A Conceptual Study of Rapidly Reconfigurable and Scalable Optical Convolutional Neural Networks Based on Free-Space Optics Using a Smart Pixel Light Modulator
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fundamental Concepts of SPOCNN
2.2. Simplifying SPOCNN with Electrical Fan-In and Fan-Out
3. Results
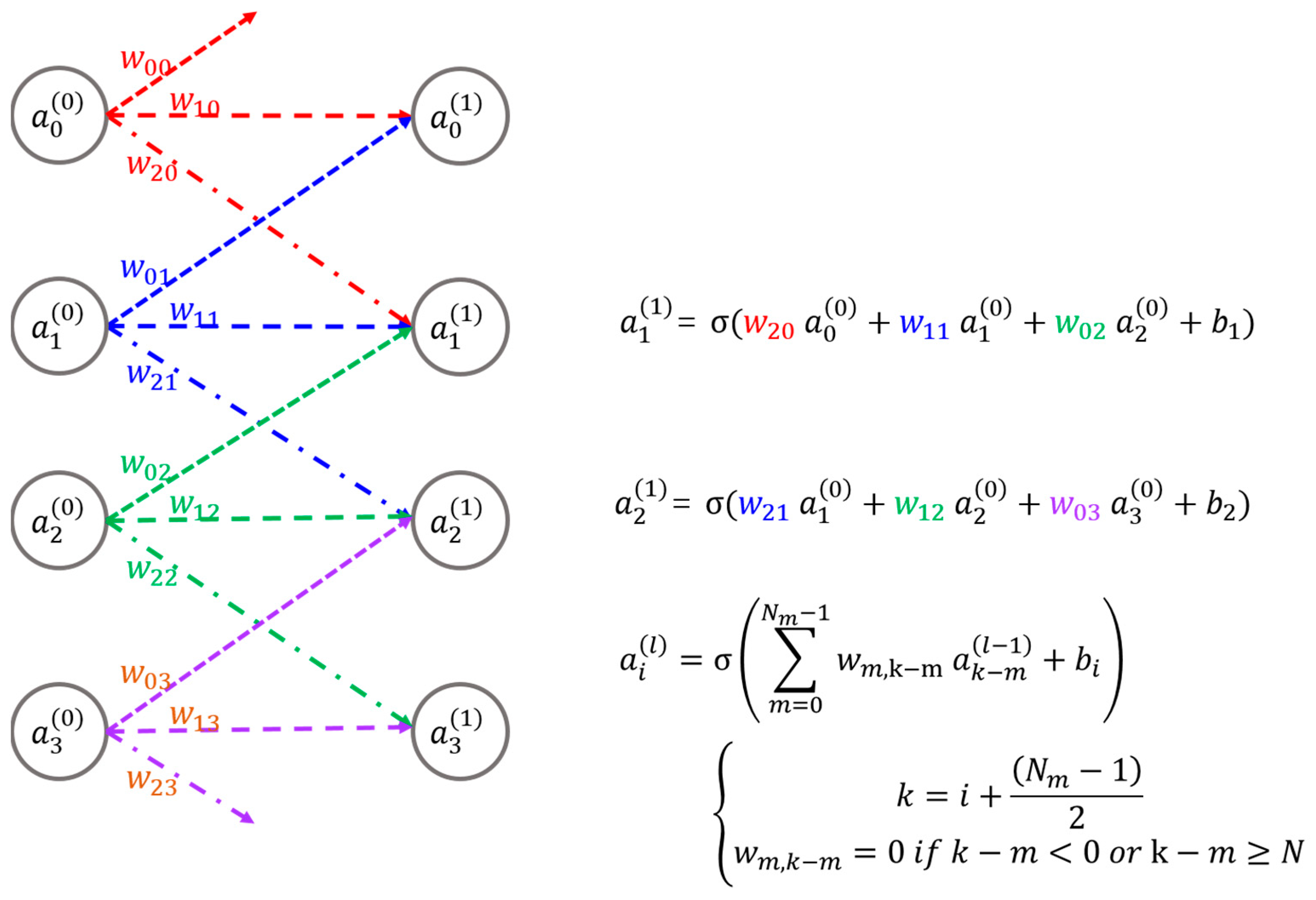
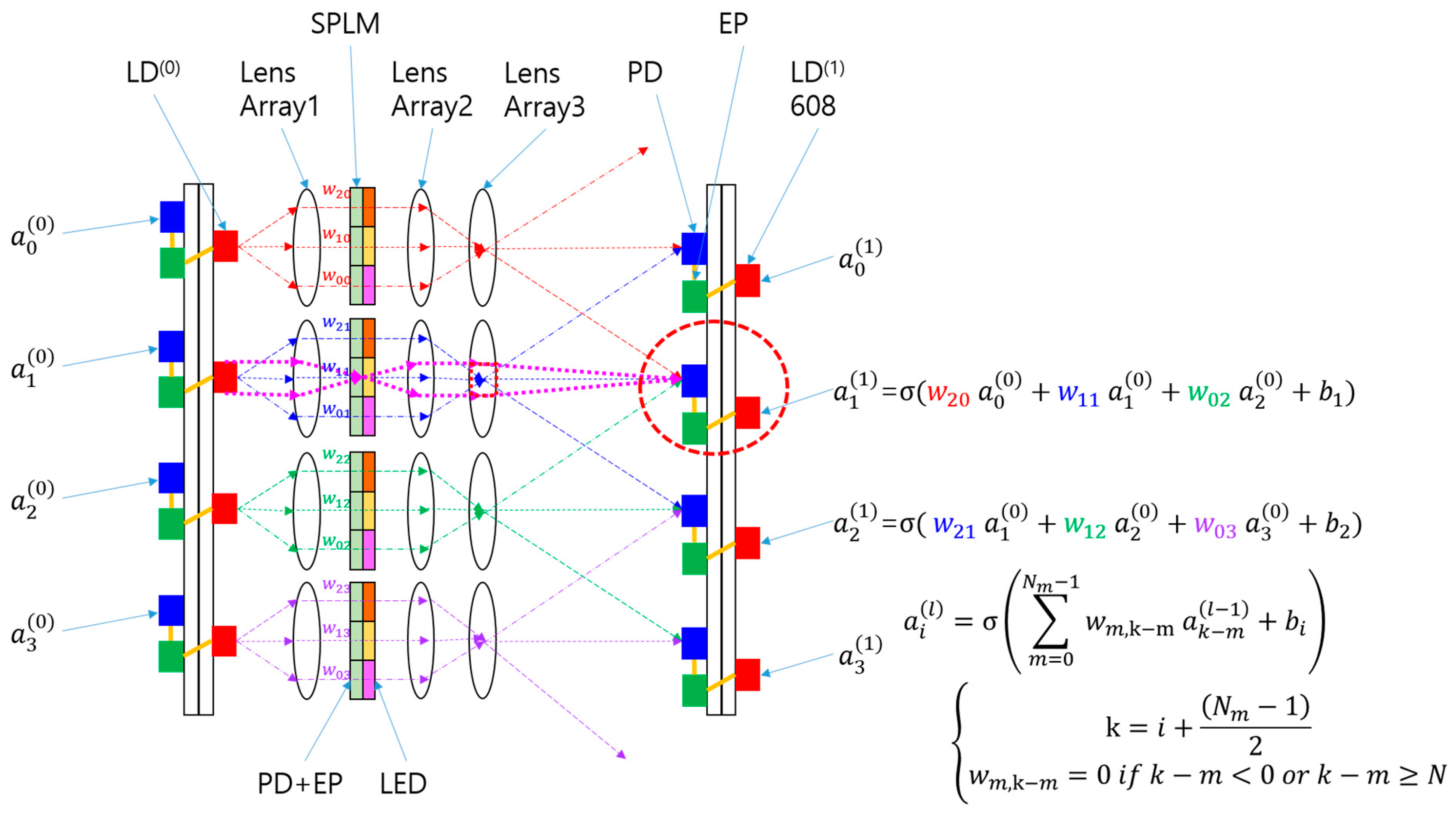
3.1. Smart Pixel-Based Bidirectional Optical Convolutional Neural Network (SPBOCNN)
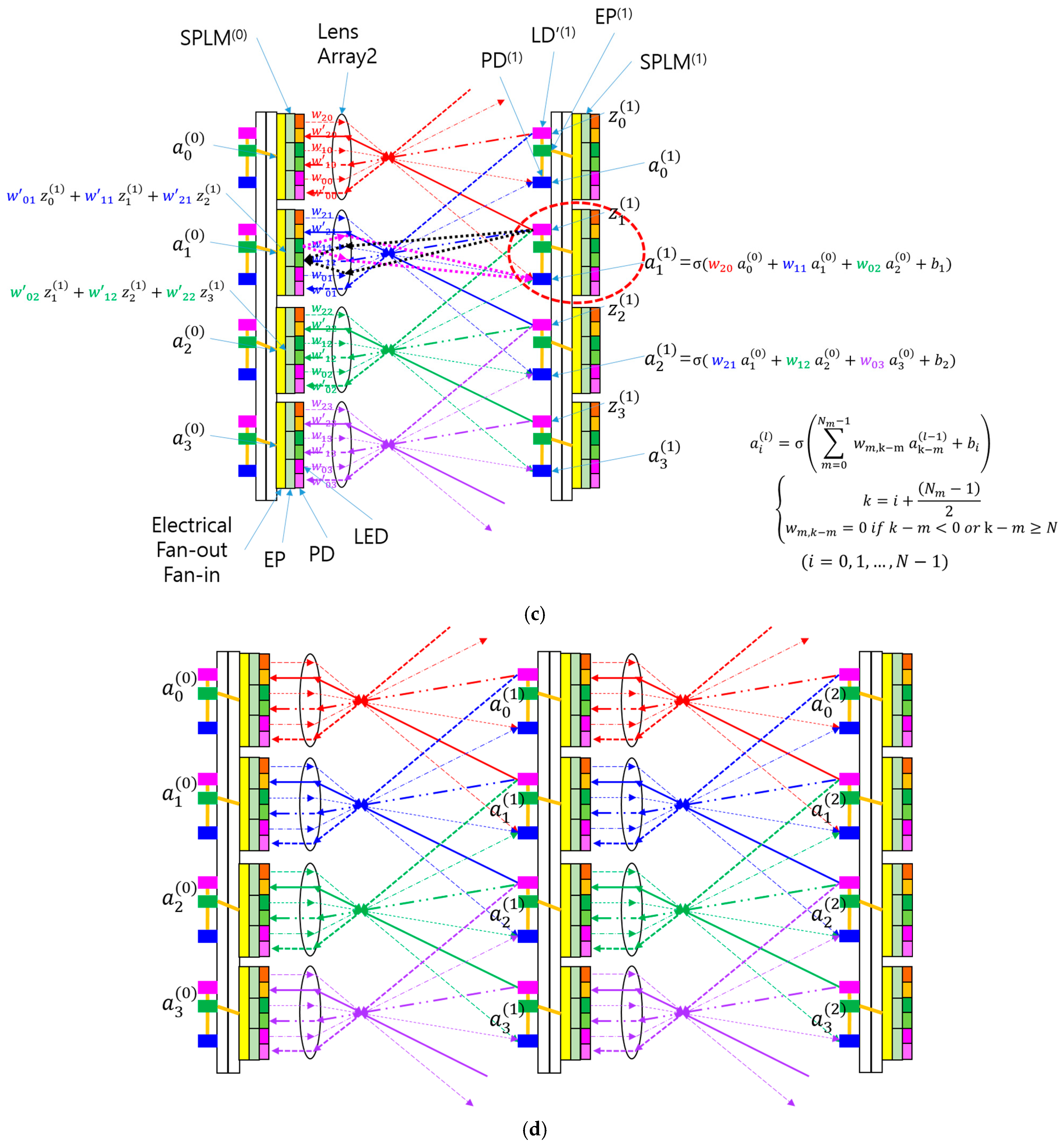
3.2. Simplifying SPBOCNN with Electrical Fan-In and Fan-Out
3.3. Application of SPBOCNN in Difference Mode and Multiple Kernel Sets
4. Discussion
4.1. Scalibility of SPOCNN
4.2. A Design Example of SPOCNN
4.3. Performance Analysis of SPOCNN Throughput
4.4. Transverse Scaling of SPBOCNN Using Smart Pixel Memory
4.5. Longitudinal Scaling of a Two-Mirror-like SPBOCNN
4.6. Application of SPBOCNN in Solving Partial Differential Equations
5. Conclusions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CNN | Convolutional neural network |
| OCNN | Optical convolutional neural network |
| GPU | Graphics processing units |
| SBP | Space-bandwidth product |
| SLM | Spatial light modulator |
| SOCNN | Scalable optical convolutional neural network |
| LCOE | Linear combination optical engine |
| SPOCNN | Smart-pixel-based optical convolutional neural network |
| SPONN | Smart-pixel-based optical neural network |
| SPLM | Smart pixel light modulator |
| BONN | Bidirectional optical neural network |
| SPBOCNN | Smart-pixel-based bidirectional optical convolutional neural network |
| TMLONN | Two-mirror-like optical neural network |
| VCSEL | Vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser |
| LD | Laser diode |
| LED | Light-emitting diode |
| PD | Photodetector or photodiode |
| EP | Electronic processor |
| TMLBONN | Two-mirror-like BONN |
| TML-SPBOCNN | Two-mirror-like SPBOCNN |
| PDE | Partial differential equation |
References
- Hinton, G.; Deng, L.; Yu, D.; Dahl, G.E.; Mohamed, A.R.; Jaitly, N.; Senior, A.; Vanhoucke, V.; Nguyen, P.; Sainath, T.N.; et al. Deep neural networks for acoustic modeling in speech recognition: The shared views of four research groups. IEEE Signal Process. Mag. 2012, 29, 82–97. [Google Scholar]
- LeCun, Y.; Bengio, Y.; Hinton, G. Deep learning. Nature 2015, 521, 436–444. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lecun, L.; Bottou, L.; Bengio, Y.; Haffner, P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc. IEEE 1998, 86, 2278–2324. [Google Scholar]
- Chetlur, S.; Woolley, C.; Vandermersch, P.; Cohen, J.; Tran, J.; Catanzaro, B.; Shelhamer, E. cuDNN: Efficient primitives for deep learning. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1410.0759v3. [Google Scholar]
- Han, S.; Pool, J.; Tran, J.; Dally, W. Learning both weights and connections for efficient neural network. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Rhu, M.; Gimelshein, N.; Clemons, J.; Zulfiqar, A.; Keckler, S.W. vDNN: Virtualized deep neural networks for scalable, memory-efficient neural network design. In Proceedings of the 2016 49th Annual IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Microarchitecture (MICRO), Taipei, Taiwan, 15–19 October 2016; pp. 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, T.; Moreau, T.; Jiang, Z.; Zheng, L.; Yan, E.; Shen, H.; Cowan, M.; Wang, L.; Hu, Y.; Ceze, L.; et al. TVM: An automated end-to-end optimizing compiler for deep learning. In Proceedings of the 13th USENIX Symposium on Operating Systems Design and Implementation (OSDI 18), Carlsbad, CA, USA, 8–10 October 2018; pp. 578–594. [Google Scholar]
- Jouppi, N.P.; Young, C.; Patil, N.; Patterson, D.; Agrawal, G.; Bajwa, R.; Bates, S.; Bhatia, S.; Boden, N.; Borchers, A.; et al. In-datacenter performance analysis of a tensor processing unit. In Proceedings of the 44th Annual International Symposium on Computer Architecture, Toronto, ON, Canada, 24–28 June 2017; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Colburn, S.; Chu, Y.; Shilzerman, E.; Majumdar, A. Optical frontend for a convolutional neural network. Appl. Opt. 2019, 58, 3179–3186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Sitzmann, V.; Dun, X.; Heidrich, W.; Wetzstein, G. Hybrid optical-electronic convolutional neural networks with optimized diffractive optics for image classification. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Rivenson, Y.; Yardimci, N.T.; Veli, M.; Luo, Y.; Jarrahi, M.; Ozcan, A. All-optical machine learning using diffractive deep neural networks. Science 2018, 361, 1004–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, X.; Wu, Q.; Liu, J.; Chen, Q.; Gu, G. A review of optical neural networks. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 70773–70783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, J.W. Introduction to Fourier Optics; Roberts and Company Publishers: Greenwood Village, CO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Cox, M.A.; Cheng, L.; Forbes, A. Digital micro-mirror devices for laser beam shaping. In Proceedings of the SPIE 11043, Fifth Conference on Sensors, MEMS, and Electro-Optic Systems, Skukuza, South Africa, 8–10 October 2018; Volume 110430Y. [Google Scholar]
- Mihara, K.; Hanatani, K.; Ishida, T.; Komaki, K.; Takayama, R. High Driving Frequency (>54 kHz) and Wide Scanning Angle (>100 Degrees) MEMS Mirror Applying Secondary Resonance For 2K Resolution AR/MR Glasses. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE 35th Inter-national Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems Conference (MEMS), Tokyo, Japan, 9–13 January 2022; pp. 477–482. [Google Scholar]
- Ju, Y.G. Scalable Optical Convolutional Neural Networks Based on Free-Space Optics Using Lens Arrays and a Spatial Light Modulator. J. Imaging 2023, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, Y.G. A scalable optical computer based on free-space optics using lens arrays and a spatial light modulator. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2023, 55, 220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arecchi, A.V.; Messadi, T.; Koshel, R.J. Field Guide to Illumination (SPIE Field Guides Vol. FG11); SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2007; p. 59. [Google Scholar]
- Greivenkamp, J.E. Field Guide to Geometrical Optics (SPIE Field Guides Vol. FG01); SPIE Press: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2004; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Seitz, P. Smart Pixels. In Proceedings of the EDMO 2001/VIENNA, Vienna, Austria, 15–16 November 2001; pp. 229–234. [Google Scholar]
- Hinton, H.S. Progress in the smart pixel technologies. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 1996, 2, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.-G. A Conceptual Study of Rapidly Reconfigurable and Scalable Bidirectional Optical Neural Networks Leveraging a Smart Pixel Light Modulator. Photonics 2025, 12, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, Y.G. Bidirectional Optical Neural Networks Based on Free-Space Optics Using Lens Arrays and Spatial Light Modulator. Micromachines 2024, 15, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Wu, C.-H.; Holonyak, N. Oxide-Confined VCSELs for High-Speed Optical Interconnects. IEEE J. Quantum Electron. 2018, 54, 2400115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James Singh, K.; Huang, Y.-M.; Ahmed, T.; Liu, A.-C.; Huang Chen, S.-W.; Liou, F.-J.; Wu, T.; Lin, C.-C.; Chow, C.-W.; Lin, G.-R.; et al. Micro-LED as a promising candidate for high-speed visible light communication. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, I. Lenslet array processors. Appl. Opt. 1982, 21, 1271–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Available online: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Relaxation_(iterative_method) (accessed on 17 March 2025).









Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ju, Y.-G. A Conceptual Study of Rapidly Reconfigurable and Scalable Optical Convolutional Neural Networks Based on Free-Space Optics Using a Smart Pixel Light Modulator. Computers 2025, 14, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14030111
Ju Y-G. A Conceptual Study of Rapidly Reconfigurable and Scalable Optical Convolutional Neural Networks Based on Free-Space Optics Using a Smart Pixel Light Modulator. Computers. 2025; 14(3):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14030111
Chicago/Turabian StyleJu, Young-Gu. 2025. "A Conceptual Study of Rapidly Reconfigurable and Scalable Optical Convolutional Neural Networks Based on Free-Space Optics Using a Smart Pixel Light Modulator" Computers 14, no. 3: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14030111
APA StyleJu, Y.-G. (2025). A Conceptual Study of Rapidly Reconfigurable and Scalable Optical Convolutional Neural Networks Based on Free-Space Optics Using a Smart Pixel Light Modulator. Computers, 14(3), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/computers14030111






