Formic Acid Dehydrogenation over a Monometallic Pd and Bimetallic Pd:Co Catalyst Supported on Activated Carbon
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Catalyst Characterization
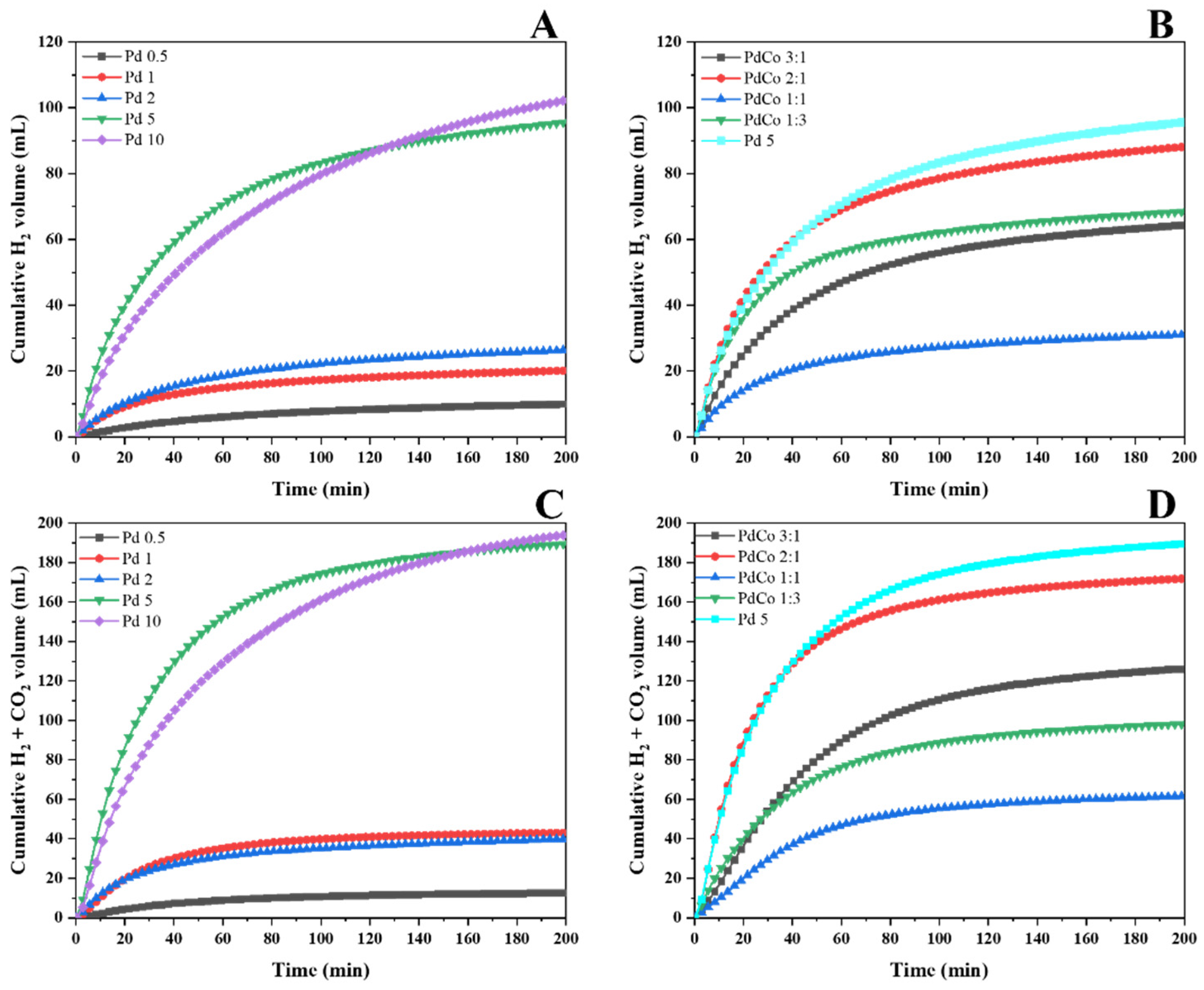
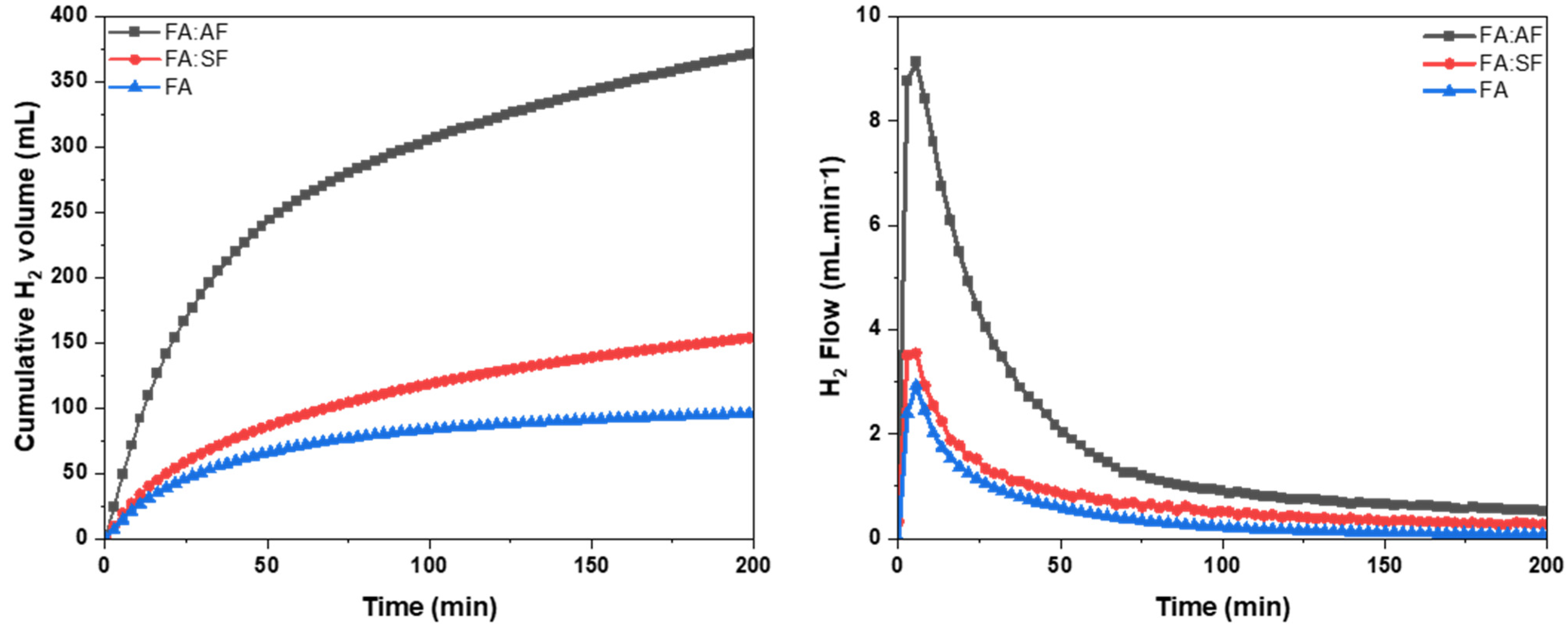
2.2. Catalytic Activity
Catalyst Screening
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalyst Preparation and Chemicals
3.2. Characterization Methods
3.3. Catalytic Tests
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sundramoorthy, A.K.; Paul, R.; Jiao, Y.; Li, Y.; Navlani-García, M.; Mori, K.; Salinas-Torres, D.; Kuwahara, Y.; Yamashita, H. New Approaches toward the Hydrogen Production from Formic Acid Dehydrogenation over Pd-Based Heterogeneous Catalysts. Front. Mater. 2019, 1, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahuguna, A.; Sasson, Y. Formate-Bicarbonate Cycle as a Vehicle for Hydrogen and Energy Storage. ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 1258–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellmann, D.R.; Sponholz, P.; Junge, H.; Beller, M. Formic acid as a hydrogen storage material-development of homogeneous catalysts for selective hydrogen release. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentini, F.; Kozell, V.; Petrucci, C.; Marrocchi, A.; Gu, Y.; Gelman, D.; Vaccaro, L. Formic acid, a biomass-derived source of energy and hydrogen for biomass upgrading. Energy Environ. Sci. 2019, 12, 2646–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.; Sang, R.; Sponholz, P.; Junge, H.; Beller, M. Reversible hydrogenation of carbon dioxide to formic acid using a Mn-pincer complex in the presence of lysine. Nat. Energy 2022, 7, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanega, R.; Ertem, M.Z.; Onishi, N.; Szalda, D.J.; Fujita, E.; Himeda, Y. CO2 Hydrogenation and Formic Acid Dehydrogenation Using Ir Catalysts with Amide-Based Ligands. Organometallics 2020, 39, 1519–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flannelly, T.; Lopes, M.; Kupiainen, L.; Dooley, S.; Leahy, J.J. Non-stoichiometric formation of formic and levulinic acids from the hydrolysis of biomass derived hexose carbohydrates. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 5797–5804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Wu, J. Sustainable production of formic acid from biomass and carbon dioxide. Mol. Catal. 2020, 483, 110716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihet, M.; Dan, M.; Barbu-Tudoran, L.; Lazar, M.D.; Blanita, G. Controllable H2 Generation by Formic Acid Decomposition on a Novel Pd/Templated Carbon Catalyst. Hydrogen 2020, 1, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellone, I.; Peruzzini, M.; Rosi, L.; Mellmann, D.; Junge, H.; Beller, M.; Gonsalvi, L. Formic acid dehydrogenation catalysed by ruthenium complexes bearing the tripodal ligands triphos andNP3. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 2495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, C.; Zhang, D.-D.; Pan, Y.; Iguchi, M.; Ajitha, M.J.; Hu, J.; Li, H.; Yao, C.; Huang, M.-H.; Min, S.; et al. Dehydrogenation of Formic Acid Catalyzed by a Ruthenium Complex with an N,N′-Diimine Ligand. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 56, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Huang, H.; Roisnel, T.; Bruneau, C.; Fischmeister, C. Base-Free Dehydrogenation of Aqueous and Neat Formic Acid with Iridium(III) Cp*(dipyridylamine) Catalysts. ChemSusChem 2019, 12, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, O.; Al-Nayili, A.; Majdi, H.S.; Albayati, T.M.; Saady, N.M.C. Formic Acid Dehydrogenation Using Noble-Metal Nanoheterogeneous Catalysts: Towards Sustainable Hydrogen-Based Energy. Catalysts 2022, 12, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, M.; Iglesia, E. HCOOH Dehydrogenation on Au Formic Acid Dehydrogenation on Au-Based Catalysts at Near-Ambient Temperatures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 4800–4803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.L.; León, C.; Monnier, G.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M.Á.; Odriozola, J.A. Bimetallic PdAu catalysts for formic acid dehydrogenation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 23056–23068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trillo, J.M.; Munuera, G.; Criado, J.M. Catalytic Decomposition of Formic Acid on Metal Oxides. Catal. Rev. 1972, 7, 51–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z. Trimetallic nanoparticles: Synthesis, characterization and catalytic degradation of formic acid for hydrogen generation. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 11503–11513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Luo, W.; Cheng, G. Monodisperse CoAgPd nanoparticles assembled on graphene for efficient hydrogen generation from formic acid at room temperature. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-L.; Yan, J.-M.; Ping, Y.; Wang, H.-L.; Zheng, W.-T.; Jiang, Q. An Efficient CoAuPd/C Catalyst for Hydrogen Generation from Formic Acid at Room Temperature. Angew. Chem. 2013, 125, 4502–4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.W.J.; Mavrikakis, M. Formic Acid: A Hydrogen-Bonding Cocatalyst for Formate Decomposition. ACS Catal. 2020, 10, 10812–10825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda, M.; Iglesia, E. Formic Acid Dehydrogenation on Au-Based Catalysts at Near-Ambient Temperatures. Angew. Chem. 2009, 121, 4894–4897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gazsi, A.; Ans, T.B.; Solymosi, F. Decomposition and Reforming of Formic Acid on Supported Au Catalysts: Production of CO-Free H2. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 15459–15466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Q.-Y.; Du, X.-L.; Liu, Y.-M.; Cao, Y.; He, H.-Y.; Fan, K.-N. Efficient Subnanometric Gold-Catalyzed Hydrogen Generation via Formic Acid Decomposition under Ambient Conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 8926–8933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.L.; Megías-Sayago, C.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M.Á.; Odriozola, J.A. Functionalized biochars as supports for Pd/C catalysts for efficient hydrogen production from formic acid. Appl. Catal. B 2021, 282, 119615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.L.; Bashir, S.; Yan, T.-H. Advanced Nanomaterials and Their Applications in Renewable Energy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chaparro-Garnica, J.; Navlani-García, M.; Salinas-Torres, D.; Berenguer-Murcia, Á.; Morallón, E.; Cazorla-Amorós, D. Efficient production of hydrogen from a valuable CO2-derived molecule: Formic acid dehydrogenation boosted by biomass waste-derived catalysts. Fuel 2022, 320, 123900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navlani-García, M.; Salinas-Torres, D.; Mori, K.; Léonard, A.F.; Kuwahara, Y.; Job, N.; Yamashita, H. Insights on palladium decorated nitrogen-doped carbon xerogels for the hydrogen production from formic acid. Catal. Today 2019, 324, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurderi, M.; Bulut, A.; Caner, N.; Celebi, M.; Kaya, M.; Zahmakiran, M. Amine grafted silica supported CrAuPd alloy nanoparticles: Superb heterogeneous catalysts for the room temperature dehydrogenation of formic acid. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 11417–11420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enthaler, S.; von Langermann, J.; Schmidt, T. Carbon dioxide and formic acid—The couple for environmental-friendly hydrogen storage? Energy Environ. Sci. 2010, 3, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.P.; Winterbottom, J.M. The conversion of polysaccharides to hydrogen gas. Part I: The palladium catalysed decomposition of formic acid/sodium formate solutions. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1988, 41, 121–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.W.J.; Bhandari, S.; Mavrikakis, M. Role of Hydrogen-bonded Bimolecular Formic Acid-Formate Complexes for Formic Acid Decomposition on Copper: A Combined First-Principles and Microkinetic Modeling Study. ACS Catal. 2021, 11, 4349–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Q.-Y.; Lin, J.-D.; Liu, Y.-M.; Du, X.-L.; Wang, J.-Q.; He, H.-Y.; Cao, Y. Hydrogen Storage An Aqueous Rechargeable Formate-Based Hydrogen Battery Driven by Heterogeneous Pd Catalysis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 13583–13587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.-T.; Zhang, J.; Chi, J.-C.; Li, Z.-H.; Liu, Y.-C.; Liu, X.-R.; Zhang, S.-Y. Efficient dehydrogenation of a formic acid-ammonium formate mixture over Au3Pd1 catalyst. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 5995–6002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, J.L.; Megías-Sayago, C.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M.A.; Odriozola, J.A. Structure-sensitivity of formic acid dehydrogenation reaction over additive-free Pd NPs supported on activated carbon. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 420, 127641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noronha, F.B.; Schmal, M.; Fréty, R.; Fréty, F.; Bergeret, G.; Moraweck, B. Evidence of Alloy Formation during the Activation of Graphite-Supported Palladium-Cobalt Catalysts. J. Catal. 1999, 186, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, C.; Quintanilla, A.; Vega, G.; Casas, J.A. Formic acid-to-hydrogen on Pd/AC catalysts: Kinetic study with catalytic deactivation. Appl. Catal. B 2022, 317, 121802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Pulleri, J.K.; Ting, S.W.; Chan, K.Y. Activity of Pd/C for hydrogen generation in aqueous formic acid solution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, D.H. Understanding the effect of Pd size on formic acid dehydrogenation via size-controlled Pd/C catalysts prepared by NaBH4 treatment. Appl. Catal. B 2019, 244, 684–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Yang, L.; Lu, M.; Lin, H. Highly efficient hydrogen storage system based on ammonium bicarbonate/formate redox equilibrium over palladium nanocatalysts. ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 813–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.L.; López, E.R.; Ivanova, S.; Monzón, A.; Centeno, M.Á.; Odriozola, J.A. Low CO2 hydrogen streams production from formic acid through control of the reaction pH. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 455, 140645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Ham, H.C.; Kim, D.H. Mechanistic insights on aqueous formic acid dehydrogenation over Pd/C catalyst for efficient hydrogen production. J. Catal. 2020, 389, 506–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-L.; Yan, J.-M.; Wang, H.-L.; Ping, Y.; Jiang, Q. Pd/C Synthesized with Citric Acid: An Efficient Catalyst for Hydrogen Generation from Formic Acid/Sodium Formate. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Xu, K.; Zou, S.; Cai, W.B. B-doped pd catalyst: Boosting room-temperature hydrogen production from formic acid-formate solutions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 4861–4864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.; Lee, K.; Yoo, I.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Ramadhani, S.; Sohn, H.; Nam, S.W.; Kim, J.; Kim, Y.; Jeong, H. Strategy for Efficient H2Production from a Mixture of Formic Acid and Formate using Operando pH Measurements. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Ryu, J.; Kim, J.Y.; Nam, S.-W.; Han, J.H.; Lim, T.-H.; Gautam, S.; Chae, K.H.; Yoon, C.W. Carbon dioxide mediated, reversible chemical hydrogen storage using a Pd nanocatalyst supported on mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2014, 2, 9490–9495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qi, G.-W.; Tan, C.-H.; Li, Y.-P.; Guo, J.; Pang, X.-J.; Zhang, S.-Y. Pd/C nanocatalyst with high turnover frequency for hydrogen generation from the formic acid-formate mixtures. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergeret, G.; Gallezot, P. Particle Size and Dispersion Measurements; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; p. 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
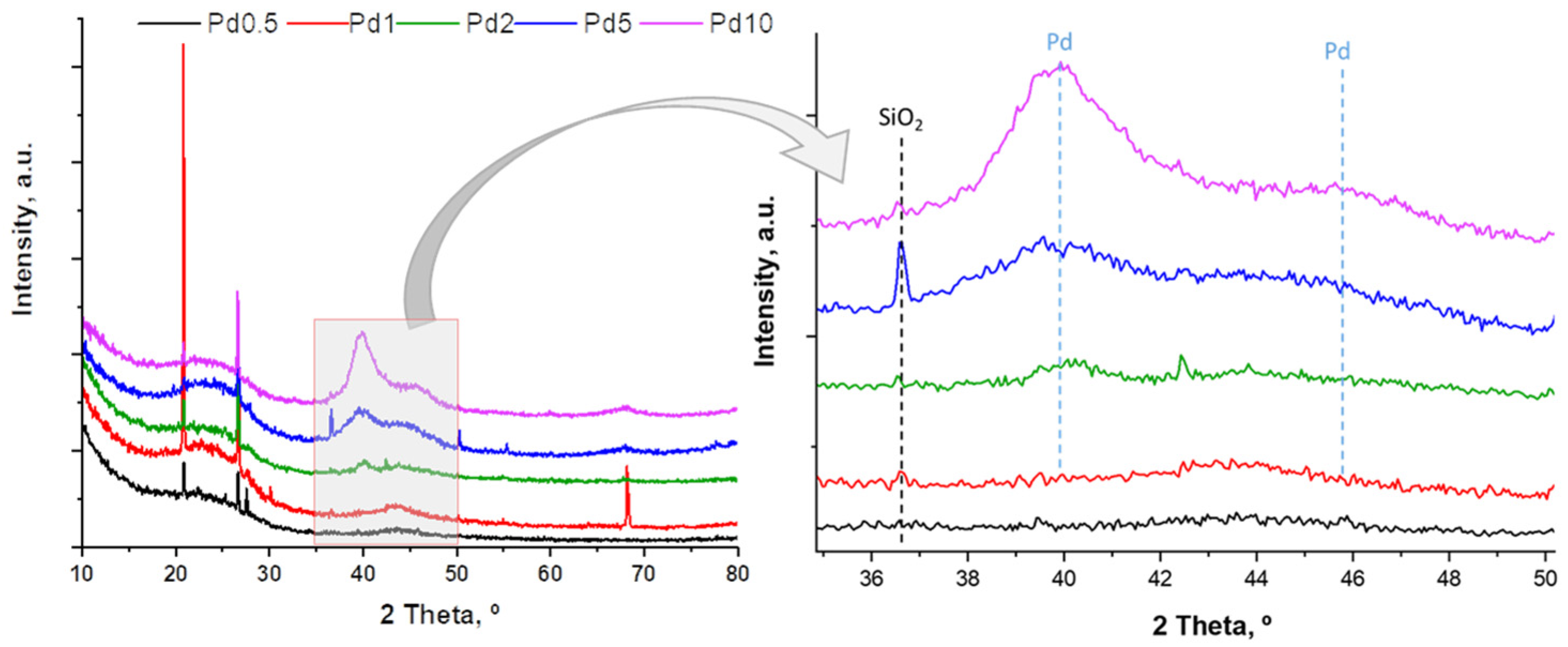
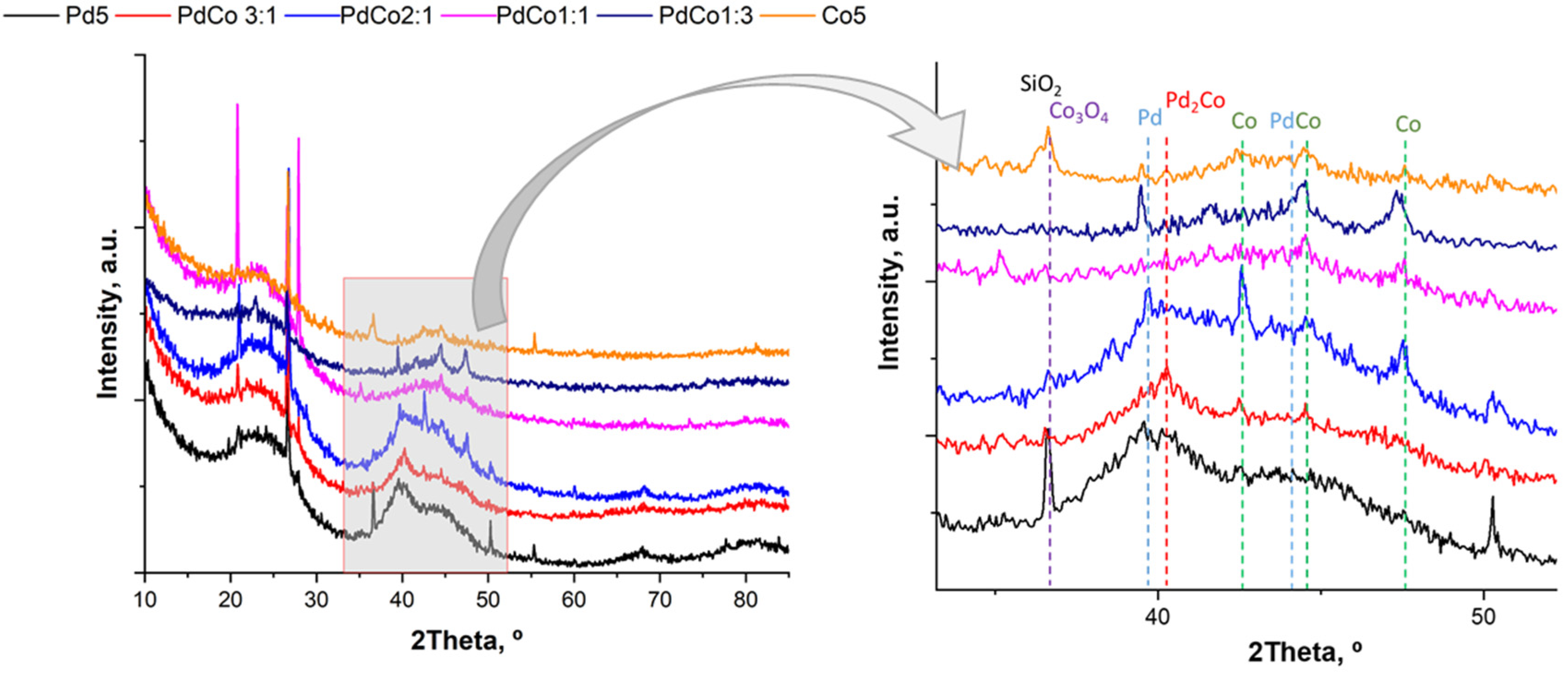
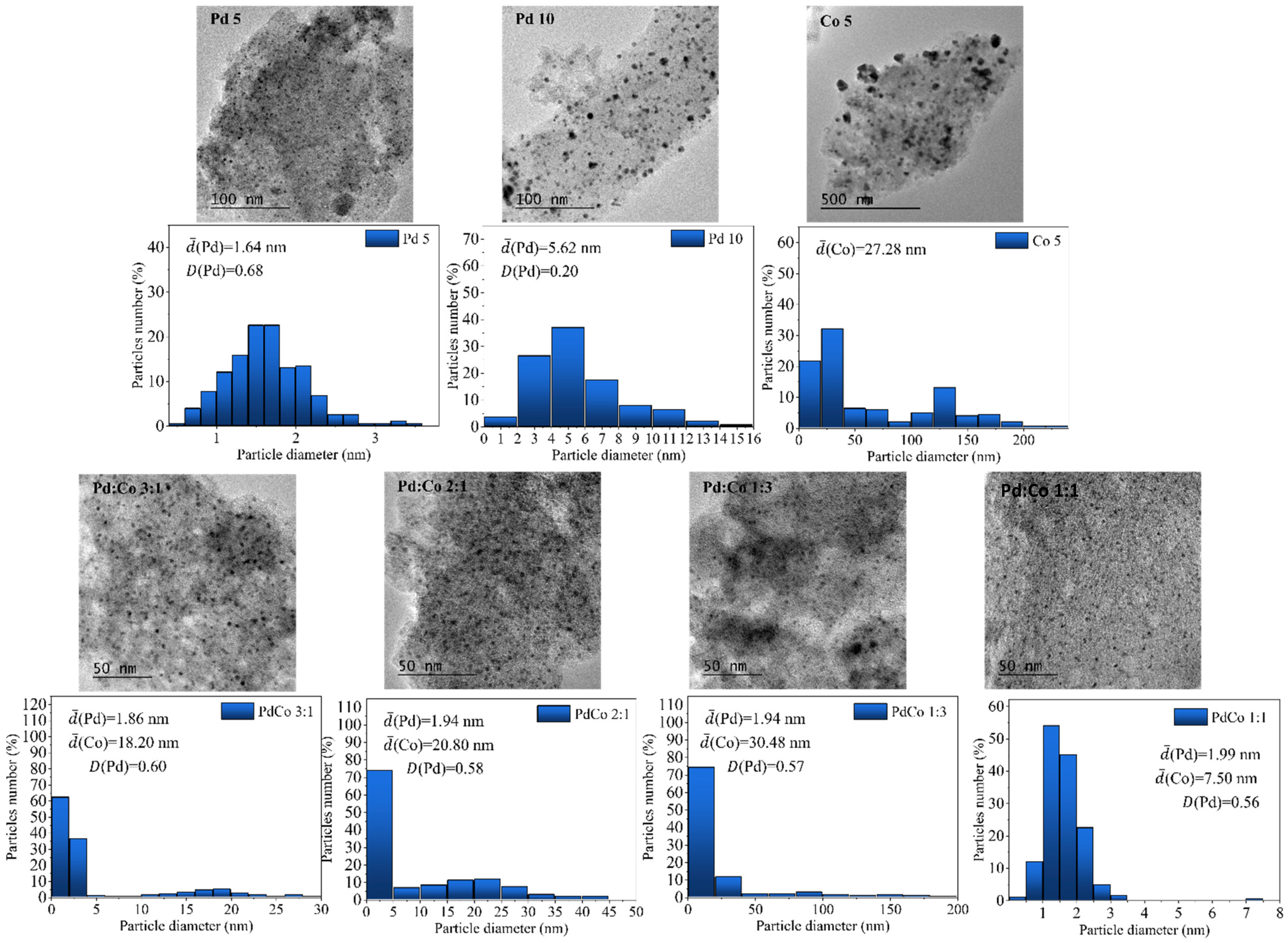
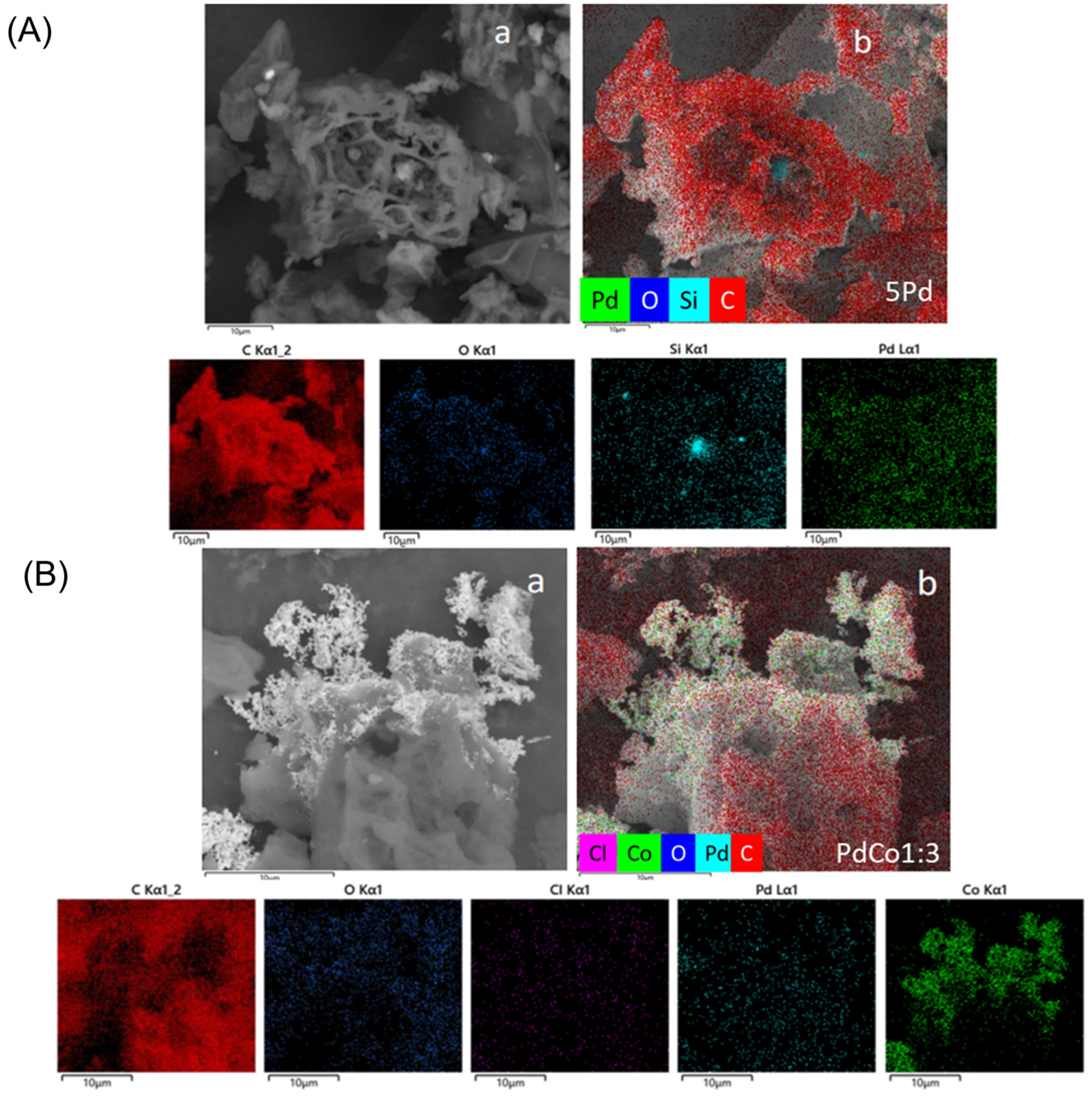

| Catalyst | ICP-OES (wt%) | Particle Size TEM, nm | Dispersion Pd | SBET (m2/g) | SEXT (m2/g) | Vpore (cm3/g) | Pore Diameter (Å) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pd | Co | Pd | Co | ||||||
| AC | - | - | - | - | - | 844 | 368 | 0.41 | 53.02 |
| Pd 0.5 | 0.5 | - | - | - | - | 852 | 371 | 0.40 | 51.49 |
| Pd 1 | 0.9 | - | - | - | - | 846 | 372 | 0.40 | 51.14 |
| Pd 2 | 1.8 | - | - | - | - | 817 | 384 | 0.45 | 54.52 |
| Pd 5 | 5.1 | - | 1.64 | - | 0.68 | 759 | 354 | 0.41 | 54.61 |
| Pd 10 | 9.6 | - | 5.62 | - | 0.2 | 736 | 316 | 0.36 | 53.82 |
| Pd:Co 5 (3:1) | 4.2 | 0.7 | 1.86 | 18.2 | 0.6 | 808 | 372 | 0.41 | 52.86 |
| Pd:Co 5 (2:1) | 3.7 | 1.2 | 1.94 | 20.8 | 0.58 | 799 | 346 | 0.39 | 52.83 |
| Pd:Co 5 (1:1) | 2.3 | 3.7 | 1.94 | 7.5 | 0.57 | 785 | 349 | 0.40 | 53.46 |
| Pd:Co 5 (1:3) | 1.7 | 3.4 | 1.99 | 30.5 | 0.56 | 787 | 351 | 0.38 | 53.33 |
| Co 5 | - | 5.3 | - | 27.3 | - | 750 | 349 | 0.39 | 53.96 |
| Catalyst | Conditions | Activity | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TON | TOF (h−1) | |||
| Pd 5 | FA 1 M, 100 mg catalyst, 60 °C | 32.3 | 193.7 | This work |
| Pd 10 | 35.8 | 214.6 | ||
| PdCo 3:1 | 27.1 | 162.6 | ||
| PdCo 2:1 | 62.3 | 373.6 | ||
| PdCo 1:1 | 32.1 | 192.6 | ||
| PdCo 1:3 | 54.1 | 324.6 | ||
| Co 5 | - | |||
| Pd 5 | FA:AF 1 M (1:9), 100 mg catalyst, 60 °C | 112.5 | 675.0 | |
| Pd 5 | FA:SF 1 M (1:9), 100 mg catalyst, 60 °C | 42.0 | 252.2 | |
| Pd/C 10% | FA 4 M, 100 mg, 60 °C | 56.5 | 339.0 | [37] |
| Pd/mpg-C3N4 9.5% | FA 1 M, 50 mg catalyst, 25 °C | 49.8 | 292.8 | [45] |
| Pd/C 9.5% | 11.9 | 70.0 | ||
| Pd/C 5% | FA:SF 2 M (1:9), 20 mg catalyst | 456.6 | 228.3 a | [46] |
| Pd0.7Co0.3/C 10% | FA 1 M, 25 °C | 38.25 | 15.3 b | [19] |
| Pd/C 6.5% | FA 1 M, 50 mg catalyst, 60 °C | 216 | 650 c | [38] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribota Peláez, M.; Ruiz-López, E.; Domínguez, M.I.; Ivanova, S.; Centeno, M.A. Formic Acid Dehydrogenation over a Monometallic Pd and Bimetallic Pd:Co Catalyst Supported on Activated Carbon. Catalysts 2023, 13, 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13060977
Ribota Peláez M, Ruiz-López E, Domínguez MI, Ivanova S, Centeno MA. Formic Acid Dehydrogenation over a Monometallic Pd and Bimetallic Pd:Co Catalyst Supported on Activated Carbon. Catalysts. 2023; 13(6):977. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13060977
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibota Peláez, María, E. Ruiz-López, M. I. Domínguez, S. Ivanova, and M. A. Centeno. 2023. "Formic Acid Dehydrogenation over a Monometallic Pd and Bimetallic Pd:Co Catalyst Supported on Activated Carbon" Catalysts 13, no. 6: 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13060977
APA StyleRibota Peláez, M., Ruiz-López, E., Domínguez, M. I., Ivanova, S., & Centeno, M. A. (2023). Formic Acid Dehydrogenation over a Monometallic Pd and Bimetallic Pd:Co Catalyst Supported on Activated Carbon. Catalysts, 13(6), 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal13060977











