Pyrolysis of Corn Straw for In Situ Dechlorination of Bio-Oil Under the Catalysis of Acidified-γ-Al2O3 Modified with Alkaline and Alkaline Earth Metal Compounds
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
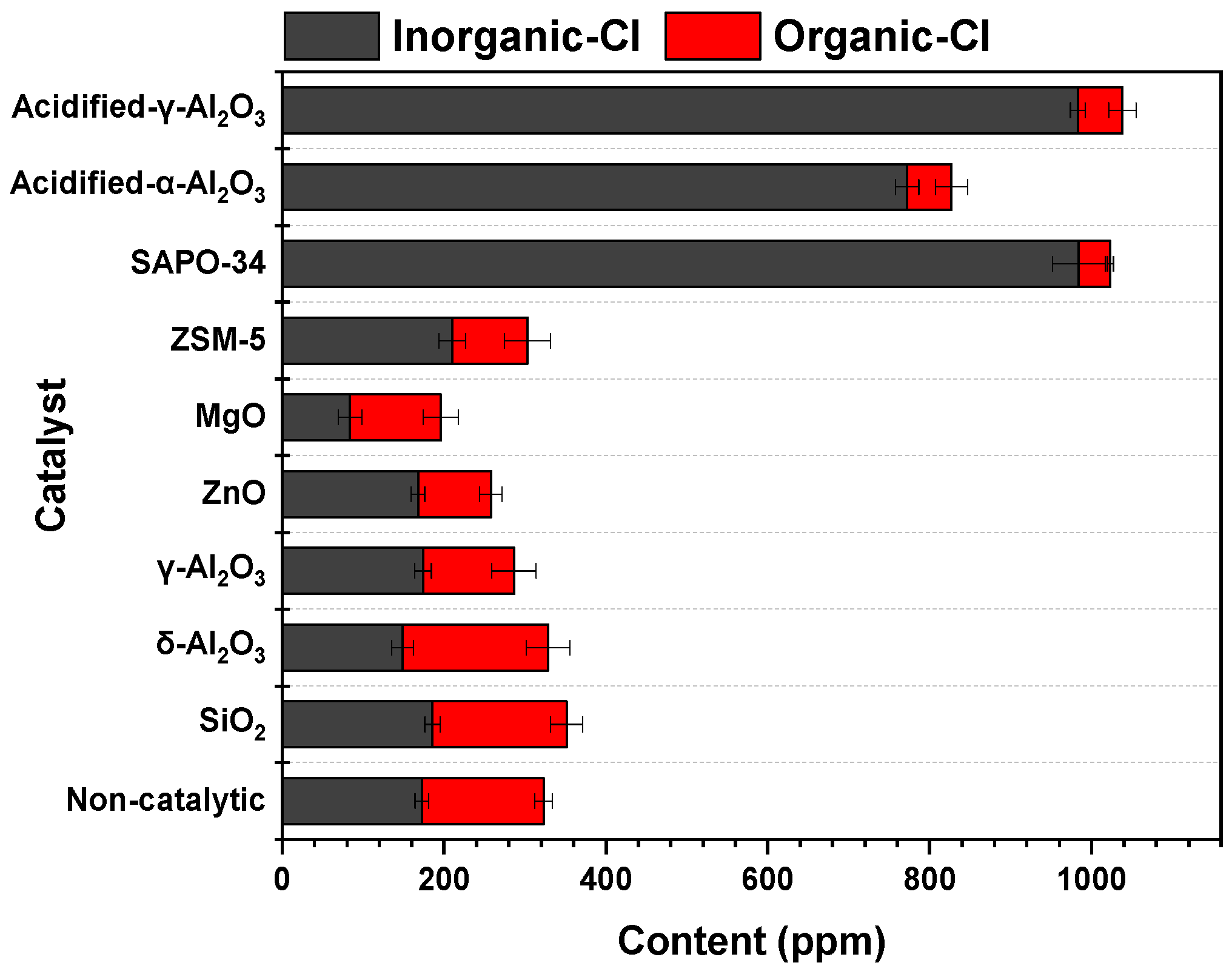
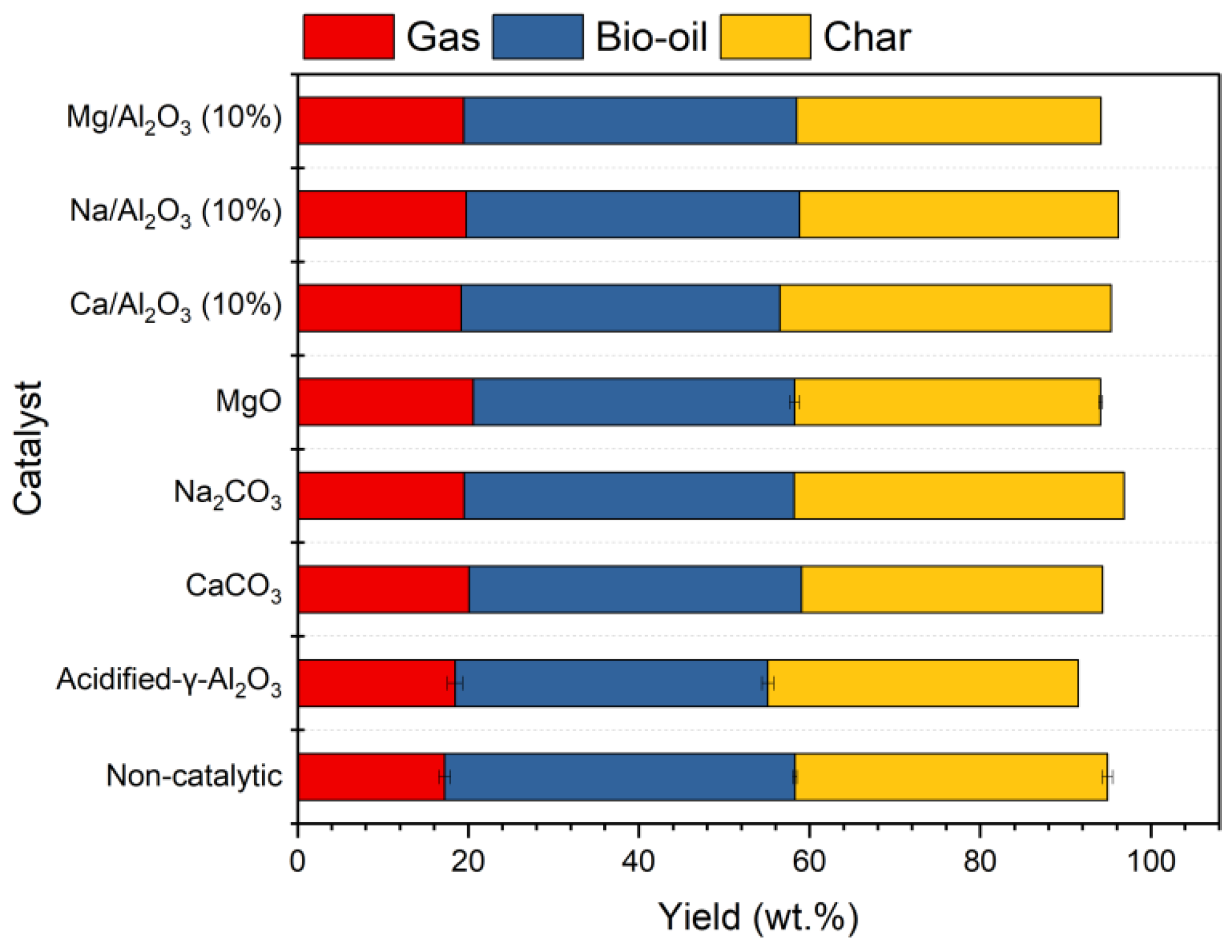
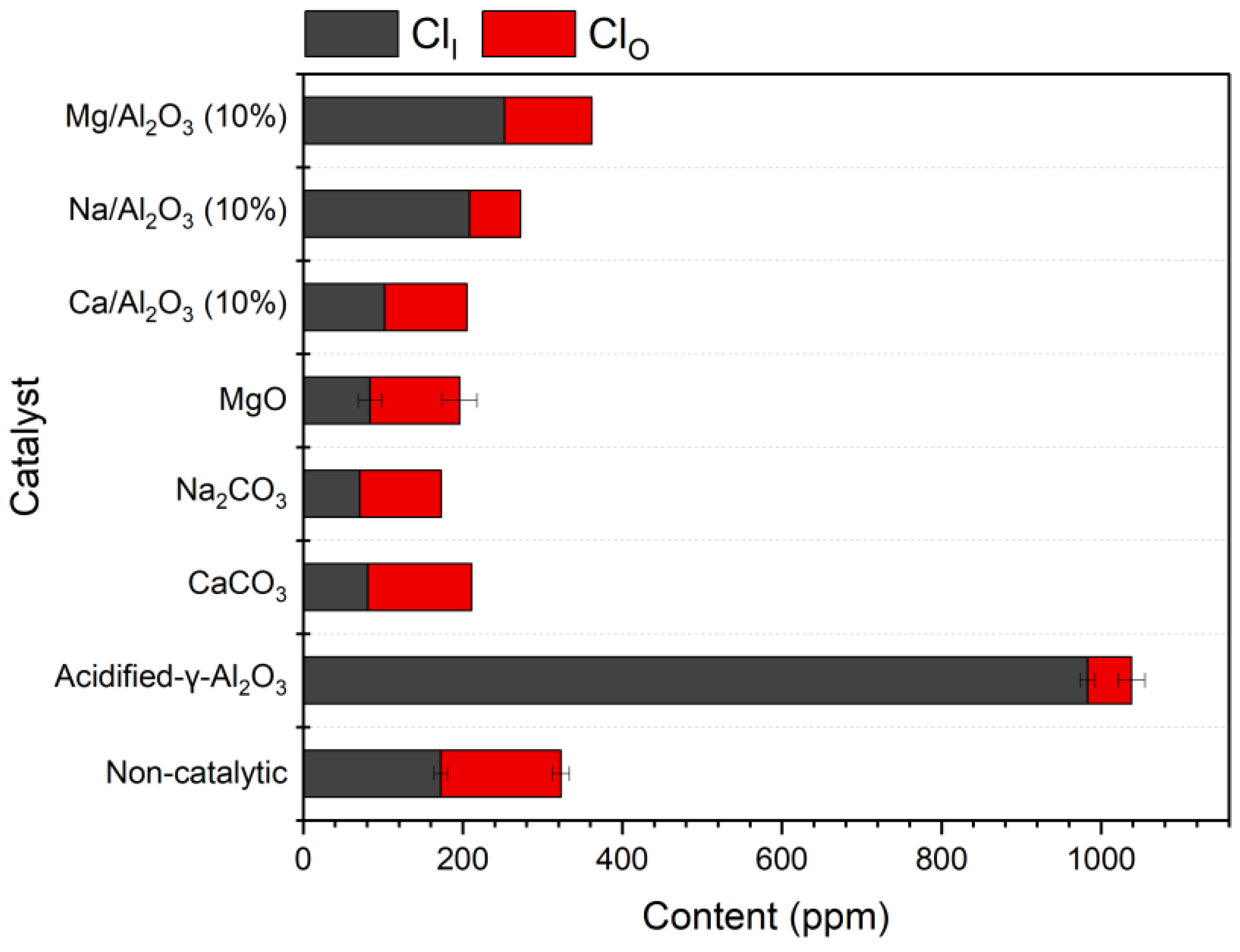
2.1. Comparison Among Different Types of Catalysts
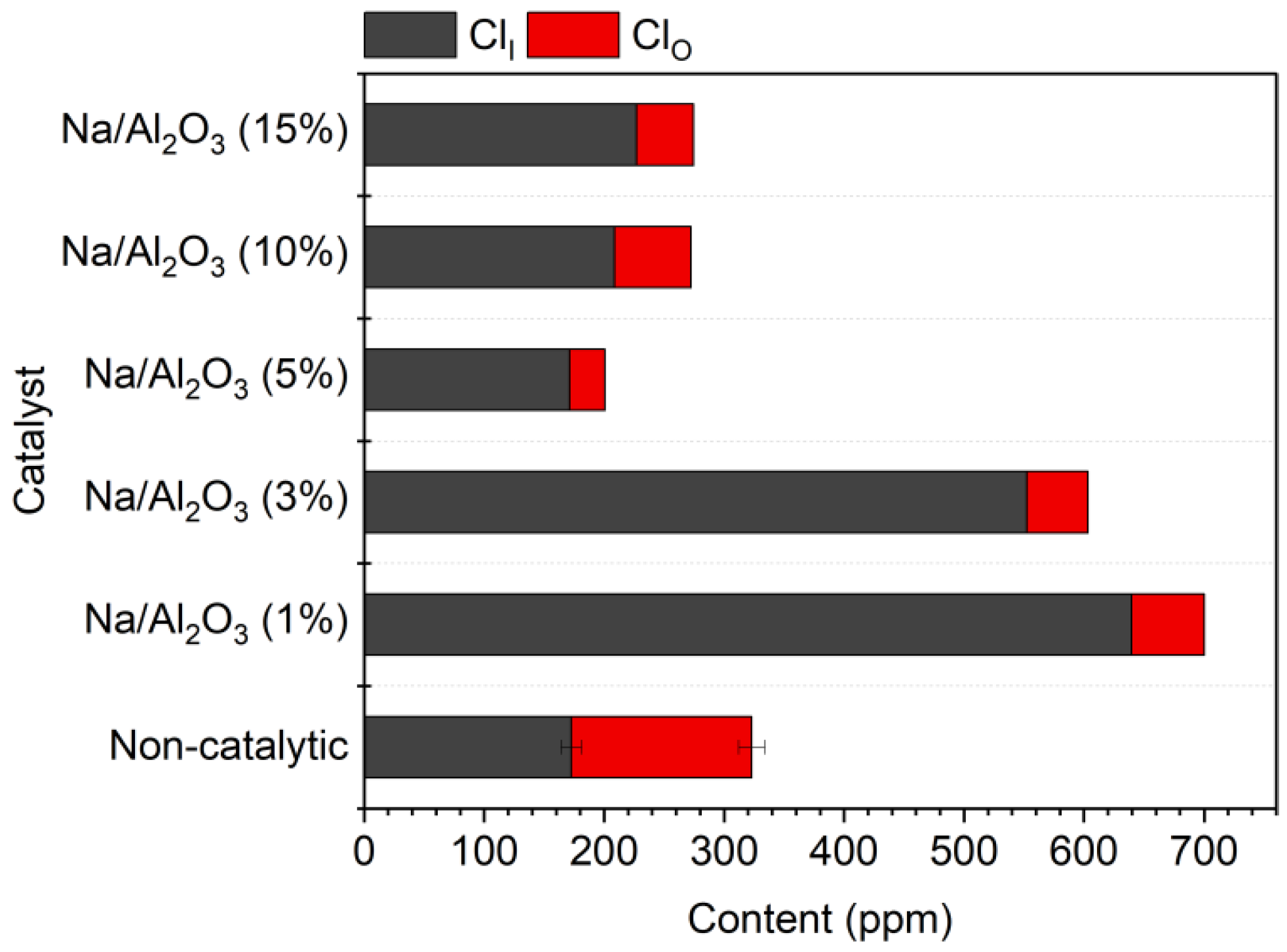
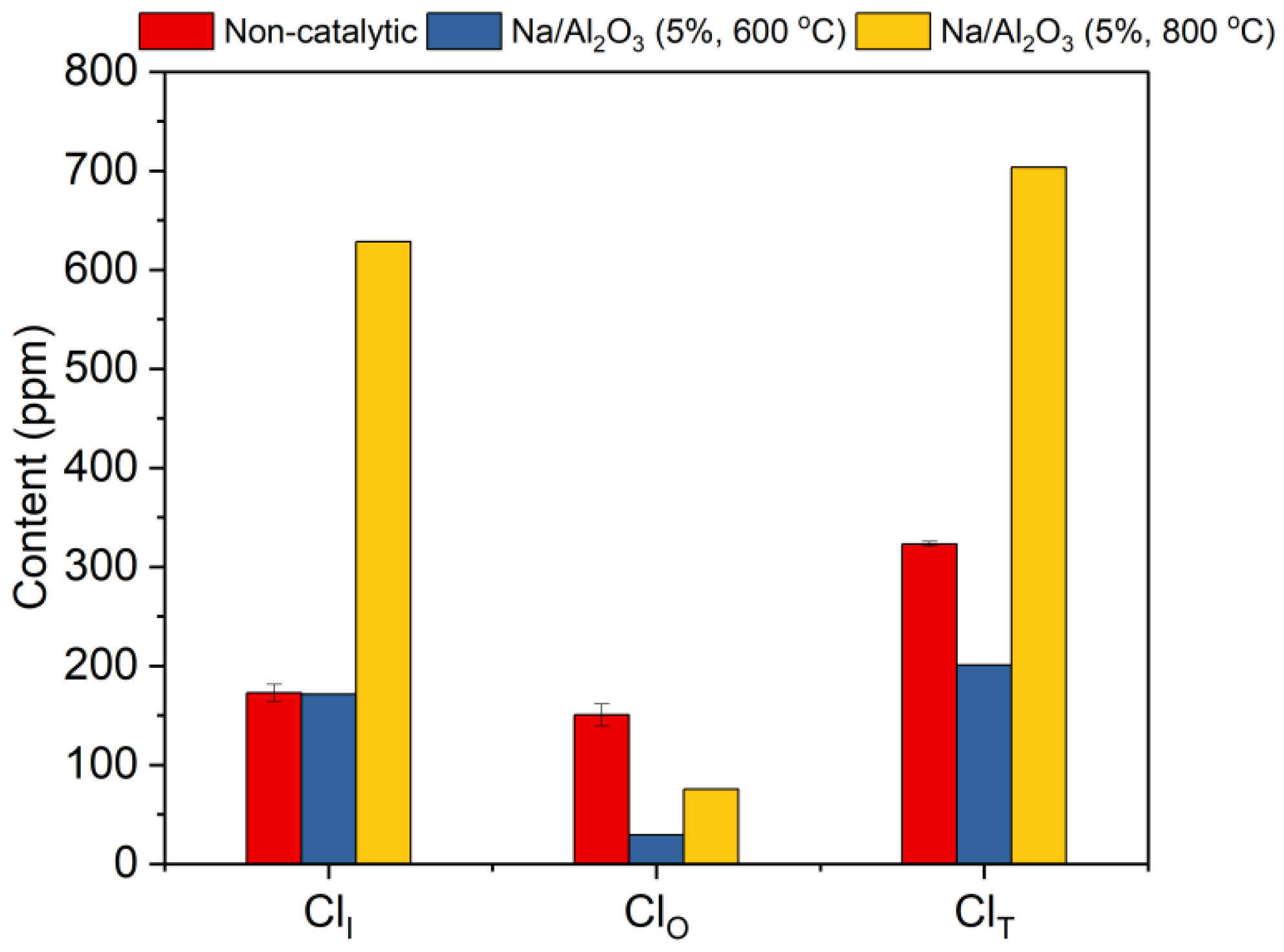
2.2. Optimization for the Performance of Na/Al2O3
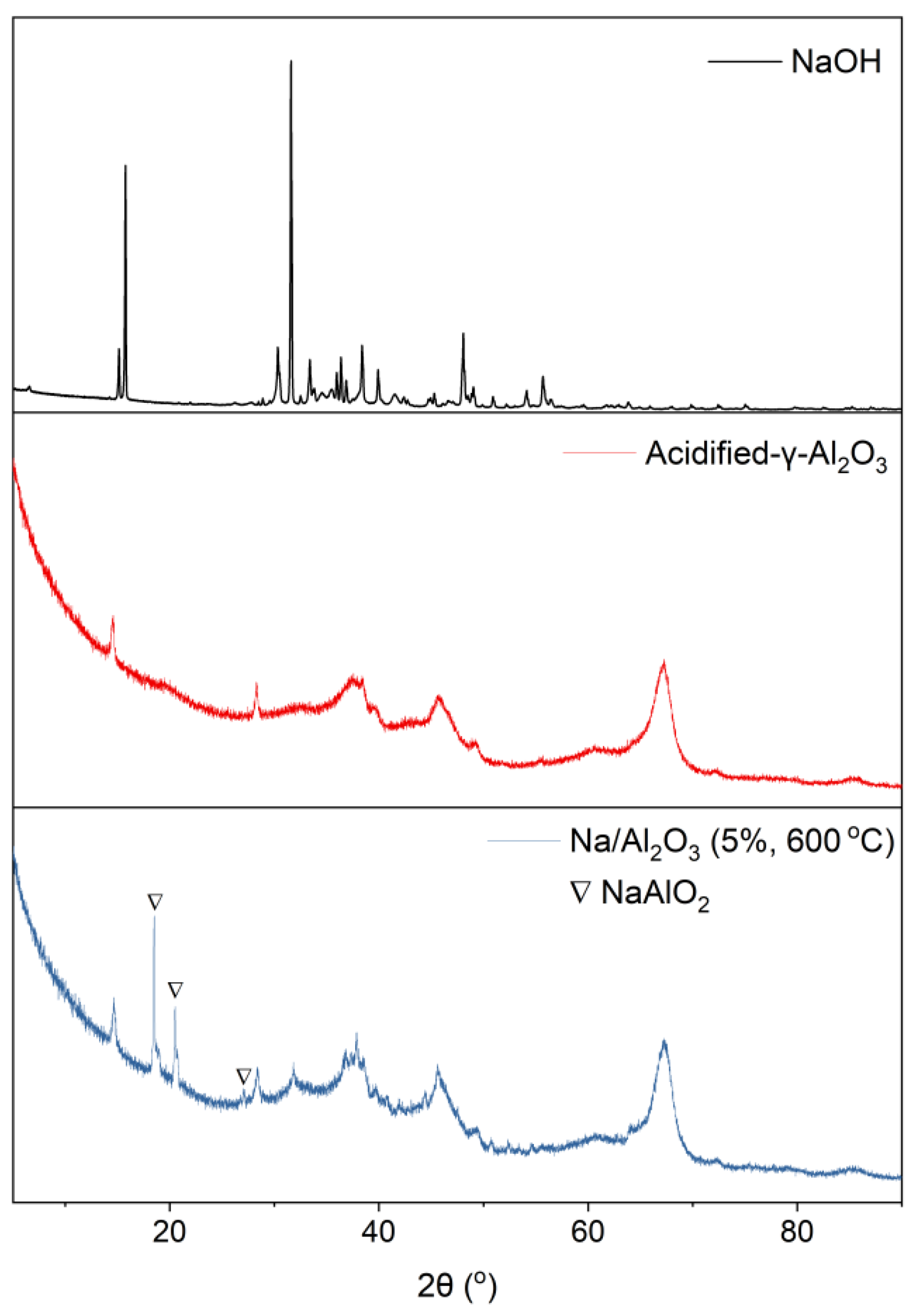
2.3. Characterization of Catalyst
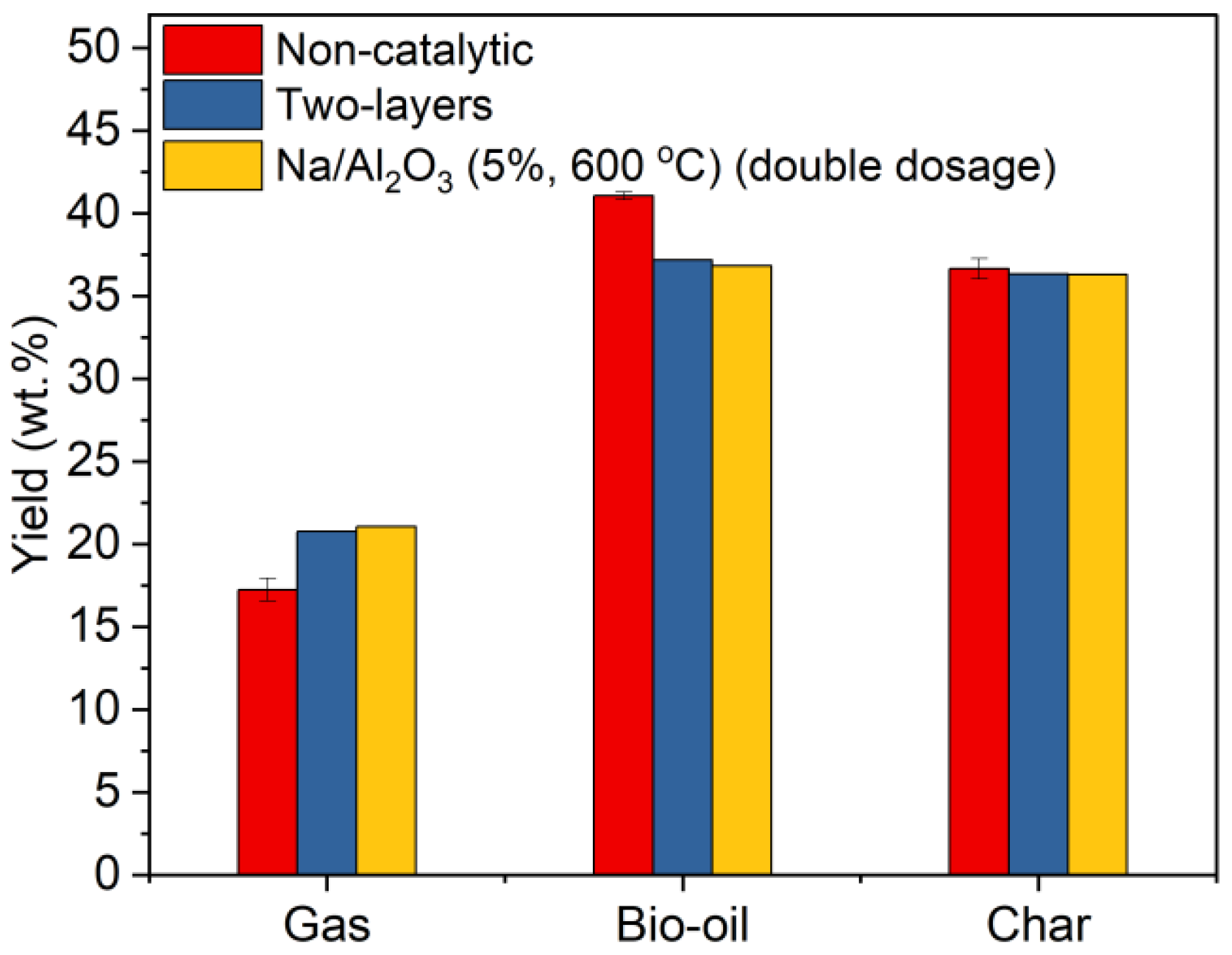
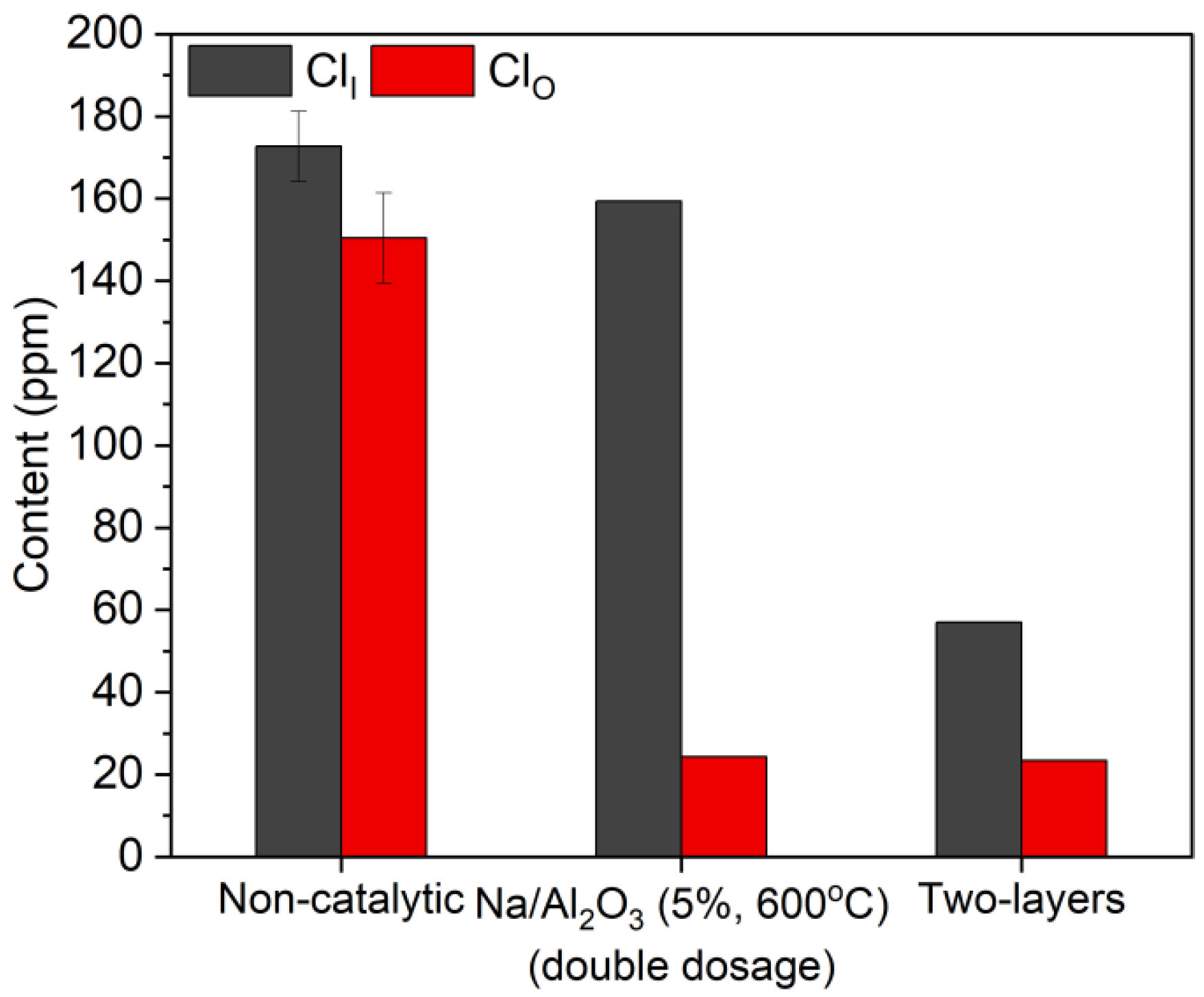
2.4. Process with a Layer of Catalyst and a Layer of HCl Absorbent
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
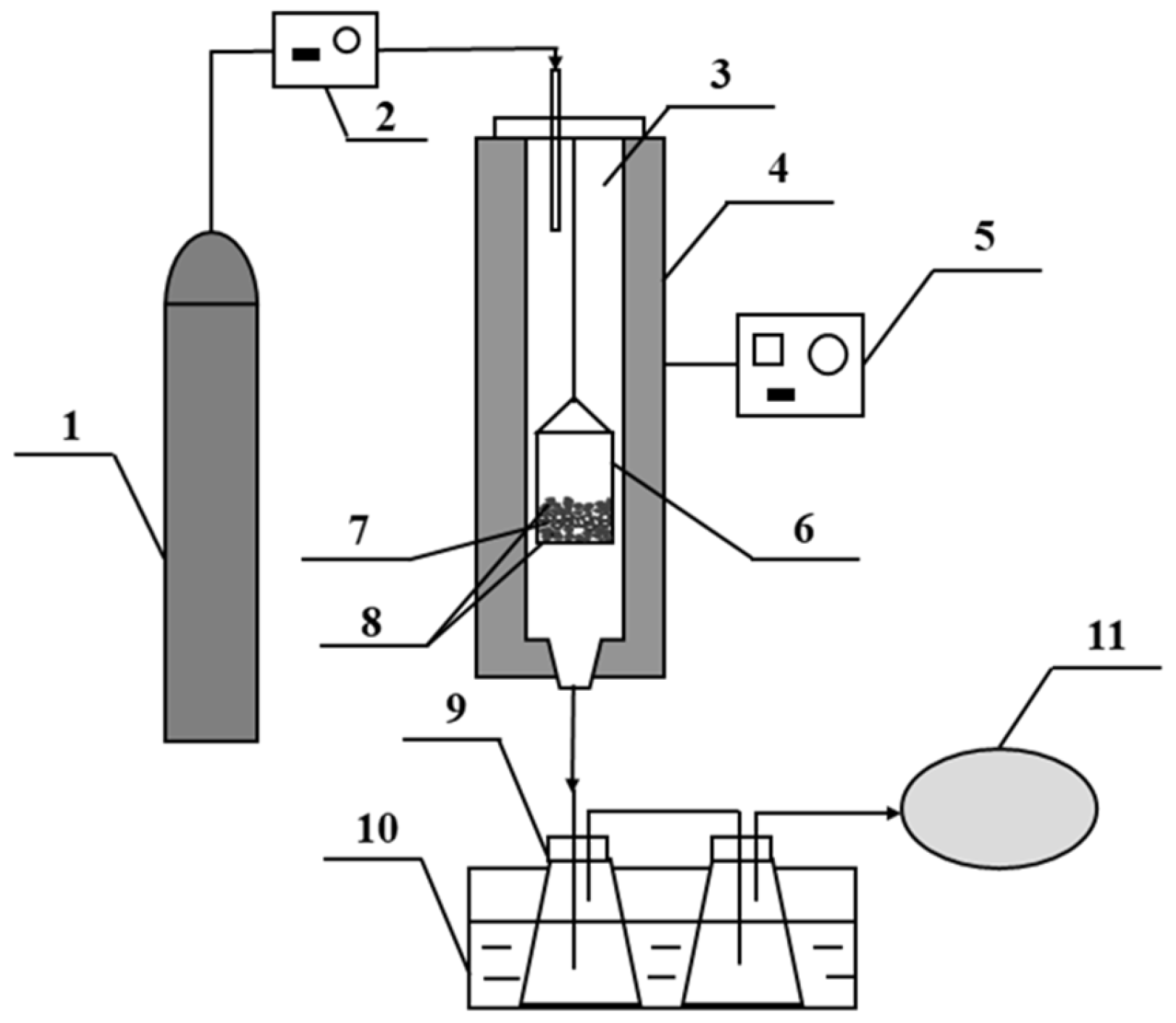
3.2. Experimental Procedural
3.3. Product Analysis
3.4. Data Processing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Motghare, K.A.; Rathod, A.P.; Wasewar, K.L.; Labhsetwar, N.K. Comparative Study of Different Waste Biomass for Energy Application. Waste Manag. 2016, 47, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, S.; Shahbazi, A. Bio-Oil Production and Upgrading Research: A Review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2012, 16, 4406–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Gholizadeh, M. Progress of the Applications of Bio-Oil. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2020, 134, 110124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brebu, M.; Ioniță, D.; Stoleru, E. Thermal Behavior and Conversion of Agriculture Biomass Residues by Torrefaction and Pyrolysis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 11505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlonka-Mędrala, A.; Evangelopoulos, P.; Sieradzka, M.; Zajemska, M.; Magdziarz, A. Pyrolysis of Agricultural Waste Biomass towards Production of Gas Fuel and High-Quality Char: Experimental and Numerical Investigations. Fuel 2021, 296, 120611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douvartzides, S.; Charisiou, N.D.; Wang, W.; Papadakis, V.G.; Polychronopoulou, K.; Goula, M.A. Catalytic Fast Pyrolysis of Agricultural Residues and Dedicated Energy Crops for the Production of High Energy Density Transportation Biofuels. Part I: Chemical Pathways and Bio-Oil Upgrading. Renew. Energy 2022, 185, 483–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildschut, J.; Mahfud, F.H.; Venderbosch, R.H.; Heeres, H.J. Hydrotreatment of Fast Pyrolysis Oil Using Heterogeneous Noble-Metal Catalysts. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2009, 48, 10324–10334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldauf, W.; Balfanz, U.; Rupp, M. Upgrading of Flash Pyrolysis Oil and Utilization in Refineries. Biomass Bioenergy 1994, 7, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheu, Y.H.E.; Anthony, R.G.; Soltes, E.J. Kinetic Studies of Upgrading Pine Pyrolytic Oil by Hydrotreatment. Fuel Process. Technol. 1988, 19, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venderbosch, R.H.; Ardiyanti, A.R.; Wildschut, J.; Oasmaa, A.; Heeres, H.J. Stabilization of Biomass-derived Pyrolysis Oils. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olcese, R.N.; Bettahar, M.; Petitjean, D.; Malaman, B.; Giovanella, F.; Dufour, A. Gas-Phase Hydrodeoxygenation of Guaiacol over Fe/SiO2 Catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2012, 115, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakovlev, V.A.; Khromova, S.A.; Sherstyuk, O.V.; Dundich, V.O.; Ermakov, D.Y.; Novopashina, V.M.; Lebedev, M.Y.; Bulavchenko, O.; Parmon, V.N. Development of New Catalytic Systems for Upgraded Bio-Fuels Production from Bio-Crude-Oil and Biodiesel. Catal. Today 2009, 144, 362–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortensen, P.M.; Grunwaldt, J.D.; Jensen, P.A.; Jensen, A.D. Screening of Catalysts for Hydrodeoxygenation of Phenol as a Model Compound for Bio-Oil. ACS Catal. 2013, 3, 1774–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, T.; Ma, L.; Yu, Y.; Chen, L. Hydrodeoxygenation of Lignin-Derived Phenolic Compounds to Hydrocarbons over Ni/SiO2–ZrO2 Catalysts. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 134, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, N.T.; Uemura, Y.; Ramli, A. Hydrodeoxygenation of Guaiacol over Al-MCM-41 Supported Metal Catalysts: A Comparative Study of Co and Ni. Procedia Eng. 2016, 148, 1252–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, R.B.; Boudart, M. Platinum-like Behavior of Tungsten Carbide in Surface Catalysis. Science 1973, 181, 547–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Chen, C.J.; Luc, W.; Chen, J.G.; Bhan, A.; Jiao, F. Ordered Mesoporous Metal Carbides with Enhanced Anisole Hydrodeoxygenation Selectivity. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 3506–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jongerius, A.L.; Gosselink, R.W.; Dijkstra, J.; Bitter, J.H.; Bruijnincx, P.C.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Carbon Nanofiber Supported Transition-metal Carbide Catalysts for the Hydrodeoxygenation of Guaiacol. ChemCatChem 2013, 5, 2964–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Gong, J.; Song, H.L.; Li, F.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.G. Preparation of Core-Shell Structured Ni2P/Al2O3@ TiO2 and Its Hydrodeoxygenation Performance for Benzofuran. Catal. Commun. 2016, 85, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berenguer, A.; Sankaranarayanan, T.M.; Gómez, G.; Moreno, I.; Coronado, J.M.; Pizarro, P.; Serrano, D.P. Evaluation of Transition Metal Phosphides Supported on Ordered Mesoporous Materials as Catalysts for Phenol Hydrodeoxygenation. Green Chem. 2016, 18, 1938–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, Y.; Richard, F.; Renème, Y.; Brunet, S. Hydrodeoxygenation of Benzofuran and Its Oxygenated Derivatives (2, 3-Dihydrobenzofuran and 2-Ethylphenol) over NiMoP/Al2O3 Catalyst. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 353, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Ge, T.; Yang, C.; Song, W.; Li, S.; Ma, R. Catalytic Pyrolysis of Corn Straw for Deoxygenation of Bio-Oil with Different Types of Catalysts. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2022, 39, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zhu, G.; Lv, T.; Kang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fang, Z.; Xu, L. Sustainable Production of Aromatic-Rich Biofuel via Catalytic Co-Pyrolysis of Lignin and Waste Polyoxymethylene over Commercial Al2O3 Catalyst. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2023, 174, 106147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.K.; Bakhshi, N.N. Catalytic Upgrading of Pyrolysis Oil. Energy Fuel 1993, 7, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katikaneni, S.P.R.; Adjaye, J.D.; Bakhshi, N.N. Performance of Aluminophosphate Molecular Sieve Catalysts for the Production of Hydrocarbons from Wood-Derived and Vegetable Oils. Energy Fuel 1995, 9, 1065–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjaye, J.D.; Katikaneni, S.P.R.; Bakhshi, N.N. Catalytic Conversion of a Biofuel to Hydrocarbons: Effect of Mixtures of HZSM-5 and Silica-Alumina Catalysts on Product Distribution. Fuel Process. Technol. 1996, 48, 115–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adjaye, J.D.; Bakhshi, N.N. Production of Hydrocarbons by Catalytic Upgrading of a Fast Pyrolysis Bio-Oil. Part I: Conversion over Various Catalysts. Fuel Process. Technol. 1995, 45, 161–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Li, X.; Luo, J.; Yu, X. Fate of Chlorine in Rice Straw under Different Pyrolysis Temperatures. Energy Fuel 2019, 33, 9272–9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, J.M.; Aho, M.; Paakkinen, K.; Taipale, R.; Egsgaard, H.; Jakobsen, J.G.; Frandsen, F.J.; Glarborg, P. Release of K, Cl, and S during Combustion and Co-Combustion with Wood of High-Chlorine Biomass in Bench and Pilot Scale Fuel Beds. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2013, 34, 2363–2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Wang, X.; Shao, J.; Yang, H.; Xu, G.; Chen, H. Releasing Behavior of Chlorine and Fluorine during Agricultural Waste Pyrolysis. Energy 2014, 74, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Qiao, Z.; Liu, H. Release and Transformation Characteristics of K and Cl during Straw Torrefaction and Mild Pyrolysis. Fuel 2016, 167, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Heo, H.S.; Park, Y.K.; Yim, J.H.; Jeon, J.K.; Park, J.; Ryu, C.; Kim, S.S. Clean Bio-Oil Production from Fast Pyrolysis of Sewage Sludge: Effects of Reaction Conditions and Metal Oxide Catalysts. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, S83–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, P.A.; Frandsen, F.J.; Dam-Johansen, K.; Sander, B. Experimental Investigation of the Transformation and Release to Gas Phase of Potassium and Chlorine during Straw Pyrolysis. Energy Fuel 2000, 14, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Yu, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhai, X.; Luo, Z. Investigation on K and Cl Release and Migration in Micro-Spatial Distribution during Rice Straw Pyrolysis. Fuel 2016, 167, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Gao, X.; Qiao, Y. Effects of Secondary Vapor-Phase Reactions on the Distribution of Chlorine Released from the Pyrolysis of KCl-Loaded Wood. Energy Fuel 2020, 34, 11717–11721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.U.; Chunjiang, Y.U.; Jisong, B.; Lianming, L.; Fang, H. Mechanism Study of Chlorine Release During Biomass Pyrolysis. Proc. Chin. Soc. Electr. Eng. 2013, 33, 75–81. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Urionabarrenechea, A.; Marco, I.; Caballero, B.M.; Laresgoiti, M.F.; Adrados, A. Upgrading of Chlorinated Oils Coming from Pyrolysis of Plastic Waste. Fuel Process. Technol. 2015, 137, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.H.; Jung, S.H.; Kim, J.S. Pyrolysis of Mixed Plastic Wastes for the Recovery of Benzene, Toluene, and Xylene (BTX) Aromatics in a Fluidized Bed and Chlorine Removal by Applying Various Additives. Energy Fuels 2010, 24, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Liu, S.; Fan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Guo, M.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, M. Enhanced HCl Removal from CO2-Rich Mixture Gases by CuOx/Na2CO3 Porous Sorbent at Low Temperature: Kinetics and Forecasting. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 381, 122738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubouchi, N.; Fukuyama, K.; Matsuoka, N.; Mochizuki, Y. Removal of Hydrogen Chloride from Simulated Coal Gasification Fuel Gases Using Honeycomb-Supported Natural Soda Ash. Fuel 2022, 317, 122231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Ge, T.; Song, W.; Li, S. Migration of Cl in the Process for Pyrolysis of Corn Straw and the Influence of Catalysis for Dechlorination of Bio-Oil. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2022, 14, 6773–6781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuttiyathil, M.S.; Ali, L.; Teoh, W.Y.; Altarawneh, M. Dechlorination of Waste Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) via Its Co-Pyrolysis with Ca(OH)2: A TG-IR-GCMS Investigation. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2025, 11, 101162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Sanchez Monsalve, D.A.; Clough, P.; Jiang, Y.; Leeke, G.A. Understanding the Dechlorination of Chlorinated Hydrocarbons in the Pyrolysis of Mixed Plastics. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 1576–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flid, M.R.; Kartashov, L.M.; Treger, Y.A. Theoretical and Applied Aspects of Hydrodechlorination Processes—Catalysts and Technologies. Catalysts 2020, 10, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Otero, J.A.; Martin-Martinez, M.; Rodriguez-Franco, D.; Rodriguez, J.J.; Gómez-Sainero, L.M. Understanding Hydrodechlorination of Chloromethanes. Past and Future of the Technology. Catalysts 2020, 10, 1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.W.; Xing, F.; Zhu, J.C.; Li, R.H.; Zhang, Z.Q. Temporal and Spatial Distribution, Utilization Status, and Carbon Emission Reduction Potential of Straw Resources in China. Environ. Sci. 2023, 44, 1149–1162. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Shan, W. High-Temperature Calcination Enhances the Activity of MnOx Catalysts for Soot Oxidation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2024, 14, 6278–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Shan, W.; He, H. High-Temperature Calcination Dramatically Promotes the Activity of Cs/Co/Ce-Sn Catalyst for Soot Oxidation. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2025, 36, 109928. [Google Scholar]
- Ramzy, K.; Ismail, T.; Alswat, M.; El-Askary, W.A. Effect of Using Zeolite as a Catalyst on Syngas Produced from Different Wastes Using Pyrolysis Technology. Therm. Sci. Eng. Prog. 2025, 65, 103904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirapanampai, C.; Phetwarotai, W.; Phusunti, N. Effect of Temperature and the Content of Na2CO3 as a Catalyst on the Characteristics of Bio-Oil Obtained from the Pyrolysis of Microalgae. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2019, 142, 104644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinopec Research Institute of Petroleum Processing, Daqing Oilfield Engineering Co., Ltd., Tarim Oilfield Exploration & Development Research Institute of Sinopec {Pei He, Shuqing Wang, Shouguo Song, Zhangling Li}. SY/T 0536-2008; Determination of Salt Content in Crude Petroleum—Coulometric Titration Method. Petroleum and Gas Industry Standards of the People’s Republic of China; National Development and Reform Commission: Beijing, China, 2008.
- Daqing Oilfield Architectural Design & Research Institute {Xuejun Yang, Xuezhi Hou, Shusheng Ge, Hong Zhang, Guangping Pan, Jing Chen}. GB/T 18612-2001; Determination of Organic Chloride Content in Crude Oil by Combustion and Microcoulometry. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China; General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2001.
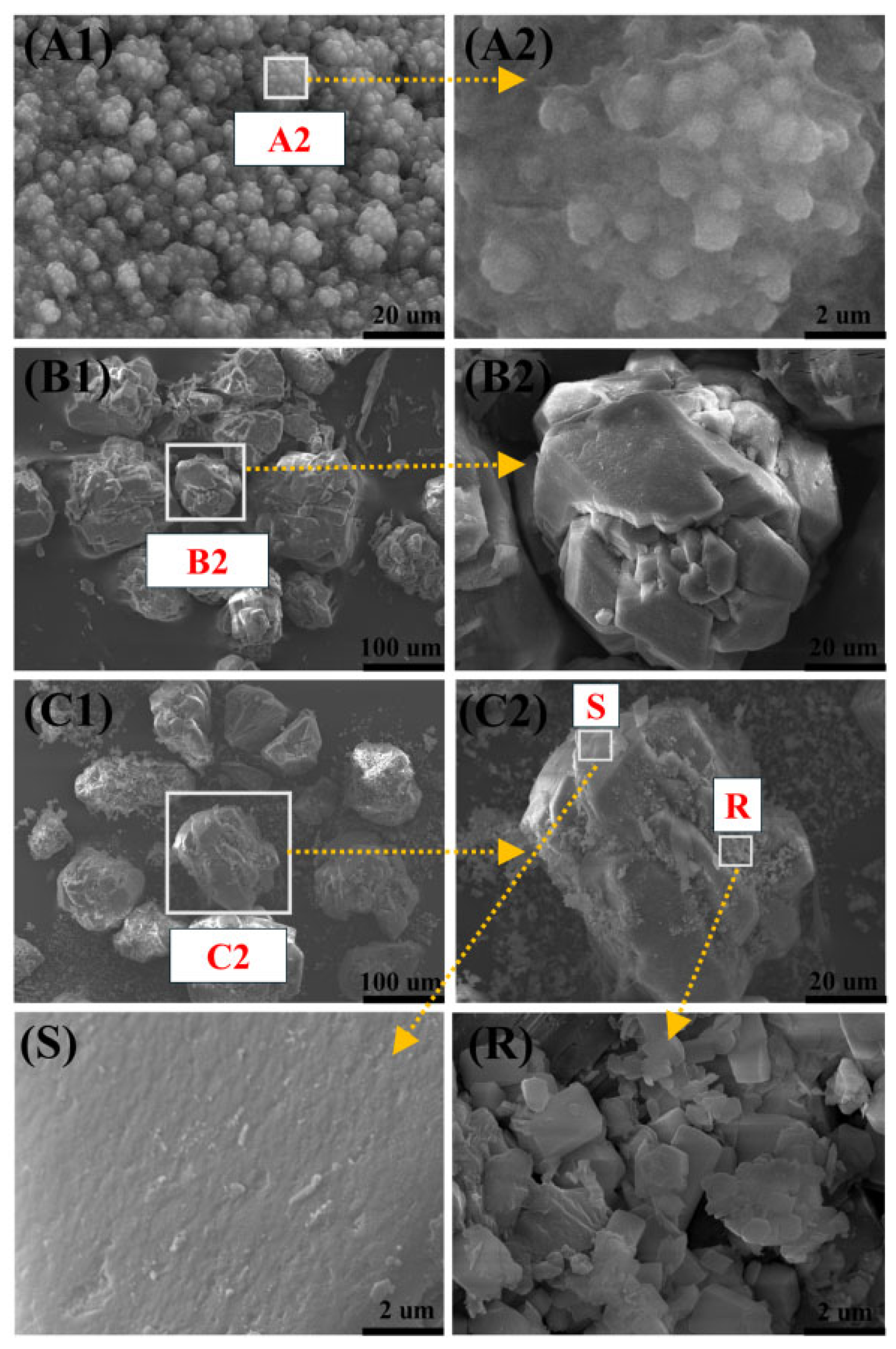
| Sample and Position | O (%) | Na (%) | Al (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NaOH (A2) | 51.29 | 48.71 | 0 |
| Acidified-γ-Al2O3 (B2) | 61.77 | 0 | 38.23 |
| Na/Al2O3 (5%, 600 °C) (C2) | 66.04 | 1.73 | 32.23 |
| Na/Al2O3 (5%, 600 °C) (S) | 64.08 | 2.56 | 33.36 |
| Na/Al2O3 (5%, 600 °C) (R) | 68.35 | 0.99 | 30.65 |
| Proximate Analysis (wt.%, d) | Ultimate Analysis (wt.%, d) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| V | FC | A | C | H | N | S | O * | Cl |
| 75.94 | 16.15 | 7.91 | 44.97 | 6.02 | 1.17 | 0.16 | 38.63 | 1.14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, S. Pyrolysis of Corn Straw for In Situ Dechlorination of Bio-Oil Under the Catalysis of Acidified-γ-Al2O3 Modified with Alkaline and Alkaline Earth Metal Compounds. Catalysts 2025, 15, 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15121142
Zhang W, Wang Z, Li S. Pyrolysis of Corn Straw for In Situ Dechlorination of Bio-Oil Under the Catalysis of Acidified-γ-Al2O3 Modified with Alkaline and Alkaline Earth Metal Compounds. Catalysts. 2025; 15(12):1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15121142
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wenkai, Ze Wang, and Songgeng Li. 2025. "Pyrolysis of Corn Straw for In Situ Dechlorination of Bio-Oil Under the Catalysis of Acidified-γ-Al2O3 Modified with Alkaline and Alkaline Earth Metal Compounds" Catalysts 15, no. 12: 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15121142
APA StyleZhang, W., Wang, Z., & Li, S. (2025). Pyrolysis of Corn Straw for In Situ Dechlorination of Bio-Oil Under the Catalysis of Acidified-γ-Al2O3 Modified with Alkaline and Alkaline Earth Metal Compounds. Catalysts, 15(12), 1142. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15121142






