Abstract
Serum uric acid (SUA) is an important biomarker for prognosis and management of gout and other diseases. The development of a low-cost, simple, rapid and reliable assay for SUA detection is of great importance. In the present study, to save the cost of enzyme production and to shorten the reaction time for uric acid quantification, bifunctional proteins with uricase and peroxidase activities were engineered. In-frame fusion of Candida utilis uricase (CUOX) and Vitreoscilla hemoglobin (VHb) resulted in two versions of the bifunctional protein, CUOX-VHb (CV) and VHb-CUOX (VC). To our knowledge, this is the first report to describe the production of proteins with uricase and peroxidase activities. Based on the measurement of the initial rates of the coupled reaction (between uricase and peroxidase), CV was proven to be the most efficient enzyme followed by VC and native enzymes (CUOX+VHb), respectively. CV was further applied for the development of an assay for colorimetric detection of SUA, which was based on VHb-catalyzed oxidation of Amplex Red in the presence of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Under the optimized conditions, the assay exhibited a linear relationship between the absorbance and UA concentration over the range of 2.5 to 50 μM, with a detection limit of 1 μM. In addition, the assay can be performed at a single pH (8.0) so adjustment of the pH for peroxidase activity was not required. This advantage helped to further reduce costs and time. The developed assay was also successfully applied to detect UA in pooled human serum with the recoveries over 94.8%. These results suggest that the proposed assay holds great potential for clinical application.
1. Introduction
Uric acid (UA) is the end product of purine nucleotide catabolism in the human body. The normal ranges of serum uric acid (SUA) in females and males are 2.4–6.0 mg/dL (143–357 μM) and 3.4–7.0 mg/dL (202–416 μM), respectively. Elevation of SUA greater than 6.8 mg/dL (405 μM) is recognized as hyperuricemia, which is known to associate with various diseases, e.g., gout, nephrolithiasis, kidney failure, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases [1]. Therefore, monitoring of SUA levels is essential for the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of these diseases. To measure the SUA level, various analytical methods such as spectral (UV, colorimetry, fluorescence), electrochemical (voltammetry, electrochemiluminescence, surface plasmon resonance), chromatographic (liquid and gas phase) and capillary electrophoresis methods have been described. The details of these techniques have been extensively reviewed elsewhere [2]. Although various modern techniques have been proposed, the most widely employed technique for UA determination by automated systems in clinical laboratories is classical spectrophotometry [3]. This is because the technique is designed with an automation-friendly protocol and the cost is more favorable. The principle of this technique is based on the cascade reactions of uricase and peroxidase enzymes [4,5].
In the presence of oxygen, uricase oxidizes uric acid to allantoin, carbon dioxide and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). The produced H2O2 is then consumed by peroxidase for the oxidation of a chromogenic substrate to a color product, which can be measured spectrophotometrically. Different types of chromogenic substrate (e.g., 3-methyl-2-benzothiazolinone hydrazine (MBTH) plus N,N-dimethylaniline (DMA) [6], 2,4-dichlorophenol (2, 4-DCP) plus 4-aminophenazone [7], p-hydroxybenzoate (PHBA) plus 4-aminoantipyrine (4-APP) [8], 3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzene sulfonic acid plus 4-aminophenazone [9], o-dianisidine [4], 2,2′-azino-bis (3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) (ABTS) [10], and 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) [11]) and different sources of uricase have been explored. Among the tested enzymes, microbial uricase (e.g., Aspergillus flavus, Candida utilis, Bacillus fastidiosus and Arthrobacter globiformis) has been shown to be superior to uricase from other higher organisms; microbial enzymes exhibited more stability and higher enzymatic activity [12,13,14,15]. Generally, uricase is more stable and exhibits the highest enzymatic activity at pH ≥ 8.0 [16], thus the measurement of UA using uricase is performed at alkaline pH. Besides uricase, the other key enzyme of the cascade reactions is a peroxidase. As opposed to the wide variety of uricase sources, the only source of peroxidase is the horseradish plant (horseradish peroxidase; HRP). This may be due to the fact that HRP has high activity, high stability and can be produced from the farmed plant (Armoracia rusticana). Nevertheless, the activity of HRP is strictly dependent on pH. The optimal pH range for the HRP reaction is 5.5–6.0 [17]. As a consequence, to assay SUA using uricase and HRP, the measurement must be done with a two-step procedure. Uricase reaction is performed first at pH ≥ 8.0 then the reaction pH is changed to <6 to facilitate HRP action [6]. This makes the uricase/HRP-based method more complicated and several reaction buffers with different pH must be prepared. In fact, one could also perform the test at a more neutral pH (7.0–7.5) [18]. However, at this pH range, HRP activity is reduced to less than 80% [17]. Besides the pH incompatibility issue, classical production of HRP from Armoracia rusticana roots is undesirable, since sufficient production of high-quality enzyme is hampered by seasonal availability, long cultivation times, low production yields and low product homogeneity [19,20]. To produce a uniform enzyme with defined characteristics, the production of recombinant HRP (rHRP) using Saccharomyces cerevisiae [21] and Pichia pastoris [20,21,22] has been attempted. The advantage of using yeast cells is that the recombinant protein can obtain glycosylation as produced in plant cells. Nonetheless, glycosylation of rHRP in yeast cells has been reported to occur non-specifically, resulting in more complicated downstream processes [20]. Besides yeast cells, production of rHRP in E. coli have also been explored [23,24,25,26,27]. The enzyme can be produced up to 1 g/1-Liter culture. However, the expressed protein formed inclusion bodies (IBs), which need to be recovered through cumbersome protein-refolding processes. Although up to 10% of rHRP can be successfully recovered from IBs, the enzyme specific activity was markedly reduced [26]. Besides direct expression in cytoplasm, rHRP was also targeted to express in the periplasmic space of E. coli. Nevertheless, the production yields and enzymatic activity of the enzyme were even lower than that of the enzyme recovered from IBs [26].
Previously, the peroxidase activity of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin (VHb) has been reported by our group [28,29,30]. The protein can catalyze a wide variety of reducing substrates such as ferrocene carboxylic acid, dopamine, L-dopa, ABTS [28] and Amplex Red [29]. Although the peroxidase activity of VHb is much lower than that of HRP, soluble and active protein can be massively produced in E. coli. Homogeneous protein with well-defined characteristics can be obtained by simple purification using immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC). The protein can also be engineered as a fusion protein while maintaining high solubility and sufficient peroxidase activity. More importantly, VHb exhibits maximum peroxidase activity at pH 7.0 [28,31], which is closely related to the optimal pH of uricase (8.0–9.0). These observations imply that uricase and VHb may be combined in a single reaction for the detection of UA without the need for changing the reaction pH.
Therefore, in this study, quantification of UA using uricase and VHb was investigated. To reduce the cost for enzyme production and to improve the reaction velocity of uricase-peroxidase cascade reactions, which, in turn, can reduce the reaction time, bifunctional proteins with uricase and peroxidase activities were engineered. The proteins were created by direct fusion of Candida utilis uricase (CUOX) and VHb. The details for production, characterization and successful application of the bifunctional protein for detection of UA in human serum are reported here.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Production of Native and Bifunctional Proteins with Uricase and Peroxidase Activities
Recombinant CUOX, VHb, CUOX-VHb (CV) fusion protein and VHb-CUOX-VHb (VC) fusion proteins were successfully expressed in E. coli BL21 (DE3) and purified to homogeneity. Genes encoding CUOX and VHb were fused in-frame, resulting in direct joining of the C-terminus of the first protein to the N-terminus of the second protein. Schematic representation for the production of a fusion protein (CV) is shown in Figure 1. To facilitate protein purification by IMAC, all proteins were designed to express with a hexahistidine tag at the N-terminus. After IMAC-purification, SDS-PAGE analysis revealed that CUOX, VHb and CV fusion protein had a molecular weight (MW) under denaturing conditions of ~35, ~17 and ~50 kDa, respectively. However, VC fusion protein presented with two protein bands with MW of ~50 kDa and ~25 kDa (data not shown). This result indicated that VC was susceptible to protein degradation, which could be due to steric effects presented within the engineered polypeptide chain. The degrading point is believed to be in the CUOX region because the purified fraction had a MW larger than that of the VHb subunit. Nevertheless, as in other IMAC-purified proteins, the mixture of full-length and degraded VC was subjected to further purification by gel-filtration chromatography. As expected, CUOX, VHb and CV showed a single protein peak in the chromatogram while VC showed two separated protein peaks (data not shown). This result suggested that the full-length and the degraded fractions of VC can be successfully separated from each other by gel-filtration chromatography.
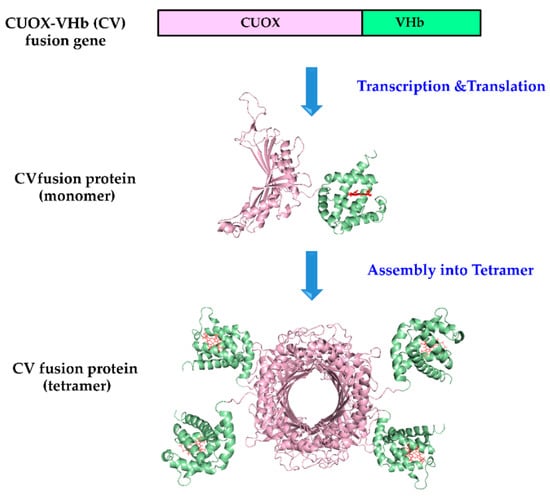
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the strategy for the engineering of bifunctional protein with uricase and peroxidase activities. In-frame fusion of Candida utilis uricase (CUOX) and Vitreoscilla hemoglobin (VHb) genes results in CUOX-VHb fusion protein, then, four monomers of the fusion protein assemble into a tetrameric complex. Construction of VHb-CUOX fusion protein was also performed by the same technique except that the VHb gene was put in front of the CUOX gene.
All purified proteins were again subjected to SDS-PAGE analysis, which revealed that they were purified to more than 95% homogeneity and the MW under denaturing condition of CUOX, VHb, CV and VC were ~35, ~17, ~50 and ~50 kDa, respectively (Figure 2a). These MW values were closely related to the values predicted by the ExPASy Compute pI/Mw tool (https://web.expasy.org/compute_pi/), which were ~35.7, ~17.4, ~51.7 and ~51.7 kDa, respectively. A 1-L culture of E. coli yielded purified CUOX, VHb, CV and VC up to 413, 118, 51 and 23 mg, respectively. In addition, based on gel-filtration chromatography, MW under the natural condition of all proteins was calculated. The result revealed that CUOX, VHb, CV and VC had natural MW of ~143 kDa, ~35 kDa, ~207 kDa and ~207 kDa, respectively (Figure 2b). This result showed that recombinant CUOX and VHb were produced in their natural forms, which are tetrameric and dimeric forms, respectively. More importantly, this result confirmed that the fusion proteins assembled into the tetrameric complex as proposed in Figure 1. One molecule of the tetrameric complex was composed of four CUOX subunits, arranged in its naturally occurring tetrameric structure, and four VHb subunits, arranged in monomeric rather than dimeric form.
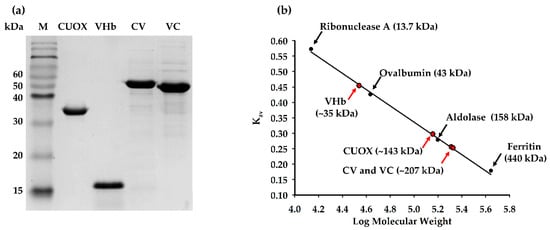
Figure 2.
(a) SDS-PAGE analysis showing purity after protein purifications and molecular weight under the denaturing condition of native and fusion proteins. Lane 1, protein molecular weight marker; lane 2, purified CUOX; lane 3, purified VHb; lane 4, purified CUOX-VHb fusion protein; and lane 5, purified VHb-CUOX fusion protein. (b) The gel-filtration chromatography calibration curve was performed according to the manufacturer’s protocol (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, PA, USA). The linear curve representing Kav values versus molecular weights of the standard proteins including ribonuclease A, ovalbumin, aldolase and ferritin. Kav of CUOX, VHb and fusion proteins are shown in red circles.
Nevertheless, VHb has been known to possess monomer-dimer equilibrium [32] and has been reported to confer maximum peroxidase activity when present in monomeric form [31]. Therefore, the absence of dimeric VHb seemed to have no effect on the peroxidase activity of the fusion proteins. Besides the abovementioned experiments, three-dimensional (3D) structure of the fusion proteins was predicted by the I-TASSER server [33]. The model with the highest C-score was evaluated by various tools [34]. The secondary structure of the predicted model was evaluated by Ramachandran Plot through PROCHECK, which showed that the model had 71.9%, 24.3%, 2.1% and 1.7% of the amino acid residues in most favored regions, additional allowed regions, generously allowed regions and disallowed regions, respectively. The residue-wise local quality of the model structure was evaluated by Pro-Q, which revealed LG-score and MaxSub-score of 2.965 and 0.126, respectively. Evaluation of the predicted structure by ProSA showed that the Z-score value was −6.59, which was within the range observed for a native set of proteins of the same size. The quality of the predicted 3D structure was also evaluated by Verify3D. The result showed that the model possessed 79.3% of amino acid with a 3D-1D profile score ≥0.2. Although the obtained value was not that high, this value was very close to the expected value (80%) of a satisfactory predicted model. Overall, the predicted model had fairly good and sufficient quality for further studies. The predicted model was then used to construct the 3D structure of the tetrameric complex by PyMol 2.3.3 software. The constructed model consisted of four CV-monomers, resulting in four active sites of CUOX and four active sites of VHb (Figure 3). Conversely, the construction of the 3D structure of the tetrameric complex of VC was not possible. The I-TAS SER-predicted model showed an infeasible structure, VHb and CUOX portions leaned closely toward each other, preventing tetramerization of this fusion protein (data not shown). This finding supported the abovementioned steric effect hypothesis on the degradation of VC. Nevertheless, although VC was indicated to be subject to steric effects, more than 20 mg of the protein in the tetrameric complex was successfully purified from a 1-L culture of E. coli. The apparent colors of the purified proteins are shown in Figure 4a. CUOX is colorless while the other proteins are red, which is characteristic of heme-containing VHb. The UV–vis absorption spectra of VHb, CV and VC exhibited the Soret peak at 412 nm (Figure 4b), indicating that all proteins contain a mixture of ferrous and ferric hemoglobin [35]. The ratios between absorbance at 412 nm and 280 nm of VHb, CV and VC were 4.3, 0.89 and 0.97, respectively. This result indicated that, as compared to that of VHb, heme content of CV and VC were 4.8- and 4.4-fold decreased, respectively. However, this is not surprising since some part of the fusion protein (CUOX part) did not contain heme prosthetic group. More importantly, both fusion proteins exhibited similar absorption spectra, including the Soret peak (412 nm) and α-bands (540 and 577 nm), to that of native VHb, implying that protein engineering in this study did not alter heme-binding characteristics of VHb.
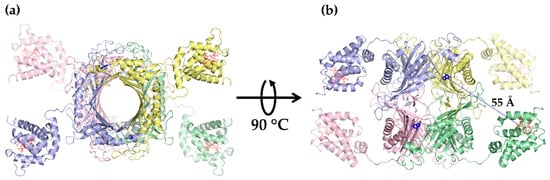
Figure 3.
Tetrameric structure of CUOX-VHb fusion protein constructed by assembly of 3D structure of CUOX-VHb predicted by I-TASSER. One color represents one fusion protein chain. Heme prosthetic groups in VHb active sites are represented by red sticks while 5-amino 6-nitro uracil molecules sitting in uricase active sites are represented by blue sticks. (a) Top view of the tetramer. (b) Side view of the tetramer. The distance between the adjacent CUOX and VHb active sites is 55 Å.
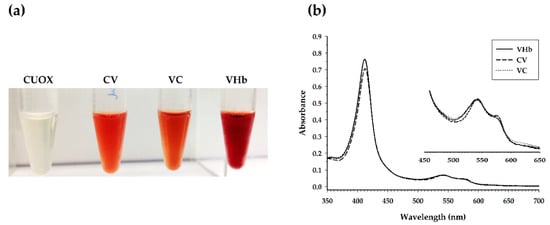
Figure 4.
(a) The apparent colors of the purified proteins. From left to right: native CUOX, CUOX-VHb fusion protein, VHb-CUOX fusion protein and native VHb. (b) UV–vis absorption spectra of the purified proteins (250–700 nm). The Soret peak is represented at 412 nm while the α-bands are represented by the peak between 540 and 577 nm.
2.2. Characterization of Enzymatic Activity and Kinetic Parameters
The engineered proteins exhibited both uricase and peroxidase activities. Optimum pH of catalysis for uricase and peroxidase was 9.0 (Figure 5a) and 7.0 (Figure 5b), respectively. Specific enzymatic activities are shown in Table 1. CV and VC retained uricase activity 69% and 60% of that of CUOX, and retained peroxidase activity 3.4% and 2.7% of that of VHb, respectively. However, when protein molecular weight was taken into account CV and VC revealed relative uricase activity up to 99% and 88% of that of CUOX, and revealed peroxidase activity up to 20% and 15% of that of VHb, respectively (Table 1). These results indicated that the engineering strategy hardly disturbs structure and, hence, the function of uricase in the fusion proteins. Conversely, peroxidase activity of VHb in the fusion proteins was markedly decreased. This is due to the following facts: firstly, the molecular weights of the fusion proteins were ~3 times higher while the numbers of VHb active sites were the same. Thus U/μmol should be used for activity comparison rather than U/mg (Table 1). Secondly, as compared to HRP, the distal histidine and arginine are missing from the VHb active site, which has been suggested to be problematic for substrate binding and account for low activity [30]. This evidence implied that peroxidase activity of VHb is highly sensitive to structural change, which can occur with fusion proteins. To improve peroxidase activity, introduction of distal histidine into VHb active site using site-directed mutagenesis may be attempted [30]. Nevertheless, the obtained peroxidase activities of the fusion proteins were sufficient for further experiments. Notably, uricase and peroxidase activities of CV were higher than those of VC. These results suggested that the structure of CV may be more energetically favorable than that of VC. This assumption was supported by the presence of protein truncation in VC but not in CV. Besides specific activity, kinetic parameters were also studied (Table 2 and Figure 6). As compared to that of CUOX, the apparent Km of CV and VC were reduced to 65.82% and 58.22% while the kcat increased 1.33-fold and 1.61-fold, respectively. These characteristics resulted in 2-fold and 2.72-fold increase in catalytic efficiency of CV and VC, respectively.
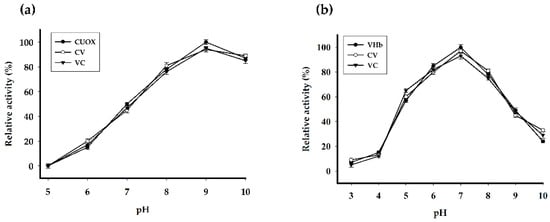
Figure 5.
Effect of pH on (a) uricase and (b) peroxidase activities of native and fusion proteins. Enzymatic activities were assayed at 25 °C, under different pH conditions.

Table 1.
Molecular weight, specific and relative activity of the produced proteins.

Table 2.
Steady-state kinetics of the produced proteins.
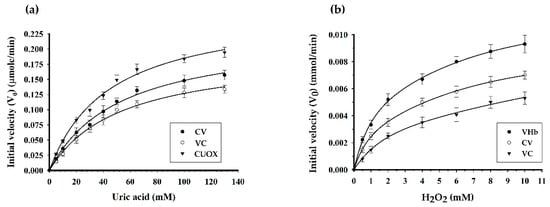
Figure 6.
Comparison of uricase activity and peroxidase activity of native and fusion proteins. In the uricase assay (a), the rate of substrate oxidation was calculated based on a linear decrease in the absorbance of uric acid. The plots show the dependence of the initial rate of oxidation on uric acid concentration. Whereas in peroxidase assay (b), the rate of substrate oxidation was calculated based on a linear increase in the absorbance of resorufin. The plots show the dependence of the initial rate of oxidation on hydrogen peroxide concentration. All plots were fitted to the Michaelis-Menten equation.
For peroxidase kinetics, as compared to that of VHb, the apparent Km of CV and VC were increased 1.15 and 2.20-fold, while the kcat were decreased 2.2 and 2.3-fold, respectively. These kinetic behaviors resulted in 2.52-fold and 5.12-fold decreases in catalytic efficiency of CV and VC, respectively. In the present study, Amplex Red was used as a reducing substrate for the measurement of peroxidase activity and kinetic parameters. In fact, both ABTS and Amplex Red were employed but only the data obtained from using Amplex Red was presented, since only Amplex red was used as a chromogenic substrate in the cascade reaction.
2.3. Optimization of Two-Enzymatic Cascade Reactions for Quantification of Uric Acid
A schematic representation of the cascade reactions is shown in Figure 7. Uricase catalyzes the oxidation of uric acid to allantoin, carbon dioxide and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). Then H2O2 and Amplex Red are stoichiometrically converted to the color product, resorufin. This final product can be followed by measuring either absorbance at 571 nm or fluorescence emission at 585 nm. Factors influencing catalysis of these cascade reactions including pH, reaction time, range of substrate concentration and enzyme (either natives or fusions) were investigated. In the previous section, we demonstrated that the optimal pH for catalysis of CUOX and VHb were 9.0 and 7.0, respectively (Figure 5a,b). However, at pH 7.0, CUOX retained uricase activity less than 50% while at pH 9.0, VHb retained peroxidase activity less than 50%. Thus, these two pH conditions are not appropriate for the cascade reactions. Nevertheless, at pH 8.0, both enzymes retained activity up to 75%–80%, and resorufin has been reported to be unstable at pH above 8.5 [36]. Therefore, pH 8.0 was chosen to study the cascade reactions. The concentrations of uric acid were varied from 5–40 μM and reaction times were varied from 5–40 min.
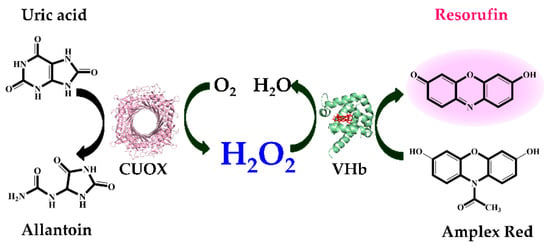
Figure 7.
Schematic illustration of the colorimetric detection of uric acid using uricase and VHb (peroxidase)-catalyzed oxidation of Amplex Red.
Three enzymatic systems including; (i). native CUOX + native VHb, (ii). CV fusion protein, and (iii). VC fusion protein, were compared. In each system, the amount of uricase was fixed at 0.5 units/reaction. Based on the specific activities shown in Table 1, the ratio of uricase: peroxidase of CV was approximately 10:1 units while that of VC was approximately 11:1 units. Thus, the ratio of uricase: peroxidase in the system with native proteins was fixed at 10:1 units. However, at this ratio, the initial rates of the reactions were very slow. Therefore, the uricase: peroxidase ratio in the system with native proteins was changed to 10:2 units. The absorbance of the reactions was recorded immediately after all components were mixed. The absorbance over time of reactions with different concentrations of uric acid, catalyzed by native enzymes, CV and VC is shown in Figure 8a,c,e, respectively. At the maximum concentration of uric acid (40 μM), the initial rates of cascaded reactions catalyzed by native enzymes, CV and VC were 41.37, 258.62 and 82.75 nmol/min (resorufin), respectively, and at maximum reaction time (40 min), these reactions gave maximum absorbances at 0.1, 0.3 and 0.15, respectively. These results indicated that CV had higher catalytic efficiency for cascade reactions than the other protein systems. This high efficiency could be due to the direct transfer of an intermediate (H2O2) produced by uricase to the adjacent VHb active site without completely mixing with the bulk phase [37,38]. The schematic demonstration of direct substrate transfer is shown in Figure 9. Besides the absorbance over time of reactions with different concentrations of uric acid, the graphs of absorbance over certain uric acid concentrations at different time points were also plotted (Figure 8b,d,f). Reactions with native enzymes showed linearity over the tested range of uric acid concentrations only when measured at 5 min, but the signals were very weak (Figure 8b). Interestingly, CV gave linearity over the tested range of uric acid concentrations at all measured time points, 5–40 min (Figure 8d). However, the graphs of measurements made at 35 and 40 min were not different from that measured at 30 min, indicating that reaction time at 30 min is enough for the cascaded reactions to reach saturation. For VC, the graph with linearity over the tested range of uric acid concentrations was not obtained (Figure 8f).
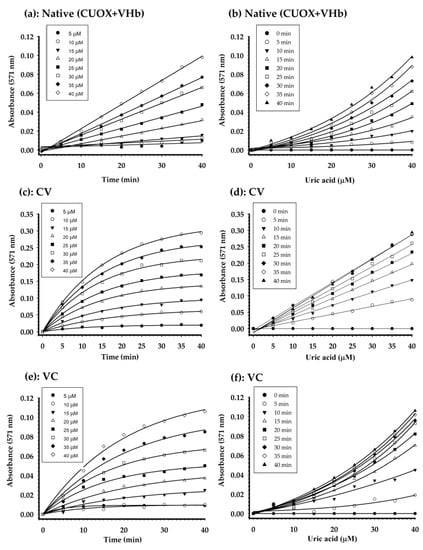
Figure 8.
Quantification of uric acid using native enzyme (CUOX+VHb) (a,b), CUOX-VHb fusion protein (c,d) and VHb-CUOX fusion proteins (e,f). The graphs representing absorbance over time of reactions with different concentrations of uric acid (a,c,e) were transformed to the graphs showing calibration curves at different time points (b,d,f).
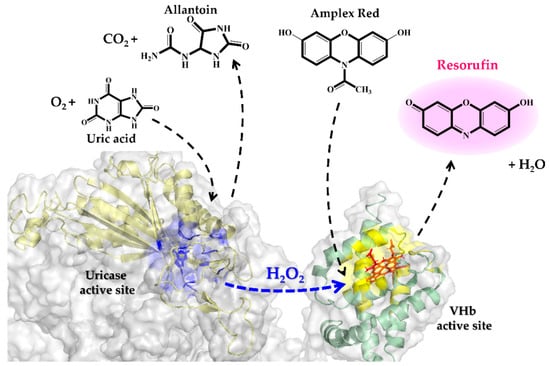
Figure 9.
Schematic demonstration of hydrogen peroxide channeling between adjacent CUOX and VHb active sites.
2.4. Uric Acid Calibration Curve
Based on the results from the previous Section 2.3, CV was shown to produce the strongest resorufin signal, which should give the best sensitivity for the assay. Therefore, only CV was chosen for the construction of a linear calibration curve. The experiment was performed using final concentrations of uric acid ranging from 1–60 μM (1, 2.5, 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60 μM). The absorbance was measured after initiation of the reaction for 10 min. As shown in Figure 10a, the absorbance increases gradually when the UA concentration increases from 0–60 μM. The color variation of the reactions, from light-pink to deep-pink, is shown in the inset. The limit of detection (LOD) as observed by eyes is as low as 10 μM. The absorbances at 571 nm from all reactions were plotted and shown in Figure 10b. The linearity of the graph was obtained when UA concentration was within the range 2.5–50 μM. The linear regression equation was A = 0.0038C − 0.0041, where A is absorbance and C is concentration of UA (μM). The correlation of coefficient (R2) was 0.9981. Comparison of the proposed assay with the other uricase-based colorimetric methods for detection of UA is shown in Table 3.
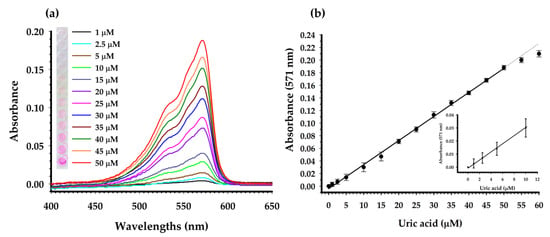
Figure 10.
(a) Absorption spectra of the assay with different concentrations of uric acid (1–50 μM) at a reaction time of 10 min. Photograph of the corresponding reactions is shown in the inset. (b) A dose-response curve between uric acid concentration and absorbance at 571 nm was constructed.

Table 3.
Comparison of different uricase-based colorimetric methods for detection of UA.
The proposed method is sensitive enough for UA detection, and is comparable or even better than the other methods. When the sample dilution factor in final reaction volume (1:10) was considered, the theoretical linear range of the proposed method is 25–500 μM, which covers the normal range of human serum uric acid, 142.77–416.41 μM (2.4–7.0 mg/dL). Besides good sensitivity, the proposed method consumed much less time than that of the other methods. In addition, most of the published methods required a 2-phases reaction, the first phase with pH ≥ 8 for uricase reaction and the second phase with pH ≤ 7 for peroxidase reaction. Thus, several reagents must be prepared and the assay must be performed through multiple steps. However, our method was performed in one step using one reaction buffer. After all reagents were mixed and stood for 10 min, the reaction was ready to be measured. More importantly, as compared to the other methods, the cost for peroxidase/peroxidase-like enzyme can be omitted, because in our work, single production of the enzyme (CV) yielded both uricase and peroxidase activities. Notably, as shown in Figure 8d, higher resorufin signals were observed when the reaction is incubated for more than 10 min. Therefore, the sensitivity of our assay may be improved if the test is incubated for more than 10 min. However, this should not exceed 30 min since the signal was not increased after 30 min.
2.5. Method Evaluation and Measurement of Uric Acid from Lyophilized Serum
Analysis of the standard curve showed that the assay had a good correlation between UA concentration and absorbance. The limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantitation (LOQ) were 1 and 2.5 μM, respectively. The systematic error of the method was assessed by performing a recovery assay. The result showed that the recovery rate of UA obtained by the standard addition method was between 94.8% and 100.1%, with RSD (n = 5) less than 2.3% (Table 4). To investigate the feasibility of the proposed method for practical application, five samples of lyophilized human serum were assayed for UA by the proposed method and a clinical chemistry analyzer, then the results obtained from the two methods were compared. As shown in Table 5, the average relative error between the two methods was 3.06%. These results indicated that the proposed method has good potential for the detection of UA in human serum.

Table 4.
Spiked recoveries of UA in pooled serum.

Table 5.
Determination of UA in lyophilized human serum using the developed assay and a clinical chemistry analyzer.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Bacterial Strains, Plasmids and Chemicals
E. coli NovaBlue and BL21(DE3) strains, and pETDuet-1 plasmid were from Novagen (EMD Bioscience, Madison, WI, USA). Restriction enzymes and T4-DNA ligase were from Fermentas (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). KOD-Plus DNA polymerase was purchased from Toyobo (Osaka, Japan). Uric acid, lithium carbonate and Amplex Red were from Sigma–Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Hydrogen peroxide (30% v/v) was obtained from Merck. The concentration of uric acid, hydrogen peroxide and resorufin were standardized using the extinction coefficient of 12.6 mM−1cm−1 at 293 nm [44], 72.8 M−1 cm−1 at 230 nm [45] and 54,000 M−1 cm−1 at 571 nm [36], respectively.
3.2. DNA Manipulations
cDNA for Candida utilis uricase (XM_020212619.1) was synthesized by Integrated DNA Technologies (Skokie, Illinois). The gene was PCR-amplified using primers shown in Table 6. PCR product was then digested with BamHI and HindIII, and cloned into pETDuet-1 plasmid pre-treated with the same enzymes. The constructed plasmid was designated as pETDuetCUOX. To construct the plasmid expressing CUOX-VHb fusion protein, endogenous XhoI restriction site and stop codon of the CUOX gene in pETDuetCUOX were removed by site-directed mutagenesis (SDM). HindIII restriction site was introduced prior to the start codon of the VHb gene in pET46VHb [29] by SDM. Then the VHb gene was excised by treating with HindIII and XhoI, and subcloned into pETDuetCUOX pretreated with the same enzymes. The resulting plasmid was designated as pETDuetCUOX-VHb. To construct the plasmid for expression of VHb-CUOX fusion protein, stop codon of VHb in pET46VHb was changed to BamHI by SDM then the CUOX gene was excised from pETDuetCUOX by treating with BamHI and XhoI then the gene was ligated to pET46VHb pretreated with the same enzymes. The resulting plasmid was designated as pET46VHb-CUOX. Sequences of all primers used for PCR and SDM reactions are shown in Table 6. The correctness of all recombinant plasmids was confirmed by DNA sequencing analysis.

Table 6.
Primers for PCR amplification and site-directed mutagenesis. BamHI and HindIII restriction sites were included in CUOX_FP (forward primer) and CUOX_RP (reverse primer), respectively. The restriction sites are indicated as underlined text.
3.3. Protein Expression and Purification
pETDuetCUOX, pET46VHb, pETDuetCUOX-VHb and pET46VHb-CUOX were individually transformed into E. coli BL21(DE3). Cells were grown in 1 L terrific broth supplemented with 100 μg/mL ampicillin at 37 °C with shaking at 180 rpm for 6–9 h. To induce protein expression and to improve the heme content of VHb, the cultures were supplemented with 1 mM isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) and 0.3 mM δ-aminolevulinic acid, respectively. Then the cultures were continued for 16 h at 30 °C with shaking at 125 rpm. Cells were collected by centrifugation, resuspended in 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer pH 8.0 supplemented with NaCl 500 and disrupted by ultrasonic disintegration. Then, cell lysate was cleared by centrifugation at 27,216× g for 10 min and the supernatant was filtered using a 0.45 μm syringe filter (Sartorius). Proteins were purified by IMAC using Ni-nitrilotriacetic acid (Ni-NTA) agarose column as previously described [34].
3.4. Molecular Weight Determination
To further purify and simultaneously determine the molecular weight of the proteins, each IMAC-purified protein was loaded onto a 16/60 Sephacryl S-300 HR gel-filtration chromatography column pre-equilibrated with 50 mM phosphate buffer at pH 7.2 containing 0.15 M EDTA. The elution was done with the same buffer at a flow rate of 1.0 mL/min. Standard protein markers ranging from 13.7 to 440 kDa were used for standard curve preparation. Experiments were run with an ÄKTA pure protein purification system (GE healthcare life sciences, Sweden) under the operation of the Unicorn 6.3 software.
3.5. Measurement of Enzymatic Activity and Kinetic Parameters
Uricase activity and kinetic parameters were determined as previously described [34]. In the kinetic assay, concentrations of uric acid ranging from 5–120 μM were used. One unit of uricase activity was defined as the amount of enzyme required to convert 1 μmol of uric acid to allantoin per minute at 25 °C, pH 8.0. Optimum pH for uricase reaction was studied over a pH range of 5.0–10.0 using 50 mM sodium citrate buffer (pH 5.0–6.0) and 50 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 7.0–10.0). VHb peroxidase activity and kinetic parameters were assayed as previously described by Kvist M, et al. [28]. In the kinetic assay, concentrations of H2O2 were varied from 0.5–10 μM. ABTS and Amplex Red were used as reducing substrates. One unit of peroxidase activity was defined as the amount of enzyme required for consumption/production of 1 μmol of substrate/product per minute at 25 °C. Optimum pH for peroxidase reaction was studied in buffers with pH 3.0–10.0 using 100 mM citrate–phosphate (pH 3.0–7.0) 100 mM Tris–HCl (pH 8.0–10.0).
3.6. Investigation of Sequential Reactions Catalyzed by Uricase (CUOX) and Peroxidase (VHb)
Catalysis of the consecutive reactions by uricase and peroxidase was studied. The principle of the reactions is shown in Figure 7. A volume of 50–400 μM of UA (50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 350 and 400 μM), 1 mM of Amplex Red and 0.5 unit/mL of uricase (native CUOX, CV, and VC) were prepared in 50 mM sodium borate buffer, pH 8.0. The solution of native CUOX also contained 0.05 units of peroxidase (VHb). The assays were performed in a 96-well microtiter plate. The reactions were started by the addition of 10 μL of enzyme solution [46] to 90 μL of the reaction mixtures containing different concentrations of UA or serum samples. Please note that the standard UA or sample was diluted 10 times in the final reaction volume. The reaction system in a total volume of 100 μL consisted of 50 mM sodium borate buffer pH 8.0, 0.1 mM Amplex Red, 0.05 units of UOX, 0.005 units of peroxidase (VHb) and 5–40 μM of UA. Production of final reaction product (resorufin) was followed by measuring the absorbance at 571 nm using a microplate reader (Synergy HTX multi-mode, BioTek, Winooski, VT, USA), at 5-min intervals for 40 min.
3.7. Preparation of a UA Calibration Curve
All reagents were prepared as mentioned in the latest experiment (3.6), except that the range of UA concentrations was 10–600 μM (10, 25, 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300, 350, 400, 500, 550, 600 μM). The reactions were performed using only CV fusion protein and the absorbance was measured at 10 min after the addition of the enzyme. All assays were performed in triplicate.
3.8. Method Evaluation and Quantification of UA from Lyophilized Human Serum
The assay was evaluated in terms of linearity, sensitivity, the limit of detection (LOD), limit of quantitation (LOQ) and recovery. Recovery was evaluated by spiking known amounts of UA (50, 75, 100, 125, 150 μM) into pooled human serum samples (Sigma–Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) then UA in each spiked sample was measured. To evaluate the reliability of the assay, five vials of lyophilized human serum with different concentrations of UA were purchased from The External Quality Assessment Schemes in Clinical Chemistry (EQAC), Faculty of Medical Technology, Mahidol University. UA value of each vial was measured using the developed assay and routine clinical method (measured by Roche Cobas C501 clinical chemistry analyzer).
3.9. Molecular Modeling
The 3D structures of single-chain CUOX-VHb and VHb-CUOX were modeled using I-TASSER server [33]. The amino acid sequences of CUOX-VHb and VHb-CUOX were uploaded in FASTA format then 3D structures were predicted in PDB format. The server generates five top models for each entry, the one with the highest confidence score (c-score) represents the best model. The models were evaluated for stereochemical quality by PROCHECK [47], Verify3D [48,49], ProSA [50] and Pro-Q [51]. The tetrameric structure of CUOX-VHb fusion protein was subsequently constructed using PyMol 2.3.3 software [52].
3.10. Statistical Analysis
Uricase activities and peroxidase activities between CV and VC were compared using the nonparametric Mann–Whitney U-test. The alpha value was set at 0.05.
4. Conclusions
Bifunctional proteins with uricase and peroxidase activities were constructed by direct fusion of CUOX and VHb. The engineered proteins offer the advantages of the low cost of enzyme production (single production yielded a protein with two enzymatic activities) and fast catalysis (due to substrate channeling between the two enzymes), which helps to shorten the reaction time. Based on VHb-catalyzed oxidation of Amplex Red, one of the engineered proteins, CV, was successfully applied for the development of a simple, rapid and reliable assay for colorimetric detection of UA. The assay had a good linear relationship (R2 = 0.9981) between absorbance at 571 nm and uric acid concentration over the range of 2.5–50 μM, which covers the normal range of SUA. In addition, the assay can be performed at a single pH (8.0), thus, adjusting the pH for peroxidase activity is not required. This helps to save both cost and time. The proposed assay was successfully applied to detect UA in pooled human serum, suggesting a promising potential for clinical application.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.P. and S.Y.; investigation, T.P., J.C., K.T., N.O. and S.Y.; writing original draft, T.P., S.W. and S.Y.; draft editing, T.P., N.O., S.W. and S.Y.; supervision, S.Y. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Thailand Research Fund (MRG6080283 and RSA6280021). The APC was partially funded by Faculty of Medical Technology, Mahidol University.
Acknowledgments
The Thailand Research Fund financial support is acknowledged.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Dalbeth, N.; Choi, H.K.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Khanna, P.P.; Matsuo, H.; Perez-Ruiz, F.; Stamp, L.K. Gout. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Wen, X.; Kong, J. Recent progress on uric acid detection: A review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2019, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Lu, W.; Liao, H.; Liao, F. Uricase based methods for determination of uric acid in serum. Microchim. Acta 2009, 164, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domagk, G.F.; Schlicke, H.H. A colorimetric method using uricase and peroxidase for the determination of uric acid. Anal. Biochem. 1968, 22, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, C.P.; James, D.R. Analytical reviews in clinical biochemistry: The measurement of urate. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 1988, 25, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gochman, N.; Schmitz, J.M. Automated determination of uric acid, with use of a uricase-peroxidase system. Clin. Chem. 1971, 17, 1154–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klose, S.; Stoltz, M.; Munz, E.; Portenhauser, R. Determination of uric acid on continuous-flow (AutoAnalyzer II and SMA) systems with a uricase/phenol/4-aminophenazone color test. Clin. Chem. 1978, 24, 250–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, R.C.; Rebar, L.; Berta, E.; Stong, L. New enzymatic method for serum uric acid at 500 nm. Clin. Chem. 1978, 24, 1908–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossati, P.; Prencipe, L.; Berti, G. Use of 3,5-dichloro-2-hydroxybenzenesulfonic acid/4-aminophenazone chromogenic system in direct enzymic assay of uric acid in serum and urine. Clin. Chem. 1980, 26, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majkić-Singh, N.; Stojanov, M.; Spasić, S.; Berkes, I. Spectrophotometric determination of serum uric acid by an enzymatic method with 2,2’-azino-di(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonate) (ABTS). Clin. Chim. Acta 1981, 116, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, Z.; Jiao, X.; Zhang, L.; Lv, Y. Uricase-Based Highly Sensitive and Selective Spectrophotometric Determination of Uric Acid Using BSA-Stabilized Au Nanoclusters as Artificial Enzyme. Spectrosc. Lett. 2012, 45, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legoux, R.; Delpech, B.; Dumont, X.; Guillemot, J.C.; Ramond, P.; Shire, D.; Caput, D.; Ferrara, P.; Loison, G. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of the gene encoding Aspergillus flavus urate oxidase. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 8565–8570. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Itaya, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Fukumoto, J. Studies on yeast uricase. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1967, 31, 1256–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, L.; Yang, G.; Tao, J.; Bu, Y.; Liao, F. Characterization of a uricase from Bacillus fastidious A.T.C.C. 26904 and its application to serum uric acid assay by a patented kinetic uricase method. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2006, 45, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Sakasegawa, S.-I.; Misaki, H.; Sugiyama, M. Molecular cloning and expression of uricase gene from Arthrobacter globiformis in Escherichia coli and characterization of the gene product. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2004, 98, 153–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomalaski, J.S.; Holtsberg, F.W.; Ensor, C.M.; Clark, M.A. Uricase formulated with polyethylene glycol (uricase-PEG 20): Biochemical rationale and preclinical studies. J. Rheumatol. 2002, 29, 1942–1949. [Google Scholar]
- Saud Al-Bagmi, M.; Shahnawaz Khan, M.; Alhasan Ismael, M.; Al-Senaidy, A.M.; Ben Bacha, A.; Mabood Husain, F.; Alamery, S.F. An efficient methodology for the purification of date palm peroxidase: Stability comparison with horseradish peroxidase (HRP). Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhao, H.; Hu, X.; Pu, J.; Liao, J.; Long, G.; Liao, F. Optimization of pH values to formulate the bireagent kit for serum uric acid assay. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2015, 62, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavery, C.B.; Macinnis, M.C.; Macdonald, M.J.; Williams, J.B.; Spencer, C.A.; Burke, A.A.; Irwin, D.J.G.; D’Cunha, G.B. Purification of peroxidase from Horseradish (Armoracia rusticana) roots. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 8471–8476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spadiut, O.; Herwig, C. Production and purification of the multifunctional enzyme horseradish peroxidase. Pharm. Bioprocess. 2013, 1, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawski, B.; Lin, Z.; Cirino, P.; Joo, H.; Bandara, G.; Arnold, F.H. Functional expression of horseradish peroxidase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia pastoris. Protein Eng. 2000, 13, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krainer, F.W.; Dietzsch, C.; Hajek, T.; Herwig, C.; Spadiut, O.; Glieder, A. Recombinant protein expression in Pichia pastoris strains with an engineered methanol utilization pathway. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.T.; Santama, N.; Dacey, S.; Edwards, M.; Bray, R.C.; Thorneley, R.N.; Burke, J.F. Expression of a synthetic gene for horseradish peroxidase C in Escherichia coli and folding and activation of the recombinant enzyme with Ca2+ and heme. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 13335–13343. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Grigorenko, V.; Chubar, T.; Kapeliuch, Y.; Börchers, T.; Spener, F.; Egorova, A. New approaches for functional expression of recombinant horseradish peroxidase C in Escherichia coli. Biocatal. Biotransform. 1999, 17, 359–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asad, S.; Dabirmanesh, B.; Ghaemi, N.; Etezad, S.M.; Khajeh, K. Studies on the refolding process of recombinant horseradish peroxidase. Mol. Biotechnol. 2013, 54, 484–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gundinger, T.; Spadiut, O. A comparative approach to recombinantly produce the plant enzyme horseradish peroxidase in Escherichia coli. J. Biotechnol. 2017, 248, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humer, D.; Spadiut, O. Improving the Performance of Horseradish Peroxidase by Site-Directed Mutagenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvist, M.; Ryabova, E.S.; Nordlander, E.; Bülow, L. An investigation of the peroxidase activity of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 12, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isarankura-Na-Ayudhya, C.; Yainoy, S.; Tantimongcolwat, T.; Bülow, L.; Prachayasittikul, V. Engineering of a novel chimera of superoxide dismutase and Vitreoscilla hemoglobin for rapid detoxification of reactive oxygen species. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2010, 110, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isarankura-Na-Ayudhya, C.; Tansila, N.; Worachartcheewan, A.; Bülow, L.; Prachayasittikul, V. Biochemical and cellular investigation of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin (VHb) variants possessing efficient peroxidase activity. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 20, 532–541. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Wu, L.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, H.; Li, Z. pH-induced quaternary assembly of Vitreoscilla hemoglobin: The monomer exhibits better peroxidase activity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1834, 2124–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giangiacomo, L.; Mattu, M.; Arcovito, A.; Bellenchi, G.; Bolognesi, M.; Ascenzi, P.; Boffi, A. Monomer-dimer equilibrium and oxygen binding properties of ferrous Vitreoscilla hemoglobin. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 9311–9316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server for protein 3D structure prediction. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yainoy, S.; Phuadraksa, T.; Wichit, S.; Sompoppokakul, M.; Songtawee, N.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Isarankura-Na-Ayudhya, C. Production and Characterization of Recombinant Wild Type Uricase from Indonesian Coelacanth (L. menadoensis) and Improvement of Its Thermostability by In Silico Rational Design and Disulphide Bridges Engineering. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.Y.; Webster, D.A. Spectral characteristics and interconversions of the reduced oxidized, and oxygenated forms of purified cytochrome o. J. Biol. Chem. 1974, 249, 4261–4266. [Google Scholar]
- Dröse, S.; Galkin, A.; Brandt, U. Chapter 26 Measurement of superoxide formation by mitochondrial complex I of Yarrowia lipolytica. Meth. Enzymol. 2009, 456, 475–490. [Google Scholar]
- Ovádi, J.; Tompa, P.; Vértessy, B.; Orosz, F.; Keleti, T.; Welch, G.R. Transient-time analysis of substrate-channelling in interacting enzyme systems. Biochem. J. 1989, 257, 187–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spivey, H.O.; Ovádi, J. Substrate channeling. Methods 1999, 19, 306–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; He, Y.; Zhou, J.; Ge, Y.; Zhou, J.; Song, G. A “naked-eye” colorimetric and ratiometric fluorescence probe for uric acid based on Ti3C2 MXene quantum dots. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1103, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yao, Q.; Tang, X.; Zhong, H.; Qiu, P.; Wang, X. A highly selective and sensitive colorimetric detection of uric acid in human serum based on MoS2-catalyzed oxidation TMB. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 943–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.-F.; Li, J.-Y.; Zhang, M.-M.; Wu, D.; Zhang, Q.-L. A highly selective and sensitive colorimetric uric acid biosensor based on Cu(II)-catalyzed oxidation of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 244, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, Q.-Q.; Lin, Z.-H.; Jiang, Y.-C.; Deng, H.-H.; He, S.-B.; Su, L.-T.; Shi, X.-Q.; Chen, W. Peroxidase-like activity of nanocrystalline cobalt selenide and its application for uric acid detection. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 3295–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Xiong, Y.; Liao, C.; Ye, F. Colorimetric detection of uric acid in human urine and serum based on peroxidase mimetic activity of MIL-53(Fe). Anal. Methods 2015, 7, 9894–9899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez, A.S.G.; Stefan, A.; Lemma, S.; Conte, E.; Hochkoeppler, A. Continuous enzyme-coupled assay of phosphate- or pyrophosphate-releasing enzymes. BioTechniques 2012, 53, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, P. The chemical nature of the second hydrogen peroxide compound formed by cytochrome c peroxidase and horseradish peroxidase. I. Titration with reducing agents. Biochem. J. 1953, 54, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R. Enzyme Assays☆. In Reference Module in Biomedical Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Laskowski, R.A.; MacArthur, M.W.; Moss, D.S.; Thornton, J.M. PROCHECK: A program to check the stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1993, 26, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowie, J.U.; Lüthy, R.; Eisenberg, D. A method to identify protein sequences that fold into a known three-dimensional structure. Science 1991, 253, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüthy, R.; Bowie, J.U.; Eisenberg, D. Assessment of protein models with three-dimensional profiles. Nature 1992, 356, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiederstein, M.; Sippl, M.J. ProSA-web: Interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W407–W410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallner, B.; Elofsson, A. Can correct protein models be identified? Protein Sci. 2003, 12, 1073–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schrodinger PyMOL: The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System; Version 1.8; Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2015.
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).