Abstract
The increasing demand for smaller batch sizes and mass customisation in production poses considerable challenges to logistics and manufacturing efficiency. Conventional methodologies are unable to address the need for expeditious, cost-effective distribution of premium-quality products tailored to individual specifications. Additionally, the reliability and resilience of global logistics chains are increasingly under pressure. Additive manufacturing is regarded as a potentially viable solution to these problems, as it enables on-demand, on-site production, with reduced resource usage in production. Nevertheless, there are still significant challenges to be addressed, including the assurance of product quality and the optimisation of production processes with respect to time and resource efficiency. This article examines the potential of integrating digital twin methodologies to establish a fully digital and efficient process chain for on-site additive manufacturing. This study focuses on wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM), a technology that has been successfully implemented in the on-site production of naval ship propellers and excavator parts. The proposed approach aims to enhance process planning efficiency, reduce material and energy consumption, and minimise the expertise required for operational deployment by leveraging digital twin methodologies. The present paper details the current state of research in this domain and outlines a vision for a fully virtualised process chain, highlighting the transformative potential of digital twin technologies in advancing on-site additive manufacturing. In this context, various aspects and components of a digital twin framework for wire arc additive manufacturing are examined regarding their necessity and applicability. The overarching objective of this paper is to conduct a preliminary investigation for the implementation and further development of a comprehensive DT framework for WAAM. Utilising a real-world sample, current already available process steps are validated and actual missing technical solutions are pointed out.
1. Introduction
The number of challenges that arise in the logistics of industrial goods is steadily increasing. Due to changing economics, the delivery and storage of required industrial goods are becoming more expensive and less reliable. Downtime at production sites or laytime in port is a critical cost factor [1].
On-site repair and production can be a solution to these actual real-world challenges of insecure logistical waterways (e.g., blockage of the Suez Canal [2]), rising import tariffs, or political crises. These uncertainties and the associated risk of delays and higher costs underscore the growing appeal of on-site production, which relies on effective and user-friendly production processes [3]. Further benefits of on-site production include:
- Reduced transport costs: Producing spare parts in comparison to ordering and delivery from overseas can reduce delivery costs by 85% [4];
- Storage and warehousing: By consolidating slow-moving and excess inventory to free up warehouse space, up to 17% of storage costs can be saved [4];
- Reduced production cost: On-site production with additive technologies, in combination with subtractive post-processing, can help to reduce the consumption of raw materials. By applying the material close to the target surface with little or no excess material, the material yield can be significantly increased. Compared with production relying solely on subtractive machining, less excess waste material is produced, e.g., in the form of chips. Compared with other processes such as casting, no additional cost-intensive moulds are required. Campatelli et al. [5] provide evidence that energy savings of up to 34% are possible.
In contrast to these potential optimisations, additive technologies, while cost-effective, present a number of challenges. Depending on the specific additive technology used, these challenges also vary and need to be addressed differently. This article focuses on wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) as a subset of directed energy deposition (DED) technologies. WAAM offers logistical advantages by allowing production facilities to be located closer to the end user. This proximity reduces transport distances and simplifies supply chain logistics, which is particularly beneficial for industries such as medical devices, as shown in [6].
Within specialised scenarios, this production technique has already been used successfully on naval ship propellers, excavator parts, or bridges [7,8]. However, despite these successful implementations, there are still challenges remaining, which prevent a broader application of the WAAM technology for on-site manufacturing. With this focus, the challenges are:
- Interdependent process parameters: In additive manufacturing, the process parameters are more demanding. For example, the temperature between two subsequent layers, often called the interlayer temperature, is a critical factor for the successful production of the component. This temperature is influenced by various aspects, including the shape of the workpiece, the material and temperature of the substrate plate, the welding parameters, control strategies, the adaptation of machining paths, simulations, measurements, and cooling methods [9,10]. Consequently, it is essential to meticulously select all other parameters with consideration given to each other;
- Complex post-processing: As the resulting shape and material properties are irregular, with visible weld beads and possible deformations within the part [9], milling conditions vary and cannot be predicted without a 3D representation of the actual shape of the part after the additive process [11];
- Complex simulation: Due to the wide variety of additive processes and the complexity of the processes compared with material removal simulations [12,13], the simulation of the additive process is still under research, unlike subtractive processes, where computer-aided simulation was already described in the 1980s and 1990s by van Hook and Glaeser [12,13]. These simulations have been extended to provide a full description of the mechanics during milling processes, including cutting forces [14], tool vibration, and chatter [15]. Simulation in additive processes is still under development, with approaches utilising finite element techniques [16] to simple shape estimation as in common 3D toolpath generation tools, such as [17,18,19];
- Comprehensive virtual process chain: The software tools that represent the virtual process chain must be able to handle the entire production process. This includes not only the additive part of the process, but also the post-processing, which can be heat treatment [20], milling, or other subtractive techniques [11,21] and more;
- Training and qualification: Because of the aforementioned aspects, additive processes require qualified personnel to plan and maintain the process. The training of qualified professionals is a major challenge [22].
These challenges illustrate that, while the use of on-site additive processes as a replacement for centralised production is promising, further research and development are required to establish additive manufacturing as a technique capable of producing a wide range of components on-site. Addressing these challenges is necessary to reduce the need for costly process development and to ensure that produced components meet given specifications.
To address these challenges, the authors propose the utilisation of digital twin methods to ensure predictable process planning and a stable process. This approach involves the use of simulations, the acquisition of sensor data, and an adapted virtual process chain consisting of harmonised software components. This approach facilitates process planning and prediction, thereby supporting the production of first-time-right parts.
The primary objective of this paper is to explore the potential integration of digital twin technology within WAAM processes. This paper aims to demonstrate the transformative potential of digital twins as a means to enhance precision, efficiency, and adaptability in WAAM systems. In conclusion, this paper attempts to establish foundations for the subsequent development and implementation of a comprehensive digital twin framework by examining the critical aspects and components necessary for its successful deployment. In this context, Section 2 provides a comprehensive overview of metal additive manufacturing and WAAM. This is followed by a brief exploration of digital twin methods in metal additive manufacturing in Section 3. In Section 4, the potential implementation of these methods in a real-world example is discussed. Finally, Section 5 offers a conclusion and outlook for future research.
2. Overview of the Current WAAM Process
2.1. WAAM as a Process and the Benefits
The major difference between additive and subtractive manufacturing processes like milling is the variety of processes, raw materials, and forms of materials. Overviews in [23,24] show that WAAM is a subprocess of the directed energy deposition (DED) processes that combines metal wire with plasma welding torches. Figure 1 illustrates a simplified scheme of these metal additive manufacturing techniques.
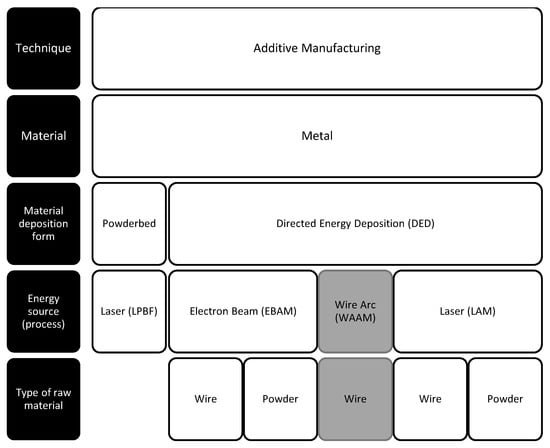
Figure 1.
Overview of metal additive manufacturing techniques with melting processes.
In the context of on-site repair and production, it is crucial to evaluate the suitability of various additive manufacturing techniques [6]. When it comes to the production of metallic components, two critical decisions must be addressed: the selection between using metal powder or wire as the raw material, and choosing between applying a laser, an electron beam, or an electric arc as the energy source. Laser-based powder bed fusion (LPBF) is also a prominent method in this domain. However, it presents challenges in terms of high production hardware costs [25] and complexities associated with the handling of metal powders. To reduce potential medical risks associated with powder exposure, stringent and costly safety measures are necessary alongside the expensive equipment [26]. Similarly, the DED techniques laser additive manufacturing (LAM) and electron beam manufacturing (EBAM) are also capable of utilising metal powder and therefore require such precautionary measures to manage the associated health risks effectively.
In contrast, WAAM offers significant advantages by using metal wire instead of powder. Wire as a raw material is easy to handle compared with metal powders. The utilisation of an arc welding source significantly reduces the need for expensive safety protocols in comparison with laser-based processes. Thus, WAAM presents itself as a more efficient and safer alternative for on-site repair and production, especially in situations where safety and cost-effectiveness are important.
WAAM leverages several welding-based techniques to produce metal parts additively, each offering unique benefits and material compatibilities. The primary WAAM processes include gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW or TIG), gas metal arc welding (GMAW or MIG), and plasma arc welding (PAW).
GTAW employs a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld; it is renowned for producing clean and high-quality welds, usable for high-melting-point and reactive materials such as titanium [27], Inconel 625 [28], and Al-alloys [29,30]. GMAW uses a continuous wire feed as both an electrode and filler, favoured for its efficiency and compatibility with a wide range of materials, including steels and aluminium [31]. Cold metal transfer (CMT) is a GMAW variant where the metal transfer occurs at lower thermal input, minimising heat impact and allowing for the precise control of deposition, which is suited for aluminium alloys [32,33] and stainless steels [34]. PAW, akin to GTAW, uses a plasma torch to focus energy more precisely on the workpiece, ideal for applications demanding tight tolerances and minimal heat distortion [35]. Rodrigues et al. [8] conducted a comprehensive study of the materials suitable for WAAM. The study suggests that all materials in the form of welding wire can be considered; however, steel, aluminium, titanium, and nickel-based alloys are the most commonly used.
Each WAAM technique varies in its applicability based on the choice of processing parameters and the material system being employed. For example, CMT’s low heat input is advantageous for materials susceptible to thermal distortion, while the precision of PAW is preferable for complex geometries requiring better surface finishes. Consequently, the choice of WAAM process is inherently linked to the material selection and the specific requirements of the manufacturing project, influencing factors such as structural integrity and mechanical performance.
The wire-based approach of WAAM ensures 100% utilisation of raw materials during the manufacturing process [32]. This efficiency is in stark contrast to that of other manufacturing techniques that often result in substantial material wastage. Notably, WAAM facilitates near-net-shape production and significantly reduces raw material requirements and, consequently, inventory costs [36], while simultaneously reducing the time required for secondary operations [37]. It further offers significant flexibility in the geometry of parts, enabling the production of complex and customised components without the necessity for special tooling [37]. This capability greatly enhances the potential for customisation and reduces the logistical challenges associated with sourcing various components from multiple suppliers.
The integration of WAAM with subtractive processes, such as milling, further underscores its potential for material savings. Campatelli et al. [5] conducted a comparative analysis between a purely subtractive milling approach and a hybrid additive-subtractive method using WAAM. Their findings indicate that the hybrid approach can realise material savings of up to 60%, accompanied by energy savings of approximately 34%. Vartanian et al. [38] pointed out that DED compared with LPBF can be ten times faster and five times lower in cost.
In general, WAAM represents a significant advance in the field of additive manufacturing, offering numerous advantages over traditional manufacturing methods. Among its primary benefits is the ability to achieve high deposition rates, with material deposition reaching 5–6 kg/h [39]. This capability enables the production of large metal components within a shorter timeframe, thus minimising the extended lead times typically associated with conventional processes, such as forging.
Overall, WAAM exemplifies a transformative approach to manufacturing that combines high efficiency with material and energy savings to provide a viable solution to today’s manufacturing challenges.
2.2. Components of a WAAM Process
WAAM systems are available in a variety of forms, but are most commonly robot-based systems [40]. Compared with traditional CNC machines, robots are more cost-efficient and flexible in use and transport. Maffia et al. [41] showed that gantry and robot-based systems are comparable in terms of quality. An automated WAAM cell typically comprises a welding torch mounted onto an industry robot. The requirements of the individual industrial application determine the need for additional hardware and security measures, such as housing and a ventilation system [42]. A brief schematic of a WAAM cell is shown in Figure 2.
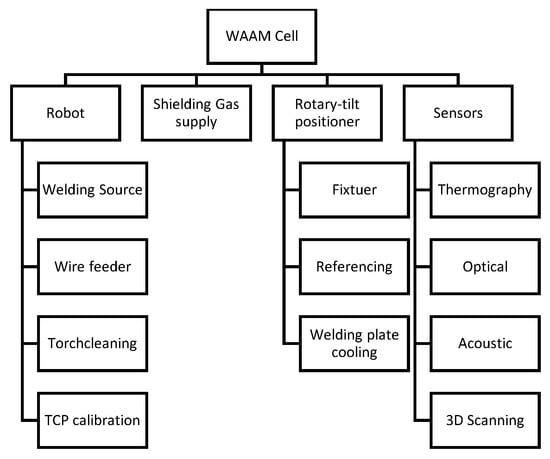
Figure 2.
Scheme for the components of a robotic WAAM cell.
The robotic arm or CNC machine is essential as the primary manipulator for executing precise movements and deposition strategies in the WAAM process. Another critical component is the welding source, which provides the energy required to melt the metal wire and deposit it onto the substrate. Closely linked to this is the wire feeder, responsible for the controlled transport of the wire material to the deposit location, ensuring a consistent and uninterrupted material flow. A rotary/tilt table is often incorporated to enhance the flexibility and range of motion during manufacturing, allowing for the realisation of complex geometries and orientations. Figure 3 shows the WAAM setup used for the experiments in this paper.
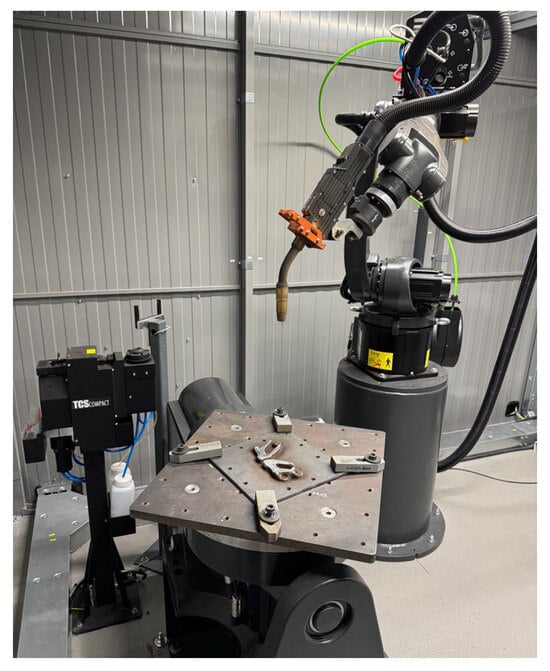

Figure 3.
Robotic cell setup for WAAM.
In addition, sensor technology can be integrated to provide further insight into process dynamics and enable closed-loop control. Other setups include refinement of the manufacturing process, where 3D scanning equipment can be used for in situ dimensional verification and quality assurance. Thermographic equipment can be employed to monitor thermal conditions throughout the process, providing real-time data to prevent overheating and ensure optimal deposition quality.
The software environment for WAAM is integral, encompassing path planning and manufacturing parameter settings that dictate the precision and efficiency of the deposition process. This software allows for the customisation of tool paths and the adjustment of critical parameters to meet the specific process requirements.
The construction and deployment of these systems are efficient all over the world. They can be assembled in standard shipping containers, thereby facilitating their transportation and installation in different locations, including remote sites such as power plants and mining operations, or areas that have been affected by disasters or do not have any industrial infrastructure.
2.3. Problem Description
Wire arc additive manufacturing represents a significant advancement in the domain of additive manufacturing, offering a potential solution to the efficient production of large-scale metal components. Despite its potential, WAAM still faces several major challenges that must be overcome in order to fully exploit the capabilities of the process and make it universally applicable in industry. Because of these challenges, traditional WAAM manufacturing relies on qualified personnel, which has prior knowledge and/or the resources for extensive testing and careful process execution. It is a common practice to meticulously plan the process layer-by-layer due to the absence of a viable option to simulate the entire process in a single iteration with parameters that align with all the restrictions and requirements of the process. In order to regulate the temperature of the workpiece, it is customary to periodically interrupt the process and allow the workpiece to cool down in a secure manner. With the suggested use of WAAM in on-site manufacturing, these resources are neither available, nor is this lack of efficiency acceptable as first-time-right manufacturing is needed but within an optimal time frame. In detail, these problems are:
- Process planning
A major challenge of WAAM is the complex process planning required to achieve consistent results in terms of near-net-shape manufacturing for complex geometries. Although WAAM as a process is well understood, complex interactions between the wide range of process parameters and their relation to the robot components and welding source add considerable barriers. These complex interactions lead to a demand for the development of comprehensive frameworks to quantify the influences and provide precise process planning and control. Kerber et al. [43] present a dynamic adaptive manufacturing strategy to improve the production of support-free overhang structures. For this, critical parameters such as wire feed speed (WFS), torch travel speed (TS), nozzle to work distance (NTWD), and torch angle must be carefully optimised [44]. Thus, there is a need for advanced software tools with a strong emphasis on the optimisation of these WAAM process parameters and facilitating the integration of WAAM into existing production environments.
- Process stability
Maintaining consistent quality of WAAM-produced components is another major challenge. Nagaraja et al. [45] highlight the critical need to minimise material defects in order to produce components with stable and improved mechanical properties, particularly when robots are employed to perform the milling postprocesses. This includes addressing inconsistencies in welding parameters, wire quality, and shielding gas flow.
Parameters such as temperature, material flow, and welding conditions significantly impact stability, with risks of defects such as cracks or porosity posing potential threats to structural integrity. The integration of WAAM into existing manufacturing systems is further complicated by these dynamics, demanding sophisticated computational solutions to ensure seamless operation. Consequently, the development and implementation of advanced software and algorithms are required to optimise production processes and maintain consistent quality.
- Standardisation and certification
A significant obstacle to WAAM is the lack of universally recognised standards for WAAM-produced components, particularly in industries with high requirements for quality and safety, such as the aerospace sector. The development of comprehensive standards and certifications is essential to ensure safety and reliability in these critical sectors. Furthermore, the qualification of personnel is a critical factor in the successful implementation of WAAM across industries. Skilled technicians, along with advanced machinery and high-quality materials, are essential to effectively execute and monitor the manufacturing process and ensure the stringent quality controls required for such critical applications.
In conclusion, while WAAM has great potential to be used as an on-site manufacturing technique, these challenges highlight the need for continued research and innovation. Addressing the issues of process planning, stability, and standardisation is essential for the overall adoption and implementation of WAAM in industrial settings.
2.4. Suggested Solution
In order to facilitate process planning through the utilisation of digital methodologies, with the objective of reducing the time and expertise required to plan on-site for a component within the production process, the authors propose the implementation of digital twin methodologies to address the aforementioned challenges. The utilisation of these methodologies has the potential to reduce the time required to produce a part without increasing the risk of unsuccessful production.
The integration of digital-twin methods offers a comprehensive solution to address the diverse challenges encountered in WAAM processes. Digital twins provide a virtual replica of physical systems, allowing for in-depth simulation and predictive analytics [46]. This capability enables the optimisation of critical process parameters, such as amperage, wire feed speed, and temperature distribution, thereby enhancing precision and efficiency in planning. With these predictive models, the necessity for extensive test runs can be significantly reduced, which in turn accelerates the implementation and advancement of WAAM processes. Moreover, these capabilities enable the implementation of predictive maintenance strategies. By examining data associated with equipment wear and tear, they can provide early warnings of potential maintenance needs, allowing for proactive intervention before failures arise. These predictive strategies help to avoid unscheduled downtime and further support continuous process improvement by iterative learning and optimisation.
By integrating a wide range of sensors and, in some instances, machine learning techniques [47], digital twins are capable of monitoring production activities in real-time [48]. This allows for the immediate detection of deviations and automatic adjustment of operating parameters to maintain consistent quality standards.
In WAAM, controlling interlayer temperature is vital to prevent unwanted phase transformations. The interlayer temperature denotes the temperature of a deposited layer immediately preceding the addition of the subsequent layer. It is a crucial parameter that influences the microstructure, residual stresses, and overall mechanical properties of the final part. Maintaining an optimal interlayer temperature helps in controlling material properties such as grain structure, reducing defects like a lack of fusion or excessive residual stresses.
Research indicates that workpieces deposited without dwell time exhibit no cracking and uniform high-hardness distribution. Maintaining the workpiece temperature above the martensitic transformation point through continuous heating is essential; a drop below this threshold can lead to temper softening in the upper layers. Therefore, interlayer temperature significantly influences deposition quality [49]. Furthermore, studies have shown that increased heat input during each weld pass results in lower residual stress levels along the welding direction of the component walls [10]. Digital twins can simulate temperature evolution and predict areas susceptible to temper softening, enabling optimised deposition strategies. Through virtual testing, the digital twin can provide in-depth thermal analysis by modelling heat-affected zones and residual stresses, critical to minimising the risk of stress-induced cracking or distortion. By analysing the location and extent of heat-affected zones, the deposition path and process parameters can be dynamically adjusted to optimise heat distribution. This proactive adjustment reduces thermal gradients, minimises residual stresses, and ultimately improves repeatability, resulting in higher-quality finished products. By facilitating virtual validation of designs and processes, digital twin methods can enable on-site production to achieve significant cost savings and streamline product development cycles. Reducing the reliance on prototypes saves material and production costs, while facilitating the implementation and scaling of WAAM.
Digital twins have been shown to enhance production process traceability by precisely documenting each step, thereby creating a data-rich environment that supports compliance with stringent industry standards. This comprehensive documentation facilitates adherence to frameworks such as ISO 15926 [50], which standardises data integration, and IEC 62443 [51], which focuses on cybersecurity in industrial automation and control systems. Furthermore, the implementation of standardised virtual-twin models facilitates cross-industry certification, streamlining compliance processes and promoting interoperability.
As this paper will subsequently provide a more in-depth discussion of relevant standards and certification frameworks, this section aims to highlight the contributions of digital twins to standardisation and regulatory alignment. The utilisation of digital twins in industry fosters enhanced quality control and optimised efficiency, and ensures compliance with certification protocols across diverse sectors. Overall, the strategic implementation of digital-twin technology within manufacturing systems, especially in areas like WAAM, effectively addresses a multitude of technical and logistical challenges. It facilitates smoother integration and scaling of production capabilities, making it a transformative approach for enhancing efficiency, quality, and competitiveness in the manufacturing sector.
3. Digital Twin Methods
3.1. Digital Twin Definition
The term digital twin was first introduced by NASA in [52] for aerospace systems. They defined a digital twin as “an integrated multi-physics, multi-scale, probabilistic simulation of a vehicle or system that uses the best available physical models, sensor updates, fleet history, etc., to mirror the life of its flying twin”.
Modern publications further distinguish between digital shadow and digital twin. The digital shadow represents a virtual replica of the real system and its current status. Sensor data are recorded and incorporated into the virtual representation. The fundamental requirement for a digital twin is the establishment of bidirectional communication [53]. This makes it possible to adapt the real system to the states of the digital twin. Both systems can therefore influence each other (Figure 4). Accordingly, the DT can be equipped with various simulation methods and influence the process based on the anticipated results. From this, the three basic functionalities of a digital twin are derived: predict, monitor, and control [54].
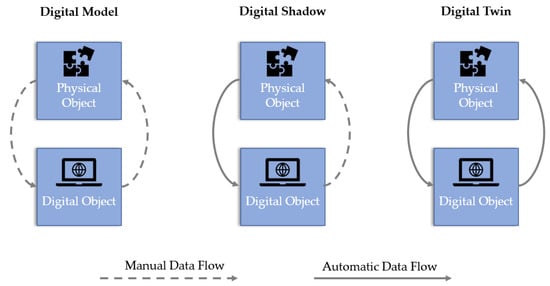
Figure 4.
Contrast of data flow in digital model, shadow, and twin frameworks according to [55].
ISO 23247 [56] establishes a universal framework designed to support the creation of digital twins in manufacturing, while defining essential terms and setting them into context. The suggested framework can be applied to observable manufacturing elements, including personnel, equipment, materials, manufacturing processes, facilities, environment, products, and supporting documents. According to the standard, a digital twin is defined as a “fit for purpose digital representation of an observable manufacturing element with synchronisation between the elements and its digital representation” [56] (p. 3), where the observable manufacturing element (OME) can represent a “physical presence or operation in manufacturing” [56] (p. 3).
Digital twins are applicable throughout the entire product lifecycle. In order to improve the performance of manufacturing systems, it incorporates aspects of the physical and virtual environment, as well as computational techniques. These include, among others, historical performance, external data sources, virtual testing, optimisation, and prediction. [56] (p. 4).
This integration positions digital twins to assist in identifying anomalies during manufacturing and accomplish a range of functional objectives, including real-time control, off-line analytics, predictive maintenance, health diagnostics, and synchronous monitoring, alongside the optimisation of manufacturing operations management (MOM), in-process adaptation, Big Data analytics, and machine learning.
In practical applications, digital twins enable the comprehensive monitoring of specific attributes of operational manufacturing elements (OMEs) by continuously updating the twins with relevant operational and environmental data, such as status, conditions, product geometries, and manufacturing resources. This capability enables digital twins to reconstruct historical states or anticipate future states of their respective OMEs. Ultimately, the enhanced visibility of processes and execution provided by digital twins facilitates improved business collaboration and generates numerous efficiencies, such as improvements in in-loop planning and validation, enhanced understanding of manufacturing elements production scheduling assurance, dynamic risk management, and cost reduction, as well as process and part/assembly traceability [56] (pp. 4–6). These benefits contribute to the optimisation of manufacturing processes, leading to enhanced efficiency and streamlining of the manufacturing process.
3.2. Recent Developments of Digital Twin in Metal Additive Manufacturing
Bong Kim et al. [57] proposed a generalised DT framework based on ISO 23247 and tailored for WAAM, emphasising real-time decision-making and control. The developed framework is supposed to receive comprehensive data during the WAAM process, such as geometrical accuracy, mechanical properties, and 1D, 2D, and 3D signatures. The communication architecture is based on the open-source, cross-platform OPC UA standard, which ensures seamless interoperability across diverse operating systems.
Building further upon ISO 23247, Mu et al. [58] developed an online simulation system embedded within a metallic additive manufacturing digital twin. Their integration of machine learning techniques enables the prediction of baseplate distortion, which is instrumental for model-predictive control and topology optimisation, thereby advancing the capabilities of additive manufacturing digital twins in general.
Kang et al. [59] focused on exploiting edge computing for digital twins, addressing the challenges associated with real-time data processing. Their framework was specifically applied to a WAAM system and demonstrated superior data processing speeds compared with other frameworks based on ISO 23247, providing an important contribution toward more efficient real-time data processing in manufacturing environments.
Mahdi et al. [60] developed a framework at the enterprise management and individual asset level that uses the OPC UA standard to support communication, security, and real-time control. The framework is characterised by the integration of 3D visualisation, real-time defect prediction, convolutional neural networks (CNNs), and structured data management. In particular, an anomaly detection module using CNNs was developed for a six-degree-of-freedom industrial robot operating in a WAAM deposition scenario.
Mu et al. [58] developed an adaptive online simulation model for predicting distortion fields in WAAM. The presented model comprises a diffusion model architecture, generative adversarial network, and recurrent neural network to predict distortion fields during the deposition process using laser-scanned point clouds. The model is pretrained offline using the finite element method. Experimental validation showed that the proposed model outperformed the pure finite element method by 143% and artificial neural networks by 151%. Future efforts will be dedicated to the integration of the proposed online simulation model into planning and control.
Karkaria et al. [61] presented a digital twin framework tailored to laser-directed energy deposition processes for real-time predictive control of process parameters. The presented framework encompassed a surrogate model utilising long-short-term memory-based machine learning leveraging Bayesian inference to predict part temperatures. The model achieved an R2 score of 0.75 for thin-wall geometries. Furthermore, the framework includes the Bayesian optimisation method for time series process optimisation to determine the optimal laser power profile. Future work will be dedicated to the implementation of the presented framework to a physical DED system.
Bevans et al. [62] introduce a data-integrated digital twin approach for the in situ qualification of LPBF part quality, predicting porosity, meltpool depth, grain size, and microhardness with an accuracy exceeding 90% (R2). The presented approach uses an experimentally validated computational thermal simulation and sensor signatures obtained by thermal and optical tomography imaging cameras as the input to a k-nearest neighbour machine learning model.
The concerted research efforts in this area focus on the development of a comprehensive DT framework tailored to the WAAM process, with individual components already implemented at various scales. ISO 23247 remains a widely adopted foundation in this effort. The evolution of machine learning techniques and neural networks augments the precision and efficacy of process monitoring. Frameworks in this area emphasise the importance of real-time communication and efficient data storage and management. The OPC UA standard, known for its real-time capabilities and interoperability, has emerged as a central element in these recent developments, further enhancing the potential of digital twins in WAAM.
3.3. Simulation Tools in Digital Twins
An important capability of a digital twin system is the integration of sophisticated algorithms developed to predict the future state of complex production systems. This requires the availability of process-relevant data in an appropriate format, as data imbalance will adversely affect the prediction results of the algorithm [63]. In DT, research has been carried out to enable algorithms to fill the gaps between the sensor data and to generate future data in order to be able to predict the characteristics of the real-world object [64]. These capabilities extend the traditional definition of a simulation, limited to experimenting with static models as in [65]. Robotic WAAM systems require comprehensive simulation algorithms to perform accurate prediction and offline experimentation applied in process planning, simulation of the system kinematics, and potential collisions among various components, such as the robot, workpiece, fixture, and turn tilt table. These simulations are crucial to ensure that the process plan will not lead to any unwanted collisions. Comparable predictions are required for each type of manufacturing process and are therefore already state-of-the-art. Software systems specialised in kinematics simulation are widely used in off-line design software, as well as in numerical control systems [66,67]. For kinematic components with dynamic geometry changes, such as tubes or wires, additional, more complex simulations are required [68].
A critical component of a complete collision prediction scheme is the simulation of the actual workpiece shape during the manufacturing process. Although simulations of the workpiece shape in milling processes have been commercially available for two decades [69,70,71], the simulation of the workpiece shape during additive processes remains a topic of scientific exploration [72]. This is because, in subtractive simulations (like milling, turning or grinding), the resulting shape can be calculated using mathematical or geometric methods with sufficient accuracy. The simulation methods utilise constructive solid geometry or rasterisation methods to approximate the toolshape, which does not change during the process [12,13]. The workpiece shapes are normally represented either with triangle meshes or triple ray representations or dexels. In additive manufacturing, especially in WAAM, the shape of the tool or, here, the volume that interacts with the workpiece is constantly changing and depends on temperature and a lot of external process influences. Therefore, a prediction of the current workpiece shape only utilising simple geometric methods is not directly possible. For a reliable prediction of potential collisions in an additive manufacturing process, knowledge of the current workpiece shape is indispensable. As suggested by the digital twin concept, the DT should include the capability to optimise trajectories based on algorithmic simulations. Complete path optimisation is not possible without information about the current shape of the workpiece, since fast and efficient movements close to the changing workpiece require detailed knowledge of its shape. The challenges associated with additive manufacturing shape simulations for WAAM include the prediction of weld bead shape, which has a significant effect on layer height and width. Irregularities in the weld bead can therefore cause large deviations in the layer geometry. The parabolic shape of the weld beads means that the distance d between them has a significant effect on the layer height. Consequently, erroneous layer distances invariably result in irregular layer heights [73]. Since this subject is not covered by current simulation tools, the optimum weld bead distance must be determined experimentally. Figure 5 illustrates the influence of weld bead distance (step-over). Excessive step-over (a) results in the formation of gaps and a wavy surface texture due to insufficient overlapping. As the step-over decreases (b), the valleys are minimised, resulting in a smoother surface. Optimal step-over distance (as shown in c) ensures a flat surface profile and a consistent layer height, which is the most desirable geometry to ensure consistent quality. On the other hand, if the step-over is excessively narrow (d), significant overlap occurs, leading to increasing layer thickness and buildup.
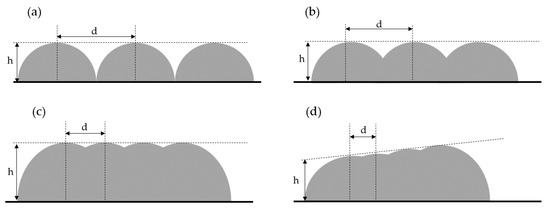
Figure 5.
Weld bead overlapping with decreasing step-over distance d from (a–d) based on [73].
In order to predict the weld bead, simulation tools must determine the influence of thermal energy that is introduced into the workpiece during the WAAM process. Finite element simulations are well-established in predicting temperature gradients during welding. These FEA simulations offer good predictions for simple shapes [74]. However, these results are also affected by the lack of shape prediction. Simulations capable of predicting temperature gradients and weld bead shape, and therefore important information for weld path planning, such as actual layer height and potential part deformations, do not exist. Moreover, the state of the internal conditions of the part, including its metallic structure, is unknown during the manufacturing process and cannot be predicted, although the ability to influence these properties represents a significant advantage in the production of additive workpieces [49]. For the planning of post-processing and the subsequent final workpiece, it is of substantial importance to have knowledge of parameters like the actual shape and metallic structure. Without such knowledge, effective planning of post-processing steps, such as grinding or milling, is not possible. Consequently, additional time-consuming steps, such as scanning or radiography for geometry and defects, are required.
In addition to the simulation itself, the results from the simulations must be transferred through the virtual process chain to enable the subsequent process step calculations to integrate the data into the subsequent calculations. Consequently, the interfaces must be equipped to facilitate the transfer of data to the subsequent process step. This requirement persists even in scenarios where an interface architecture is employed, incorporating a centralised data management component. Consequently, process tools must be equipped with the capability to utilise the supplementary information.
As simulations cannot be fully utilised to create a virtual representation of the WAAM process chain, the acquisition of sensor data gains more importance to retrieve missing data during the running process and overcome gaps in predictability because of current technical limitations in the simulation algorithms.
3.4. Data Exchange
Effective data exchange is a cornerstone in the implementation of digital twins within additive manufacturing processes. Achieving a synchronised digital representation necessitates the continuous integration of real-time data from various sources. In WAAM, this includes monitoring parameters, such as the substrate plate temperature, component temperature, welding settings, wire feed rate, and the precise movements of the CNC or robot axes and consequently the tool centre point (TCP). A critical aspect of this data exchange is interoperability, which is effectively addressed by employing standardised protocols like the OPC Unified Architecture (OPC UA). OPC UA is a cross-platform, open-source standard designed to ensure secure and reliable data exchange from sensors to cloud applications, thus facilitating interoperability across various industrial equipment and systems. Additionally, it is essential to emphasise data security and privacy. Protecting sensitive information from unauthorised access while ensuring data integrity and confidentiality is paramount. OPC UA directly addresses these concerns by incorporating robust security measures, including user authentication, access control, and data encryption. The protocol employs industry-standard transport layer security (TLS) for message signing and encryption, safeguarding data during transmission. The integration of real-time data enables advanced analytics and machine learning applications, which analyse collected data to extract valuable insights and perform predictive assessments, optimising production processes. For instance, the analysis of temperature fluctuations and welding parameters can lead to real-time adjustments that enhance product quality and minimise material waste. Digital twins of metal AM systems offer substantial potential for optimising build speed and part performance, reducing costs, and increasing the utility of metal AM for a broader range of manufacturing applications [75]. Implementing feedback loops is essential for real-time adjustments within the production environment. By continuously analysing data within the digital twin framework, the system can promptly identify deviations and implement corrective measures, thereby ensuring that the manufacturing process remains within the desired parameters. The digital twin enables the manufacturing process to be continuously monitored, studied, and optimised in real-time. Digital twins (DTs) have emerged as an important tool in the additive manufacturing industry, allowing manufacturers to enhance the process, improve product quality, decrease costs, and accelerate innovation. However, the development of DT in AM is an iterative and continuous process [76]. This approach aligns with the principles of Industry 4.0, which emphasises the digitisation and interconnectivity of production systems [77]. DTs, supported by secure and interoperable data exchange protocols like OPC UA, enable a more flexible and adaptive manufacturing environment. This integration allows for seamless communication between machines, sensors, and control systems, fostering an ecosystem where data-driven decisions enhance efficiency and innovation [78]. However, several challenges must be addressed to fully realise these benefits. Selecting appropriate technologies tailored to specific manufacturing requirements is crucial. Ensuring data quality and accuracy is another significant concern, as erroneous data can lead to flawed analyses and suboptimal decisions. Additionally, optimising data processing and utilisation requires a well-structured approach to manage the vast amounts of information generated in real-time, necessitating scalable data architectures and efficient algorithms. In summary, effective data exchange within digital twins for additive manufacturing processes hinges on real-time data integration, interoperability through standards like OPC UA, and robust data security measures. Addressing these elements facilitates advanced analytics, real-time feedback mechanisms, and seamless integration into Industry 4.0 frameworks, thereby enhancing the efficiency and adaptability of modern manufacturing systems.
3.5. Path Planning
Path planning in WAAM requires advanced computational strategies to optimise the paths in terms of efficiency and accuracy due to the dynamic interaction between the welding parameters and the material properties and geometries. For this reason, significant research efforts are being dedicated to the development of new deposition strategies [79,80].
State-of-the-art research has addressed these challenges through advanced path-planning approaches. Ding et al. [81] proposed a tool-path generation model that decomposes layers into polygons, filling each area while automatically generating a closed-loop tool path to minimise start/stops and crossovers of weld paths. Further developments in WAAM path planning were introduced by Ding et al. [82]. They provided a medial axis transformation method that divides the slice geometry into bisector segments, where branch points are created at intersections of more than two segments. Paths are then generated by recursively offsetting counter-clockwise around the segment connecting two branch points, ensuring a more efficient and controlled deposition process. Integrating such methodologies into CAD/CAM software enhances process reliability and precision, addressing key challenges in WAAM path planning. There are several more path strategies that have been developed for specialised geometries like 90° walls [30] or T-type structures [83].
Rodrigues et al. [8] investigated discontinuities found to be caused by layers starting and ending at the same position. At the beginning of the deposition, excessive heat dissipation reduces weld penetration, whereas at the end of the layer, insufficient heat dissipation due to elevated temperatures leads to a drop in layer height. This inconsistency accumulates across successive layers, ultimately compromising the process. To mitigate these issues, it is crucial to dynamically adjust welding parameters according to the different phases of layer deposition. Additionally, seamless communication between the robotic system and the welding source is essential to ensure precise control. All process parameters and adaptations must be pre-planned within the CAD/CAM software to optimise deposition quality and maintain geometric accuracy.
In WAAM, there are several additional challenges in path planning that can significantly affect the quality and integrity of fabricated components, particularly when depositing overhangs without support structures. In such cases, the molten material lacks underlying support, leading to potential sagging or collapse, which necessitates advanced path-planning strategies to ensure structural stability. Since additive manufacturing typically builds in a vertically upward direction perpendicular to a horizontal worktable, depositing near-horizontal features without temporary supports can be particularly challenging. A potential solution involves utilising a 6-DOF robotic system to control the torch, combined with a pan/tilt table, enabling more flexible deposition strategies. Additionally, a multi-directional approach, as tested by Yuan et al. [44], further enhances the ability to fabricate complex geometries without supports. Ultimately, manufacturing support-free complex parts requires not only advanced hardware components, but also precise path-planning software capable of accurately calculating robot movements and optimising torch-to-workpiece orientation.
4. Real-World Sample-GE Aircraft Engine Bracket Challenge
To demonstrate the necessity and applicability of digital twin methods within the context of on-site production, the authors used a real-world sample to implement the aforementioned methods. The goal was to demonstrate the functionality of individual methods and to verify their interoperability with each other qualitatively. The resulting current state encompasses only direct communication from the physical entity to the digital entity, therefore representing only a digital shadow. This provides an indication of the areas in which digital twin methods require enhancement to address the constraints mentioned in Section 2.
The “GE Aircraft Engine Bracket Challenge” was initiated in 2013 with the objective of leveraging a “crowdsourcing” approach to optimise and manufacture a titanium aircraft engine bracket. The primary objectives of this optimisation process included reducing the weight of the component and the utilised resources during production. Constraints imposed included preserving the structural capabilities while ensuring conformity to the maximum design dimensions and mechanical specifications [84]. This challenge, although started in 2013, is still relevant nowadays and has become an accepted standard dataset for design optimisation research [85,86].
The following discusses the manufacturing of the aerospace bracket by Ruhr West University of Applied Sciences using the WAAM cell presented in Section 2.2, as well as the digital methods employed. These digital methods are discussed in more detail with a view to identifying potential applications in digital twin technology.
4.1. Application of WAAM to the Sample
The design of the bracket serves as a well-known, realistic, and industry-related part. Common to all older solutions proposed within the challenge is the emphasis on optimising the component for 3D printing using metal powder-bed manufacturing techniques, like laser-based powder-bed fusion. For a WAAM-based additive manufacturing approach, the optimisation must respect different design constraints. The part must be and remain “WAAMable”, i.e., the optimised part must not have any overlapping surfaces or wall thicknesses that cannot be achieved within the process parameters. A new structural optimisation tool is needed to ensure that the part can be built with reduced volume and manufacturing costs, but within specified capabilities. Although the concept of on-site production does not directly imply any form of optimisation of the part, it is a crucial step in ensuring that production and the product itself are efficient.
Optimisation must be carried out in a semi-automated process. This is to ensure that a single part is ready for production in the shortest possible time in the on-site manufacturing scenario. Here, the product “Möbius” from Rafinex S.à r.l. in Senningerberg, Luxembourg [87] was used to optimise the original part while respecting the constraints of the WAAM process. Figure 6 shows the original part geometry compared with the optimised geometry as a triangle mesh. The algorithm used in the tool managed to reduce the volume to 21% of the original volume (463.270 mm3 and 97.320 mm). The functional surfaces were not altered during the process. The optimised part is split into two pieces, as the weld base plate, which is not within the optimiser geometry, joins the two halves of the bracket. The optimisation process was solely focused on the geometry of the object, with no consideration given to the necessary levels of stiffness or rigidity.

Figure 6.
Rendering of the original part (left), optimised volume, and surface of the part using Rafinex Möbius [87] (right).
4.2. Setup of the WAAM Cell
The additive process was carried out using a Reis Robotics WAAM Cell, with a KUKA KR10 R1440 robot with 10 kg capacity. The control unit is a KR C5 together with a KP2 HV500 tilt turn positioner table. As a welding source, an EWM Phoenix 402 Expert was used. To ensure security, this system is placed in a closed enclosure that also allows the extraction of the welding fumes using a KEMPER WeldFil Compact extraction system. Systems like this can be integrated into shipping containers that then directly serve as an enclosure.
4.3. Applied Digital Twin Methods
The basis for the implemented digital twin methods is a universal digital shadow developed in the 3D engine Unity, which is able to represent individual robot cells. Although this 3D engine was originally designed for use in computer games, it is becoming more and more a standard framework for simulation environments [88]. A network connection using OPC/UA was established to communicate with the robot, monitoring in situ, among others, axis positions, velocities, process parameters, and programmable logic controller (PLC) states. Simultaneously, the data are recorded by the robot system locally. The historical process data are stored in an extensive database and can be used to simulate processes using digital twin methods. This allows the simulation and results to be correlated in order to identify the relationship between process parameters and results, which in turn allows for a more precise prediction of the process to be made. In the future, a direct connection between the welding current supply and the digital twin is planned via OPC/UA. Furthermore, the first virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) functionalities have already been implemented. They enable the operator to monitor the process more effectively on-site or remotely. Simultaneously with the implementation of VR/AR technologies, a training programme is currently being developed in order to facilitate the training of qualified process operators. This directly addresses a major challenge, the support for educating qualified personnel; see Section 1.
The developed DT methods were designed according to ISO 23247 following a modular approach. Each functionality was developed in an independent encapsulated system. The aim was to allow the DT to be highly customisable and applicable to various individual robotic manufacturing environments. In the future, particular emphasis will be placed on the development of comprehensive APIs, enabling the DT to be implemented along the entire software chain. This enables the simulation results of the DT to be fed back into the CAD development for topology optimisation or the current sensor data regarding the process status to be incorporated into the path planning of the subsequent paths.
4.4. Utilisation of Sensors for the Digital Shadow
A variety of sensors can be applied to improve the WAAM process. In this regard, infrared temperature sensors have already been applied with the aim of measuring the interlayer temperature. The interlayer temperature has a high influence on the achieved material properties. Additionally, it is used to prevent the part from overheating during the welding process, as high temperature decreases the shape accuracy. Furthermore, the sensors can be used to evaluate the results of future temperature simulations. The temperature control system could be expanded to incorporate a thermal camera overlooking the process. In addition to measuring the temperature, a thermal camera can be used to monitor the weld bead shape and apply corrective actions if deviations from the planned result occur.
Further, the implementation of several more sensors is planned. This includes an acoustic sensor, which can be used to detect irregularities during the weld process. Bevans et al. [89] applied acoustic sensors to achieve reliable fault detection. Other sensors monitor external process data, like the mixture of the shielding gas. With the increasing number of sensors, the fusion of the sensor data becomes more and more challenging. Timestamps are provided with each measurement, but depending on the location of the sensor, the calculation of the exact influence of the measured data in time and space needs extensive calculations.
4.5. CAM for WAAM
Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) for process planning is an important item in the virtual process chain to ensure automated manufacturing. The aim is to automate complex path planning and parameter selection during the whole manufacturing process and therefore reduce preparatory tasks considerably. Modern CAM software offers a wide range of functionality and customisability for various manufacturing tasks.
In this context, the ‘toolpaths for additive’ engine contributed by ModuleWorks GmbH in Aachen, Germany was successfully employed for the cross-process CAM of the hybrid processing chain, enabling 3 and 3+2 axis additive and subtractive manufacturing in the same reference frame. In order to validate and control the toolpath planning, the first layers were analysed using 3D scanning (EinScan HX from Shining 3D in Hangzhou, China with a scan accuracy of 0.04 mm). Figure 7 shows that, within the same layer, the height values dz differ significantly. A height difference of 4.37 mm was measured between point a (highest) and point b (lowest). The underlying cause of this issue can be attributed to inadequate optimisation and the failure to consider the aforementioned factors during the process of path planning.
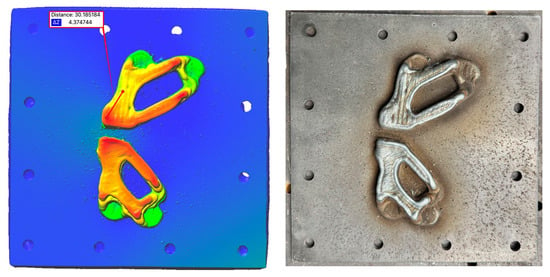
Figure 7.
Height deviation in early layers of the unoptimised WAAM process.
To produce flawless parts, path planning and parameter selection must be carefully matched, as the manufacturing parameters affect the weld bed shape, which in turn affects the path planning. It is therefore currently necessary to carry out extensive tests to optimise the path planning parameters prior to manufacturing. This includes tests to determine the required distance between two parallel paths, as well as perpendicular paths. As stated in Section 3.5, the weld bead can be characterised by its asymmetrical shape regarding the start- and endpoints. This may result in an uneven infill distribution. Therefore, an optimised path planning approach has to be tailored to the part geometry. One solution is the application of the infill path in a zigzag approach. While this approach may compensate the asymmetric weld bead geometry, it could result in an unfavourable heat distribution. Another solution is to apply a variant offset from infill to boundary regarding of it being a startpoint, endpoint, or a parallel path. This strategy has already been applied manually to simple test t-crossing geometries. For this purpose, t-crossings with different offsets between infill and boundary were welded. The distance from the boundary to infill was varied from 1 mm to −4 mm. In total, 21 lanes were welded travelling towards the boundary and 21 lanes in the opposite direction. The optimal offset at which the intersection had the lowest height deviation was determined using 3D scanning. The results are shown in Figure 8. The red boxes highlight the weld beads with the lowest height deviation and therefore the optimal parameter. However, such functionality still has to be implemented within the automatic path planning.
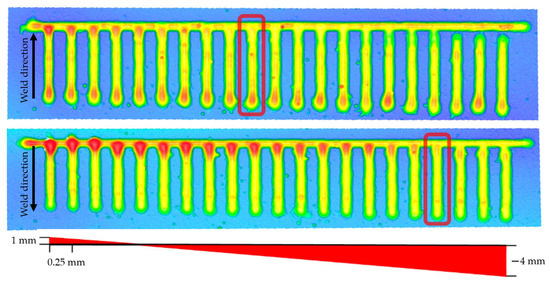
Figure 8.
Height analysis of t-crossing testing geometries, including an indicator for the distance between infill and boundary.
Another WAAM-related problem is the heat development during the manufacturing process. The temperature of the part significantly influences the weld bead [90,91] and mechanical properties [92,93] of the resulting part. The heat dissipation itself is dependent on the part geometry. Therefore, a comprehensive thermal simulation or in-loop parameter adjustment is necessary to achieve consistent results [94].
4.6. Simulation of the Part Shape and Inner Temperatures
During the definition of the WAAM paths, knowledge of the workpiece temperature during the process is essential for ensuring a proper interlayer temperature. This is essential to prevent the occurrence of any potential collapse of the workpiece. During the manufacturing process, the interlayer temperature is usually monitored and controlled using thermal sensors and an active cooling system. One simplistic approach is to apply extensive wait times between each layer to ensure that the temperature is dropped sufficiently. Although this is a secure method of avoiding high temperatures, this leads to increased production times. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that elevated levels of cooling can result in an increased tendency for cracking and the formation of pores.
Knowing the temperatures in advance during process planning offers several advantages. There is no need for complex measurement of the current temperature or to pause the process between the layers. Moreover, a temperature simulation enables the determination of optimal wait times and the alteration of toolpath planning to weld on areas of the workpiece that have already been cooled down. In [95], a dexel-based metal cutting and deposition simulation is combined with a temperature prediction based on the Lattice-Bolzmann method [95]. This is directly integrated into the toolpath planning algorithm when defining a build-up strategy and print order for a given part geometry. More general approaches utilise finite element approaches using standard software simulation tools [74]. Temperature simulation via FEA is well tested and there are various setups for different material combinations; however, these simulations are time-consuming and can therefore not be applied when calculating weld paths simultaneously. Both approaches provide a good picture of the current temperature within the workpiece. As illustrated in Figure 9, the temperatures are represented by a colour gradient following the termination of the weld paths. In this instance too, a simulation of the weld shape is absent, and a simplified model was utilised instead.
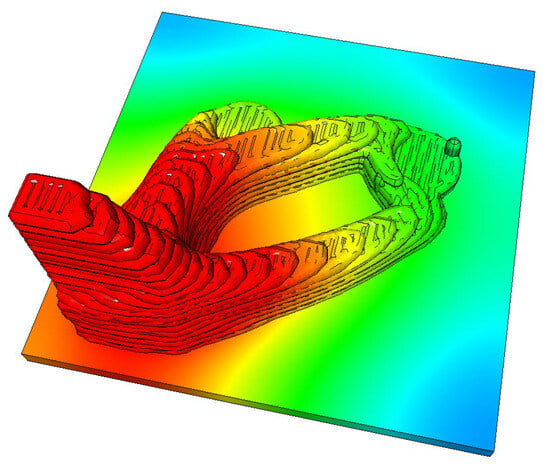
Figure 9.
Temperature simulation in an incremental approach utilising the Lattice-Boltzmann method as in Mauthner et al. [95].
The current challenges concerning temperature issues, in conjunction with the issue of determining the weld bead shape, hinder the advancement of a printed shape simulation that is as close to the real workpiece surface, as it is already common in simulations of cutting processes, such as milling or turning. This discrepancy gives rise to a number of uncertainties and underscores the necessity for further research to facilitate the development of automatic CAM for additive processes, particularly WAAM. However, this is a prerequisite for the goal of efficient on-site production without the need for expert knowledge on site.
4.7. CAM for Milling
Whilst path planning for the additive part of the process has the aforementioned challenges, the succeeding subtractive part of the process (e.g., milling, grinding, or waterjet cutting) is, as a result, more challenging than a conventional, purely subtractive process. This is again due to the unknown state of the actual shape of the part and its internal metal structure. As mentioned above, the additive simulations of the shape cannot currently predict the final shape with the accuracy required to use it for effective planning of subsequent process steps. Figure 10 illustrates the targeted surface and the predicted surface using an additive material simulation.
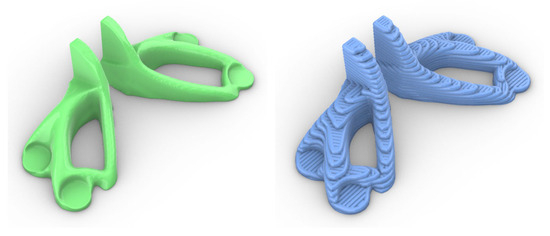
Figure 10.
Digital representations of the WAAM bracket; the target shape as a result of the Rafinex optimisation (left) and simulated shape using ModuleWorks AddSim (right).
The weld beads in the simulation are clearly separated and distinguishable, since this is an idealised view of the process not concerning weld flow and other temperature influences. This model is not suitable for utilising it as an initial stock in planning a subtractive process. For the test part, this was solved using sensors for scanning the surface shape. In these first tests, the internal TOF (time of flight) lidar sensor of an Apple iPhone 15 pro was used. Although they lack the precision of professional systems, these quick and simple scans already allowed the digital process chain to be tested. These scans show that the weld beads and the part are already deformed to an extent that requires careful consideration when planning the milling process. In Figure 11, two renderings show that, within the scan picture (left), the weld beads are not visible. On the right side is the distance comparison of the deformations of the scan. The colours indicate sufficient, excess material (green) and insufficient material deposition (red).
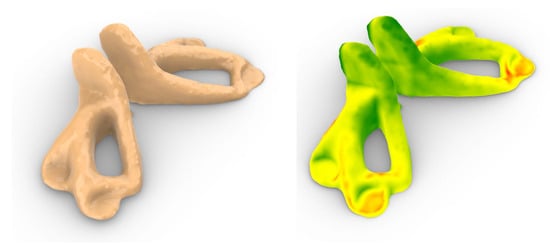
Figure 11.
3D-Scan of the actual workpiece after WAAM (left); comparison of the scan with the target surface as in Figure 10 (right).
This quick evaluation also showed that referencing the exact position of the part needs to be included in process planning. In order to use the digital representation of the target part and the scan of the actual part to plan further machining, both need to be aligned in 3D space. The current shape deviates from the target surface and the deviation is, as shown, not constant nor only in positive offset. There are two approaches to calculating the deviation on a single point. When a precise reference of the part to the target part is possible, e.g., markings on a baseplate, this reference can be used to align the geometries. This will result in an exact placing. However, with the occurring deformations, this can lead to surface areas that must be processed, but in this context, have already insufficient material. Therefore, the process with this part could not be continued.
The second approach is to reorient the target surface in the actual surface shape in a way that the deviation across all surface points is minimised. This was achieved by using an additional optimisation approach, which placed the target part in the actual workpiece minimising the mean deviation as in Figure 11.
For milling the part, standard milling 3+2 operations have been used to postprocess the functional surface areas (Figure 12). The operations included planar milling and drilling in the surface areas around the six boreholes of the original part.

Figure 12.
Final part after WAAM process before milling (left) and while milling (right).
The tests with this real-world sample show that digital twin methods are not only helpful, but necessary to have an automated process that can be used for on-site production. However, it is also evident that some methods, such as temperature and shape simulation, are not yet fully applicable. In addition, it was also evident that the process development is still composed of various only loosely connected process steps and software interactions. To reduce the need for expert personnel, these steps and software tools need to be integrated into one comprehensive environment. This allows for efficient training of personnel and ensures that any part can be produced on-site within a short time. Within the utilised environment, this was shown by the DT integration into the Unity 3D engine version 2022.3.28f1 from Unity Technologies in San Francisco USA.
5. Outlook
In the context of this paper, the necessity and applicability of digital twin methods in robot-based WAAM have been shown. All examined components of the framework yield a high potential for optimisation in near-net-shape manufacturing, material properties, as well as time and energy consumption throughout the process. The functionality of primary components has already been assessed qualitatively. Future research efforts will be dedicated to the implementation of these methods for quantitative assessment using real-world examples.
In general, the integration of advanced technologies, such as digital twins, is essential to optimise the manufacturing processes and ensure high-quality results. WAAM is valued for its ability to efficiently produce large metal parts, but there are several challenges that need to be addressed to fully realise its potential. Adaptive path planning, complemented by digital twin methods, plays a critical role in overcoming these challenges by enabling real-time monitoring, simulation, and process optimisation.
The key aspects of robot-based WAAM include:
- Integration and feedback loops: Establishing a dynamic feedback system through digital twins supports continuous optimisation and improvement of the manufacturing process;
- Thermal management: Effective management of heat distribution reduces thermal gradients, minimising residual stresses and distortion in the parts produced;
- Dimensional accuracy and surface finish: Real-time adjustments ensure that the parts produced meet precise dimensional specifications and have a high-quality surface finish;
- Residual stresses and distortion: By accurately predicting and controlling stress accumulation, potential distortion in the part is minimised, improving part integrity;
- Weld direction and torch angle: Optimising weld paths and torch angles improves material flow and layer adhesion, resulting in higher-quality assemblies;
- Macroscopic material properties: Tailoring material properties through predictive simulation ensures the final product meets specific performance criteria;
- Post-processing considerations: By streamlining the manufacturing process, digital twins reduce the need for extensive post-processing, resulting in time and cost savings.
Taken together, these aspects highlight the importance of integrating adaptive path planning with digital twin methods into the WAAM process, resulting in enhanced control, precision, and quality of manufactured components. By addressing these critical factors, manufacturers can significantly advance the capabilities and efficiencies of WAAM, further advancing its industrial applications. This paper sets out the argument that this is a critical, yet as yet unfulfilled, component that is essential for enabling WAAM as a process for the on-site production of arbitrary metal parts. It has been demonstrated that, by addressing these challenges, a significant contribution can be made to the resolution of impending issues in the domain of logistics chains.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.S. and M.S.; software, K.V.; writing-original draft preparation, S.S., K.V. and M.S.; writing-review and editing, S.S. and K.V. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding. Internal funding by Hochschule Ruhr West within the project “Digitalisierung des Robotik-Labors”.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AM | Additive manufacturing |
| AR | Augmented reality |
| CAD | Computer-aided design |
| CAM | Computer-aided manufacturing |
| CMT | Cold metal transfer |
| CNC | Computerised numerical control |
| CNN | Convolutional neuronal network |
| DED | Direct energy deposition |
| DS | Digital shadow |
| DT | Digital twin |
| FEA | Finite element analysis |
| GMAW | Gas metal arc welding |
| GTAW | Gas tungsten arc welding |
| LPBF | Laser-based powder bed fusion |
| MAG | Metal active gas welding |
| MIG | Metal inert gas welding |
| NTWD | Nozzle to work distance |
| OME | Observable manufacturing element |
| OPC/UA | Open platform communications unified architecture |
| PAW | Plasma arc welding |
| PLC | Programmable logic controller |
| TCP | Tool centre point |
| TIG | Tungsten inert gas welding |
| TOF | Time of flight |
| TS | Torch travel speed |
| VR | Virtual reality |
| WAAM | Wire arc additive manufacturing |
| WFS | Wire feed speed |
References
- Abdelati, M.H.; Abdelwali, H.A. Evaluating the Impact of Transportation Costs, Supply Chain Reliability, and Operational Efficiency on Global Import Decisions. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Bus. Sci. 2024, 5, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z. The Suez Canal Blockage in March 2021: The Causation of the Incident and Its Economic and Social Influences. AEMPS 2024, 60, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuo, Q.; Qin, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; You, J. Supply chain risks and geographical supplier distribution strategy. Account. Financ. 2024, 64, 3841–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, A.; Harrison, T.P. Additive Manufacturing in an End-to-End Supply Chain Setting. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2015, 2, 65–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campatelli, G.; Montevecchi, F.; Venturini, G.; Ingarao, G.; Priarone, P.C. Integrated WAAM-Subtractive Versus Pure Subtractive Manufacturing Approaches: An Energy Efficiency Comparison. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green Technol. 2020, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuñez Rodriguez, J.; Andrade Sosa, H.H.; Villarreal-Archila, S.M.; Ortiz, A. The Impact of Additive Manufacturing on Supply Chain Management from a System Dynamics Model—Scenario: Traditional, Centralized, and Distributed Supply Chain. Processes 2022, 10, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nota, C.; Rückert, G.; Heuzé, J.L.; Carlino, L.; Quenez, J.M.; Courregelongue, L. A First Feedback on Manufacturing and in-Service Behaviour of a WAAM-Made Propeller for Naval Application. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40194-023-01475-w#citeas (accessed on 13 March 2025).
- Rodrigues, T.A.; Duarte, V.; Miranda, R.M.; Santos, T.G.; Oliveira, J.P. Current Status and Perspectives on Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM). Materials 2019, 12, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, W.; Wu, N.; Zhou, W. Effect of Interpass Temperature on Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing Using High-Strength Metal-Cored Wire. Metals 2022, 12, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandtke, K.; Schroepfer, D.; Scharf-Wildenhain, R.; Haelsig, A.; Kannengiesser, T.; Kromm, A.; Hensel, J. Influence of the WAAM process and design aspects on residual stresses in high-strength structural steels. Weld. World 2023, 67, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, C.; Fritz, C.; Zaeh, M.F. Impact of wire and arc additively manufactured workpiece geometry on the milling process. Prod. Eng. Res. Dev. 2023, 17, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hook, T. Real-time shaded NC milling display. ACM SIGGRAPH Comput. Graph. 1986, 20, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaeser, G.; Gröller, E. Efficient Volume-Generation During the Simulation of NC-Milling. In Mathematical Visualization; Hege, H.-C., Polthier, K., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998; pp. 89–106. ISBN 978-3-642-08373-0. [Google Scholar]
- Cabral, G.F. Modeling and Simulation of Tool Engagement and Prediction of Process Forces in Milling. Ph.D. Thesis, Universitätsbibliothek der RWTH Aachen, Aachen, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Surmann, T. Modelling and Visualization of the Surface Resulting from the Milling Process. In Computer Graphics; Mukai, N., Ed.; InTech: Vienna, Austria, 2012; ISBN 978-953-51-0455-1. [Google Scholar]
- Sampaio, R.; Pragana, J.; Bragança, I.; Silva, C.; Nielsen, C.V.; Martins, P. Modelling of wire-arc additive manufacturing—A review. Adv. Ind. Manuf. Eng. 2023, 6, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alessandro, R. Contributors. Slic3r. Open Source Community. 2024. Available online: https://slic3r.org/ (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Prusa Research. PrusaSlicer; Prusa Research, a.s: Prague, Czech Republic, 2024; Available online: https://www.prusa3d.com/page/prusaslicer_424/ (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Ultimaker. Ultimaker Cura; Ultimaker B.V: Utrecht, The Netherlands, 2024; Available online: https://ultimaker.com/software/ultimaker-cura (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- Abdallah, S.; Pervaiz, S. Reviewing Post-Processing Techniques to Enhance Mechanical Properties of Parts Fabricated Using WAAM. In Volume 2A: Advanced Manufacturing. Proceedings of the ASME 2021 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, Virtual, 1–5 November 2021; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 2021; ISBN 978-0-7918-8555-0. [Google Scholar]
- Son, H.J.; Seo, B.W.; Kim, C.J.; Kim, S.; Cho, Y.T. Coordinate system setting for post-machining of impeller shape by wire arc DED and evaluation of processing efficiency. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.; Aliyev, R.; Zeidler, H.; Krinke, S. A Review of the Recent Developments and Challenges in Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) Process. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2023, 7, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Su, C.; Zhu, J. Comprehensive review of wire arc additive manufacturing: Hardware system, physical process, monitoring, property characterization, application and future prospects. Results Eng. 2022, 13, 100330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athaib, N.H.; Haleem, A.H.; Al-Zubaidy, B. A review of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) of Aluminium Composite, Process, Classification, Advantages, Challenges, and Application. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2021, 1973, 12083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.S.; Gilbert, S.W. Costs and Cost Effectiveness of Additive Manufacturing; NIST Special Publication: Gaithersburg, MD, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Khanna, N.; Salvi, H.; Karaş, B.; Fairoz, I.; Shokrani, A. Cost Modelling for Powder Bed Fusion and Directed Energy Deposition Additive Manufacturing. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2024, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sames, W.J.; List, F.A.; Pannala, S.; Dehoff, R.R.; Babu, S.S. The metallurgy and processing science of metal additive manufacturing. Int. Mater. Rev. 2016, 61, 315–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.F.; Sun, Q.J.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.P.; Feng, J.C. Effect of location on microstructure and mechanical properties of additive layer manufactured Inconel 625 using gas tungsten arc welding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 676, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, W.; Ouyang, J.; Kovacevic, R. Rapid prototyping of 4043 Al-alloy parts by VP-GTAW. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2004, 148, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Li, J.; Xiong, J.; Lin, X.; Zhang, F. Optimization of wire feed for GTAW based additive manufacturing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2017, 243, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Williams, S.; Colegrove, P.; Antonysamy, A.A. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Wire and Arc Additive Manufactured Ti-6Al-4V. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 968–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Pan, Z.; Cuiuri, D.; Li, H. Wire-feed additive manufacturing of metal components: Technologies, developments and future interests. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2015, 81, 465–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wu, X.; Li, G.; Yan, H.; Yu, Z. Rapid prototyping of 4043 Al-alloy parts by cold metal transfer. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2018, 23, 527–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caballero, A.; Ding, J.; Ganguly, S.; Williams, S. Wire + Arc Additive Manufacture of 17-4 PH stainless steel: Effect of different processing conditions on microstructure, hardness, and tensile strength. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 268, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Lv, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xu, B. Microstructural evolution and mechanical property of Ti-6Al-4V wall deposited by continuous plasma arc additive manufacturing without post heat treatment. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 69, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, S.W.; Martina, F.; Addison, A.C.; Ding, J.; Pardal, G.; Colegrove, P. Wire + Arc Additive Manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2016, 32, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpagaraj, A.; Baskaran, S.; Arunnellaiappan, T.; Kumar, N.R. A review on the suitability of wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM) for stainless steel 316. In Advances in Mechanical Design, Materials and Manufacture: Proceeding of the Second International Conference on Design, Materials and Manufacture (ICDEM 2019), Surathkal, India, 6–8 December 2019; AIP Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2019; p. 50001. [Google Scholar]
- Vartanian, K.; Brewer, L.; Manley, K.; Cobbs, T. Powder Bed Fusion vs. Directed Energy Deposition Benchmark Study: Mid-Sizepart with Simple Geometry. Available online: https://www.optomec.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/PBF-vs-DED-BENCHMARK-STUDY_7March_2018-03.pdf (accessed on 18 February 2025).
- Tabernero, I.; Paskual, A.; Álvarez, P.; Suárez, A. Study on Arc Welding Processes for High Deposition Rate Additive Manufacturing. Procedia CIRP 2018, 68, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisch, R.T.; Hauser, T.; Lutz, B.; Tsakpinis, A.; Winter, D.; Kamps, T.; Knoll, A. Context awareness in process monitoring of additive manufacturing using a digital twin. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2022, 119, 3483–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maffia, S.; Chiappini, F.; Maggiani, G.; Furlan, V.; Guerrini, M.; Previtali, B. Comparison between Eight-Axis Articulated Robot and Five-Axis CNC Gantry Laser Metal Deposition Machines for Fabricating Large Components. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, C.R.; Flynn, J.M.; Shokrani, A.; Dhokia, V.; Newman, S.T. Invited review article: Strategies and processes for high quality wire arc additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerber, E.; Fahrendholz, J.L.; Brell-Cokcan, S.; Dewald, P.; Sharma, R.; Reisgen, U. Dynamic WAAM: Adaptive processes for equivalent contact surface (ECS) optimization. Constr. Robot. 2023, 7, 309–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Pan, Z.; Ding, D.; Yu, Z.; van Duin, S.; Li, H.; Li, W.; Norrish, J. Fabrication of metallic parts with overhanging structures using the robotic wire arc additive manufacturing. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 63, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Nagaraja, K.M.; Zhang, R.; Malik, A.; Lu, H.; Li, W. Integrating robotic wire arc additive manufacturing and machining: Hybrid WAAM machining. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2023, 129, 3247–3259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segovia, M.; Garcia-Alfaro, J. Design, Modeling and Implementation of Digital Twins. Sensors 2022, 22, 5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Tao, F. Digital Twin and Big Data Towards Smart Manufacturing and Industry 4.0: 360 Degree Comparison. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 3585–3593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.; Noh, S.D. Design and Implementation of Digital Twin Factory Synchronized in Real-Time Using MQTT. Machines 2024, 12, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirono, Y.; Mori, T.; Sugimoto, S.; Miyata, Y. Investigation on influence of thermal history on quality of workpiece created by directed energy deposition. CIRP Ann. 2024, 73, 133–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 15926-1:2004; Industrial Automation Systems and Integration—Integration of Life-Cycle Data for Process Plants Including Oil and Gas Production Facilities. ISO International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2004.
- IEC 62443-1-1:2009; Industrial Communication Networks. Network and System Security. Terminology, Concepts and Models. British Standards Institution: London, UK, 2009.
- Shafto, M.; Conroy, M.; Doyle, R.; Glaessgen, E.; Kemp, C.; LeMoigne, J.; Wang, L. NASA Modeling, Simulation. In Information Technology & Processing—TA11; NASA: Washington, DC, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Errandonea, I.; Beltrán, S.; Arrizabalaga, S. Digital Twin for maintenance: A literature review. Comput. Ind. 2020, 123, 103316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, B.; Zhang, X.; Duan, J.; Wan, C.; Hu, Y. An effective MBSE approach for constructing industrial robot digital twin system. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2023, 80, 102455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, A.; Fan, Z.; Day, C.; Barlow, C. Digital Twin: Enabling Technologies, Challenges and Open Research. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 108952–108971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 23247-1:2021; Automation Systems and Integration—Digital Twin Framework for Manufacturing—Overview and General Principles. ISO International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- Bong Kim, D.; Shao, G.; Jo, G. A digital twin implementation architecture for wire + arc additive manufacturing based on ISO 23247. Manuf. Lett. 2022, 34, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, H.; He, F.; Yuan, L.; Hatamian, H.; Commins, P.; Pan, Z. Online distortion simulation using generative machine learning models: A step toward digital twin of metallic additive manufacturing. J. Ind. Inf. Integr. 2024, 38, 100563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.-S.; Lee, D.-H.; Bajestani, M.S.; Kim, D.B.; Noh, S.D. Edge Computing-Based Digital Twin Framework Based on ISO 23247 for Enhancing Data Processing Capabilities. Machines 2025, 13, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, M.M.; Bajestani, M.S.; Noh, S.D.; Kim, D.B. Digital twin-based architecture for wire arc additive manufacturing using OPC UA. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2025, 94, 102944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karkaria, V.; Goeckner, A.; Zha, R.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, Q.; Cao, J.; Gao, R.X.; Chen, W. Towards a digital twin framework in additive manufacturing: Machine learning and bayesian optimization for time series process optimization. J. Manuf. Syst. 2024, 75, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevans, B.D.; Carrington, A.; Riensche, A.; Tenequer, A.; Barrett, C.; Halliday, H.; Srinivasan, R.; Cole, K.D.; Rao, P. Digital twins for rapid in-situ qualification of part quality in laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 93, 104415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.; Hu, T.; Zhou, T.; Ye, Y. Data Construction Method for the Applications of Workshop Digital Twin System. J. Manuf. Syst. 2021, 58, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieves, M. Digital twin: Manufacturing excellence through virtual factory replication. White Pap. 2014, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- White, K.P.; Ingalls, R.G. Introduction to simulation. In Proceedings of the 2009 Winter Simulation Conference—(WSC 2009), Austin, TX, USA, 13–16 December 2009; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 12–23, ISBN 978-1-4244-5770-0. [Google Scholar]
- Mills, J.K.; Nguyen, C.V. Robotic Manipulator Collisions: Modeling and Simulation. J. Dyn. Sys. Meas. Control 1992, 114, 650–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatib, O.; Yokoi, K.; Brock, O.; Chang, K.; Casal, A. Robots in human environments. In Proceedings of the First Workshop on Robot Motion and Control. RoMoCo’99 (Cat. No.99EX353), Kiekrz, Poland, 29 June 1999; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 1999; pp. 213–221, ISBN 0-7803-5655-1. [Google Scholar]
- Heisenberg, G.; Göbel, M.; Hambürger, T.; Hornung, N.; Klein, U.; Nikitin, I.; Rattay, O.; Scharping, J.; Troche, K.; Wienss, C. Realtime dynamics simulation of cables, hoses and wiring harnesses for high accuracy digital mockups and load analysis. In Proceedings of the Automotive Power Electronics, Paris, France, 26–27 September 2007. [Google Scholar]
- FormTec GmbH. FormTec NCSpeed: Optimization and Simulation for CNC Machining; FormTec GmbH: Dornstetten, Germany, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- MachineWorks Ltd. MachineWorks: Simulation & Verification Software for CNC Machining; MachineWorks Ltd.: Sheffield, UK, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- ModuleWorks GmbH. ModuleWorks CutSim: Real-Time Material Removal Simulation; ModuleWorks GmbH: Aachen, Germany, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Korneev, S.; Wang, Z.; Thiagarajan, V.; Nelaturi, S. Fabricated shape estimation for additive manufacturing processes with uncertainty. Comput.-Aided Des. 2020, 127, 102852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhu, S.; Liang, X.; Wang, W. Overlapping model of beads and curve fitting of bead section for rapid manufacturing by robotic MAG welding process. Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2011, 27, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Söntgen, J. FEM Basierte Simulation des WAAM-Prozesses mit Ansys-Mechanical. Bachelor’s Thesis, Hochschule Ruhr-West, Mülheim an der Ruhr, Germany, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Phua, A.; Davies, C.; Delaney, G.W. A digital twin hierarchy for metal additive manufacturing. Comput. Ind. 2022, 140, 103667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Amor, S.; Elloumi, N.; Eltaief, A.; Louhichi, B.; Alrasheedi, N.H.; Seibi, A. Digital Twin Implementation in Additive Manufacturing: A Comprehensive Review. Processes 2024, 12, 1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Vengayil, H.; Lu, Y.; Xu, X. A Cyber-Physical Machine Tools Platform using OPC UA and MTConnect. J. Manuf. Syst. 2019, 51, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reisch, R.; Hauser, T.; Kamps, T.; Knoll, A. Robot Based Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing System with Context-Sensitive Multivariate Monitoring Framework. Procedia Manuf. 2020, 51, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plakhotnik, D.; Glasmacher, L.; Vaneker, T.; Smetanin, Y.; Stautner, M.; Murtezaoglu, Y.; van Houten, F. CAM planning for multi-axis laser additive manufacturing considering collisions. CIRP Ann. 2019, 68, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabernero, I.; Calleja, A.; Lamikiz, A.; López de Lacalle, L.N. Optimal Parameters for 5-axis Laser Cladding. Procedia Eng. 2013, 63, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Pan, Z.; Cuiuri, D.; Li, H. A multi-bead overlapping model for robotic wire and arc additive manufacturing (WAAM). Robot. Comput.-Integr. Manuf. 2015, 31, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Shen, C.; Pan, Z.; Cuiuri, D.; Li, H.; Larkin, N.; van Duin, S. Towards an automated robotic arc-welding-based additive manufacturing system from CAD to finished part. Comput.-Aided Des. 2016, 73, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturini, G.; Montevecchi, F.; Scippa, A.; Campatelli, G. Optimization of WAAM Deposition Patterns for T-crossing Features. Procedia CIRP 2016, 55, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, W.T.; Emo, D.J.; Abbott, D.H.; Bruck, C.E.; Wilson, G.H.; Wolfe, J.B.; Finkhousen, D.M.; Tepper, A.; Stevens, R.G. The GE Aircraft Engine Bracket Challenge: An Experiment in Crowdsourcing for Mechanical Design Concepts; University of Texas at Austin: Austin, TX, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tyflopoulos, E.; Steinert, M. Combining Macro- and Mesoscale Optimization: A Case Study of the General Electric Jet Engine Bracket. Designs 2021, 5, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gülbahçe, E.; Sezgen, H.Ç.; Çakan, A. Topology Design and Modal Analysis of a Bracket via FEA. Appl. Eng. Lett. 2019, 4, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafinex. Möbius: Optimize Robust Topologies. Available online: https://rafinex.com/products/ (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Wang, Z.; Han, K.; Tiwari, P. Digital Twin Simulation of Connected and Automated Vehicles with the Unity Game Engine. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 1st International Conference on Digital Twins and Parallel Intelligence (DTPI), Beijing, China, 15 July–15 August 2021; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bevans, B.; Ramalho, A.; Smoqi, Z.; Gaikwad, A.; Santos, T.G.; Rao, P.; Oliveira, J.P. Monitoring and flaw detection during wire-based directed energy deposition using in-situ acoustic sensing and wavelet graph signal analysis. Mater. Des. 2023, 225, 111480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zimmer-Chevret, S.; Léonard, F.; Abba, G. Prediction of bead geometry with consideration of interlayer temperature effect for CMT-based wire-arc additive manufacturing. Weld. World 2021, 65, 2255–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baier, D.; Wolf, F.; Weckenmann, T.; Lehmann, M.; Zaeh, M.F. Thermal process monitoring and control for a near-net-shape Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing. Prod. Eng. Res. Dev. 2022, 16, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panicker, S.; Nagarajan, H.P.; Tuominen, J.; Patnamsetty, M.; Coatanéa, E.; Haapala, K.R. Investigation of thermal influence on weld microstructure and mechanical properties in wire and arc additive manufacturing of steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 853, 143690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyen, T.M.T.; Minh, P.S.; Nguyen, V.-T.; Do, T.T.; Nguyen, V.T.; Le, M.-T.; van Nguyen, T.T. Trajectory Strategy Effects on the Material Characteristics in the WAAM Technique. Micromachines 2023, 14, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Jia, Y.; Chen, S.; Shi, J.; Li, F. Process planning strategy for wire-arc additive manufacturing: Thermal behavior considerations. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 32, 100935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauthner, G.; Stautner, M.; Sell, S.; Frings, M.; Lorenz, A.; Plakhotnik, D.; Bleicher, F. Wire-Arc Additive Manufacturing Toolpath Optimization Using a Dexel-Based Temperature Prediction Model. In Sustainable Manufacturing as a Driver for Growth; Kohl, H., Seliger, G., Dietrich, F., Mur, S., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2025; pp. 730–737. ISBN 978-3-031-77428-7. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).