Abstract
Companies face uncertainties evaluating their own capabilities when implementing data analytics or data mining. Data mining is a valuable process used to analyze data and support decisions based on the knowledge generated, creating a pipeline from the phases of data collection to data preparation and data mining. In order to assess the target state of a company in terms of its data mining capabilities, maturity models are viable tools. However, no maturity models exist that focus on the data mining process and its particular phases. This article discusses existing maturity models in the broader field of data mining, such as data management, machine learning, or artificial intelligence. Focusing on the most cost-relevant phase of data preparation, the critical influences for the development of a maturity model for the phase of data preparation are identified and categorized. Additionally, a data preparation maturity model prototype is proposed. This provides the first step towards the design of a maturity model for data mining.
1. Introduction
Companies that want to implement technologies in the field of artificial intelligence (AI), such as data analytics or data mining, are often faced with the question of whether their data stock is suitable to serve as the basis for extensive analyses or individual data processing procedures. The increasing amount of available data in industry requires efficient methods for extracting the relevant knowledge. Data mining is an important process for discovering hidden patterns and correlations in large data sets [1]. This process is based on procedural models for the discovery of knowledge and comprises different phases. These often include target definition, data selection, data preparation, data mining, and post-processing [2]. Each of these phases has diverging demands regarding the input and output. Data preparation plays a crucial role, as it adapts the raw data to the requirements of the data mining algorithms; thus, it is a mandatory step to make data mining possible [3]. The entire data mining process is based on an underlying database, whose structure and content can result in a less successful analysis, high efforts and costs, and even failure. The evaluation of a dataset is, therefore, relevant and must be carried out in an appropriate level of detail in order to correctly determine the requirements for data mining and data preparation on the raw dataset.
In particular, company departments, who are supposed to assess a dataset, often come to different conclusions, such as with regard to the data quality and its dimensions [4]. For this reason, the use of assessment tools is suitable for gaining a common understanding of the degree of maturity of the company or its processes with respect to analytics, as well as the underlying data and company structures. The areas to be assessed for the maturity of these aspects are referred to as areas of expertise or dimensions [5]. Sadiq et al. [6] name a variety of alternative terms that are used in the literature, including terms such as constructs, elements, and indicators. This article refrains from further discussion of this diverse terminology.
Various instruments from different disciplines are available to assess maturity, such as maturity models. The International Organization for Standardization [7] defines maturity models as means of evaluating the current state of maturity. Hereby, maturity is defined as the state of a system (demonstrated by special characteristics) that permits it to operate in accordance with its business goals as a result of transformation. A maturity model generally has the task of evaluating the current status in a specific area and making targeted improvements. According to Schumacher et al. [8], the purpose of this instrument is to check the maturity level of an organization or a process with regard to a specific target state. Maturity models are available in multiple versions. A well-known example of a maturity model is the Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI), which is primarily used in the software development sector. In particular, there are design guides for creating maturity models suitable for data mining in the IT sector [9].
Ref. [9] have developed a catalogue of requirements that serves as a manual in combination with a derived process model. All objects are suitable for consideration but these are primarily from companies and processes in the IT sector. Ref. [9] extensively examined the existing models and the literature and identified the list of requirements for the design and development of maturity models, as stated in Table 1.

Table 1.
Requirements based on [9].
However, the underlaying research question is which maturity model seems suitable for evaluating the use of specific data mining process models. In particular, this discussion in Section 2.2, Section 2.3, Section 2.4, Section 2.5 and Section 2.6 examines the question of whether different maturity models must be used in individual phases of the data mining process. Due to the complexity of evaluating data mining process models regarding the different demands in each phase, subordinate maturity models must be developed for different phases and combined in a superordinate data mining maturity model. In this article, a maturity model prototype is developed for the most laborious phase of data preparation. In Section 2, maturity models in the field of data mining are discussed, such as maturity models for machine learning, artificial intelligence, or data management. In Section 3, an overview of the data preparation phase is given in the context of data mining. In Section 4, the information from the previous sections is combined in order to derive the influences on the data preparation pipeline, creating a basis for maturity model development, which is used for the data preparation maturity model prototype. The maturity model prototype is designed based on the requirements outlined in [9] and stated in Table 1. The article finishes with a short discussion, summary, and outlook.
2. Searching for Data Mining Maturity Models
2.1. Overview of Maturity Models in the Field of Data Mining
When discussing maturity models for the purpose of data mining in companies, the overarching topic of AI is an obvious starting point. Data mining and AI are closely related, as AI algorithms are often used in the field of data mining. In general, however, AI encompasses a wider range, such as technologies, frameworks, and tools [10]. There are different models (some of which are individualized) that are used to evaluate the possibilities of using AI in companies. In the literature, these models can be found under many catchphrases, such as big data maturity models, digital maturity models, or Industry 4.0 and 5.0 maturity models. Most models are based on question catalogues, which are usually evaluated according to a simple binary scheme, thereby determining the AI maturity level. Alternatively, there is occasionally a matrix scheme that is implemented either as a simple decision matrix or in a few cases via a rating scale. The maturity level is either specified as a percentage or in corresponding steps or levels (on average five; cf. [5]). In general, a higher nominal or percentage value means a higher maturity level. It is striking that a large number of the models originate from practice, and only a few of them have been published by scientific institutions. Table 2 lists relevant representatives of the large number of practical models.

Table 2.
Approaches of maturity models.
Table 2 emphasizes the differences in structure and focus of maturity models regarding the areas of expertise. An overview of further AI maturity models and their possible applications can be found in [5,6,14].
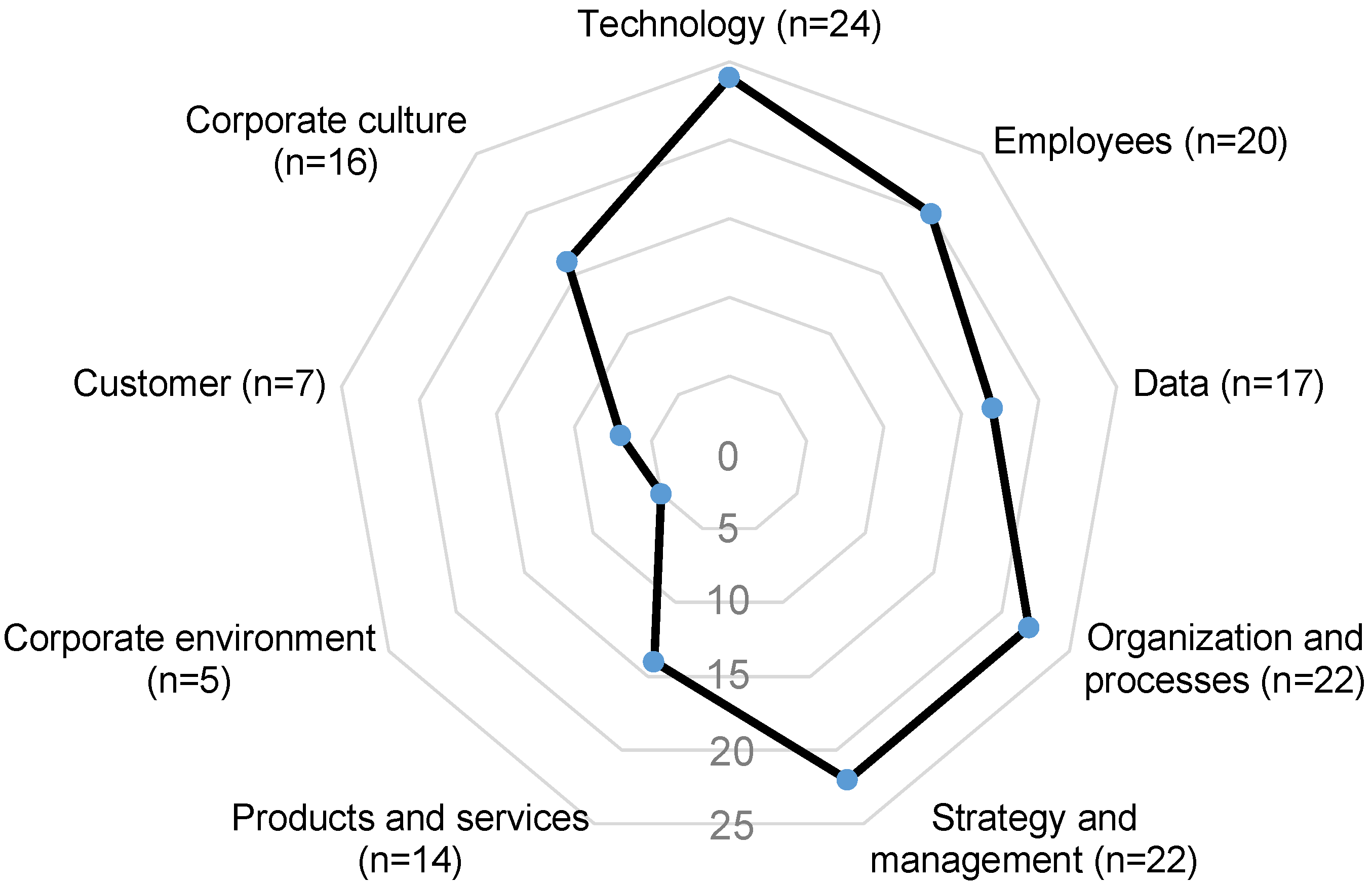
Data play a prominent role in most maturity models. In a number of models, there are dimensions that address data acquisition, data storage, and further processing separately. Other contributions address the use of AI specifically for data quality problems, e.g., uncertainties or incomplete data, and call for data to be treated as a special object of investigation [15]. Hein-Pensel et al. [16] have examined n = 24 models for the maturity of Industry 5.0, categorizing areas of expertise in dimensions depicted in Figure 1, in which the models show a large overlap with AI maturity models and show that 17 models address the dimension of data.
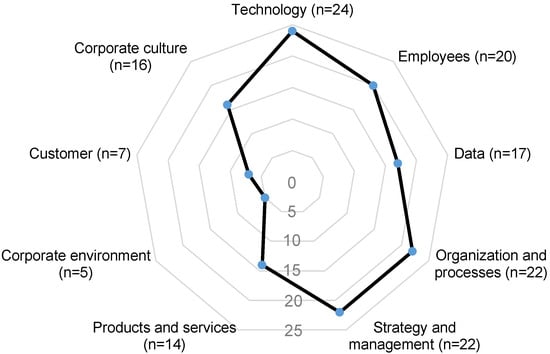
Figure 1.
Maturity model dimensions for Industry 5.0 according to [16].
Figure 1 depicts technology, organization and processes, strategy and management, employees and corporate culture as being highly relevant. When trying to apply these models to data mining, it is noticeable that most of the models are too general, and only a subset of the dimensions of the existing maturity models can also be used in data mining. In addition, the use of data mining technologies is sometimes already part of the question catalogue, which is evident, for example, in Accenture’s question “Do you use data science and machine learning teams effectively throughout the AI development lifecycle?”.
For these reasons, it seems expedient to consider maturity models that are specifically suitable for the use of data mining. These models can be found in the literature under analytics maturity models. For example, Grossman [17] generally classifies analytics models as statistical or data mining models and differentiates between the model, infrastructure, and operations in the area of data mining in his maturity framework. A well-known representative of analysis maturity models is the DELTA framework, which was finally published in 2010 [18]. Analytics maturity models are used in different domains. Lismont et al. [19] show that just under 30% come from the pure analytics sector, closely followed by the IT and finance sectors with 14% each. The area of production and logistics is not listed as a separate domain in these articles. Further models can be found in [20,21].
2.2. Maturity Models and Process Models for Data Mining
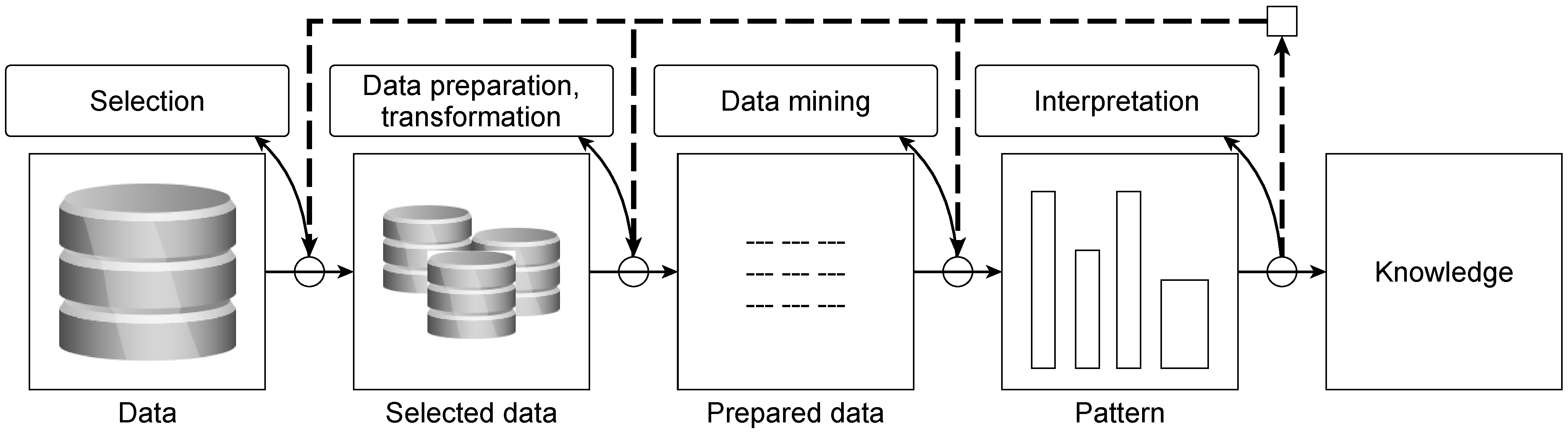
The difficulty in analyzing maturity models is that classic process models such as SEMMA [22], CRISP-DM [23], or the knowledge discovery in databases (KDD) process model from Fayyad et al. [1] are also referred to as maturity models, although the focus here is on the iterative process of knowledge discovery. Figure 2 shows an example of the KDD process model.
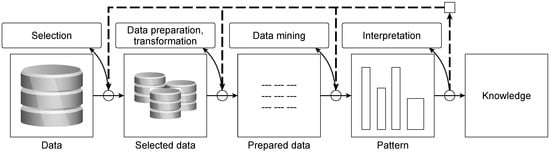
Figure 2.
KDD process model according to [1].
In Figure 2, the individual phases of selection, data preparation, transformation, data mining, and interpretation, as well as the respective phase results in the KDD process model, are presented. The iterative procedure of the KDD process model is indicated by the dashed arrows and can be applied after each phase. Although it is possible to draw conclusions about the maturity of the company with regard to the use of data mining when executing process models, the objectives regarding maturity and process models differ [10]. Overall, it can be stated that a data mining process model defines the process according to which data mining is carried out, while a data mining maturity model evaluates the maturity of a company with regard to the use of data mining.
2.3. Process Mining Maturity Models
The literature has some specific maturity models for mining topics that differ from the analytics approach, with process mining (PM) dominating the literature. Maturity models in process mining aim to assess the maturity level of a company in terms of its processes and their optimization. These models evaluate the current status of processes in a company and identify weaknesses in order to identify potential for improvement. A good overview of PM maturity models in the context of logistics can be found in the paper by Jacobi et al. [24] and approaches to the PM maturity model in software development in the paper by Samalikova et al. [25]. The typical dimensions of these maturity models are process documentation, process automation, process measurement and analysis, and optimization aspects. In summary, adaptation for data mining or even individual process model phases is not trivial.
2.4. Maturity Models for Machine Learning
Other approaches to determining the maturity level for data mining involve maturity models in the field of machine learning and its representatives such as deep learning models. One well-known representative is the Gartner Maturity Model, which assesses the maturity level of a company in terms of its ability to successfully implement and use machine learning [21]. However, the transitions between analysis tasks and machine learning, which is a classic analysis task, are fluid and are also assigned differently in various literature analyses. The Machine Learning Maturity Model from SAS is representative for a model family of maturity level tools from SAS [21]. The model evaluates the maturity level of the organization in terms of its ability to use machine learning successfully. A description of the models in this section and further models can be found in the paper by Król and Zdonek [21]. Here, depending on the model, the scope appears to be very broad and the use for data mining or individual phases is sometimes not sufficiently specific and involves major adaptations.
2.5. Maturity Models for Data
A further approach to selecting a suitable maturity model for data mining is to determine the maturity level of the data. This is also addressed, for example, in the statement by Heap [26]: “Data maturity boils down to how well a company leverages data for decision-making”. Lismont et al. [19] state that data management and the integration and sharing of data are major challenges when it comes to the maturity of a company’s analytical capabilities. The managed data are also of importance for the implementation and results of data mining [10]. This paper follows the understanding that data are aggregated, unified, and standardized in preparation for data mining. Hereby, preparation involves the task of integrating and harmonizing data from different sources and formats in order to provide a consistent database for data mining. To judge whether a company can successfully implement data preparation processes, the dimensions of the data from the AI maturity models already discussed here can be used. Depending on the model, other dimensions such as technologies or tools can also be used.
The maturity models that deal with data in practice and science show very different structures and areas of impact. Some maturity models focus on data quality or further processing, while others include concepts such as data spaces [27]. An overview of common models and their dimensions can be found in the paper by Belghith et al. [28]. However, their overview also illustrates the basic theme of the overlaps between the individual maturity models. In the list provided by Belghith et al. [28], the area of analytics is a sub-area of the data dimension. The authors emphasize data and information governance as particularly relevant. By looking at maturity models from the data and information governance family perspective, organizational aspects of data management are linked with process-related decision-making powers of data governance. The assessment spectra of the individual models range from data infrastructures and data processing tools to the topics already addressed here, such as big data competencies or big data reference architectures. Comparable to the AI models, in recent years maturity models have been increasingly developed from practical experience. Some common representatives are listed in Table 3.

Table 3.
Representatives of companies’ maturity models.
Table 3 shows differences in maturity models regarding the structure and focus of the areas of expertise, comparable to the approaches listed in Table 2. The maturity levels to be achieved also vary greatly. For example, Snowplow specifies five possible maturity levels in its model. These levels include ‘aware’ through to ‘data informed’ and the highest level ‘pioneer’, which also focuses on ‘data security’. A comprehensive list of other models relating to data or analytics can be found in the paper by Belghith et al. [28].
2.6. Ethic Maturity Models
In AI and machine learning research, the ethics considerations have considerably advanced over the last years [32]. Here, governments have provided a set of principles to be considered when AI-based systems are designed and used [33]. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) protects data from individuals via anonymization, consent management, or data minimization [34]. An assessment based on the GDPR is researched in the literature [35] but not in regards to maturity. Furthermore, the EU Artificial Intelligence Act prohibits certain AI practices such as manipulative techniques or real-time biometric identification systems in public spaces [36]. A previous study [37] names Article 21 of the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights, which prohibits bias based on for instance race, sex, or disabilities.
Thus, bias has to be reduced, such as racial bias [38], which can be addressed using different bias mitigation strategies [39]. While bias mitigation strategies often decrease the machine learning performance on one hand, they should be able to increase fairness on the other, without decreasing the machine learning performance remarkably [40].
Additionally, ethics maturity models have been developed to address these considerations [41], balancing the demands of security and privacy, fairness, accountability, and understandability considerations for AI maturity models. Representatives of ethics maturity models are listed in Table 4.

Table 4.
Ethics maturity models.
Table 4 shows the extent of different areas of expertise for ethics maturity models. These considerations are also applicable to data mining maturity models due to their comparable procedures and dependencies.
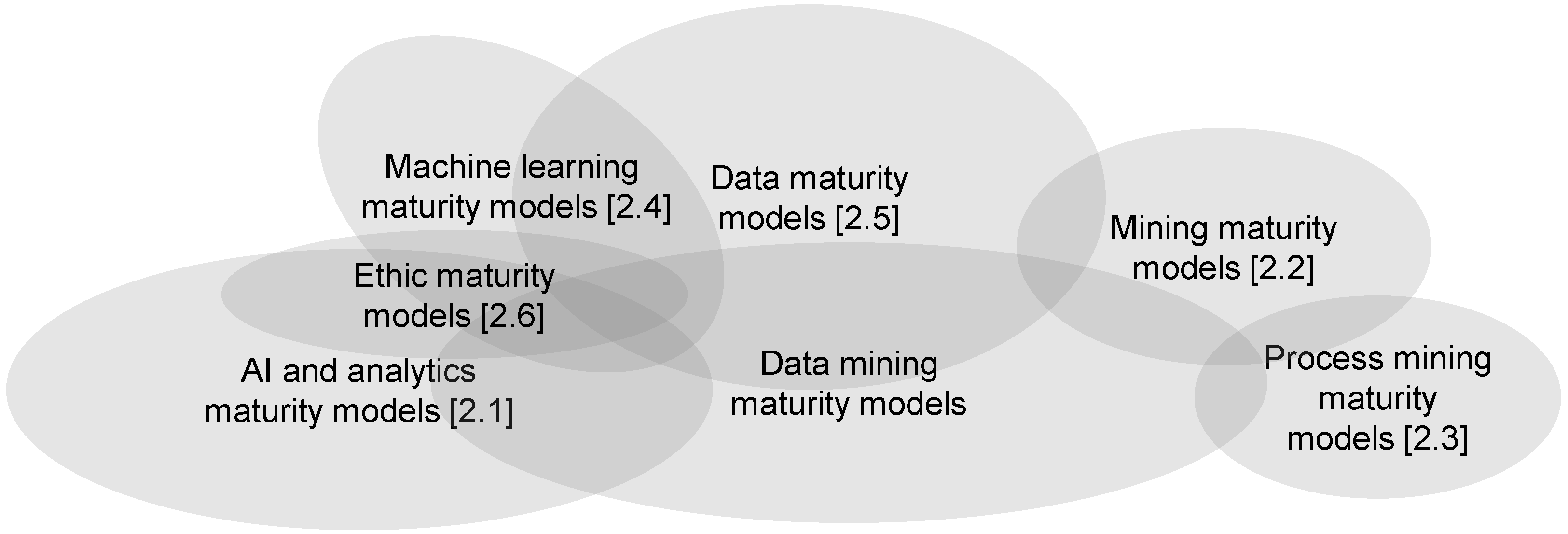
In summary, it is not trivial to make a statement about data mining maturity using the existing maturity models, as a variety of models can be used in individual cases, such as those schematically depicted in Figure 3 with references to the sections of this paper.
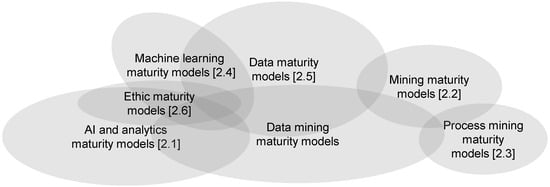
Figure 3.
Schematic representation of overlapping terms in relation to maturity models in the analyzed literature.
Figure 3 also portrays overlaps of maturity models from different fields such as AI and analytics maturity models, ethic maturity models, machine learning maturity models, and data maturity models, as well as data maturity models and mining maturity models, plus the overlap of mining maturity models and process mining maturity models. As a result, it seems promising to consider individual phases of data mining and to discuss whether different maturity models are selected for these partial considerations. This article focuses on the preparation phase of data mining and discusses the specifics and requirements.
3. Data Preparation for Data Mining
3.1. Overview of Data Prepararion in the Context of Data Mining
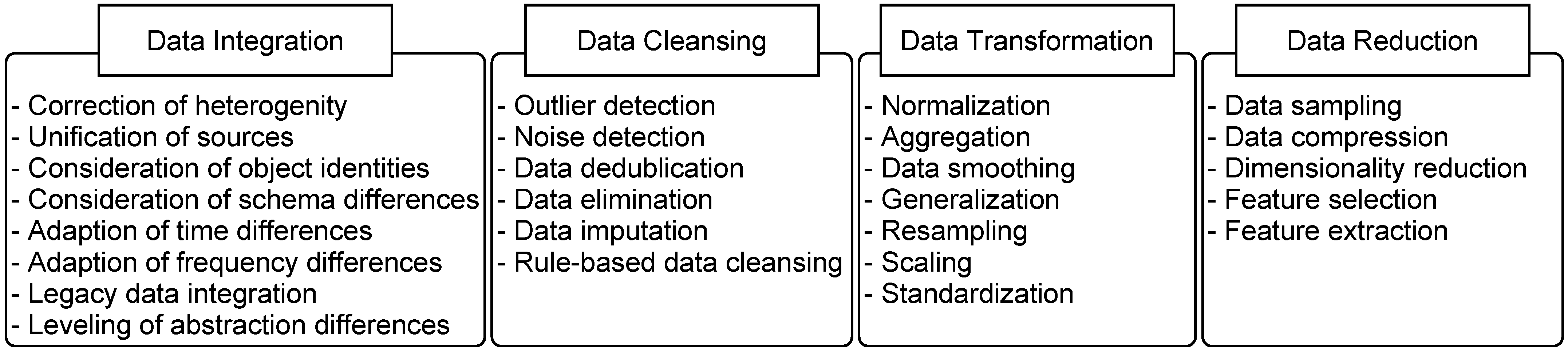
According to García et al. [3], data preparation involves adapting the data to be processed to the requirements of the data mining algorithms, thereby making data mining possible. The data preparation phase is described differently in the various data mining process models. In the literature, the definition of the exact task and scope of the data preparation phase differs depending on the process model, as does the data preparation phase itself. For example, Fayyad et al. [1] separate data preparation and data reduction into individual phases, whereas this is not the case with CRISP-DM [23]. With regards to the often included phases in data mining process models [2], all steps between the selection of the data to be used on the basis of a superordinate question and the data mining are defined as data preparation in this paper. As per García et al. [44], this includes the steps of data integration, data cleansing, data transformation, and data reduction. Before data mining can be applied, the data preparation phase must fulfill different tasks that are derived from the requirements of the data mining algorithms, requiring procedures for processing these tasks. Due to the fuzzy definitions of the individual steps between different sources of data preparation, the tasks to be performed for suitable data preparation are outlined below and summarized in Figure 4.
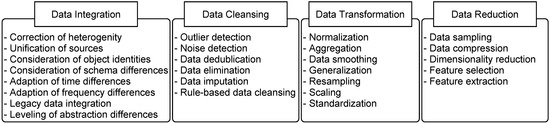
Figure 4.
Overview of the data preparation tasks.
Figure 4, however, does not imply that all listed tasks are to be performed for all data mining processes. Often fewer preparation tasks must be completed, and sometimes tasks must be addressed more than once.
The data preparation phase not only has to ensure the technical soundness of the data mining process. Similar to the implications for ethical maturity models mentioned in Section 2.6, ethical considerations must also be addressed in the data preparation phase. A previous paper [45] considered combatting bias and ensuring fairness as a part of the data quality assessment. Despite the focus on AI, ref. [42] gives an extensive overview towards privacy and ethics in terms of explainability, privacy, technical robustness and safety, transparency, data use and design, societal well-being, and accountability that is relevant for data preparation. Multiple data preparation tasks can lead to bias, e.g., elimination, imputation, outliers, sampling differences [46], and data integration [47], as well as generally biased removal or addition of data. A previous paper [37] presents a comprehensive survey of techniques that address bias in data preprocessing.
3.2. Data Integration
Companies usually have distributed databases, often with different data models. Therefore, different databases have to be merged for data mining. The linking of different databases is often referred to as data integration. Ethics considerations necessitate bias discovery during data integration, for example by using approximate conditional functional dependencies [48], to identify the need for action. The challenges in data integration include missing homogeneity of the data (e.g., tables, XML documents, unstructured texts), the number of sources, object identity and schema differences, time and frequency differences, the handling of legacy data, abstraction level differences, and data quality deficiencies [49].
3.3. Data Cleansing
These data quality deficiencies are measurable and require appropriate handling depending on the deficiency and its context. The elimination of data quality deficiencies, often referred to as data cleansing, can be divided into more specific tasks [50] such as noise detection [51], data deduplication [52], data elimination [53], data imputation [54], rule-based data cleansing [55], and outlier detection [56].
Noise detection identifies imperfections in data, such as measuring errors, to either ignore the noise, filter it out, or correct it [51]. Redundancies in data and databases are removed or compressed using data deduplication techniques to reduce storage space or avoid duplications in a target dataset [52,57]. Data deduplication, thus, is closely connected to data reduction, and relevant when cleansing an analyzed dataset with regard to false weights on duplicate data or logic issues, e.g., a machine working on an identical product twice at the same time. Missing values can be countered by using data elimination and imputation. Data elimination involves deleting excerpts from the dataset, so that the missing value has no or a reduced effect [53]. However, data imputation inserts values into the missing spots, resolving this issue [54]. Certain considerations for fairness in imputation should be made [58]. Rule-based data cleansing mechanisms enforce data quality rules such as integrity constraints, reducing inconsistencies in the data [55]. Outlier detection is one of the most classical and complex tasks in data preparation. Different types of outliers require specialized methods to detect values that deviate from the expected data [59].
Especially in the task of outlier detection, the degree of complexity for an application of preparation methods depends on different factors. This covers a spectrum ranging from very simple trimming of 25% of the lowest and highest values [60] up to complex outlier interpretation procedures as a separate data mining process [59]. There are similar differences in the degree of complexity of other tasks used for correcting data quality deficiencies. Often, preparatory transformations of the dataset are not only necessary for the application of data mining procedures in the data mining phase but also for data preparation procedures.
3.4. Data Transformation
Data transformations convert data into adequate forms of representation for the respective processes [61]. Possible transformations are, for example, normalizations [62], aggregations [63], data smoothing [64], discretizations [65], generalizations [66], resampling [67], scaling [68], and standardization [69]. Singh and Singh [62] describe normalization as scaling or transforming data to ensure an equal contribution from each feature. Aggregations refer to the act of locating, collecting, and presenting data in a summary format for an analysis, depending on the type of data and preparation task [70]. Data smoothing is based on functions having similar values for close observations [64], which can be used to reduce deviations in the data structure. Discretizations are used to find concise data representations as categories that are adequate for algorithms, retaining as much information in the original continuous attribute as possible [65]. Generalizations are necessary to enable the use of algorithms on different datasets or domains. For example, lots of methods of domain generalization such as domain alignment or data augmentation can be used [66]. Resampling uses sample data for the purpose of statistical inference without parametric assumptions, which cannot be verified in practice [67]. Scaling can, for example, change the scale of an attribute, such as changing a weight attribute in British imperial units from one system or dataset to metric units [10]. Data standardization can remove obstacles, such as meta data uncertainties, data transfer obstacles, and missing data, leading to smoother data flows and better machine learning [69].
Aggregations and standardizations in particular often overlap with data integration and data reduction. Additionally, other overlaps with data reduction exist, such as discretization or data smoothing. The transformations are in most cases a prerequisite for the application of subsequent methods, such as normalization as a frequent antecedent for clustering methods according to Patel and Thakral [71]. In addition to requirements for the structure of data, the data mining algorithm can also have requirements for the quantity of data.
3.5. Data Reduction
To decrease the amount of data, the dataset is converted into a reduced representation [44]. In the literature, this selection procedure is often referred to as data reduction. Data reduction includes, for example, data sampling [72], data compression [73], dimensionality reduction, feature selection, and feature extraction [74]. Sampling provides a fast approximation to the data that can be used as a preview without the need for full data reconstruction, thereby reducing the output data size [72]. Data compression transforms the data to a compressed form utilizing patterns in the data [73]. Dimensionality reduction is applied in order to ameliorate the accuracy of learning features and to decrease the training time by eliminating irrelevant data, noise, and redundant features [74]. Feature selection can be used to reduce the size of the data, decrease the needed storage, increase the prediction accuracy, evade overfitting, and reduce the processing time by generating and evaluating a subset of the dataset [74]. Feature extraction creates new features that depend on the original input feature in order to decrease the high dimensionality of the feature vector used in the analysis [74].
Some tasks overlap with data transformation and data integration, such as the aggregation of multiple attributes, as well as data cleansing processes, such as the task of deleting data. However, separation is possible due to the goal of reducing the amount of data. This is also a difference between the tasks of data preparation and legislation because the principles of purpose limitation and storage limitation of the GDPR concern data collection and selection but not data reduction, although data is also excluded.
3.6. Models Targeting Data Preparation
The necessity of using data preparation processes is derived on the one hand from the underlying data and on the other hand from the requirements of the subsequent data mining algorithm. With over 60% of the time required for the entire data mining process being spent on preparation [75], the majority of costs and effort are generated during data preparation. This is reinforced by the often subjective nature of the implementation of the data preparation phase in the assessment of intermediate steps. Users must identify the necessary data preparation steps and decide which methods to apply to the dataset. This causes challenges in the proper assessment of the situation and risks in decreasing the overall analysis quality by applying unsuitable or incorrectly used methods. While research is being conducted into the partial automation or simplification of data preparation methods [76], problems with the underlying data are the reason behind the time-consuming data preparation phase. Maharana et al. [70] list the three simple categories of problems with real data and their possible solutions: too much data, too little data, and distributed data. To address the problems related to using appropriate data preparation techniques, the problems need to be identified and assessed by a domain expert or a machine. This underlines the importance of appropriate data management and the use of existing skills in companies to ensure an effective data preparation phase and improve the quality of the analysis results.
In addition to the maturity models listed in Section 2, frameworks exist in the context of data mining, such as the Framework for Data Quality in Knowledge Discovery Tasks [77] or the Big Data Quality Management Framework [78]. These postulate a structured approach from the detection of data quality deficiencies to the actual analysis, without full consideration of the data quality dimensions and data preparation procedures. Possible reasons include the complexity of data quality assessment and the data preparation phase, as well as their inconsistent definitions. Therefore, directly assigning an identified data quality deficiency in existing data to the best possible procedure for remedying this deficiency is not possible.
However, there are approaches for assigning a selection of procedures to treat a given problem. Maharana et al. [70], for example, provide a brief overview of general problems and their solutions. Direct conclusions based on data quality deficiencies are also possible for procedure groups, such as the need to use imputation or elimination procedures in the case of an undesirable incompleteness in the available data set due to missing values. Nevertheless, such direct conclusions can only be drawn in consultation with technical experts, as the missing values mentioned in the example may also contain a known desired underlying mechanism, as Vetrò et al. [79] found in their field study. Close collaboration between data analysts and experts from the respective domain is, therefore, crucial in order to find effective solutions to data quality problems and improve the quality of the analysis results.
4. Maturity Model Implications for Data Preparation
4.1. Description of the Data Preparation Pipeline
The data preparation tasks outlined in Section 3 must be captured by taking a holistic view of the state in which a company finds itself in the context of data mining. A maturity model can be used to assess this state but it must take into account the broad spectrum of possibilities within the data preparation phase and the associated requirements. In accordance with the dependency of the data preparation phase on the application of the planned data mining algorithms, the tasks of data preparation are defined by the required output of the data preparation phase, which simultaneously represents the input for the data mining algorithms. On the other hand, the tasks of data preparation impose requirements on the underlying raw data. Thus, the feasibility of a specific data preparation phase for a selected data mining algorithm can be evaluated on the basis of the raw data. Companies can either use selected data mining algorithms or the available raw data as a basis for deciding how to carry out the data mining process. In the case of selected data mining algorithms, the analysis is carried out on the basis of an expectation. Insofar as the analysis options are to be checked on the basis of the raw data, this requires knowledge about data mining algorithms, such as the overview by Gupta and Chandra [80]. In both cases, it is possible that no analysis is feasible because the raw data are insufficient, requiring a decision to adapt the data collection process.
It is not expedient to develop maturity models solely to assess the applicability of a data mining algorithm through data preparation, as the applicability of a data mining algorithm is no guarantee for the quality of the data mining results. Incorrect findings based on the data mining results can cause high costs and effort and discredit the actual justification for the application of data mining processes. According to the principle of “garbage in, garbage out”, only an appropriate data preparation phase supports desirable results [44]. It is not only the recognition of the necessary data preparation tasks that is relevant here but also the best possible execution of the tasks in the given context. Thus, for example, imputation with average values of an attribute is an improvement in data completeness that can make the otherwise impossible application of a data mining algorithm possible. However, it also represents a possible cause of incorrect data mining results because the imputed values can often have unrealistic combinations of values with other attributes. More complex imputation methods, which estimate the missing values for each data set based on the available data, frequently show more realistic combinations of values, allowing the data mining algorithm to be trained on suitable combinations of values.
4.2. Influences on the Data Preparation Pipeline
4.2.1. General Influences on the Data Preparation Pipeline
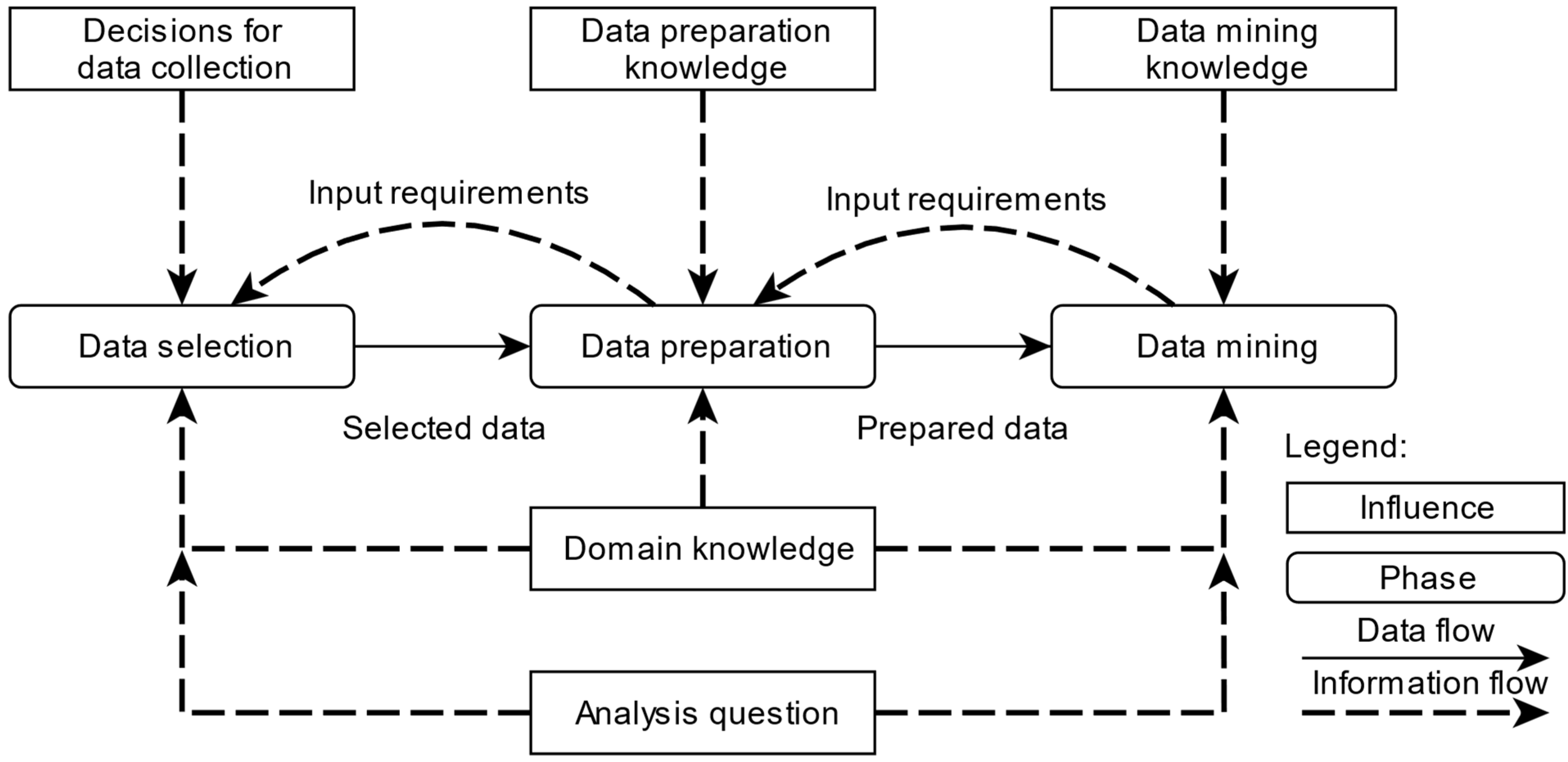
The explanations in Section 4.1 show the predominant influences on data preparation in particular. Figure 5 illustrates the influences on the data preparation pipeline described by Aggarwal [81] based on the KDD process model of Fayyad et al. [1] shown in Figure 2.
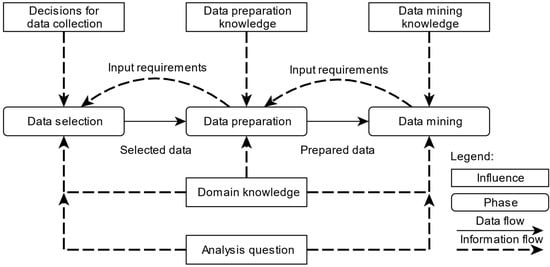
Figure 5.
Influences on the data preparation pipeline.
In Figure 5, the three discussed phases of the data mining process and the raw data flow of the selected data used for data preparation and prepared data for data mining are depicted. In addition to the data flow, there are different information flows. The aforementioned input requirements from data mining to data preparation and from data preparation to data selection, which determine the raw data, show the technical demands on the respective preceding phase. Different information flows of external influences also affect the data preparation pipeline in the respective phases. The higher-level analysis question can influence the data selection and data mining processes, whereby the data mining task should be specified to define the input requirements of the phases or deliberately kept open in order to check the applicable data mining algorithms. The latter may require an iterative approach between data preparation and data mining. All phases require domain knowledge and subject matter experts to make decisions with regard to the content background. In addition to the analysis question, data selection is based in particular on the existing data, which are defined by past decisions made on data collection. This process also includes the collected errors. Data preparation requires expert knowledge about the applicable data preparation procedures, which are subordinate to the implementation of data preparation tasks. Finally, expert knowledge of data mining algorithms and the technical applicability to answer the analysis question are required for the data mining phase. While the phases in the data preparation pipeline have been explained above, the influences are the subsequent subject of consideration, as the maturity models for data preparation precisely consider these influences for the evaluation of the data preparation phase.
4.2.2. Direct Influences on the Data Preparation Pipeline
Data collection is often part of analytics maturity models and includes an assessment of the technical infrastructure and collection approach. The decisions made here were either tailored to specific analyses, to collect general data without a specific goal, or were made for planned analyses and are now used for other purposes in the data preparation pipeline. With data collection for specific analyses, tailoring to specific data mining algorithms can be ensured, when the decisions for data collection match the input requirements of data preparation. However, this is impossible without specific data collection. It is then necessary to compare the input requirements with the available data on the basis of the domain knowledge, ethical considerations, and analysis question. It is also possible to draw conclusions from specialist knowledge about the data preparation phase in order to adapt decisions for data collection. This emphasizes the importance of cooperation within the executing data specialist teams.
Data preparation knowledge has to consider the initial state of the company’s data in the data preparation pipeline and the planned objectives to be achieved by the analysis. This knowledge is not targeted specifically by existing maturity models in the literature. Sonntag et al. [5] explicitly mention data preparation in their maturity model but without going into detail. In data management maturity models, the focus is predominantly on the administration of data in the context of metadata, governance, management, and data quality. The level of detail required for the evaluation of data in the context of analyses and the best possible preparation cannot be seen from the meta-studies by Belghith et al. [28], Curry and Tuikka [27], Hein-Pensel et al. [16], Król and Zdonek [21], and Sadiq et al. [6]. However, many of the maturity models listed in these studies place the administration of data management and data quality assessment in the context of organizational decisions and evaluate them accordingly.
Data mining knowledge includes the selection of suitable algorithms based on the available data and on the higher-level analysis question. This is included in process models for data mining such as CRISP-DM, SEMMA, or the KDD process model according to Fayyad et al. [1] but missing in maturity models. Transfers from existing maturity models are conceivable, particularly from the area of algorithms, such as in the models by Gentsch [82] or Coates and Martin [83]. The influence of technical experts and project teams for algorithm selection is particularly relevant.
4.2.3. Indirect Influences on the Data Preparation Pipeline
While the direct influences based on the data preparation pipeline have been presented in Section 4.2.2, the related indirect influences have not been considered. These indirect influences include, in particular, administrative and organizational framework conditions. Maturity models from the field of data management cover these framework conditions by considering data governance and data management as a focus. The consideration of human resources, infrastructure, and resource management in maturity models is also emphasized in the area of analytics. Ethical maturity models consider fairness and bias reductions by contemplating awareness and culture, policy, governance, data privacy, transparency, and human interaction. This is supported by statements by Sadiq et al. [6] on AI maturity models, in which data, analytics, technology and tools, intelligent automation, governance, people, and organization are particularly relevant.
4.3. Derivation of Influence Groups
The considerations of Section 4.2.2 and Section 4.2.3 for the selection of a suitable maturity model resulted in the following influence groups. Several influences were taken from the data preparation pipeline and supplemented with technical requirements. Based on existing maturity models, particularly from data management, the relevance of people and organizational structures can be seen. Following the ethics maturity models given in Section 2.6, privacy and ethics considerations have a significant impact. In Table 5, the relevant influences on maturity models for evaluating the data preparation phase, and based on this data mining, are summarized.

Table 5.
Overview of relevant influences on maturity models for data preparation.
Table 5 lists the influences on data preparation and the assignment of the influences to the expert knowledge, technical requirements, and administration groups explained in the following statements. The expert knowledge group comprises experience-based influences on the data preparation phase. The obvious influences are expert knowledge for data preparation, data mining, and the domain. Additionally, this group includes the decisions for data collection as prior expert knowledge on possible analyses and relevant information, as well as the analysis question, as task-related expert knowledge on the framework of planned analyses and its usefulness. In the technical requirements group, the technical infrastructure is included as an assessment of the hardware and software implementation of databases, servers, and other relevant media. The input requirements for data preparation and the input requirements for data mining also belong to this group, as they reduce the total number of data preparation procedures and data mining algorithms on the basis of procedure- and algorithm-related technical restrictions. The number of possible procedures and algorithms is also limited by the company’s existing data and willingness to adapt their data collection process. The last group to be mentioned is administration, which comprises privacy and ethics, people, the organizational structure, and governance. This group includes the structural and legal influences that cannot be assigned to the actual data preparation phase. Privacy and ethics address ethical principles, e.g., the purpose or storage limitations of the data, to ensure compliance with legislation such as the GDPR, the EU Artificial Intelligence Act, or Article 21 of the EU Charter of Fundamental Rights mentioned in Section 2.6. Additionally, people represents the general influence of a company’s employees, which can be considered via data literacy or the willingness to change. Furthermore, the organizational structure, as a summary of data management, team structures, and collaboration intensity, shows the relevance of communication in a company. This is supplemented by governance, in which processes and procedures, as well as contact persons and responsibilities, are clearly regulated, thereby providing organizational support for data preparation in the background.
In summary, the three groups comprising expert knowledge, technical requirements, and administration tasks should be considered for the data preparation maturity model design. The existing maturity models fail to evaluate expert knowledge and technical requirements in detail but are partly applicable to the administration group. Utilizing this, conclusions can be drawn for maturity model prototype development.
4.4. Requirements for the Data Preparation Maturity Model Prototype
For the development of a maturity model prototype for data preparation, various requirements for maturity models must be considered. The development of this maturity model was based on the requirements listed in Table 1. Thus, the requirements set out by Becker et al. [9] are evaluated individually below before the prototype is described in Section 4.5.
The first requirement comparison is fulfilled. The substantial literature overview given in Section 2 shows the necessity of a maturity model for data mining and data preparation. The possible inclusion of excerpts of existing maturity models and notable differences are discussed in Section 4.3.
The second requirement, an iterative procedure, is partly fulfilled. Earlier development cycles demonstrated the complexity of evaluating maturity for data mining and the KDD process model. The development of the prototype is conducted as the first iteration step for the creation of a superordinate data mining maturity model that includes the complex phase of data preparation.
The third requirement evaluation is fulfilled. Section 4.2 describes the theoretical basis for the evaluation of data preparation phase, and Section 4.3 and Section 4.5 list the evaluation criteria for the maturity model. As this maturity model is a prototype, the extensive practical testing partly referenced in [9] is still in process. Thus, ref. [9] recommends pilot case studies in companies considering using the prototype before extensive usage.
The fourth requirement, a multi-methodological procedure, is fulfilled. Using the influence groups described in Section 4.3, a multi-methodological approach for maturity evaluation can be derived.
The fifth requirement, identification of relevance, is fulfilled. In Section 4.1, the complexity of the data preparation pipeline in the context of data mining is discussed. As companies struggle to decide which data preparation techniques anteceding data mining should be used for specific tasks and data, the relevance of a maturity model concerning data preparation is evident.
The sixth requirement, problem definition, is fulfilled. This maturity model prototype targets the phase of data preparation for data mining. Therefore, the application domain of data analytics and knowledge discovery; the conditions of following a KDD process model; and the benefits of identifying weaknesses, benchmarking, and standardization are given.
The seventh requirement, result presentation, is partly fulfilled. The necessary factors for evaluating the results to be presented are listed in Section 4.3. However, for this prototype, no presentation was tested with users in this stage of development. Nevertheless, the practitioner is advised to be guided by the referenced existing maturity models in Section 2.
The eighth requirement, documentation, is fulfilled. The scientific process of maturity model prototype development is given in this manuscript. When applying the model, documentation of the process steps, parties involved, applied methods, and results is recommended. An overview concerning the fulfilment of the requirements is presented in Table 6.

Table 6.
Fulfilment of the requirements by the developed maturity model prototype.
In summary, the maturity model prototype for data preparation in the context of data mining is both a novelty and a first step towards the development of a maturity model for data mining. The evaluation criteria from Section 4.2 and Section 4.3 can be used to apply multi-methodological procedures. In the complex field of data preparation and data mining, the maturity model assists companies with process evaluation. Decision support based on evaluation results can be realized, as well as the applied maturity model based on rigorous documentation. Thus, with the overall fulfillment of the requirements listed in Table 6, the prototype of the data preparation maturity model can be designed.
4.5. Prototype of the Data Preparation Maturity Model
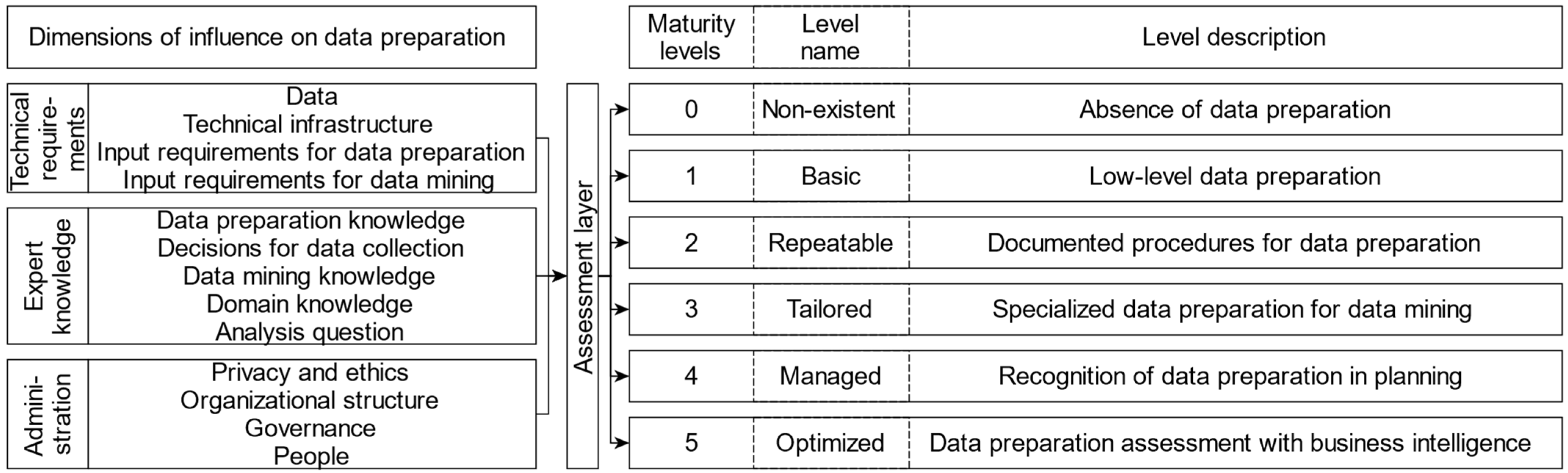
Based on the findings of Section 4.1, Section 4.2, Section 4.3 and Section 4.4, a prototype of the maturity model for data preparation was proposed in the context of data mining. This prototype is presented in Figure 6.
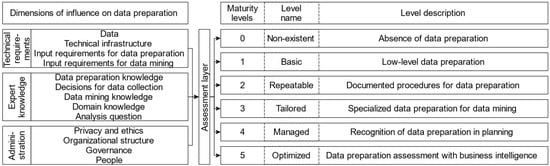
Figure 6.
Data preparation maturity model prototype.
In Figure 6, the dimensions influencing data preparation and their respective groups (see Table 5) are stated on the left-hand side. An assessment layer evaluates the levels of maturity in each dimension and concludes an overall maturity level on the right-hand side. Additionally, the order of the respective dimensions indicates for which maturity level each dimension is most relevant. However, a one-to-one relationship between an influence dimension and a maturity level cannot be established, as the order only shows a basic tendency. Thus, the impact of the dimensions on each maturity level must be individually considered. In this prototype, the assessment layer conducts the overall maturity level assessment based on the dimensions. The application of different levels of importance for the dimensions in relation to each maturity level is recommended in order to paint a realistic picture. For example, the organizational structure influences maturity level two by offering low-level systemization approaches but the influence is less relevant than the consideration of data preparation and data mining requirements. However, some dimensions for higher maturity levels should not be considered for lower maturity levels, such as focusing on the organizational structure instead of acquiring basic knowledge about data preparation. The privacy and ethics dimension must be considered separately. Although this dimension plays a very important role in applications with sensitive personal data, it is hardly relevant for applications without such data, such as for error detection in a machine. Therefore, the consideration of privacy and ethics can be a legal requirement to process data overall or may only be relevant for the planning of future developments at the highest maturity levels. The levels of importance recommended by the authors for each dimension in relation to the maturity level are represented by the order of the dimensions in Figure 6. In the following, the maturity levels are described based on the recommended levels of importance focusing on the technical realization, with the addition of the relevance of privacy and ethics as a separate consideration for affected datasets.
At maturity level zero, the technical requirements are not fulfilled and data preparation is impossible. This means that the data mining process cannot be executed. Maturity level one recognizes data preparation as feasible, which is the baseline and only means there is someone preparing the data. Under consideration of the input requirements for both data preparation and data mining, the application of data preparation methods can be successful for an analysis. Article 6 of the GDPR [34] for data collection and processing must already be considered if personal data are prepared at a low level. However, the EU Artificial Intelligence Act is dependent on the risk assessment of the application.
At maturity level two, a more systematic approach exists. The preparation of data is documented and clearly defined for the same data and data mining algorithm that are used. Thus, the data preparation phase is repeatable with an identical outcome. Based on knowledge about the data preparation tasks, the decisions for data collection can be improved (see Section 4.2.2). If knowledge about data mining and the domain is considered, a specific data preparation pipeline for an analysis can be defined. With systemization, an early integration of privacy and ethics considerations should be included, which can involve privacy via anonymization and transparency of the conducted processes in addition to the baseline legislation of the GDPR.
Maturity level three includes specialized data preparation pipelines for flexible analysis tasks. The consideration of the analysis question in combination with the technical requirements and knowledge about data preparation, data mining, and the domain enables the company to evaluate if an analysis question can be examined and to what quality level. Then, it is possible to tailor the data preparation pipeline for the selection of possible data mining algorithms, answering the analysis question. This highly specialized process of KDD requires the cooperation of multiple departments within a company. With highly specialized pipelines, considerations for privacy and ethics need to be integrated rigorously, which involves explainability, privacy, technical robustness and safety, transparency, data use and design, societal well-being, and accountability. These require proper documentation and metrics of evaluation.
At maturity level four, the interconnection between departments, interests, and expenses are considered. The management executives recognize data preparation and data analysis processes when planning activities for new processes. Additionally, the organizational structure facilitates the exchange of data and knowledge between departments. The spillover effects on a department reduce the data preparation efforts and increase the preparation quality. For example, the establishment of data governance roles such as chief data stewards can reform company culture to recognize data as an asset. Company-wide systematic privacy and ethics policies can be implemented and controlled. Regular bias audits can enable the protection of vulnerable groups and prohibition of discrimination.
Maturity level five contains optimization, automation, and organizational flexibility considerations. One the one hand, this requires sophisticated technical implementations for automation and optimization. On the other hand, the company culture needs to enable people to be data-literate and incorporate data preparation considerations in projects, as well as workflows. The combination of technical advances with the support for implementation within the workforce can result in the continuous optimization of data preparation phase within the company. Privacy and ethics considerations are automatically or semi-automatically tested and ensured by trusted and independently controlled institutions.
Several findings can be derived from the comparison of the proposed data preparation maturity model prototype with the data mining process models. The data preparation phase in CRISP-DM, SEMMA, and the KDD process model by Fayyad et al. [1] is described via technical operations, without consideration of dimensions in the maturity model prototype in the categories of expert knowledge or administration. However, those categories are generally recognized in the understanding of the application domain in KDD in [1] and the business understanding in CRISP-DM, respectively. Every data mining process must be based on a process model starting at least at maturity level one. With increasing maturity levels, the data preparation phase is more systematic, specialized, interconnected, and optimized, improving the overall data mining process.
Based on the connection of the preparation phase and the data mining process, the relevance of the dimensions to the other phases of target definition, data selection, data mining, and post-processing can be derived. The administration group could be relevant for the complete data mining process.
- The dimensions of domain knowledge and the analysis question could be relevant for target definition.
- The dimensions of data, technical infrastructure, decisions made for data collection, domain knowledge, and analysis question could be relevant for data selection.
- The dimensions of data in the sense of the prepared data, technical infrastructure input requirements for data mining, data mining knowledge, domain knowledge, and analysis question could be relevant for data mining.
- The dimensions of data mining knowledge, domain knowledge, and the analysis question could be relevant for the post-processing phase.
5. Discussion of the Necessity of a New Maturity Model for Data Mining
The discussion of data preparation in data mining and the examination of the existing maturity models have shown that the existing models have weaknesses. In particular, it has been shown that the models do not adequately cover the requirements of data preparation in data mining. However, it has also been possible to show that there are maturity models that are of great benefit in certain aspects, especially for data preparation.
A maturity model for data preparation should at least be based on the groups listed in Section 4.3 and refer to the requirements of Section 4.4. A prototype considering these implications was outlined in Section 4.5. The prototype uses an assessment layer to determine the maturity level based on the dimensions and individual levels of importance while considering the maturity levels.
The metrics for the evaluation of individual dimensions from the groups are sometimes complex, such as the evaluation of the existing knowledge for all areas of the expert knowledge group. In contrast, the technical requirements are easier to assess in terms of maturity due to the requirements defined in the assessment based on the analysis question and the decisions for data collection. A major problem is the multi-layered nature of the technical requirements for each individual application of the data preparation pipeline in the company, as different assessments of maturity would have to take place depending on the applicable data, processes, and algorithms. This requires an overarching general assessment of the technical feasibility of the data preparation pipeline for the company. One field that is already frequently examined in maturity models is the administration group, justifying the recommendation of using excerpts from the existing maturity models presented in Section 2, such as in the overview by Belghith et al. [28] and the paper discussing privacy and ethics by Mylrea and Robinson [42].
The given analysis and data preparation maturity model prototype are the first steps toward the development of a data mining maturity model. This superordinate maturity model for data mining is required to condense the developed prototype into a phase within the superordinate model. As the data preparation pipeline covers all steps towards the application of data mining, the superordinate maturity model must consider at least the target definition, data selection, selection and application of the data mining algorithm and the post-processing of the KDD process.
6. Conclusions and Outlook
Data preparation is an indispensable phase prior to the application of data mining and other analyses. Therefore, assessing the maturity of an organization in terms of data preparation is essential for decision support in the selection of approaches and analyses. The existing maturity models do not cover the level of detail required for a holistic evaluation of the data preparation phase and the influences on this phase for companies. In this article, direct and indirect influences on the data preparation phase were derived and discussed in order to provide an overview of the most relevant influencing factors and to support the development of a maturity model prototype for evaluating data preparation phase in a company. Table 5 and Section 4.4 can be used to derive research needs in relation to maturity models for data preparation, as well as to select excerpts from existing maturity models. Figure 6 shows the data preparation maturity model prototype based on these considerations. Considering the development of a maturity model for the entire data mining process, these are important first steps. For practical iterative improvements, extensive case studies with the data preparation maturity model prototype in different domains are recommended. In order to further advance this research, the identification of the relevant influences on data mining in particular, as well as the influences on other phases of the data mining process, are the next steps. Additionally, the real-time applications for data mining processes and data preparation have further implications for specialization opportunities of the maturity model. Finally, a rigorous meta-study of maturity models in the related fields of AI and analytics maturity models, machine learning maturity models, data maturity models, mining maturity, and process mining maturity models is recommended to recognize synergy possibilities.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.A.S. and F.H.; methodology, A.A.S. and F.H.; validation, A.A.S. and F.H.; investigation, A.A.S. and F.H.; resources, M.R.; writing—original draft preparation, A.A.S. and F.H.; writing—review and editing, A.A.S., F.H. and M.R.; visualization, F.H.; supervision, M.R.; project administration, M.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| AI | Artificial intelligence |
| CMMI | Capability Maturity Model Integration |
| GDPR | General Data Protection Regulation |
| KDD | Knowledge discovery in databases |
| PM | Process mining |
References
- Fayyad, U.; Piatetsky-Shapiro, G.; Smyth, P. From Data Mining to Knowledge Discovery in Databases. AI Mag. 1996, 17, 37–54. [Google Scholar]
- Scheidler, A.A.; Rabe, M. Integral Verification and Validation for Knowledge Discovery Procedure Models. Int. J. Bus. Intell. Data Min. 2021, 18, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, S.; Ramírez-Gallego, S.; Luengo, J.; Benítez, J.M.; Herrera, F. Big Data Preprocessing: Methods and Prospects. Big Data Anal. 2016, 1, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moges, H.-T.; van Vlasselaer, V.; Lemahieu, W.; Baesens, B. Determining the Use of Data Quality Metadata (DQM) for Decision Making Purposes and its Impact on Decision Outcomes—An Exploratory Study. Decis. Support Syst. 2016, 83, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonntag, M.; Mehmann, S.; Mehmann, J.; Teuteberg, F. Development and Evaluation of a Maturity Model for AI Deployment Capability of Manufacturing Companies. Inf. Sys. Manag. 2024, 42, 37–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, R.B.; Safie, N.; Abd Rahman, A.H.; Goudarzi, S. Artificial Intelligence Maturity Model: A Systematic Literature Review. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/TR 13054:2012; International Organization for Standardization. Knowledge Management of Health Information Standards. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012.
- Schumacher, A.; Erol, S.; Sihn, W. A Maturity Model for Assessing Industry 4.0 Readiness and Maturity of Manufacturing Enterprises. Procedia CIRP 2016, 52, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.; Knackstedt, R.; Pöppelbuß, J. Developing Maturity Models for IT Management. Bus. Inf. Syst. Eng. 2009, 1, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Pei, J.; Tong, H. Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques, 4th ed.; Elsevier: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2023; ISBN 978-0-128-11760-6. [Google Scholar]
- Accenture. The Art of AI Maturity: Advancing from Practice to Performance. 2022. Available online: https://www.accenture.com/content/dam/accenture/final/a-com-migration/manual/r3/pdf/pdf-4/Accenture-Art-of-AI-Maturity-Report.pdf#zoom=40 (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Redaktion DIGITAL X. Digital Maturity Model: Company Digitisation Put to the Test. Available online: https://www.digital-x.eu/en/magazine/article/dx-xplain/digital-maturity-model (accessed on 1 July 2024).
- Britze, N.; Schulze, A.; Fenge, K.; Woltering, M.; Gross, M.; Menge, F.; Mucke, A.; Ensinger, A.; Keller, H.; Oldenburg, L.; et al. Reifegradmodell Digitale Geschäftsprozesse. 2022. Available online: https://www.bitkom.org/sites/main/files/2020-04/200406_lf_reifegradmodell_digitale-geschaftsprozesse_final.pdf (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Schuster, T.; Waidelich, L.; Volz, R. Reifegradmodelle zur Bewertung Künstlicher Intelligenz in kleinen und mittleren Unternehmen. In Proceedings of Informatik 2021, Berlin, Germany, 27 September–1 October 2021; Gesellschaft für Informatik: Bonn, Germany, 2021; pp. 1237–1246. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullah, M.F.; Ahmad, K. Business Intelligence Model for Unstructured Data Management. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics. ICEEI, Legian-Bali, Indonesia, 4 October–4 November 2015; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 473–477, ISBN 978-1-4673-7319-7. [Google Scholar]
- Hein-Pensel, F.; Winkler, H.; Brückner, A.; Wölke, M.; Jabs, I.; Mayan, I.J.; Kirschenbaum, A.; Friedrich, J.; Zinke-Wehlmann, C. Maturity Assessment for Industry 5.0: A Review of Existing Maturity Models. J. Manuf. Syst. 2023, 66, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossman, R.L. A Framework for Evaluating the Analytic Maturity of an Organization. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2018, 38, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, T.H.; Harris, J.G.; Morison, R. Analytics at Work; Harvard Business Review Press: Brighton, UK, 2010; ISBN 978-1-422-15712-1. [Google Scholar]
- Lismont, J.; Vanthienen, J.; Baesens, B.; Lemahieu, W. Defining Analytics Maturity Indicators: A Survey Approach. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 2017, 37, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosic, R.; Shanks, G.; Maynard, S. Towards a Business Analytics Capability Maturity Model. In Proceedings of the ACIS 2012 Proceedings, Melbourne, Australia, 3–5 December 2012; Volume 14. [Google Scholar]
- Król, K.; Zdonek, D. Analytics Maturity Models: An Overview. Information 2020, 11, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, A.; Santos, M.F. KDD, SEMMA and CRISP-DM: A Parallel Overview. In Proceedings of the IADIS European Conference on Data Mining. IADIS 2008, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 22–27 July 2008; Abraham, A.P., Ed.; pp. 182–185, ISBN 978-972-8924-63-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wirth, R.; Hipp, J. CRISP-DM: Towards a Standard Process Model for Data Mining. In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on the Practical Application of Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, Manchester, UK, 11–13 April 2000; Mackin, N., Ed.; Practical Application Company: Blackpool, UK, 2000; pp. 29–39, ISBN 1902426088. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobi, C.; Meier, M.; Herborn, L.; Furmans, K. Maturity Model for Applying Process Mining in Supply Chains: Literature Overview and Practical Implications. Logist. J. Proc. 2020, 2020, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samalikova, J.; Kusters, R.J.; Trienekens, J.J.M.; Weijters, A.J.M.M. Process Mining Support for Capability Maturity Model Integration-Based Software Process Assessment, in Principle and in Practice. J. Softw. Evol. Process. 2014, 26, 714–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heap. The Four Stages of Data Maturity—And How to Ace Them. Available online: https://www.heap.io/blog/the-four-stages-of-data-maturity (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Curry, E.; Tuikka, T. An Organizational Maturity Model for Data Spaces: A Data Sharing Wheel Approach. In Data Spaces: Design, Deployment and Future Directions; Curry, E., Scerri, S., Tuikka, T., Eds.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 21–42. ISBN 978-3-030-98636-0. [Google Scholar]
- Belghith, O.; Skhiri, S.; Zitoun, S.; Ferjaoui, S. A Survey of Maturity Models in Data Management. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 12th International Conference on Mechanical and Intelligent Manufacturing Technologies. ICMIMT, Cape Town, South Africa, 13–15 May 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 298–309, ISBN 978-1-6654-1453-1. [Google Scholar]
- Alation. Discover the Depth of Your Data Culture Maturity. Available online: https://www.alation.com/dcmm-assessment/ (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Snowplow Team. The Snowplow Data Maturity Model. Available online: https://snowplow.io/blog/the-snowplow-data-maturity-model/ (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Office of Data Governance. Data Management Maturity Model. Available online: https://www.dol.gov/agencies/odg/data-management-maturity-model (accessed on 10 June 2024).
- Krijger, J.; Thuis, T.; de Ruiter, M.; Ligthart, E.; Broekman, I. The AI Ethics Maturity Model: A Holistic Approach to Advancing Ethical Data Science in Organizations. AI Ethics 2023, 3, 355–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vakkuri, V.; Jantunen, M.; Halme, E.; Kemell, K.-K.; Nguyen-Duc, A.; Mikkonen, T.; Abrahamsson, P. Time for AI (Ethics) Maturity Model Is Now. In Proceedings of the Workshop on Artificial Intelligence Safety 2021, SafeAI 2021, Virtual, 8 February 2021; Espinoza, H., McDermid, J., Huang, X., Castillo-Effen, M., Chen, X.C., Hernández-Orallo, J., Ó hÉigeartaigh, S., Mallah, R., Eds.; CEUR Workshop Proceedings: Aachen, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- GDPR EU. GDPR: General Data Protection Regulation. Available online: https://www.gdpreu.org/ (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Cortina, S.; Valoggia, P.; Barafort, B.; Renault, A. Designing a Data Protection Process Assessment Model Based on the GDPR. In Systems, Software and Services Process Improvement, Proceedings of the European Conference on Software Process Improvement, Edinburgh, UK, 18–20 September 2019; Walker, A., O’Connor, R.V., Messnarz, R., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 136–148. ISBN 978-3-030-28005-5. [Google Scholar]
- Future of Life Institute. The EU Artificial Intelligence Act. Available online: https://artificialintelligenceact.eu/ (accessed on 6 March 2025).
- Tawakuli, A.; Engel, T. Make your Data Fair: A Survey of Data Preprocessing Techniques that Address Biases in Data Towards Fair AI. J. Eng. Res. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Galal, G.; Etemadi, M.; Vaidyanathan, M. Evaluation and Mitigation of Racial Bias in Clinical Machine Learning Models: Scoping Review. JMIR Med. Inform. 2022, 10, e36388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazer, L.H.; Zatarah, R.; Waldrip, S.; Ke, J.X.C.; Moukheiber, M.; Khanna, A.K.; Hicklen, R.S.; Moukheiber, L.; Moukheiber, D.; Ma, H.; et al. Bias in Artificial Intelligence Algorithms and Recommendations for Mitigation. PLoS Digit. Health 2023, 2, e0000278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhang, J.M.; Sarro, F.; Harman, M. A Comprehensive Empirical Study of Bias Mitigation Methods for Machine Learning Classifiers. ACM Trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 2023, 32, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarighatar, P.; Pappas, I.; Vassilakopoulou, P. A Sociotechnical Perspective for Responsible AI Maturity Models: Findings from a Mixed-method Literature Review. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2023, 3, 100193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylrea, M.; Robinson, N. Artificial Intelligence (AI) Trust Framework and Maturity Model: Applying an Entropy Lens to Improve Security, Privacy, and Ethical AI. Entropy 2023, 25, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuel, A.; Connolly, P.; Meimandi, K.J.; Tewari, S.; Wiatrak, J.; Venkatesh, D.; Kochenderfer, M. Responsible AI in the Global Context: Maturity Model and Survey. Comput. Soc. 2024, arXiv:2410.09985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, S.; Luengo, J.; Herrera, F. Data Preprocessing in Data Mining; Springer International: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-10246-7. [Google Scholar]
- Restat, V.; Klettke, M.; Störl, U. Towards a Holistic Data Preparation Tool. In Proceedings of the Workshop Proceedings of the EDBT/ICDT2022 Joint Conference. EDBT/ICDT2022, Edinburgh, UK, 29 March 2022; Ramanath, M., Palpanas, T., Eds.; CEUR Workshop Proceedings: Aachen, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Acito, F. Predictive Analytics with KNIME: Analytics for Citizen Data Scientists; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; ISBN 978-3-031-45629-9. [Google Scholar]
- Mazilu, L.; Paton, N.W.; Konstantinou, N.; Fernandes, A.A.A. Fairness-aware Data Integration. J. Data Inf. Qual. 2022, 14, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzalini, F. Data Integration and Ethical Quality: Fundamental Steps of the Data Analysis Pipeline. Ph.D. Thesis, Polytechnic University of Milan, Milan, Italy, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Abdallah, Z.S.; Du, L.; Webb, G.I. Data Preparation. In Encyclopedia of Machine Learning and Data Mining, 2nd ed.; Sammut, C., Webb, G.I., Eds.; Springer Nature: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 318–327. ISBN 978-1-4899-7687-1. [Google Scholar]
- Ilyas, I.F.; Chu, X. Data Cleaning; Association for Computing Machinery: New York, NY, USA, 2019; ISBN 978-1-450-37155-1. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, C.M. A Comparison of Noise Handling Techniques. In Proceedings of the Fourteenth International Florida Artificial Intelligence Research Society Conference, Key West, FL, USA, 21–23 May 2001; Russel, I., Kolen, J.F., Eds.; AAAI Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2001; pp. 269–273, ISBN 978-1-57735-133-7. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, W.; Jiang, H.; Feng, D.; Douglis, F.; Shilane, P.; Hua, Y.; Fu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y. A Comprehensive Study of the Past, Present, and Future of Data Deduplication. Proc. IEEE 2016, 104, 1681–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, P.D. Missing Data. In The SAGE Handbook of Quantitative Methods in Psychology; Millsap, R.E., Maydeu-Olivares, A., Eds.; SAGE Publications Ltd.: London, UK, 2009; pp. 72–90. ISBN 978-1-4129-3091-8. [Google Scholar]
- Seu, K.; Kang, M.-S.; Lee, H. An Intelligent Missing Data Imputation Techniques: A Review. Int. J. Inform. Vis. 2022, 6, 278–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Azhir, E.; Ahmed, O.H.; Ghafour, M.Y.; Ahmed, S.H.; Rahmani, A.M.; Vo, B. Data Cleansing Mechanisms and Approaches for Big Data Analytics: A Systematic Study. J. Ambient Intell. Hum. Comput. 2021, 14, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, C.C. Outlier Analysis, 2nd ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; ISBN 978-3-319-47577-6. [Google Scholar]
- Prajapati, P.; Shah, P. A Review on Secure Data Deduplication: Cloud Storage Security Issue. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022, 34, 3996–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caton, S.; Malisetty, S.; Haas, C. Impact of Imputation Strategies on Fairness in Machine Learning. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2022, 74, 1011–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochkamp, F.; Rabe, M. Outlier Detection in Data Mining: Exclusion of Errors or Loss of Information? In Proceedings of the Changing Tides: The New Role of Resilience and Sustainability in Logistics and Supply Chain Management—Innovative Approaches for the Shift to a New Era, Hamburg International Conference of Logistics (HICL), Hamburg, Germany, 21–23 September 2022; Kersten, W., Jahn, C., Blecker, T., Ringle, C.M., Eds.; epubli GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2022; pp. 91–117, ISBN 978-3-756541-95-9. [Google Scholar]
- Wainer, H. Robust Statistics: A Survey and Some Prescriptions. J. Educ. Stat. 1976, 1, 285–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleve, J.; Lämmel, U. Data Mining, 3rd ed.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany; Boston, MA, USA, 2020; ISBN 978-3-110-67627-3. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, D.; Singh, B. Investigating the Impact of Data Normalization on Classification Performance. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 97, 105524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, M.; Munjal, A. Data Aggregation Algorithms for Wireless Sensor Network: A Review. Ad Hoc Netw. 2020, 100, 102083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonoff, J.S.; Tutz, G. Smoothing Methods for Discrete Data. In Smoothing and Regression: Approaches, Computation, and Application; Schimek, M.G., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez-Gallego, S.; García, S.; Mouriño-Talín, H.; Martínez-Rego, D.; Bolón-Canedo, V.; Alonso-Betanzos, A.; Benítez, J.M.; Herrera, F. Data Discretization: Taxonomy and Big Data Challenge. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2016, 6, 5–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K.; Liu, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Xiang, T.; Loy, C.C. Domain Generalization: A Survey. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2023, 45, 4396–4415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernick, M.R. Resampling Methods. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2012, 2, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahsan, M.M.; Mahmud, M.A.P.; Saha, P.K.; Gupta, K.D.; Siddique, Z. Effect of Data Scaling Methods on Machine Learning Algorithms and Model Performance. Technologies 2021, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gal, M.; Rubinfeld, D.L. Data Standardization. N. Y. Univ. Law Rev. 2018, 94, 737–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharana, K.; Mondal, S.; Nemade, B. A Review: Data Pre-processing and Data Augmentation Techniques. Glob. Transit. Proc. 2022, 3, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, K.M.A.; Thakral, P. The Best Clustering Algorithms in Data Mining. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing 2016, Batu, India, 6–8 April 2016; Iyer, B., Nalbalwar, S.L., Pawade, R.S., Eds.; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 2042–2046. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, A.; Dutta, S.; Turton, T.L.; Ahrens, J. Sampling for Scientific Data Analysis and Reduction. In In Situ Visualization for Computational Science; Childs, H., Bennett, J.C., Garth, C., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 11–36. ISBN 978-3-030-81626-1. [Google Scholar]
- Jayasankar, U.; Thirumal, V.; Ponnurangam, D. A Survey on Data Compression Techniques: From the Perspective of Data Quality, Coding Schemes, Data Type and Applications. J. King Saud Univ. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2021, 33, 119–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zebari, R.; Abdulazeez, A.; Zeebaree, D.; Zebari, D.; Saeed, J. A Comprehensive Review of Dimensionality Reduction Techniques for Feature Selection and Feature Extraction. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. Trends 2020, 1, 56–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munson, M.A. A Study on the Importance of and Time Spent on Different Modeling Steps. ACM SIGKDD Explor. Newsl. 2012, 13, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.; Biancolillo, A.; Roger, J.M.; Marini, F.; Rutledge, D.N. New Data Preprocessing Trends Based on Ensemble of Multiple Preprocessing Techniques. Trends Anal. Chem. 2020, 132, 116045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrales, D.C.; Ledezma, A.; Corrales, J.C. A Conceptual Framework for Data Quality in Knowledge Discovery Tasks (FDQ-KDT): A Proposal. J. Comp. 2015, 10, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taleb, I.; Serhani, M.A.; Bouhaddioui, C.; Dssouli, R. Big Data Quality Framework: A Holistic Approach to Continuous Quality Management. J. Big Data 2021, 8, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetrò, A.; Canova, L.; Torchiano, M.; Minotas, C.O.; Iemma, R.; Morando, F. Open Data Quality Measurement Framework: Definition and Application to Open Government Data. Gov. Inf. Q. 2016, 33, 325–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, M.K.; Chandra, P. A Comprehensive Survey of Data Mining. Int. J. Inf. Tecnol. 2020, 12, 1243–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, C.C. Data Mining: The Textbook; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; ISBN 978-3-319-14141-1. [Google Scholar]
- Gentsch, P. AI Business: Framework and Maturity Model. In AI in Marketing, Sales and Service: How Marketers Without a Data Science Degree Can Use AI, Big Data and Bots; Gentsch, P., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 27–78. ISBN 978-3-319-89957-2. [Google Scholar]
- Coates, D.L.; Martin, A. An Instrument to Evaluate the Maturity of Bias Governance Capability in Artificial Intelligence Projects. IBM J. Res. Dev. 2019, 63, 7:1–7:15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).