White Matter Microstructure Differences Between Congenital and Acquired Hearing Loss Patients Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) and Machine Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection of Participants
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Basic Theory of DTI Metrics
2.4. Data Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
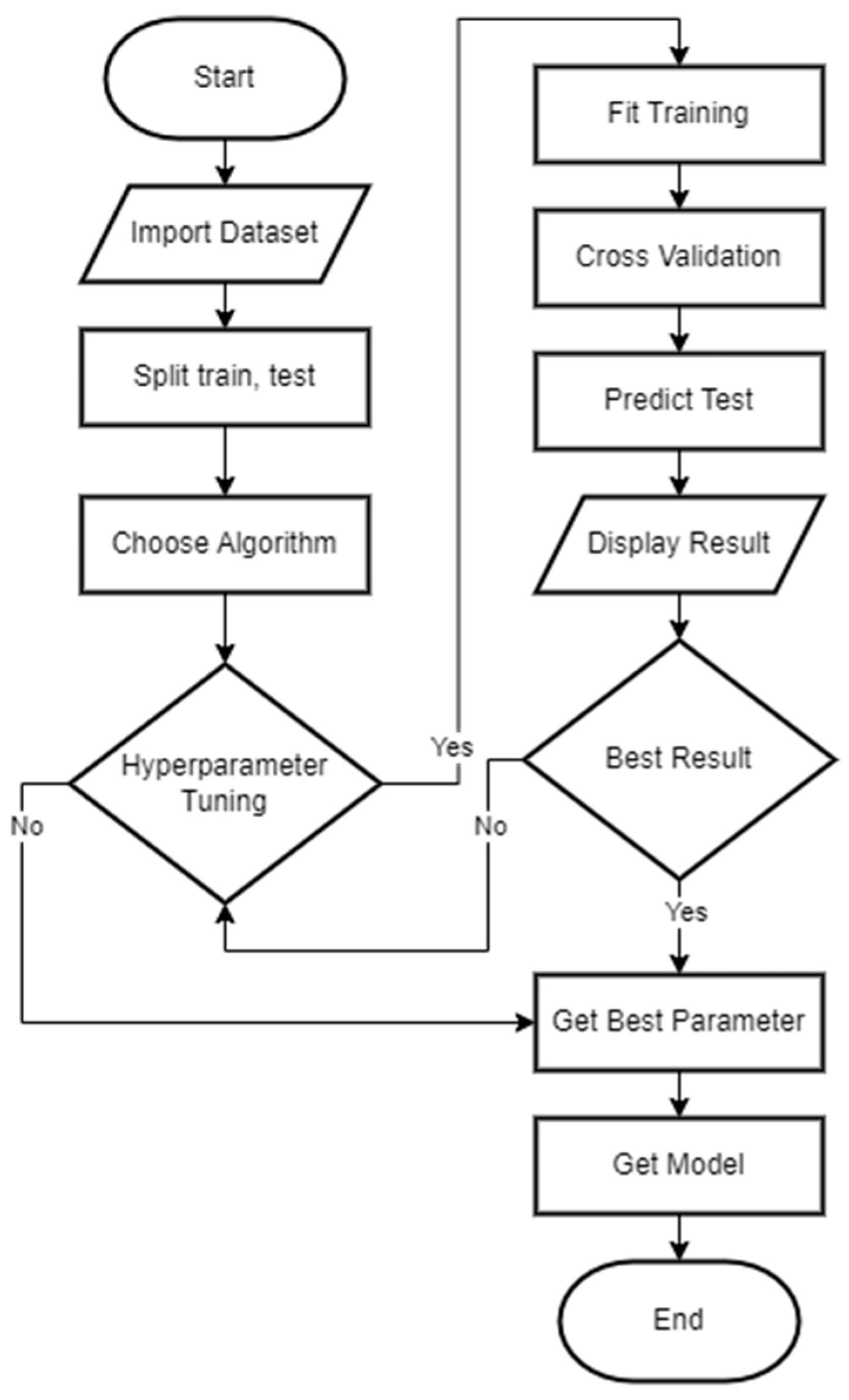
2.6. Machine Learning
- Support vector machine classifier (SVC): A supervised learning model that effectively separates data points by finding the optimal hyperplane that maximizes the margin between different classes. SVC utilizes kernel functions (e.g., linear, polynomial, and radial basis function) to transform the input data into higher-dimensional spaces. This transformation enables SVC to handle complex, nonlinear relationships between the input features. This study used SVC to classify patients based on DTI metrics [33,34].
- Random forest (RF): An ensemble learning method that constructs multiple decision trees during training. RF employs bootstrapping, a resampling technique, to create multiple datasets from the original dataset. Each decision tree is trained on a different bootstrap sample, ensuring diversity and robustness in the ensemble. At each node of decision trees, RF randomly selects a subset of features for splitting, reducing the correlation between trees and enhancing model generalization. RF is a robust classification model capable of handling small datasets and minimizing bias–variance trade-offs [35].
- Multilayer perceptron (MLP): MLP is an artificial neural network that utilizes backpropagation algorithms to optimize model parameters (weights and biases) by iteratively adjusting them based on the difference between predicted and actual outputs. MLP consists of input, hidden, and output layers [36].
2.7. Evaluation Metrics
3. Results
3.1. Statistical and Correlation Analysis
3.2. Model Development and Evaluation
4. Discussion
4.1. White Matter Microstructure Analysis
4.2. Machine Learning Analysis
- Experiment 1
- Experiment 2
5. Limitations and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DTI | Diffusion Tensor Imaging |
| FA | Fractional Anisotropy |
| AD | Axial Diffusivity |
| RD | Radial Diffusivity |
| MD | Mean Diffusivity |
| IC | Inferior Colliculus |
| LL | Lateral Lemniscus |
| CN | Cochlear Nucleus |
| AR | Auditory Radiation |
| IFOF | Inferior Fronto-Occipital Fasciculus |
| SVC | Support Vector Machine Classifier |
| RF | Random Forest |
| MLP | Multilayer Perceptron |
References
- Eggermont, J.J. Acquired hearing loss and brain plasticity. Hear. Res. 2017, 343, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, L.L.; Tucci, D.L. Hearing loss in adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2465–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moeller, M.P.; Gale, E.; Szarkowski, A.; Smith, T.; Birdsey, B.C.; Moodie, S.T.; Carr, G.; Stredler-Brown, A.; Yoshinaga-Itano, C.; FCEI-DHH International Consensus Panel; et al. Family-centered early intervention deaf/hard of hearing (FCEI-DHH): Introduction. J. Deaf Stud. Deaf. Educ. 2024, 29, SI3–SI7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrocchi-Bartal, L.; Khoza-Shangase, K.; Kanji, A. Early intervention for hearing-impaired children—From policy to practice: An integrative review. Audiol. Res. 2025, 15, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menteri Kesehatan Republik Indonesia. Keputusan Menteri Kesehatan Republik Indonesia Nomor HK.01.07/MENKES/1989/2022 tentang Pedoman Nasional Pelayanan Kedokteran Tata Laksana Tuli Sensorineural Kongenital; Menteri Kesehatan Republik Indonesia: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Widuri, A.; Arifianto, M.P. The influence of parents knowledge and health care access to the identification of children with hearing impairment. Berk. Kedokteran. 2019, 15, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allisha, F.; Wijana; Mahdiani, S. Hearing profile of children below three years old at Jatinangor Integrative Health Care Center, West Java, Indonesia. Althea Med. J. 2022, 9, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, P.S.; Falerina, R.; Perdana, R.F.; Faizah, Z.; Fathoni, A.N.; Kurniawan, A.M.; Arsy, D.H. Early detection of hearing impairments training: Enhacing community hearing health degrees in Pacitan, East Java. J. Layanan Masy. (J. Public Serv.) 2023, 7, 490–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNICEF. Empowering Every Child: Embracing Diversity and Inclusion for all—Landscape Analysis on Children with Disabilities in Indonesia; UNICEF: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Purves, D.; Augustine, G.J.; Fitzpatrick, D.; Hall, W.C.; LaMantia, A.S.; Mooney, R.D.; Platt, M.L.; White, L.E. Neuroscience, 6th ed.; Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Michalski, N.; Petit, C. Central auditory deficits associated with genetic forms of peripheral deafness. Hum. Genet. 2021, 141, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos Macías, Á.; Borkoski-Barreiro, S.A.; Falcón González, J.C.; de Miguel Martínez, I.; Ramos de Miguel, Á. Single-sided deafness and cochlear implantation in congenital and acquired hearing loss in children. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2018, 44, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salat, D.H. Diffusion tensor imaging in the study of aging and age-associated neural disease. In Diffusion MRI; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 257–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korver, A.M.; Smith, R.J.; Van Camp, G.; Schleiss, M.R.; Bitner-Glindzicz, M.A.; Lustig, L.R.; Usami, S.-I.; Boudewyns, A.N. Congenital hearing loss. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 16094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoy, D.O.; Karagoz, Y.; Kaldirimoglu, K.F.; Ulusan, M.B.; Mahmutoglu, A.S. Diffusion tensor imaging of auditory pathway: A comparison of pediatric cochlear implant candidates and healthy cases. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2023, 19, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rance, G.; Tomlin, D. Maturation of the central auditory nervous system in children with auditory processing disorder. Semin. Hear. 2016, 37, 074–083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koirala, N.; Deroche, M.L.; Wolfe, J.; Neumann, S.; Bien, A.G.; Doan, D.; Goldbeck, M.; Muthuraman, M.; Gracco, V.L. Dynamic networks differentiate the language ability of children with cochlear implants. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1141886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.-H.; Lee, H.-J.; Kang, H.; Oh, S.-H.; Lee, D.S. Brain plasticity can predict the cochlear implant outcome in adult-onset deafness. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boisvert, I.; McMahon, C.M.; Dowell, R.C.; Lyxell, B. Long-term asymmetric hearing affects cochlear implantation outcomes differently in adults with pre- and postlingual hearing loss. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manno, F.A.M.; Rodríguez-Cruces, R.; Kumar, R.; Ratnanather, J.T.; Lau, C. Hearing loss impacts gray and white matter across the lifespan: Systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression. Neuroimage 2021, 231, 117826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grégoire, A.; Deggouj, N.; Dricot, L.; Decat, M.; Kupers, R. Brain morphological modifications in congenital and acquired auditory deprivation: A systematic review and coordinate-based meta-analysis. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 850245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Ding, G.; Booth, J.R.; Huang, R.; Lv, Y.; Zang, Y.; He, Y.; Peng, D. Sensitive period for white-matter connectivity of Superior Temporal Cortex in deaf people. Hum. Brain Mapping. 2011, 33, 349–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winklewski, P.J.; Sabisz, A.; Naumczyk, P.; Jodzio, K.; Szurowska, E.; Szarmach, A. Understanding the physiopathology behind axial and radial diffusivity changes—What do we know? Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figley, C.R.; Uddin, M.N.; Wong, K.; Kornelsen, J.; Puig, J.; Figley, T.D. Potential pitfalls of using fractional anisotropy, axial diffusivity, and radial diffusivity as biomarkers of cerebral white matter microstructure. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 15, 799576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, F.Q.; Huang, O.; Kleindienst Robler, S.; Morton, S.; Platt, A.; Egger, J.R.; Emmett, S.D.; Palmeri, M.L. A hybrid deep learning approach to identify preventable childhood hearing loss. Ear Hear. 2023, 44, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, D.; Ying, J.; Miao, J.; Lan, L.; Wang, D.; Zhao, L.; Yin, Z.; Yu, L.; Guan, J.; Wang, Q. Predicting the hearing outcome in sudden sensorineural hearing loss via machine learning models. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2018, 43, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlSamhori, J.F.; AlSamhori, A.R.; Amourah, R.M.; AlQadi, Y.; Koro, Z.W.; Haddad, T.R.; Kakish, D.; Kawwa, M.J.; Zuriekat, M.; Nashwan, A.J. Artificial Intelligence for hearing loss prevention, diagnosis, and Management. J. Med. Surg. Public Health 2024, 3, 100133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Li, F.; Xu, W.; Hong, K.; Yang, T.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.; Wu, H. Machine learning-based genetic diagnosis models for hereditary hearing loss by the GJB2, SLC26A4 and MT-RNR1 variants. eBioMedicine 2021, 69, 103322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingsley, P.B. Introduction to diffusion tensor imaging mathematics: Part I. Tensors, rotations, and eigenvectors. Concepts Magn. Reson. A 2006, 28A, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poitelon, Y.; Kopec, A.M.; Belin, S. Myelin fat facts: An overview of lipids and fatty acid metabolism. Cells 2020, 9, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahyuningsih, H.P.; Kusmiyati, Y. Anatomi Fisiologi; Kementerian Kesehatan Republik Indonesia: Jakarta, Indonesia, 2017; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Handayani, S. Anatomi dan Fisiologi Tubuh Manusia; Media Sains Indonesia: Kota Bandung, Indonesia, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Gholami, R.; Fakhari, N. Support vector machine: Principles, parameters, and applications. In Handbook of Neural Computation; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 515–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, R.; Awad, M.; Khanna, A. Efficient Learning Machines: Theories, Concepts, and Applications for Engineers and System Designers; Apress: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Belgiu, M.; Drăguţ, L. Random forest in remote sensing: A review of applications and future directions. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2016, 114, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, C.C. Neural Networks and Deep Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Zhu, L.; Cai, Z. Evaluation measures of the classification performance of Imbalanced Data Sets. In Communications in Computer and Information Science; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 461–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, A.C.; Guido, S. Introduction to Machine Learning with Python; O’Reilly Media: Sebastopol, CA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mangold, S.A.; Das, J.M. Neuroanatomy, Cortical Primary Auditory Area. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Felix, R.A.; Gourévitch, B.; Portfors, C.V. Subcortical pathways: Towards a better understanding of auditory disorders. Hear. Res. 2018, 362, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Wen, Z.; Long, L.; Wong, C.W.; Ye, N.; Zee, C.; Chen, B.T. Assessing cerebral white matter microstructure in children with congenital sensorineural hearing loss: A tract-based spatial statistics study. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wieringen, A.; Boudewyns, A.; Sangen, A.; Wouters, J.; Desloovere, C. Unilateral congenital hearing loss in children: Challenges and potentials. Hear. Res. 2019, 372, 29–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibussek, D.; Meister, H.; Walger, M.; Foerst, A.; von Wedel, H. Hearing loss in early infancy affects maturation of the auditory pathway. Dev. Med. Child Neurol. 2002, 44, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
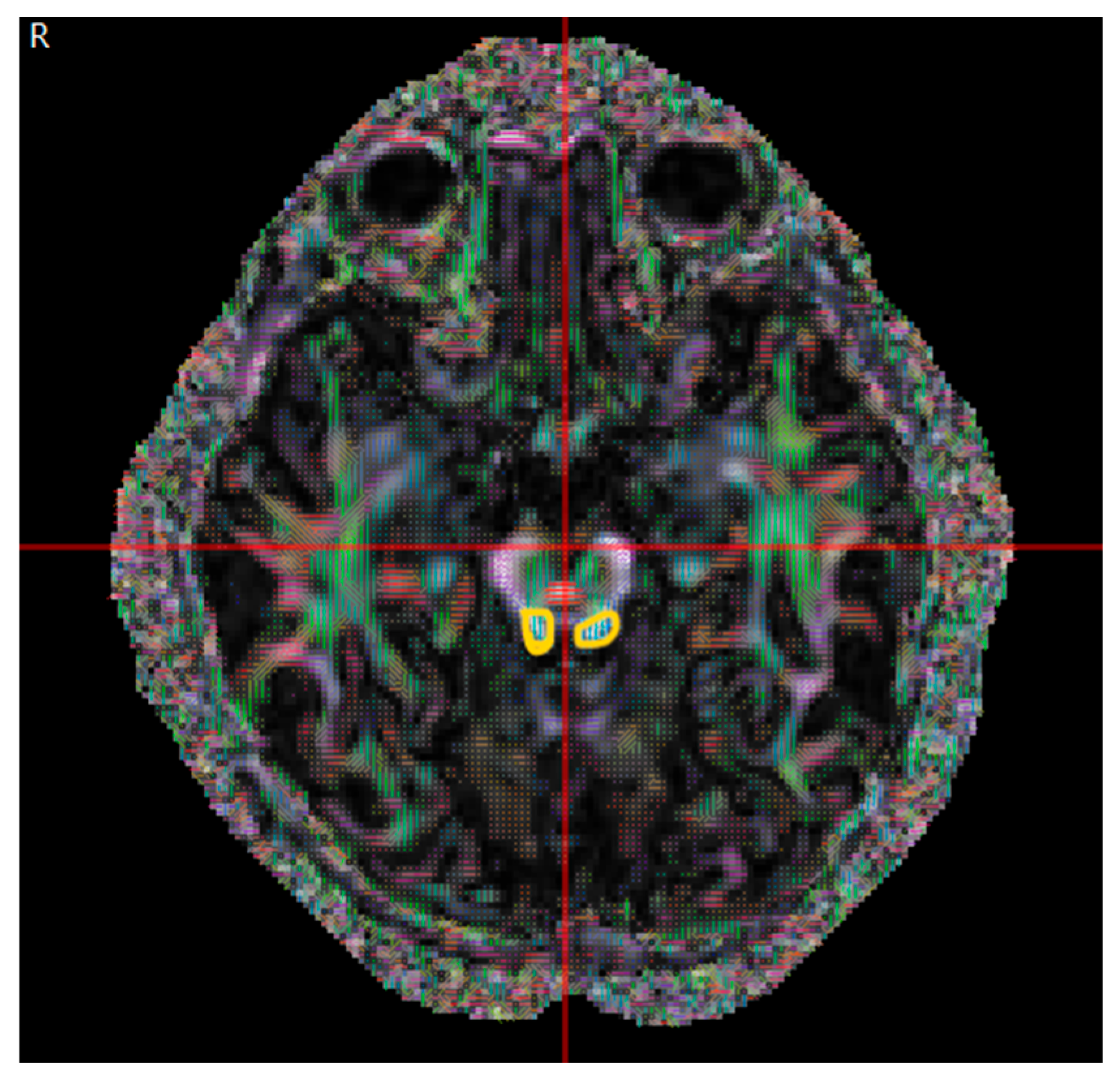
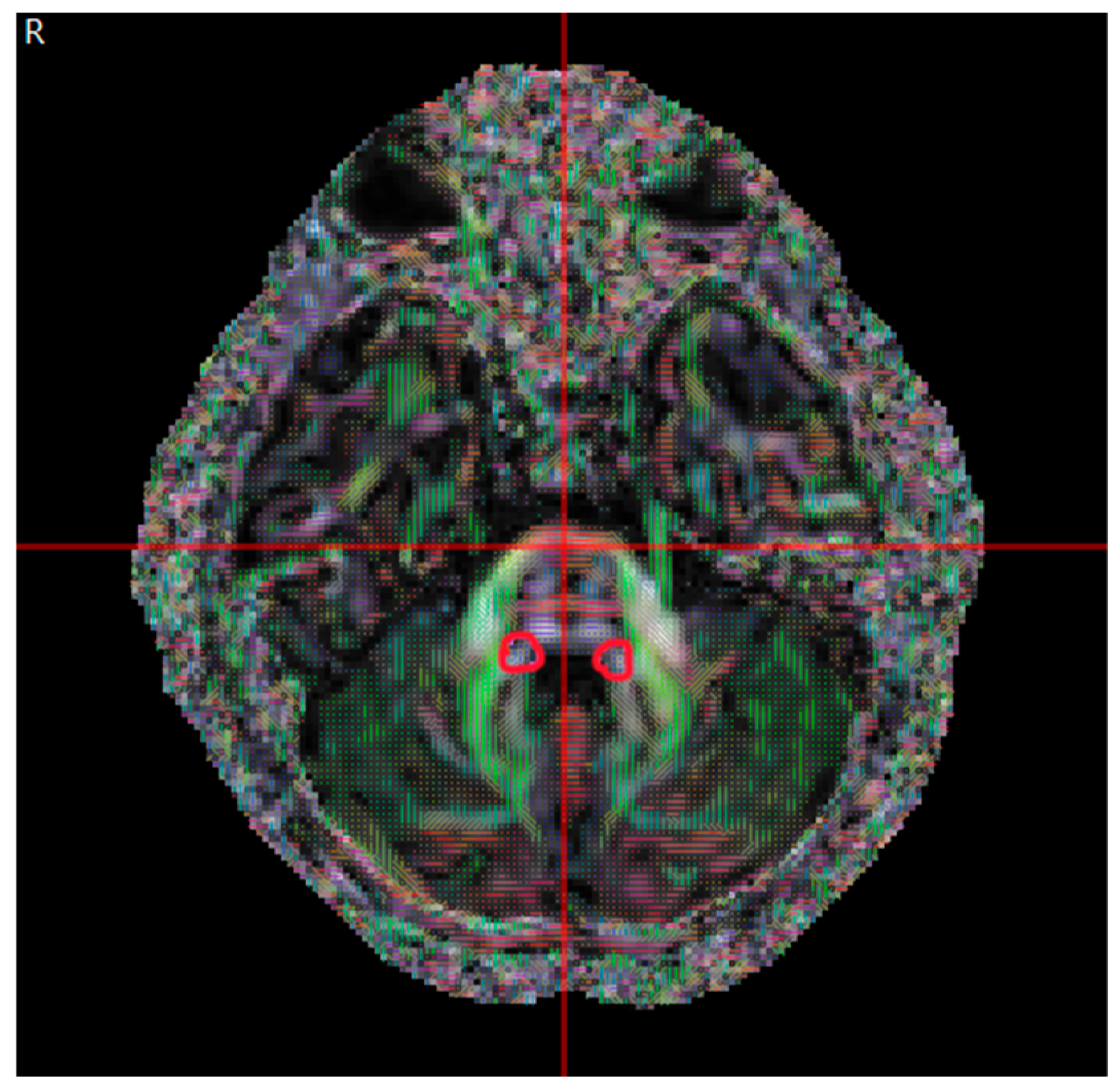
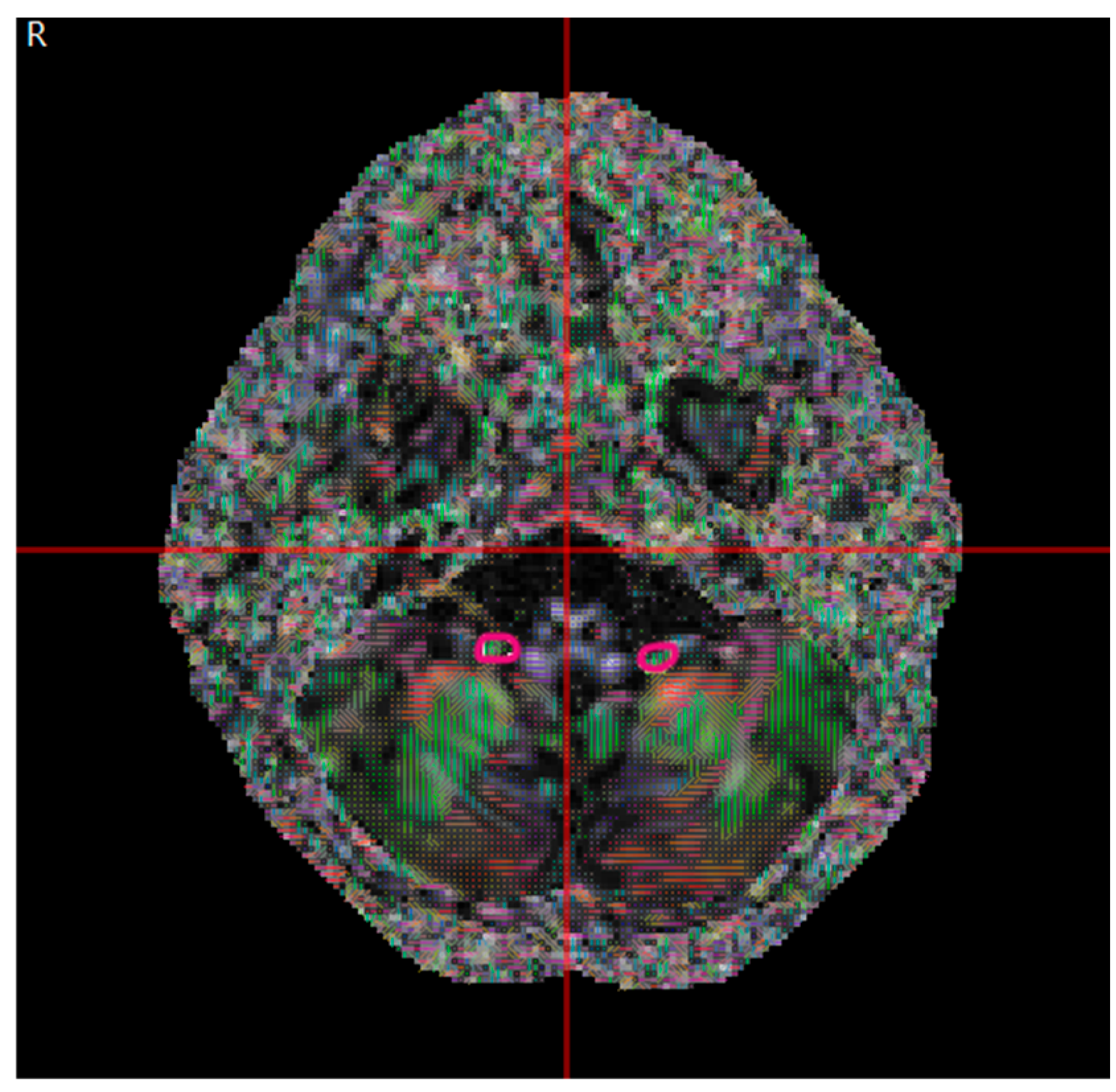




| Congenital Group (µ ± σ) | Acquired Group (µ ± σ) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IC Left | |||
| FA | 0.545 ± 0.078 | 0.606 ± 0.042 | 0.073 |
| MD | 0.787 ± 0.102 | 0.730 ± 0.105 | 0.227 |
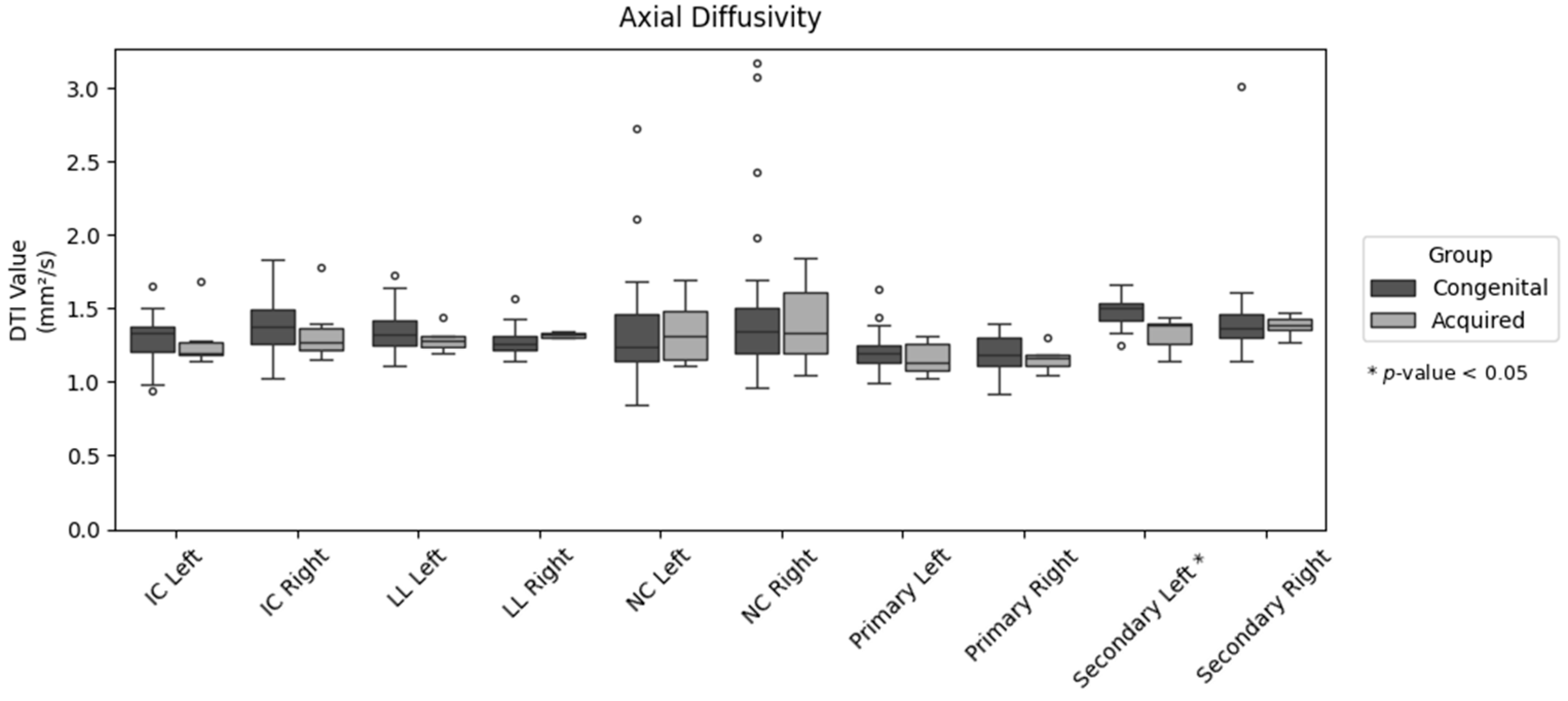
| AD | 1.292 ± 0.157 | 1.282 ± 0.200 | 0.898 |
| RD | 0.534 ± 0.102 | 0.454 ± 0.066 | 0.077 |
| IC Right | |||
| FA | 0.543 ± 0.069 | 0.595 ± 0.021 | 0.075 |
| MD | 0.850 ± 0.122 | 0.788 ± 0.120 | 0.265 |
| AD | 1.371 ± 0.172 | 1.347 ± 0.231 | 0.765 |
| RD | 0.590 ± 0.113 | 0.509 ± 0.072 | 0.105 |
| LL Left | |||
| FA | 0.499 ± 0.078 | 0.545 ± 0.085 | 0.202 |
| MD | 0.874 ± 0.162 | 0.797 ± 0.073 | 0.270 |
| AD | 1.347 ± 0.147 | 1.29 ± 0.086 | 0.375 |
| RD | 0.638 ± 0.177 | 0.551 ± 0.087 | 0.255 |
| LL Right | |||
| FA | 0.525 ± 0.083 | 0.568 ± 0.122 | 0.295 |
| MD | 0.790 ± 0.092 | 0.795 ± 0.111 | 0.895 |
| AD | 1.273 ± 0.097 | 1.321 ± 0.019 | 0.241 |
| RD | 0.548 ± 0.115 | 0.533 ± 0.161 | 0.782 |
| CN Left | |||
| FA | 0.321 ± 0.094 | 0.323 ± 0.119 | 0.967 |
| MD | 1.018 ± 0.333 | 1.005 ± 0.244 | 0.929 |
| AD | 1.352 ± 0.357 | 1.346 ± 0.237 | 0.971 |
| RD | 0.851 ± 0.330 | 0.835 ± 0.256 | 0.908 |
| CN Right | |||
| FA | 0.329 ± 0.147 | 0.28 ± 0.107 | 0.441 |
| MD | 1.124 ± 0.553 | 1.081 ± 0.294 | 0.853 |
| AD | 1.482 ± 0.554 | 1.401 ± 0.308 | 0.732 |
| RD | 0.946 ± 0.565 | 0.921 ± 0.293 | 0.917 |
| Primary Left | |||
| FA | 0.298 ± 0.054 | 0.359 ± 0.052 | 0.016 |
| MD | 0.924 ± 0.076 | 0.833 ± 0.068 | 0.011 |
| AD | 1.208 ± 0.130 | 1.161 ± 0.120 | 0.425 |
| RD | 0.782 ± 0.068 | 0.669 ± 0.062 | 0.001 |
| Primary Right | |||
| FA | 0.304 ± 0.056 | 0.360 ± 0.091 | 0.205 |
| MD | 0.910 ± 0.083 | 0.841 ± 0.036 | 0.055 |
| AD | 1.190 ± 0.117 | 1.160 ± 0.087 | 0.549 |
| RD | 0.770 ± 0.085 | 0.681 ± 0.080 | 0.026 |
| Secondary Left | |||
| FA | 0.402 ± 0.081 | 0.506 ± 0.039 | 0.005 |
| MD | 1.018 ± 0.080 | 0.838 ± 0.082 | 0.000 |
| AD | 1.486 ± 0.093 | 1.329 ± 0.117 | 0.001 |
| RD | 0.784 ± 0.109 | 0.593 ± 0.069 | 0.000 |
| Secondary Right | |||
| FA | 0.401 ± 0.081 | 0.471 ± 0.051 | 0.052 |
| MD | 1.009 ± 0.319 | 0.901 ± 0.050 | 0.0416 |
| AD | 1.438 ± 0.325 | 1.386 ± 0.069 | 0.703 |
| RD | 0.795 ± 0.322 | 0.658 ± 0.056 | 0.312 |
| Dataset | Specificity | Experiment Mode | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVC | RF | MLP | ||
| Selected features | 0.8549 | 0.8712 | 0.8622 | Experiment 1 |
| All-in | 0.7512 | 0.8165 | 0.7278 | |
| FA only | 0.8379 | 0.7735 | 0.6873 | Experiment 2 |
| MD only | 0.7275 | 0.7585 | 0.6970 | |
| AD only | 0.7268 | 0.7373 | 0.6892 | |
| RD only | 0.7522 | 0.7571 | 0.7122 | |
| Dataset | F1 Score | Experiment Mode | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVC | RF | MLP | ||
| Selected features | 0.9688 | 0.9688 | 0.9495 | Experiment 1 |
| All-in | 0.6612 | 0.7583 | 0.6335 | |
| FA only | 0.7410 | 0.6303 | 0.5607 | Experiment 2 |
| MD only | 0.6327 | 0.6361 | 0.5810 | |
| AD only | 0.6231 | 0.6406 | 0.5633 | |
| RD only | 0.6553 | 0.6308 | 0.6100 | |
| Dataset | AUC-ROC | Experiment Mode | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SVC | RF | MLP | ||
| Selected features | 0.7431 | 0.8056 | 0.7778 | Experiment 1 |
| All-in | 0.6242 | 0.7274 | 0.5758 | |
| FA only | 0.7528 | 0.6175 | 0.4922 | Experiment 2 |
| MD only | 0.5808 | 0.5984 | 0.5138 | |
| AD only | 0.5808 | 0.5940 | 0.4964 | |
| RD only | 0.6267 | 0.5901 | 0.5414 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kameela, F.K.; Putranto, F.M.; Yusuf, P.A.; Pujitresnani, A.; Valindria, V.V.; Sudiana, D.; Rizkinia, M. White Matter Microstructure Differences Between Congenital and Acquired Hearing Loss Patients Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) and Machine Learning. Computers 2025, 14, 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14080303
Kameela FK, Putranto FM, Yusuf PA, Pujitresnani A, Valindria VV, Sudiana D, Rizkinia M. White Matter Microstructure Differences Between Congenital and Acquired Hearing Loss Patients Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) and Machine Learning. Computers. 2025; 14(8):303. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14080303
Chicago/Turabian StyleKameela, Fatimah Kayla, Fikri Mirza Putranto, Prasandhya Astagiri Yusuf, Arierta Pujitresnani, Vanya Vabrina Valindria, Dodi Sudiana, and Mia Rizkinia. 2025. "White Matter Microstructure Differences Between Congenital and Acquired Hearing Loss Patients Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) and Machine Learning" Computers 14, no. 8: 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14080303
APA StyleKameela, F. K., Putranto, F. M., Yusuf, P. A., Pujitresnani, A., Valindria, V. V., Sudiana, D., & Rizkinia, M. (2025). White Matter Microstructure Differences Between Congenital and Acquired Hearing Loss Patients Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI) and Machine Learning. Computers, 14(8), 303. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14080303







