Abstract
The performance of Large Language Models, such as ChatGPT, generally increases with every new model release. In this study, we investigated to what degree different GPT models were able to solve the exams of three different undergraduate courses on warehousing. We contribute to the discussion of ChatGPT’s existing logistics knowledge, particularly in the field of warehousing. Both the free version (GPT-4o mini) and the premium version (GPT-4o) completed three different warehousing exams using three different prompting techniques (with and without role assignments as logistics experts or students). The o1-preview model was also used (without a role assignment) for six runs. The tests were repeated three times. A total of 60 tests were conducted and compared with the in-class results of logistics students. The results show that the GPT models passed a total of 46 tests. The best run solved 93% of the exam correctly. Compared with the students from the respective semester, ChatGPT outperformed the students in one exam. In the other two exams, the students performed better on average than ChatGPT.
1. Introduction
In 2023, OpenAI’s ChatGPT beat the Turing Test [1]. The development of Large Language Models (LLMs) is rapid [2] and an LLM’s performance generally improves with each new version. The community also tests and evaluates new models using different methods. In this regard, OpenAI’s models are in the top positions [3,4]. They use, for example, a graduate-level Google Proof Q&A Benchmark with over 400 science questions, reading comprehension questions and professional translation tests. Even though many consider LLM performance tests to be highly informative, there is criticism that the tests can be cheated with the right training data. Developers specifically tune the models with the desired answers in order to pass the tests very successfully [5]. Moreover, it is well known that LLMs tend to hallucinate, have a bias or even produce false results (c.f. [6,7,8]). Nevertheless, LLMs like ChatGPT are used for a wide range of applications [9,10,11].
However, despite their widespread use in various studies, there is little research in the field of logistics, particularly in warehousing. Warehousing is an important part of our lives, even if it may not always be apparent to us. In 2024, the industry revenue of general warehousing and storage in the U.S. was USD 25 billion [12]. The market is correspondingly large and has a tremendous impact on the economy as a whole. Artificial intelligence (AI) has already found its way into warehousing operations. There are many use cases for decision support or even automation using AI [13,14,15]. AI holds a tremendous amount of potential to support and simplify future warehousing projects and operations. Logistics is a very application-oriented domain in which a lot of knowledge remains in companies and offers proprietary solutions that can be acquired commercially (c.f [16,17]). Yet, little is known about how much LLMs or ChatGPT knows or can answer about warehousing. Many companies also use LLMs in e-commerce, for example, [18]. The answers and used data also have an impact on warehouse logistics, among other things. Further studies indicate that ChatGPT may have potential for logistics. Users are aware of the benefits and are using the technology in supply chain management, for example. Nevertheless, there are open fields of research due to the complexity and limited research [19,20,21].
This contribution tested ChatGPT’s knowledge of warehousing using three different exams from a German university’s undergraduate logistics degree. The answers of the LLM were evaluated as if it were a student and they were compared with the results of the actual written exam of the winter semester 2022–2023 at TU Dortmund University. Just like cheating in performance benchmarks in LLMs, students can also cheat unnoticed in the respective exams. We used the exams from Warehouse Management Systems (WMS), Material Flow Systems I (MFS I) and Material Flow Systems II (MFS II), which cover the basics of warehousing and other logistics-related topics. These three exams are the only ones at the university in undergraduate courses that test specific knowledge of warehousing and technical logistics. Exams or tests from other national and international exams are not publicly available. We were therefore the first to conduct such a test and to publish the results and exams. The graduate courses offered by TU Dortmund University are even more specific to warehousing and ask for a lot of calculations. The complexity of this knowledge is even higher than in the undergraduate courses and was therefore excluded from the tests.
In September 2024, OpenAI published the o1-preview and o1-mini models. At the launch of these new models, only 30 and 50 prompts per week were possible, respectively [22]. Due to the limitations of the latest models, the GPT-4o mini and GPT-4o models were used for this study, in addition to the o1-preview. At the time of the investigation, the GPT-4o mini model was free of charge and the GPT-4o model could also be used free of charge for a dynamic number of prompts. After this, it could only be used with a paid subscription. This work contributes to understanding ChatGPT’s capability to replicate logistics and warehousing knowledge. In addition, it became known how well different types of exam questions are handled and where the limitations are, either in the way of answering qualitative questions or in solving math problems.
The structure of this paper is as follows: The next section explains the relevant work regarding the development of LLMs and their use in education. The Material and Methods Section explains the methodology used and the exams. The results and their analysis are explained in Section 4. In Section 5, the results are discussed. This includes an overall assessment of the exams, as well as ChatGPT’s strengths and weaknesses. The section ends with the limitations and an outlook. The last section summarizes the most important statements. The entire process is shown in Figure 1.
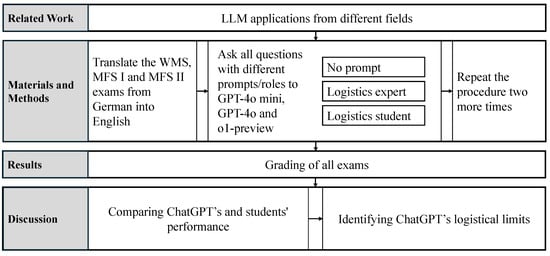
Figure 1.
Overview of the process and paper structure.
2. Related Work
Over four generations, language models developed from specific task helpers in the 1990s to general-purpose task solvers in the 2020s [23]. During this evolution process, they continuously improved their task-solving capacity. LLMs represent the latest generation of language models. As a category of foundation models, LLMs are designed to understand and generate natural (human) language [24]. To achieve this, they assign a probability to a sequence of words [23,25]. This prediction process is based on LLM training with ever larger data sets and was accelerated by increased computational capabilities and technological breakthroughs, such as transformers [26,27,28]. This enables LLMs, such as Open AI’s ChatGPT, to answer questions with human-like capabilities [29,30]. However, more recent LLMs, such as GPT-4, have undergone a paradigm shift and focus not only on generating text data, but on solving complex, diverse tasks, which is considered a step toward artificial general intelligence [23,31,32]. Hence, they have aroused interest in both industry and academia [31,33].
More recently, with the launch of ChatGPT in 2022, a discourse on the impact of LLMs on education arose [34,35,36,37]. Significant branches of the discussion consider how LLMs can support instructors in their teaching, how they can support student learning and issues related to LLMs in education [34,35,36,38,39,40,41]. Along with this discussion, many scholars have since presented the obvious question of whether LLMs are capable of passing exams at the university level.
As for ChatGPT-3, the results were very different depending on the domain. ChatGPT-3.5 performed outstandingly in the domains of economics [42] and critical and higher-order thinking [43]; outstandingly to satisfactorily in programming [44,45]; satisfactorily in English language comprehension [46]; barely satisfactorily to unsatisfactorily in law [47,48] and medical education [49,50,51,52,53]; and unsatisfactorily in mathematics [54], software testing [55] and multiple-choice-based exams across subjects [56].
In comparison, testing showed that GPT-4 can solve novel and arguably challenging tasks from different fields of expertise, covering the natural sciences, life sciences, engineering and social sciences [32]. In the field of medical education, GPT-4 achieved considerably better results than GPT-3 [57,58,59,60,61]. The same is true for higher education programming and university-level coding courses [62,63], mechanical engineering [64] and law school [65].
3. Materials and Methods
The ChatGPT web interface was used for all the tests. The models used were GPT-4o mini, GPT-4o and o1-preview. All tests were performed in November 2024. At that time, no API (Application Programming Interface) could be used for the o1-preview model, so all questions were prompted in the web interface manually. For a better comparability and exam performance evaluation, all the tests were repeated a total of three times. The WMS, MFS I and MFS II exams from the 2022–2023 winter semester represented the use case. The teaching materials are not publicly available for download in slide format but are instead in a protected area. The course content was based on literature in German that is publicly accessible or commercially available. However, the content was equivalent to various fundamentals of warehousing, which are also available in English [66,67]. The first step was to translate the respective exams from German to English. After the translation, all exam questions were provided to the respective model. The translation step was carried out for reasons of transparency in order to make the content available to the global research community. The translation was conducted with great care to ensure that the translation was accurate. Three different roles or prompting techniques were used for GPT-4o mini and GPT-4o. The role assignment had an influence on how ChatGPT behaved when answering questions. The reasons for this are difficult to identify [11,68]. Therefore, in the first test, we investigated the performance by asking the questions without an initial prompt. In the second test, the model was asked to put itself in the role of a logistics expert (LE). Finally, the model was asked to take on the role of a logistics student (LS). These prompts were used at the beginning of the session:
- Please put yourself in the role of a logistics expert and answer all the questions below.
- Please put yourself in the role of a logistics student and answer all the questions below.
ChatGPT saved the role assignment and took this into account when answering the questions. Since a role assignment can have an influence, it was crucial to observe whether this was the case here. This procedure was repeated two more times. A total of 60 runs were carried out using this procedure: 21 times each with WMS and MFS II and 18 times with MFS I. Since the MFS I exam included image interpretation in the exam, the o1-preview model could not be used because it did not allow for uploading images at the time of testing. The o1-preview model was therefore only used for WMS and MFS II without prompting due to its limited usability. The investigations using the o1-preview model as a logistics student and logistics expert were not conducted. Finally, all exams were evaluated using the sample solution of the exams. The grading system for the exams can be found in the Appendix A in Table A1. In German universities, a grading system from 1.0 (best) to 5.0 (worst) is used, which was adapted to the internationally understood U.S. form from A (best) to F (worst) for clarity. Both systems use equivalent grade increments. The overview of the procedure for the tests and findings is summarized in Figure 1. All answers of the respective runs are publicly accessible in the protocol under [69].
According to the module description, the WMS course provided basic knowledge on the practical use of information technology (IT) in logistics [70]. The content dealt with the computer-aided management and monitoring of logistics processes in a warehouse. Accompanying this, logistical data processing was covered with a focus on methods for evaluating, preparing and presenting company data using standard programs. The WMS exam consisted of 32 questions, which were divided into eight different topic blocks. The questions included 24 single- and 8 multiple-choice questions. In terms of content, knowledge questions, logic questions, programming questions and simple math questions were asked. The points awarded per question ranged from one to four points. When translating them, two questions from block seven of the WMS exam had to be adapted. Question 7.1 used specific abbreviations of German words, which were adapted to the English abbreviations. For the translation of abbreviations, known equivalents were used and it was ensured that they could be correctly interpreted by ChatGPT. Question 7.3 asked for an interpretation of English terms that have a different connotation in German (so-called “false friends”). The context for the different interpretations in German has been added.
The MFS I course covered the equipment and systems required for internal logistics in materials handling technology. Students learned about the systematic classification of devices, their structure and their essential characteristics, as well as their application criteria. In addition to the interaction of the material flow, they learned which standards, guidelines and laws are important for the operation of these devices and systems. The MFS I exam consisted of a total of 17 questions, divided into five content blocks. Block one contained 2 single-choice and 11 multiple-choice questions. Content from all lectures was tested here. Block two contained a free-text question on the topic of order picker guidance systems. The last three blocks were math problems with several sub-tasks [70].
In the MFS II course, students learned the methods, procedures and instruments required for planning and operating warehousing systems. The aim of this course was to plan and optimize material flow systems, to design and use the necessary IT, and to create the organizational processes and structures. Attending the MFS I course in advance was recommended but not mandatory. Students could freely choose their subjects, and therefore, attend MFS II before MFS I or, depending on their studies, choose only one of the two. The MFS II exam also consisted of 17 questions, divided into four content blocks. Block one contained questions on storage systems, block two on the course fundamentals, block three on order picking and block four contained mixed questions. The question types consisted of single-choice, multiple-choice and free-text questions, as well as two math problems [70]. For all three exams, a total of 60 points were awarded, with a duration of 60 min.
A large proportion of the questions in all exams were classified in Bloom’s taxonomy in the categories of remember, understand and apply. Only a few questions asked for the categories analyze and evaluate. In the WMS exam, all questions were categorized as remember, understand and apply. For MFS I, one sub-question was assigned to the categories analyze and evaluate. For MFS II, there were four questions. Experience showed that only a few students answered these questions completely correctly. Bloom’s taxonomy is a framework for assessing educational goals. Originally, the framework contained the categories knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis and evaluation [71]. In 2001, it was revised, and the categories remember, understand, apply, analyze, evaluate and create were introduced [72,73].
4. Results
From a total of 60 runs, ChatGPT passed 46. All 21 runs of the WMS exams were passed. The grades ranged from A- to C. In the MFS I exam, 17 out of 18 runs were passed. Here, only D+ and D grades were assigned to the runs that were passed. Of the 21 runs in MFS II, 8 were also passed. One run passed with a C-. The remaining grades were D+ and D. An overview of the distribution of grades across the exams is shown in Figure 2.
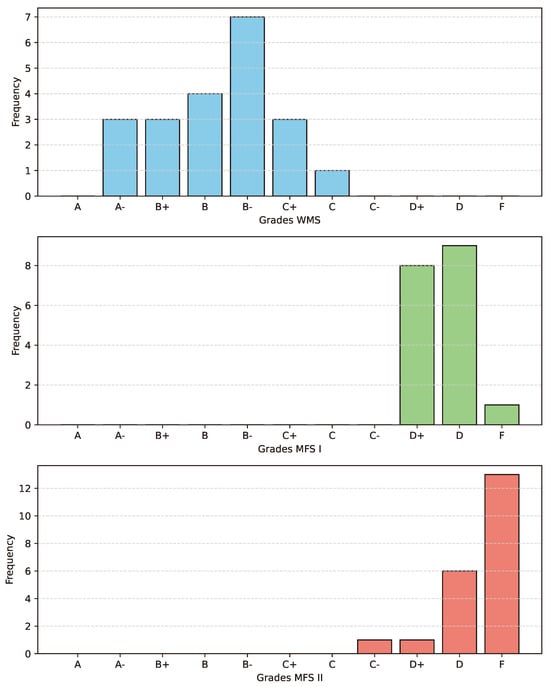
Figure 2.
Bar charts showing the distributions of grades across all runs.
Looking at the differences between the models, GPT-4o mini passed 66.7% of the 27 runs made to the model. GPT-4o passes 81.5% (22) of the 27 runs. All six runs with the o1-preview model were successful. Within the different prompts, the approach without a prompt had the highest success rate, with 83.3% of runs passing. The passed runs as a logistics expert were 77.8% and as a logistics student 66.7% (14 and 12 passed runs out of 18 runs, respectively). It should be noted that the runs of the o1-preview model were included in the approach without prompting. Without these runs, the success rate was also 77.8% (14 out of 18 runs). Table 1 shows the summary of all exam runs, with the median and range of the points. A detailed summary of the results of the three individual runs can be found in the Appendix A in Table A2, Table A3 and Table A4. The visualization of the runs, the average and the standard deviation are shown in Figure 3.

Table 1.
Summary measures of the exam results of the three different exams (WMS, MFS I, MFS II), GPT models (4o mini, 4o and o1-preview) and prompts (NP, LE, LS). The percentage and grade columns display the results corresponding to the median exam score shown in the third column.
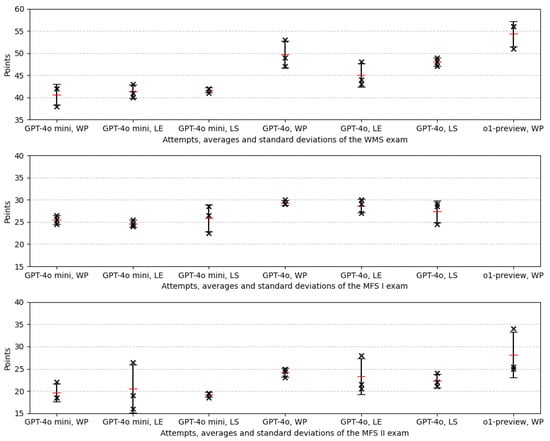
Figure 3.
Statistical analysis results for the three exams. The red line shows the average and the crosses show the runs. The bars show the standard deviation.
WMS: The median scores ranged between 41 and 56 points, with the averages closely aligned, indicating consistent central tendencies across prompts. The highest median score (56) was achieved by o1-preview without a prompt. The average scores ranged between 40.67 and 54.33 points. The points exhibited low variability, with standard deviations that ranged from 0.58 to 3.06. The LS prompt consistently showed the lowest standard deviation, which reflected stable results. The coefficient of variation was uniformly low (1.39% to 6.15%), which emphasized the consistency of performance, especially for the GPT-4o mini and LS prompt combinations.
MFS I: The median scores ranged between 24.5 and 29 points, where the averages remained close to these values. The highest median score (29) was achieved by GPT-4o with both the NP and LE prompts. The variability was moderate, with standard deviations that ranged from 0.58 to 3.06. The LS prompt showed slightly higher variability, indicating less consistent results compared with the other prompts. The coefficient of variation varied between 1.97% and 11.83%. While the NP and LE prompts exhibited low results, the LS prompt showed the highest value, suggesting greater inconsistency in performance.
MFS II: The median scores ranged from 18.5 to 25.5, where the averages were slightly higher in most cases. GPT-4o achieved the highest median (24.5) with the NP prompt, while o1-preview produced the highest average (28.17). The variability was the highest in this exam, where the standard deviations ranged from 0.58 to 5.41. The LE prompt stood out with particularly high variability. The coefficient of variation was significantly higher compared with the other exams, where it ranged from 3.01% to 26.38%. The LE prompt showed the largest coefficient of variation, reflecting considerable inconsistency, while the LS prompt had the lowest coefficient of variation, indicating a comparatively stable performance.
When comparing the three exams, WMS demonstrated the highest scores and most consistent performance, followed by MFS I with moderate variability. MFS II had the lowest scores and highest variability, reflecting challenges in achieving consistent results.
5. Discussion
Summary: When comparing the results of ChatGPT with the results of the students from the winter semester 2022–2023, ChatGPT was superior in the WMS exam. For the other two exams, the students performed better. The concrete results are discussed below.
WMS: A total of six students participated in the WMS exam in the winter semester 2022–2023, all of whom passed the exam. The low number of participants was due to the fact that the associated course is regularly offered in the summer semester. Students still have the opportunity to take each exam once per semester. Participation in the off-semester exam varies greatly. In comparison, 40 students took the exam in the summer semester 2022. A total of 38 passed the exam. The grades A and A- were each awarded once. The remaining 36 grades ranged from B to D (one B, six B-’s, eight C+’s, four C’s, six C-’s, seven D+’s and four D’s). The students’ average grade was a C. The distribution for the six winter semester grades was as follows: one B+, and the remaining five grades were evenly distributed between C+ and D. Thus, the students achieved an average grade of C. In comparison, ChatGPT performed better, with median grades between A- and C+ across all the models and prompts. On average, the median grade was a B. The particularly good performance in the exam could be attributed to both the question types and the content. Single-choice and multiple-choice questions leave little room for interpretation and can be answered clearly. As the content of the exam not only asked for specific logistics knowledge but also required logic and IT knowledge, ChatGPT could most likely benefit from its logical reasoning abilities [74]. According to Bloom’s taxonomy, the questions were exclusively in the categories remember, understand and apply. The exam was designed to cover as much content as possible in a short space of time, so the next-highest categories could not be asked in this format. The scores achieved show that ChatGPT could solve the lower levels of the Bloom’s taxonomy well to very well.
MFS I: The MFS I exam was taken by 74 students in the winter semester. Of these, 69 passed the exam. The grades were distributed as follows: seven A-’s, four B+’s, eight B’s, ten B-’s, nine C+’s, eight C’s, ten C-’s, eight D+’s, five D’s and five F’s. In comparison, ChatGPT performed below the students’ average in the MFS I exam, with median grades between D+ and D. In MFS I, most single-choice and multiple-choice questions were also answered correctly. The free-text task was correctly solved in every run. The three math problems, worth a total of 31 points, had a high influence on the overall score. ChatGPT provided some plausible solutions, often earning partial points for correctly handling subsequent errors or providing the right reasoning when interpreting results. However, as the tasks became more complicated, the number of correct answers decreased. In calculation task 5.1, all the ChatGPT models scored zero points across all runs. This task relied on logistics principles that required accurate knowledge from the literature to correctly apply the calculation method. In the exam, the single- and multiple-choice questions were classified in the Bloom’s taxonomy categories remember and understand. The free-text and calculation tasks were assigned to the categories apply, analyze and evaluate. Participants in the exam needed to apply and critically classify calculation rules.
MFS II: A total of 37 students participated in the MFS II exam in the winter semester 2022–2023, 29 of whom passed the exam. This meant that 78.38% passed and 21.62% (eight participants) failed. The grade distribution was as follows: one B-, six D+’s, six D’s, seven C+’s, seven C’s, two C-’s and eight F’s. The students also performed better than ChatGPT on the MFS II exam. Here, its median grade was between D (two times) and F (five times). Across the three different runs, large point variations were observed for the two LE prompts and the o1-preview model. The difficulty of this exam lay not only in the math problems, worth 27 points, but also the single-choice and multiple-choice questions. These included an additional rule: a correct combination earned two points, while a wrong combination gave zero points. The lack of partial points and the inclusion of more specific logistics questions compared with the WMS and MFS I exams resulted in a higher difficulty level. In comparison, the ChatGPT models often completed the free-text tasks with a high-to-full score. As with MFS I, partial points could be awarded for two calculation tasks. These were often incorrect, as the GPT models did not apply the correct procedures or formulas. In the MFS II exam, the questions were classified according to Bloom’s taxonomy in the same way as in MFS I. It is worth noting that the critical classifications (evaluate) were handled well by ChatGPT and points were awarded here. However, the basis for the answers were calculations that were incorrect, and accordingly, the questions in the categories apply and analyze from Bloom’s taxonomy were not solved correctly.
5.1. ChatGPT’s Limited Knowledge of Warehousing
General: ChatGPT’s performance on the exams highlighted its limitations in warehousing. The calculation tasks showed that even simple dimensioning of storage techniques could not be solved. Many of the calculation principles were based on basic logistics literature and/or standards (c.f. [75,76]). ChatGPT did not apply these calculation rules. In many cases, partial points were awarded in the exam, as ChatGPT provided a calculation path that allowed for partial points because of subsequent errors. However, there were also calculations where only the final result was given without explanations. As these were almost always incorrect, zero points were awarded here. There were also cases where only the final question was answered correctly but without explanation (see MFS II run 2, question 1.3, o1-preview). ChatGPT’s answer in part (b) was 16 compartments, without any further explanation. In this example, the answer was correct, but it was not possible to determine whether a correct calculation had taken place or the guess was correct. It could also be observed that during prompting, the math problems were not always fully answered. In a few cases, the answer had to be re-generated until all partial answers were given. This problem could be resolved using the API access instead of the UI.
Images: The results also show that the GPT-4o mini and GPT-4o models had problems with the interpretation of images. In the MFS I exam, two tasks used a picture to ask which warehouse technology was involved. Task 1.3 was answered incorrectly in all runs. Task 1.9, which asked for the exact name of the technology and the corresponding categorization, was always answered incorrectly by the GPT-4o model. It is noteworthy that the weaker model GPT-4o mini recognized the categorization correctly in all cases, and therefore, received partial points.
Contradictions: In the WMS exam, ChatGPT sometimes contradicted itself within its own responses. An example is given in Figure 4, which displays GPT-4o’s answer to question 6.2 of the WMS exam under the LS prompt. The same contradictory answer was given by GPT-4o mini.

Figure 4.
Question 6.2 of the WMS exam and GPT-4o’s answer as a logistics student (prompt LS).
The model answered option (c) first. After explaining the individual possibilities, it came to the conclusion that answer (d) was correct. As answer (c) was the first to be given in bold, it was also scored and ChatGPT therefore received zero points. The correct answer is (d). The model explained the reasoning here in a chain of thought [77]. However, since in our example, two different answers were given within one output, it was difficult for the reader to assess the correct result.
Model differences and similarities: As can already be seen from the examples (no explanation on answers, missing image interpretation and Figure 4), we observed discrepancies in all three models (for example, question 2.2 in the MFS II exam was only answered correctly by the o1-preview model). From the results in Table 1, it can be seen that the scores achieved increased from GPT-4o mini to GPT-4o and o1-preview. The GPT-4o mini model performed the worst for all three exams, and the o1-preview achieved the best grades. However, there were also some questions that could not be answered by any of the models. An example was question 1.1 in the WMS exam:
- Which cross-docking process has picking as a key feature? [Single Choice] (1/60)
- a.
- Cross-docking with collection in the storage system
- b.
- Cross-docking as a throughput system
- c.
- Cross-docking with breaking up the load units
- d.
- Cross-docking with pick families (clustering)
The correct answer is (c). Relatively simple questions that were based on logic-based or generally valid assumptions, were always answered correctly by all models. An example was question 4.5 in the MFS II exam:
- Give two examples of the risk of industrial trucks tipping over. [2 pt]
Correct answers are, among others, driving too fast on bends, driving with a raised load and driving against obstacles. As long as the answer showed a plausible reason, it was considered correct. There were few differences between the prompts (NP, LE, LS). From the median values in Table 1, it can be seen that the LE prompt achieved the worst results, except for MFS I model GPT-4o. From the given answers, it was often only minor details that differed. Only once did ChatGPT refer literally to the initial prompt. In the MFS II exam, run 3, GPT-4o started the answer with the following sentence: As a logistics student, I interpret the designation 07-12-2 for a storage location as a structured label that provides essential information about the pallet’s position in the warehouse.
Clear differences in the response length were difficult to distinguish. In most cases, the responses within the prompts were approximately the same length. In a few cases, the lengths of the responses differed significantly. However, here, the prompts alternated and there was not one prompt that always resulted in the longest responses.
5.2. Limitations and Future Work
Our work was limited in so far as only three different exams from one semester were taken by ChatGPT. In addition, these were evaluated using a sample solution, but by one reviewer (the first author) only. It is common for exams to be evaluated by only one person. There was a sample solution for each exam, which specified the desired solution and a corridor for deviating solutions. This ensured that reliable corrections were made even with one examiner. The exams used a fixed phrasing. It could be interesting to investigate different phrasings to see how LLMs could provide the best performance. The tested warehousing knowledge could not provide a conclusive assessment of the training data from ChatGPT, but it did show the limitations of the models for simple logistics questions. It also made sense to test the latest models, the o1-preview and o1-mini, in more detail, which was only possible to a limited extent at the time of writing. In the future, it would be important to test for further logistics knowledge related to warehousing beyond exams. Tests should also not be limited to ChatGPT models but be extended to its competitors as well.
Researchers and users in logistics and warehousing would benefit from public and shared data or models. The FAIR principles could serve as a reference here [78]. We believe that LLMs can become valuable tools for supporting planning, data analysis or even to completely automate specific process steps. However, this requires more precise and weighted data with which the models are trained. There is literature in English that explains the basics of warehousing [66,67]. ChatGPT itself says that it has a lot of information about warehousing, drawing on sources from books, scientific articles and industry solutions (see Figure A1). In logistics and warehouse planning, a great amount of experience-based knowledge is used. LLMs must recognize which data are given and specifically ask for parameters that have the greatest influence on the problem. Only when these relationships have been learned can an LLM replace planning tasks. To test this, it is useful to ask both consultants and various LLMs specific questions from logistics planning in the future and compare the results (i.e., requirements engineering). It is also recommended to investigate different prompts, as the experiments showed that the role assignment had an influence on the result. The need for better models was also recognized by OpenAI itself and a Reinforcement Fine-Tuning Research Program was recently launched [79].
For educators and their teaching content, it is clear that content will need to be adapted in the future. LLMs are able to comprehend the categories remembering; understanding; and, in parts, apply from Bloom’s taxonomy. Students can use AI tools to explore these categories and be able to fulfill the Bloom’s taxonomy categories analyze; evaluate; and especially, create themselves. In this way, efficient learning and performance could be achieved. Increased use of AI tools can also make everyday life easier by solving repetitive tasks.
6. Conclusions
In summary, the question regarding whether ChatGPT can pass undergraduate exams from warehousing can be answered based on the experiments conducted in this contribution. Questions that belonged to the categories remember and understand in Bloom’s taxonomy were solved very reliably. In our experiments, these were the single-choice, multiple-choice and free-text questions. The Bloom’s taxonomy categories apply, analyze and evaluate were solved in parts. Calculations that used formulas from the relevant literature, however, could not be accessed or derived by the model. Moreover, when the questions became highly domain-specific, ChatGPT was seemingly unable to access the relevant sources, and thus, could not answer said questions. However, the selected ChatGPT calculations still showed clear deficits and showed that accurate dimensioning in warehousing is not yet possible. This was probably due to a lack of training data. Looking at the investigated exams, WMS was solved above average compared with the students, while the MFS I and II exams were completed with noticeable weaknesses. To obtain correct answers, the question type was crucial. The role assigned to the model influenced its performance: overall, the answers as a logistics student were often the ones with the worst results. Prompting as a logistics expert or without role assignment led to better outcomes. The reasons for this phenomenon could not be identified. Nevertheless, it was clear that there were differences. To sum up, a basic knowledge of warehousing was present in the ChatGPT models, but there is still a lot of potential for improvement. A consequence for future exams is that questions should be designed to test knowledge that can only be solved by humans. This requires follow-up studies to determine the areas in which humans will remain indispensable in logistics. In addition, more LLM applications should be developed for warehousing planning. Furthermore, the ability of LLMs to accurately interpret images with logistics content is needed. To make rapid progress within warehousing, knowledge must be shared and models, applications and teaching must be adapted.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.F. and M.P.; methodology, S.F.; investigation, S.F.; data curation, S.F. and M.P.; writing—original draft preparation, S.F. and C.P.; writing—review and editing, J.R., C.P., C.R., M.P. and A.K.; visualization, J.R.; supervision, C.R.; project administration, S.F. All authors read and agreed to the published version of this manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
All answers of the respective runs from ChatGPT are publicly accessible in the protocol under [69].
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| API | Application Programming Interface |
| IT | Information technology |
| LE | Logistics expert |
| LLM | Large Language Model |
| LS | Logistics student |
| MFS I | Material Flow Systems I |
| MFS II | Material Flow Systems II |
| NP | No prompt |
| WMS | Warehouse Management Systems |
Appendix A

Table A1.
Evaluation scheme for all exams.
Table A1.
Evaluation scheme for all exams.
| Percentage Points [%] | Grade | German Grading System |
|---|---|---|
| 94–100 | A | 1.0 |
| 88–93.99 | A- | 1.3 |
| 82–87.99 | B+ | 1.7 |
| 76–81.99 | B | 2.0 |
| 70–75.99 | B- | 2.3 |
| 64–69.99 | C+ | 2.7 |
| 58–63.99 | C | 3.0 |
| 52–57.99 | C- | 3.3 |
| 46–51.99 | D+ | 3.7 |
| 40–45.99 | D | 4.0 |
| 0–39.99 | F | 5.0 |

Figure A1.
ChatGPT’s answer on how many sources it has about warehousing.

Table A2.
Run 1 of the exam attempts.
Table A2.
Run 1 of the exam attempts.
| Version | Prompt 1 | Total Points | Passed | Percentage [%] | Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WMS | |||||
| GPT-4o mini | NP | 42 | Yes | 70 | B- |
| GPT-4o mini | LE | 41 | Yes | 68 | C+ |
| GPT-4o mini | LS | 42 | Yes | 70 | B- |
| GPT-4o | NP | 47 | Yes | 78 | B |
| GPT-4o | LE | 44 | Yes | 73 | B- |
| GPT-4o | LS | 48 | Yes | 80 | B |
| o1-preview | NP | 56 | Yes | 93 | A- |
| MFS I | |||||
| GPT-4o mini | NP | 25.5 | Yes | 43 | D |
| GPT-4o mini | LE | 25.5 | Yes | 43 | D |
| GPT-4o mini | LS | 22.5 | No | 38 | F |
| GPT-4o | NP | 30 | Yes | 50 | D+ |
| GPT-4o | LE | 30 | Yes | 50 | D+ |
| GPT-4o | LS | 28.5 | Yes | 48 | D+ |
| o1-preview | NP | Model could not analyze pictures or answer all questions. | |||
| MFS II | |||||
| GPT-4o mini | NP | 22 | No | 37 | F |
| GPT-4o mini | LE | 26.5 | Yes | 44 | D |
| GPT-4o mini | LS | 18.5 | No | 31 | F |
| GPT-4o | NP | 25 | Yes | 42 | D |
| GPT-4o | LE | 28 | Yes | 47 | D+ |
| GPT-4o | LS | 21 | No | 35 | F |
| o1-preview | NP | 25 | Yes | 42 | D |
1 NP for no prompt, LE for logistics expert and LS for logistics student.

Table A3.
Run 2 of the exam attempts.
Table A3.
Run 2 of the exam attempts.
| Version | Prompt 1 | Total Points | Passed | Percentage [%] | Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WMS | |||||
| GPT-4o mini | NP | 42 | Yes | 70 | B- |
| GPT-4o mini | LE | 43 | Yes | 72 | B- |
| GPT-4o mini | LS | 42 | Yes | 70 | B- |
| GPT-4o | NP | 49 | Yes | 82 | B+ |
| GPT-4o | LE | 48 | Yes | 80 | B |
| GPT-4o | LS | 49 | Yes | 82 | B+ |
| o1-preview | NP | 56 | Yes | 93 | A- |
| MFS I | |||||
| GPT-4o mini | NP | 26.5 | Yes | 44 | D |
| GPT-4o mini | LE | 24.5 | Yes | 41 | D |
| GPT-4o mini | LS | 28.5 | Yes | 48 | D+ |
| GPT-4o | NP | 29 | Yes | 48 | D+ |
| GPT-4o | LE | 27 | Yes | 45 | D |
| GPT-4o | LS | 24.5 | Yes | 41 | D |
| o1-preview | NP | Model could not analyze pictures or answer all questions. | |||
| MFS II | |||||
| GPT-4o mini | NP | 18.5 | No | 31 | F |
| GPT-4o mini | LE | 16 | No | 27 | F |
| GPT-4o mini | LS | 19.5 | No | 33 | F |
| GPT-4o | NP | 23 | No | 38 | F |
| GPT-4o | LE | 21.5 | No | 36 | F |
| GPT-4o | LS | 24 | Yes | 40 | D |
| o1-preview | NP | 34 | Yes | 57 | C- |
1 NP for no prompt, LE for logistics expert and LS for logistics student.

Table A4.
Run 3 of the exam attempts.
Table A4.
Run 3 of the exam attempts.
| Version | Prompt 1 | Total Points | Passed | Percentage [%] | Grade |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WMS | |||||
| GPT-4o mini | NP | 38 | Yes | 63 | C |
| GPT-4o mini | LE | 40 | Yes | 67 | C+ |
| GPT-4o mini | LS | 41 | Yes | 68 | C+ |
| GPT-4o | NP | 53 | Yes | 88 | A- |
| GPT-4o | LE | 43 | Yes | 72 | B- |
| GPT-4o | LS | 47 | Yes | 78 | B |
| o1-preview | NP | 51 | Yes | 85 | B+ |
| MFS I | |||||
| GPT-4o mini | NP | 24.5 | Yes | 41 | D |
| GPT-4o mini | LE | 24 | Yes | 40 | D |
| GPT-4o mini | LS | 26.5 | Yes | 44 | D |
| GPT-4o | NP | 29 | Yes | 48 | D+ |
| GPT-4o | LE | 29 | Yes | 48 | D+ |
| GPT-4o | LS | 29 | Yes | 48 | D+ |
| o1-preview | NP | Model could not analyze pictures or answer all questions. | |||
| MFS II | |||||
| GPT-4o mini | NP | 18.5 | No | 31 | F |
| GPT-4o mini | LE | 19 | No | 32 | F |
| GPT-4o mini | LS | 19.5 | No | 33 | F |
| GPT-4o | NP | 24.5 | Yes | 41 | D |
| GPT-4o | LE | 20.5 | No | 34 | F |
| GPT-4o | LS | 22 | No | 37 | F |
| o1-preview | NP | 25.5 | Yes | 43 | D |
1 NP for no prompt, LE for logistics expert and LS for logistics student.
References
- Biever, C. ChatGPT broke the Turing test-the race is on for new ways to assess AI. Nature 2023, 619, 686–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Tang, R. Performance Law of Large Language Models. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.09895. [Google Scholar]
- Chatbot Arena LLM Leaderboard: Community-Driven Evaluation for Best LLM and AI Chatbots. Available online: https://lmarena.ai/?leaderboard (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- GitHub OpenAI Repository Simple-Evals. Available online: https://github.com/openai/simple-evals?tab=readme-ov-file#benchmark-results (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Zhou, K.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhao, W.X.; Chen, X.; Lin, Y.; Wen, J.R.; Han, J. Don’t make your llm an evaluation benchmark cheater. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2311.01964. [Google Scholar]
- Rutinowski, J.; Franke, S.; Endendyk, J.; Dormuth, I.; Roidl, M.; Pauly, M. The Self-Perception and Political Biases of ChatGPT. Hum. Behav. Emerg. Technol. 2024, 2024, 7115633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snyder, B.; Moisescu, M.; Zafar, M.B. On early detection of hallucinations in factual question answering. In Proceedings of the 30th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Barcelona, Spain, 25–29 August 2024; pp. 2721–2732. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Z.; Yu, T.; Xu, Y.; Lee, N.; Ishii, E.; Fung, P. Towards mitigating LLM hallucination via self reflection. In Proceedings of the Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: EMNLP 2023, Singapore, 6–10 December 2023; pp. 1827–1843. [Google Scholar]
- Palen-Michel, C.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, D.; Xu, C.; Wu, Z. Investigating LLM Applications in E-Commerce. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2408.12779. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Gomaa, A.; Semrau, S.; Haderlein, M.; Lettmaier, S.; Weissmann, T.; Grigo, J.; Tkhayat, H.B.; Frey, B.; Gaipl, U.; et al. Benchmarking ChatGPT-4 on a radiation oncology in-training exam and Red Journal Gray Zone cases: Potentials and challenges for ai-assisted medical education and decision making in radiation oncology. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1265024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, E.; Rutinowski, J.; Pauly, M. Behind the Screen: Investigating ChatGPT’s Dark Personality Traits and Conspiracy Beliefs. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2402.04110. [Google Scholar]
- Bureau, S.U.C. Industry Revenue of “General Warehousing and Storage“ in the U.S. from 2012 to 2024. Available online: https://www.statista.com/forecasts/409692/general-warehousing-and-storage-revenue-in-the-us (accessed on 22 January 2025).
- Chen, J.; Zhao, W. Logistics automation management based on the Internet of things. Clust. Comput. 2019, 22, 13627–13634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouda, A.; Ghanem, A.; Reining, C. DoPose-6d dataset for object segmentation and 6d pose estimation. In Proceedings of the 2022 21st IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications (ICMLA), Nassau, Bahamas, 12–14 December 2022; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 477–483. [Google Scholar]
- Franke, S.; Bommert, A.; Brandt, M.J.; Kuhlmann, J.L.; Olivier, M.C.; Schorning, K.; Reining, C.; Kirchheim, A. Smart pallets: Towards event detection using imus. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE 29th International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation (ETFA), Padova, Italy, 10–13 September 2024; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- 4flow. Warehouse and Distribution. Available online: https://www.4flow.com/solutions/warehouse-and-distribution.html (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- DHL. Warehousing Solutions. Available online: https://www.dhl.com/de-en/home/supply-chain/solutions/warehousing.html (accessed on 28 January 2025).
- Maliugina, D. 45 Real-World LLM Applications and Use Cases from Top Companies. Available online: https://www.evidentlyai.com/blog/llm-applications (accessed on 22 January 2025).
- Kmiecik, M. ChatGPT in third-party logistics–The game-changer or a step into the unknown? J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2023, 9, 100174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voß, S. Successfully Using ChatGPT in Logistics: Are We There Yet? In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computational Logistics, Berlin, Germany, 6–8 September 2023; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023; pp. 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Frederico, G.F. ChatGPT in supply chains: Initial evidence of applications and potential research agenda. Logistics 2023, 7, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenAI. Model Release Notes. Available online: https://help.openai.com/en/articles/9624314-model-release-notes (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Zhao, W.X.; Zhou, K.; Li, J.; Tang, T.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Min, Y.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Z.; et al. A survey of large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.18223. [Google Scholar]
- IBM. What Are Large Language Models (LLMs)? Available online: https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/large-language-models (accessed on 15 December 2024).
- Carlini, N.; Tramer, F.; Wallace, E.; Jagielski, M.; Herbert-Voss, A.; Lee, K.; Roberts, A.; Brown, T.; Song, D.; Erlingsson, U.; et al. Extracting training data from large language models. In Proceedings of the 30th USENIX Security Symposium (USENIX Security 21), Virtual, 11–13 August 2021; pp. 2633–2650. [Google Scholar]
- Raffel, C.; Shazeer, N.; Roberts, A.; Lee, K.; Narang, S.; Matena, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, P.J. Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer. J. Mach. Learn. Res. 2020, 21, 1–67. [Google Scholar]
- Naveed, H.; Khan, A.U.; Qiu, S.; Saqib, M.; Anwar, S.; Usman, M.; Akhtar, N.; Barnes, N.; Mian, A. A comprehensive overview of large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2307.06435. [Google Scholar]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. Available online: https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper_files/paper/2017/file/3f5ee243547dee91fbd053c1c4a845aa-Paper.pdf (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Kirchenbauer, J.; Geiping, J.; Wen, Y.; Katz, J.; Miers, I.; Goldstein, T. A watermark for large language models. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, Honolulu, HI, USA, 23–29 July 2023; pp. 17061–17084. [Google Scholar]
- OpenAI. Introducing ChatGPT. Available online: https://openai.com/index/chatgpt/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Chang, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhu, K.; Chen, H.; Yi, X.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. A survey on evaluation of large language models. ACM Trans. Intell. Syst. Technol. 2024, 15, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bubeck, S.; Chandrasekaran, V.; Eldan, R.; Gehrke, J.; Horvitz, E.; Kamar, E.; Lee, P.; Lee, Y.T.; Li, Y.; Lundberg, S.; et al. Sparks of artificial general intelligence: Early experiments with gpt-4. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2303.12712. [Google Scholar]
- Bommasani, R.; Hudson, D.A.; Adeli, E.; Altman, R.; Arora, S.; von Arx, S.; Bernstein, M.S.; Bohg, J.; Bosselut, A.; Brunskill, E.; et al. On the opportunities and risks of foundation models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.07258. [Google Scholar]
- Adeshola, I.; Adepoju, A.P. The opportunities and challenges of ChatGPT in education. Interact. Learn. Environ. 2023, 32, 6159–6172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sok, S.; Heng, K. ChatGPT for education and research: A review of benefits and risks. Cambodian J. Educ. Res. 2023, 3, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.K. What is the impact of ChatGPT on education? A rapid review of the literature. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montenegro-Rueda, M.; Fernández-Cerero, J.; Fernández-Batanero, J.M.; López-Meneses, E. Impact of the implementation of ChatGPT in education: A systematic review. Computers 2023, 12, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassini, S. Shaping the future of education: Exploring the potential and consequences of AI and ChatGPT in educational settings. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Watanobe, Y. ChatGPT for education and research: Opportunities, threats, and strategies. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halaweh, M. ChatGPT in education: Strategies for responsible implementation. Contemp. Educ. Technol. 2023, 15, ep421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasneci, E.; Seßler, K.; Küchemann, S.; Bannert, M.; Dementieva, D.; Fischer, F.; Gasser, U.; Groh, G.; Günnemann, S.; Hüllermeier, E.; et al. ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education. Learn. Individ. Differ. 2023, 103, 102274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geerling, W.; Mateer, G.D.; Wooten, J.; Damodaran, N. Is ChatGPT Smarter Than a Student in Principles of Economics. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4356034 (accessed on 4 December 2024).
- Susnjak, T.; McIntosh, T.R. ChatGPT: The end of online exam integrity? Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stutz, P.; Elixhauser, M.; Grubinger-Preiner, J.; Linner, V.; Reibersdorfer-Adelsberger, E.; Traun, C.; Wallentin, G.; Wöhs, K.; Zuberbühler, T. Ch (e) atGPT? an anecdotal approach addressing the impact of ChatGPT on teaching and learning Giscience. GI_Forum 2023, 11, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchberger, B. Is ChatGPT Smarter Than Master’s Applicants; Research Institute for Symbolic Computation: Linz, Austria, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- de Winter, J.C. Can ChatGPT pass high school exams on English language comprehension? Int. J. Artif. Intell. Educ. 2023, 34, 915–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.H.; Hickman, K.E.; Monahan, A.B.; Schwarcz, D. ChatGPT goes to law school. J. Leg. Educ. 2021, 71, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, S. Words Are Flowing Out Like Endless Rain Into a Paper Cup’: ChatGPT &. Law School Assessments, SSRN Electronic Journal. 2023. Available online: https://ssrn.com/abstract=4359407 (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Kung, T.H.; Cheatham, M.; Medenilla, A.; Sillos, C.; De Leon, L.; Elepaño, C.; Madriaga, M.; Aggabao, R.; Diaz-Candido, G.; Maningo, J.; et al. Performance of ChatGPT on USMLE: Potential for AI-assisted medical education using large language models. PLoS Digit. Health 2023, 2, e0000198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilson, A.; Safranek, C.W.; Huang, T.; Socrates, V.; Chi, L.; Taylor, R.A.; Chartash, D. How does ChatGPT perform on the United States Medical Licensing Examination (USMLE)? The implications of large language models for medical education and knowledge assessment. JMIR Med. Educ. 2023, 9, e45312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fijačko, N.; Gosak, L.; Štiglic, G.; Picard, C.T.; Douma, M.J. Can ChatGPT pass the life support exams without entering the American heart association course? Resuscitation 2023, 185, 109732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Gong, Z.; Wang, G.; Jia, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Fan, Q.; Wu, S.; Hu, W.; Li, X. ChatGPT performs on the Chinese national medical licensing examination. J. Med. Syst. 2023, 47, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huh, S. Are ChatGPT’s knowledge and interpretation ability comparable to those of medical students in Korea for taking a parasitology examination?: A descriptive study. J. Educ. Eval. Health Prof. 2023, 20, 1. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Frieder, S.; Pinchetti, L.; Griffiths, R.R.; Salvatori, T.; Lukasiewicz, T.; Petersen, P.; Berner, J. Mathematical capabilities of chatgpt. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2023, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, S.; Rafi, S.; LaToza, T.D.; Moran, K.; Lam, W. Chatgpt and software testing education: Promises & perils. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE International Conference on Software Testing, Verification and Validation Workshops (ICSTW), Dublin, Ireland, 16–20 April 2023; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2023; pp. 4130–4137. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, P.; Xiromeriti, M. ChatGPT performance on multiple choice question examinations in higher education. A pragmatic scoping review. Assess. Eval. High. Educ. 2024, 49, 781–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, N.; Choi, G.S.; Lee, W.Y. ChatGPT goes to the operating room: Evaluating GPT-4 performance and its potential in surgical education and training in the era of large language models. Ann. Surg. Treat. Res. 2023, 104, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, M.G.; Cai, N.; Constantinescu, D. The performance of ChatGPT on orthopaedic in-service training exams: A comparative study of the GPT-3.5 turbo and GPT-4 models in orthopaedic education. J. Orthop. 2024, 50, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Currie, G.M. GPT-4 in nuclear medicine education: Does it outperform GPT-3.5? J. Nucl. Med. Technol. 2023, 51, 314–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, S.; Watari, T.; Erabi, A.; Sakaguchi, K. Performance of GPT-3.5 and GPT-4 on the Japanese medical licensing examination: Comparison study. JMIR Med. Educ. 2023, 9, e48002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.K.; Lee, H.E.; Kim, E. Performance of ChatGPT-3.5 and GPT-4 in national licensing examinations for medicine, pharmacy, dentistry, and nursing: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Med. Educ. 2024, 24, 1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savelka, J.; Agarwal, A.; An, M.; Bogart, C.; Sakr, M. Thrilled by your progress! large language models (gpt-4) no longer struggle to pass assessments in higher education programming courses. In Proceedings of the 2023 ACM Conference on International Computing Education Research, Chicago, IL, USA, 7–11 August 2023; Volume 1, pp. 78–92. [Google Scholar]
- Yeadon, W.; Peach, A.; Testrow, C. A comparison of human, GPT-3.5, and GPT-4 performance in a university-level coding course. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 23285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Hou, J.; Wu, Z.; Shu, P.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Gu, B.; Filla, N.; Li, Y.; Liu, N.; et al. Assessing Large Language Models in Mechanical Engineering Education: A Study on Mechanics-Focused Conceptual Understanding. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2401.12983. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, D.M.; Bommarito, M.J.; Gao, S.; Arredondo, P. Gpt-4 passes the bar exam. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2024, 382, 20230254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzini, R.; Accorsi, R.; Bozer, Y.A.; Heragu, S. Warehousing and Material Handling Systems for the Digital Industry. In Warehousing and Material Handling Systems for the Digital Industry: The New Challenges for the Digital Circular Economy; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Diaz, A.; Smith, J.M. Facilities Planning and Design; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- White, J.; Fu, Q.; Hays, S.; Sandborn, M.; Olea, C.; Gilbert, H.; Elnashar, A.; Spencer-Smith, J.; Schmidt, D.C. A prompt pattern catalog to enhance prompt engineering with chatgpt. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2302.11382. [Google Scholar]
- Franke, S. Test Results: Can ChatGPT Solve Undergraduate Exams from Logistics Studies? An Investigation. Zenodo. Available online: https://zenodo.org/records/14412298 (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- TU Dortmund University. Module Description Bachelor’s Degree in Logistics. Available online: https://mb.tu-dortmund.de/storages/mb/r/Formulare/Studiengaenge/B.Sc._Logistik.pdf (accessed on 5 December 2024).
- Bloom, B.S.; Engelhart, M.D.; Furst, E.J.; Hill, W.H.; Krathwohl, D.R. Taxonomy of Educational Objectives; Longmans, Green: New York, NY, USA, 1964; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Krathwohl, D. A Revision Bloom’s Taxonomy: An Overview. In Theory into Practice; Taylor & Francis, Ltd.: Abingdon, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Forehand, M. Bloom’s taxonomy. Emerg. Perspect. Learn. Teaching Technol. 2010, 41, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Ning, R.; Teng, Z.; Liu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, Y. Evaluating the logical reasoning ability of chatgpt and gpt-4. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.03439. [Google Scholar]
- Großeschallau, W. Materialflussrechnung: Modelle und Verfahren zur Analyse und Berechnung von Materialflusssystemen; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ten Hompel, M.; Schmidt, T.; Dregger, J. Materialflusssysteme: Förder-und Lagertechnik; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Wang, X.; Schuurmans, D.; Bosma, M.; Ichter, B.; Xia, F.; Chi, E.; Le, Q.V.; Zhou, D. Chain-of-thought prompting elicits reasoning in large language models. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2022, 35, 24824–24837. [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson, M.D.; Dumontier, M.; Aalbersberg, I.J.; Appleton, G.; Axton, M.; Baak, A.; Blomberg, N.; Boiten, J.W.; da Silva Santos, L.B.; Bourne, P.E. The FAIR Guiding Principles for scientific data management and stewardship. Sci. Data 2016, 3, 160018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OpenAI. OpenAI’s Reinforcement Fine-Tuning Research Program. 2024. Available online: https://openai.com/form/rft-research-program/ (accessed on 7 December 2024).
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).