3D-Printed Raney-Cu POCS as Promising New Catalysts for Methanol Synthesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
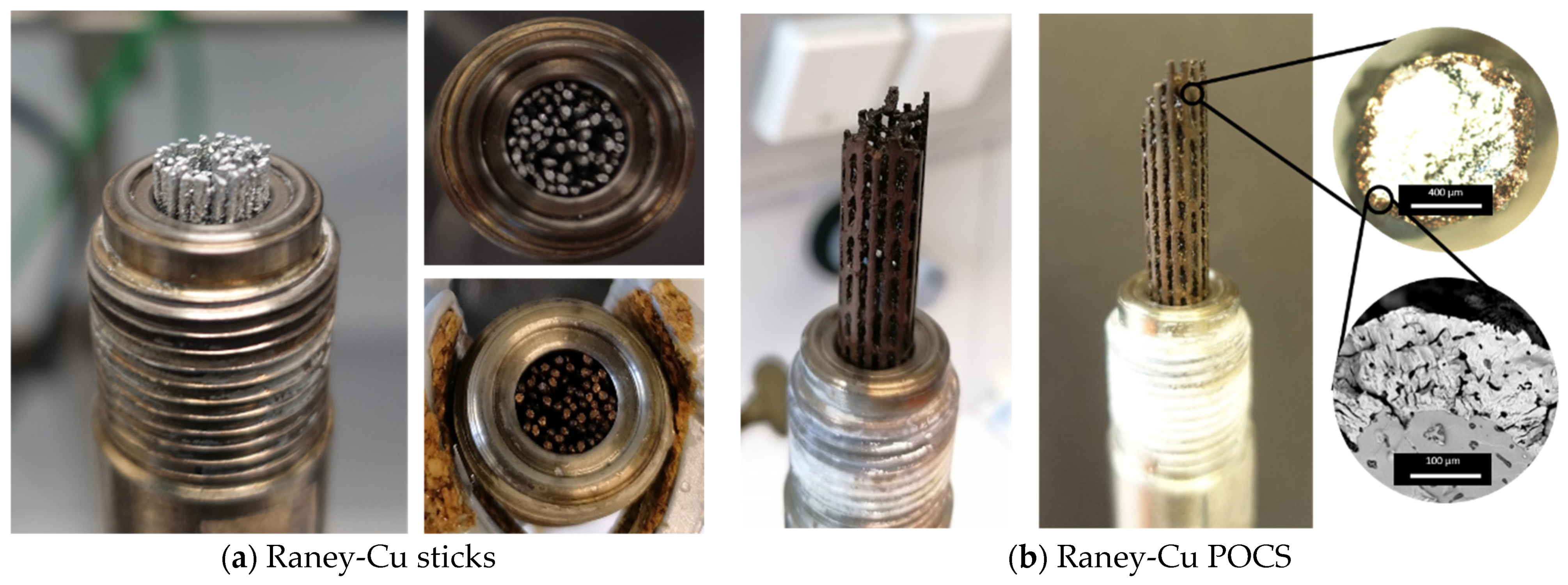
2.1. Fabrication of PBF-EB Sticks and POCS Based on Cu50Al50 Alloy
2.2. Catalytic Activation
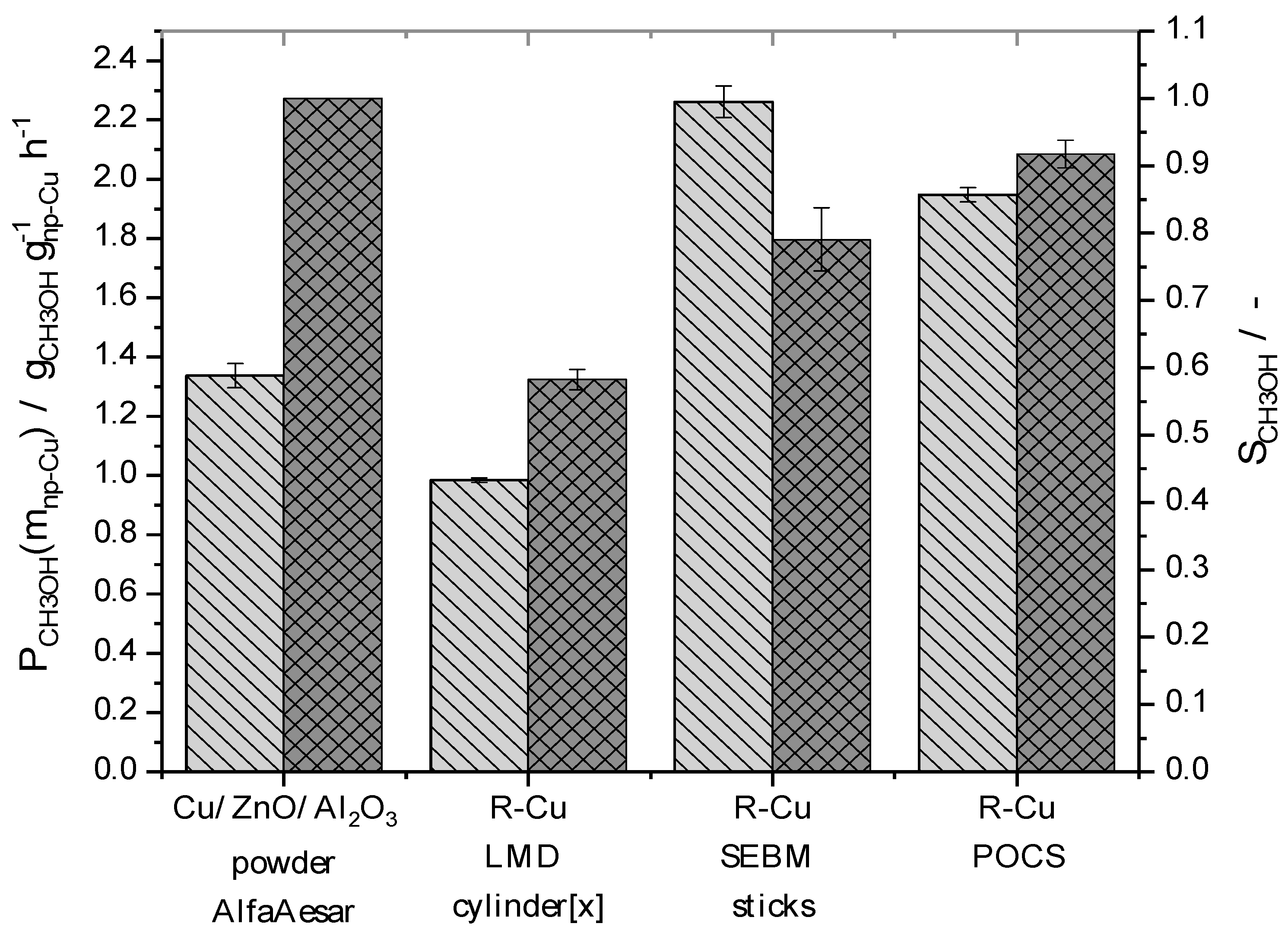
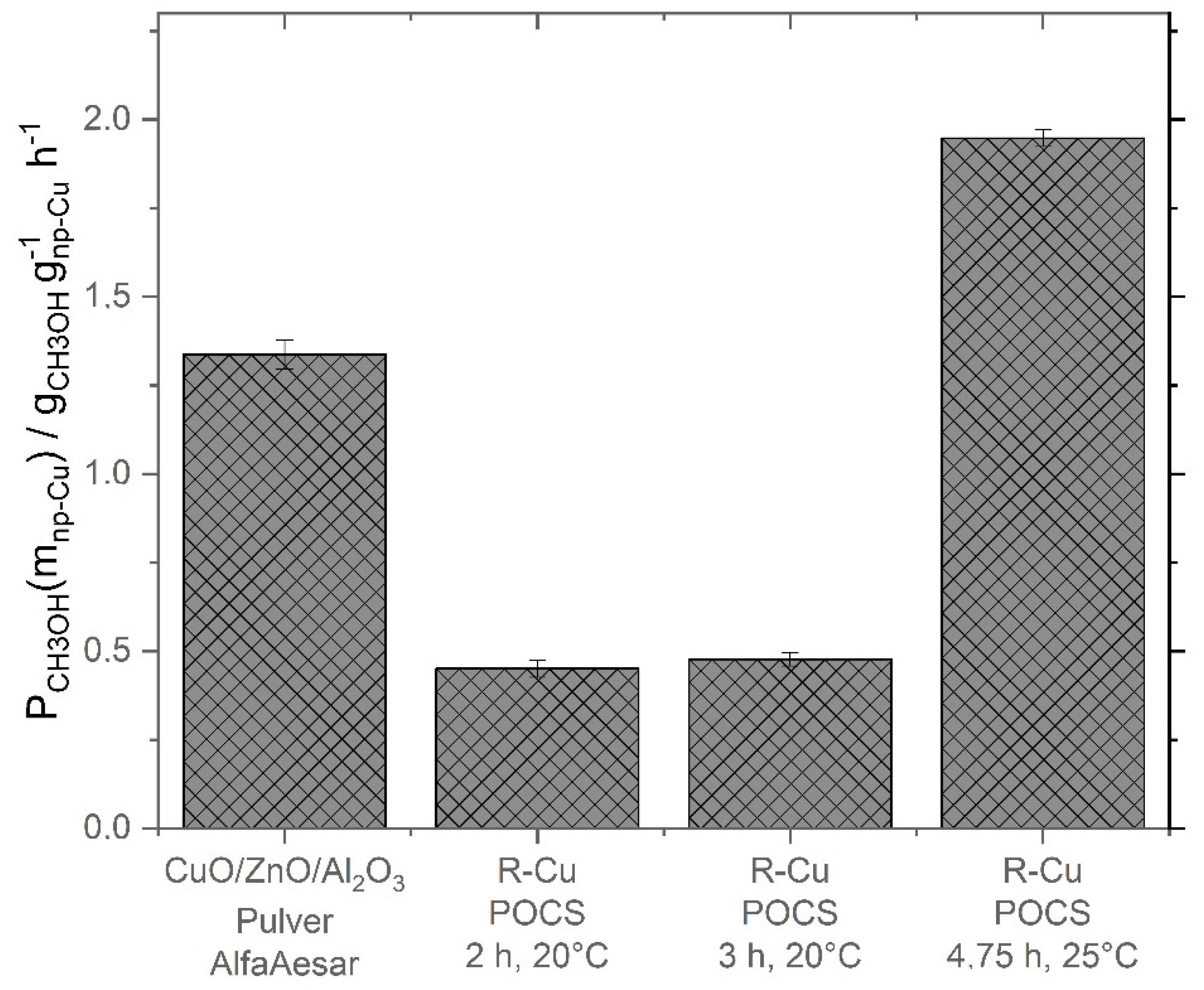
2.3. Methanol Synthesis in a Fixed-Bed Reactor
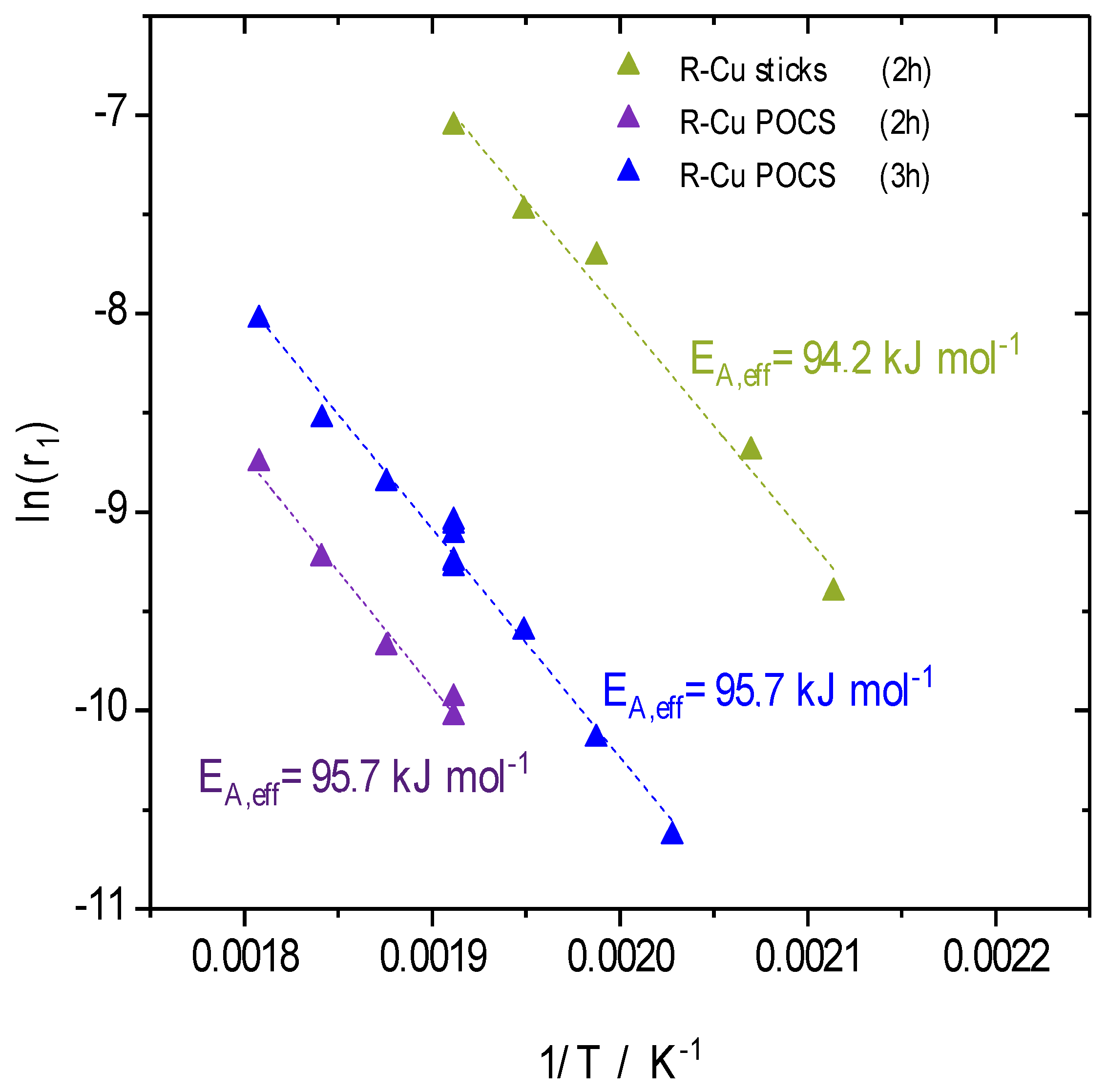
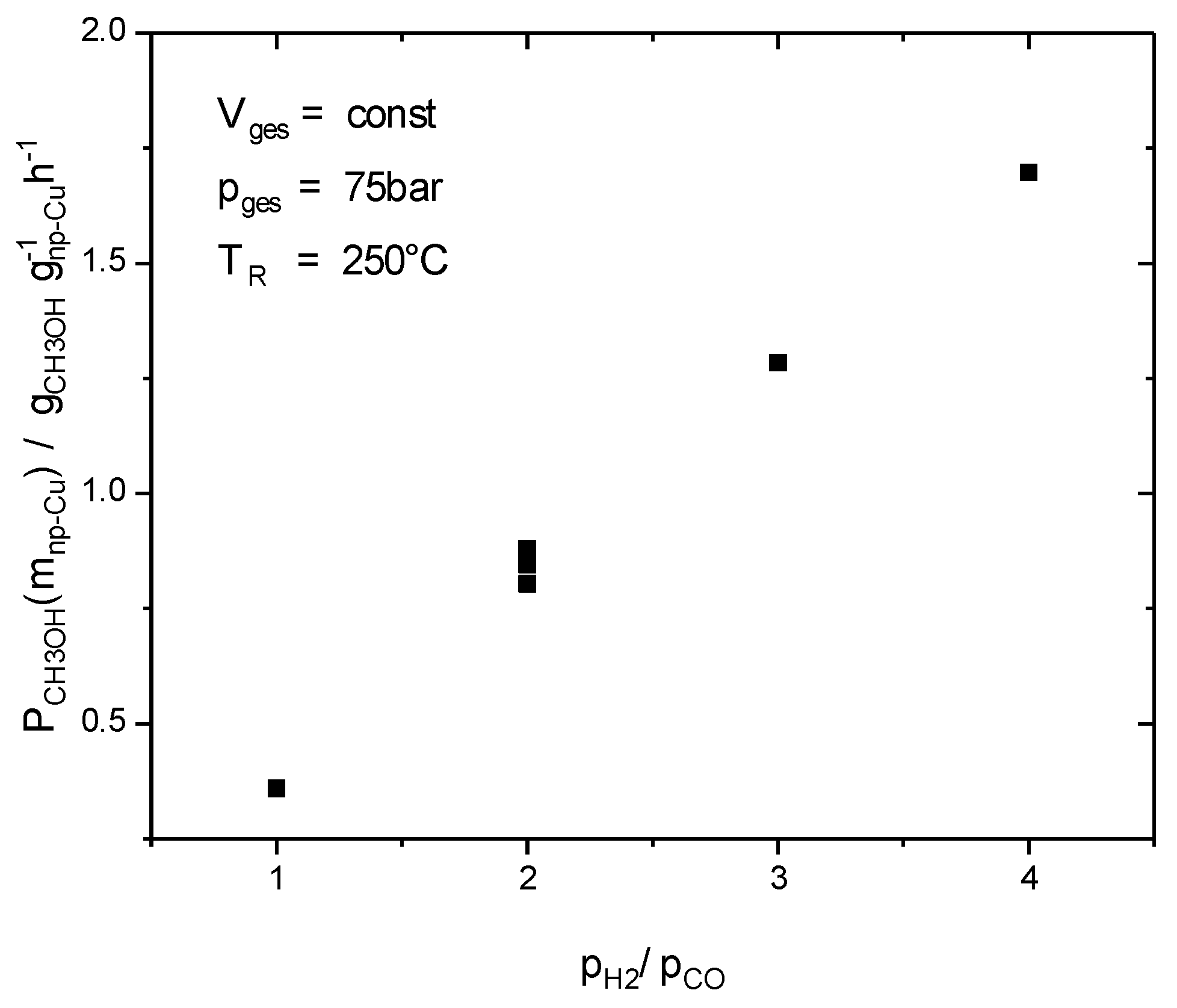
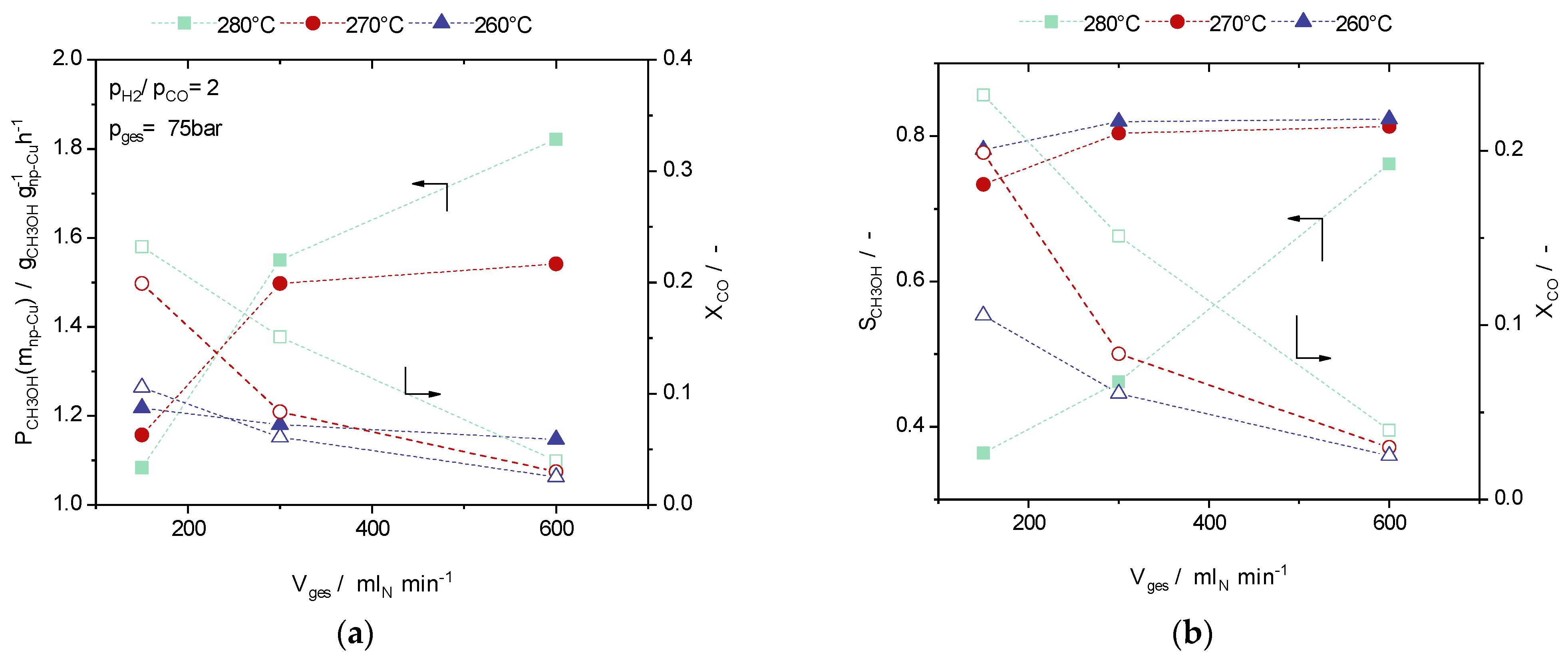
2.4. Reaction Engineering Studies
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of Periodic Open Cellular Raney-Cu Structures
3.1.1. Selective Electron Beam Melting of the Cu50Al50 Alloy
3.1.2. Catalytic Activation of PBF-EB Sticks and POCS
3.1.3. Catalyst Characterization
3.2. Catalytic Activity for Methanol Synthesis
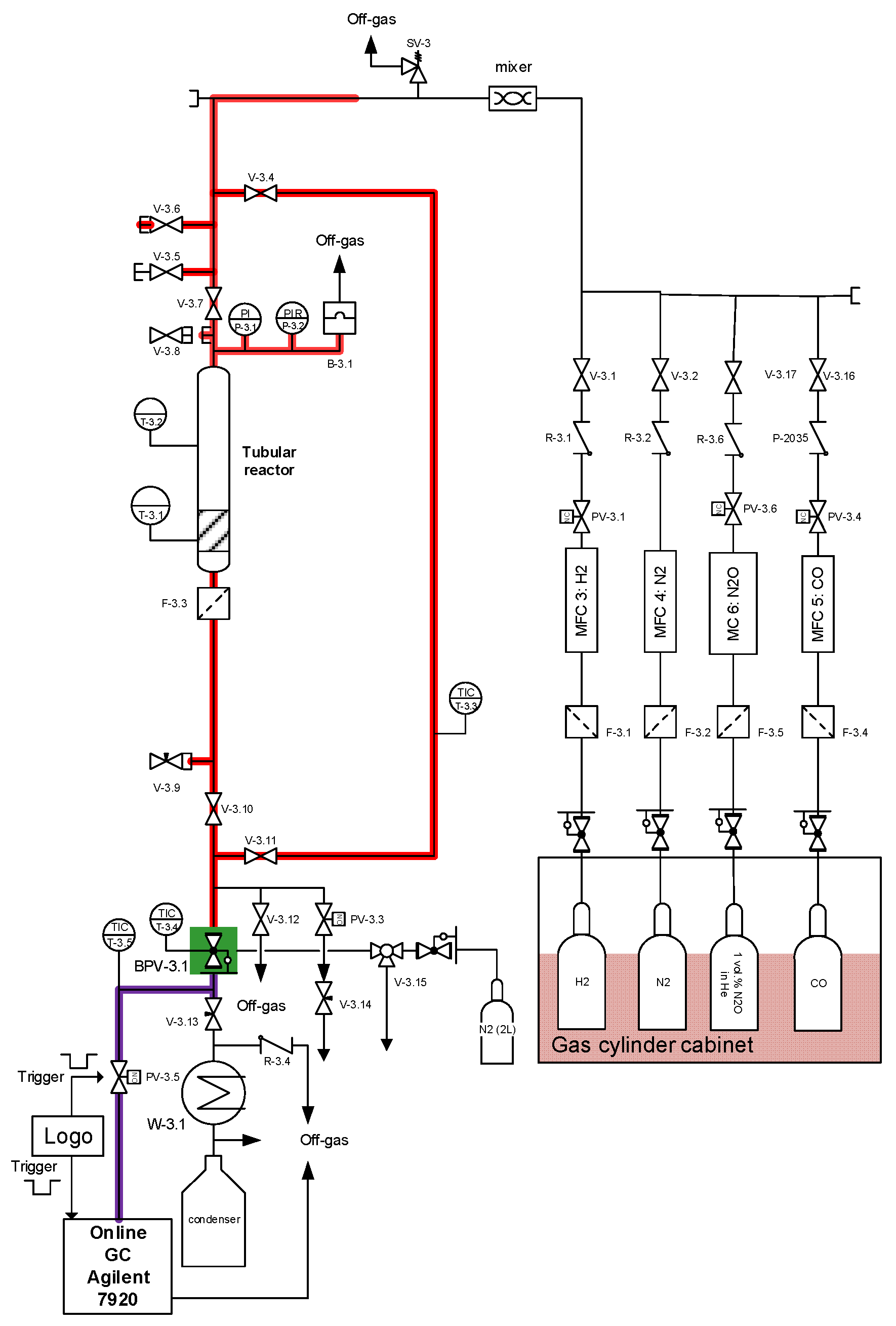
3.2.1. Test-Setup and Experimental Procedure
3.2.2. Data Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Narkhede, N.; Singh, S.; Patel, A. Recent Progress on Supported Polyoxometalates for Biodiesel Synthesis via Esterification and Transesterification. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 89–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Daw, P.; Milstein, D. Homogeneous Catalysis for Sustainable Energy: Hydrogen and Methanol Economies, Fuels from Biomass, and Related Topics. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 385–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.W.; Williams, B.P.; Kelly, G.J.; Fitzpatrick, T.J. Methanol Synthesis Process. WO 2010/146380, 17 June 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Kung, H.H. Deactivation of Methanol Synthesis Catalysts—A Review. Catal. Today 1992, 11, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castoldi, M.C.M.; Câmara, L.D.T.; Aranda, D.A.G. Kinetic Modeling of Sucrose Hydrogenation in the Production of Sorbitol and Mannitol with Ruthenium and Nickel-Raney Catalysts. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 2009, 98, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Turek, T.; Mleczko, L. Structured Raney Nickel Catalysts for Liquid-Phase Hydrogenation. Chem. Eng. Technol. 2016, 39, 1933–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, M.S.; Trimm, D.L. Methanol Synthesis and Water-Gas Shift Reactions on Raney Copper Catalysts. Catal. Today 1995, 23, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raney, M. Catalysts from Alloys. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1940, 32, 1199–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, M.S.; Twigg, M.V. Metal Catalyst Design and Preparation In Control of Deactivation. Annu. Rev. Mater. Res. 2005, 35, 427–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, A.J.; Wainwright, M.S. Skeletal Metal Catalysts. In Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalysis; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostgard, D.; Moebus, K.; Berweiler, M.; Bender, B.; Stein, G. Fixed Bed Catalysts. US 2002/0037808, 25 August 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Schuetz, P.; Burmeister, R.; Despeyroux, B.; Moesinger, H.; Krause, H.; Deller, K. Catalyst Precursor for an Activated Raney Metal Fixed-Bed Catalyst, an Activated Raney Metal Fixed-Bed Catalyst and a Process for Its Preparation and Use, and a Method of Hydrogenating Organic Compounds Using Said Catalyst. US 5,536,694, 16 July 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Hansen, J.B.; Hojlund Nielsen, P.E. Methanol Synthesis. In Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalysis; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2008; Volume 2, pp. 2920–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, P.; Kabelac, S.; Kind, M.; Mewes, D.; Schaber, K.; Wetzel, T. VDI-Wärmeatlas, 11th ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klumpp, M.; Inayat, A.; Schwerdtfeger, J.; Körner, C.; Singer, R.F.; Freund, H.; Schwieger, W. Periodic Open Cellular Structures with Ideal Cubic Cell Geometry: Effect of Porosity and Cell Orientation on Pressure Drop Behavior. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 242, 364–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, C.; Freund, H.; Schwieger, W. Intensification of Heat Transfer in Catalytic Reactors by Additively Manufactured Periodic Open Cellular Structures (POCS). Chem. Eng. Process. Process Intensif. 2018, 124, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, T.; Fu, Z.; Ye, J.; Heßelmann, C.; Pistor, J.; Albert, J.; Wasserscheid, P.; Körner, C. Periodic Open Cellular Raney-Copper Catalysts Fabricated via Selective Electron Beam Melting. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22, 1901524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montebelli, A.; Visconti, C.G.; Groppi, G.; Tronconi, E.; Ferreira, C.; Kohler, S. Enabling Small-Scale Methanol Synthesis Reactors through the Adoption of Highly Conductive Structured Catalysts. Catal. Today 2013, 215, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heßelmann, C.; Wolf, T.; Galgon, F.; Körner, C.; Albert, J.; Wasserscheid, P. Additively Manufactured RANEY®-Type Copper Catalyst for Methanol Synthesis. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlfaAesar. 45776 Copper Based Methanol Synthesis Catalyst. Available online: https://www.alfa.com/de/catalog/045776/ (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- Renz, C. Strukturierte Raney-Cu-Katalysatoren für den Einsatz in der Methanolsynthese. Ph.D Thesis, FAU Erlangen-Nürnberg, Erlangen, Germany, October 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Chanchlani, K. Methanol Synthesis from H2, CO, and C02 over Cu/ZnO Catalysts. J. Catal. 1992, 136, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadgar, F.; Myrstad, R.; Pfeifer, P.; Holmen, A.; Venvik, H.J. Direct Dimethyl Ether Synthesis from Synthesis Gas: The Influence of Methanol Dehydration on Methanol Synthesis Reaction. Catal. Today 2016, 270, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, W.K.; Frolich, P.K. Synthesis of Methanol from Carbon Monoxide and Hydrogen 1. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1928, 20, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

 denote determined by ICP-OES of liquid samples of leaching solution (left axis), filled triangles
denote determined by ICP-OES of liquid samples of leaching solution (left axis), filled triangles  denote determined by ICP-OES of solid sample after leaching reaction (also left axis), ( = 1 → all Aluminum is leached out), empty squares denote the temperature observed during the leaching process (right axis); leaching conditions: room temperature, 100 mL 4.9 M NaOH/0.5 M Na2Zn(OH)4, msticks = 4 g.
denote determined by ICP-OES of solid sample after leaching reaction (also left axis), ( = 1 → all Aluminum is leached out), empty squares denote the temperature observed during the leaching process (right axis); leaching conditions: room temperature, 100 mL 4.9 M NaOH/0.5 M Na2Zn(OH)4, msticks = 4 g.
 denote determined by ICP-OES of liquid samples of leaching solution (left axis), filled triangles
denote determined by ICP-OES of liquid samples of leaching solution (left axis), filled triangles  denote determined by ICP-OES of solid sample after leaching reaction (also left axis), ( = 1 → all Aluminum is leached out), empty squares denote the temperature observed during the leaching process (right axis); leaching conditions: room temperature, 100 mL 4.9 M NaOH/0.5 M Na2Zn(OH)4, msticks = 4 g.
denote determined by ICP-OES of solid sample after leaching reaction (also left axis), ( = 1 → all Aluminum is leached out), empty squares denote the temperature observed during the leaching process (right axis); leaching conditions: room temperature, 100 mL 4.9 M NaOH/0.5 M Na2Zn(OH)4, msticks = 4 g.
 : determined by ICP-OES of liquid samples of leaching solution, ☐: determined by ICP-OES of solid sample after leaching reaction, ( = 1 → all Aluminum is leached out), leaching conditions: 20 or 25 °C, 100 mL 4.9 M NaOH/0.5 M Na2Zn(OH)4, mPOCS = 2.7–4.4 g.
: determined by ICP-OES of liquid samples of leaching solution, ☐: determined by ICP-OES of solid sample after leaching reaction, ( = 1 → all Aluminum is leached out), leaching conditions: 20 or 25 °C, 100 mL 4.9 M NaOH/0.5 M Na2Zn(OH)4, mPOCS = 2.7–4.4 g.
 : determined by ICP-OES of liquid samples of leaching solution, ☐: determined by ICP-OES of solid sample after leaching reaction, ( = 1 → all Aluminum is leached out), leaching conditions: 20 or 25 °C, 100 mL 4.9 M NaOH/0.5 M Na2Zn(OH)4, mPOCS = 2.7–4.4 g.
: determined by ICP-OES of liquid samples of leaching solution, ☐: determined by ICP-OES of solid sample after leaching reaction, ( = 1 → all Aluminum is leached out), leaching conditions: 20 or 25 °C, 100 mL 4.9 M NaOH/0.5 M Na2Zn(OH)4, mPOCS = 2.7–4.4 g.
 ) and 4.9 M NaOH/0.5 M Na2Zn(OH)4 (
) and 4.9 M NaOH/0.5 M Na2Zn(OH)4 ( ) for different leaching times: (a) leaching effectiveness factors; (b) leaching depths; (c) specific surface areas; and (d) active copper surface areas.
) for different leaching times: (a) leaching effectiveness factors; (b) leaching depths; (c) specific surface areas; and (d) active copper surface areas.
 ) and 4.9 M NaOH/0.5 M Na2Zn(OH)4 (
) and 4.9 M NaOH/0.5 M Na2Zn(OH)4 ( ) for different leaching times: (a) leaching effectiveness factors; (b) leaching depths; (c) specific surface areas; and (d) active copper surface areas.
) for different leaching times: (a) leaching effectiveness factors; (b) leaching depths; (c) specific surface areas; and (d) active copper surface areas.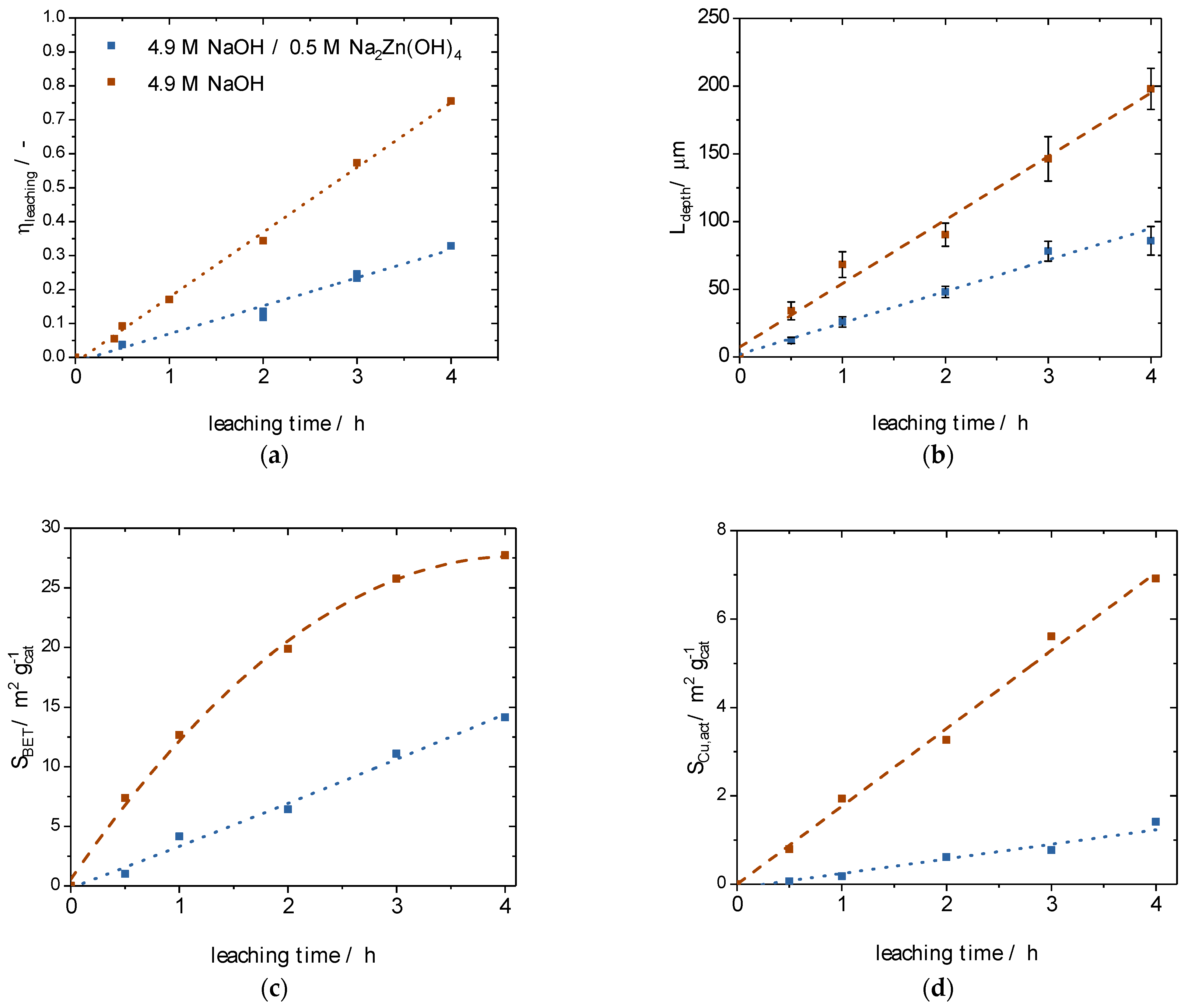
| Time | Tleaching | Composition | Zn/Cu a | c | SCu,act d | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [h] | [°C] | [wt.-%] | [-] | [-] | [-] | |||||
| Cu | Al | Zn | ||||||||
| Raney-Cu sticks | ||||||||||
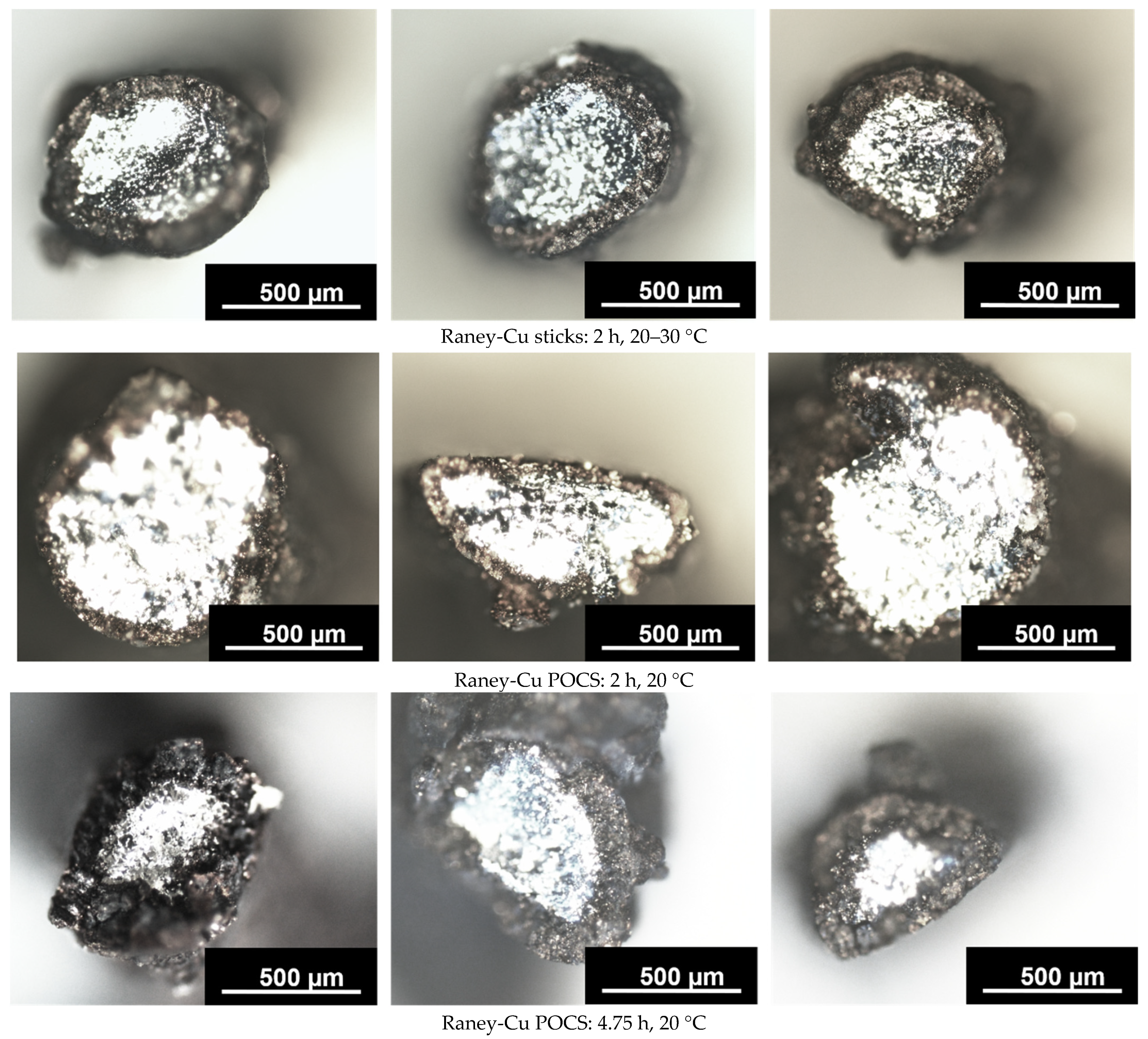
| 2 | 20–30 | total a | 56.3 | 36.6 | 7.1 | 0.35 | 91 ± 11 | 3.1 | 16.0 | |
| np-layer b | - | - | - | 0.38 | ||||||
| Raney-Cu POCS | ||||||||||
| 2 | 20 | total | 51.1 | 42.2 | 6.0 | 0.18 | 51 ± 9 | 0.3 | 3.0 | |
| np-layer | 63.4 | 8 | 28.6 | 0.65 | ||||||
| 3 | 20 | total | 53.2 | 38.6 | 8.2 | 0.28 | 73 ± 6 | 0.7 | 4.6 | |
| np-layer | 68.7 | 6.0 | 25.3 | 0.56 | ||||||
| 4.75 | 25 | total | 59.2 | 30.9 | 9.9 | 0.48 | 153 ± 23 | 3.5 | 12.2 | |
| np-layer | 78.7 | 7.6 | 13.7 | 0.35 | ||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Poller, M.J.; Renz, C.; Wolf, T.; Körner, C.; Wasserscheid, P.; Albert, J. 3D-Printed Raney-Cu POCS as Promising New Catalysts for Methanol Synthesis. Catalysts 2022, 12, 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101288
Poller MJ, Renz C, Wolf T, Körner C, Wasserscheid P, Albert J. 3D-Printed Raney-Cu POCS as Promising New Catalysts for Methanol Synthesis. Catalysts. 2022; 12(10):1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101288
Chicago/Turabian StylePoller, Maximilian J., Christina Renz, Torsten Wolf, Carolin Körner, Peter Wasserscheid, and Jakob Albert. 2022. "3D-Printed Raney-Cu POCS as Promising New Catalysts for Methanol Synthesis" Catalysts 12, no. 10: 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101288
APA StylePoller, M. J., Renz, C., Wolf, T., Körner, C., Wasserscheid, P., & Albert, J. (2022). 3D-Printed Raney-Cu POCS as Promising New Catalysts for Methanol Synthesis. Catalysts, 12(10), 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12101288







