Improving the Reproducibility of Oxygen Reduction Reaction Activity Assessment for Pt-Based Electrocatalysts on a Rotating Disk Electrode via Catalytic Layer Optimization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
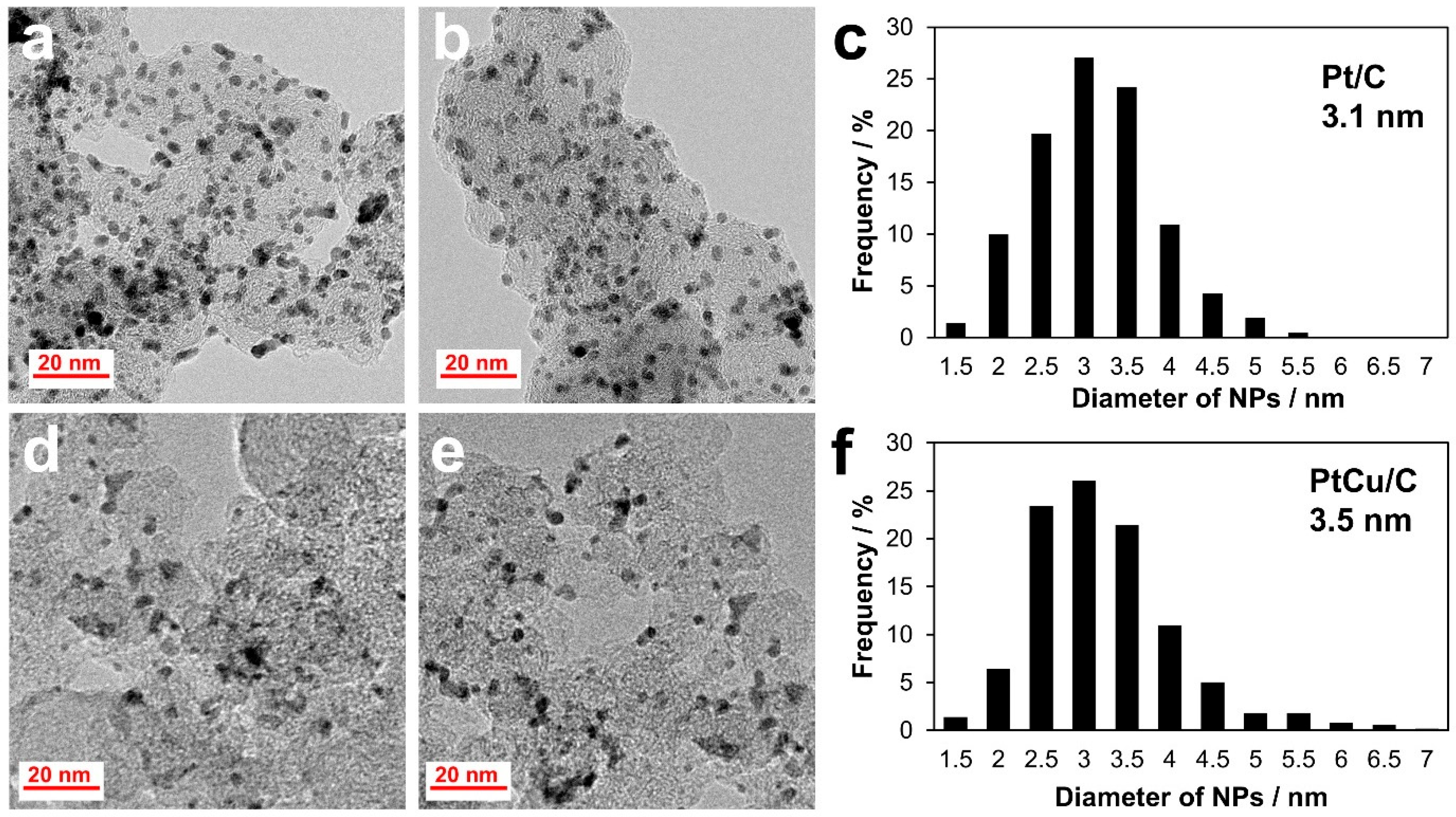
2.1. Microstructure of the Catalysts
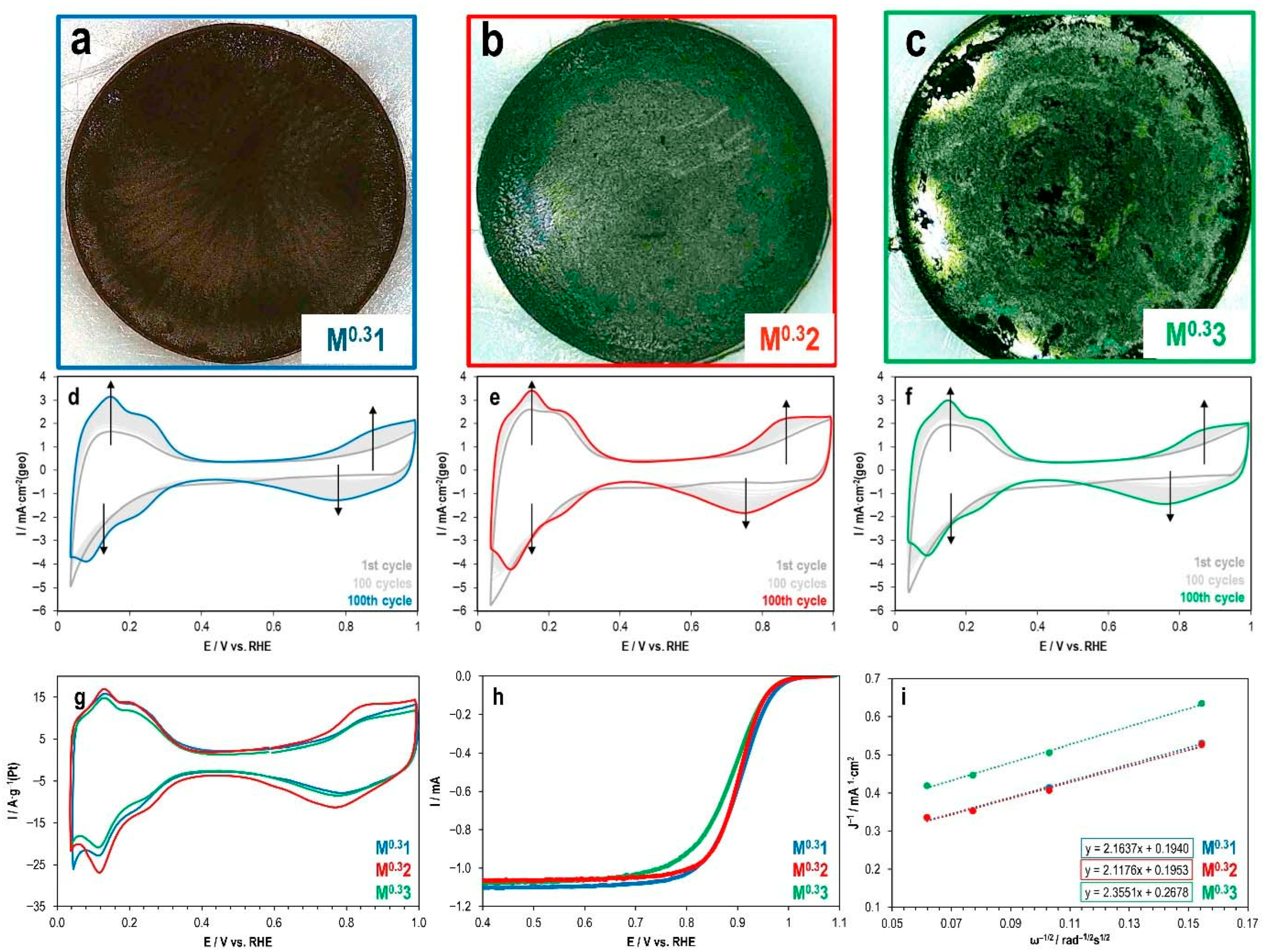
2.2. Effect of Ink Solvent Composition on the Electrochemical Performance of Pt/C Catalyst
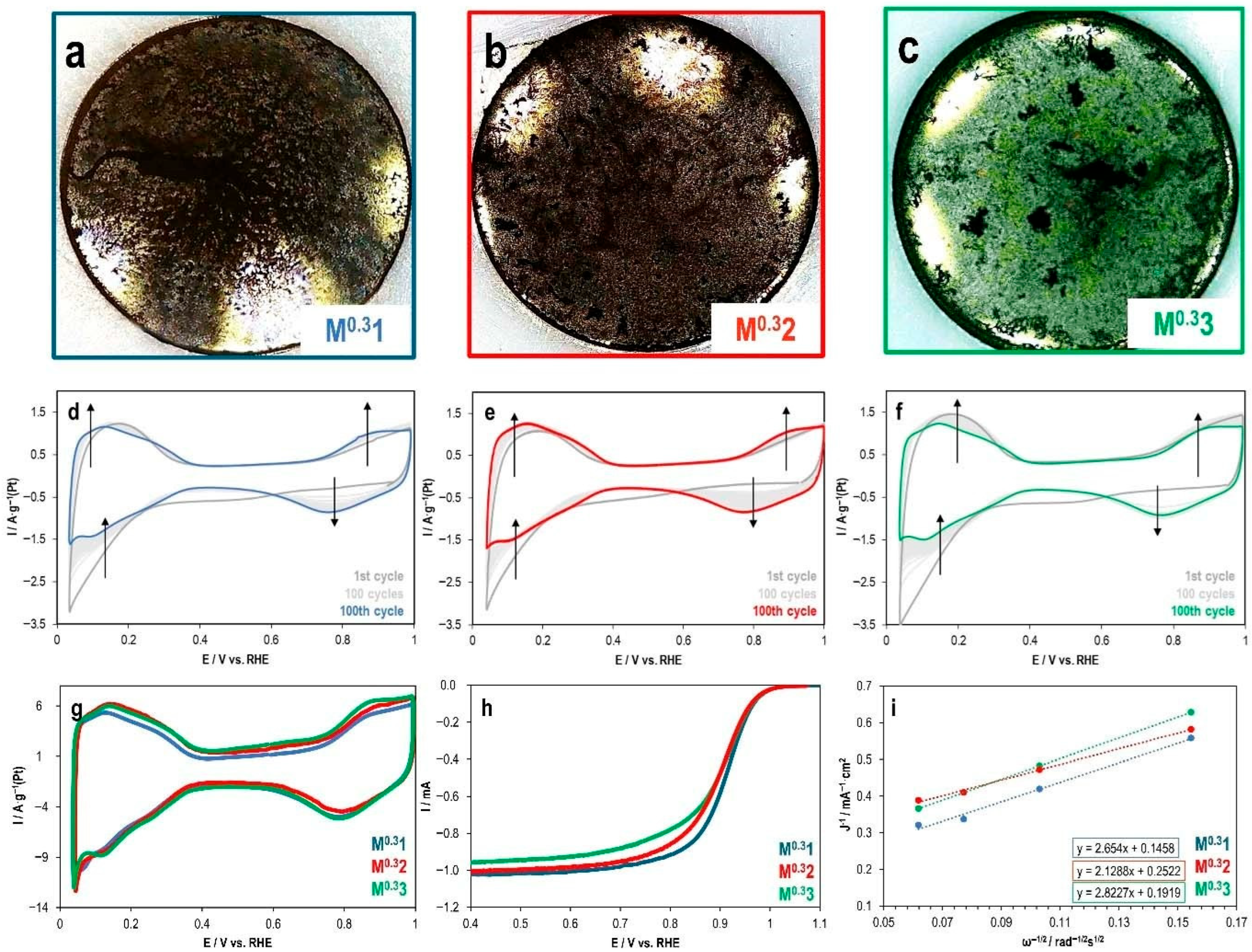
2.3. Effect of Ink Solvent Composition on the Electrochemical Performance of PtCu/C Catalyst
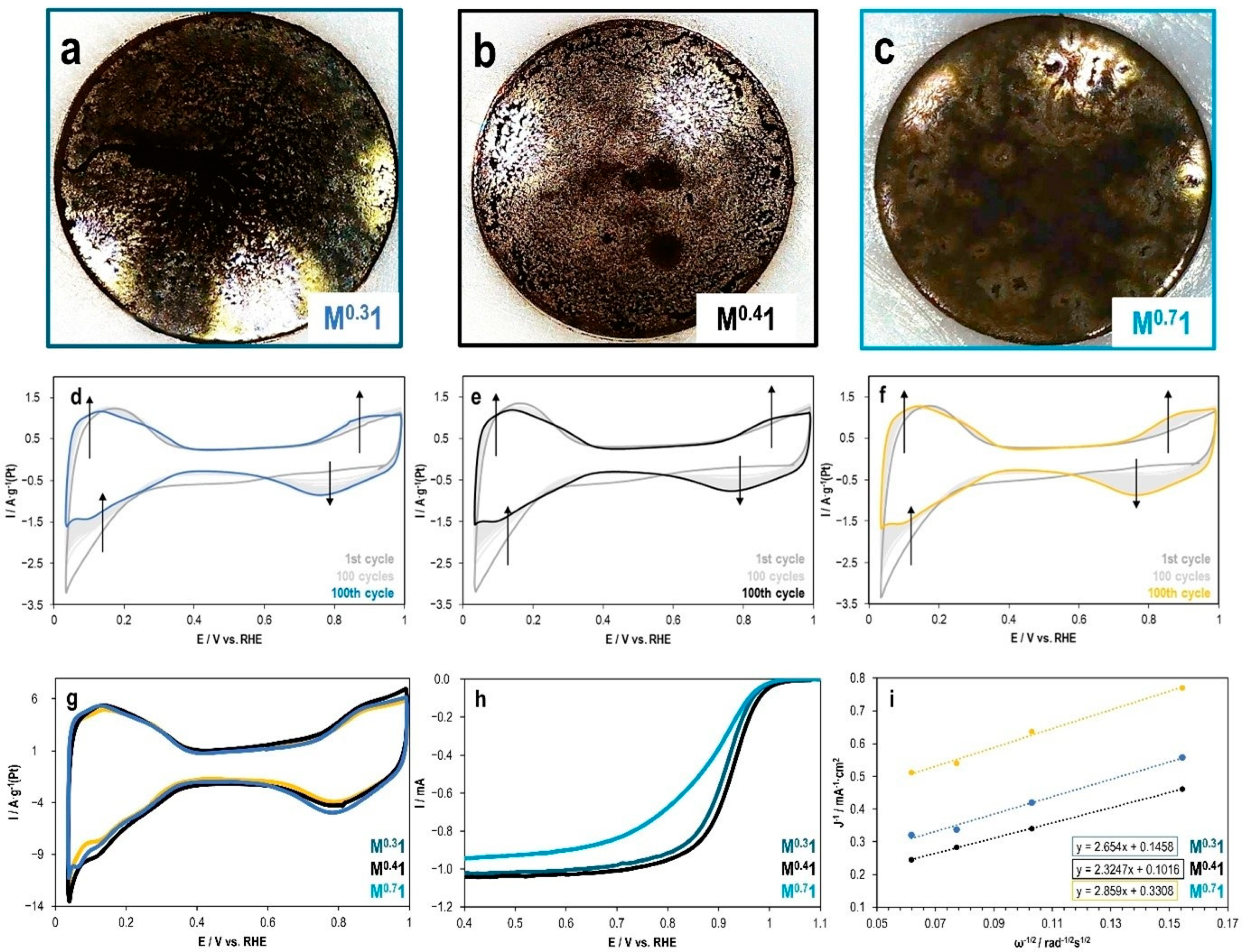
2.4. Influence of Ionomer-to-Carbon Ratio in Catalytic Inks on the Electrochemical Properties of PtCu/C Catalyst
3. Materials and Methods
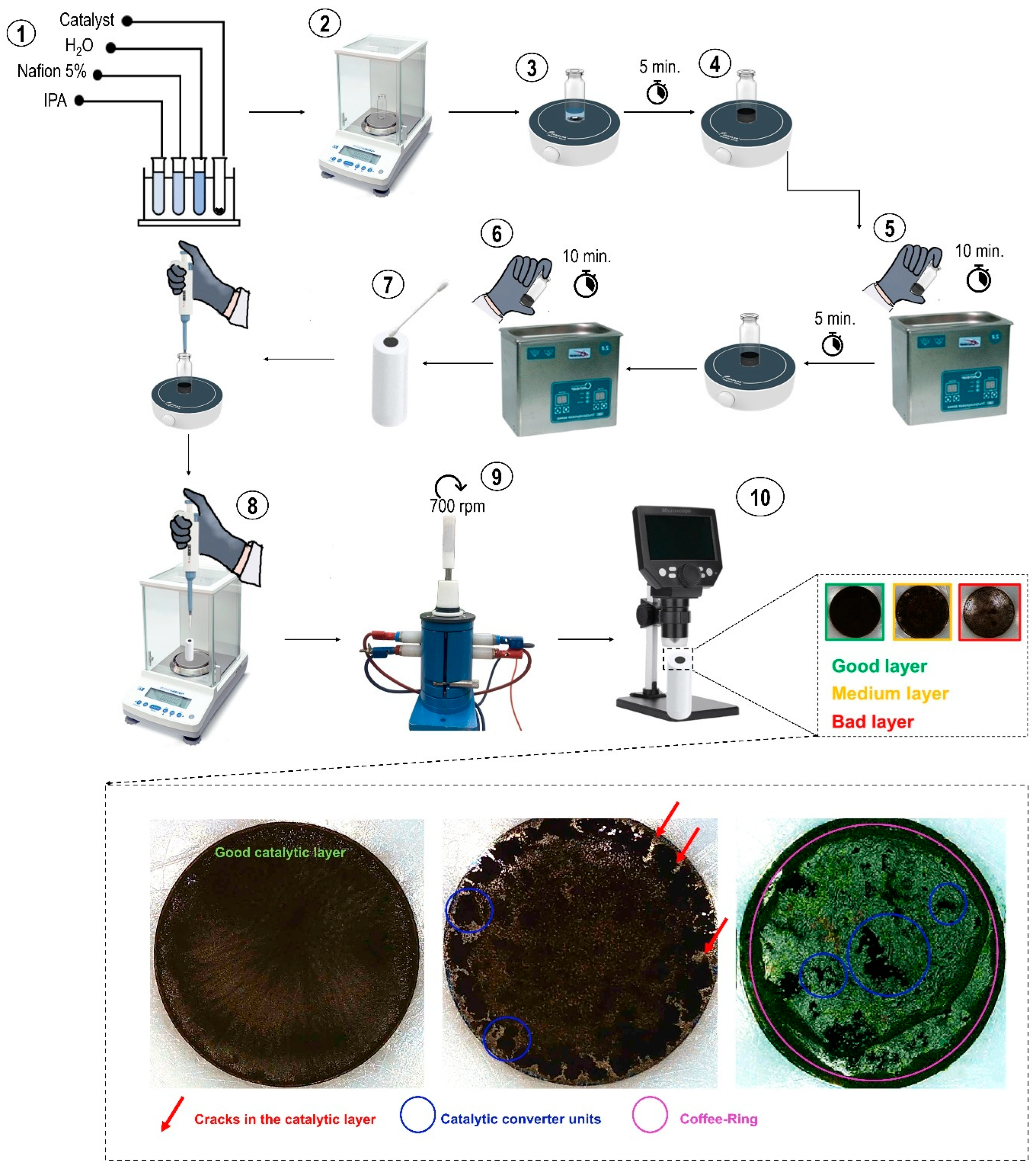
3.1. Preparation of Catalytic Inks
3.2. Fabrication of the Catalytic Layer on the Rotating Disk Electrode (RDE)
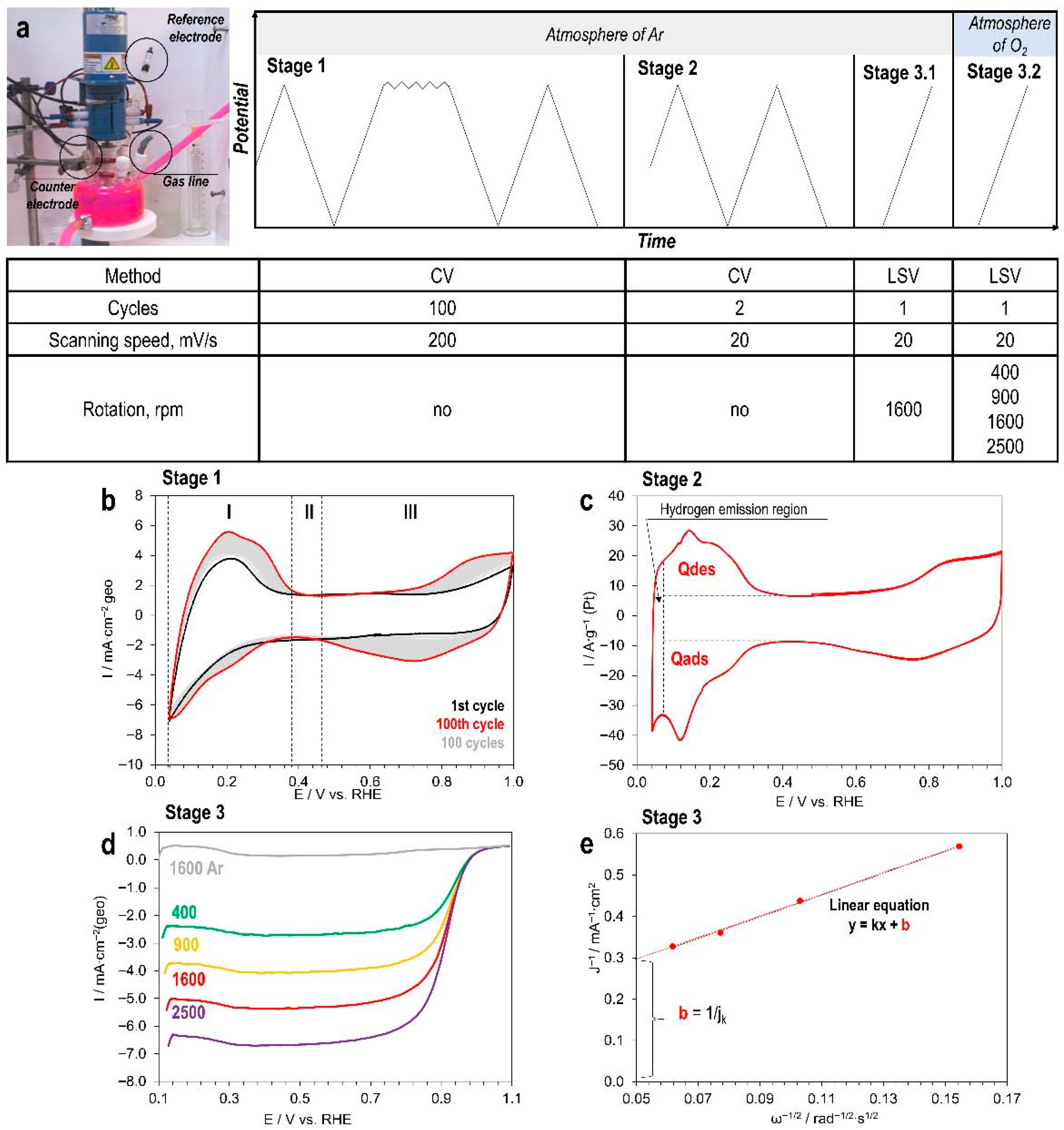
3.3. Electrochemical Measurements
3.3.1. Determination of Electrochemical Active Surface Area (ECSA)
- ECSA is the electrochemical active surface area of platinum, m2/g;
- Qads is the electric charge associated with hydrogen adsorption (after double-layer correction), μC;
- Qdes—is the electric charge associated with hydrogen desorption (after double-layer correction), μC;
- 210 μC/cm2 is the charge required for the adsorption of a hydrogen monolayer on a smooth polycrystalline Pt surface.
3.3.2. Determination of Activity in the ORR
- Eset is the potential set value, V;
- Eref is the reference electrode potential, V;
- EpH is the adjustment for pH of the solution; and
- iR is the ohmic potential drop equal to the product of the current strength by the resistance of the cell. This resistance was no greater than 25 Ω.
- I(O2) is the current for the ORR at a given potential, obtained from the measurement in an oxygen-saturated electrolyte.
- I(Ar) is the background (capacitive) current at a given potential, obtained from the measurement in an argon-saturated electrolyte.
- i is the measured current at the disk electrode,
- ik is the kinetic current,
- id is the diffusion-limited current,
- ω is the electrode rotation rate (rad/s),
- n is the number of electrons transferred in the electrochemical reaction,
- F is the Faraday constant (C/mol),
- D is the diffusion coefficient of oxygen (cm2/s),
- υ is the kinematic viscosity of the electrolyte (cm2/s),
- C is the bulk concentration of oxygen in the solution (mol/cm3).
- jk is the kinetic current density (A/cm2),
- b is the y-intercept of the linear fit in the Koutecký–Levich plot (A−1 cm2),
- ik is the kinetic current (A),
- A is the geometric area of the RDE (0.19625 cm2 for a 5 mm diameter disk).
- i0.9 is the current measured at a potential of 0.9 V vs. RHE;
- idif is the diffusion-limited current.
- Current correction for ohmic drop (iR compensation) and background subtraction using measurements in an argon or nitrogen (Ar/N2) atmosphere.
- The preparation of thin, uniform catalytic layers with low platinum group metal loading to minimize mass-transport limitations within the layer itself.
4. Conclusions
- A method for the visual assessment of catalytic layer quality was proposed, enabling the rapid and cost-effective determination of optimal catalytic ink preparation parameters without the need for expensive equipment (e.g., SEM or AFM). This approach is based on analyzing the macroscopic homogeneity of the layer and the absence of defects (aggregates, coffee rings), which correlates with electrochemical activity. Visualization using a digital benchtop microscope proved highly effective for the preliminary screening of catalytic layer quality prior to electrochemical measurements, thereby reducing sample preparation time and minimizing non-representative experiments.
- The highest quality catalytic layer for the Pt/C catalyst was formed using an ink preparation method with a solvent ratio of H2O:IPA = 1:3 and an I/C ratio of 0.3. This method ensures the most uniform distribution of the catalytic material on the RDE surface, leading to the highest mass activity of 353 A/g(Pt).
- The best results for the PtCu/C catalyst were achieved using ink preparation method M0.41 with a solvent ratio of H2O:IPA = 1:3 and an I/C ratio of 0.4. This ink composition facilitates the formation of a uniform catalytic layer. The mass activity of PtCu/C under these conditions is 491 A/g(Pt), which is 25–30% higher than the values obtained with other investigated ink formulations.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Yang, J.; Lei, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Tang, Y.; Mao, Z. Recent advances in Pt-based electrocatalysts for PEMFCs. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 13316–13328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, Y.; Gao, L.; Zeng, G.; Li, M.; Huang, H. Stabilizing Pt-Based Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction: Fundamental Understanding and Design Strategies. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2006494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, L.; Jia, W.; Li, C.; Lei, Y. Mechanisms for Enhanced Performance of Platinum-Based Electrocatalysts in Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 361–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuvanendran, N.; Ravichandran, S.; Xu, Q.; Maiyalagan, T.; Su, H. A quick guide to the assessment of key electrochemical performance indicators for the oxygen reduction reaction: A comprehensive review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 7113–7138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-J.; Zhao, N.; Fang, B.; Li, H.; Bi, X.T.; Wang, H. Carbon-Supported Pt-Based Alloy Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction in Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells: Particle Size, Shape, and Composition Manipulation and Their Impact to Activity. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 3433–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamenkovic, V.; Mun, B.S.; Mayrhofer, K.J.J.; Ross, P.N.; Markovic, N.M.; Rossmeisl, J.; Greeley, J.; Nørskov, J.K. Changing the Activity of Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction by Tuning the Surface Electronic Structure. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 2897–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crawley, J.W.M.; Gow, I.E.; Lawes, N.; Kowalec, I.; Kabalan, L.; Catlow, C.R.A.; Logsdail, A.J.; Taylor, S.H.; Dummer, N.F.; Hutchings, G.J. Heterogeneous Trimetallic Nanoparticles as Catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 6795–6849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Zhang, D.; Liu, Z.; Li, C.; Zhang, T.; Yin, S.; Song, Y.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Li, C. Carbon-anchoring synthesis of Pt1Ni1@Pt/C core-shell catalysts for stable oxygen reduction reaction. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Y.; Li, B.; Lv, C.; Zang, Z.; Li, L.; Lu, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Yu, X. Stabilizing platinum-based electrocatalysts for oxygen reduction reaction in acid media: A mini review. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 51, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garsany, Y.; Baturina, O.A.; Swider-Lyons, K.E.; Kocha, S.S. Experimental Methods for Quantifying the Activity of Platinum Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 6321–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garsany, Y.; Singer, I.L.; Swider-Lyons, K.E. Impact of film drying procedures on RDE characterization of Pt/VC electrocatalysts. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 662, 396–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; Kong, D.; He, P.; Zhang, T.; Sun, C. A Smart Workflow for Performing the Electrochemical Evaluation of Fuel Cell Catalysts in a Precise Way with Ultra-High Reproducibility. ACS Electrochem. 2025, 1, 2190–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Meng, X.; Lin, Y.; Shao, Z. Microstructure formation mechanism of catalyst layer and its effect on fuel cell performance: Effect of dispersion medium composition. J. Energy Chem. 2022, 73, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhu, F.; Tang, M.; Chen, S. Effects of Ink Water/Isopropanol Ratio on Structural and Oxygen Transport Properties of Pt/Ionomer Interface: Insights from Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Renewables 2024, 2, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, I.; Kocha, S.S. Examination of the activity and durability of PEMFC catalysts in liquid electrolytes. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 6312–6322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yang, D.; Li, B.; Yang, D.; Ming, P.; Zhang, C. Effect of Dispersion Solvents and Ionomers on the Rheology of Catalyst Inks and Catalyst Layer Structure for Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 27119–27128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Kayo, N.; Jayawickrama, S.M.; Phua, Y.K.; Tanaka, N.; Fujigaya, T. Effect of alcohol content on the ionomer adsorption of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 5915–5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, M.; Aoyama, Y.; Eda, N.; Ohta, A. New Preparation Method for Polymer-Electrolyte Fuel Cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1995, 142, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarokh, A.; Karan, K.; Ponnurangam, S. Atomistic MD Study of Nafion Dispersions: Role of Solvent and Counterion in the Aggregate Structure, Ionic Clustering, and Acid Dissociation. Macromolecules 2020, 53, 288–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauger, S.A.; Khandavalli, S.; Iyer, R.; Park, J.; Osmieri, L.; Cetinbas, F.; Myers, D.J.; Ulsh, M.; Neyerlin, K.C. The Effect of Dispersion-Medium Composition and Ionomer Concentration on the Microstructure and Rheology of Fe-N-C Platinum Group Metal-Free Catalyst Inks for Polymer Electrolyte Membrane Fuel Cells. Meet. Abstr. 2020, MA2020-02, 2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Lu, J.; Dunseath, O.; Ronovský, M.; Guo, A.; Klingenhof, M.; Wang, X.; Hornberger, E.; Bonastre, A.M.; Burdett, H.; et al. Unveiling the origins of the activity gap between rotating disk electrodes and membrane electrode assemblies: Pt seed-mediated iridium-doped octahedral platinum nickel catalysts for proton exchange membrane fuel cells. EES Catal. 2025, 3, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, T.; Tsushima, S.; Hirai, S. Effects of Nafion® ionomer and carbon particles on structure formation in a proton-exchange membrane fuel cell catalyst layer fabricated by the decal-transfer method. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2011, 36, 12361–12369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Jung, D.-W.; Kim, J. Optimum Ratio between Nafion and 20, 40 wt% Pt/C Catalysts for MEAs. J. Korean Electrochem. Soc. 2011, 14, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ney, L.; Zamel, N.; Li, X. Effect of Catalyst Ink and Formation Process on the Multiscale Structure of Catalyst Layers in PEM Fuel Cells. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, K.; Zack, J.W.; Pylypenko, S.; Pivovar, B.S.; Kocha, S.S. Oxygen Reduction Reaction Measurements on Platinum Electrocatalysts Utilizing Rotating Disk Electrode Technique: II. Influence of Ink Formulation, Catalyst Layer Uniformity and Thickness. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, F1384–F1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garsany, Y.; Ge, J.; St-Pierre, J.; Rocheleau, R.; Swider-Lyons, K.E. Analytical Procedure for Accurate Comparison of Rotating Disk Electrode Results for the Oxygen Reduction Activity of Pt/C. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, F628–F640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inaba, M.; Quinson, J.; Bucher, J.R.; Arenz, M. On the Preparation and Testing of Fuel Cell Catalysts Using the Thin Film Rotating Disk Electrode Method. JoVE 2018, 133, 57105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, K.; Hiroshima, K.; Kamitaka, Y.; Hatanaka, T.; Morimoto, Y. An accurate evaluation for the activity of nano-sized electrocatalysts by a thin-film rotating disk electrode: Oxygen reduction on Pt/C. Electrochim. Acta 2012, 72, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Larson, R.G. Marangoni Effect Reverses Coffee-Ring Depositions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7090–7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, M.; Walter, J.; Harrer, J.; Perez, C.M.; Chiera, S.; Nair, S.; Ickler, M.; Fuchs, A.; Michaud, M.; Uttinger, M.J.; et al. Versatile strategy for homogeneous drying patterns of dispersed particles. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howard, N.S.; Archer, A.J.; Sibley, D.N.; Southee, D.J.; Wijayantha, K.G.U. Surfactant Control of Coffee Ring Formation in Carbon Nanotube Suspensions. Langmuir 2023, 39, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, K.; Zack, J.W.; Richards, R.M.; Pivovar, B.S.; Kocha, S.S. Oxygen Reduction Reaction Measurements on Platinum Electrocatalysts Utilizing Rotating Disk Electrode Technique: I. Impact of Impurities, Measurement Protocols and Applied Corrections. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 162, F1144–F1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali-Löytty, H.; Hannula, M.; Valden, M.; Eilert, A.; Ogasawara, H.; Nilsson, A. Chemical Dissolution of Pt(111) during Potential Cycling under Negative pH Conditions Studied by Operando X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 25128–25134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Sun, Y.; Shen, T.; Yin, G.; Zhang, J. 7-Applications of RDE and RRDE Methods in Oxygen Reduction Reaction. In Rotating Electrode Methods and Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysts; Xing, W., Yin, G., Zhang, J., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 231–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Yin, G.; Zhang, J. Rotating Ring-Disk Electrode Method. Rotating Electrode Methods and Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysts; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 199–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wang, L.; Yang, C.; Song, L. An Ancient BCR-like Signaling Promotes ICP Production and Hemocyte Phagocytosis in Oyster. iScience 2020, 23, 100834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alekseenko, A.; Belenov, S.; Mauer, D.; Moguchikh, E.; Falina, I.; Bayan, J.; Pankov, I.; Alekseenko, D.; Guterman, V. Activity of Platinum-Based Cathode Electrocatalysts in Oxygen Redaction for Proton-Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells: Influence of the Ionomer Content. Inorganics 2024, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alekseenko, A.A.; Guterman, V.E.; Belenov, S.V.; Menshikov, V.S.; Tabachkova NYu Safronenko, O.I.; Moguchikh, E.A. Pt/C electrocatalysts based on the nanoparticles with the gradient structure. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 3676–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlets, A.; Alekseenko, A.; Menshchikov, V.; Belenov, S.; Volochaev, V.; Pankov, I.; Safronenko, O.; Guterman, V. Influence of Electrochemical Pretreatment Conditions of PtCu/C Alloy Electrocatalyst on Its Activity. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalysts | PROMETHEUS R&D LLC Research and Production Enterprise. PROMETHEUS R&D LLC n.d. Available online: https://www.prometheusrd.com (accessed on 16 October 2025).
- E3 Series Rotating Disk Electrode, 1018 Carbon Steel, PEEK Shroud | Pine Research Instrumentation n.d. Available online: https://pineresearch.com/products/e3-rde-1018-peek/ (accessed on 16 October 2025).
- How to Polish Your Electrode. 2020. Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=B1vndNRUnV4 (accessed on 14 September 2025).
- Mayrhofer, K.J.J.; Strmcnik, D.; Blizanac, B.B.; Stamenkovic, V.; Arenz, M.; Markovic, N.M. Measurement of oxygen reduction activities via the rotating disc electrode method: From Pt model surfaces to carbon-supported high surface area catalysts. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 3181–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, H.A.; Kocha, S.S.; Sompalli, B.; Wagner, F.T. Activity benchmarks and requirements for Pt, Pt-alloy, and non-Pt oxygen reduction catalysts for PEMFCs. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2005, 56, 9–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001; p. 335. [Google Scholar]
- van der Vliet, D.; Strmcnik, D.S.; Wang, C.; Stamenkovic, V.R.; Markovic, N.M.; Koper, M.T.M. On the importance of correcting for the uncompensated Ohmic resistance in model experiments of the Oxygen Reduction Reaction. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2010, 647, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, E.; Uchida, H.; Watanabe, M. Effect of loading level in platinum-dispersed carbon black electrocatalysts on oxygen reduction activity evaluated by rotating disk electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2005, 583, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, J. Kinetics of oxygen reduction reaction on three different Pt surfaces of Pt/C catalyst analyzed by rotating ring-disk electrode in acidic solution. J. Power Sources 2014, 255, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treimer, S.; Tang, A.; Johnson, D.C. A Consideration of the Application of Koutecký-Levich Plots in the Diagnoses of Charge-Transfer Mechanisms at Rotated Disk Electrodes. Electroanalysis 2002, 14, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinozaki, K.; Zack, J.W.; Pylypenko, S.; Richards, R.M.; Pivovar, B.S.; Kocha, S.S. Benchmarking the oxygen reduction reaction activity of Pt-based catalysts using standardized rotating disk electrode methods. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 16820–16830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Chen, J.; Song, Y. A convenient protocol for the evaluation of commercial Pt/C electrocatalysts toward oxygen reduction reaction. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 870, 114172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moguchikh, E.; Paperzh, K.; Pankov, I.; Belenov, S.; Alekseenko, A. Durability of Commercial Catalysts within Relevant Stress Testing Protocols. Catalysts 2023, 13, 923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilenko, M.; Guterman, V.; Paperzh, K.; Alekseenko, A.; Nikulin, A. Kinetics of Nanoparticles Nucleation/Growth and Control of the Pt/C Catalysts Microstructure and Activity. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 987, 012022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, F.S.; Easton, E.B. Assessment of the ethanol oxidation activity and durability of Pt catalysts with or without a carbon support using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy. J. Power Sources 2014, 246, 392–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angel, G.M.A.; Mansor, N.; Jervis, R.; Rana, Z.; Gibbs, C.; Seel, A.; Kilpatrick, A.F.R.; Shearing, P.R.; Howard, C.A.; Brett, D.J.L.; et al. Realising the electrochemical stability of graphene: Scalable synthesis of an ultra-durable platinum catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 16113–16122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.X.; Tan, Z.H.; Zeng, M.; Wang, J.N. Carbon nanocages: A new support material for Pt catalyst with remarkably high durability. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; Tang, Y.; Mao, Z.; Sasaki, K. H2-induced thermal treatment significantly influences the development of a high performance low-platinum core-shell PtNi/C alloyed oxygen reduction catalyst. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 4773–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belenov, S.; Nevelskaya, A.; Nikulin, A.; Tolstunov, M. The Effect of Pretreatment on a PtCu1/C Catalyst’s Structure and Functional Characteristics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Huang, J.; Lai, S.; Zhang, S.; Fang, J.; Zhao, J. Pt skin coated hollow Ag-Pt bimetallic nanoparticles with high catalytic activity for oxygen reduction reaction. J. Power Sources 2017, 365, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Yan, Z.; Li, B.; Higgins, D.C.; Wang, J.; Lv, H.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, C. Highly active and durable Pt–Co nanowire networks catalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction in PEMFCs. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 18592–18601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yin, K.; Zhang, J.; Si, C.; Chen, X.; Lv, L.; Ma, W.; Gao, H.; Zhang, Z. A nanoporous PtCuTi alloy with a low Pt content and greatly enhanced electrocatalytic performance towards methanol oxidation and oxygen reduction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 14657–14668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, T.; Zhang, S.; Huang, J.; Cai, D.; Li, J.; Zhao, J. Direct One-pot Synthesis of Carbon Supported Ag-Pt Alloy Nanoparticles as High Performance Electrocatalyst for Fuel Cell Application. Fuel Cells 2019, 19, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.L.; Wang, Q.; Du, H.; Liang, T.; An, H.M.; Li, C.M. Sub-15 nm Pd@PtCu concave octahedron with enriched atomic steps as enhanced oxygen reduction electrocatalyst. J. Power Sources 2019, 434, 226742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Garcia, R.M.; Li, J.; Xie, Y.; Yin, J.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Shelnutt, J.A.; et al. One-step synthesis of carbon-supported foam-like platinum with enhanced activity and durability. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 21562–21568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensharapov, R.M.; Ivanova, N.A.; Spasov, D.D.; Kukueva, E.V.; Zasypkina, A.A.; Seregina, E.A.; Grigoriev, S.A.; Fateev, V.N. Carbon-Supported Pt-SnO2 Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction Reaction over a Wide Temperature Range: Rotating Disk Electrode Study. Catalysts 2021, 11, 1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Park, A.-H.; Kwon, Y.-U. Scalable synthesis of (Pd,Cu)@Pt core-shell catalyst with high ORR activity and durability. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 918, 116451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.-U.; Park, A.-H.; Shi, W.; Park, G.-G.; Kwon, Y.-U. Ternary core-shell PdM@Pt (M = Mn and Fe) nanoparticle electrocatalysts with enhanced ORR catalytic properties. Ultrason. Sonochemistry 2019, 58, 104673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paperzh, K.; Bayan, Y.; Gerasimov, E.; Pankov, I.; Konstantinov, A.; Menshchikov, V.; Mauer, D.; Beskopylny, Y.; Alekseenko, A. High-performance electrocatalyst for PEMFC cathode: Combination of ultra-small platinum nanoparticles and N-doped carbon support. Carbon. Trends 2024, 16, 100383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, K.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Mai, J.; Liu, G.; Sugumar, M.K.; Liu, X.; Zhan, F.; Tan, R. Nano-engineered catalysts for high-performance oxygen reduction reaction. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2024, 35, 109423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Methodology | Replicate | ECSA, m2/g(Pt) | E1/2, B | Number of ē | Koutecký–Levich Equation | Polarization Curve at 1600 rpm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ik, mA | Imass, A/g(Pt) | Isp, A/m2 (Pt) | Ik, mA | Imass, A/g(Pt) | Isp, A/m2 (Pt) | ||||||||
| Absolute Value | Average Value | Absolute Value | Average Value | Absolute Value | Average Value | ||||||||
| Stage 1 | |||||||||||||
| M0.31 | 1 | 66 | 70 ± 4 | 0.90 | 4.2 | 1.0 | 277 | 4.2 | 1.1 | 314 | 353 ± 50 | 4.8 | 5.0 ± 0.8 |
| 2 | 70 | 0.91 | 4.2 | 1.5 | 374 | 5.3 | 1.6 | 403 | 5.8 | ||||
| 3 | 74 | 0.91 | 3.5 | 1.4 | 351 | 4.7 | 1.4 | 343 | 4.6 | ||||
| M0.32 | 1 | 66 | 67 ± 1 | 0.89 | 3.6 | 1.0 | 241 | 3.7 | 0.9 | 229 | 256 ± 53 | 3.5 | 3.8 ± 0.8 |
| 2 | 67 | 0.89 | 4.3 | 1.0 | 267 | 4.0 | 1.2 | 309 | 4.6 | ||||
| 5 | 67 | 0.88 | 4.7 | 0.7 | 189 | 2.8 | 0.9 | 230 | 3.4 | ||||
| M0.33 | 1 | 68 | 68 ± 4 | 0.88 | 3.7 | 0.7 | 185 | 2.7 | 0.7 | 188 | 192 ± 4 | 2.8 | 2.8 ± 0.3 |
| 3 | 64 | 0.89 | 3.8 | 0.7 | 184 | 2.9 | 0.8 | 196 | 3.1 | ||||
| 5 | 71 | 0.88 | 4.1 | 0.7 | 179 | 2.5 | 0.8 | 193 | 2.7 | ||||
| Methodology | Replicate | ECSA, m2/g(Pt) | E1/2, B | Number of ē | Koutecký–Levich Equation | Polarization Curve at 1600 rpm | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ik, mA | Imass, A/g(Pt) | Isp, A/m2 (Pt) | Ik, mA | Imass, A/g(Pt) | Isp, A/m2 (Pt) | ||||||||
| Absolute Value | Average Value | Absolute Value | Average Value | Absolute Value | Average Value | ||||||||
| Stage 2 | |||||||||||||
| M0.31 | 1 | 31 | 29 ± 2 | 0.92 | 3.9 | 1.9 | 340 | 9.1 | 2.1 | 337 | 324 ± 46 | 10.9 | 11.0 ± 1.3 |
| 2 | 29 | 0.91 | 4.4 | 1.2 | 304 | 9.1 | 1.4 | 357 | 12.3 | ||||
| 3 | 28 | 0.9 | 4.5 | 1.2 | 306 | 9.1 | 1.1 | 278 | 9.9 | ||||
| M0.32 | 1 | 30 | 29 ± 2 | 0.9 | 4.3 | 0.8 | 189 | 5.1 | 0.9 | 222 | 193 ± 29 | 7.4 | 6.7 ± 0.9 |
| 2 | 27 | 0.88 | 4.0 | 0.6 | 171 | 5.1 | 0.7 | 185 | 6.9 | ||||
| 3 | 30 | 0.88 | 3.4 | 0.8 | 183 | 5.1 | 0.7 | 173 | 5.8 | ||||
| M0.33 | 1 | 28 | 29 ± 3 | 0.9 | 3.7 | 1.0 | 253 | 8.1 | 1.0 | 245 | 226 ± 22 | 8.8 | 7.7 ± 1.1 |
| 2 | 32 | 0.9 | 3.7 | 0.9 | 213 | 5.1 | 0.9 | 228 | 7.1 | ||||
| 3 | 28 | 0.89 | 3.3 | 0.9 | 206 | 6.1 | 0.9 | 204 | 7.3 | ||||
| Stage 3 | |||||||||||||
| M0.31 | 1 | 31 | 29 ± 2 | 0.92 | 3.9 | 1.9 | 340 | 9.1 | 2.1 | 337 | 324 ± 46 | 10.9 | 11.0 ± 1.3 |
| 2 | 29 | 0.91 | 4.4 | 1.2 | 304 | 9.1 | 1.4 | 357 | 12.3 | ||||
| 3 | 28 | 0.9 | 4.5 | 1.2 | 306 | 9.1 | 1.1 | 278 | 9.9 | ||||
| M0.41 | 1 | 28 | 29 ± 2 | 0.92 | 3.9 | 1.9 | 491 | 16.1 | 2.0 | 523 | 462 ± 61 | 18.7 | 16.0 ± 2.7 |
| 2 | 28 | 0.92 | 4.2 | 1.3 | 318 | 10.1 | 1.8 | 438 | 15.6 | ||||
| 3 | 31 | 0.92 | 4.1 | 1.5 | 377 | 11.1 | 1.7 | 424 | 13.7 | ||||
| M0.71 | 1 | 30 | 29 ± 1 | 0.87 | 3.2 | 0.6 | 155 | 4.1 | 0.6 | 153 | 131 ± 22 | 5.1 | 4.5 ± 0.6 |
| 2 | 28 | 0.84 | 2.6 | 0.6 | 137 | 3.1 | 0.5 | 112 | 4.0 | ||||
| 3 | 29 | 0.87 | 2.5 | 0.6 | 156 | 4.1 | 0.5 | 129 | 4.4 | ||||
| Methodology Designation | H2O:IPA | I/C | VH2O, μL | VIPA, μL | VNafion 5%, μL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pt/C | |||||
| Stage 1 | |||||
| M0.31 | 1:3 | 0.3 | 492.5 | 1492.5 | 15 |
| M0.32 | 1:1 | 992.5 | 992.5 | 15 | |
| M0.33 | 3:1 | 1492.5 | 492.5 | 15 | |
| PtCu/C | |||||
| Stage 2 | |||||
| M0.31 | 1:3 | 0.3 | 492.5 | 1492.5 | 15 |
| M0.32 | 1:1 | 992.5 | 992.5 | 15 | |
| M0.33 | 3:1 | 1492.5 | 492.5 | 15 | |
| Stage 3 | |||||
| M0.31 | 1:3 | 0.3 | 492.5 | 1492.5 | 15 |
| M0.41 | 0.4 | 490.0 | 1490.0 | 20 | |
| M0.71 | 0.7 | 483.0 | 1483.0 | 34 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kokhanov, A.A.; Moguchikh, E.A.; Pavlets, A.S.; Pankov, I.V.; Alekseenko, D.V.; Alekseenko, A.A. Improving the Reproducibility of Oxygen Reduction Reaction Activity Assessment for Pt-Based Electrocatalysts on a Rotating Disk Electrode via Catalytic Layer Optimization. Catalysts 2025, 15, 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15121140
Kokhanov AA, Moguchikh EA, Pavlets AS, Pankov IV, Alekseenko DV, Alekseenko AA. Improving the Reproducibility of Oxygen Reduction Reaction Activity Assessment for Pt-Based Electrocatalysts on a Rotating Disk Electrode via Catalytic Layer Optimization. Catalysts. 2025; 15(12):1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15121140
Chicago/Turabian StyleKokhanov, Andrey A., Elizaveta A. Moguchikh, Angelina S. Pavlets, Ilya V. Pankov, Danil V. Alekseenko, and Anastasia A. Alekseenko. 2025. "Improving the Reproducibility of Oxygen Reduction Reaction Activity Assessment for Pt-Based Electrocatalysts on a Rotating Disk Electrode via Catalytic Layer Optimization" Catalysts 15, no. 12: 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15121140
APA StyleKokhanov, A. A., Moguchikh, E. A., Pavlets, A. S., Pankov, I. V., Alekseenko, D. V., & Alekseenko, A. A. (2025). Improving the Reproducibility of Oxygen Reduction Reaction Activity Assessment for Pt-Based Electrocatalysts on a Rotating Disk Electrode via Catalytic Layer Optimization. Catalysts, 15(12), 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15121140









