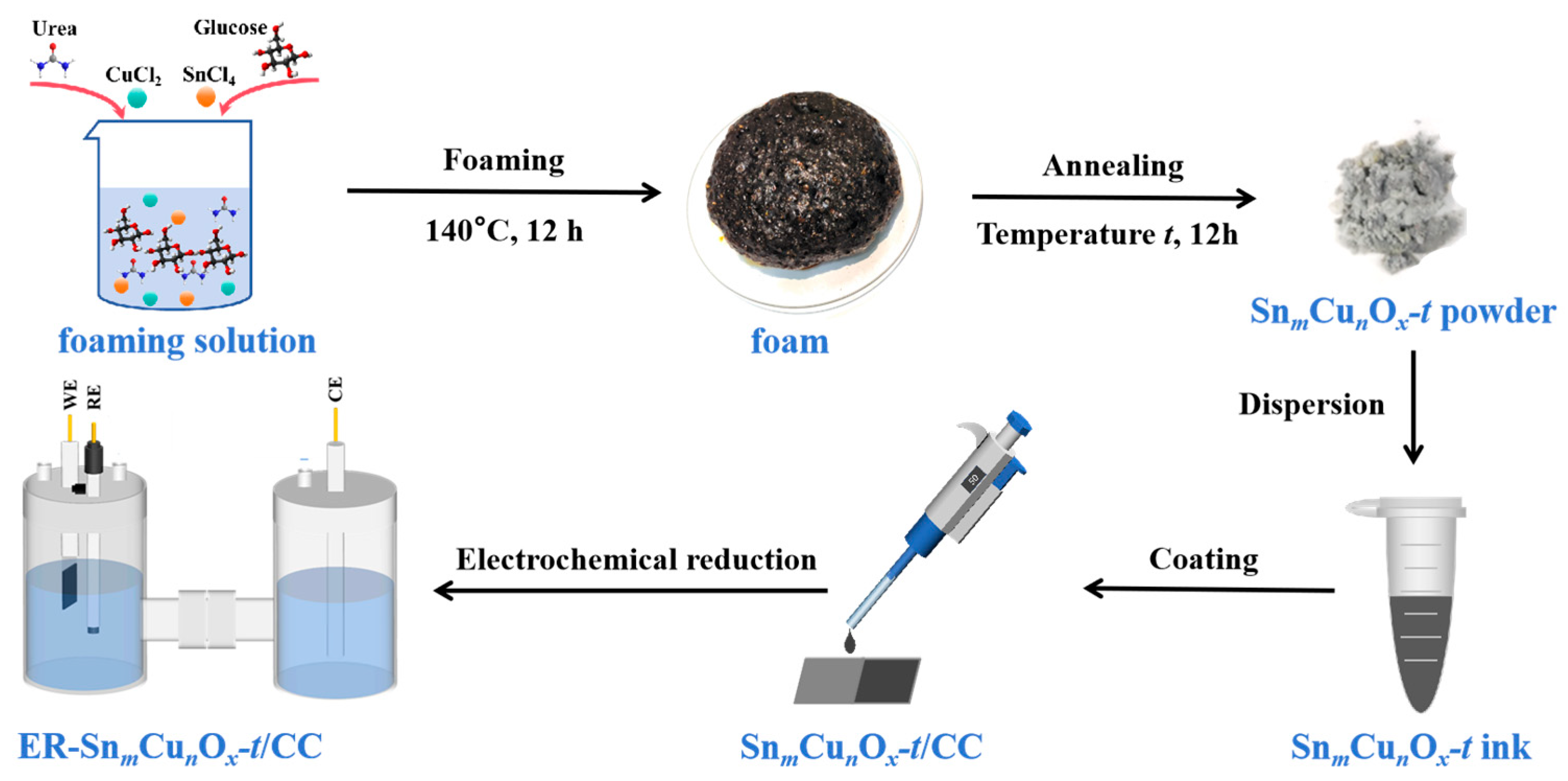
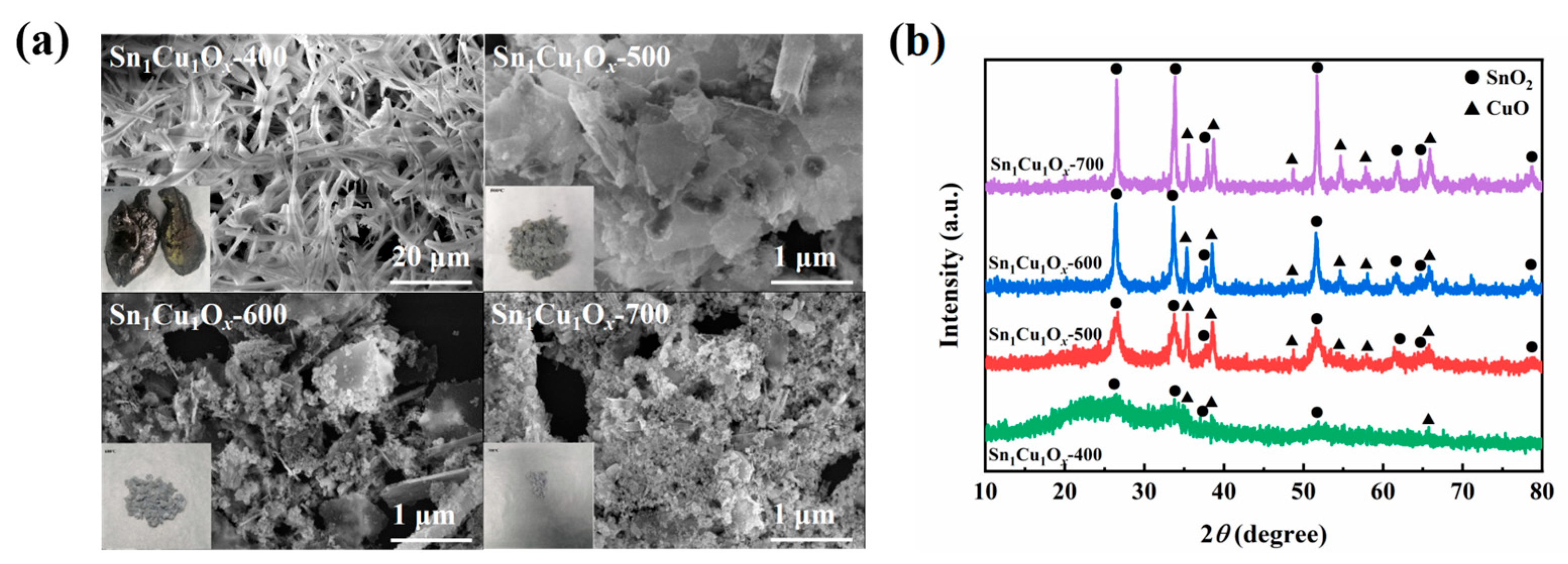
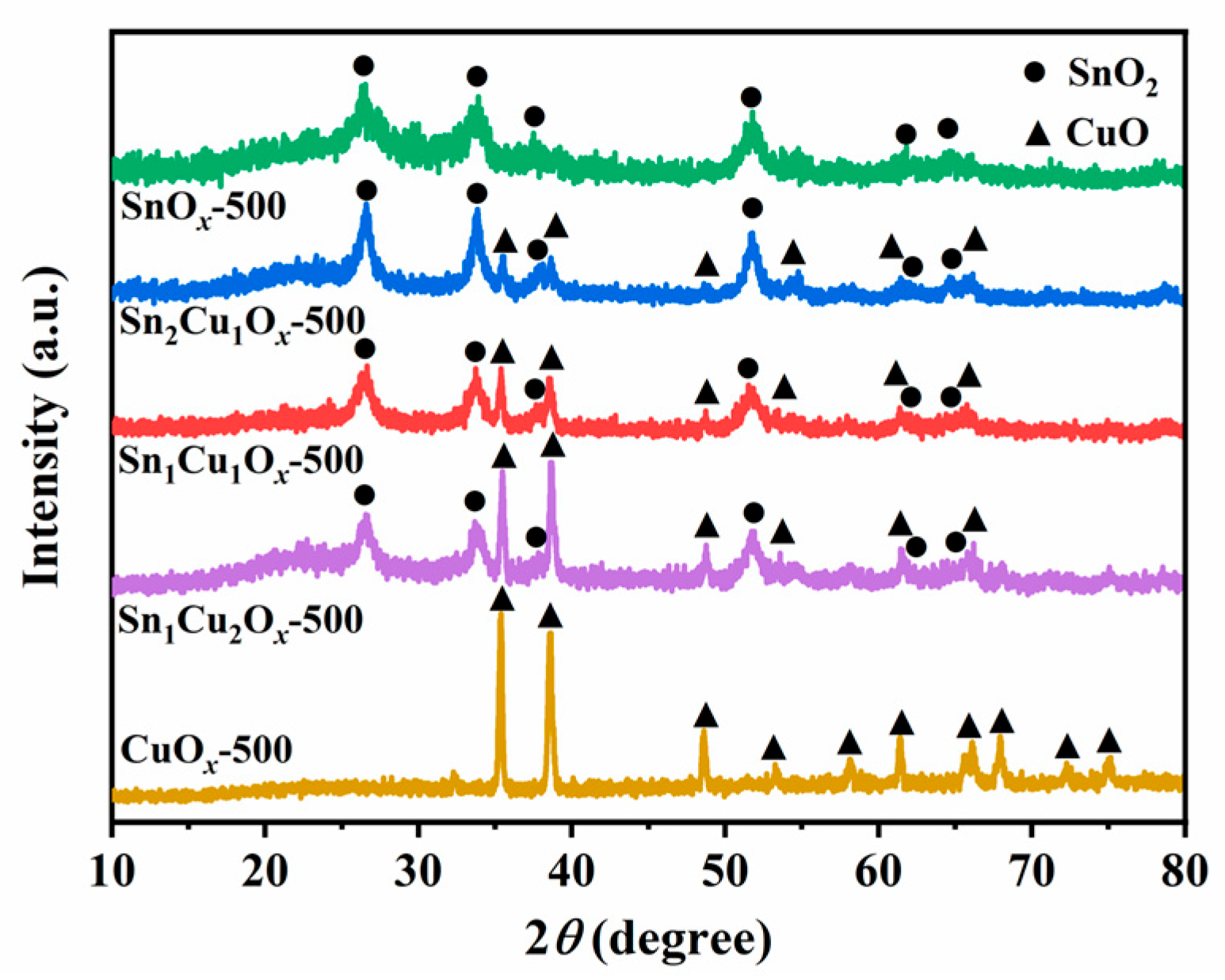
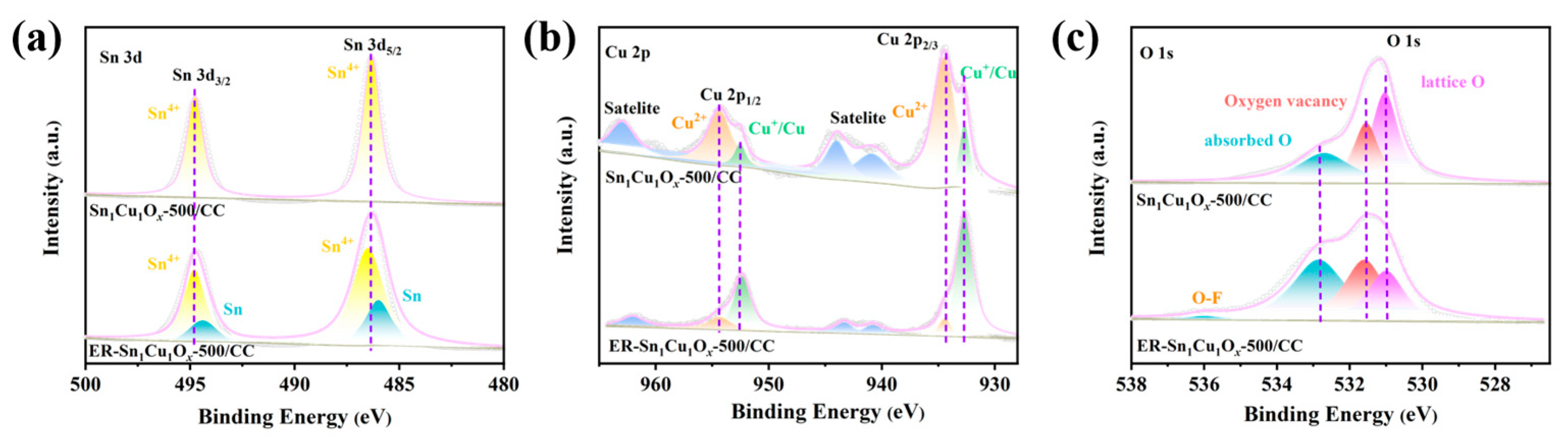
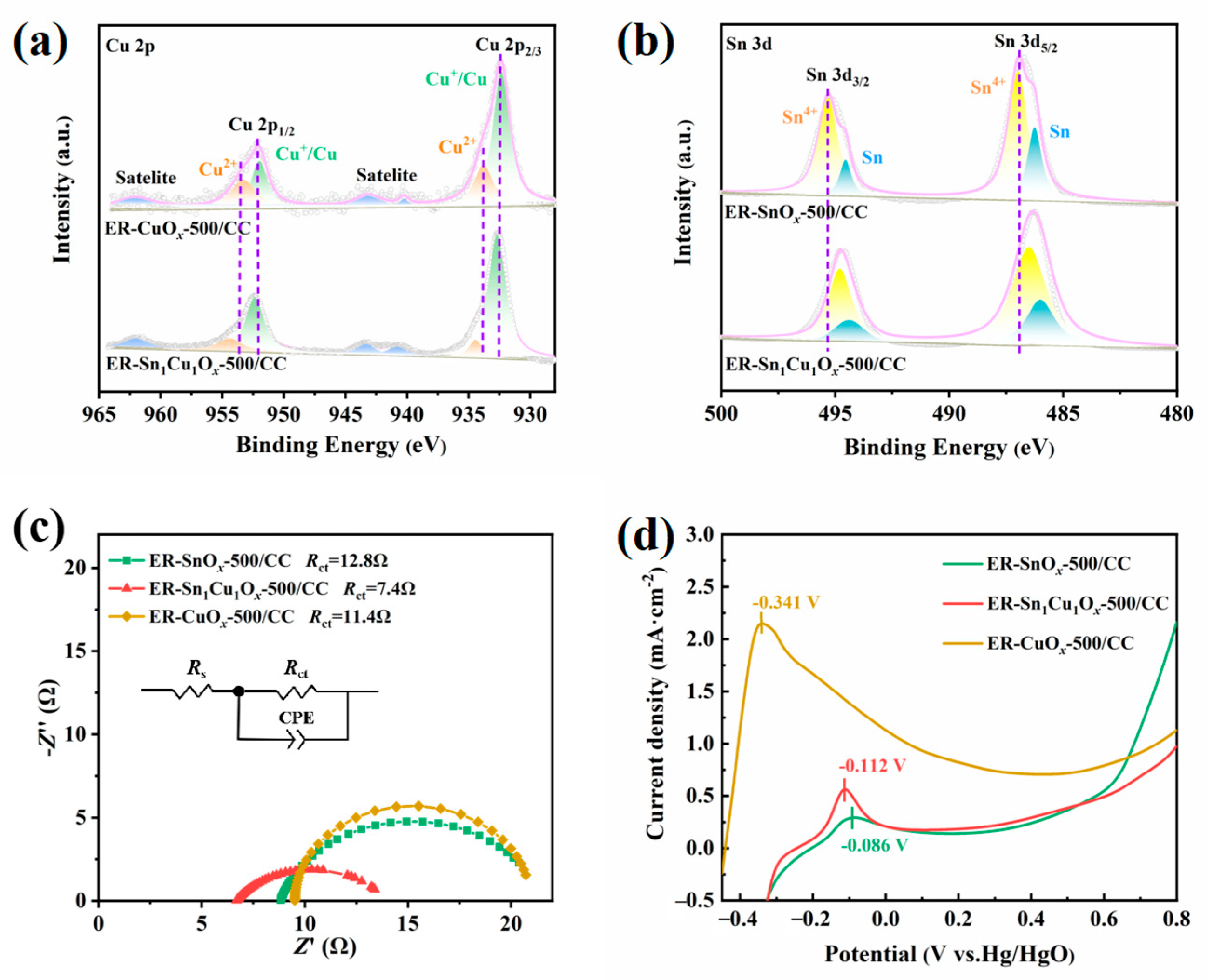
2.1. Synthesis and Characterizations of Catalysts
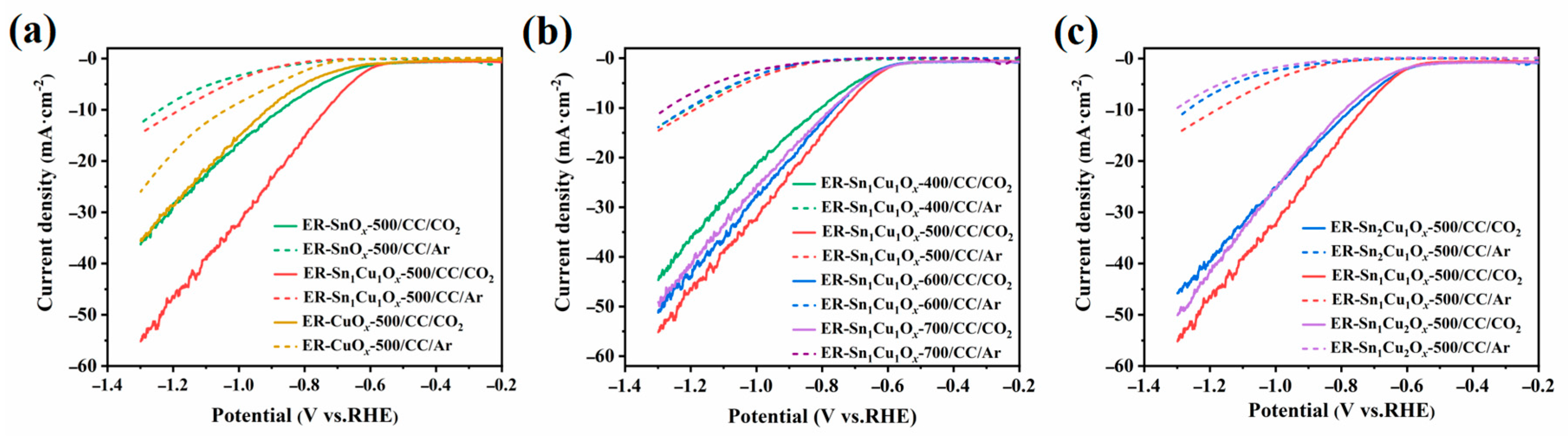
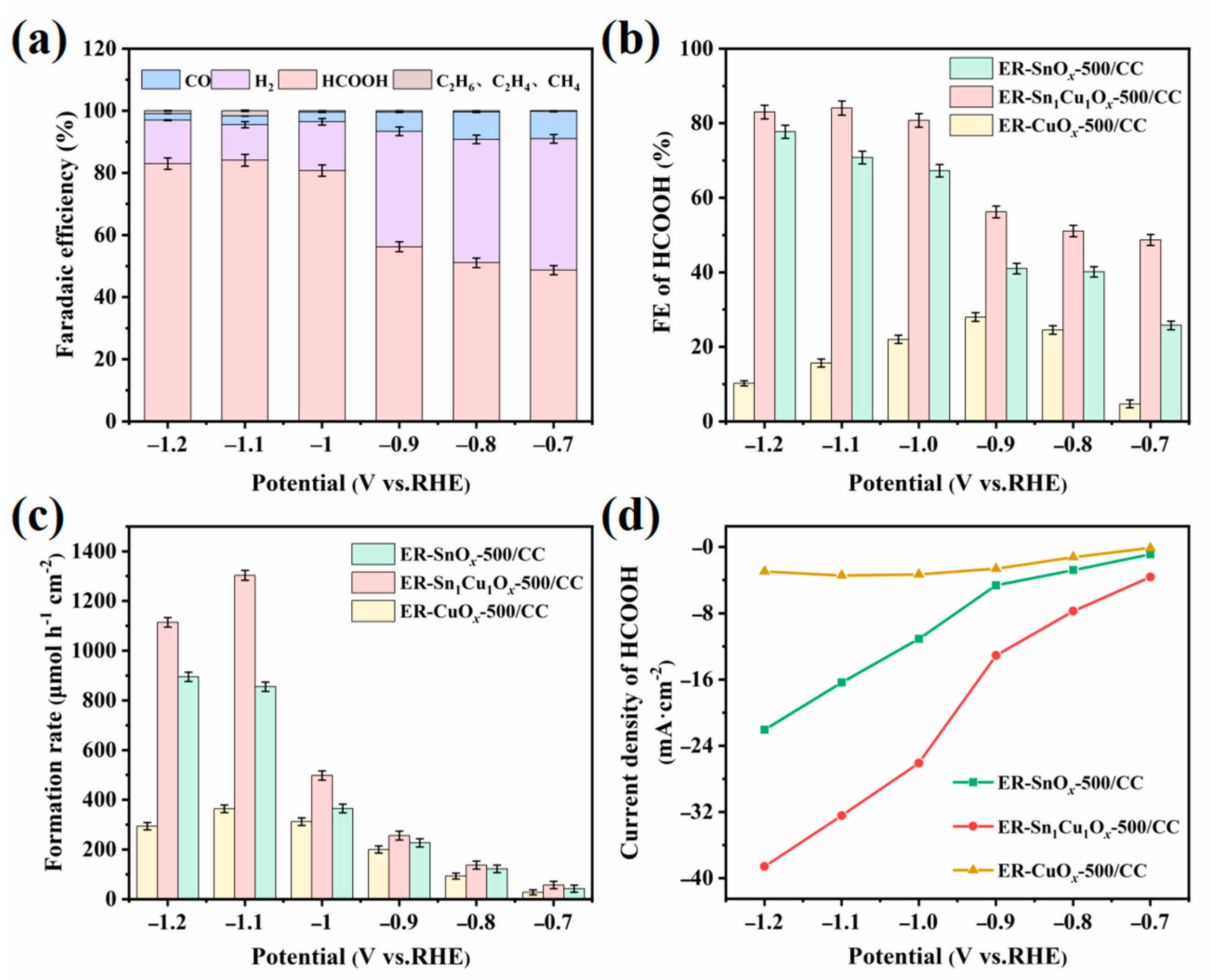
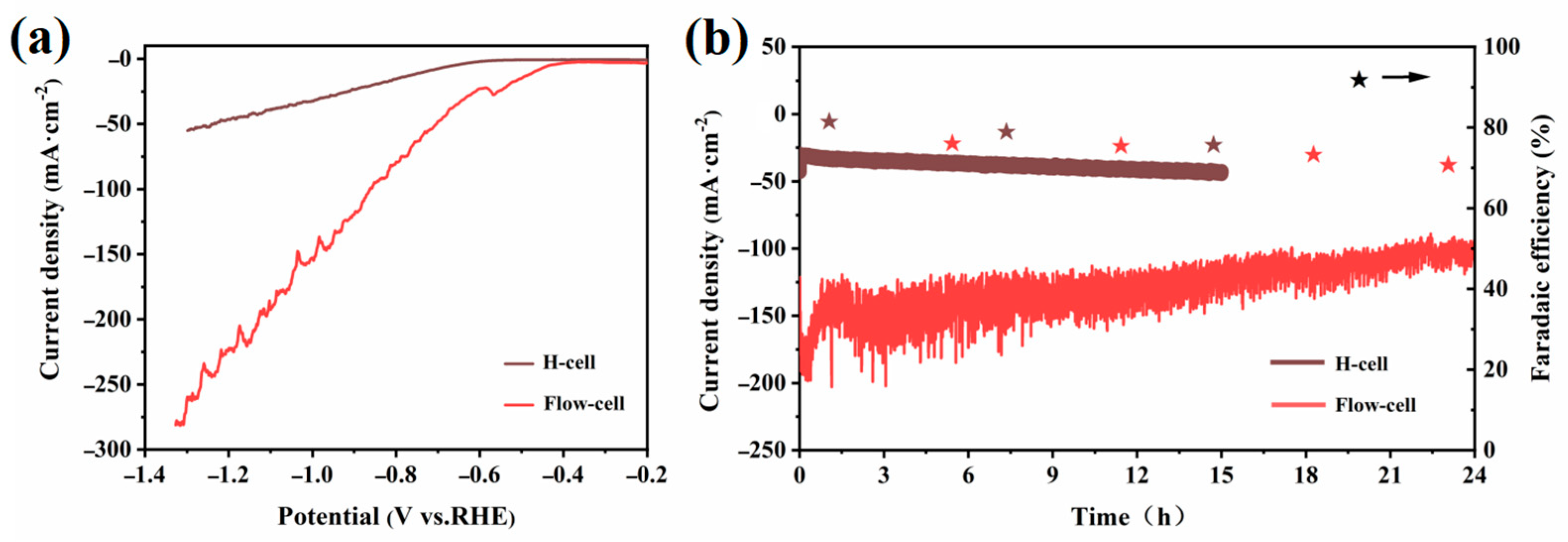
2.2. Electrocatalytic CO2RR Performance of the Catalysts
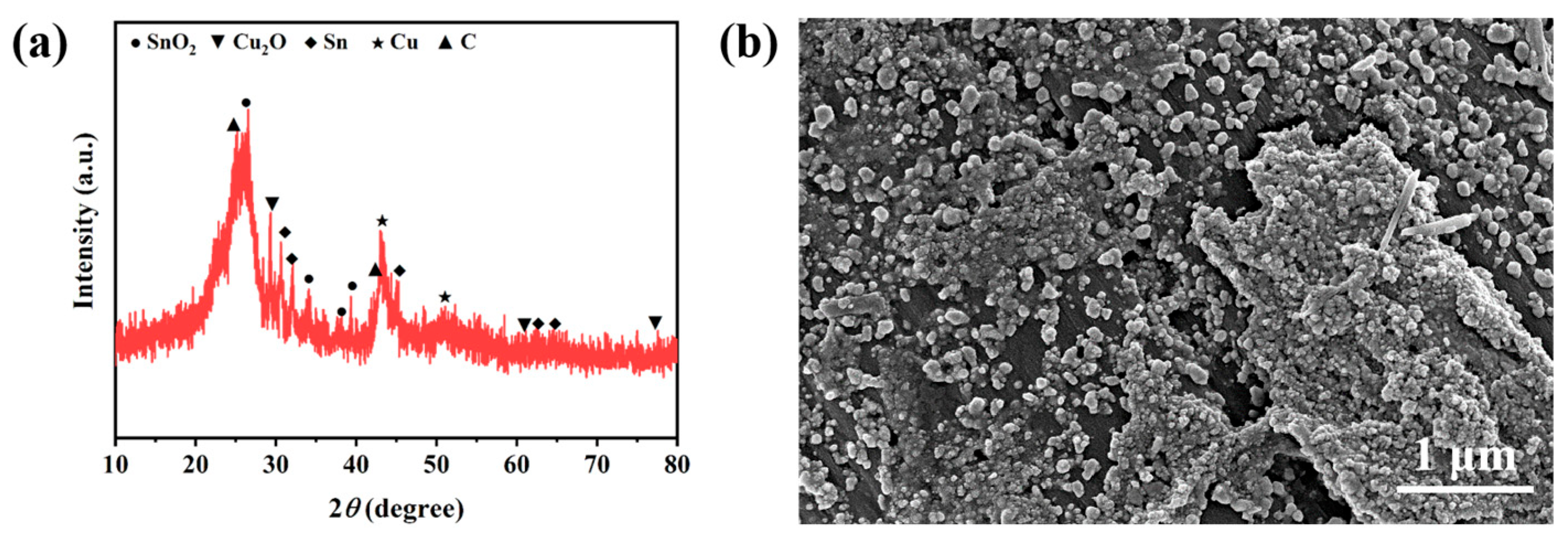
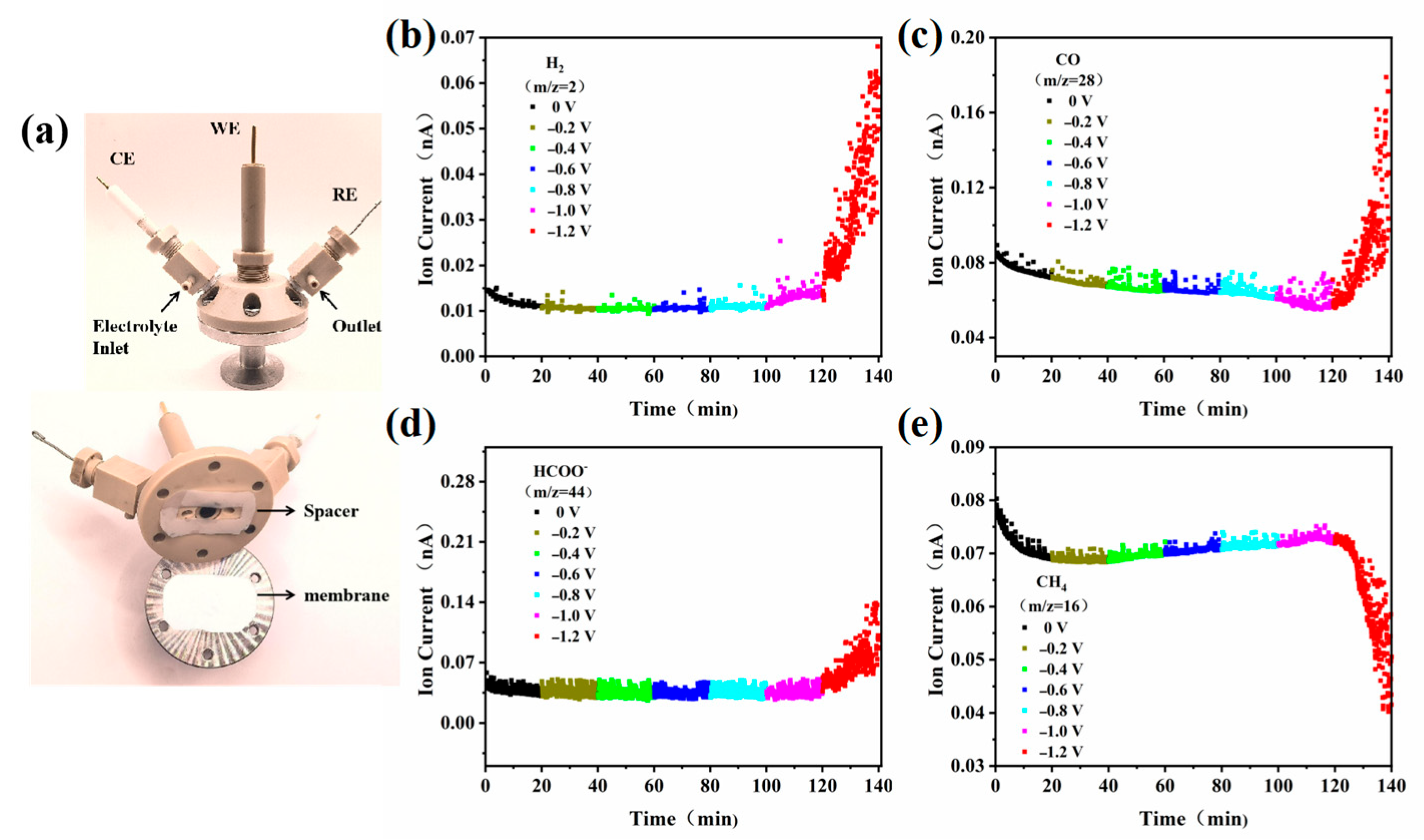
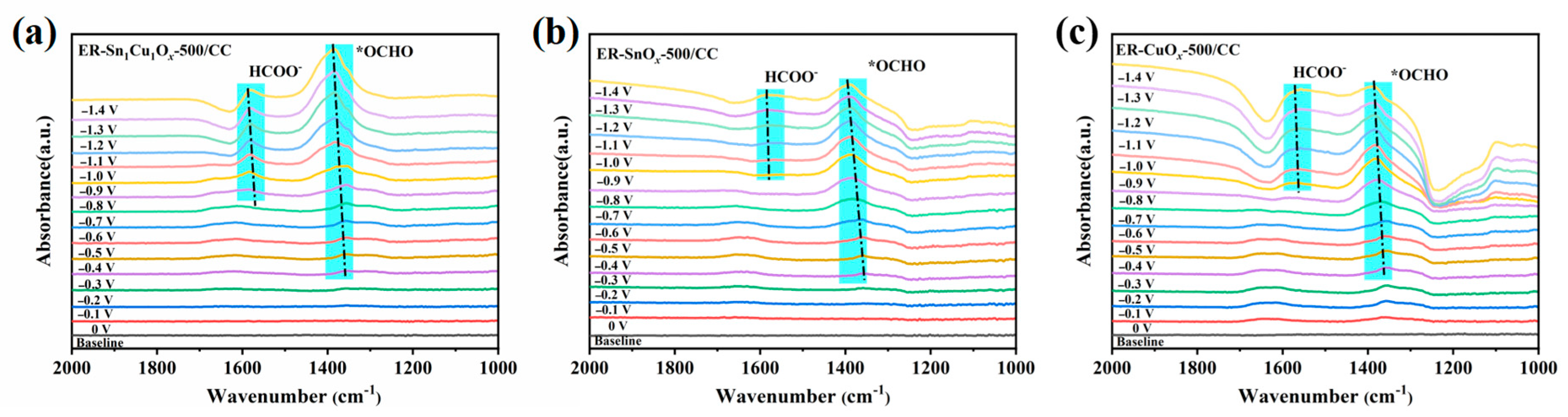
2.3. Electrocatalytic Mechanism Study of ECO2RR
3. Experiments and Methods
3.1. Preparation of SnmCunOx-t
3.2. Fabrication of ER-SnmCunOx-t/CC
3.3. Characterization
3.4. Electrochemical Measurements
3.5. Product Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Houghton, R. Global carbon budgets and the role of remote sensing. Remote Sens. Handb. 2024, 4, 395–422. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Wang, L.; Geng, R.; Li, J.; Zhang, C.; Lu, F. Comparison of international low-carbon and sustainable district evaluation systems and the implications for China. EDP Sci. 2025, 618, 3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, P.; Yuan, T.; Cheng, D.; Zhen, S.; Gao, H.; Wang, T.; Zhao, Z.; Gong, J. Modulation of *CHxO adsorption to facilitate electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to CH4 over Cu-based catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 6622–6627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, G.; Wang, Y.; Sun, M.; Zhang, H.; Li, L.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Cui, X.; Lo, T.; Huang, B. Size effects of highly dispersed bismuth nanoparticles on electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide to formic acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 14133–14142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Chen, S.; Bo, S.; Fan, W.; Li, J.; Jia, C.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Q.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, F. Single atom Bi decorated copper alloy enables C−C coupling for electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 into C2+ products. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, 62, e202303048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, R.; Wu, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, L.; Wang, G.; Li, F.; Shi, Z. Progress in catalysts for formic acid production by electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide. Top. Curr. Chem. 2025, 383, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, N. Constructing strain in electrocatalytic materials for CO2 reduction reactions. Green Chem. 2024, 26, 4449–4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Guan, Z.; Chen, G.; Wu, J.; Pan, Y.; Guo, Y.; Yang, Z. Advances and strategies in the electrocatalytic conversion of carbon dioxide to valuable chemicals and fuels. Fuel 2024, 377, 132539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X. Research and significance of Electroenzymatic conversion of carbon dioxide. Appl. Comput. Eng. 2025, 123, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Chen, W. Carbon dioxide capture and conversion using metal-organic framework (MOF) materials: A comprehensive review. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.; Zhai, Y.; Mei, G.; Guo, W.; Fang, Z.; Jiao, L.; Zhu, Z.; Lu, X.; Tang, J. In situ generated controllable Ag0-Ag+ sites for enhanced eletroreduction of CO2 to CO. Electrochim. Acta. 2023, 470, 143328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Gao, X.; Tang, Z.; Li, S.; Hou, Z.; Wang, X.; Nie, K.; Xie, J. Engineering COBridge adsorption in Cu2O-TiO2 heterojunction catalyst for selective electrochemical CO2 reduction to ethanol. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2023, 6, 11448–11457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Qin, X.; Deng, C.; Cai, W.; Jiang, K. Electrocatalytic CO2 and HCOOH interconversion on Pd-based catalysts. Adv. Sens. Energy Mater. 2022, 1, 100007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Sun, S.; Liu, J.; Niu, Q.; Dong, L.; Huang, Q.; Liu, J.; Wang, R.; Xin, Z.; Zhang, D. Calixarene-functionalized stable bismuth oxygen clusters for specific CO2-to-HCOOH electroreduction. ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 14436–14444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Liu, C.; Guo, C.; Zhang, M.; Li, X.; Jiang, Q.; Xue, W.; Li, H.; Li, A.; Pao, C. Copper-catalysed exclusive CO2 to pure formic acid conversion via single-atom alloying. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2021, 16, 1386–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Wang, M.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, B.; Cui, B.; Chen, B.; Liu, T.; Zhang, X. Efficient electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to CO by Cu-doped carbon materials derived from ZIF-8. Chem. Select. 2024, 9, e202304917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Bao, K.; Huang, H.; Kang, Z. Highly selective conversion of carbon dioxide to methane by copper single atom electrocatalysts. ChemSusChem 2025, 18, e202401314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, H.; Luo, W.; Sherrell, P.; Chen, J.; Yang, J. Heterogeneous Single-atom catalysts for electrochemical CO2 reduction reaction. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2001848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Sainz, G.; Fernández-Caso, K.; Ávila-Bolívar, B.; Montiel, V.; Solla-Gullón, J.; Alvarez-Guerra, M.; Irabien, A. Advances in the development of innovative Bi-Sn-Sb-based gas diffusion electrodes for continuous CO2 electroreduction to formate. J. CO2 Util. 2025, 95, 103070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Caso, K.; Díaz-Sainz, G.; Álvarez-Guerra, M.; Irabien, A. Electroreduction of CO2: Advances in the continuous production of formic acid and formate. ACS Energy Lett. 2023, 8, 1992–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Zhao, H.; Li, T.; Luo, Y.; Fan, G.; Chen, G.; Gao, S.; Shi, X.; Lu, S.; Sun, X. Metal-based electrocatalytic conversion of CO2 to formic acid/formate. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2020, 8, 21947–21960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peña-Rodríguez, A.; Fernández-Caso, K.; Díaz-Sainz, G.; Álvarez-Guerra, M.; Montiel, V.; Solla-Gullón, J. Single-Pass Electrooxidation of glycerol on bismuth-modified platinum electrodes as an anodic process coupled to the continuous CO2 electroreduction toward formate. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 3671–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.; Ding, P.; He, L.; Li, Y.; Li, Y. Promises of main group metal-based nanostructured materials for electrochemical CO2 reduction to formate. Adv. Energy Mater. 2020, 10, 1902338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Sainz, G.; Álvarez-Guerra, M.; Irabien, A. Continuous electrochemical reduction of CO2 to formate: Comparative study of the influence of the electrode configuration with Sn and Bi-based electrocatalysts. Molecules 2020, 25, 4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Tamreh, S.A.; Ibrahim, M.H.; El-Naas, M.H.; Vaes, J.; Pant, D.; Benamor, A.; Amhamed, A. Electroreduction of carbon dioxide into formate: A comprehensive review. ChemElectroChem 2021, 8, 3207–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abarca, J.A.; Abdolhosseini, G.; Sanz, J.M.; Solla-Gullón, J.; Garcés-Pineda, F.A.; Díaz-Sainz, G.; Irabien, A. Coupling Ni-based anodes for textile industry process stream electrooxidation with electrocatalytic CO2 reduction to formate in gas phase. J. CO2 Util. 2025, 93, 103053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarah, P.; Haldar, D.; Yadav, V.; Purkait, M.K. Progress in the electrochemical reduction of CO2 to formic acid: A review on current trends and future prospects. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proietto, F.; Patel, U.; Galia, A.; Scialdone, O. Electrochemical conversion of CO2 to formic acid using a Sn based electrode: A critical review on the state-of-the-art technologies and their potential. Electrochim. Acta. 2021, 389, 138753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, Y.F.; Tan, Z.H.; Lum, Y. Engineering Sn-based catalytic materials for efficient electrochemical CO2 reduction to formate. ChemNanoMat 2021, 7, 380–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, N.; Shaikh, J.; Márquez, V.; Pathan, S.; Mali, S.; Patil, J.; Hong, C.; Kanjanaboos, P.; Fontaine, O.; Tiwari, A. New perspectives, rational designs, and engineering of Tin (Sn)-based materials for electrochemical CO2 reduction. Mater. Today Sustain. 2023, 22, 100384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, A.; Nørskov, J. Activity descriptors for CO2 electroreduction to methane on transition-metal catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2012, 3, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Lu, X.; Zhang, C.; Wei, Z.; Si, R.; Lu, T. Decorating graphdiyne on ultrathin bismuth subcarbonate nanosheets to promote CO2 electroreduction to formate. Sci. Bull. 2021, 66, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Cao, A.; Zheng, Q.; Fu, Y.; Wang, T.; Arul, K.; Chen, J.; Yang, B.; Adli, N.; Lei, L.; et al. Elucidation of the synergistic effect of dopants and vacancies on promoted selectivity for CO2 electroreduction to formate. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2005113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Yang, H.; Xu, Y.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Zhong, M.; Cheng, T.; Shao, Q. Synergized Cu/Pb core/shell electrocatalyst for high-efficiency CO2 reduction to C2+ liquids. ACS Nano 2020, 15, 1039–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Yang, H.; Guo, M.; Gao, M.; Zhang, E.; Tian, H.; Liang, Z.; Liu, X. Synthesis and characterization of (Cu, S) Co-doped SnO2 for electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to formate at low overpotential. ChemElectroChem 2018, 5, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiee, H.; Zhang, X.; Ge, L.; Hu, S.; Li, M.; Smart, S.; Zhu, Z.; Yuan, Z. Tuning the product selectivity of the Cu hollow fiber gas diffusion electrode for efficient CO2 reduction to formate by controlled surface Sn electrodeposition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 21670–21681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Huang, L.; Tian, Y.; Liu, T.; Zhen, L.; Feng, Y. Facile synthesis of porous Cu-Sn alloy electrode with prior selectivity of formate in a wide potential range for CO2 electrochemical reduction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 292, 120119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yang, J.; You, X.; Yan, J.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, X.; Dong, S. Electron fixation of Sn2+/Cu+ bimetallic catalyst on flexible carbon fiber cloth for highly converting gaseous CO2 to formate at moderate potential. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 2114–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Maiyalagan, T.; Wang, X. Review on recent progress in nitrogen-doped graphene: Synthesis, characterization, and its potential applications. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 781–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, S.; Kwon, W.S.; Hong, D.; Lee, T.; Oh, S.; Bae, D.; Kim, J.; Lim, S.; Joo, Y.; Nam, D. Thermodynamic Phase Control of Cu-Sn Alloy Electrocatalysts for Selective CO₂ Reduction. Nanoscale Horiz. 2024, 9, 2295–2305. [Google Scholar]
- Stojkov, S.; El-Nagar, G.A.; Firschke, F.; Pardo Pérez, L.; Choubrac, L.; Najdoski, M.; Mayer, M. Electrocatalyst derived from waste Cu-Sn bronze for CO₂ conversion into CO. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 38161–38169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Zhao, S.; Meng, H.; Han, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, B.; Shi, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R. RuCoOx nanofoam as a high-performance trifunctional electrocatalyst for rechargeable zinc-air batteries and water splitting. Nano Lett. 2021, 21, 9633–9641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, R.; Wang, J.; Wang, L.; Qin, Y.; Chen, P.; Hou, Z. Platinum supported on reduced graphene oxide as a catalyst for hydrogenation of nitroarenes. Carbon 2012, 50, 586–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Yang, L.; Deng, W.; Tan, Y.; Xie, Q. Macroporous graphitic carbon foam decorated with polydopamine as a high-performance anode for microbial fuel cell. J. Power Sources 2017, 363, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Qian, L.; Zheng, R.; Yang, D.; Lu, X. Elucidating mass transport within nanoporous Au for CO₂ electroreduction. Catalysts 2023, 13, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.; Kong, C.; King, A.; Babbe, F.; Prabhakar, R.; Kubiak, C.; Ager, J. Role of mass transport in electrochemical CO2 reduction to methanol using immobilized cobalt phthalocyanine. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2024, 7, 3091–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Hawks, S.; Horwood, C.; Biener, J.; Biener, M. Mitigating mass transport limitations: Hierarchical nanoporous gold flow-through electrodes for electrochemical CO2 reduction. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Sun, X.; Jia, S.; Han, S.; Yao, T.; Zhou, D.; Xie, Y.; Xia, W.; Wu, H.; Han, B. In situ formation of Cu-Sn bimetallic catalysts for CO2 electroreduction to formate with high efficiency. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2023, 13, 2303–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Li, X.; Kong, Y.; Deng, C.; Li, X.; Hu, Q.; Yang, H.; He, C. Oxidation State Modulation of bimetallic tin-copper oxide nanotubes for selective CO2 electroreduction to formate. Small 2022, 18, 2204148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, G.; Chen, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Yu, Y.; Yu, J. Oxygen vacancies in metal oxides: Recent progress towards advanced catalyst design. Sci. China Mater. 2020, 63, 2089–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Jin, S.; Park, S.; Kim, Y.; Jang, D.; Seo, M.H.; Kim, W. Plasma-induced oxygen vacancies in amorphous MnOx boost catalytic performance for electrochemical CO2 reduction. Nano Energy 2021, 79, 105492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhi, K.; Park, D.; Al-Bahily, K.; Cha, W.; Viswanathan, B.; Choy, J.; Vinu, A. Mesoporous carbon nitrides: Synthesis, functionalization, and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 72–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sun, M.; Xu, H.; Hao, F.; Wa, Q.; Su, J.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, J.; Zhang, P. Coordination environment engineering of metal centers in coordination polymers for selective carbon dioxide electroreduction toward multicarbon products. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 7192–7203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Yang, P. Addressing the “alkalinity problem” in CO₂ electrolysis with catalyst design and translation. Joule 2021, 5, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Kwon, T.; Lee, Y. Tailoring the product selectivity of electrochemical CO2 reduction at copper-tin composite oxide nanofibers. J. Alloys Comp. 2025, 1013, 178574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabe, Y.; Ito, Y.; Hori, Y.; Kukunuri, S.; Shiokawa, F.; Nishiuchi, T.; Jeong, S.; Katagiri, K.; Xi, Z.; Li, Z.; et al. 1T/1H-SnS2 sheets for electrochemical CO2 reduction to formate. ACS Nano. 2023, 17, 11318–11326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, L.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Xiao, C.; Chen, R.; Zhang, L.; Li, Y.; Li, C. Tunable selectivity on copper-bismuth bimetallic aerogels for electrochemical CO2 reduction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2022, 317, 121650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Yue, Y.; Wu, S.; Li, Z.; Huang, Q. Synchronous introduction of S into Cu3BiS3 bi-active sites catalyst for synergistic electrocatalysis towards the conversion of CO2 into HCOOH. Surf. Interfaces 2025, 56, 105538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Wu, M.; Xu, Y.; Wang, S.; Wang, D.; Wang, W.; Mitsuzaki, N.; Chen, Z. Electrodeposition of CuxBi1-x-MOF for electrochemical reduction of CO2. J. Solid State Chem. 2024, 338, 124804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, S.; Weng, Z.; Wu, Z.; Zhong, Y.; Wu, Y.; Fang, J.; Wang, H. Coupled metal/oxide catalysts with tunable product selectivity for electrocatalytic CO₂ reduction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 28519–28526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ji, Y.; Shao, Q.; Yin, R.; Guo, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, X. Phase and structure modulating of bimetallic CuSn nanowires boosts electrocatalytic conversion of CO₂. Nano Energy 2019, 59, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Xiong, Z.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y. Pd-doped tin oxide nanostructured catalysts for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide. Electrocatalysis 2025, 16, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Garcia-Esparza, A.; Lee, J.; Kang, G.; Shin, S.; Jeon, S.; Lee, H. Electrodeposited Sn-Cu@Sn dendrites for selective electrochemical CO2 reduction to formic acid. Nanoscale 2022, 14, 9297–9303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Hou, L.; Wei, X.; Liu, X.; Qin, Q. Enhancing the selectivity of CO2-to-HCOOH conversion by constructing tensile-strained Cu catalyst. Mater. Today Phys. 2023, 38, 101247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Chen, C.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Ding, H.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, X. Theoretical investigation of Cu-Au alloy for carbon dioxide electroreduction: Cu/Au ratio determining C1/C2 selectivity. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 8002–8009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Kang, P.; Jeon, S.; Lee, H. Electrochemically deposited Sn catalysts with dense tips on a gas diffusion electrode for electrochemical CO₂ reduction. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2020, 8, 9032–9038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Xie, S.W.; Liang, J.B.; Ma, B.Z.; Fu, J.N.; Wu, J.; Feng, Y.J.; Feng, Z.M. Structure regulated CuSn alloy catalyst for selective electrochemical CO₂-to-formate conversion at higher current densities. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2024, 340, 126545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Shao, J.; Li, H.; Xu, Q. Copper-tin bimetallic aerogel alloy for the electroreduction of CO2 to formate. New J. Chem. 2025, 49, 2201–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempasiddaiah, M.; Samanta, R.; Panigrahy, S.; Barman, S. Interface-rich highly oxophilic copper/tin-oxide nanocomposite on reduced graphene oxide for efficient electroreduction of CO2 to formate. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2023, 6, 3020–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, B.; Liu, M.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, C. Defect engineered SnO2 nanoparticles enable strong CO2 chemisorption toward efficient electroconversion to formate. Dalton Trans. 2022, 51, 3512–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Chen, S.; Wulan, B.; Zhang, J. Surface modification of SnO2 nanosheets via ultrathin N-doped carbon layers for improving CO2 electrocatalytic reduction. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 421, 130003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Shan, J.; Wang, P.; Huang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Qiao, S.-Z. Stabilizing oxidation state of SnO2 for highly selective CO2 electroreduction to formate at large current densities. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 3101–3108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Jiang, H. Advances in Sn-based oxide catalysts for the electroreduction of CO2 to formate. Green Carbon 2024, 2, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón, F.H.; Gonzalez, I.; Coaquira, J.; Hidalgo, P.; Brito, H.; Ardisson, J.; Macedo, W.; Morais, P. Structural and surface study of praseodymium-doped SnO2 nanoparticles prepared by the polymeric precursor method. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2016, 18, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Niu, K.; Zhang, L.; Tian, J.; Zhou, K.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Hong, M. Engineering oxygen vacancies in mesocrystalline CuO nanosheets for water oxidation. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 6135–6144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Catalyst | Cell | Electrolyte | Main Product | FE (%) | Current Density at Controlled Potential (mA·cm−2) | Controlled Potential (V vs. RHE) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CuSn2Oy | H-cell | 0.1 mol·L−1 KHCO3 | HCOOH | 90.0 | 3.0 | −1.1 | [55] |
| 1T/1H-SnS2 | H-cell | 0.1 mol·L−1 KHCO3 | HCOOH | 63.3 | 11.0 | −1.31 | [56] |
| Cu1Sn3-CC | H-cell | 0.5 mol·L−1 KHCO3 | HCOOH | 91.4 | 13.79 | −0.8 | [57] |
| Cu3BiS3 | H-cell | 0.5 mol·L−1 KHCO3 | HCOOH | 88.8 | 25.48 | −0.99 | [58] |
| Cux/Bi1-x-BTC | H-cell | 0.1 mol·L−1 KHCO3 | HCOOH | 73.4 | 14.4 | −1.5 | [59] |
| CuOy/SnOx-CNT | H-cell | 0.1 mol·L−1 KHCO3 | HCOOH | 79.0 | 6.2 | −1.1 | [60] |
| CuSn NWs/C-Air | H-cell | 0.5 mol·L−1 KHCO3 | HCOOH | 87.0 | 21.8 | −1.1 | [61] |
| ER-Sn1Cu1Ox | H-cell | 0.5 mol·L−1 KHCO3 | HCOOH | 84.1 | 32.4 | −1.1 | This work |
| 0.5 Pd/SnO2 | Flow cell | 1 mol·L−1 KOH | HCOOH | 63.0 | 90.59 | −1.2 | [62] |
| Sn-Cu@Sn | Flow cell | 1.0 mol·L−1 KHCO3 | HCOOH | 84.2 | 30.0 | −0.68 | [63] |
| In2O3/Cu | Flow cell | 0.5 mol·L−1 KHCO3 | HCOOH | 87.5 | 70.0 | −1.4 | [64] |
| PEI–Sn/Cu foam | Flow cell | 0.5 mol·L−1 KHCO3 | HCOOH | 92.3 | 57.1 | −0.97 | [65] |
| SnDT | Flow cell | 1.0 mol·L−1 KHCO3 | HCOOH | 62.5 | 18.7 | −0.76 | [66] |
| CuSn4 | Flow cell | 0.5 mol·L−1 KHCO3 | HCOOH | 69.0 | 61.0 | −1.1 | [67] |
| ER-Sn1Cu1Ox | Flow cell | 0.5 mol·L−1 KHCO3 | HCOOH | 70.0 | 192.5 | −1.1 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, C.; Yu, A.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wu, Z.; Xu, M.; Qu, D.; Duan, J.; Li, X. Cu-Sn Electrocatalyst Prepared with Chemical Foaming and Electroreduction for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction. Catalysts 2025, 15, 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15050484
Zhu C, Yu A, Zhang Y, Chen W, Wu Z, Xu M, Qu D, Duan J, Li X. Cu-Sn Electrocatalyst Prepared with Chemical Foaming and Electroreduction for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction. Catalysts. 2025; 15(5):484. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15050484
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Caibo, Ao Yu, Yin Zhang, Wenbo Chen, Zhijian Wu, Manni Xu, Deyu Qu, Junxin Duan, and Xi Li. 2025. "Cu-Sn Electrocatalyst Prepared with Chemical Foaming and Electroreduction for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction" Catalysts 15, no. 5: 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15050484
APA StyleZhu, C., Yu, A., Zhang, Y., Chen, W., Wu, Z., Xu, M., Qu, D., Duan, J., & Li, X. (2025). Cu-Sn Electrocatalyst Prepared with Chemical Foaming and Electroreduction for Electrochemical CO2 Reduction. Catalysts, 15(5), 484. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15050484







