Boosting Hydrogen Evolution via Phase Engineering-Modulated Crystallinity of Ruthenium–Zinc Bimetallic MOFs
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
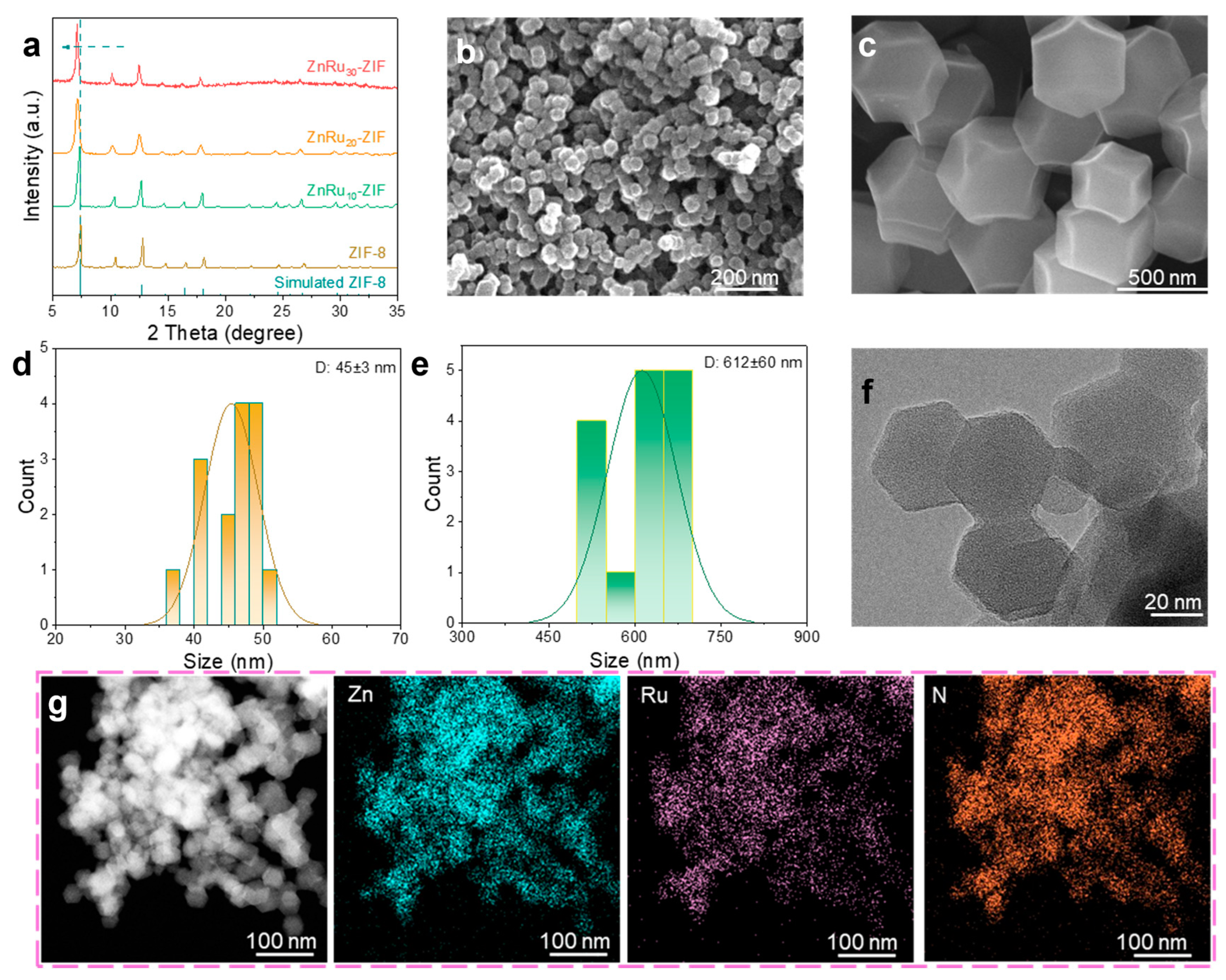
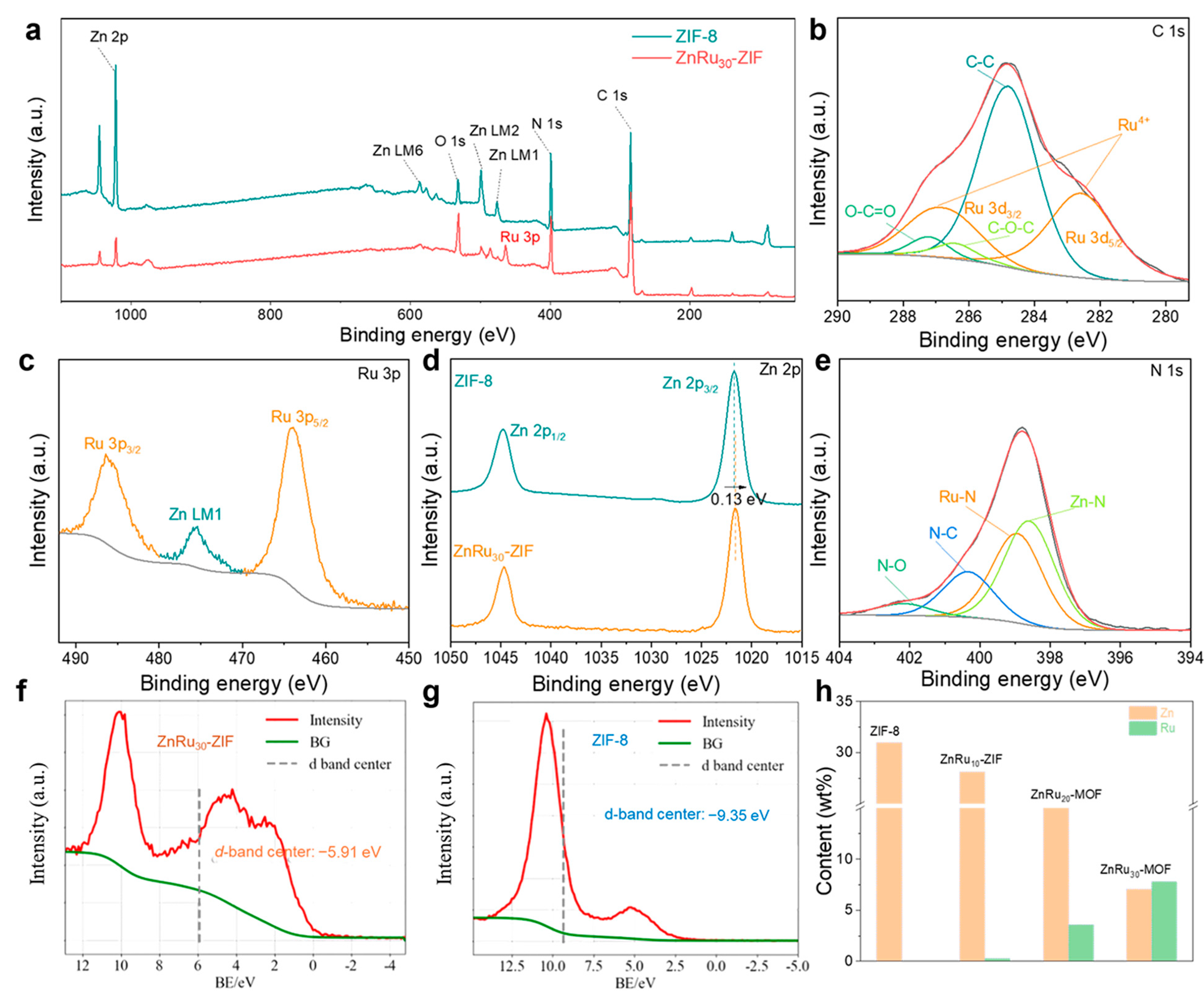
2.1. Morphological and Structural Characterizations
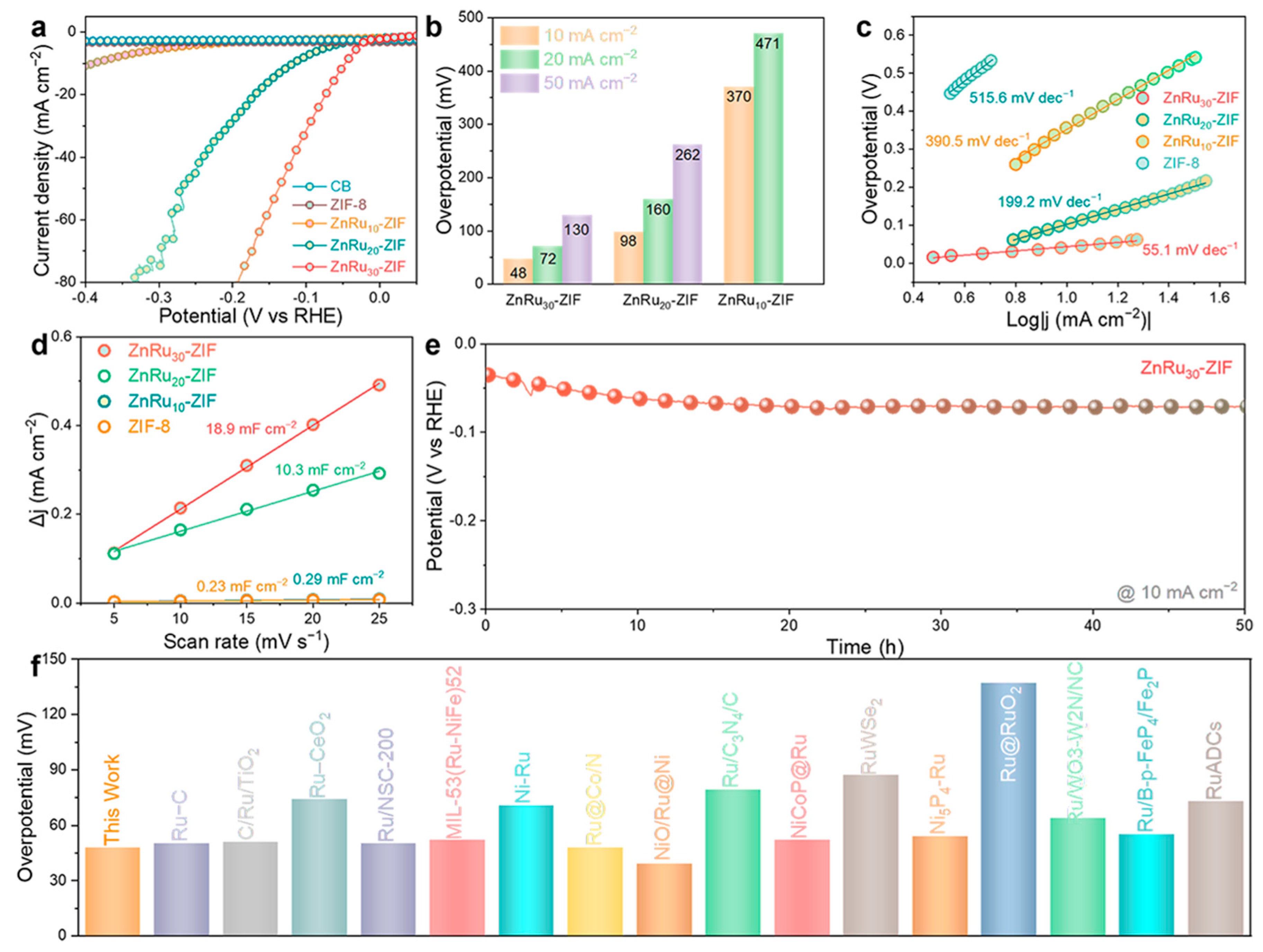
2.2. Electrocatalytic HER Performance
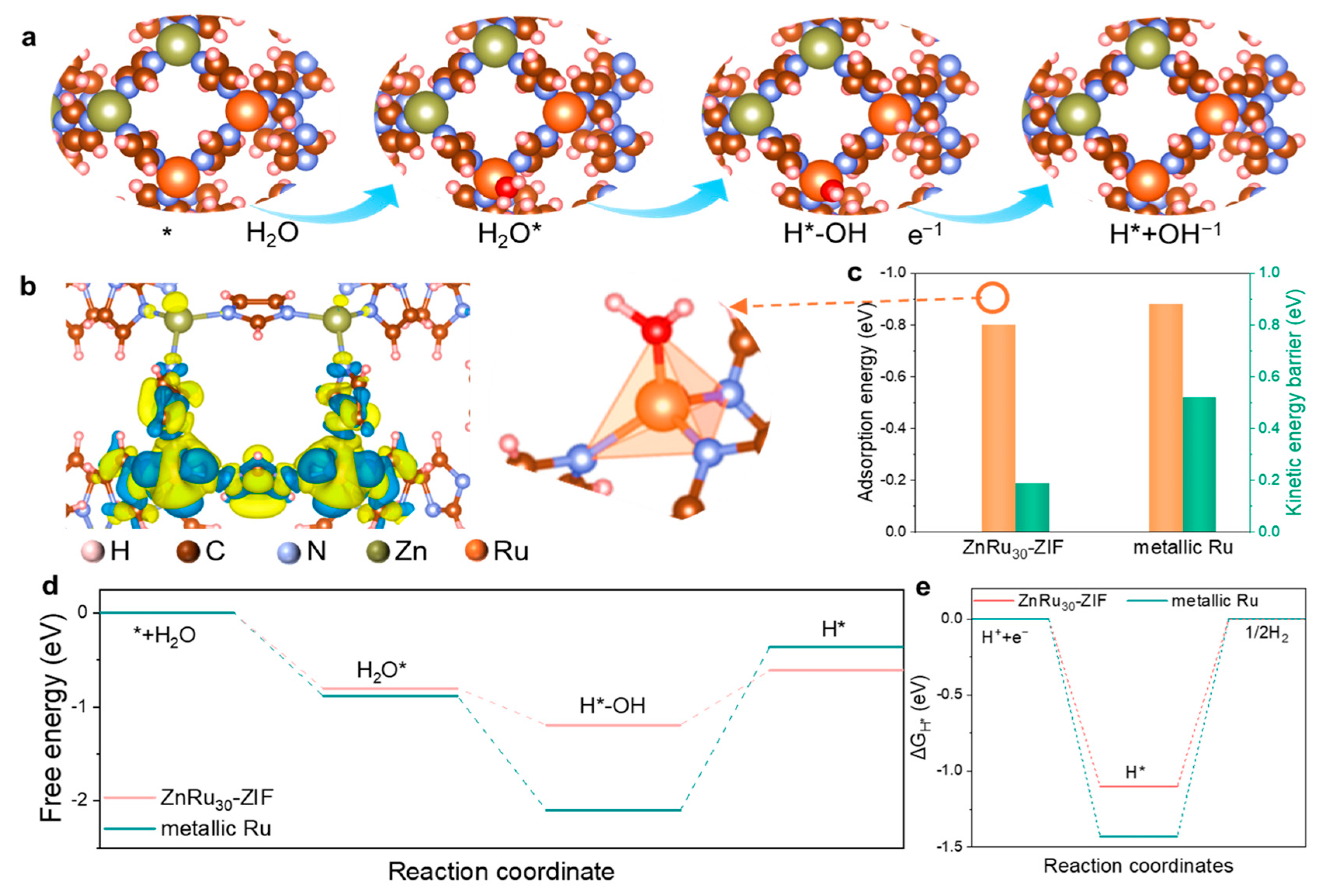
2.3. DFT Calculations
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Synthesis of ZIF-8
3.3. Synthesis of ZnRu30-ZIF
3.4. Material Characterizations
3.5. Electrochemical Measurement
3.6. Theoretical Calculations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Wei, J.; An, C.; Tang, H.; Deng, Q.; Li, J. Electrocatalyst design for the conversion of energy molecules: Electronic state modulation and mass transport regulation. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 10907–10924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pattengale, B.; Huang, Y.; Yan, X.; Yang, S.; Younan, S.; Hu, W.; Li, Z.; Lee, S.; Pan, X.; Gu, J.; et al. Dynamic evolution and reversibility of single-atom Ni(II) active site in 1T-MoS2 electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Zeng, L.; Yu, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, F.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; et al. Charge redistribution of Ru nanoclusters on Co3O4 porous nanowire via the oxygen regulation for enhanced hydrogen evolution reaction. Nano Energy 2021, 85, 105940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Jang, H.; Qin, Q.; Hou, L.; Kim, M.G.; Liu, S.; Liu, X.; Cho, J. Boosting Hydrogen Evolution Reaction by Phase Engineering and Phosphorus Doping on Ru/P-TiO2. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202212196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Deng, C.; Sun, Y.; Yan, C.; Qian, T. 2 A cm−2 Level Large-Scale Production of Hydrogen Enabled by Constructing Higher Capacity of Interface “Electron Pocket”. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 15504–15515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, Y.; Liu, T.; Wu, Y.; Yang, C.; Liu, B.; Hu, B.; Jiang, W.; Liu, C.; Che, G. Modulating the electronic structure of Ru using a self-reconstructed MOF-NiFeOOH heterointerface for improved electrocatalytic water splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 17404–17412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, W.; Tang, H.; Li, J. Tailoring the acidity of WO3/ZrO2 to regulate the energy barrier of water dissociation in alkaline hydrogen evolution. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 460, 141783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, Z.; Chang, Y.; Gyu Kim, M.; Jang, H.; Cho, J.; Hou, L.; Liu, X. Substantial Impact of Built-in Electric Field and Electrode Potential on the Alkaline Hydrogen Evolution Reaction of Ru−CoP Urchin Arrays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202400069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Han, G.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Ahn, S.H. Electrochemical fabrication of Ni-P-B ternary catalyst for hydrogen production in proton exchange membrane water electrolyzer. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 46, 5988–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhao, L.; Wang, L.; Cao, D.; Gong, Y. Ru doped bimetallic phosphide derived from 2D metal organic framework as active and robust electrocatalyst for water splitting. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 536, 147952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Lu, R.; Yao, Y.; Wu, D.; Zhao, H.; Yu, R.; Pu, Z.; Wang, P.; Zhu, J.; Yu, J.; et al. Duetting electronic structure modulation of Ru atoms in RuSe2@NC enables more moderate H* adsorption and water dissociation for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2022, 10, 7637–7644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Wang, P.; Niu, H.-J.; Che, Z.; Li, G.; Zhou, W. Single Ru atoms dispersed on MoSe2/MXene nanosheets with multiple interfaces for enhanced acidic hydrogen evolution. Carbon 2024, 218, 118758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Yi, H.; Yang, Z.; Wang, C. Bimetallic Sulfur-Doped Nickel–Cobalt Selenides as Efficient Bifunctional Electrocatalysts for the Complete Decomposition of Water. Small 2024, 20, 2402954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, E.; Song, W. Review—Self-Supporting Electrocatalysts for HER in Alkaline Water Electrolysis. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2024, 171, 052503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zong, L.; Fan, K.; Song, F.; Gao, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L. High temperature shock synthesis of superfine Ru nanoparticles anchored on TiO2 @nitrogen-doped carbon for pH-universal hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 969, 172279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Y.; Chen, P. Nanostructure engineering of ruthenium-modified electrocatalysts for efficient electrocatalytic water splitting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 3844–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.W.; Li, J.; Ou, P.; Huang, J.E.; Wen, Z.; Chen, L.; Yao, X.; Cai, G.; Yang, C.C.; Singh, C.V.; et al. Unusual Sabatier principle on high entropy alloy catalysts for hydrogen evolution reactions. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Li, Y.; Pei, C.; Lu, Y.; Kim, J.K.; Park, H.S.; Pang, H. Interfacial Design of Ti3C2Tx MXene/Graphene Heterostructures Boosted Ru Nanoclusters with High Activity Toward Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2310013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, R.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, X.Y. Rational Design of Heterostructured Ru Cluster-Based Catalyst for pH Universal Hydrogen Evolution Reaction and High-Performance Zn-H2O Battery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 34, 2301925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Li, W.; Xie, Y.; Liu, H.; Shang, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z.; Gu, L.; et al. A General Route to Prepare Low-Ruthenium-Content Bimetallic Electrocatalysts for pH-Universal Hydrogen Evolution Reaction by Using Carbon Quantum Dots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 59, 1718–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, R.; Li, Z.; Li, R.; Jiang, C.; Qi, R.; Liu, M.; Lin, H.; Huang, R.; Luo, C.; Peng, H. Ultrafine Ru nanoparticles derived from few-layered Ti3C2Tx MXene templated MOF for highly efficient alkaline hydrogen evolution. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 47, 32787–32795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Kim, S.H.; Lim, H.Y.; Sun, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Noh, H.J.; Kim, S.J.; Baek, J.; Kwak, S.K.; Baek, J.B. Self-Accommodation Induced Electronic Metal–Support Interaction on Ruthenium Site for Alkaline Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2301369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhou, W.; Li, J. Catalyst-Support Interactions Promoted Acidic Electrochemical Oxygen Evolution Catalysis: A Mini Review. Molecules 2023, 28, 2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelghafar, F.; Xu, X.; Jiang, S.P.; Shao, Z. Designing single-atom catalysts toward improved alkaline hydrogen evolution reaction. Mater. Rep. Energy 2022, 2, 100144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Ji, L.; Wang, J.; Shen, J.; Liao, J.; He, X.; Wang, T.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S. Ultrafine Ruthenium Nanoparticles Anchored on S,N-Codoped Carbon Nanofibers for H2 and Electricity Coproduction. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 17406–17416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Hung, S.-F.; Deng, L.; Zeng, W.-J.; Xiao, T.; Li, S.; Kuo, C.-H.; Chen, H.-Y.; Hu, F.; Peng, S. Constructing regulable supports via non-stoichiometric engineering to stabilize ruthenium nanoparticles for enhanced pH-universal water splitting. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wei, W.; Xu, X.; Gu, X.; Huang, C.; Wei, W.; Shao, Z.; Ni, B.-J.; Chen, H. Reconstructed anti-corrosive and active surface on hierarchically porous carbonized wood for efficient overall seawater electrolysis. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 2337–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, B.; Liu, D.; Feng, X.; Shao, M.; Zhang, Y. Ru Nanoparticles Supported on Co-Embedded N-Doped Carbon Nanotubes as Efficient Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Evolution in Basic Media. Chem. Res. Chin. Univ. 2020, 36, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.; Wang, J.; Zhang, D.; Xu, J.; Guo, F.; Zhang, Y.; Pang, R.; Cao, A.; Shang, Y. Defective Amorphous Carbon-Coated Carbon Nanotube-Loaded Ruthenium Nanoparticles as Efficient Electrocatalysts for Hydrogen Production. Small Struct. 2023, 4, 2300098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, L.; Li, G.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, H.; Chen, B.H. Reduced graphene oxide-supported ruthenium nanocatalysts for highly efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. Int. J. Energy Res. 2022, 47, 39853–39863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, A.; Ren, H.-D.; Al-Ansi, N.; Tan, H.; Yu, F.; Yanchun, L.; Thamer, B.M.; Al-Salihy, A.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y. Dispersing small Ru nanoparticles into boron nitride remodified by reduced graphene oxide for high-efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 644, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Kim, B.; Li, Z.; Thapa, R.; Zhang, Y.; Seo, J.M.; Guan, R.; Tang, F.; Baek, J.H.; Kim, Y.H.; et al. Direct Electroplating Ruthenium Precursor on the Surface Oxidized Nickel Foam for Efficient and Stable Bifunctional Alkaline Water Electrolysis. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2403151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Wang, C.; Guo, L.; Wang, Y. Ru-modulated morphology and electronic structure of nickel organic framework bifunctional electrocatalyst for efficient overall water splitting. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 470, 143300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Yang, W.; Jiao, L.; Li, L.; Yu, S.H.; Jiang, H.L. Boosting Catalysis of Pd Nanoparticles in MOFs by Pore Wall Engineering: The Roles of Electron Transfer and Adsorption Energy. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2000041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Hu, F.; Ma, M.; Huang, S.C.; Xiong, Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Li, L.; Peng, S. Electronic Modulation Caused by Interfacial Ni-O-M (M=Ru, Ir, Pd) Bonding for Accelerating Hydrogen Evolution Kinetics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021, 60, 22276–22282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yu, S.; Ren, T.; Liu, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, H. Hydrophilic/Aerophobic Hydrogen-Evolving Electrode: NiRu-Based Metal-Organic Framework Nanosheets In Situ Grown on Conductive Substrates. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 34728–34735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adegoke, K.A.; Ogunjinmi, O.E.; Adegoke, O.R.; Bello, O.S. Bifunctional two-dimensional metal organic frameworks for oxygen reaction and water splitting. Nano Energy 2024, 128, 109897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, P.; Kang, J.; Zhong, Y.; Xiang, R.; Wang, S.; Li, S.; Liu, X.; Li, G. Recent advances of two-dimensional metal-organic frameworks in alkaline electrolysis water for hydrogen production. Sci. China Chem. 2023, 66, 1924–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, A.; Ren, H.-D.; Al-Ansi, N.; Al-Salihy, A.; Qaraah, F.A.; Mahyoub, S.A.; Ahmed, A.A.; Drmosh, Q.A. Interface Engineering Induced by Low Ru Doping in Ni/Co@NC Derived from Ni-ZIF-67 for Enhanced Electrocatalytic Overall Water Splitting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 60310–60320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezaee, S.; Shahrokhian, S. Ruthenium/Ruthenium oxide hybrid nanoparticles anchored on hollow spherical Copper-Cobalt Nitride/Nitrogen doped carbon nanostructures to promote alkaline water splitting: Boosting catalytic performance via synergy between morphology engineering, electron transfer tuning and electronic behavior modulation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 626, 1070–1084. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.-Y.; Cai, S.-H.; Zhu, J.-Y.; Yang, S.; Li, J.-S. MOF-derived ruthenium-doped amorphous molybdenum dioxide hybrid for highly efficient hydrogen evolution reaction in alkaline media. Chem. Commun. 2022, 58, 100–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Xue, Z.; Liu, Q.; Jia, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, K.; Lin, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, G.; Su, C.-Y. Modulating electronic structure of metal-organic frameworks by introducing atomically dispersed Ru for efficient hydrogen evolution. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Xia, Y. Crystal-phase and surface-structure engineering of ruthenium nanocrystals. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2020, 5, 440–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, L.; Yao, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; Yang, H.; Chi, B.; Liang, J.; et al. Phase Engineering of Nanomaterials: Transition Metal Dichalcogenides. Chem. Rev. 2024, 124, 4479–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.; Zhong, Y.; Wajrak, M.; Bhatelia, T.; Jiang, S.P.; Shao, Z. Grain boundary engineering: An emerging pathway toward efficient electrocatalysis. InfoMat 2024, 6, 10608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Han, J.; Sun, T.; Zhao, J.; Pi, X.; Xu, J.; Chen, K. Amorphous Ruthenium–Selenium Nanoparticles as a pH-Universal Catalyst for Enhanced Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. ACS Catal. 2024, 14, 1914–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, M.; Xiao, L.; Tang, H.; Li, J.; Kou, Z.; Li, J. Epitaxial heterointerfacial electron bridge synchronizes oxygen evolution activity and stability on a layered double hydroxide surface. EES Catal. 2024, 2, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forgan, R.S. Modulated self-assembly of metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Sci. 2020, 11, 4546–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemura, A.; Diring, S.; Furukawa, S.; Uehara, H.; Tsuruoka, T.; Kitagawa, S. Morphology Design of Porous Coordination Polymer Crystals by Coordination Modulation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15506–15513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacirhonde, P.M.; Mohamed, A.Y.; Han, B.; Cho, D.Y.; Devendra, S.; Choi, J.W.; Lim, C.R.; Afranie, E.O.; Baik, K.H.; Kang, K.; et al. Ruthenium Engineered A2B2O6-Hybrid Columbite Ferrite for Bifunctional pH-Universal Water Splitting. Adv. Energy Mater. 2023, 13, 2300174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, Z.A.; Chen, S. 3D Hierarchical Carbon-Supported Ultrafine Ru Nanoparticles for pH Universal Hydrogen Evolution Reactions. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 7555–7561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-C.; Ji, P.-C.; Teng, Y.; Jia, H.-L.; Guan, M.-Y. Preparation of carbon coated hyperdispersed Ru nanoparticles supported on TiO2 HER electrocatalysts by dye-sensitization. New J. Chem. 2023, 47, 9628–9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Najib, A.S.B.; Iqbal, M.; Zakaria, M.B.; Shoji, S.; Cho, Y.; Peng, X.; Ueda, S.; Hashimoto, A.; Fujita, T.; Miyauchi, M.; et al. Active faceted nanoporous ruthenium for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 19788–19792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, M.; Fonseca, H.A.B.; Verga, L.G.; Rafe Hatshan, M.; Da Silva, J.L.F.; Varela, H.; Shahgaldi, S. Facile synthesis of Ru nanoclusters embedded in carbonaceous shells for hydrogen evolution reaction in alkaline and acidic media. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2023, 929, 117116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, H.; Li, W.; Li, J.; Yi, L.; Hu, W.; Li, C.M. Ru-Doping Enhanced Electrocatalysis of Metal–Organic Framework Nanosheets toward Overall Water Splitting. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 26, 17091–17096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Q.-Q.; Bai, X.; Du, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, Z.-Y.; Yue, X.-Z. Facet modulation of nickel-ruthenium nanocrystals for efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 633, 275–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Hu, G.; Feng, L. Ru Nanoclusters Coupled on Co/N-Dopde Carbon Nanotubes Efficiently Catalyzed the Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 9136–9144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Zhou, Q.; Li, S.; Cao, L.; Li, J.; Shen, Z.; Ma, H.; Liu, J.; Lu, M.; Zhang, H. Enhanced synergistic catalysis by a novel triple-phase interface design of NiO/Ru@Ni for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 2344–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Li, L.H.; Han, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jaroniec, M.; Qiao, S.-Z. High Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Activity of an Anomalous Ruthenium Catalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 16174–16181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, Q.; Lv, Y.; Chen, B.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Q.; Che, C.; Chen, C. Ru decorated with NiCoP: An efficient and durable hydrogen evolution reaction electrocatalyst in both acidic and alkaline conditions. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 13153–13156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Mao, G.; Huang, C.; Cai, P.; Cheng, G.; Luo, W. Decorating WSe2 nanosheets with ultrafine Ru nanoparticles for boosting electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution in alkaline electrolytes. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2019, 6, 1382–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Tian, D.; Jiang, H.; Cao, D.; Wei, S.; Liu, D.; Song, P.; Lin, Y.; Song, L. Achieving Efficient Alkaline Hydrogen Evolution Reaction over a Ni5P4 Catalyst Incorporating Single-Atomic Ru Sites. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, R.; Tran, D.T.; Li, J.; Chu, D. Ru@RuO2 Core-Shell Nanorods: A Highly Active and Stable Bifunctional Catalyst for Oxygen Evolution and Hydrogen Evolution Reactions. Energy Environ. Mater. 2019, 2, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, T.; Cui, Z.; Guo, P.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Wang, W.; Li, Z. Fabrication of Ru/WO3-W2N/N-doped carbon sheets for hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2023, 636, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, P.; Liu, D.; Jin, W.; Xiao, W.; Xiao, Z.; Wu, Z.; Wang, L. Amorphous Ru Coupled with Defect-Abundant B-Doped FeP4/Fe2P Porous Nanospheres as an Electrocatalyst for Hydrogen Generation with a Wide pH Range. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2023, 6, 19905–19914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Si, C.; Escobar-Bedia, F.J.; LaGrow, A.P.; Xu, J.; Sabater, M.J.; Amorim, I.; Araujo, A.; Sousa, J.P.S.; Meng, L.; et al. Bifunctional atomically dispersed ruthenium electrocatalysts for efficient bipolar membrane water electrolysis. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2022, 9, 4142–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, J.; Wang, D.; Huang, T.; He, Z.; Cui, Y.; Li, J. Boosting Hydrogen Evolution via Phase Engineering-Modulated Crystallinity of Ruthenium–Zinc Bimetallic MOFs. Catalysts 2025, 15, 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15010058
Wang J, Wang D, Huang T, He Z, Cui Y, Li J. Boosting Hydrogen Evolution via Phase Engineering-Modulated Crystallinity of Ruthenium–Zinc Bimetallic MOFs. Catalysts. 2025; 15(1):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15010058
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Jia, De Wang, Tianci Huang, Zhenyu He, Yong Cui, and Junsheng Li. 2025. "Boosting Hydrogen Evolution via Phase Engineering-Modulated Crystallinity of Ruthenium–Zinc Bimetallic MOFs" Catalysts 15, no. 1: 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15010058
APA StyleWang, J., Wang, D., Huang, T., He, Z., Cui, Y., & Li, J. (2025). Boosting Hydrogen Evolution via Phase Engineering-Modulated Crystallinity of Ruthenium–Zinc Bimetallic MOFs. Catalysts, 15(1), 58. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal15010058






