Abstract
Processing of social media text like tweets is challenging for traditional Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools developed for well-edited text due to the noisy nature of such text. However, demand for tools and resources to correctly process such noisy text has increased in recent years due to the usefulness of such text in various applications. Literature reports various efforts made to develop tools and resources to process such noisy text for various languages, notably, part-of-speech (POS) tagging, an NLP task having a direct effect on the performance of other successive text processing activities. Still, no such attempt has been made to develop a POS tagger for Urdu social media content. Thus, the focus of this paper is on POS tagging of Urdu tweets. We introduce a new tagset for POS-tagging of Urdu tweets along with the POS-tagged Urdu tweets corpus. We also investigated bootstrapping as a potential solution for overcoming the shortage of manually annotated data and present a supervised POS tagger with an accuracy of 93.8% precision, 92.9% recall and 93.3% F-measure.
1. Introduction
Recent years have witnessed immense popularity of social media platforms among Internet users, researchers and organizations from several domains. Furthermore, micro-blogging websites are facilitating and inspiring several modern life aspects such as business, education, technology and government affairs, to name a few [1]. With around 326 million to date, Twitter is a popular micro-blogging web service which nowadays is a major source of information for all the major events and latest happenings around the world. Twitter allows its users to write or share tweets of up to 280 characters about countless topics such as their opinions about certain aspects of life, reviews of products, films, games, discussions about relationship issues, government affairs, pandemics etc. These tweets can be utilized further for a variety of activities such as using opinion mining to forecast or explain real-world outcomes, mining users’ interests for targeted advertisement campaigns, acquiring customer opinions about brands, government policies, etc.
Language on Twitter, however, is quite different from well-edited text of news, books, etc., due to the presence of unconventional orthography, punctuation and grammatical mistakes, along with Twitter-specific conventions such as hashtags, emoticons, usernames and retweet tokens [2]. Such language style variation is often characterized as noisy user-generated text [3]. Since the performance of Natural Language Processing (NLP) applications depends on the type of text being processed [4], the effect of this language style variation of user-generated text on the performance of standard NLP tools has been explored by Foster et al. [5] and Petrov and McDonald [6]. Similarly, studies by Owoputi et al. [7], Gimpel et al. [8], Ritter, Clark and Etzioni [9], Seddah et al. [10] and Kong et al. [11] have shown that adaptation of NLP tools and resources is necessary to accommodate language differences in such noisy text.
Part-of-speech (POS) tagging is a fundamental step of numerous NLP applications [8] such as information extraction, information retrieval, text-to-speech processing, parsing, etc. While POS tagging is a well researched domain, POS tagging of user-generated noisy text is still challenging and has received significant attention recently. In literature, studies related to POS tagging of tweets in English [8], Arabic [12], Hindi [13], German [14], etc., have been reported. So far, there is no study available for Urdu language.
With a total of around 300 million speakers worldwide, Urdu is a prominent language of the East [15] and is Pakistan’s national language. Recently, Urdu Language Processing became the current research trend due to the experimentation of several NLP tasks on Urdu language, for example, [16,17,18,19,20,21]. However, despite all these efforts, Urdu is still a low-resourced language and a lack of resources poses additional challenges when considering data-driven NLP tasks.
Thus, the current study is undertaken for the design and implementation of a POS tagging model for Urdu tweets using statistical data-driven methods. To this end, a new POS tagset is designed for tagging of Urdu tweets, a novel hand-annotated POS tagged corpus according to the new POS tagset is produced which is then used to overcome the bottleneck of manual annotation by means of supervised bootstrapping and finally the performance of a data-driven POS tagger (Stanford) on this corpus is evaluated.
The structure of this paper is as follows. In Section 2, a brief overview of previous research concerning POS tagging of tweets is presented. A new POS tagset for Urdu tweets is introduced in Section 3 and the process of corpus collection and manual annotation is detailed in Section 4. In Section 5, training and evaluation of the POS tagger by means of bootstrapping experiments are given followed by a discussion of results and error analysis in Section 6 and finally the conclusions are presented in Section 7.
2. Related Work
Numerous studies have been conducted for the development of POS taggers for tweets. English is the most studied language followed by a limited number of studies in other languages as well.
The authors of [8] attempted English tweet POS tagging first by designing and building a tagging system for English tweets. The system includes features of frequently capitalized tokens, distributional similarity obtained from a large unannotated English tweet set and English phonetic normalization. However, the reported accuracy level of 92% of this system is obviously lower than the traditional genres.
In [7], the authors extended the work presented in [8] to improve Twitter and Internet Relay Chat (IRC) POS tagging by assessing the usage of lexical features and large-scale unsupervised word clustering. Compared with the system developed by Gimpel et al. [8], there Twitter tagging has been improved by 3%. A dataset of English tweets was also released by the authors which is labelled according to their POS annotation guidelines.
A POS tagger for Dutch tweets is presented in [22]. An enhanced version of the D-Coi project’s tagset is utilized for the tagging of Twitter-specific tokens. Their POS tagger is based on the Dutch POS tagger, Frog, which performs tagging using the D-Coi tagset. A post-processing component modifies Frog’s output by introducing Twitter-specific tags wherever needed.
The authors of [3] re-trained existing versions of the Stanford tagger [23] and the ARK Tagger [7] with Irish tweets and presented first the Irish tweets gold-standard POS tagged corpus. In [12], the authors utilized existing standard POS taggers for modern standard Arabic (MSA) rather than developing a separate Arabic tweets tagger. For accuracy improvement, pre- and post-processing modules were used. They also utilized agreement-based bootstrapping of unannotated data for the creation of annotated training tweets to retrain the Stanford tagger for Arabic tweets.
In [13], the authors modified the Indian languages standard POS tagset for Hindi tweet POS tagging by introducing Twitter-specific tags borrowed from [8]. Fifty tweets were manually annotated and then 1300 tweets were automatically annotated using a CRF-based classifier using bootstrapping. A publicly available POS tagger produced by the Society for Natural Language Technology Research (SNLTR) is used by transforming the SNLTR tagset into the tagset they proposed. The SNLTR system was trained on 1200 tweets and tested on 100 tweets. Their system achieved an accuracy of 86.99%.
The authors of [24] used an existing formal Indonesia POS tagger [25] to automatically annotate Indonesian tweets and added five new tags for Twitter data. Semi-automatic data annotation is employed by the tagger to automatically annotate the new data and the annotation results are manually corrected. The model is rebuilt by adding this resultant data into the training data. The model has been trained several times, with a data volume of 1000, 1600 and 1800 tweets achieving 66.36% accuracy.
As far as we know, there is currently no research study available for Urdu tweet POS tagging in literature. This paper is the first step towards filling this gap.
3. Urdu Tweet Part-of-Speech Tagset
There are various POS tagsets available for Urdu, including Hardie’s tagset [26], the Sajjad and Schmid tagset [27] and the CLE POS tagset [28], to name a few. All these tagsets are designed for well-edited Urdu text. However, the performance of the taggers trained on well-edited text decreases on out-of-domain data such as tweets [8]. We evaluated the accuracy of two publicly available Urdu POS taggers, IIIT Urdu Shallow Parser [29] and CLE’s Statistical POS Tagger for Urdu [30], on well-edited news text (1856 tokens) as well as on tweets (1862 tokens). The results of this experiment are presented in Table 1. For accuracy evaluation, precision (fraction of correct POS tags from total tagged tokens), recall (ratio of correctly identified labels over the total number of correct tags in the input data) and F-Measure (harmonic mean of precision and recall) are used. Equations (1)–(3) describe their calculations, respectively:

Table 1.
Accuracy of Urdu Taggers on News Text and Tweets.
While high accuracy was achieved by both taggers in tagging news text, the same was not the case with tweets. The experimental results clearly show a performance drop of both taggers on tweets. Both taggers failed to properly tag typographical divergences (e.g., فرانسسی instead of فرانسیسی), unknown words (e.g., یوٹیوبر) and bad segmentation (e.g., بھا ری instead of بھاری) of tweets. Similarly, the presence of emoticons, hashtags and other Twitter-specific elements was also problematic for both the taggers. These tokens never or hardly ever appear in news text. The experimental results show that POS tagging for Twitter is quite different from corresponding tags in more formal texts due to the informal, less grammatical nature and lexical divergences of tweets as compared to well-edited Urdu text, confirming that the findings of [16] also hold true for Urdu tweets. Still, we could have used any of the existing tagsets and trained a statistical POS tagger for tweets. However, the case of tweets is not just the problem of plain domain adoption where transfer of learning can improve tagger accuracy. Lexical divergence of tweets makes it a whole new genre as compared to standard, well-edited text on which these taggers are trained. Moreover, the tagsets used by these taggers do not have appropriate tags for tagging Twitter-specific elements of tweets. These reasons motivated us to propose a new Twitter-specific tagset for Urdu. This tagset contains 33 part-of-speech tags for annotating standard parts of speech (nouns, verbs, etc.) along with groups of token variations found largely in Urdu tweets. The tagset is motivated from the Google Universal POS tagset [31] and the CLE POS tagset [28]. We refer to this tagset as the Urdu Noisy Text POS (UNTPOS) Tagset
Tags and their descriptions are given in the following subsections, whereas the complete list of tags is provided in Appendix A.
3.1. ADJ: Adjective
Used to modify the nouns by specifying their properties or characteristics. Examples of Urdu adjectives are: “اچھا/good”, “بھاری/heavy”, “عمر رسیدہ/old”, etc.
3.2. ADP: Adposition
There are two sub-tags of adposition in Urdu: Prepositions (ADP) appear before complement noun phrases (noun, pronoun) and postposition (ADPT) occurs after complement noun phrases (noun, pronoun). Adposition forms a single structure with the complement to represent its grammatical and semantic relationship with another unit in the clause. Examples of preposition (ADP) are: “از/from”, “تا/until”, “اثنا/meanwhile”, etc. A few examples of postposition (ADPT) are: “پر/on”, “سے/from”, “کو/to”.
3.3. ADV: Adverb
An adverb modifies a verb, an adjective or another adverb. The UNT tagset uses two sub-classes of adverb: General adverb (ADV) and negation (NEG). Examples include: “نہ/no”, “فی الحال/right away”.
3.4. AUX: Auxiliary Verb
Auxiliary verbs in Urdu are the verbs that can form a compound verb together with the main verb. Examples are: “/ہیں is”, “تھا/was”, “/گی will”, etc.
3.5. CONJ: Coordinating Conjunction
These are the words that are used to join two independent clauses in a compound sentence. Some examples are “اور/and”,” نیز/also”, “تاہم/however”.
3.6. DET: Determiner
In Urdu, determiners are not considered as separate word classes as most determiners are treated as demonstrative pronouns. However, determiners are terms that narrow down the referents of the following noun in the scope of a conversation, whereas demonstrative pronouns can entirely replace a noun in a sentence. Examples of DET are: “یہ/this”, “کئی/many”, “چند/few”, and so on.
3.7. INTJ: Interjection
Interjections are used to express emotion, volition and mood. There are two sub-categories for interjection used in the UNTPOST tagset: “INTJ” which expresses emotions in the form of words and “INTJE” which is used to mark smiley emoticons/emojis as they also show emotions but in image form. Examples of INTJ are: “واہ/well done”, “اوہ/oh”, “ارے/hey”, etc. Examples of INTJE are: “😒”, “🤔”, “😢”.
3.8. NOUN: Noun
Nouns are parts of speech that denote people, places, things, animals and ideas. Examples include: “آدمی/man”, “کمپیوٹر/computer”, “گھر/house”.
3.9. NUM: Numeral
Numerals are categorized as “NUM” to represent natural numbers, “NUMQ” to represent quantity, “NUMO” to represent place numbers, “NUMF” to denote fraction and “NUMY” to represent frequency. Examples of NUM are: “24 August”, “1500 Rupees”, “Year 1990”, “ہزار/1000”, etc. Examples of NUMQ are: “کچھ/some”, “کم/less”, “کافی/enough”, etc. Examples of NUMO are: “دوسرا/second”,” یکم/first”, etc. Examples of NUMF are: “آدھا/half”, “چوتھائی/quarter”, etc. Examples of NUMY are: “دگنا/double”,”/تہراtriple”.
3.10. PART: Particle
Particles do not belong to any of the inflected grammatical word classes; they usually lack their own grammatical functions and form relationships between other parts of speech or expressive clauses. Examples are: “والے/ones”, “بھی/also”, etc.
3.11. PRON: Pronoun
The Urdu Tweet tagset uses five subcategories of pronoun. Personal pronoun (PRON) is used to replace a noun. Examples are: “میں/me”, “وہ/that”, etc. A possessive pronoun (PRONP) is a pronoun that shows the ownership relation. Examples are: “تیرا/yours”, “/میراmine”. A reflexive pronoun (PRONR) is used for referring to oneself. An example is: “خود/self”. A demonstrative pronoun (PROND) points to specific objects within a sentence and comes before a noun. A few examples are: “وہی/the same”, “وہ/they”, “کس/who”. A relative pronoun (PRONRD) is one that is used to refer to nouns mentioned previously. Some examples are: “جس/which”, “جیسا/like”, “جو/that”.
3.12. PROPN: Proper Noun
A proper noun denotes the names of specific people, things or places. Examples are: “پاکستان/Pakistan”, “تاج محل/Taj Mahal”, ”محمد احمد/Muhammad Ahmed”, etc. Tweet mentions of the form “@mshaanshahid” are also tagged as PROPN as these usernames represent a real person in the social media world. Similarly, in the case of multiword proper nouns such as “فردوس جمال/Firdous Jamal”, both words will be tagged as PROPN
3.13. PUNCT: Punctuation
These are symbols used to delineate linguistic components in text. Examples are: “?/question mark”, “./full stop”, “;/semi colon”, etc.
3.14. SCONJ: Subordinating Conjunction
These are words that are used to join and show the relationship between the words, clauses or phrases that it joins. Some examples of SCONJ are: “کہ/that”, “اگر/if”, “کیونکہ/because”.
3.15. SYM: Symbol
A symbol is an entity like a word and is different from normal words in its function, form or both. Examples are: “$/dollar”, “%/percentage”.
3.16. VERB: Verb
Verbs are a class of words used to denote an event or action. They can form in a clause the smallest predicate and control the types and number of other components that may appear in the clause. Examples are: “رکھ/keep”, “کہا/said”, “یاد/remeber”, etc.
3.17. RET: Retweet
A retweet is used to mark a reposted or forwarded message on Twitter. An example tweet is shown below:
“RT@faheemabbasii: اگر نوازشریف نے اسلام آباد لاکڈاون میں مولانا فضل الرحمان کا ساتھ دیا”.
3.18. ICO: Icon
ICO is used to tag all emoticons/emojis except smileys. A few examples are: “🏃”, “🍵”, “🐅”.
3.19. LINK: Link
A link is used to mark email addresses and web links in the noisy text. An example tweet is shown below:
“یہ ویڈیو بھارت کی مدد سے باجوہ پر حملہ ثابت کرتی ہے https://youtu.be/oqW6IWVAYSg”.
3.20. REP: Reply
Reply is used to mark a response to another person’s tweet. An example tweet is shown below:
“RP @SulemanZartasha: “اکثر کامیاب یوٹیوبر اپنے چینلز کی باقائدہ کمپنیاں بنا چکے ہیں ۔”.
3.21. HASH: Hash
Twitter hashtags are sometimes used as ordinary words and other times as topic markers. HASH is used to mark both. Some Examples are “#StopKillingsOnLOC”, “#خاموشی”.
3.22. X: Others
X is used for foreign words, i.e., words from languages other than Urdu, or words which do not fall in any of the specified part-of-speech tag. Examples are: “DP”, “ﷺ”, “اکثراوقات”.
4. Urdu Tweet Corpus
Since no annotated or unannotated corpus for Urdu tweets is publicly available, a new corpus was created for this study. Figure 1 shows the process of corpus creation and the following sections describe the process in detail.
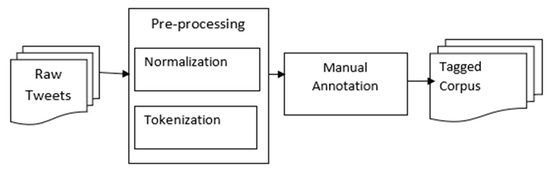
Figure 1.
Corpus Development Process.
4.1. Dataset for Corpus Creation
A total of 5000 Urdu tweets comprising a multitude of topics such as business, politics, sports, entertainment, etc., have been collected using the Twitter search and stream API.
4.2. Pre-Processing
Pre-processing prepares the dataset for machine learning [32]. Proper pre-processing improves the effectiveness of machine learning while reducing its training time. This involves data cleaning and sentence segmentation.
In our research, in the data cleaning stage, after data collection, all duplicated tweets were removed from raw corpus. Similarly, those tweets that were written in Urdu but also contained words from languages such as Sindhi, Punjabi, Pushto were also discarded. Very short tweets of 2 to 3 words were also discarded, leaving behind a corpus of 3420 tweets. This raw corpus was than normalized using the UrduHack library [33].
An important pre-processing step, tokenization, breaks long text strings into linguistic units, or tokens. We developed our own tokenizer to perform tokenization of special cases such as “RP@SulemanZ:”, “😘” “https://youtu.be/oqW6IWVAYSg” in Urdu tweets.
4.3. Manual Annotation
Correctly annotated tweets are a basic requirement to evaluate the POS tagger output in order to compare the POS tagger output against this gold standard. Since, a new POS tagset is designed specifically for Urdu tweets, no such gold standard corpus exists, highlighting the need for manually developing a correctly annotated gold standard POS tagged Urdu tweets corpus.
To develop the initial gold standard corpus, manual annotation of POS tags was performed on randomly sampled 300 tokenized Urdu tweets (8034 tokens) by two annotators; this set was then checked and corrected by an expert who is a native Urdu speaker with a linguistics background. Rectification of these 300 tweets formed the foundation for evaluating the tagset intuitiveness. The tagset was finalized after numerous discussions and revisions. The next 200 randomly sampled tweets (4689 tokens) were annotated in accordance with the revised tagset, using the first 300 tagged tweets as a reference. An example of a tokenized, part-of-speech tagged Urdu tweet is shown in Figure 2.

Figure 2.
An Example of a Part-of-Speech tagged Urdu Tweet.
Nonetheless, manual annotation of the text was quite time intensive. Therefore, we opted for bootstrapping, a form of semi-supervised learning which creates annotated training data from large amounts of unannotated data [34] to speed up the manual annotation process as discussed in the next section.
5. Bootstrapping
We performed five-fold cross validation of the manually annotated dataset to check its consistency and correctness. We divided the dataset into five complementary sets, each with one validation file (gold standard file) having 10% of the texts and one training file including 90% of the text. Each set was evaluated by training an instance of the Stanford POS tagger with the training file and then the validation file was tagged with the trained model (the outcome was the test file). The test file was then evaluated against the gold standard file. This was done five times and the average gives the final five-fold cross validation result. The result of five-fold cross validation is shown in Table 2.

Table 2.
Five-fold Cross Validation of Urdu Tweet Corpus.
The average score of five-fold cross validation gave us the baseline score, which was then used to evaluate all future models’ performances. For bootstrapping experiments, the corpus of 500 manually annotated tweets (12,723 tokens) was used in this stage by splitting it into a seed training set of 300 tweets (8034 tokens) and development (2383 tokens) and test (2306 tokens) sets of 100 tweets each. To avoid and prevent subjective and accidental bias, 500 tweets (13,643 tokens) were sampled randomly from the corpus for the purpose of bootstrapping experiments. An initial POS tagger model was trained using the Stanford POS tagger on 300 tweet training data. This model was evaluated against the development set to calculate the model’s accuracy at this stage. Then, five iterations of the bootstrapping experiment were performed using this model to tag 100 sentences at each iteration. At the end of each iteration, tagged tweets were manually corrected and added to the training set to retrain a new model of the tagger. The newly trained model was then used to tag the next 100 sentences and the accuracy of the model was checked against the development set using precision, recall and f-measure.
The overall bootstrapping process is described in the following points (1–7):
- Divide the manually tagged gold standard corpus of 500 sentences into training (300 sentences), development (100 sentences) and test set (100 sentences).
- On the training set, train the initial Stanford tagger model and evaluate its accuracy against the development set.
- Use the baseline model of step 2 to parse 100 sentences and correct the output manually.
- Train the new tagger model by adding 100 automatically tagged and manually rectified sentences to the training set.
- Use the new tagger model to tag an additional 100 sentences and check model accuracy against the development set.
- Repeat steps 4 and 5 for five iterations.
- At the end of fifth iteration, check final model’s accuracy against the test set.
6. Discussion
The results of the bootstrapping experiments are presented in Table 3. The precision of the initial model (84.3%) was higher than the average precision (82.6%) of five-fold validation. However, recall (80.4%) and f-measure (82.3%) of the initial model were lower than those of average five-fold score (83.3% and 82.9%, respectively), but the results for the initial evaluation were encouraging. At every iteration, we observed a steady increase in the accuracy of newly induced models and the maximum scoring models occured at the fifth iteration, attaining 92.5% precision, 93.5% recall and 93% f-measure for the Stanford tagger. The test set showed similar tendencies to that of the development set in the final evaluation with 93.8% precision, 92.9% recall and 93.3% f-measure.

Table 3.
Stanford Tagger Evaluation.
The total percentage of errors made was 12.4% for the Stanford tagger on the test set of 2306 tokens. Based on our analysis, we categorized sources of POS tagging errors in three major categories: Low-frequency words, unseen words and ambiguous words shown statistically in Figure 3.
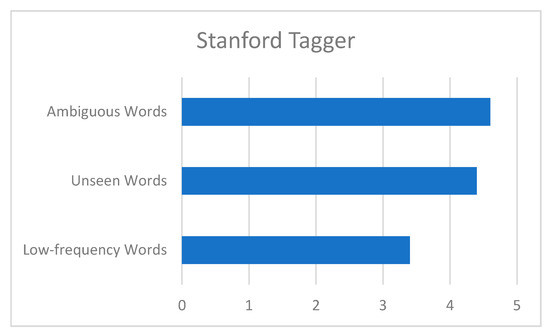
Figure 3.
Major Error Categories and their Statistics in Test Corpus.
It is well known that low-frequency words are more difficult to learn and accurately predict. In our test set, one source of tagging errors was low-frequency words, i.e., English words transliterated in Urdu such as “ٹرول” (troll), “اوسم” (awesome), etc., slang, hashtags and links. Additionally, frequent misclassification of emoticons and, in some cases, punctuation was also observed. These errors were mostly due to several sequences of multiple emoticons (😊😉😍😘😚😜) and punctuation marks (?????) in the test set but were absent in the training data where emoticons and punctuation always occur in isolation. The error rate for low-frequency words is 3.4%.
Unseen words are words that were not found in the training data but are present in the test set. The majority of these words in our test set are named entities, emoticons, slang, English words transliterated into Urdu, etc. Of those unknown words, the error rate of Stanford is 4.4%.
The largest source of tagging errors in our test set as ambiguous words for the Stanford tagger with a 4.6% error rate. There are several reasons for ambiguous words. Firstly, Urdu tweets are written conversations and consequently some words have multiple written versions. Some examples are: “امریکہ vs. امریکا”, “ن لیگ vs. نون لیگ”, “سعودیہ vs. سعودی عرب”, etc. Similarly, the insertion of unnecessary spaces also causes tagger confusion. Two such cases are the words “نااہل” and “بےضرر” which are basically adjectives (ADJ) but wrongly tagged as two separate words “PART” and “NOUN” due to the insertion of a space between them. Another case of tagger confusion is where two or more words are joined together such as “اس لیے” written as “اسلیے” causing PRON and ADP to be marked PRON mistakenly. The same was the case for the words “اس طرح” written as “اسطرح”, causing it to be marked as NOUN instead of DET and NOUN. Similarly, there are issues with spelling mistakes and the treatment of punctuation and other special characters. One such case of spelling mistakes which frequently occurred in the test set was SCONJ “کہ” written as “کے”, causing taggers to tag it as ADP.
Another difficulty that the tagger faced was confusion between words that have the same word form but multiple meanings depending on usage. One such case is between particle “تو”, pronoun “تو” and subordinate conjunction “تو”. In most cases, taggers tagged particle (PART) “تو” and pronoun (PRONP) “تو” mistakenly as subordinate conjunction (SCONJ) “تو”. Another similar case is that of pronouns and some determinative articles. In the sentence “یہ شاگرد فرانسیسی زبان بولتا ہے/this student speaks French”, “یہ” is DET, whereas in “یہ فرانسیسی زبان بولتا ہے/he speaks French”, “یہ” is a pronoun. The same is the case for DET “یا” in “یا اللہ” and CCONJ “یا”.
Additionally, the most frequent mistakes encountered in tagging were confusion between proper nouns (PROP), common nouns (NOUN) and adjectives (ADJ). This is common mistake in tagging, since there are many nouns that occur both as proper nouns and as common nouns. For example, in Urdu “حنا”, “اظہار”, “ڈار”, etc., can be proper nouns as well as common nouns.
Overall, the results in Table 3 confirm that bootstrapping POS taggers is useful. As compared to manual annotation, much less time is required for automatic tagging and manual correction effort, whereas the final induced model acquired satisfactory results.
7. Conclusions
In this paper, a new POS-tagged dataset constructed from Urdu tweets is presented along with its tagging scheme, thereby expanding Urdu language NLP research for the processing of Urdu social media text. We performed an experiment where we evaluated the performance of two pre-trained Urdu taggers on well-edited Urdu text as well as Urdu tweets. The results showed a significant decrease in the performance of these taggers on Urdu tweets. Thereby highlighting the need for specific tools and resources for this domain. We report on the development of a manually tagged dataset of 500 Urdu tweets, the consistency of which was evaluated by using five-fold cross validation. We also produced a trained model for the Stanford POS tagger with an accuracy of 93.8% precision, 92.9% recall and 93.3% f-measure. Further, we show how bootstrapping can be used to leverage the lack of annotated data for a less-resourced language.
The POS-tagged corpus developed in this research is publicly available [35] for the research community. We also plan on including data from other social media platforms in order to create a more balanced corpus. We used a normalized module in our pre-processing stage but error analysis of our corpus showed that there is a need for a customized normalization model designed according to the requirements of noisy data just like the tokenizer we developed for such data. Additionally, we also plan to investigate and compare the performance of other statistical taggers on our dataset in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, investigation, data curation: A.B. (Amber Baig) and M.U.R.; methodology, software, formal analysis, resources, writing—original draft preparation: A.B. (Amber Baig); validation, M.U.R and A.B. (Ahsanullah Baloch); writing—review and editing, M.U.R. and H.K.; supervision, H.K.; project administration, A.B. (Ahsanullah Baloch). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A

Table A1.
Urdu Noisy Text Part-of-Speech Tagset.
Table A1.
Urdu Noisy Text Part-of-Speech Tagset.
| Urdu Noisy Text Part-of-Speech Tagset (UNTPOS) | ||
|---|---|---|
| S.No | Tag Name | Example |
| 1 | ADJ | اچھا، بھاری، عمر رسیدہ |
| 2 | ADP | از، تا |
| 3 | ADPT | پر، سے، کو |
| 4 | ADV | بہت، فی الحال |
| 5 | NEG | نہ، نہیں |
| 6 | AUX | ہیں تھا، گی، |
| 7 | CONJ | اور، نیز، تاہم |
| 8 | DET | یہ، کئی، چند |
| 9 | INTJ | واہ، اوہ، ارے |
| 10 | INTJE | 😢 ، 🤔 ، 😒 |
| 11 | NOUN | آدمی، کمپیوٹر، گھر |
| 12 | NUM | ہزار، 7 جون، بارہ |
| 13 | NUMQ | کچھ، کم، |
| 14 | NUMO | دوسرا، یکم |
| 15 | NUMF | آدھا، چوتھائی |
| 16 | NUMY | دگنا، تہرا |
| 17 | PART | والا، والے، ہی، بھی |
| 18 | PRON | میں، وہ |
| 19 | PRONP | تیرا، میرا، تمہارے |
| 20 | PRONR | خود، آپ |
| 21 | PROND | وہی، وہ، کس |
| 22 | PRONRD | جس، جیسا، جو |
| 23 | PROPN | ، پاکستان، فردوس جمال @mshaanshahid |
| 24 | PUNCT | ۔ ، ؛ ‘ “ |
| 25 | SCONJ | کہ، اگر، کیونکہ |
| 26 | SYM | $ ٪ & |
| 27 | VERB | رکھ، کہا، یاد |
| 28 | RET | RT@faheemabbasii: |
| 29 | ICO | 🏃 🍵 🐅 |
| 30 | LINK | https://youtu.be/oqW6IWVAYSg |
| 31 | REP | RP @SulemanZartasha: |
| 32 | HASH | #StopKillingsOnLOC #خاموشی، |
| 33 | X | ﷺ, DP, اکثراوقات |
References
- Nawaz, M.S.; Bilal, M.; Lali, M.I.; Ul Mustafa, R.; Aslam, W.; Jajja, S. Effectiveness of social media data in healthcare communication. J. Med Imaging Health Inform. 2017, 7, 1365–1371. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstein, J. What to do about bad language on the internet. In Proceedings of the 2013 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Atlanta, GA, USA, 9–14 June 2013; Association for Computational Linguistics: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2013; pp. 359–369. [Google Scholar]
- Lynn, T.; Scannell, K.; Maguire, E. Minority language twitter: Part-of-speech tagging and analysis of Irish tweets. In Proceedings of the ACL 2015 Workshop on Noisy User-generated Text, Bejing, China, 31 July 2015; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- AlKhwiter, W.; Al-Twairesh, N. Part-of-speech Tagging for Arabic Tweets using CRF and BiLSTM. Comput. Speech Lang. 2020, 65, 101138. [Google Scholar]
- Foster, J.; Cetinoglu, O.; Wagner, J.; Le Roux, J.; Hogan, S.; Nivre, J.; Hogan, D.; Van Genabith, J. # hardtoparse: POS Tagging and Parsing the Twitterverse. Available online: https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00702445/file/aaai_mt_2011.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Petrov, S.; McDonald, R. Overview of the 2012 shared task on parsing the web. Available online: https://www.petrovi.de/data/sancl12.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Owoputi, O.; O’Connor, B.; Dyer, C.; Gimpel, K.; Schneider, N.; Smith, N.A. Improved part-of-speech tagging for online conversational text with word clusters. In Proceedings of the 2013 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies, Atlanta, GA, USA, 9–14 June 2013; pp. 380–390. [Google Scholar]
- Gimpel, K.; Schneider, N.; O’Connor, B.; Das, D.; Mills, D.; Eisenstein, J.; Heilman, M.; Yogatama, D.; Flanigan, J.; Smith, N.A. Part-of-Speech Tagging for Twitter: Annotation, Features, and Experiments. In Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies: Short Papers-Volume 2, Portland, OR, USA, 19–24 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Ritter, A.; Clark, S.; Etzioni, O. Named entity recognition in tweets: An experimental study. In Proceedings of the 2011 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing; Association for Computational Linguistics: Florence, Italy, 2011; pp. 1524–1534. [Google Scholar]
- Seddah, D.; Sagot, B.; Candito, M.; Mouilleron, V.; Combet, V. The French Social Media Bank: A Treebank of Noisy User Generated Content. Available online: https://www.aclweb.org/anthology/C12-1149.pdf (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Kong, L.; Schneider, N.; Swayamdipta, S.; Bhatia, A.; Dyer, C.; Smith, N.A. A dependency parser for tweets. In Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), Doha, Qatar, 25–29 October 2014; pp. 1001–1012. [Google Scholar]
- Albogamy, F.; Ramsay, A. Fast and robust POS tagger for Arabic tweets using agreement-based bootstrapping. In Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation (LREC’16), Portorož, Slovenia, 23–28 May 2016; pp. 1500–1506. [Google Scholar]
- Jamatia, A.; Das, A. Part-of-speech tagging system for indian social media text on twitter. In Proceedings of the Social-India 2014, First Workshop on Language Technologies for Indian Social Media Text, at the Eleventh International Conference on Natural Language Processing (ICON-2014), Goa, India, 21 December 2014; pp. 21–28. [Google Scholar]
- Rehbein, I. Fine-grained pos tagging of german tweets. In Language Processing and Knowledge in the Web; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 162–175. [Google Scholar]
- Raza, A.A.; Habib, A.; Ashraf, J.; Javed, M. A review on Urdu language parsing. Int. J. Adv. Comput. Sci. Appl. 2017, 8, 93–97. [Google Scholar]
- Adeeba, F.; Hussain, S. Experiences in building urdu wordnet. In Proceedings of the 9th Workshop on Asian Language Resources 2011, Chiang Mai, Thailand, 12–13 November 2011; pp. 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Khalid, S.; Aslam, M.H. Pattern based comprehensive urdu stemmer and short text classification. IEEE Access 2017, 6, 7374–7389. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Khalid, S.; Saleemi, M. Comprehensive stemmer for morphologically rich urdu language. Int. Arab J. Inf. Technol. 2019, 16, 138–147. [Google Scholar]
- Anwar, W.; Wang, X.; Li, L.; Wang, X.-L. A statistical based part of speech tagger for Urdu language. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics, Hong Kong, China, 19–22 August 2007; pp. 3418–3424. [Google Scholar]
- Ehsan, T.; Butt, M. Dependency Parsing for Urdu: Resources, Conversions and Learning. In Proceedings of the 12th Language Resources and Evaluation Conference, Marseille, France, 11–16 May 2020; pp. 5202–5207. [Google Scholar]
- Ehsan, T.; Hussain, S. Development and evaluation of an Urdu treebank (CLE-UTB) and a statistical parser. Lang. Resour. Eval. 2020, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avontuur, T.; Balemans, I.; Elshof, L.; Van Noord, N.; Van Zaanen, M. Developing a part-of-speech tagger for Dutch tweets. Comput. Linguist. Neth. J. 2012, 2, 34–51. [Google Scholar]
- Toutanova, K.; Klein, D.; Manning, C.D.; Singer, Y. Feature-rich part-of-speech tagging with a cyclic dependency network. In Proceedings of the 2003 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics on Human Language Technology, Edmonton, AB, Canada, 27 May–1 June 2003; Volume 1, pp. 173–180. [Google Scholar]
- Suryawati, E.; Munandar, D.; Riswantini, D.; Abka, A.F.; Arisal, A. POS-Tagging for informal language (study in Indonesian tweets). In Proceedings of the International Conference on Data and Information Science, Nantes, France, 29–31 May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Abka, A.F. Evaluating the use of word embeddings for part-of-speech tagging in Bahasa Indonesia. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computer, Control, Informatics and Its Applications (IC3INA), Jakarta, Indonesia, 3–5 October 2016; pp. 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Hardie, A. Developing a Tagset for Automated Part-of-Speech Tagging in Urdu. Available online: http://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.218.513&rep=rep1&type=pdf (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Sajjad, H.; Schmid, H. Tagging Urdu text with parts of speech: A tagger comparison. In Proceedings of the 12th Conference of the European Chapter of the ACL (EACL 2009), Athens, Greece, 30 March–3 April 2009; pp. 692–700. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, T.; Urooj, S.; Hussain, S.; Mustafa, A.; Parveen, R.; Adeeba, F.; Hautli, A.; Butt, M. The CLE urdu POS tagset. In Proceedings of the LREC 2014, Ninth International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation, Reykjavik, Iceland, 26–31 May 2014; pp. 2920–2925. [Google Scholar]
- Urdu Shallow Parser. Available online: http://ltrc.iiit.ac.in/analyzer/urdu/index.cgi (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Center for Language Engineering. Available online: http://www.cle.org.pk/software/langproc/POS_tagger.htm (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Petrov, S.; Das, D.; McDonald, R. A universal part-of-speech tagset. arXiv 2011, arXiv:1104.2086. [Google Scholar]
- Sebastiani, F. Machine learning in automated text categorization. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2002, 34, 1–47. [Google Scholar]
- Urduhack: A Python NlP Library for Urdu Language. Available online: https://pypi.org/project/urduhack/ (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Albogamy, F.; Ramsay, A. POS tagging for Arabic tweets. In Proceedings of the International Conference Recent Advances in Natural Language Processing, Varna, Bulgaria, 2–4 September 2019; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Urdu-Noisy-Text. Available online: https://github.com/amberbaig/Urdu-Noisy-Text (accessed on 5 November 2020).
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).