Structural Studies of Bypass of Forespore Protein C from Bacillus Subtilis to Reveal Its Inhibitory Molecular Mechanism for SpoIVB
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
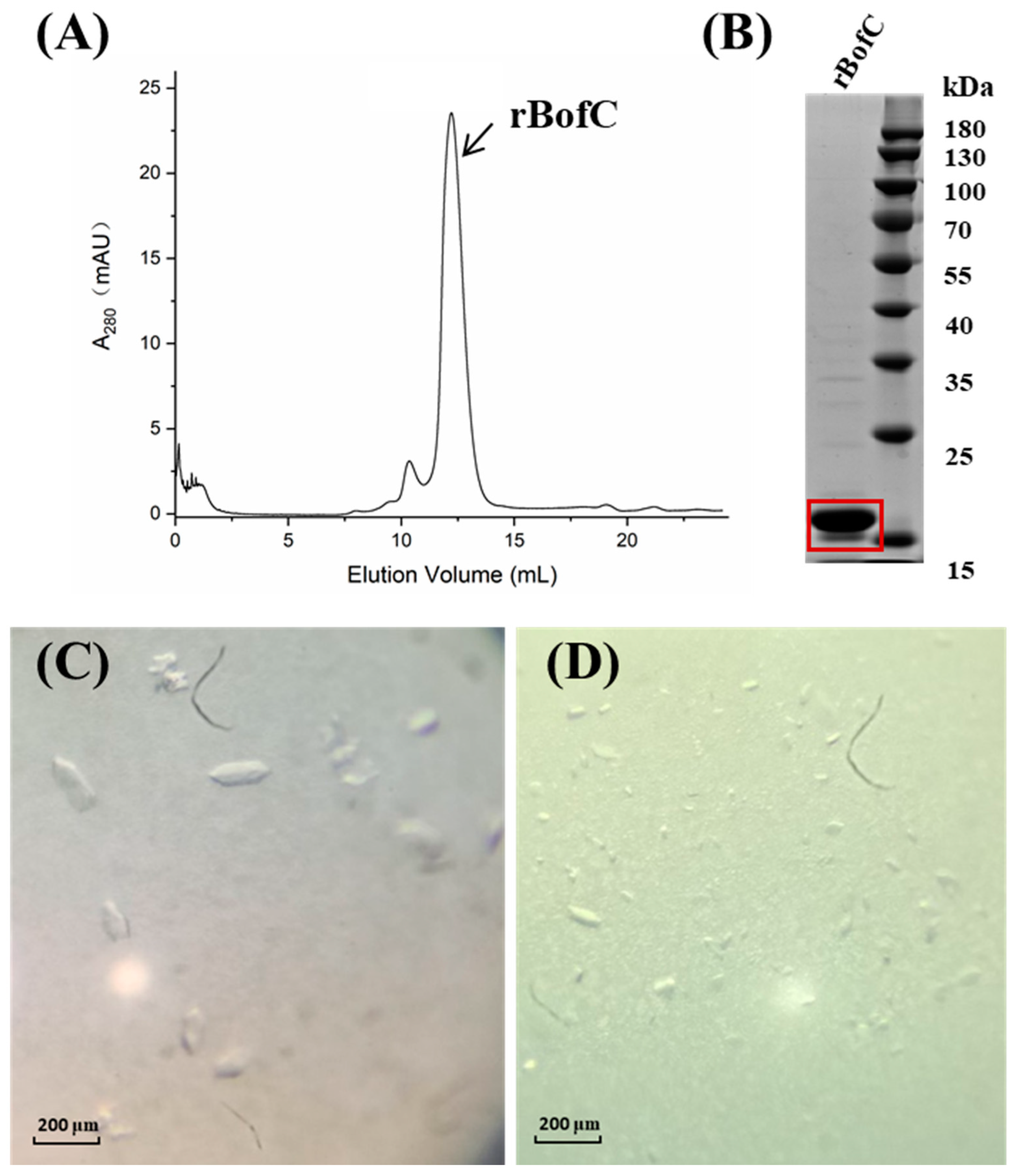
2.1. Expression, Purification and Crystallization of the Recombinant BofC (rBofC)
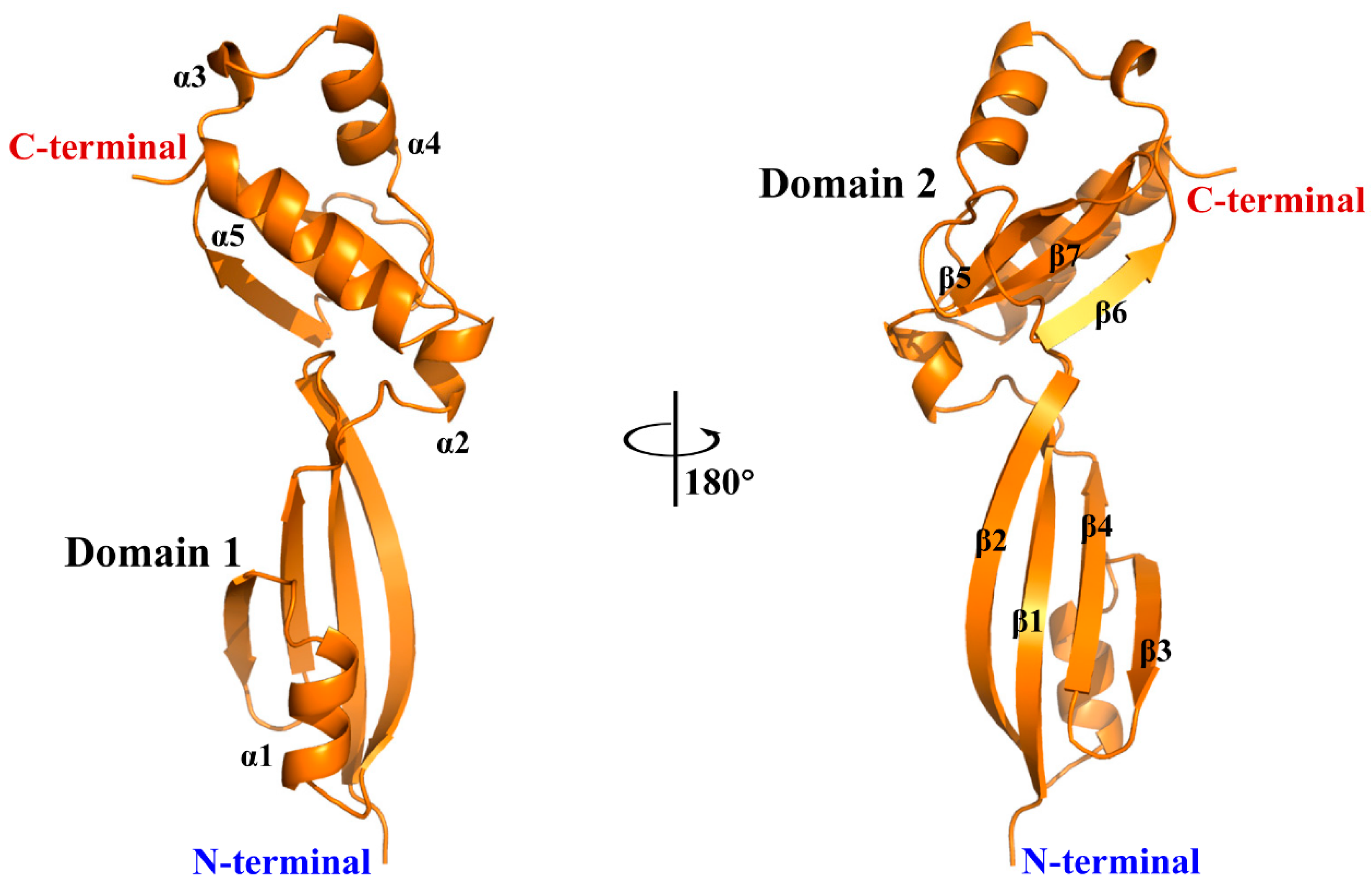
2.2. X-ray Crystallographic Studies of rBofC
2.3. Structural Prediction of BofC–SpoIVB Interactions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. PCR Amplification of bofC Gene
3.2. Construction and Identification of rBofC Expression Plasmid
3.3. Expression and Purification of the Recombinant BofC (rBofC)
3.4. Crystallization of rBofC
3.5. Data Collection and Processing
3.6. Phasing and Refinement
3.7. Structural Prediction of BofC–SpoIVB Interactions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koch, R. Die Ätiologie der Milzbrand-Krankheit: Begründet auf die Entwicklungsgeschichte des Bacillus Anthracis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1876. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, Z.; Dekker, H.L.; Roseboom, W.; Swarge, B.N.; Setlow, P.; Brul, S.; Kramer, G. High Resolution Analysis of Proteome Dynamics during Bacillus subtilis Sporulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errington, J. Bacillus subtilis sporulation: Regulation of gene expression and control of morphogenesis. Microbiol. Rev. 1993, 57, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, D.; Dworkin, J. Recent progress in Bacillus subtilis sporulation. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 36, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kroos, L.; Kunkel, B.; Losick, R. Switch Protein Alters Specificity of RNA Polymerase Containing a Compartment-Specific Sigma Factor. Science 1989, 243, 526–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Yang, M.; Jiang, L.; Huang, M. Regulation of pro-sigma(K) activation: A key checkpoint in Bacillus subtilis sporulation. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 2366–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutting, S.; Oke, V.; Driks, A.; Losick, R.; Lu, S.; Kroos, L. A forespore checkpoint for mother cell gene expression during development in B. subtilis. Cell 1990, 62, 239–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konovalova, A.; Søgaard-Andersen, L.; Kroos, L. Regulated proteolysis in bacterial development. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2014, 38, 493–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cutting, S.; Roels, S.; Losick, R. Sporulation operon spoIVF and the characterization of mutations that uncouple mother-cell from forespore gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. J. Mol. Biol. 1991, 221, 1237–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricca, E.; Cutting, S.; Losick, R. Characterization of bofA, a gene involved in intercompartmental regulation of pro-sigma K processing during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 3177–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, R.; Kroos, L. Serine proteases from two cell types target different components of a complex that governs regulated intramembrane proteolysis of pro-σK during Bacillus subtilis development. Mol. Microbiol. 2005, 58, 835–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resnekov, O.; Alper, S.; Losick, R. Subcellular localization of proteins governing the proteolytic activation of a developmental transcription factor in Bacillus subtilis. Genes Cells 1996, 1, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudner, D.Z.; Losick, R. A sporulation membrane protein tethers the pro-ςK processing enzyme to its inhibitor and dictates its subcellular localization. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Campo, N.; Rudner, D.Z. SpoIVB and CtpB are both forespore signals in the activation of the sporulation transcription factor σK in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 6021–6027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaiser, D.; Losick, R. How and why bacteria talk to each other. Cell 1993, 73, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, N.; Rudner, D.Z. A branched pathway governing the activation of a developmental transcription factor by regulated intramembrane proteolysis. Mol. Cell 2006, 23, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Guadiana, F.H.; Rodrigues, C.D.A.; Marquis, K.A.; Campo, N.; Barajas-Ornelas, R.D.C.; Brock, K.; Marks, D.S.; Kruse, A.C.; Rudner, D.Z. Evidence that regulation of intramembrane proteolysis is mediated by substrate gating during sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gomez, M.; Cutting, S.M. bofC encodes a putative forespore regulator of the Bacillus subtilis sigma(K) checkpoint. Microbiology 1997, 143, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wakeley, P.; Hoa, N.G.; Cutting, S. BofC negatively regulates SpolVB-mediated signalling in the Bacillus subtilis sigma(K)-checkpoint. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 36, 1415–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagyan, I.; Hobot, J.; Cutting, S. A compartmentalized regulator of developmental gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 1996, 178, 4500–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patterson, H.M.; Brannigan, J.A.; Cutting, S.M.; Wilson, K.S.; Wilkinson, A.J.; AB, E.; Diercks, T.; de Jong, R.N.; Truffault, V.; Folkers, G.E.; et al. The structure of bypass of forespore C, an intercompartmental signaling factor during sporulation in Bacillus. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 36214–36220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Z.; Treado, J.D.; Grigas, A.T.; Levine, Z.A.; Regan, L.; O’Hern, C.S. Analyses of protein cores reveal fundamental differences between solution and crystal structures. Proteins 2020, 88, 1154–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garbuzynskiy, S.O.; Melnik, B.S.; Lobanov, M.Y.; Finkelstein, A.V.; Galzitskaya, O.V. Comparison of X-ray and NMR structures: Is there a systematic difference in residue contacts between X-ray- and NMR-resolved protein structures? Proteins 2005, 60, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krissinel, E.; Henrick, K. Inference of macromolecular assemblies from crystalline state. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 372, 774–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnarjuna, B.; Sugiki, T.; Morales, R.A.V.; Seow, J.; Fujiwara, T.; Wilde, K.L.; Norton, R.S.; MacRaild, C.A. Transient antibody-antigen interactions mediate the strain-specific recognition of a conserved malaria epitope. Commun. Biol. 2018, 1, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oliveira, L.F.V.d.; Wallau, G.d.L.; Loreto, E.L.S. Isolation of high quality DNA: A protocol combining rennet and glass milk. Electron. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 12, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Z.; Elledge, S.J. Harnessing homologous recombination in vitro to generate recombinant DNA via SLIC. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 251–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otwinowski, Z.; Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. Methods Enzym. 1997, 276, 307–326. [Google Scholar]
- Vagin, A.; Teplyakov, A. MOLREP: An Automated Program for Molecular Replacement. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1997, 30, 1022–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshudov, G.N.; Vagin, A.A.; Dodson, E.J. Refinement of Macromolecular Structures by the Maximum-Likelihood Method. Acta Crystallogr. 1997, 53, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delano, W.L. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System; De-Lano Scientific: San Carlos, CA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Zidek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desta, I.T.; Porter, K.A.; Xia, B.; Kozakov, D.; Vajda, S. Performance and Its Limits in Rigid Body Protein-Protein Docking. Structure 2020, 28, 1071–1081.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vangone, A.; Bonvin, A.M. Contacts-based prediction of binding affinity in protein-protein complexes. Elife 2015, 4, e07454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, L.C.; Rodrigues, J.P.; Kastritis, P.L.; Bonvin, A.M.; Vangone, A. PRODIGY: A web server for predicting the binding affinity of protein-protein complexes. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3676–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Crystal | rBofC |
|---|---|
| data collection | |
| X-ray source wavelength (Å) | 1.0 |
| resolution limits (Å) | 50.00–1.98 (2.07–1.98) |
| space group | P212121 |
| temperature of experiments (K) | 100 |
| cell constants | a = 33.43 Å, b = 46.00 Å, c = 93.04 Å, α = β =γ = 90° |
| completeness (%) | 97.9 |
| multiplicity | 11.8 |
| Rmerge a | 0.057 (1.421) |
| number of observations | 120935 |
| number of unique reflections | 10268 |
| refinement data | |
| R factor | 0.234 |
| R free | 0.269 |
| average B-factor (Å2) of protein | 50.85 |
| r.m.s deviation of bond lengths (Å) | 0.008 |
| r.m.s deviation of angle (°) | 1.650 |
| Ramachandran analysis (%) | 93.28 b, 6.72 c, 0 d |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Sun, G.; Yuan, C.; Jiang, L.; Huang, M. Structural Studies of Bypass of Forespore Protein C from Bacillus Subtilis to Reveal Its Inhibitory Molecular Mechanism for SpoIVB. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12121530
Zhang X, Sun G, Yuan C, Jiang L, Huang M. Structural Studies of Bypass of Forespore Protein C from Bacillus Subtilis to Reveal Its Inhibitory Molecular Mechanism for SpoIVB. Catalysts. 2022; 12(12):1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12121530
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xinyun, Gaohui Sun, Cai Yuan, Longguang Jiang, and Mingdong Huang. 2022. "Structural Studies of Bypass of Forespore Protein C from Bacillus Subtilis to Reveal Its Inhibitory Molecular Mechanism for SpoIVB" Catalysts 12, no. 12: 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12121530
APA StyleZhang, X., Sun, G., Yuan, C., Jiang, L., & Huang, M. (2022). Structural Studies of Bypass of Forespore Protein C from Bacillus Subtilis to Reveal Its Inhibitory Molecular Mechanism for SpoIVB. Catalysts, 12(12), 1530. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12121530







