An Efficient Hybrid 3D Computer-Aided Cephalometric Analysis for Lateral Cephalometric and Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Systems
Abstract
1. Introduction
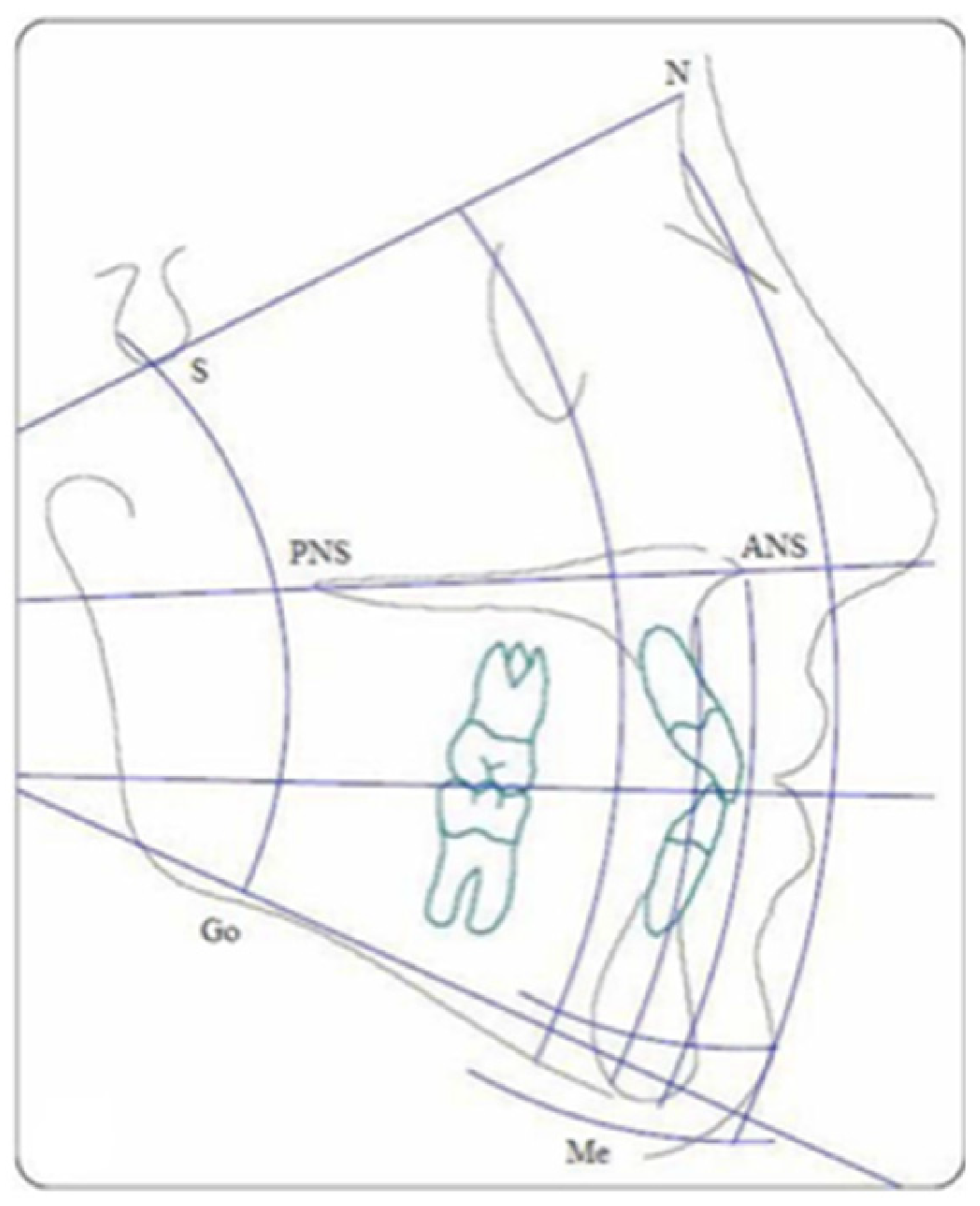
1.1. Biological Background
1.1.1. Characteristic of CBCT
1.1.2. 2D and CBCT
1.1.3. Similarities Between 2D and 3D Cephalometric X-Rays
1.2. Literature Review
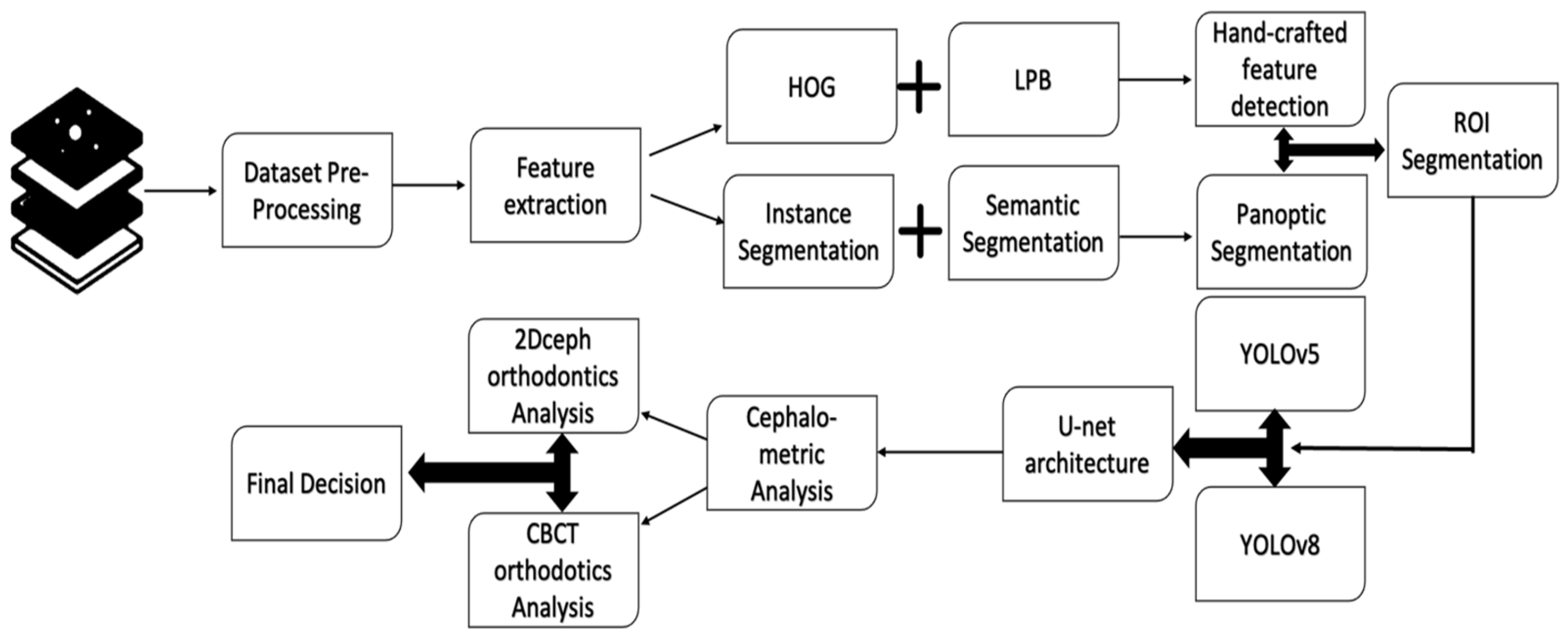
2. Materials and Methods
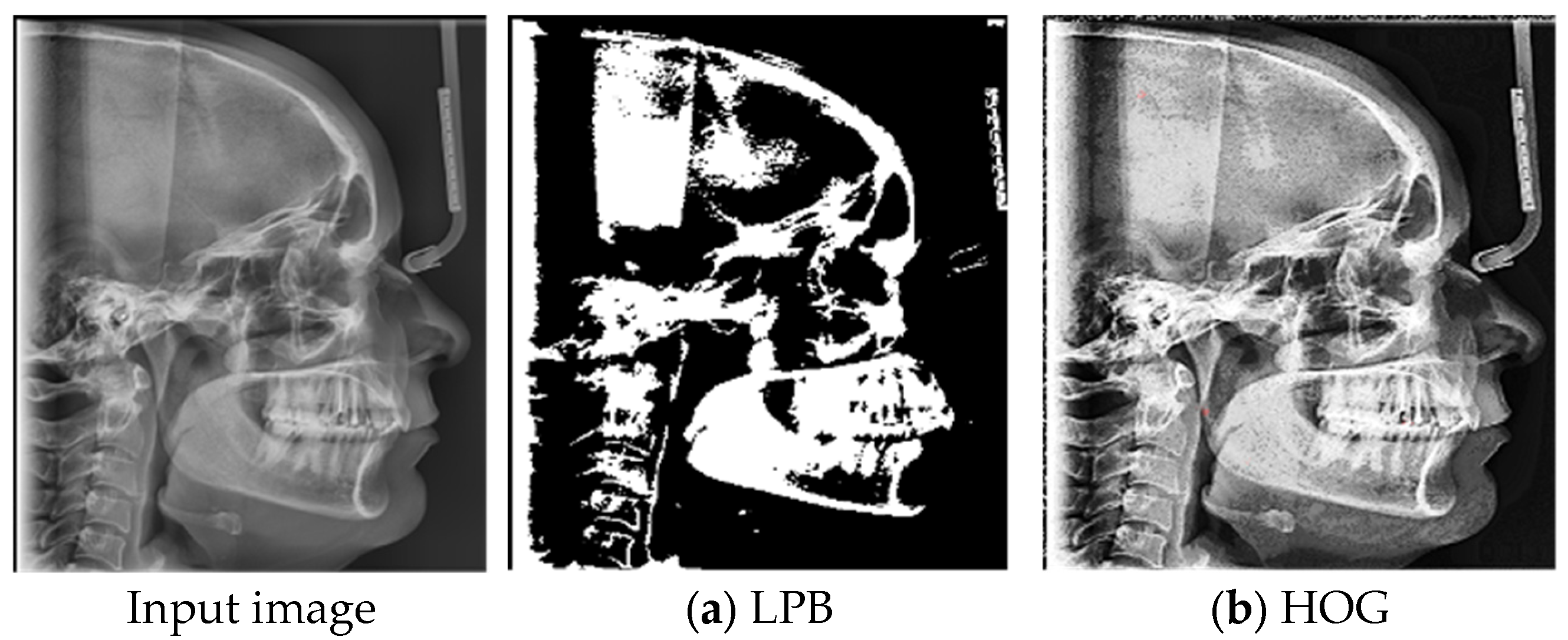
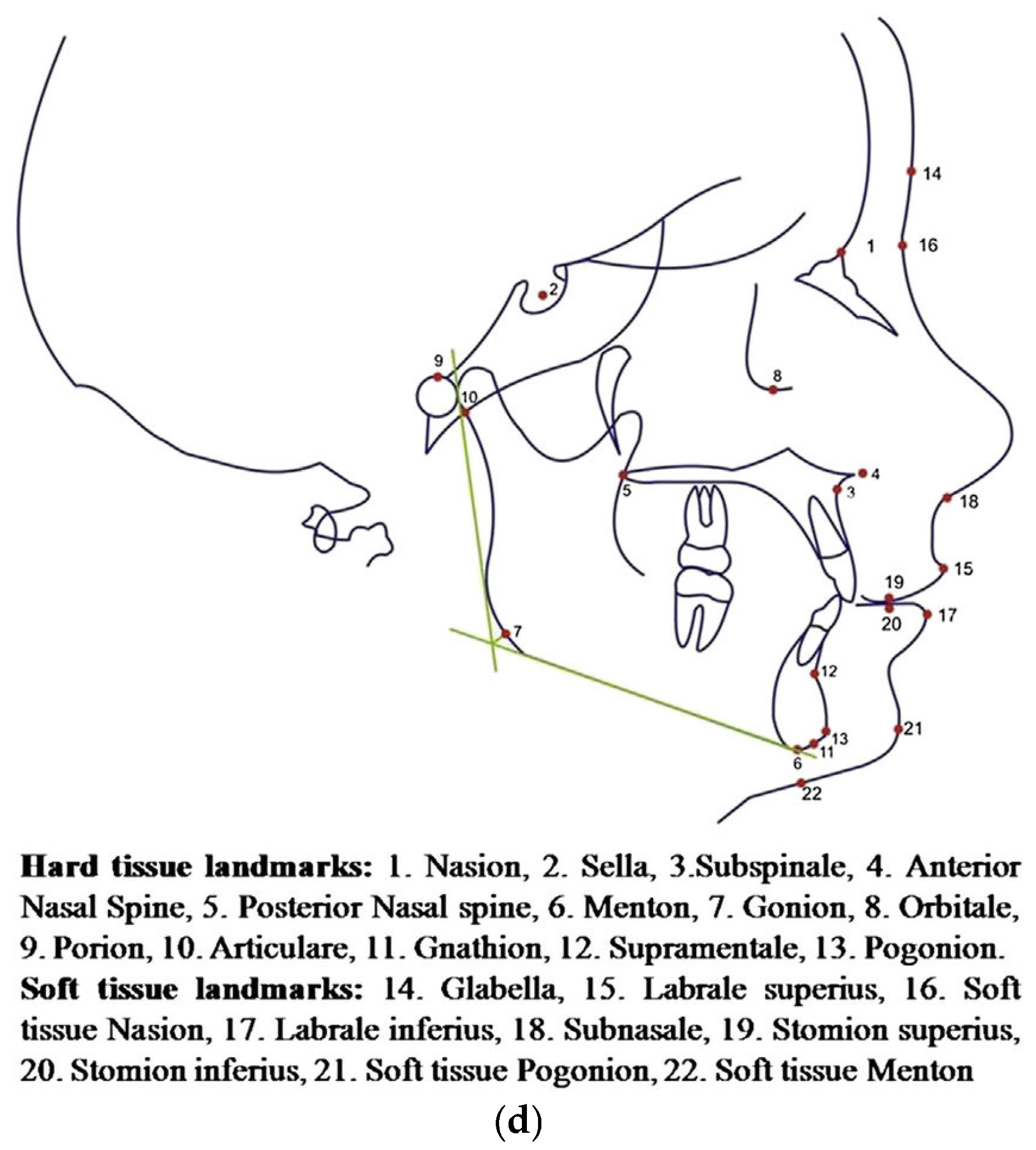
2.1. Radiographic Image Enhancement and Pre-Processing Using “Local Contrast Enhancement” Technique
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
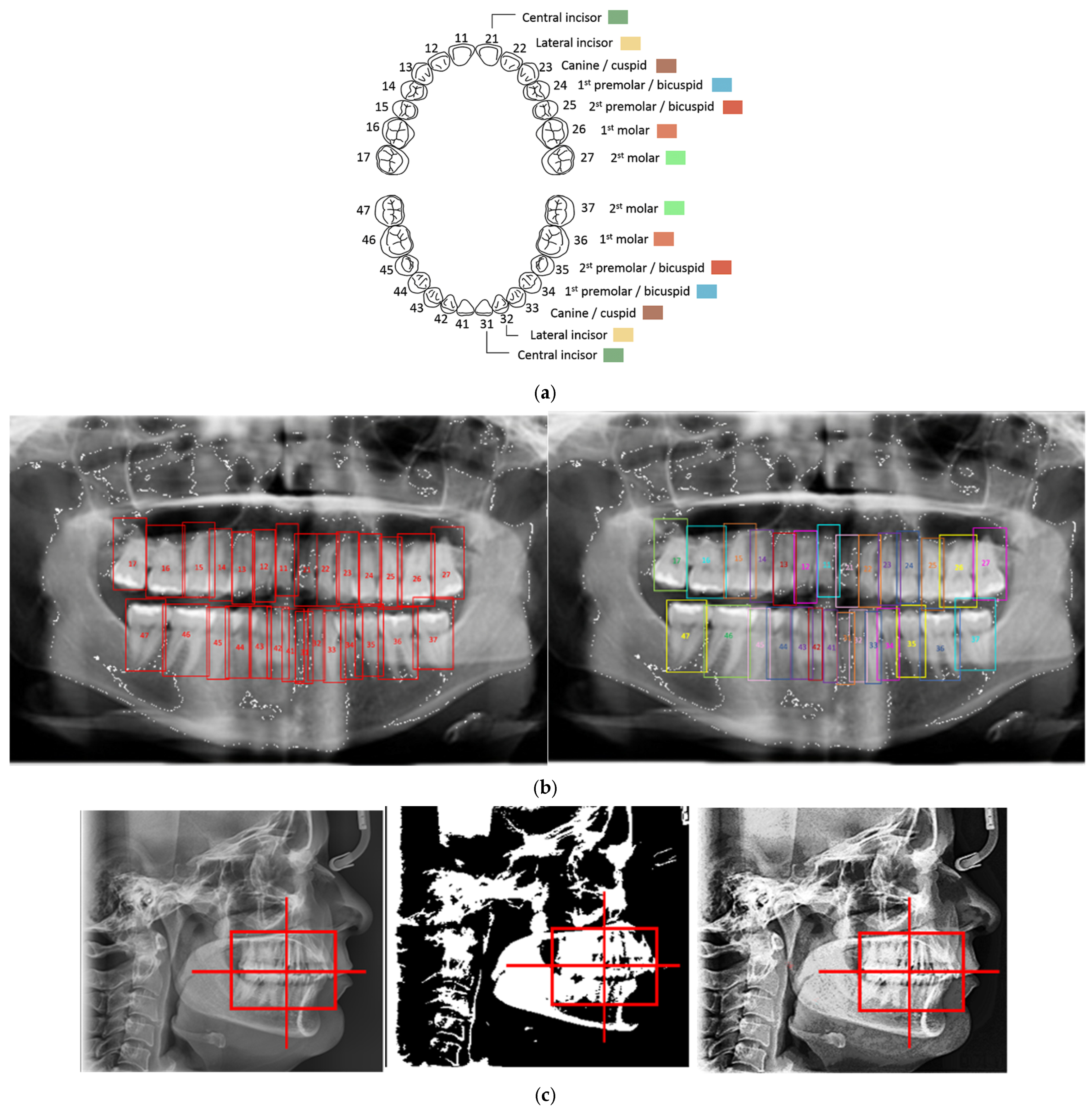
2.2. ROI Handcrafted Feature Detection
2.3. ROI Identification, YOLO-UNet-Based
2.4. Line Tracing and Analysis Using Different AI Models
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Environment
3.2. Dataset Description
3.3. Results Obtained from 2D Lateral Cephalogram Analysis Applying AI Techniques
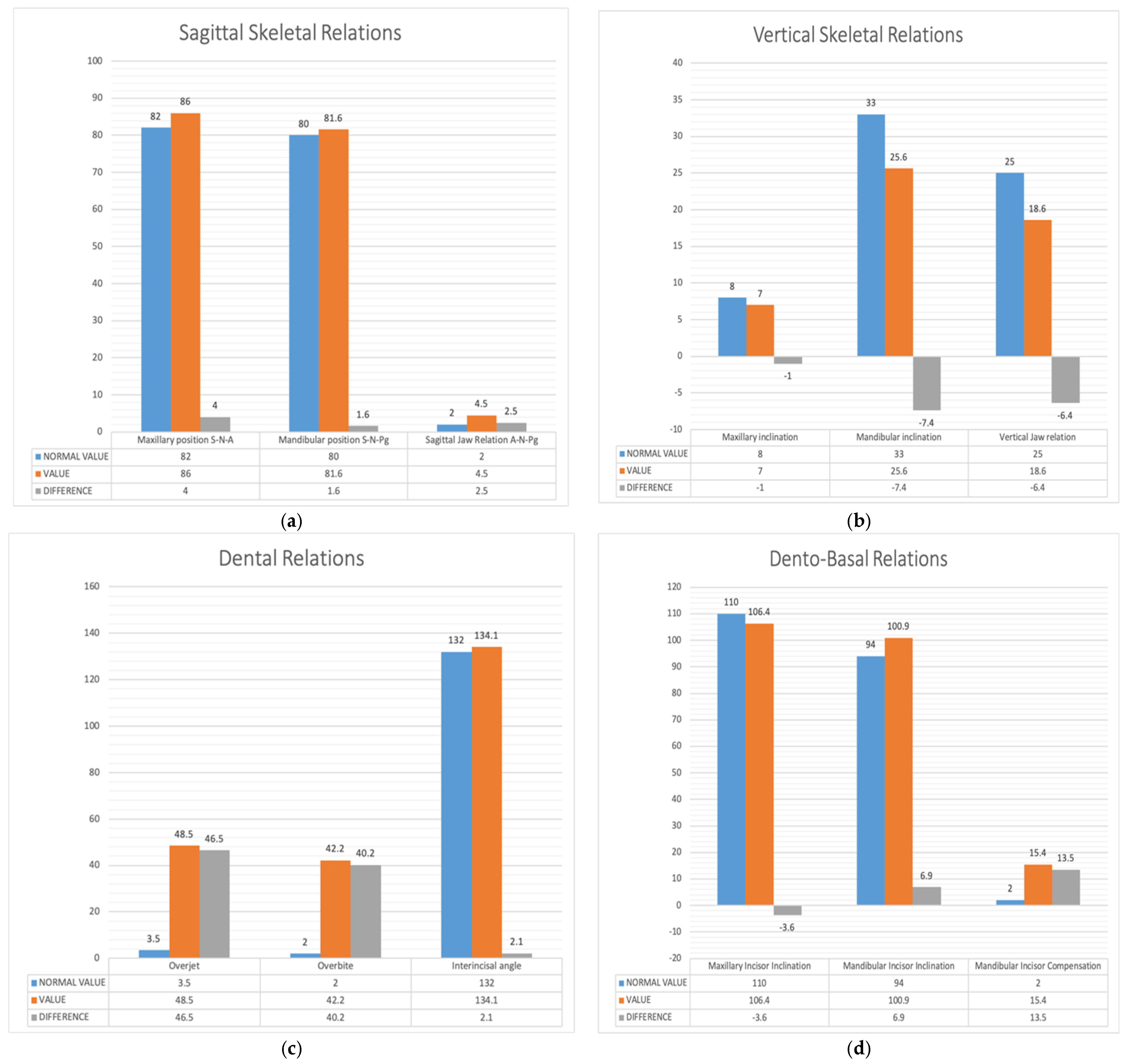
4. Discussion
4.1. Proposed Model Performance Measures
4.2. Comparison Between This Architecture and the Launched Software’s Results
4.3. Comparison Between This Architecture and Recent Software Result
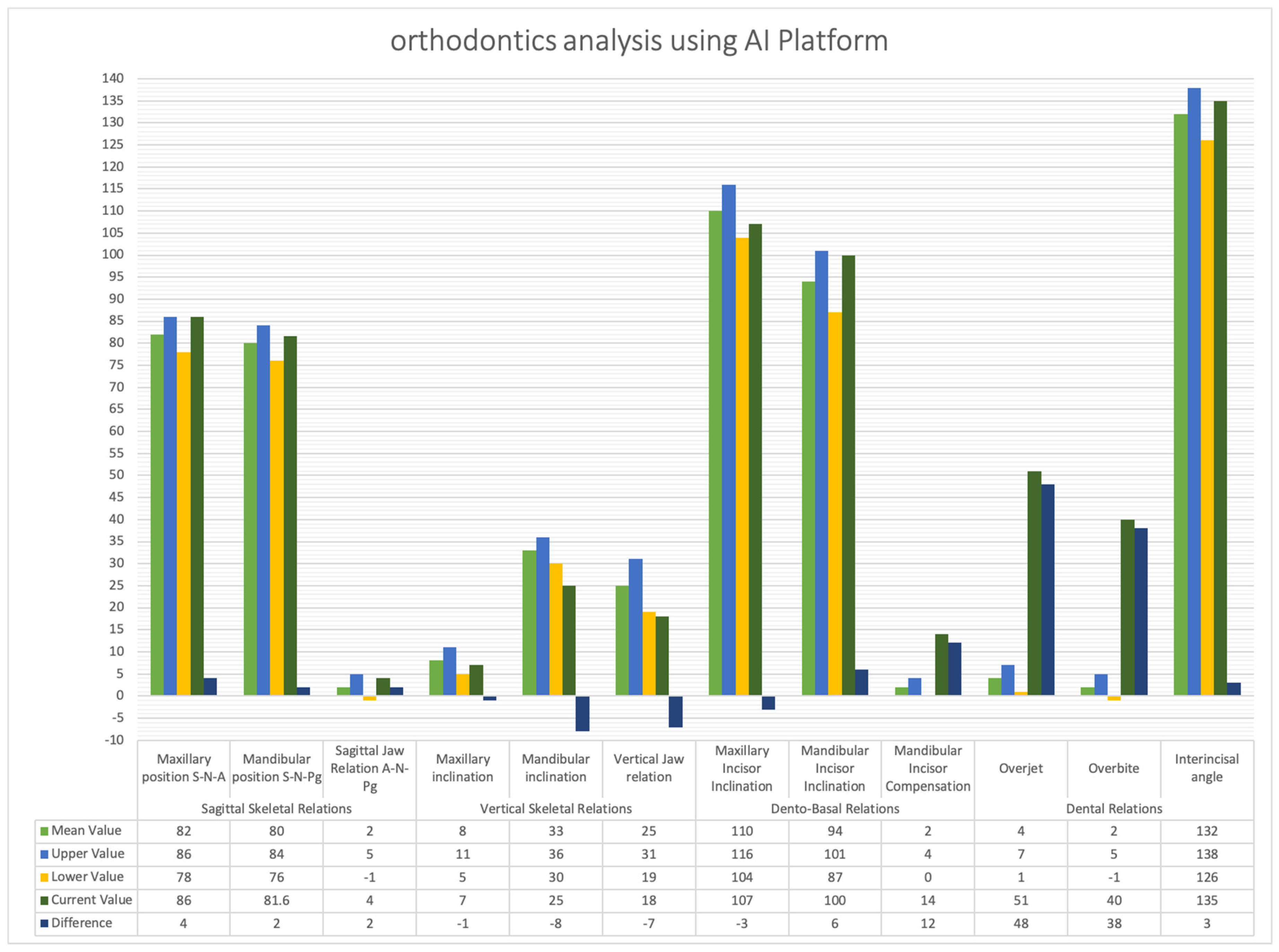
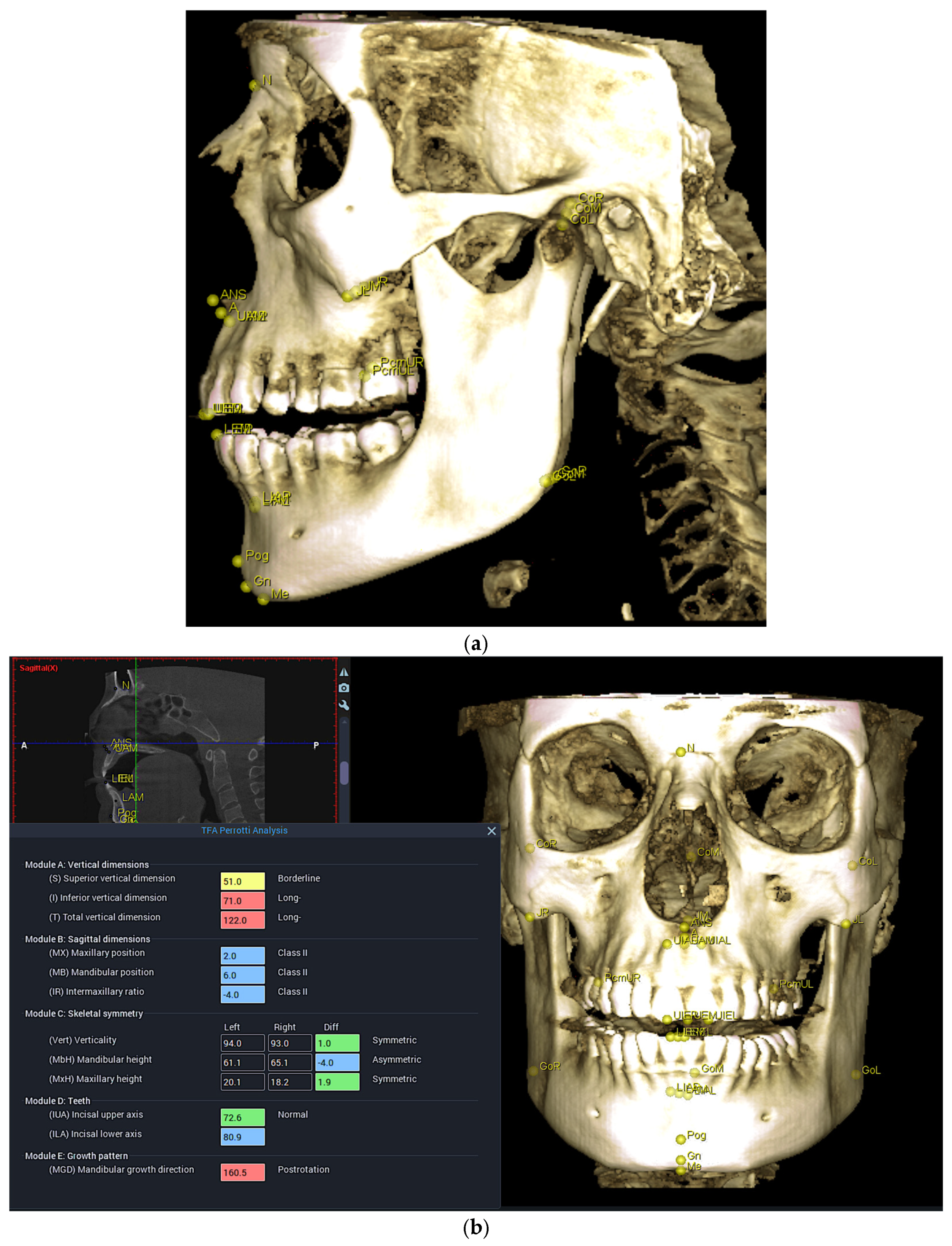
4.4. CBCT Analysis Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- MarketsandMarkets. Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Healthcare Market Worth $148.4 Billion by 2029—Exclusive Report by MarketsandMarketsTM; PR Newswire: New York, NY, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Meade, M.J.; Dreyer, C.W. Tooth agenesis: An overview of diagnosis, aetiology and management. Jpn. Dent. Sci. Rev. 2023, 59, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Grahnen, H. Hypodontia in the permanent dentition: A clinical and genetical investigation. Odont. Revy 1956, 7, 1–100. [Google Scholar]
- Neela, P.K.; Atteeri, A.; Mamillapalli, P.K.; Sesham, V.M.; Keesara, S.; Chandra, J.; Monica, U.; Mohan, V. Genetics of dentofacial and orthodontic abnormalities. Glob. Med. Genet. 2020, 7, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lee, H.; Cho, J.M.; Ryu, S.; Ryu, S.; Chang, E.; Jung, Y.S.; Kim, J.Y. Automatic identification of posteroanterior cephalometric landmarks using a novel deep learning algorithm: A comparative study with human experts. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kazimierczak, W.; Wajer, R.; Wajer, A.; Kiian, V.; Kloska, A.; Kazimierczak, N.; Janiszewska-Olszowska, J.; Serafin, Z. Periapical lesions in panoramic radiography and CBCT imaging—Assessment of AI’s diagnostic accuracy. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dipalma, G.; Inchingolo, A.D.; Inchingolo, A.M.; Piras, F.; Carpentiere, V.; Garofoli, G.; Azzollini, D.; Campanelli, M.; Paduanelli, G.; Palermo, A.; et al. Artificial intelligence and its clinical applications in orthodontics: A systematic review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surendran, A.; Daigavane, P.; Shrivastav, S.; Kamble, R.; Sanchla, A.D.; Bharti, L.; Shinde, M. The future of orthodontics: Deep learning technologies. Cureus 2024, 16, e62045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- MedlinePlus. Understanding Genetics: What Is a Gene? Available online: https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/understanding/basics/gene/ (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Cleveland Clinic. Malocclusion. Available online: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22010-malocclusion (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Watted, N.; Lone, I.M.; Midlej, K.; Zohud, O.; Awadi, O.; Masarwa, S.; Watted, A.; Paddenberg, E.; Krohn, S.; Kirschneck, C.; et al. The complexity of skeletal transverse dimension: From diagnosis, management, and treatment strategies to the application of Collaborative Cross (CC) mouse model. J. Funct. Morphol. Kinesiol. 2024, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- CephX. Comparison of 2D and 3D Cephalometric Analyses. Available online: https://cephx.com/comparison-2d-3d-cephalometric-analyses-2/ (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Baldini, B.; Cavagnetto, D.; Baselli, G.; Sforza, C.; Tartaglia, G.M. Cephalometric measurements performed on CBCT and reconstructed lateral cephalograms: A cross-sectional study providing a quantitative approach of differences and bias. BMC Oral Health 2022, 22, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hage, L.; Kmeid, R.; Amm, E. Comparison between 2D cephalometric and 3D digital model superimpositions in patients with lateral incisor agenesis treated by canine substitution. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2024, 165, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossini, G.; Cavallini, C.; Cassetta, M.; Barbato, E. 3D cephalometric analysis obtained from computed tomography. Review of the literature. Ann. Stomatol. 2011, 2, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelkarim, A. Cone-beam computed tomography in orthodontics. Dent. J. 2019, 7, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porto, L.F.; Lima, L.N.C.; Flores, M.R.P.; Valsecchi, A.; Ibanez, O.; Palhares, C.E.M.; Vidal, F.D.B. Automatic Cephalometric Landmarks Detection on Frontal Faces: An Approach Based on Supervised Learning Techniques. Digit. Investig. 2019, 30, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, P.T. Homeobox genes and orofacial development. Connect. Tissue Res. 1995, 32, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakasima, A.; Ichinose, M.; Nakata, S.; Takahama, Y. Hereditary factors in the craniofacial morphology of Angle’s Class II and Class III malocclusions. Am. J. Orthod. 1982, 82, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Coster, P.J.; Marks, L.A.; Martens, L.C.; Huysseune, A. Dental agenesis: Genetic and clinical perspectives. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2009, 38, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, N.; Kazimierczak, W.; Serafin, Z.; Nowicki, P.; Nożewski, J.; Janiszewska-Olszowska, J. AI in orthodontics: Revolutionizing diagnostics and treatment planning—A comprehensive review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauniyar, S.; Jena, S.; Sahoo, N.; Mohanty, P.; Dash, B.P. Artificial intelligence and machine learning for automated cephalometric landmark identification: A meta-analysis previewed by a systematic review. Cureus 2023, 15, e40934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, F.; Stellzig-Eisenhauer, A.; Widmaier, L.M.; Zeman, F.; Boldt, J. Assessment of the quality of different commercial providers using artificial intelligence for automated cephalometric analysis compared to human orthodontic experts. Untersuchung der Auswertequalität kommerzieller Anbieter für KI-basierte FRS Analysen im Vergleich zu einem Experten-Goldstandard. J. Orofac. Orthop. 2023, 86, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durão, A.R.; Pittayapat, P.; Rockenbach, M.I.; Olszewski, R.; Ng, S.; Ferreira, A.P.; Jacobs, R. Validity of 2D lateral cephalometry in orthodontics: A systematic review. Prog. Orthod. 2013, 14, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsubai, S. A Critical Review on the 3D Cephalometric Analysis Using Machine Learning. Computers 2022, 11, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-H.; Hwang, H.-W.; Moon, J.-H.; Yu, Y.; Kim, H.; Her, S.-B.; Srinivasan, G.; Aljanabi, M.N.A.; Donatelli, R.E.; Lee, S.-J. Automated identification of cephalometric landmarks: Part 1—Comparisons between the latest deep-learning methods YOLOV3 and SSD. Angle Orthod. 2019, 89, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cambridge in Colour. Local Contrast Enhancement. Available online: https://www.cambridgeincolour.com/tutorials/local-contrast-enhancement.htm (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Mady, H.; Hilles, S.M.S. Face recognition and detection using Random forest and combination of LBP and HOG features. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Smart Computing and Electronic Enterprise (ICSCEE), Shah Alam, Malaysia, 11–12 July 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirjalili, F.; Hardeberg, J.Y. On the quantification of visual texture complexity. J. Imaging 2022, 8, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Li, Z.; Fan, H.; Wu, X. Feature based local binary pattern for rotation invariant texture classification. Expert Syst. Appl. 2017, 88, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Analytics Vidhya. Feature Engineering for Images—Introduction to HOG Feature Descriptor. Available online: https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2019/09/feature-engineering-images-introduction-hog-feature-descriptor/ (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Pareto, A.I. Semantic Segmentation. Available online: https://pareto.ai/blog/semantic-segmentation (accessed on 11 May 2025).
- Kirillov, A.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Rother, C.; Dollar, P. Panoptic segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 9396–9405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M. YOLO-v1 to YOLO-v8, the rise of YOLO and its complementary nature toward digital manufacturing and industrial defect detection. Machines 2023, 11, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Qiao, H.; Wang, X.; Zhan, Q.; Li, Y.; Zheng, W.; Li, Y. Comparison of the accuracy of 2D and 3D cephalometry: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Australas. Orthod. J. 2022, 38, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashame, L.A.; Youssef, S.M.; ElAgamy, M.N.; El-Sheikh, S.M. An enhanced assistive model for diagnosis of dental 3D panoramic radiographs integrating the fusion of handcrafted features with deep learning architectures. In Proceedings of the 2024 International Conference on Machine Intelligence and Smart Innovation (ICMISI), Alexandria, Egypt, 12–14 May 2024; pp. 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oktay, A.B. Tooth detection with convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the 2017 Medical Technologies National Conference (TIPTEKNO), Trabzon, Turkey, 12–14 October 2017; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xie, Y.; Liu, L.; Xia, B.; Cao, Z.; Guo, C. Automated dental image analysis by deep learning on small dataset. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 42nd Annual Computer Software and Applications Conference (COMPSAC), Tokyo, Japan, 3–27 July 2018; pp. 492–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wu, J.; Chen, H.; Lyu, P. An effective teeth recognition method using label tree with cascade network structure. Comput. Med. Imaging Graph. 2018, 68, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.K.; Raza, K. Progress in Deep Learning-Based Dental and Maxillofacial Image Analysis: A Systematic Review. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 199, 116968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muramatsu, C.; Morishita, T.; Takahashi, R.; Hayashi, T.; Nishiyama, W.; Ariji, Y.; Zhou, X.; Hara, T.; Katsumata, A.; Ariji, E.; et al. Tooth detection and classification on panoramic radiographs for automatic dental chart filing: Improved classification by multi-sized input data. Oral Radiol. 2021, 37, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzoff, D.V.; Tuzova, L.N.; Bornstein, M.M.; Krasnov, A.S.; Kharchenko, M.A.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Sveshnikov, M.M.; Bednenko, G.B. Tooth detection and numbering in panoramic radiographs using convolutional neural networks. Dentomaxillofac. Radiol. 2019, 48, 20180051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laishram, A.; Thongam, K. Detection and classification of dental pathologies using faster-RCNN in orthopantomogram radiography image. In Proceedings of the 2020 7th International Conference on Signal Processing and Integrated Networks (SPIN), Noida, India, 27–28 February 2020; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 423–428. [Google Scholar]
- Eun, H.; Kim, C. Oriented tooth localization for periapical dental X-ray images via convolutional neural network. In Proceedings of the 2016 Asia-Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA), Jeju, Republic of Korea, 13–15 December 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





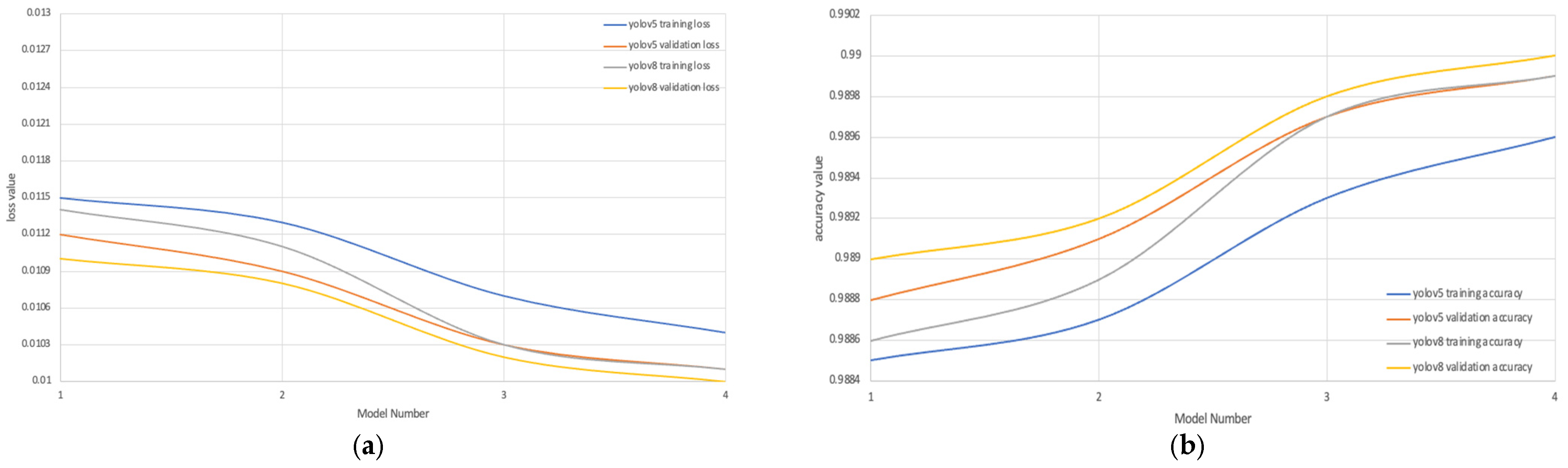
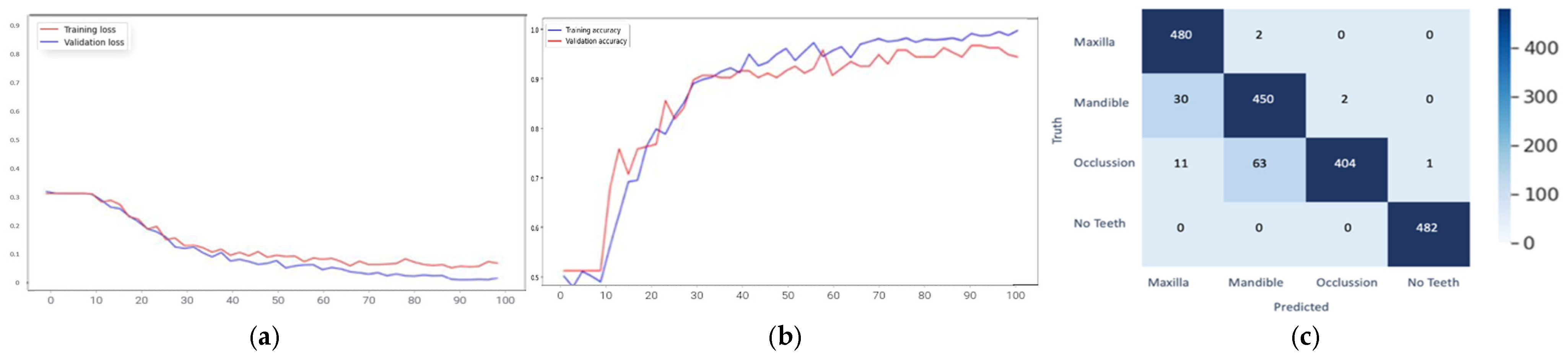

| YOLOv5 | YOLOv8 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Training Loss | Training Accuracy | Validation Loss | Validation Accuracy | Training Loss | Training Accuracy | Validation Loss | Validation Accuracy | |
| Model 1 LBP | 0.0215 | 0.9785 | 0.0212 | 0.9788 | 0.0114 | 0.9886 | 0.011 | 0.989 |
| Model 2 HOG | 0.0213 | 0.9787 | 0.0209 | 0.9791 | 0.0111 | 0.9889 | 0.0108 | 0.9892 |
| Model 3 Segmentation | 0.0107 | 0.9893 | 0.0103 | 0.9897 | 0.0103 | 0.9897 | 0.0102 | 0.9898 |
| Model 4 Proposed Model | 0.0104 | 0.9896 | 0.0101 | 0.9899 | 0.0101 | 0.9899 | 0.01 | 0.99 |
| Class | Original | Yolov5 | Yolov8 | Mean Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 |  | 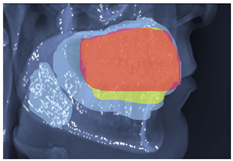 | 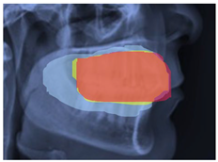 | 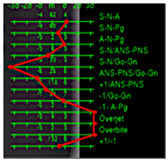 |
| Class 2 |  | 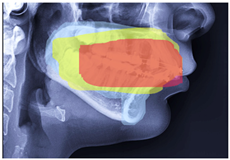 | 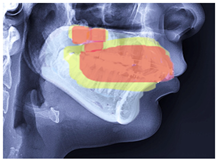 |  |
| Class 3 | 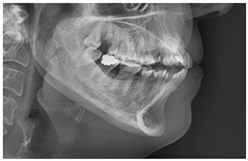 | 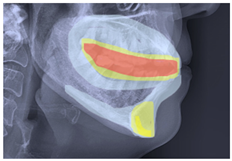 | 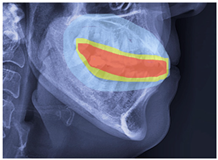 |  |
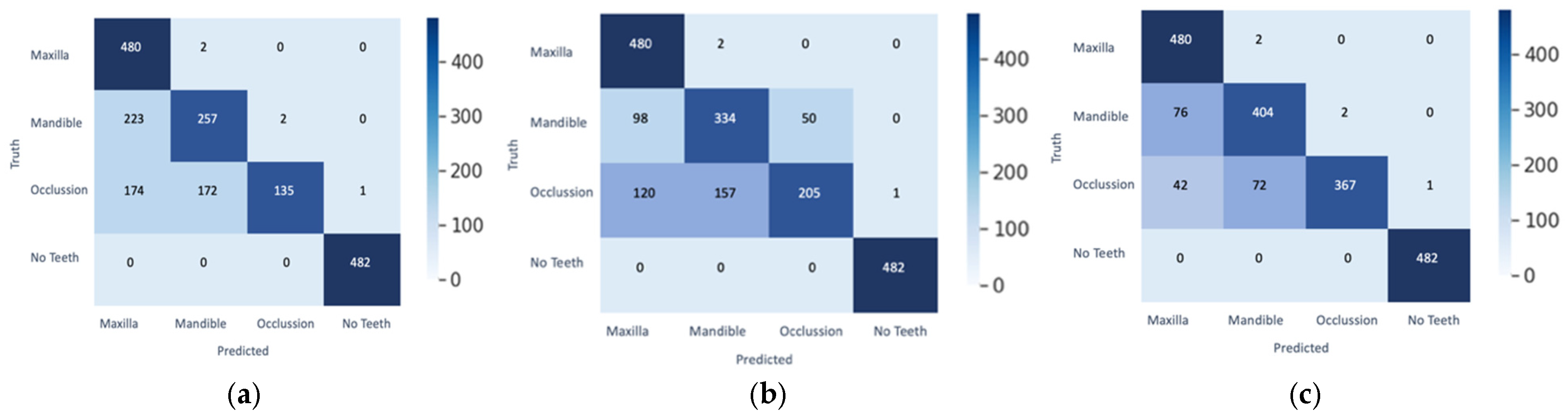
| Original | Predict Phase | Heat Maps | Confusion Matrix |
|---|---|---|---|
 |  |  |  |
 | 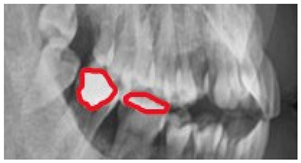 | 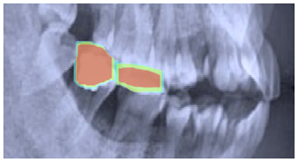 |
| Authors | Method | Remark | Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Oktay, 2017) [37] | CNN AlexNet | CNN and AlexNet used for tooth detection and classification | Acc = 0.943, |
| (Yang et al., 2018) [38] | CNN | CNN on small dataset for automated diagnosis | Pre = 0.756, |
| (Zhang et al., 2018) [39] | CNN | CNN-based cascade network used to identify tooth loss, filled and decay | Pr = 0.958, |
| (Singh et al., 2022) [40] | CNN | CNN-based UNet employed to segment mandibule | training = 0.768, validation = 0.805 |
| (Muramatsu et al., 2020) [41] | CNN Res-Net | Res-net with CNN, a small size of image | Acc for cnn = 0.932, Acc for Resnet = 0.98 |
| (Tuzoff et al., 2019) [42] | CNN | Faster region-based CNN approach, moderate dataset size | Pr = 0.994 |
| (Laishram & Thongam, 2020) [43] | CNN | Faster region-based CNN applied for tooth detection and classification | Detection Acc = 0.910, Classification = 0.99 |
| (Eun & Kim, 2017) [44] | CNN | CNN; teeth localization | Acc = 0.90 |
| This proposed model | Fusion between handcrafted features and segmentation based on YOLO-UNet | Different experimental scenarios employed to test the performance of the proposed model | ACC = 0.99 Pre = 0.98 Avg. improvement = 0.087 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ashame, L.A.; Youssef, S.M.; Elagamy, M.N.; El-Sheikh, S.M. An Efficient Hybrid 3D Computer-Aided Cephalometric Analysis for Lateral Cephalometric and Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Systems. Computers 2025, 14, 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14060223
Ashame LA, Youssef SM, Elagamy MN, El-Sheikh SM. An Efficient Hybrid 3D Computer-Aided Cephalometric Analysis for Lateral Cephalometric and Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Systems. Computers. 2025; 14(6):223. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14060223
Chicago/Turabian StyleAshame, Laurine A., Sherin M. Youssef, Mazen Nabil Elagamy, and Sahar M. El-Sheikh. 2025. "An Efficient Hybrid 3D Computer-Aided Cephalometric Analysis for Lateral Cephalometric and Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Systems" Computers 14, no. 6: 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14060223
APA StyleAshame, L. A., Youssef, S. M., Elagamy, M. N., & El-Sheikh, S. M. (2025). An Efficient Hybrid 3D Computer-Aided Cephalometric Analysis for Lateral Cephalometric and Cone-Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) Systems. Computers, 14(6), 223. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14060223





