Detection of Dopamine Using Hybrid Materials Based on NiO/ZnO for Electrochemical Sensor Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
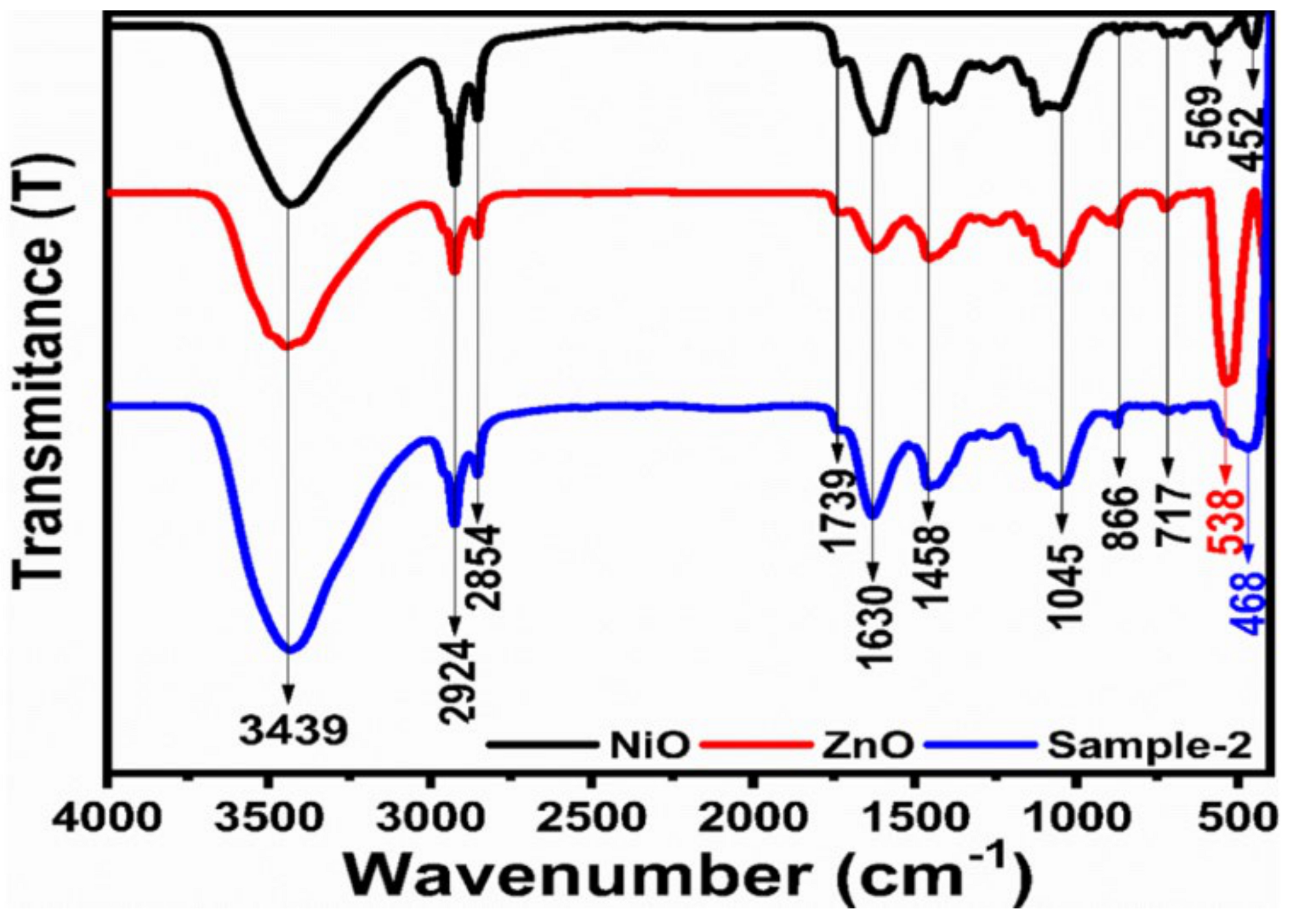
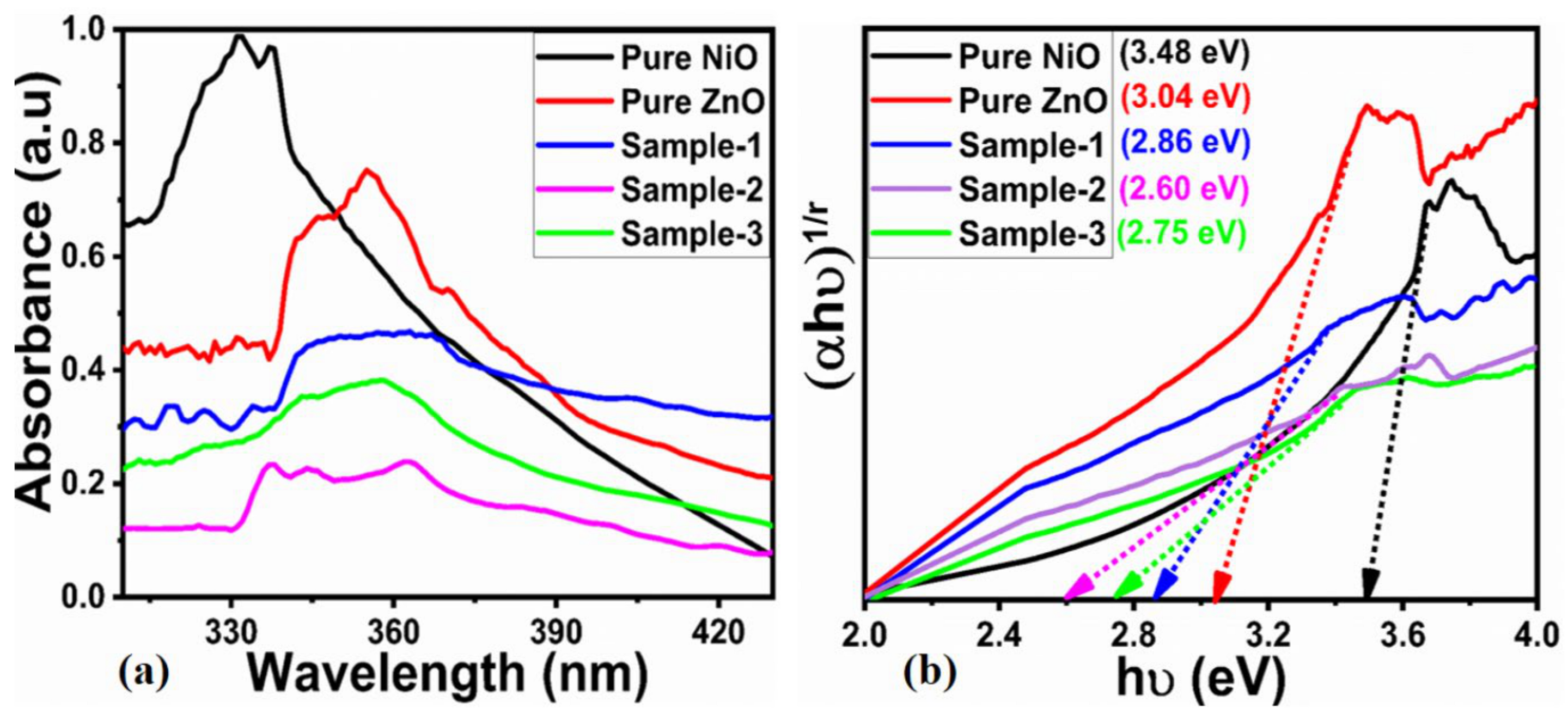
2.1. Crystal Quality, Morphology and Chemical Bonding Investigation NiO/ZnO Composites
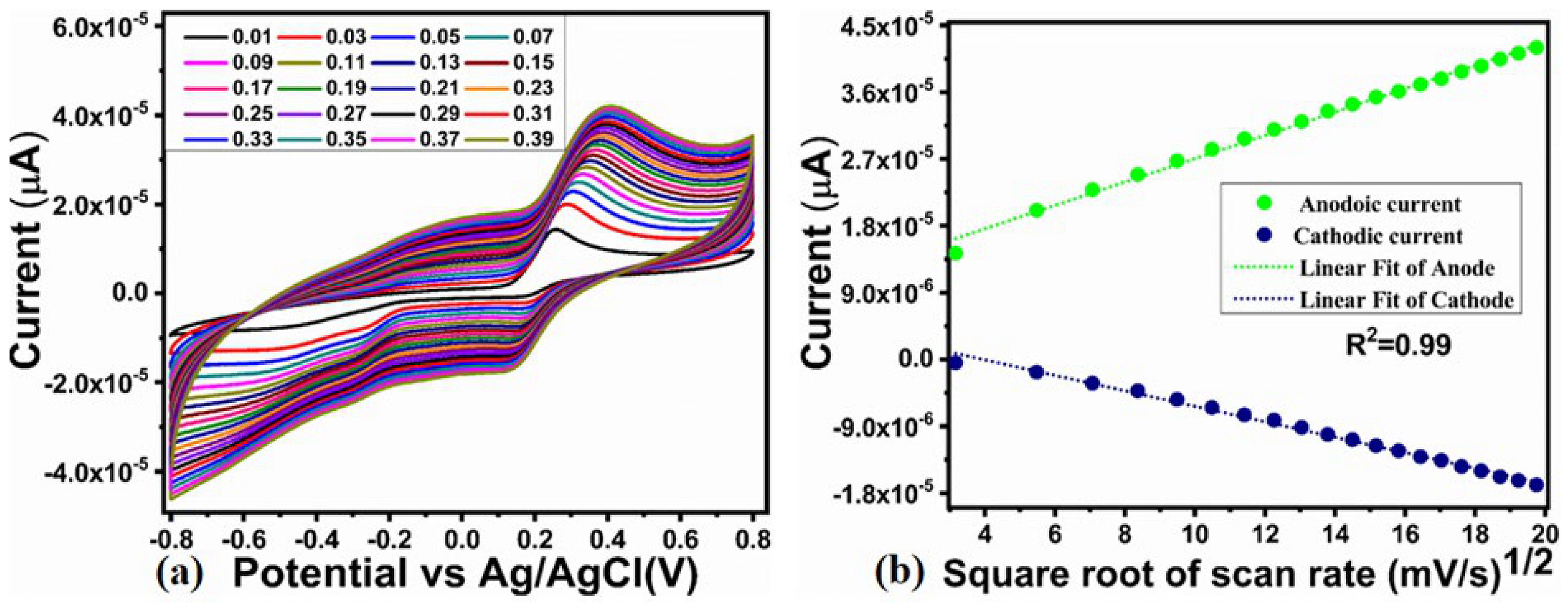
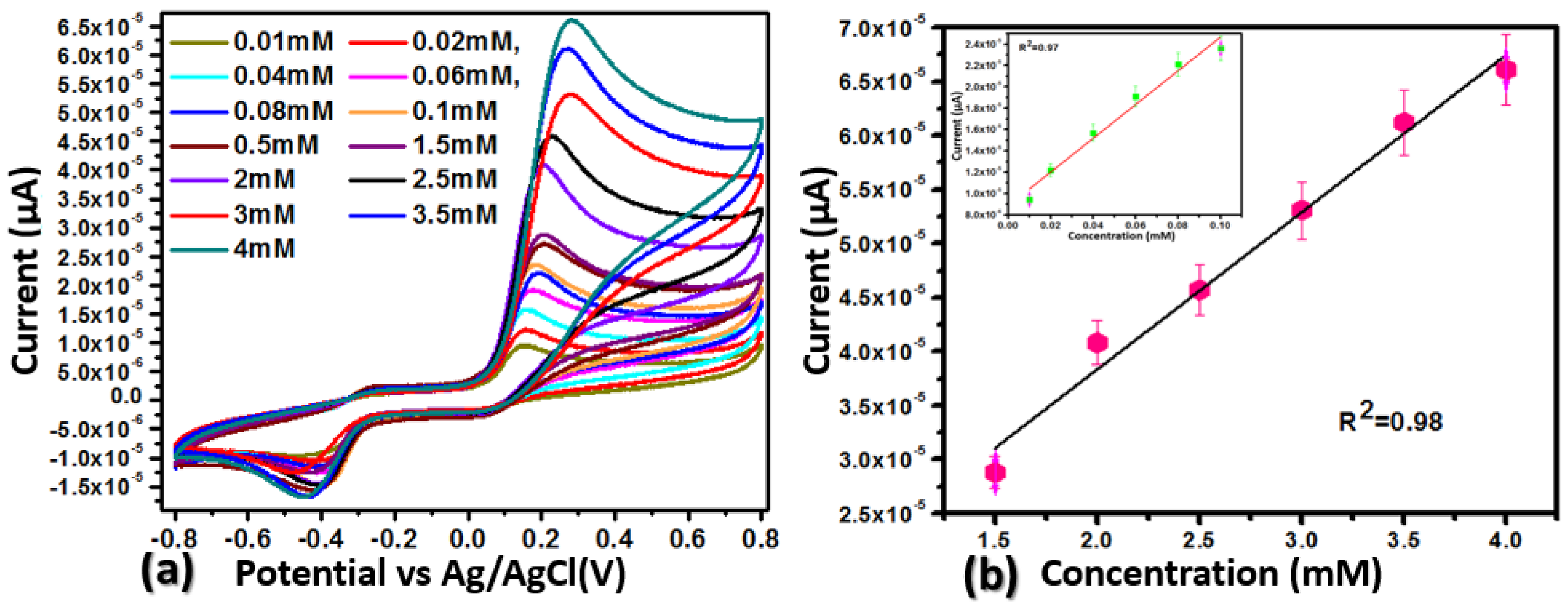
2.2. Enzyme-Free Dopamine Sensor Hybrid Materials Based on NiO/ZnO
3. Used Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical Reagents
3.2. Hydrothermal Preparation of NiO/ZnO Using Date Fruit Juice as Natural Reducing and Surface Modifying Gent
3.3. Electrochemical Measurements for the Non-Enzymatic Sensor for Dopamine
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eddin, F.B.K.; Fen, Y.W. Recent Advances in Electrochemical and Optical Sensing of Dopamine. Sensors 2020, 20, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, L.; Qian, C.-G.; Xiao, X.; Han, X.; Shen, Q.-D. Near-Infrared Fluorescent Nanoprobes for Revealing the Role of Dopamine in Drug Addiction. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 4359–4368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitton, A.E.; Reinen, J.M.; Slifstein, M.; Ang, Y.-S.; McGrath, P.J.; Iosifescu, D.V.; Abi-Dargham, A.; Pizzagalli, D.A.; Schneier, F.R. Baseline reward processing and ventrostriatal dopamine function are associated with pramipexole response in depression. Brain 2020, 143, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napier, T.C.; Kirby, A.; Persons, A.L. The role of dopamine pharmacotherapy and addiction-like behaviors in Parkinson’s disease. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 102, 109942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katthagen, T.; Kaminski, J.; Heinz, A.; Buchert, R.; Schlagenhauf, F. Striatal Dopamine and Reward Prediction Error Signaling in Unmedicated Schizophrenia Patients. Schizophr. Bull. 2020, 46, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Kaminga, A.C.; Wen, S.W.; Wu, X.; Acheampong, K.; Liu, A. Dopamine and Dopamine Receptors in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinay, M.M.; Arthoba Nayaka, Y. Iron oxide (Fe2O3) nanoparticles modified carbon paste electrode as an advanced material for electrochemical investigation of paracetamol and dopamine. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2019, 4, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, M.; Xing, Y.; Liu, G.; Hou, S.; Hou, S. Electrochemical sensor based on Ti3C2 membrane doped with UIO-66-NH2 for dopamine. Microchim. Acta 2022, 189, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaidukevic, J.; Aukstakojyte, R.; Barkauskas, J.; Niaura, G.; Murauskas, T.; Pauliukaite, R. A novel electrochemical sensor based on thermally reduced graphene oxide for the sensitive determination of dopamine. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 592, 153257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostami, S.; Mehdinia, A.; Jabbari, A. Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of graphene nanoribbons for label-free colorimetric detection of dopamine. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 114, 111034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasheed, P.A.; Lee, J.-S. Recent advances in optical detection of dopamine using nanomaterials. Microchim. Acta 2017, 184, 1239–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roychoudhury, A.; Francis, K.A.; Patel, J.; Jha, S.K.; Basu, S. A decoupler-free simple paper microchip capillary electrophoresis device for simultaneous detection of dopamine, epinephrine and serotonin. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 25487–25495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iftikhar, I.; El-Nour, K.M.A.; Brajter-Toth, A. Detection of transient dopamine antioxidant radicals using electrochemistry in electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 249, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promsuwan, K.; Soleh, A.; Saisahas, K.; Saichanapan, J.; Kanatharana, P.; Thavarungkul, P.; Guo, C.; Li, C.M.; Limbut, W. Discrimination of dopamine by an electrode modified with negatively charged manganese dioxide nanoparticles decorated on a poly(3,4 ethylenedioxythiophene)/reduced graphene oxide composite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 597, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Li, D.; Ma, W.; Yang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, D. Preparation of a glassy carbon electrode modified with reduced graphene oxide and overoxidized electropolymerized polypyrrole, and its application to the determination of dopamine in the presence of ascorbic acid and uric acid. Mikrochim. Acta 2019, 186, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashed, M.A.; Ahmed, J.; Faisal, M.; Alsareii, S.A.; Jalalah, M.; Tirth, V.; Harraz, F.A. Surface modification of CuO nanoparticles with conducting polythiophene as a non-enzymatic amperometric sensor for sensitive and selective determination of hydrogen peroxide. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 31, 101998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Faisal, M.; Harraz, F.A.; Jalalah, M.; Alsareii, S.A. Porous silicon-mesoporous carbon nanocomposite based electrochemical sensor for sensitive and selective detection of ascorbic acid in real samples. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2021, 125, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Rashed, M.A.; Faisal, M.; Harraz, F.A.; Jalalah, M.; Alsareii, S.A. Novel SWCNTs-mesoporous silicon nanocomposite as efficient non-enzymatic glucose biosensor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 552, 149477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Faisal, M.; Harraz, F.A.; Jalalah, M.; Alsareii, S.A. Development of an amperometric biosensor for dopamine using novel mesoporous silicon nanoparticles fabricated via a facile stain etching approach. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2022, 135, 114952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarri, D.; Lombardo, S.; Lisci, R.; De Pascale, V.; Vieri, M. AgroBot Smash a Robotic Platform for the Sustainable Precision Agriculture. In Innovative Biosystems Engineering for Sustainable Agriculture, Forestry and Food Production; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 793–801. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, H.-H.; Hong, G.-L.; Lin, F.-L.; Liu, A.-L.; Xia, X.-H.; Chen, W. Colorimetric detection of urea, urease, and urease inhibitor based on the peroxidase-like activity of gold nanoparticles. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 915, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Chen, W. In Situ Growth of Surfactant-Free Gold Nanoparticles on Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots for Electrochemical Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide in Biological Environments. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 1903–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Ji, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, T. Electrodeposition synthesis of reduced graphene oxide–carbon nanotube hybrids on indium tin oxide electrode for simultaneous electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 106307–106314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Chen, M.; Diao, G. Calix[4,6,8]arenesulfonates Functionalized Reduced Graphene Oxide with High Supramolecular Recognition Capability: Fabrication and Application for Enhanced Host–Guest Electrochemical Recognition. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 828–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Lv, S.; Zhu, D.; Wu, T.; You, T. Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid at a nitrogen-doped carbon nanofiber modified electrode. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 11925–11932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-L.; Lee, H.-H.; Yang, J.-M.; Wu, C.-C. The simultaneous electrochemical detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine, and uric acid using graphene/size-selected Pt nanocomposites. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3450–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ying, Y. Simultaneous determination of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid using high-performance screen-printed graphene electrode. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 34, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, S.; Tahira, A.; Solangi, A.; Beni, V.; Morante, J.R.; Liu, X.; Falhman, M.; Mazzaro, R.; Ibupoto, Z.H.; Vomiero, A. A practical non-enzymatic urea sensor based on NiCo2O4 nanoneedles. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 14443–14451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.S.; Das, G.; Yoon, H.H. Nickel/cobalt oxide-decorated 3D graphene nanocomposite electrode for enhanced electrochemical detection of urea. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetti, N.P.; Malode, S.J.; Nayak, D.S.; Bagihalli, G.B.; Kalanur, S.S.; Malladi, R.S.; Reddy, C.V.; Aminabhavi, T.M.; Reddy, K.R. Fabrication of ZnO nanoparticles modified sensor for electrochemical oxidation of methdilazine. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 496, 143656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetti, N.P.; Bukkitgar, S.D.; Reddy, K.R.; Reddy, C.V.; Aminabhavi, T.M. ZnO-based nanostructured electrodes for electrochemical sensors and biosensors in biomedical applications. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 141, 111417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beitollahi, H.; Tajik, S.; Garkani Nejad, F.; Safaei, M. Recent advances in ZnO nanostructure-based electrochemical sensors and biosensors. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 5826–5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-H.; Chen, X.-J.; Li, W.-T.; Zhou, W.-H.; Guo, X.-C.; Kang, W.-Y.; Kou, D.-X.; Zhou, Z.-J.; Meng, Y.-N.; Tian, Q.-W.; et al. ZnO nanotubes supported molecularly imprinted polymers arrays as sensing materials for electrochemical detection of dopamine. Talanta 2018, 176, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weldekirstos, H.D.; Habtewold, B.; Kabtamu, D.M. Surfactant-Assisted Synthesis of NiO-ZnO and NiO-CuO Nanocomposites for Enhanced Photocatalytic Degradation of Methylene Blue Under UV Light Irradiation. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 832439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budhiraja, N.; Sharma, A.; Dahiya, S.; Parmar, R.; Vidyadharan, V. Synthesis and Optical Characteristics of Silver Nanoparticles on Different Substrates. Int. Lett. Chem. Phys. Astron. 2013, 19, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, A.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.-Q.; Xu, W.; Huo, J.; Li, R.-W.; Qiu, H.; Chen, M. Flexible supercapacitor electrodes fabricated by dealloying nanocrystallized Al-Ni-Co-Y-Cu metallic glasses. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 772, 164–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goharshadi, E.K.; Ding, Y.; Jorabchi, M.N.; Nancarrow, P. Ultrasound-assisted green synthesis of nanocrystalline ZnO in the ionic liquid [hmim][NTf2]. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2009, 16, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Li, W.; Abouelamaiem, D.I.; Xu, C.; Jiang, H.; Han, W.; He, G. Hollow Cu-doped NiO microspheres as anode materials with enhanced lithium storage performance. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 20963–20967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Xiao, H.; Gu, M.; Chen, Z.; Cao, L. Ultrasensitive label-free electrochemical immunosensor based on core-shell Au@PtNPs functionalized rGO-TEPA/PB nanocomposite for HBsAg detection. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 890, 115216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fayemi, O.E.; Adekunle, A.S.; Kumara Swamy, B.E.; Ebenso, E.E. Electrochemical sensor for the detection of dopamine in real samples using polyaniline/NiO, ZnO, and Fe3O4 nanocomposites on glassy carbon electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 818, 236–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, M.; Chen, J.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Huang, L.; Xiong, W.; Zhao, P.; Xie, Y.; Fei, J. A high-sensitive dopamine electrochemical sensor based on multilayer Ti3C2 MXene, graphitized multi-walled carbon nanotubes and ZnO nanospheres. Microchem. J. 2022, 178, 107410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sharma, G.; Kumar, A.; Shekh, M.I.; Stadler, F.J. Fabrication and characterization of Ni/Ag/Zn trimetal oxide nanocomposites and its application in dopamine sensing. Mater. Today Commun. 2021, 29, 102726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Ni, B.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Li, G. A simple and efficient voltammetric sensor for dopamine determination based on ZnO nanorods/electro-reduced graphene oxide composite. Surf. Interfaces 2021, 26, 101375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masood, T.; Asad, M.; Riaz, S.; Akhtar, N.; Hayat, A.; Shenashen, M.A.; Rahman, M.M. Non-enzymatic electrochemical sensing of dopamine from COVID-19 quarantine person. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 289, 126451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Faisal, M.; Alsareii, S.A.; Jalalah, M.; Harraz, F.A. A novel gold-decorated porous silicon-poly(3-hexylthiophene) ternary nanocomposite as a highly sensitive and selective non-enzymatic dopamine electrochemical sensor. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 931, 167403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Niu, B.; Guo, H.; Chen, Z. A high-activity Fe-based MOFs fabricated through ultrasound strategy for electrochemical sensor of heavy metal ions and dopamine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2024, 957, 118129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Ren, J.; Zhao, P.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Y.; Fei, J. A novel dopamine electrochemical sensor based on a β-cyclodextrin/Ni-MOF/glassy carbon electrode. Microchem. J. 2023, 194, 109328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



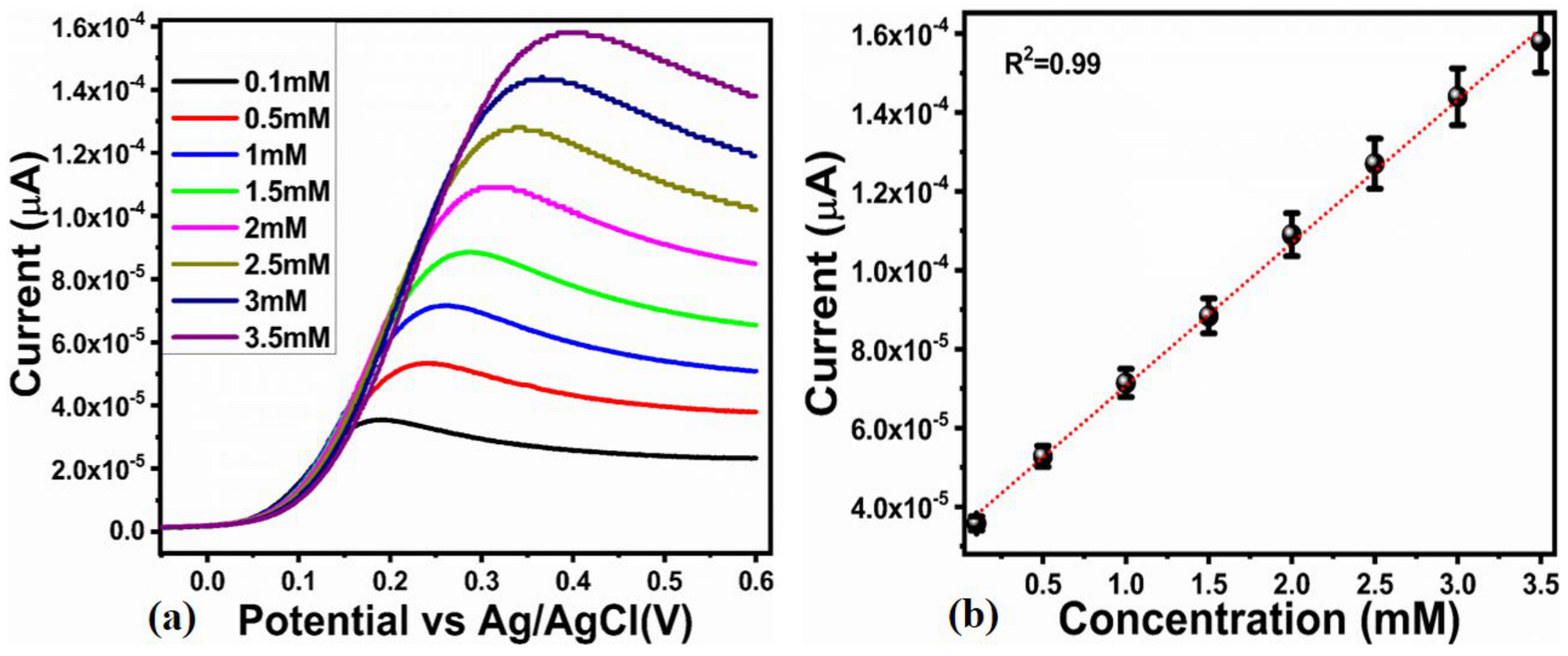


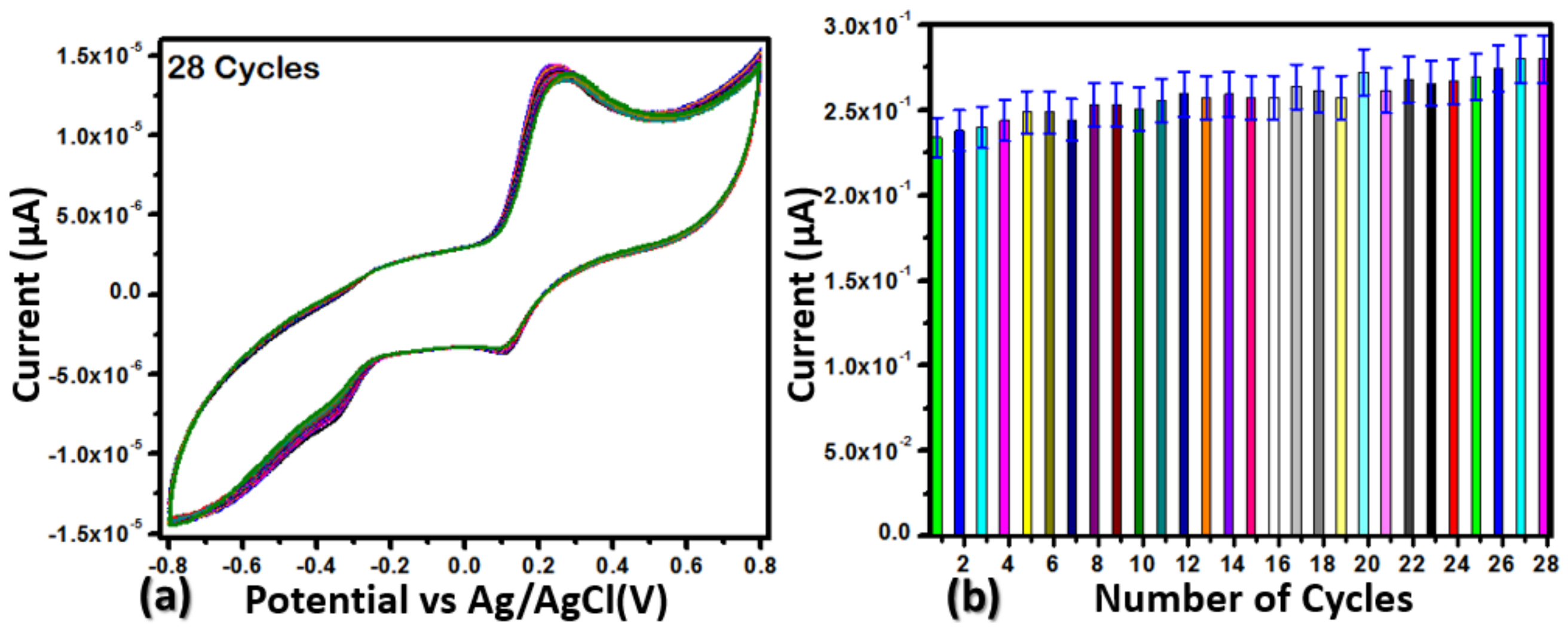
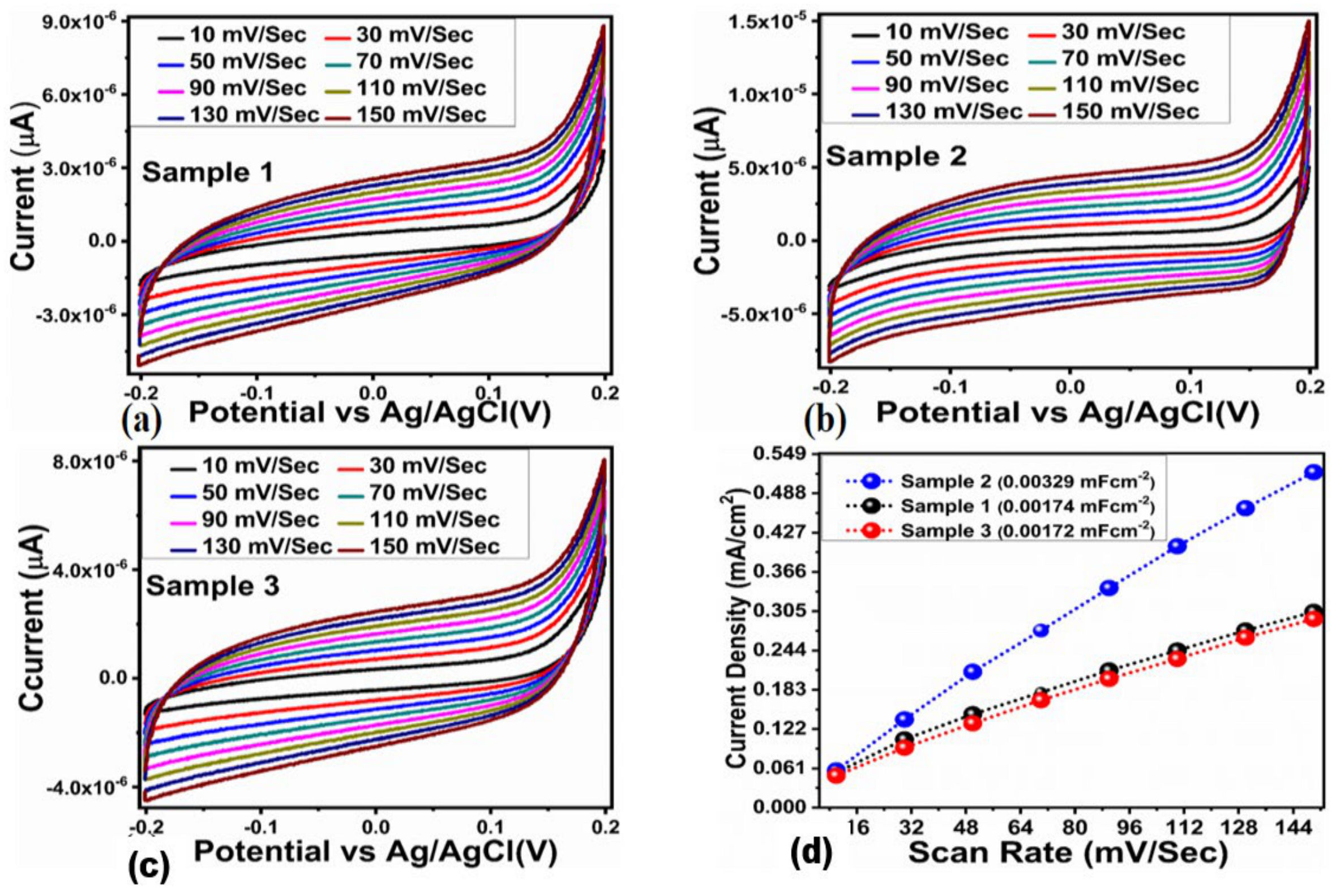

| Electrode Material | Linear Range (mM) | Limit of Detection (LOD μM) | Sensing Material | Method of Detection | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ZnO-rGO-AuNPs/SPE) | 0.5 μM to 100 μM | 0.294 μM | Dopamine | Non-Enzymatic | [39] |
| GCE/PANI-NiO, GCE/PANI-ZnO, and GCE/PANI-Fe3O4 sensors | 2.0 × 10−5 to 2.4 × 10−6 M | 0.153 × 10−7, 0.166 × 10−7, and 0.176 × 10−7 M | Dopamine | Non-Enzymatic | [40] |
| Ti3C2/G-MWCNTs/ZnO/GCE | 0.01–30 μM | 3.3 nM | Dopamine | Non-Enzymatic | [41] |
| Ni/Ag/Zn | 0.96 μA/μM cm2 | 0.3 μM | Dopamine | Non-Enzymatic | [42] |
| ZnONRs/ERGO/GCE | 0.01 to 6.0 μM and 6.0 to 80 μM | 3.6 nM | Dopamine | Non-Enzymatic | [43] |
| ZIF-67/PEDOT | 15–240 μM | 0.04 μM | Dopamine | Non-Enzymatic | [44] |
| Au/PSi-P3HT | 1.0–460 μM | ∼0.63 μM | Dopamine | Non-Enzymatic | [45] |
| NH2-MIL-101(Fe)/CPE | 0.3 to 450 μM | 0.025 μM | Dopamine | Non-Enzymatic | [46] |
| Ni–MOF | 0.7–310.2 μM | 0.227 μM | Dopamine | [47] | |
| NiO/ZnO/GCE | 0.01–4 mM | 0.03 μM | Dopamine | Non-Enzymatic | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naz, I.; Tahira, A.; Mallah, A.B.; Dawi, E.; Saleem, L.; Ibrahim, R.M.; Ibupoto, Z.H. Detection of Dopamine Using Hybrid Materials Based on NiO/ZnO for Electrochemical Sensor Applications. Catalysts 2025, 15, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15020116
Naz I, Tahira A, Mallah AB, Dawi E, Saleem L, Ibrahim RM, Ibupoto ZH. Detection of Dopamine Using Hybrid Materials Based on NiO/ZnO for Electrochemical Sensor Applications. Catalysts. 2025; 15(2):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15020116
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaz, Irum, Aneela Tahira, Arfana Begum Mallah, Elmuez Dawi, Lama Saleem, Rafat M. Ibrahim, and Zafar Hussain Ibupoto. 2025. "Detection of Dopamine Using Hybrid Materials Based on NiO/ZnO for Electrochemical Sensor Applications" Catalysts 15, no. 2: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15020116
APA StyleNaz, I., Tahira, A., Mallah, A. B., Dawi, E., Saleem, L., Ibrahim, R. M., & Ibupoto, Z. H. (2025). Detection of Dopamine Using Hybrid Materials Based on NiO/ZnO for Electrochemical Sensor Applications. Catalysts, 15(2), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15020116






