Preparation and Performances of ZIF-67-Derived FeCo Bimetallic Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Light Olefins
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
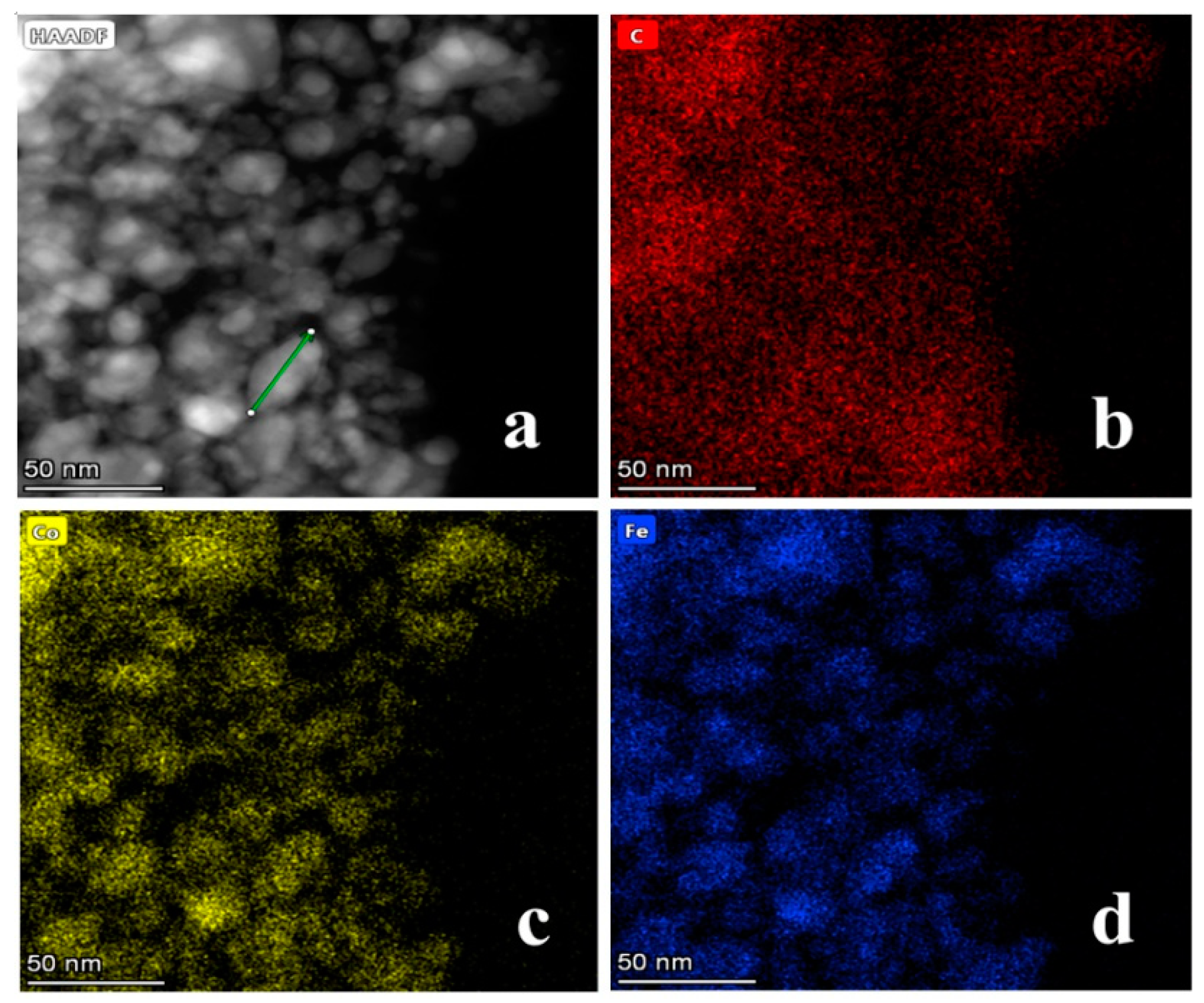
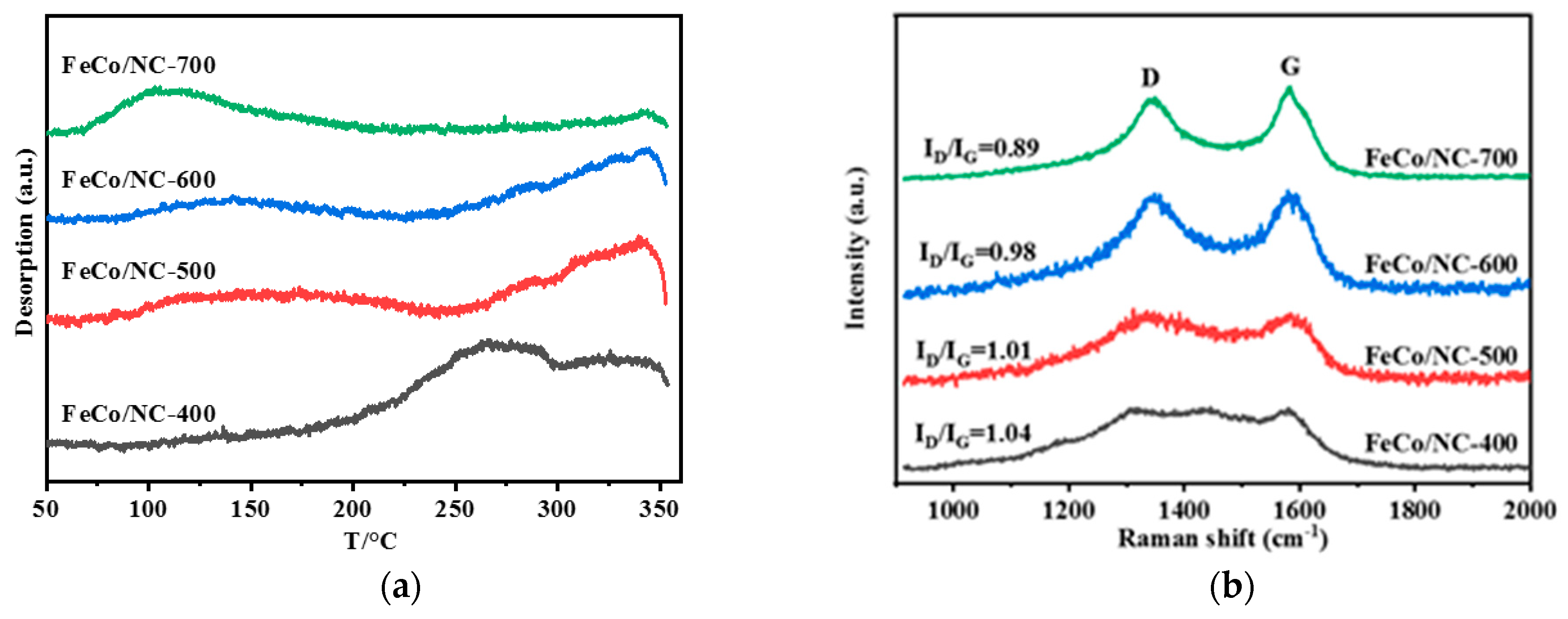
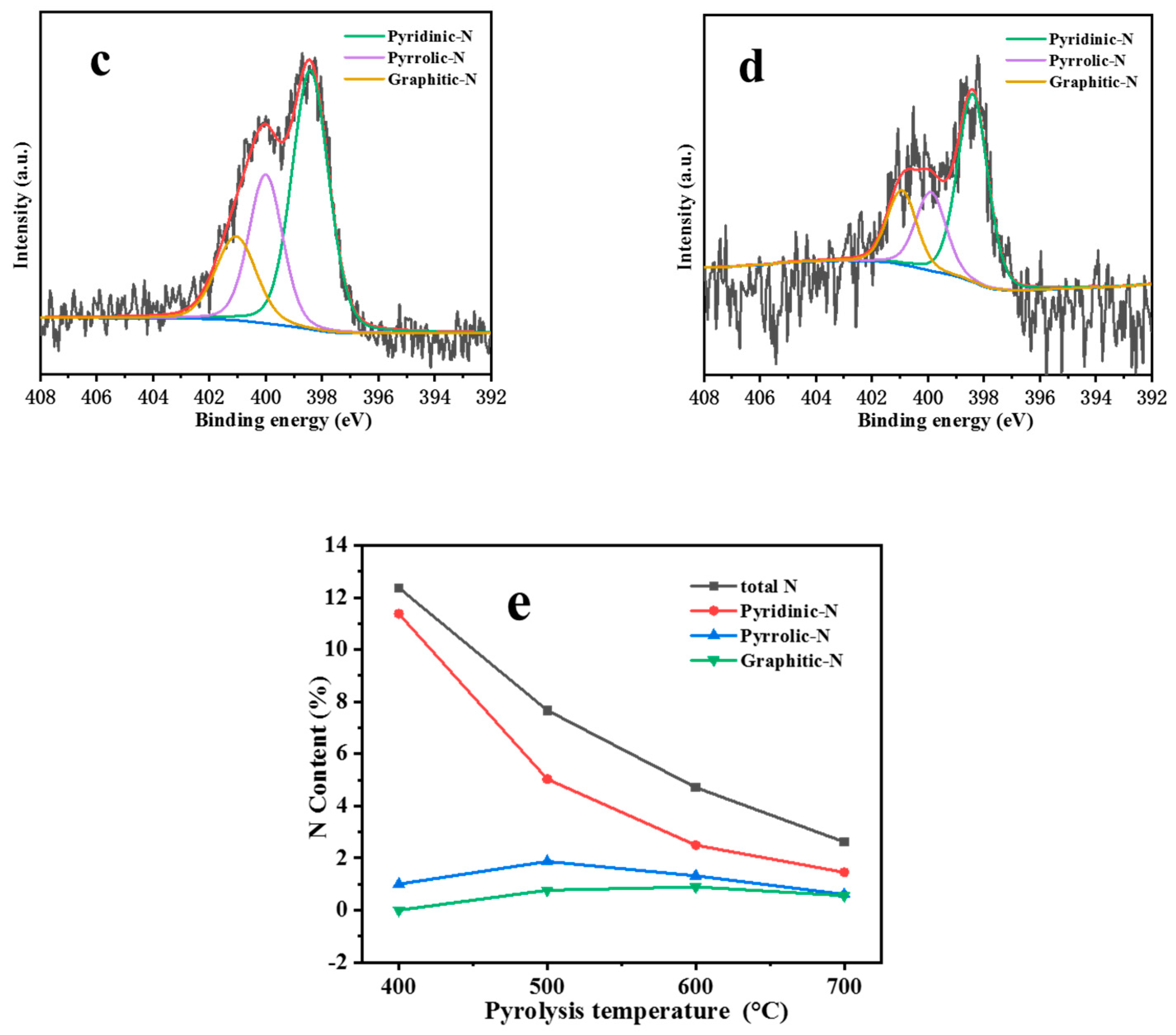
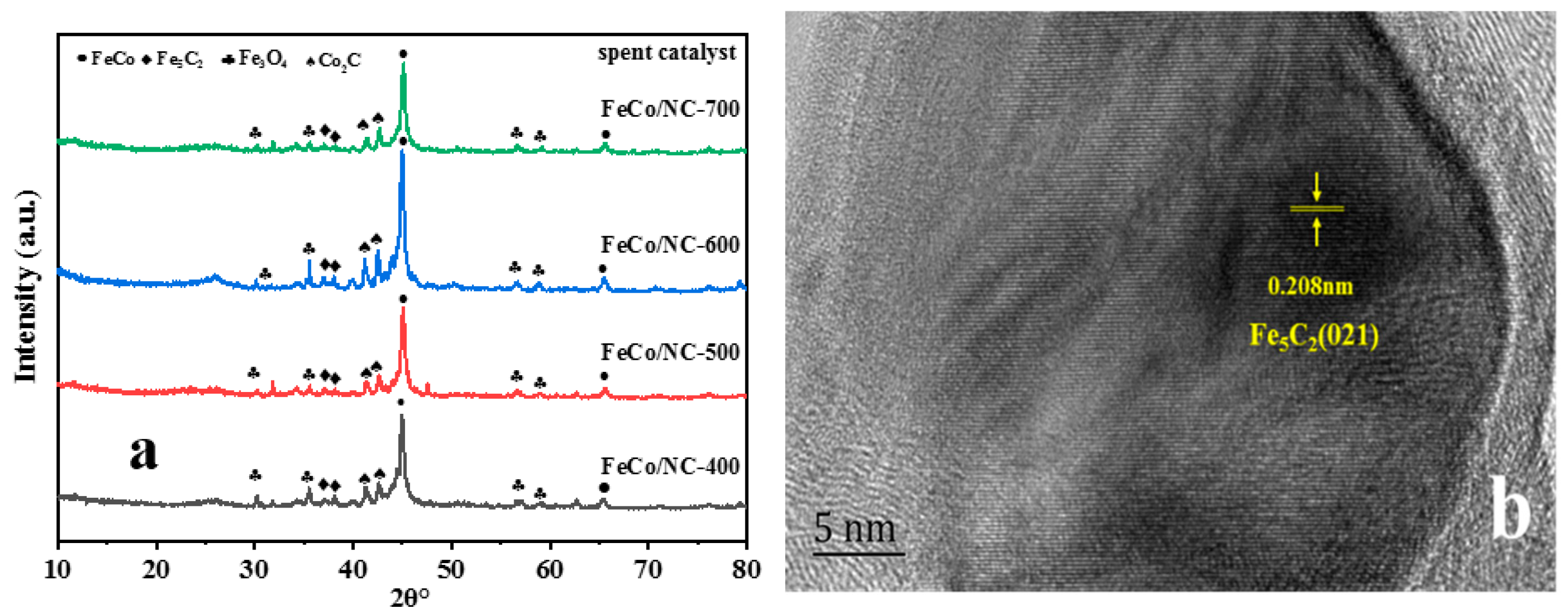
2.1. Physical and Chemical Properties of Catalyst
2.2. Activity Test
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Catalysis Preparation
3.1.1. Preparation of Fe/ZIF-67
3.1.2. Preparation of FeCo/NC
3.1.3. Synthesis of FeCo/Al2O3
3.2. Catalyst Characterization
3.3. Catalytic Performances
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Centi, G.; Quadrelli, E.A.; Perathoner, S. Catalysis for CO2 conversion: A key technology for rapid introduction of renewable energy in the value chain of chemical industries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1711–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C. Global challenges and strategies for control, conversion and utilization of CO2 for sustainable development involving energy, catalysis, adsorption and chemical processing. Catal. Today 2006, 115, 2–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, C.; Gao, P.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Zhong, L.; Wei, W.; Sun, Y. A review of the catalytic hydrogenation of carbon dioxide into value-added hydrocarbons. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2017, 7, 4580–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratenko, E.V.; Mul, G.; Baltrusaitis, J.; Larrazábal, G.O.; Pérez-Ramírez, J. Status and perspectives of CO2 conversion into fuels and chemicals by catalytic, photocatalytic and electrocatalytic processes. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3112–3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Sun, J.; Ji, X.; Wei, J.; Wen, Z.; Yao, R.; Xu, H.; Ge, Q. Directly converting carbon dioxide to linear α-olefins on bio-promoted catalysts. Commun. Chem. 2018, 1, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Dang, S.; Li, S.; Bu, X.; Liu, Z.; Qiu, M.; Yang, C.; Wang, H.; Zhong, L.; Han, Y.; et al. Direct Production of Lower Olefins from CO2 Conversion via Bifunctional Catalysis. ACS Catal. 2017, 8, 571–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, M.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, W.; Cheng, K.; Kang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Deng, W.; Wang, Y. Selective transformation of carbon dioxide into lower olefins with a bifunctional catalyst composed of ZnGa2O4 and SAPO-34. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 140–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, H.; Jiang, X.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Z.; Guo, X.; Song, C. A short review of recent advances in CO2 hydrogenation to hydrocarbons over heterogeneous catalysts. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 7651–7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, X.; Wang, H.; Janik, M.J.; Chen, Y.; Guo, X.; Song, C. Mechanistic Insight into C–C Coupling over Fe–Cu Bimetallic Catalysts in CO2 Hydrogenation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 13164–13174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Jha, A.; Shende, P.; Maskara, R.; Das, A.K. Catalytic performance of Co and Ni doped Fe-based catalysts for the hydrogenation of CO2 to CO via reverse water-gas shift reaction. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visconti, C.G.; Martinelli, M.; Falbo, L.; Infantes-Molina, A.; Lietti, L.; Forzatti, P.; Iaquaniello, G.; Palo, E.; Picutti, B.; Brignoli, F. CO2 hydrogenation to lower olefins on a high surface area K-promoted bulk Fe-catalyst. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2017, 200, 530–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Chen, C.; Yu, Y.; Su, J.; Li, Y.; Somorjai, G.A.; Yang, P. Tandem Catalysis for CO2 Hydrogenation to C2-C4 Hydrocarbons. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 3798–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muleja, A.A.; Gorimbo, J.; Masuku, C.M. Effect of Co-Feeding Inorganic and Organic Molecules in the Fe and Co Catalyzed Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis: A Review. Catalysts 2019, 9, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yi, Y.; Wang, L.; Guo, H.; Bogaerts, A. Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide to Value-Added Chemicals by Heterogeneous Catalysis and Plasma Catalysis. Catalysts 2019, 9, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puga, A.V. On the nature of active phases and sites in CO and CO2 hydrogenation catalysts. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2018, 8, 5681–5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Ning, W.; Han, W.; Liu, H.; Huo, C. Preparation of Iron Carbides Formed by Iron Oxalate Carburization for Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis. Catalysts 2019, 9, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herranz, T.; Rojas, S.; Pérez-Alonso, F.J.; Ojeda, M.; Terreros, P.; Fierro, J.L.G. Hydrogenation of carbon oxides over promoted Fe-Mn catalysts prepared by the microemulsion methodology. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2006, 311, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Chen, J.; Ma, Q.; Fan, S.; Zhao, T.-S. Effect of preparation methods on the structure and catalytic performance of Fe–Zn/K catalysts for CO2 hydrogenation to light olefins. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2018, 26, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Dossary, M.; Ismail, A.A.; Fierro, J.L.G.; Bouzid, H.; Al-Sayari, S.A. Effect of Mn loading onto MnFeO nanocomposites for the CO2 hydrogenation reaction. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2015, 165, 651–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jiang, X.; Wang, X.; Song, C. Fe–Cu Bimetallic Catalysts for Selective CO2 Hydrogenation to Olefin-Rich C2+ Hydrocarbons. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 4535–4542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Sun, J.; Wen, Z.; Fang, C.; Ge, Q.; Xu, H. New insights into the effect of sodium on Fe3O4- based nanocatalysts for CO2 hydrogenation to light olefins. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 4786–4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lu, S.; Su, X.; Fan, S.; Ma, Q.; Zhao, T. Selective formation of light olefins from CO2 hydrogenation over Fe–Zn–K catalysts. J. CO2 Util. 2015, 12, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Krishnamoorthy, S.; Li, A.; Meitzner, G.D.; Iglesia, E. Promoted Iron-Based Catalysts for the Fischer–Tropsch Synthesis: Design, Synthesis, Site Densities, and Catalytic Properties. J. Catal. 2002, 206, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, K.-W.; Lee, S.-J.; Kim, H. Support effects of the promoted and unpromoted iron catalysts in CO2 hydrogenation. Stud. Surf. Sci. Catal. 1998, 114, 345–350. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Lin, L.; Li, M.; Deng, Y.; Wang, X.; Ge, B.; Yang, C.; et al. Tuning the Selectivity of Catalytic Carbon Dioxide Hydrogenation over Iridium/Cerium Oxide Catalysts with a Strong Metal-Support Interaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2017, 56, 10761–10765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Numpilai, T.; Witoon, T.; Chanlek, N.; Limphirat, W.; Bonura, G.; Chareonpanich, M.; Limtrakul, J. Structure-activity relationships of Fe-Co/K-Al2O3 catalysts calcined at different temperatures for CO2 hydrogenation to light olefins. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2017, 547, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Oh, K.; Liu, F.; Seo, J.H.; Somorjai, G.A.; Lee, J.H.; An, K. Specific Metal–Support Interactions between Nanoparticle Layers for Catalysts with Enhanced Methanol Oxidation Activity. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 5391–5398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larmier, K.; Chizallet, C.; Raybaud, P. Tuning the metal-support interaction by structural recognition of cobalt-based catalyst precursors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 6824–6827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Wu, B.; Xiang, H.; Li, Y. Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis: Influence of Support Incorporation Manner on Metal Dispersion, Metal–Support Interaction, and Activities of Iron Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2012, 2, 1877–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, L.M.; Kangvansura, P.; Ruland, H.; Schulte, H.J.; Somsen, C.; Xia, W.; Eggeler, G.; Worayingyong, A.; Muhler, M. Effect of nitrogen doping on the reducibility, activity and selectivity of carbon nanotube-supported iron catalysts applied in CO2 hydrogenation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 482, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Lin, J.; Wu, T.; Wang, H.; Xie, S.; Pei, Y.; Yan, S.; Qiao, M.; Zong, B. Mg and K dual-decorated Fe-on-reduced graphene oxide for selective catalyzing CO hydrogenation to light olefins with mitigated CO2 emission and enhanced activity. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 204, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, D.L.; Herdes, C.; Torrente, M.L.; Matthew, D.J.; Davide, M. N-Doped Fe@CNT for Combined RWGS/FT CO2 Hydrogenation. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 7395–7402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cai, X.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, K.H.L.; Hong, J.; Chen, B.; Kuo, D.-H.; Wang, W. Highly Dispersed Metal Carbide on ZIF-Derived Pyridinic-N-Doped Carbon for CO2 Enrichment and Selective Hydrogenation. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, A.; Gevers, L.; Bavykina, A.; Ould-Chikh, S.; Gascon, J. Metal Organic Framework-Derived Iron Catalysts for the Direct Hydrogenation of CO2 to Short Chain Olefins. ACS Catal. 2018, 8, 9174–9182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Cheng, P.; Xu, J.; Han, J.; Wang, D.; Hao, C.; Alanagh, H.R.; Long, C.; Shi, X.; Tang, Z. MOF-derived nitrogen-doped nanoporous carbon for electroreduction of CO2 to CO: The calcining temperature effect and the mechanism. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 4911–4917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liu, M.; Ding, F.; Song, C.; Zhang, G.; Guo, X. Hydrothermally stable MOFs for CO2 hydrogenation over iron-based catalyst to light olefins. J. CO2 Util. 2016, 15, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Sun, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, A.; Song, C.; Guo, X. Pyrolyzing ZIF-8 to N-doped porous carbon facilitated by iron and potassium for CO2 hydrogenation to value-added hydrocarbons. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 25, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, A.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, G.; Sun, Y.; Liu, M.; Ding, F.; Song, C.; Guo, X. Overcoating the Surface of Fe-Based Catalyst with ZnO and Nitrogen-Doped Carbon toward High Selectivity of Light Olefins in CO2 Hydrogenation. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 4017–4023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, A.; Liu, M.; Hu, S.; Ding, F.; Song, C.; Guo, X. Fe-MOF-derived highly active catalysts for carbon dioxide hydrogenation to valuable hydrocarbons. J. CO2 Util. 2017, 21, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Liu, Y.; He, Y.; Kuhn, A.N.; Shih, P.C.; Sun, C.J.; Wen, X.; Shi, C.; Yang, H. Cobalt-Based Nonprecious Metal Catalysts Derived from Metal-Organic Frameworks for High-Rate Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 27717–27726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; An, B.; Hong, Y.; Meng, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, C.; Lin, J.; Lin, W.; Wang, Y. Pyrolysis of metal-organic frameworks to hierarchical porous Cu/Zn-nanoparticle@carbon materials for efficient CO2 hydrogenation. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 2405–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Yu, F.; An, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Li, Z.; Lin, T.; Lin, Y.; Qi, X.; Dai, Y.; et al. Cobalt carbide nanoprisms for direct production of lower olefins from syngas. Nature 2016, 538, 84–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanamani, M.K.; Jacobs, G.; Keogh, R.A.; Shafer, W.D.; Sparks, D.E.; Hopps, S.D.; Thomas, G.A.; Davis, B.H. Fischer-Tropsch synthesis: Effect of pretreatment conditions of cobalt on activity and selectivity for hydrogenation of carbon dioxide. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2015, 499, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satthawong, R.; Koizumi, N.; Song, C.; Prasassarakich, P. Bimetallic Fe–Co catalysts for CO2 hydrogenation to higher hydrocarbons. J. CO2 Util. 2013, 3, 102–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satthawong, R.; Koizumi, N.; Song, C.; Prasassarakich, P. Light olefin synthesis from CO2 hydrogenation over K-promoted Fe–Co bimetallic catalysts. Catal. Today 2015, 251, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, A.; Jiang, X.; Janik, M.J.; Qiu, J.; Liu, Z.; Guo, X.; Song, C. The anti-sintering catalysts: Fe–Co–Zr polymetallic fibers for CO2 hydrogenation to C2 = –C4 = –rich hydrocarbons. J. CO2 Util. 2018, 23, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Cui, Y.; Li, H.; Fang, Y.; Prasert, R.; Wu, J.; Yang, G.; Yoneyama, Y.; Tsubaki, N. Selective formation of linear-alpha olefins (LAOs) by CO2 hydrogenation over bimetallic Fe/Co-Y catalyst. Catal. Commun. 2019, 130, 105759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-H.; Zhang, J.-L.; Liu, J.-M.; Xiong, Z.-H.; Chen, X. Selective and Competitive Adsorption of Azo Dyes on the Metal–Organic Framework ZIF-67. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zhang, X.; Feng, P.; Chai, H.; Huang, Y. ZIF-67 derived hollow cobalt sulfide as superior adsorbent for effective adsorption removal of ciprofloxacin antibiotics. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 344, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Salunkhe, R.R.; Liu, J.; Torad, N.L.; Imura, M.; Furukawa, S.; Yamauchi, Y. Thermal conversion of core-shell metal-organic frameworks: A new method for selectively functionalized nanoporous hybrid carbon. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 1572–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Olivos-Suarez, A.I.; Osadchii, D.; Romero, M.J.V.; Kapteijn, F.; Gascon, J. Single cobalt sites in mesoporous N-doped carbon matrix for selective catalytic hydrogenation of nitroarenes. J. Catal. 2018, 357, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, Z.; Xie, L.; Zhu, L.; Cao, X. ZIF-67-Derived N-Doped Co/C Nanocubes as High-Performance Anode Materials for Lithium-Ion Batteries. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 16619–16628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unni, S.M.; Anilkumar, G.M.; Matsumoto, M.; Tamaki, T.; Imaicd, H.; Yamaguchi, T. Direct synthesis of a carbon nanotube interpenetrated doped porous carbon alloy as a durable Pt-free electrocatalyst for the oxygen reduction reaction in an alkaline medium. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2017, 1, 1449–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liang, X.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Xiao, H.; Xu, P.; Zhang, T.; Liu, Z. Fe, N co-doped carbonaceous hollow spheres with self-grown carbon nanotubes as a high performance binary electrocatalyst. Carbon 2019, 154, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Meiling, X.; Jin, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhu, J.; Ge, J.; Xing, W. Correlating Fe source with Fe-N-C active site construction Guidance for rational design of high-performance ORR catalyst. J. Energy Chem. 2018, 27, 1668–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; Xie, Y.; Ci, S.; Jia, J.; Cai, P.; Yi, L.; Wen, Z. Multifunctional high-activity and robust electrocatalyst derived from metal–organic frameworks. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 17288–17298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, D.; Zou, H.; Zhu, L.; Xue, M.; Fang, Q.; Qiu, S. Guidance from an in situ hot stage in TEM to synthesize magnetic metal nanoparticles from a MOF. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 10513–10516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Suarez, O.A.I.; Arteta, O.L.; Rozhko, E.; Osadchii, D.; Anastasiya, B.; Kapteijn, F.; Gascon, J. Metal-Organic Framework Mediated CobaltNitrogen-Doped Carbon Hybrids as Efficient and Chemoselective Catalysts for the Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes. ChemCatChem 2017, 9, 1854–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Qian, W.; Zhang, H.; Ma, H.; Sun, Q.; Ying, W. Effect of Li promoter on FeMn/CNTs for light olefins from syngas. Catal. Commun. 2019, 124, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Hwang, S.; Wang, M.; Feng, Z.; Karakalos, S.; Luo, L.; Qiao, Z.; Xie, X.; Wang, C.; Su, D.; et al. Single Atomic Iron Catalysts for Oxygen Reduction in Acidic Media: Particle Size Control and Thermal Activation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 14143–14149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Long, Y.; Yang, J.; Hu, X.; Xu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, Z. Biomass Sucrose-Derived Cobalt@Nitrogen-Doped Carbon for Catalytic Transfer Hydrogenation of Nitroarenes with Formic Acid. ChemSusChem 2018, 11, 4156–4165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wen, C.; Zou, X.; Jimenez, J.; Sun, J.; Xia, Y.; Fonseca Rodrigues, M.-T.; Vinod, S.; Zhong, J.; Chopra, N.; et al. Carbon Dioxide Hydrogenation over a Metal-Free Carbon-Based Catalyst. ACS Catal. 2017, 7, 4497–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanfield, R.M.; Delgass, W.N. Mӧssbauer Spectroscopy of Supported Fe–Co Alloy Catalysts for Fischer-Tropsch Synthesis. J. Catal. 1981, 72, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyubutin, I.S.; Lin, C.R.; Korzhetskiy, Y.V.; Dmitrieva, T.V.; Chiang, R.K. Mössbauer spectroscopy and magnetic properties of hematite/magnetite nanocomposites. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 034311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.; Liu, C.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Structural evolution of carbon in an Fe@C catalyst during the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis reaction. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2019, 9, 1013–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanamani, M.K.; Jacobs, G.; Hamdeh, H.H.; Shafer, W.D.; Liu, F.; Hopps, S.D.; Thomas, G.A.; Davis, B.H. Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide over Co–Fe Bimetallic Catalysts. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
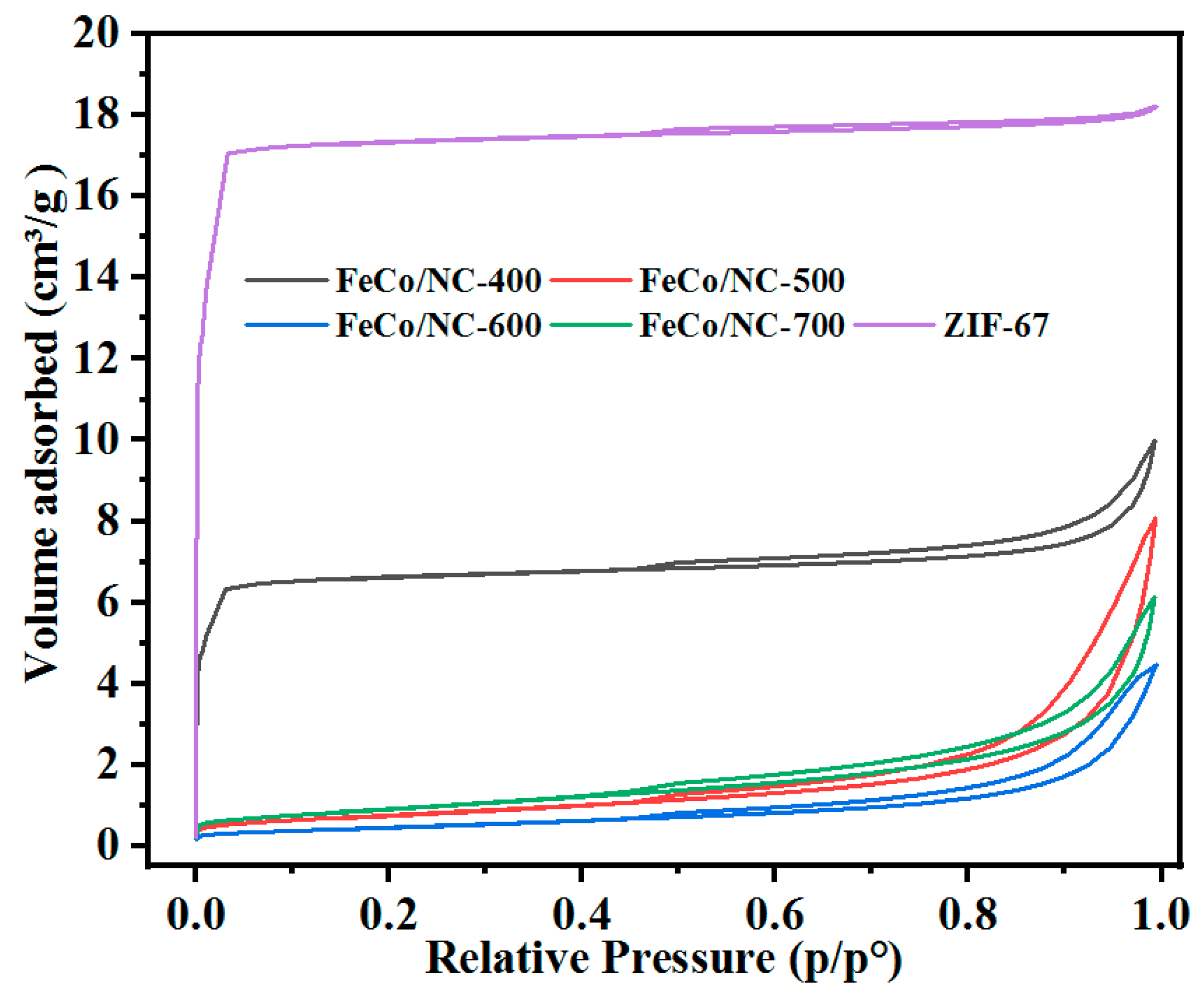
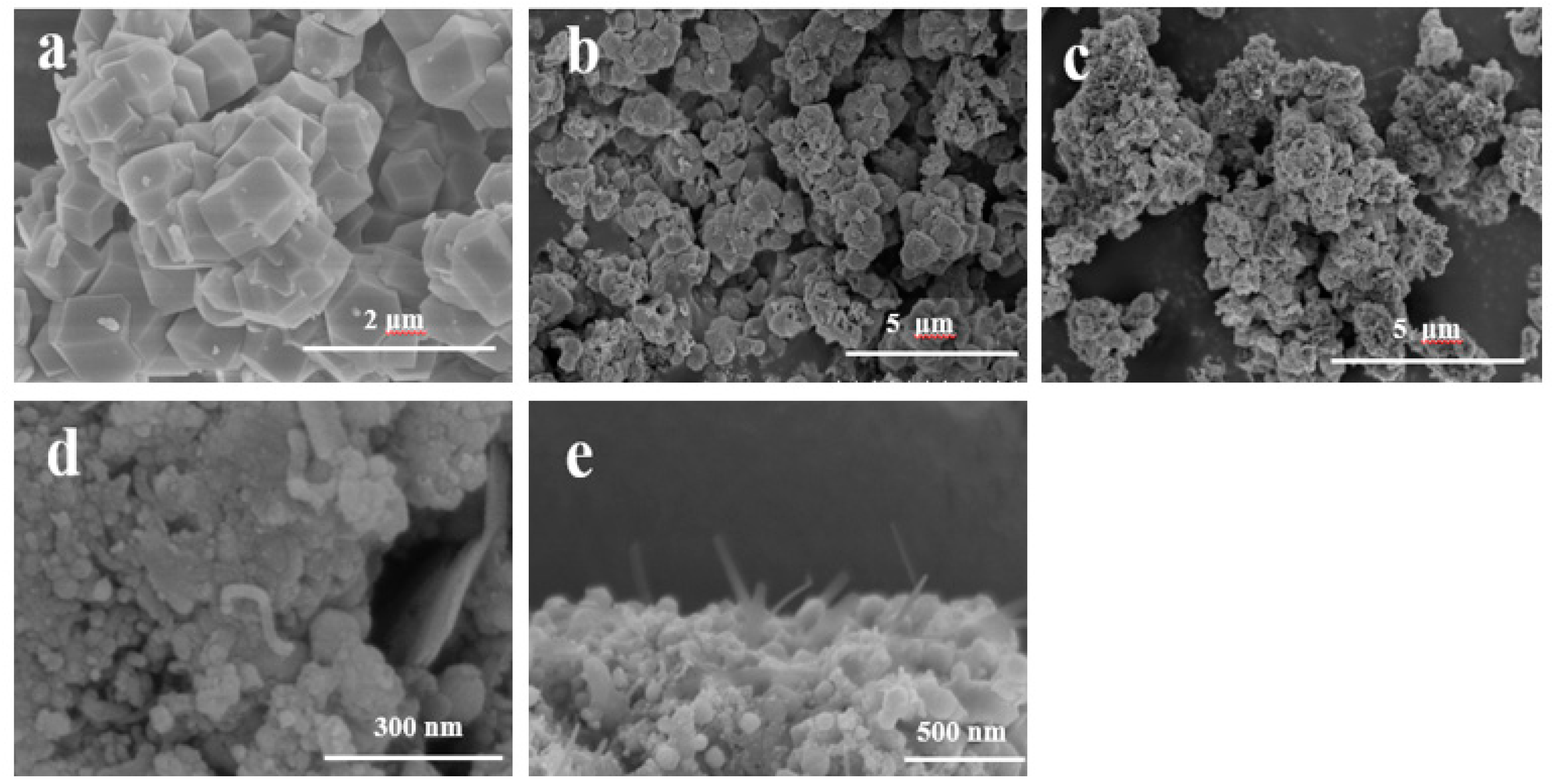
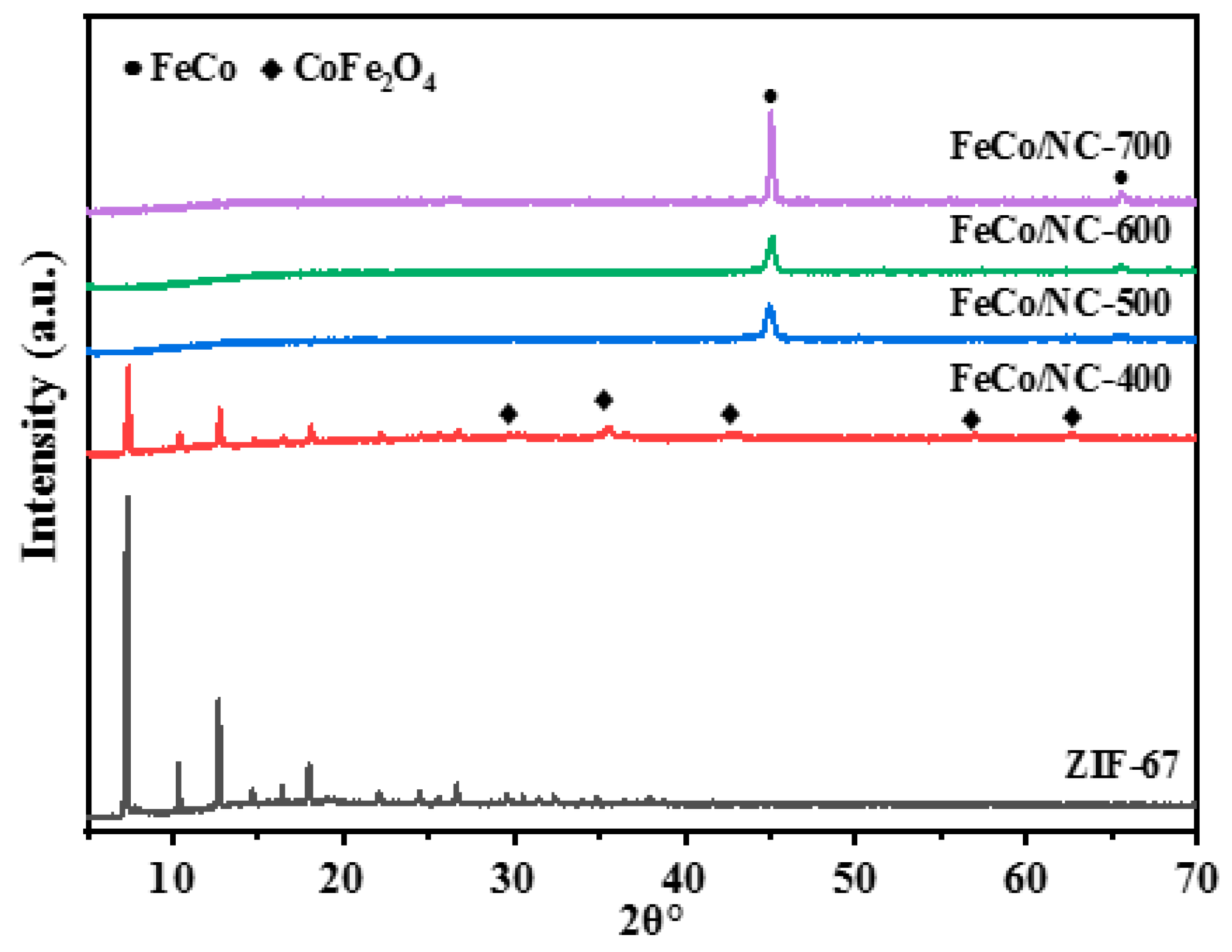

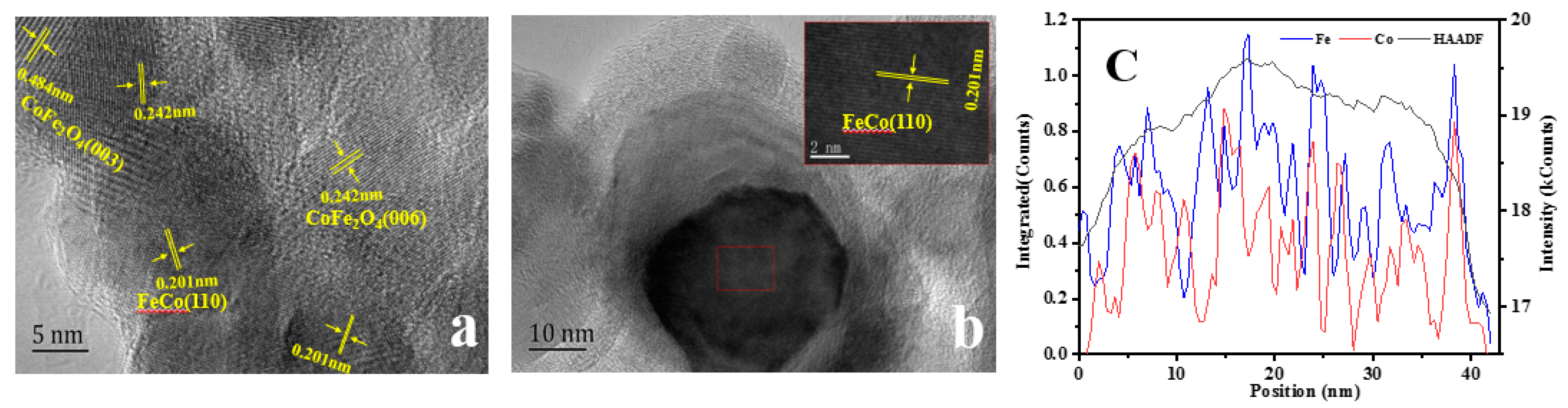


| Catalyst | T a(°C) | Metal content (wt %) b | SBET (m2g−1) | Smicro (m2g−1) | Smeso (m2g−1) | Vmicro (cm−3g−1) | Vmeso (cm−3g−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | Co | Fe/Co | |||||||
| FeCo/NC | 400 | 12.67 | 24.02 | 0.53 | 507 | 454 | 52.8 | 0.207 | 0.068 |
| 500 | 18.13 | 34.89 | 0.52 | 61.0 | 0 | 61.6 | 0 | 0.137 | |
| 600 | 19.21 | 36.24 | 0.53 | 36.4 | 0 | 40.8 | 0 | 0.086 | |
| 700 | 20.60 | 40.0 | 0.52 | 72.9 | 0 | 74.9 | 0 | 0.124 | |
| ZIF-67 | - | - | - | - | 1318 | 1265 | 53.6 | 0.578 | 0.043 |
| Catalyst | CO2 conv. (%) | TOF (h−1) | Product Sel (C-mol%) | O/Pa | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO | CH4 | C2–C4 | C2= − C4= | C5+ | alcohol | ||||
| FeCo/NC-400 | 48.37 | 10.75 | 1.39 | 67.31 | 14.12 | 11.14 | 0.86 | 5.19 | 0.79 |
| FeCo/NC-500 | 47.45 | 7.37 | 0.00 | 57.88 | 15.52 | 19.15 | 1.04 | 6.41 | 1.24 |
| FeCo/NC-600 | 37.03 | 5.43 | 1.13 | 44.50 | 20.75 | 27.05 | 1.63 | 4.95 | 1.30 |
| FeCo/NC-700 | 35.89 | 4.91 | 0.00 | 47.40 | 15.21 | 25.65 | 1.22 | 10.52 | 1.69 |
| FeCo/Al2O3 | 48.58 | 7.82 | 0.27 | 76.19 | 22.62 | 0.02 | 0.30 | 0.50 | |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, Z.; Zhao, J.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wu, Y. Preparation and Performances of ZIF-67-Derived FeCo Bimetallic Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Light Olefins. Catalysts 2020, 10, 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040455
Dong Z, Zhao J, Tian Y, Zhang B, Wu Y. Preparation and Performances of ZIF-67-Derived FeCo Bimetallic Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Light Olefins. Catalysts. 2020; 10(4):455. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040455
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Zichao, Jie Zhao, Yajie Tian, Bofeng Zhang, and Yu Wu. 2020. "Preparation and Performances of ZIF-67-Derived FeCo Bimetallic Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Light Olefins" Catalysts 10, no. 4: 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040455
APA StyleDong, Z., Zhao, J., Tian, Y., Zhang, B., & Wu, Y. (2020). Preparation and Performances of ZIF-67-Derived FeCo Bimetallic Catalysts for CO2 Hydrogenation to Light Olefins. Catalysts, 10(4), 455. https://doi.org/10.3390/catal10040455





