Generation of Cobalt-Containing Nanoparticles on Carbon via Pyrolysis of a Cobalt Corrole and Its Application in the Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes
Abstract
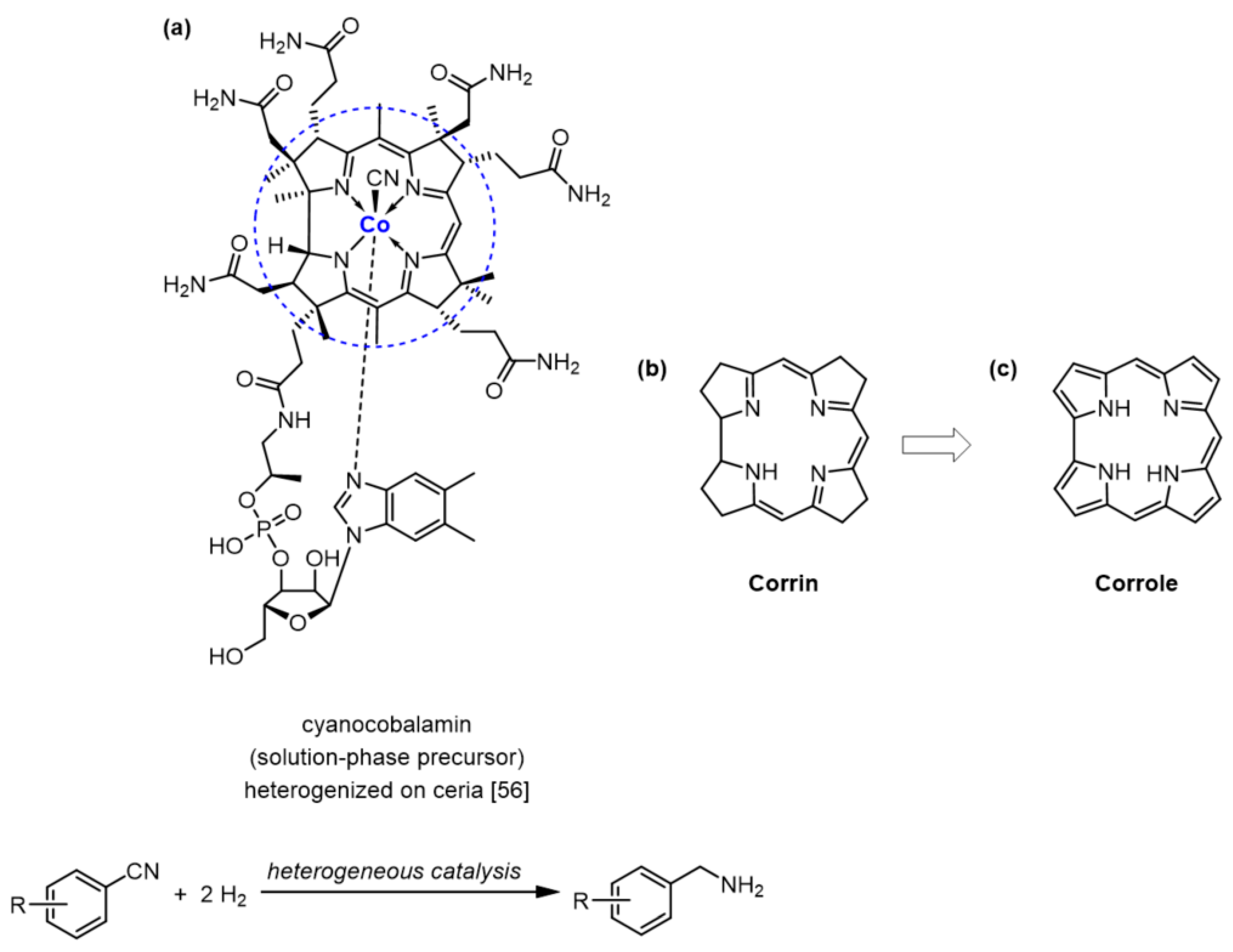
:1. Introduction
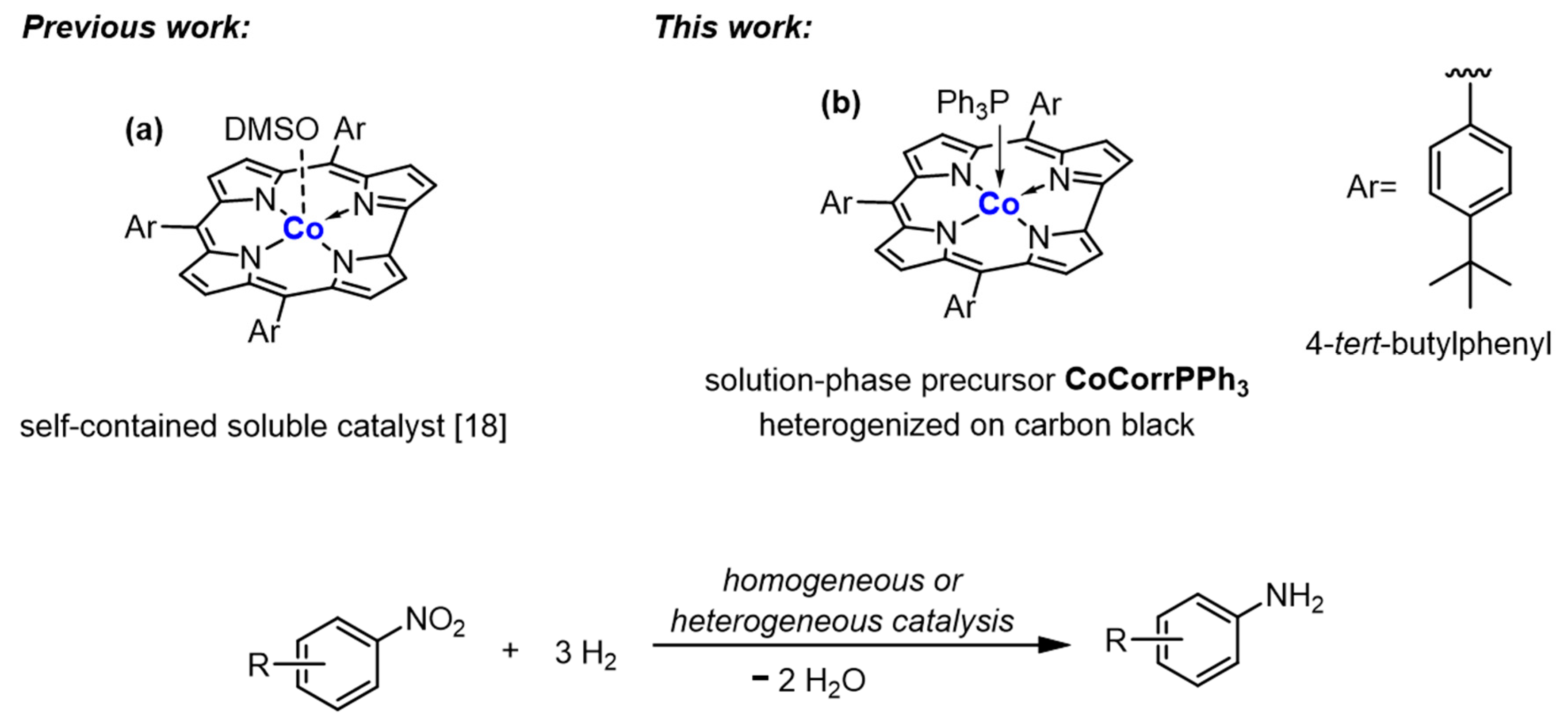
2. Results and Discussion
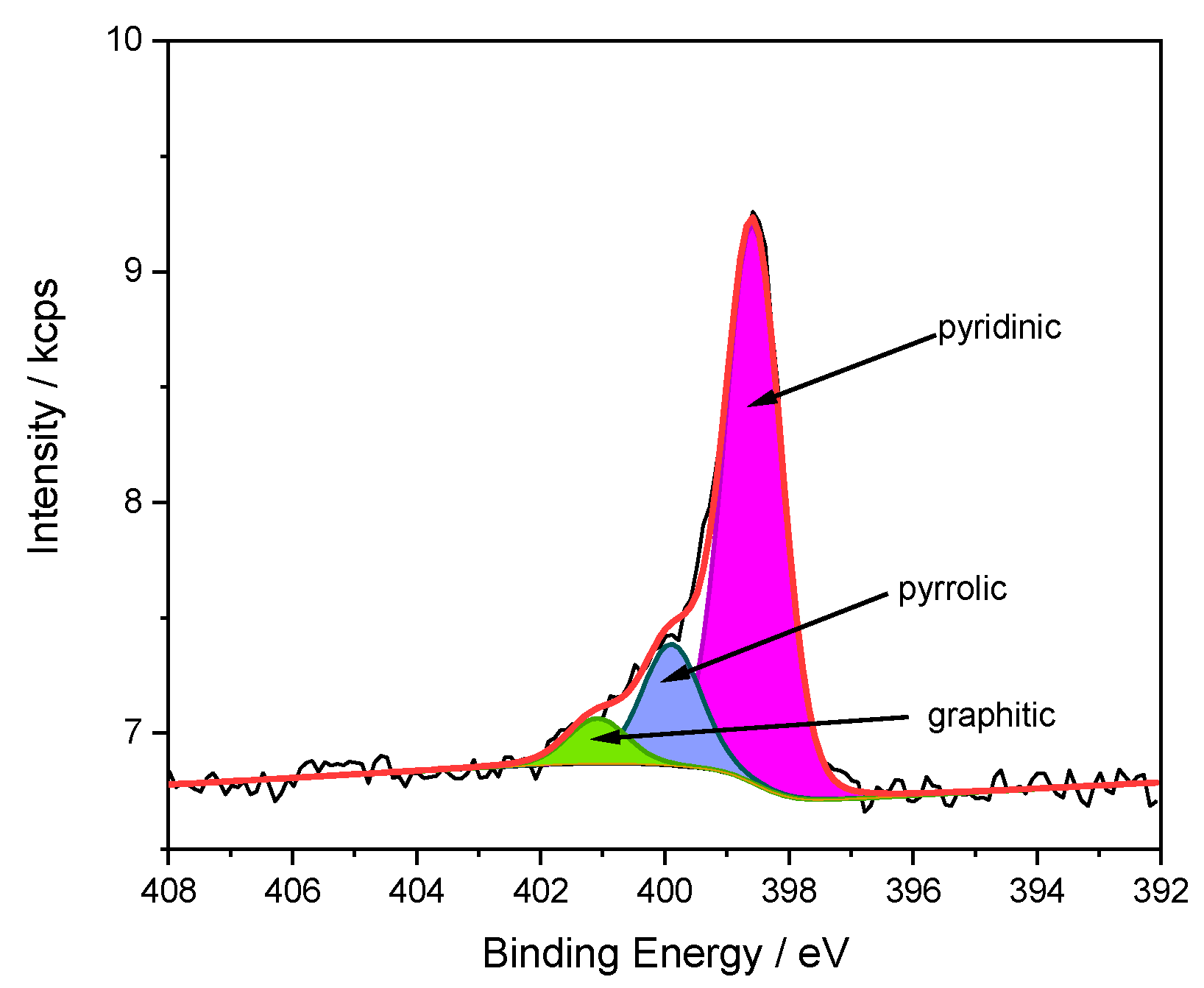
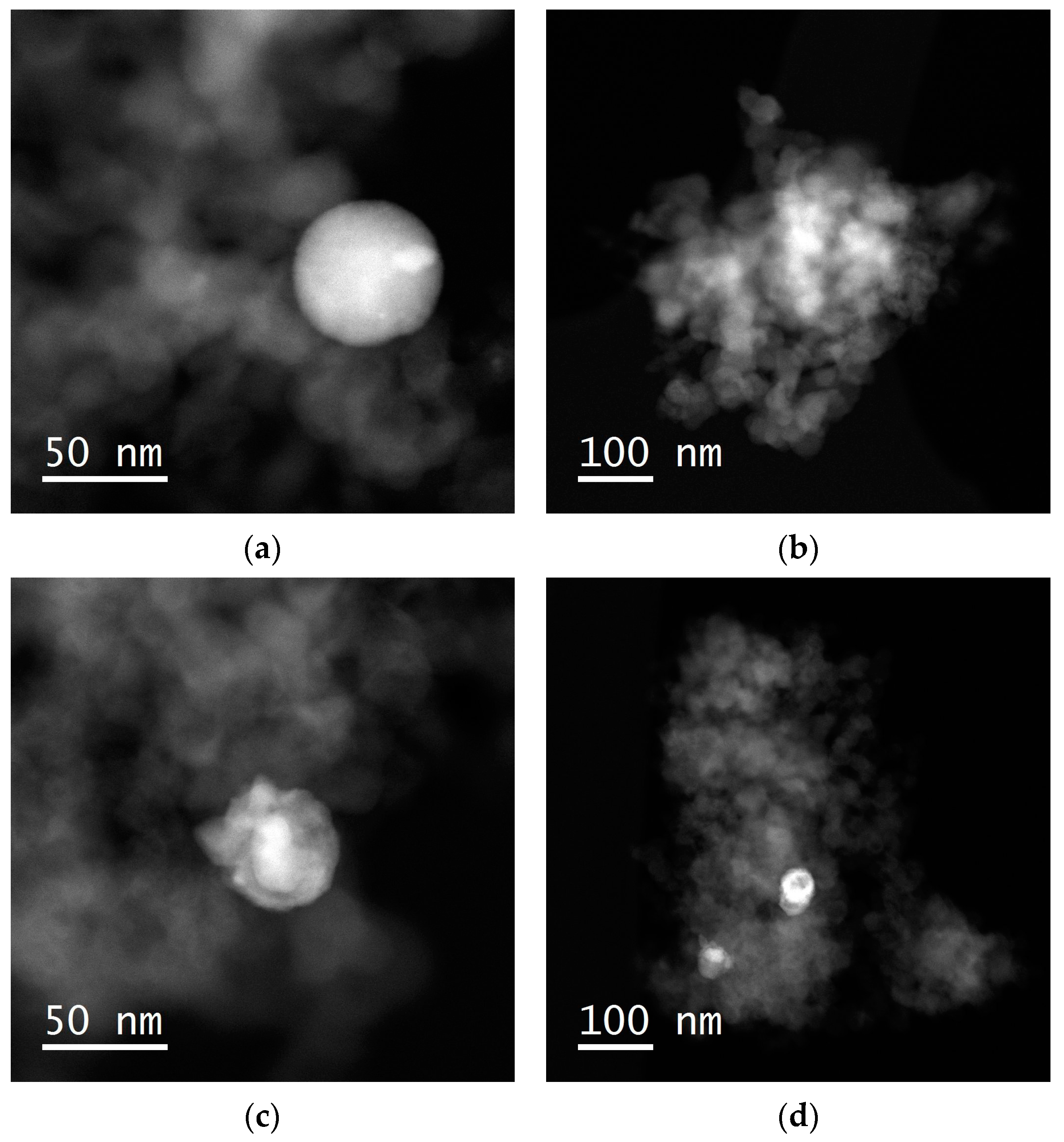
2.1. Catalyst Preparation and Characterization
2.2. Catalytic Tests
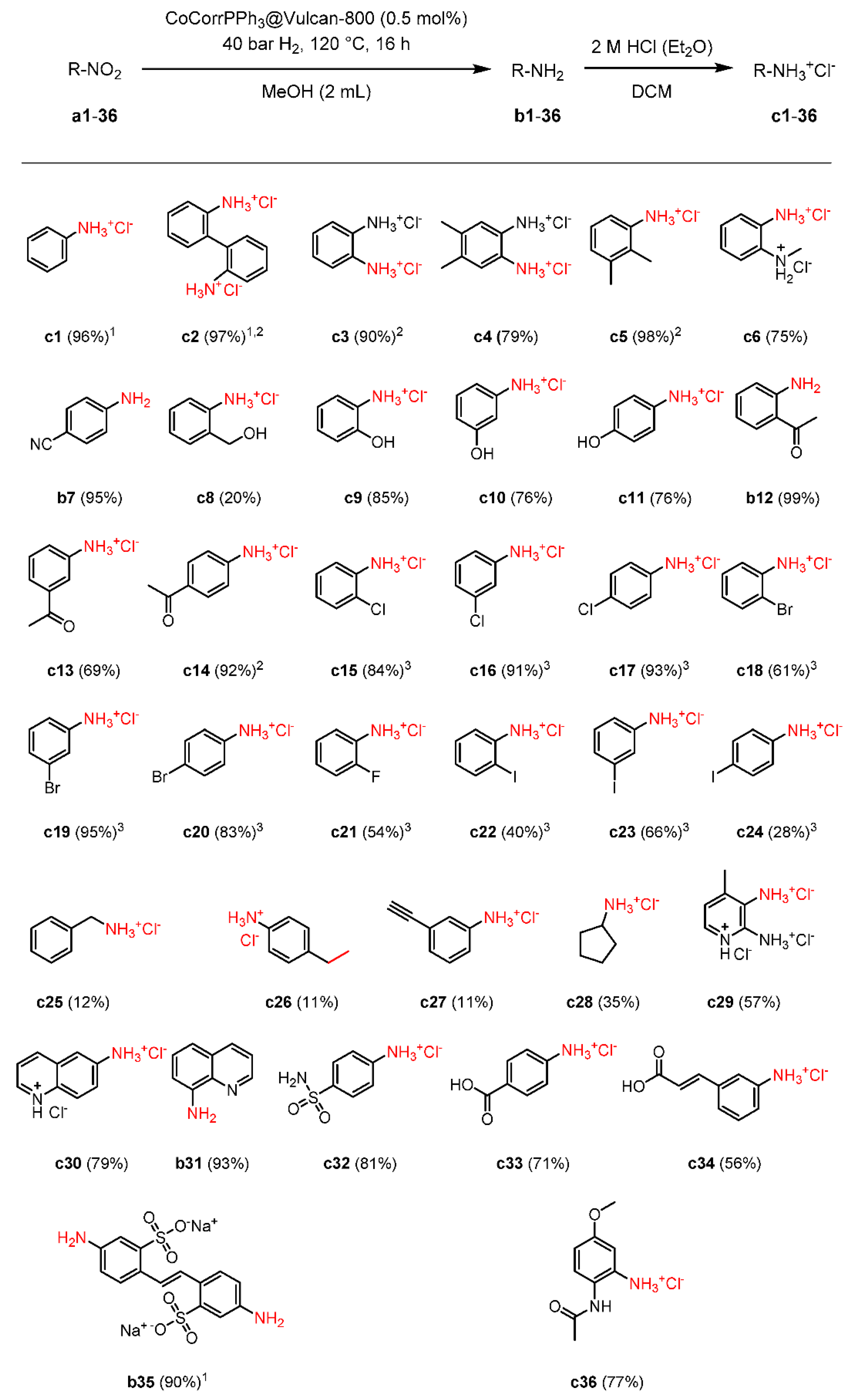
2.3. Scope and Limitations
2.4. Recyclability Tests
3. Experimental
3.1. Procedure for the Pyrolytic Synthesis of the Supported Cobalt-Corrole-Based Heterogeneous Catalyst
3.2. General Procedure for the Catalytic Hydrogenation Reactions
Safety Statement concerning the Use of Pressurized Hydrogenation Gas
3.3. General Procedure for the Isolation of the Organic Ammonium Salts
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Béchamp, A. De l’action des protosels de fer sur la nitronaphtaline et la nitrobenzine. nouvelle méthode de formation des bases organiques artificielles de Zinin. Ann. Chim. Phys. 1854, 42, 186–196. [Google Scholar]
- Downing, R.; Kunkeler, P.; van Bekkum, H. Catalytic syntheses of aromatic amines. Catal. Today 1997, 37, 121–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaser, H.-U.; Steiner, H.; Studer, M. Selective Catalytic Hydrogenation of Functionalized Nitroarenes: An Update. ChemCatChem 2009, 1, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandi, M.; Brenna, D.; Harms, R.; Jost, S.; Benaglia, M. Recent developments in the reduction of aromatic and aliphatic nitro compounds to amines. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2018, 22, 430–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, D.; Ferretti, F.; Scharnagl, F.; Beller, M. Reduction of Nitro Compounds Using 3d-Non-Noble Metal Catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2018, 119, 2611–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A.; González-Arellano, C.; Iglesias, M.; Sánchez, F. Gold complexes as catalysts: Chemoselective hydrogenation of nitroarenes. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 356, 99–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsy, S.G. Homogeneous hydrogenation of nitroaliphatic compounds catalyzed by group VIII transition metal phosphine complexes. Tetrahedron 1990, 46, 7403–7412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Liao, S.; Xu, Y.; Yang, B.; Yu, D. Hydrogenation of nitroaromatics by polymer-anchored bimetallic palladium-ruthenium and palladium-platinum catalysts under mild conditions. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 1997, 120, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Xi, X.; Shi, J.; Cao, S. A homogeneous catalyst made of poly(4-vinylpyridine-co-N-vinylpyrrolidone)-Pd(0) complex for hydrogenation of aromatic nitro compounds. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2000, 160, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakhariev, A.; Ivanova, V.; Khidekel, M.L.; Chepaikin, E.G.; Shopov, D. Hydrogenation of aromatic nitro compounds in the presence of the platinum(II) complex of 1-phenylazo-2-naphthol in DMF. React. Kinet. Catal. Lett. 1978, 8, 195–201. [Google Scholar]
- Chepaikin, E.G.; Ivanova, V.V.; Zakhariev, A.I.; Shopov, D.M. Homogeneous catalytic hydrogenation of aromatic nitrocompounds by complexes of the platinum group metal with dyes. The reaction of nitrobenzene with a complex of rhodium with the anion-radical of potassium indigodisulfonate. J. Mol. Catal. 1980, 10, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knifton, J.F. Homogeneous catalyzed reduction of nitro compounds. IV. Selective and sequential hydrogenation of nitroaromatics. J. Org. Chem. 1976, 41, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toti, A.; Frediani, P.; Salvini, A.; Rosi, L.; Giolli, C. Hydrogenation of single and multiple N–N or N–O bonds by Ru(II) catalysts in homogeneous phase. J. Organomet. Chem. 2005, 690, 3641–3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deshmukh, A.A.; Prashar, A.K.; Kinage, A.K.; Kumar, R.; Meijboom, R. Ru(II) Phenanthroline Complex As Catalyst for Chemoselective Hydrogenation of Nitro-Aryls in a Green Process. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2010, 49, 12180–12184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshpande, R.M.; Mahajan, A.N.; Diwakar, M.M.; Ozarde, P.S.; Chaudhari, R.V. Chemoselective Hydrogenation of Substituted Nitroaromatics Using Novel Water-Soluble Iron Complex Catalysts. J. Org. Chem. 2004, 69, 4835–4838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wienhöfer, G.; Baseda-Krüger, M.; Ziebart, C.; Westerhaus, F.A.; Baumann, W.; Jackstell, R.; Junge, K.; Beller, M. Hydrogenation of nitroarenes using defined iron–phosphine catalysts. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9089–9091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zubar, V.; Dewanji, A.; Rueping, M. Chemoselective Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes Using an Air-Stable Base-Metal Catalyst. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 2742–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timelthaler, D.; Schöfberger, W.; Topf, C. Selective and Additive-Free Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes Mediated by a DMSO-Tagged Molecular Cobalt Corrole Catalyst. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2021, 2021, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhaus, F.A.; Jagadeesh, R.V.; Wienhöfer, G.; Pohl, M.-M.; Radnik, J.; Surkus, A.-E.; Rabeah, J.; Junge, K.; Junge, H.; Nielsen, M.; et al. Heterogenized cobalt oxide catalysts for nitroarene reduction by pyrolysis of molecularly defined complexes. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeesh, R.V.; Surkus, A.-E.; Junge, H.; Pohl, M.-M.; Radnik, J.; Rabeah, J.; Huan, H.; Schünemann, V.; Brückner, A.; Beller, M. Nanoscale Fe2O3-based catalysts for selective hydrogenation of nitroarenes to anilines. Science 2013, 342, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, D.; Topf, C.; Junge, K.; Ragaini, F.; Beller, M. Fe2O3/NGr@C- and Co–Co3O4/NGr@C-catalysed hydrogenation of nitroarenes under mild conditions. Cat. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 4473–4477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagadeesh, R.V.; Murugesan, K.; Alshammari, A.S.; Neumann, H.; Pohl, M.-M.; Radnik, J.; Beller, M. MOF-derived cobalt nanoparticles catalyze a general synthesis of amines. Science 2017, 358, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, P.; Jiang, L.; Wang, F.; Deng, K.; Lv, K.; Zhang, Z. High performance of a cobalt–nitrogen complex for the reduction and reductive coupling of nitro compounds into amines and their derivatives. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1601945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, L.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, S.; Chi, Q. Synthesis of Secondary Amines from One-Pot Reductive Amination with Formic Acid as the Hydrogen Donor over an Acid-Resistant Cobalt Catalyst. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 12556–12565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Zhou, P.; Zhang, Z.; Chi, Q.; Jin, S. Environmentally friendly synthesis of secondary amines via one-pot reductive amination over a heterogeneous Co–Nx catalyst. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 11991–11997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, B.; Formenti, D.; Topf, C.; Bachmann, S.; Scalone, M.; Junge, K.; Beller, M. Biomass-Derived Catalysts for Selective Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes. ChemSusChem 2017, 10, 3035–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.; Liang, K.; Tian, M.; Zhu, Y.; Ma, J.; Dong, Z. Cobalt nanoparticles supported on N-doped mesoporous carbon as a highly efficient catalyst for the synthesis of aromatic amines. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 501, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, P.L.; Tripathi, M.; Arundhathi, R.; Rawat, D.S. Chemoselective Hydrazine-mediated Transfer Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes by Co3O4Nanoparticles Immobilized on an Al/Si-mixed Oxide Support. Chem.–Asian J. 2017, 12, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stadler, L.; Homafar, M.; Hartl, A.; Najafishirtari, S.; Colombo, M.; Zboril, R.; Martin, P.; Gawande, M.B.; Zhi, J.; Reiser, O. Recyclable Magnetic Microporous Organic Polymer (MOP) Encapsulated with Palladium Nanoparticles and Co/C Nanobeads for Hydrogenation Reactions. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 7, 2388–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.Y.; Choi, T.J.; Gil Kim, J.; Chang, J.Y. A Cobalt Tandem Catalyst Supported on a Compressible Microporous Polymer Monolith. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 8745–8751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullangi, D.; Chakraborty, D.; Pradeep, A.; Koshti, V.; Vinod, C.P.; Panja, S.; Nair, S.; Vaidhyanathan, R. Highly stable COF-supported Co/Co(OH)2 nanoparticles heterogeneous catalyst for reduction of nitrile/nitro compounds under mild conditions. Small 2018, 14, 1801233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Li, X.; Deng, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y. Shape Engineering of Biomass-Derived Nanoparticles from Hollow Spheres to Bowls through Solvent-Induced Buckling. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 2540–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Olivos-Suarez, A.I.; Osadchii, D.; Romero, M.J.V.; Kapteijn, F.; Gascon, J. Single cobalt sites in mesoporous N-doped carbon matrix for selective catalytic hydrogenation of nitroarenes. J. Catal. 2018, 357, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Long, J.; Zhao, W.; Li, H.; Yang, S. Efficient Transfer Hydrogenation of Nitro Compounds to Amines Enabled by Mesoporous N-Stabilized Co-Zn/C. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, Y.; Jiang, C.; Xu, M.; Bian, B.; Lu, D.; Yang, Y. Cobalt in N-doped carbon matrix catalyst for chemoselective hydrogenation of nitroarenes. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2019, 580, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Cao, C.; Liu, J.; Shi, Y.; Si, R.; Gu, L.; Song, W. Cobalt single atoms anchored on N-doped ultrathin carbon nanosheets for selective transfer hydrogenation of nitroarenes. Sci. China Mater. 2019, 62, 1306–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Samanta, D.; Roy, S.; Radhakantha, V.P.H.; Maji, T.K. In situ Stabilization of Au and Co Nanoparticles in a Redox-Active Conjugated Microporous Polymer Matrix: Facile Heterogeneous Catalysis and Electrocatalytic Oxygen Reduction Reaction Activity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 5455–5461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Artz, J.; Broicher, C.; Junge, K.; Hartmann, H.; Besmehn, A.; Palkovits, R.; Beller, M. Superior activity and selectivity of heterogenized cobalt catalysts for hydrogenation of nitroarenes. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 9, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanadegani, Z.S.; Nemati, F.; Elhampour, A.; Rangraz, Y. Cobalt oxide NPs immobilized on environmentally benign biological macromolecule-derived N-doped mesoporous carbon as an efficient catalyst for hydrogenation of nitroarenes. J. Solid State Chem. 2020, 292, 121645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bustamante, T.M.; Campos, C.H.; Fraga, M.A.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Pecchi, G. Promotional effect of palladium in Co-SiO2 core@shell nanocatalysts for selective liquid phase hydrogenation of chloronitroarenes. J. Catal. 2020, 385, 224–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Liu, K.; Wu, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Q. In situ-formed cobalt embedded into N-doped carbon as highly efficient and selective catalysts for the hydrogenation of halogenated nitrobenzenes under mild conditions. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2020, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, T.D.; Ncibi, M.C.; Certenais, M.; Viitala, M.; Sillanpää, M. Cobalt-lignosulfonate complex derived non-noble catalysts: Facile valorization for high-performance redox conversion of organic pollutants. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 253, 120013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.; Shang, N.; Gao, S.; Wang, C.; Gao, Y. Transfer Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes Catalyzed by CoCu Anchored on Nitrogen-doped Porous Carbon. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2020, 34, e5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez-Tarriño, S.; Rojas-Buzo, S.; Lopes, C.W.; Agostini, G.; Calvino, J.J.; Corma, A.; Oña-Burgos, P. Cobalt nanoclusters coated with N-doped carbon for chemoselective nitroarene hydrogenation and tandem reactions in water. Green Chem. 2021, 23, 4490–4501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhou, P.; Jin, S.; Zhang, Z. Co–Nx catalyst: An effective catalyst for the transformation of nitro compounds into azo compounds. React. Chem. Eng. 2020, 6, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, D.; Ferretti, F.; Topf, C.; Surkus, A.-E.; Pohl, M.-M.; Radnik, J.; Schneider, M.; Junge, K.; Beller, M.; Ragaini, F. Co-based heterogeneous catalysts from well-defined α-diimine complexes: Discussing the role of nitrogen. J. Catal. 2017, 351, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohapatra, S.K.; Sonavane, S.U.; Jayaram, R.V.; Selvam, P. Heterogeneous catalytic transfer hydrogenation of aromatic nitro and carbonyl compounds over cobalt(II) substituted hexagonal mesoporous aluminophosphate molecular sieves. Tetrahedron Lett. 2002, 43, 8527–8529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, A.S.; Jayaram, R.V. Liquid phase catalytic transfer hydrogenation of aromatic nitro compounds on perovskites prepared by microwave irradiation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2003, 252, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y. Transfer hydrogenation of unsaturated bonds in the absence of base additives catalyzed by a cobalt-based heterogeneous catalyst. Chem. Commun. 2014, 51, 2331–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, P.; Alex, H.; Hassfeld, J.; Lovis, K.; Platzek, J.; Steinfeldt, N.; Hübner, S. Selective Hydrogenation of Halogenated Nitroaromatics to Haloanilines in Batch and Flow. Org. Process. Res. Dev. 2015, 20, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.-J.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Wang, K.-X.; Su, J.; Wei, X.; Li, X.-H. General transfer hydrogenation by activating ammonia-borane over cobalt nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 102736–102740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Mao, S.; Sun, F.; Wang, J.; Mei, B.; Chen, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. The synergic effects at the molecular level in CoS2 for selective hydrogenation of nitroarenes. Green Chem. 2017, 20, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, S.-T.; Wang, C.-H.; Du, H.-Y.; Hsu, H.-C.; Kang, C.-M.; Chen, C.-C.; Wu, J.C.S.; Yen, S.-C.; Huang, W.-F.; Chen, L.-C.; et al. Vitalizing fuel cells with vitamins: Pyrolyzed vitamin B12 as a non-precious catalyst for enhanced oxygen reduction reaction of polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Energy Environ. Sci. 2012, 5, 5305–5314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, M.; He, D.; Shao, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, F.; Dai, L. Pyrolysis of Animal Bones with Vitamin B12: A Facile Route to Efficient Transition Metal-Nitrogen-Carbon (TM-N -C) Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 22, 2896–2901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.-W.; Brüller, S.; Dong, R.; Zhang, J.; Feng, X.; Müllen, K. Molecular metal–Nx centres in porous carbon for electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, B.; Shang, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, S. Mesoporous carbon derived from vitamin B12: A high-performance bifunctional catalyst for imine formation. Chem. Commun. 2015, 52, 481–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraccioli, R.; Borovika, D.; Surkus, A.-E.; Kreyenschulte, C.; Topf, C.; Beller, M. Synthesis of cobalt nanoparticles by pyrolysis of vitamin B12: A non-noble-metal catalyst for efficient hydrogenation of nitriles. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koszarna, B.; Gryko, D.T. Efficient Synthesis of meso-Substituted Corroles in a H2O−MeOH Mixture. J. Org. Chem. 2006, 71, 3707–3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Shan, W.; Desbois, N.; Quesneau, V.; Brandès, S.; Van Caemelbecke, E.; Osterloh, W.R.; Blondeau-Patissier, V.; Gros, C.P.; Kadish, K.M. Mono-DMSO ligated cobalt nitrophenylcorroles: Electrochemical and spectral characterization. New J. Chem. 2018, 42, 8220–8229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quesneau, V.; Shan, W.; Desbois, N.; Brandès, S.; Rousselin, Y.; Vanotti, M.; Blondeau-Patissier, V.; Naitana, M.; Fleurat-Lessard, P.; van Caemelbecke, E.; et al. Cobalt corroles with bis-ammonia or mono-DMSO axial ligands. Electrochemical, spectroscopic characterizations, and ligand binding properties. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 38, 4265–4277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardis, S.; Mandoj, F.; Stefanelli, M.; Paolesse, R. Metal complexes of corrole. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2019, 388, 360–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterloh, W.R.; Quesneau, V.; Desbois, N.; Brandès, S.; Shan, W.; Blondeau-Patissier, V.; Paolesse, R.; Gros, C.P.; Kadish, K.M. Synthesis and the Effect of Anions on the Spectroscopy and Electrochemistry of Mono(dimethyl sulfoxide)-Ligated Cobalt Corroles. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 59, 595–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osterloh, W.R.; Desbois, N.; Quesneau, V.; Brandès, S.; Fleurat-Lessard, P.; Fang, Y.; Blondeau-Patissier, V.; Paolesse, R.; Gros, C.P.; Kadish, K.M. Old Dog, New Tricks: Innocent, Five-coordinate Cyanocobalt Corroles. Inorg. Chem. 2020, 59, 8562–8579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lei, H.; Liu, J.; Zhao, X.; Ding, S.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, W.; Zheng, X.; et al. Carbon Nanotubes with Cobalt Corroles for Hydrogen and Oxygen Evolution in pH 0–14 Solutions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 15070–15075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadish, K.M.; Frémond, L.; Ou, Z.; Shao, J.; Shi, C.; Anson, F.C.; Burdet, F.; Gros, C.P.; Barbe, A.J.-M.; Guilard, R. Cobalt(III) Corroles as Electrocatalysts for the Reduction of Dioxygen: Reactivity of a Monocorrole, Biscorroles, and Porphyrin−Corrole Dyads. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 5625–5631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöfberger, W.; Faschinger, D.-I.F.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Bhakta, S.; Mondal, B.; Elemans, J.A.A.W.; Müllegger, S.; Tebi, M.S.S.; Koch, R.; Klappenberger, P.-D.D.F.; et al. A Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Oxygen Evolution and Oxygen Reduction Reactions in Water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 2350–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honig, H.C.; Krishnamurthy, C.B.; Borge-Durán, I.; Tasior, M.; Gryko, D.T.; Grinberg, I.; Elbaz, L. Structural and Physical Parameters Controlling the Oxygen Reduction Reaction Selectivity with Carboxylic Acid-Substituted Cobalt Corroles Incorporated in a Porous Carbon Support. J. Phys. Chem. C 2019, 123, 26351–26357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, R.; Gonglach, S.; Paul, S.; Haas, M.; Sreejith, S.S.; Gerschel, P.; Apfel, U.-P.; Vuong, T.H.; Rabeah, J.; Roy, S.; et al. Electrocatalytic reduction of CO2 to acetic acid by a molecular manganese corrole complex. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10527–10534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonglach, S.; Paul, S.; Haas, M.; Pillwein, F.; Sreejith, S.S.; Barman, S.; De, R.; Müllegger, S.; Gerschel, P.; Apfel, U.-P.; et al. Molecular cobalt corrole complex for the heterogeneous electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barbe, J.-M.; Canard, G.; Brandès, S.; Jérôme, F.; Dubois, G.; Guilard, R. Metallocorroles as sensing components for gas sensors: Remarkable affinity and selectivity of cobalt(iii) corroles for CO vs. O2 and N2. Dalton Trans. 2004, 8, 1208–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wo, Y.; Meyerhoff, M.E. Polymeric optical sensors for selective and sensitive nitrite detection using cobalt(III) corrole and rhodium(III) porphyrin as ionophores. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 843, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Meyerhoff, M.E. Study of Cobalt(III) Corrole as the Neutral Ionophore for Nitrite and Nitrate Detection via Polymeric Membrane Electrodes. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 2579–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, S.; Peng, L.; Huang, P.; Wang, X.; Sun, Y.; Cao, C.; Song, W. Nitrogen, Phosphorus, and Sulfur Co-Doped Hollow Carbon Shell as Superior Metal-Free Catalyst for Selective Oxidation of Aromatic Alkanes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4016–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahyari, M.; Nasrollah, G.J. Cobalt porphyrin supported on N and P co-doped graphene quantum dots/graphene as an efficient photocatalyst for aerobic oxidation of alcohols under visible-light irradiation. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 3641–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Cui, G. Cobalt-boron-oxide supported on N, P dual-doped carbon nanosheets as the trifunctional electrocatalyst and its application in rechargeable Zn-air battery and overall water-electrolysis. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 327, 134980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Rao, L.; Yao, Y.; Chen, H. Phosphorus-doped carbon fibers as an efficient metal-free bifunctional catalyst for removing sulfamethoxazole and chromium (VI). Chemosphere 2019, 246, 125783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Clark, J.H.; Geng, T.; Zhang, H.; Cao, F. A carbon catalyst co-Doped with P and N for efficient and selective oxidation of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural into 2,5-diformylfuran. ChemSusChem 2020, 14, 456–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Lian, C.; Xu, Q.; Liu, M.; Liu, H.; Jiang, H.; Li, C. Interfacial charge polarization in Co2P2O7@N, P co-doped carbon nanocages as Mott-Schottky electrocatalysts for accelerating oxygen evolution reaction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2019, 268, 118417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, M.; Wang, B.; Yu, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Yang, D. FeNi3-modified Fe2O3/NiO/MoO2 heterogeneous nanoparticles immobilized on N, P co-doped CNT as an efficient and stable electrocatalyst for water oxidation. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 3777–3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ren, J.-T.; Yuan, Z.-Y. Atomic heterojunction-induced electron interaction in P-doped g-C3N4 nanosheets supported V-based nanocomposites for enhanced oxidative desulfurization. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 387, 124164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guan, X.; Huang, B.; Wei, Q.; Xie, Z. One-Step Synthesis of N, P-Codoped Carbon Nanosheets Encapsulated CoP Particles for Highly Efficient Oxygen Evolution Reaction. Front. Chem. 2020, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zeng, H.C. Hybrid OER Electrocatalyst Combining Mesoporous Hollow Spheres of N, P-Doped Carbon with Ultrafine Co2NiOx. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 50324–50332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Li, D.; Lu, G.; Cai, C. Hydrogen Auto-transfer synthesis of quinoxalines from o-nitroanilines and biomass-based diols catalyzed by MOF-derived N, P co-doped cobalt catalysts. ChemCatChem 2020, 13, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Dong, H.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y. Cobalt anchored on porous N, P, S-doping core-shell with generating/activating dual reaction sites in heterogeneous electro-Fenton process. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 406, 125990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, W. Synthesis of oxygen vacancy-enriched N/P co-doped CoFe2O4 for high-efficient degradation of organic pollutant: Mechanistic insight into radical and nonradical evolution. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 270, 116092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Z.; Wang, H.; Chi, Y.; Wang, M.; Cheng, D.; Zhang, J.; Wu, C.; Zhao, Z. Noble-metal-free Co@Co2P/N-doped carbon nanotube polyhedron as an efficient catalyst for hydrogen generation from ammonia borane. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 9030–9039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, S. N, P co-doped microporous carbon as a metal-free catalyst for the selective oxidation of alcohols by air in water. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 13877–13884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Luo, F.; Long, X.; Yu, X.; Qu, K.; Yang, Z. N, P doped carbon nanotubes confined WN-Ni Mott-Schottky heterogeneous electrocatalyst for water splitting and rechargeable zinc-air batteries. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2021, 298, 120511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, A.H.; Rafique, N.; Hirani, R.A.K.; Wu, H.; Shi, L.; Sun, H. Heterogeneous activation of peroxymonosulfate by Co-doped Fe2O3 nanospheres for degradation of p-hydroxybenzoic acid. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2021, 604, 390–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, G.; Pan, Z.; Kang, S.; Ma, S.; Shen, P.K.; Zhu, J. One-pot synthesis of Mn2P-Mn2O3 heterogeneous nanoparticles in a P, N- doped three-dimensional porous carbon framework as a highly efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for overall water splitting. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 428, 131190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, X.; Li, Z.; Gao, G.; Sun, P.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Zhong, J.; Jiang, Z.; Li, F. Graphitic phosphorus coordinated single Fe atoms for hydrogenative transformations. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, S.; Yamaguchi, S.; Yamasaki, J.; Nakajima, K.; Yamazoe, S.; Mizugaki, T.; Mitsudome, T. Ni2P Nanoalloy as an Air-Stable and Versatile Hydrogenation Catalyst in Water: P-Alloying Strategy for Designing Smart Catalysts. Chem. Eur. J. 2020, 27, 4439–4446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appleby, A.P.; Müller, F.; Carpy, A. Weed Control. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Vogt, P.F.; Gerulis, J.J. Amines, Aromatic. In Ullmann’s Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2000. [Google Scholar]

| Entry | Catalyst | Pyrolysis T (°C) | Conversion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CoCorrPPh3@Vulcan | 800 | 79 |
| 2 | CoCorrPPh3@CeO2 | 800 | 26 |
| 3 | CoCorrPPh3@SiO2 | 800 | 7 |
| 4 | CoCorrPPh3@Al2O3 | 800 | 3 |
| 5 | CoCorrPPh3 | 800 | 60 |
| 6 | CoCorrPPh3 | non-pyrolyzed | 7 |
| 7 | CoCorrPPh3@Vulcan | non-pyrolyzed | 0 |
| Entry | Catalyst (mol%) | Conversion (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.10 | 9 |
| 2 | 0.25 | 25 |
| 3 | 0.50 | 79 |
| 4 | 1.00 | >99 |
| 5 | no catalyst | 0 |
| Entry | Catalyst | Pyrolysis T (°C) | Conversion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CoCorrPPh3@Vulcan | 400 | 22 |
| 2 | CoCorrPPh3@Vulcan | 600 | 46 |
| 3 | CoCorrPPh3@Vulcan | 700 | 69 |
| 4 | CoCorrPPh3@Vulcan | 800 | 79 |
| 5 | CoCorrPPh3@Vulcan | 900 | 54 |
| 6 | CoCorrPPh3@Vulcan | non-pyrolyzed | 0 |
| Entry | Solvent | Conversion (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | MeOH | 79 |
| 2 | MeOH | >99 1, (96) 1 |
| 3 | H2O | >99 1, (55) 1 |
| 4 | THF | 14 |
| 5 | n-heptane | 0 |
| 6 | toluene | 0 |
| 7 | CHCl3 | 0 |
| Entry | Run | Conversion (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | >99 |
| 2 | 2 | 90 |
| 3 | 3 | 59 |
| 4 | 4 | 49 |
| 5 | 5 | 44 |
| 6 | 6 | 40 |
| 7 | 7 | 39 |
| 8 | 8 | 37 |
| 9 | 9 | 36 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Michalke, J.; Haas, M.; Krisch, D.; Bögl, T.; Bartling, S.; Rockstroh, N.; Schöfberger, W.; Topf, C. Generation of Cobalt-Containing Nanoparticles on Carbon via Pyrolysis of a Cobalt Corrole and Its Application in the Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes. Catalysts 2022, 12, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12010011
Michalke J, Haas M, Krisch D, Bögl T, Bartling S, Rockstroh N, Schöfberger W, Topf C. Generation of Cobalt-Containing Nanoparticles on Carbon via Pyrolysis of a Cobalt Corrole and Its Application in the Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes. Catalysts. 2022; 12(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleMichalke, Jessica, Michael Haas, Dominik Krisch, Thomas Bögl, Stephan Bartling, Nils Rockstroh, Wolfgang Schöfberger, and Christoph Topf. 2022. "Generation of Cobalt-Containing Nanoparticles on Carbon via Pyrolysis of a Cobalt Corrole and Its Application in the Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes" Catalysts 12, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12010011
APA StyleMichalke, J., Haas, M., Krisch, D., Bögl, T., Bartling, S., Rockstroh, N., Schöfberger, W., & Topf, C. (2022). Generation of Cobalt-Containing Nanoparticles on Carbon via Pyrolysis of a Cobalt Corrole and Its Application in the Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes. Catalysts, 12(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal12010011







