Exploring the Role of RGD-Recognizing Integrins in Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
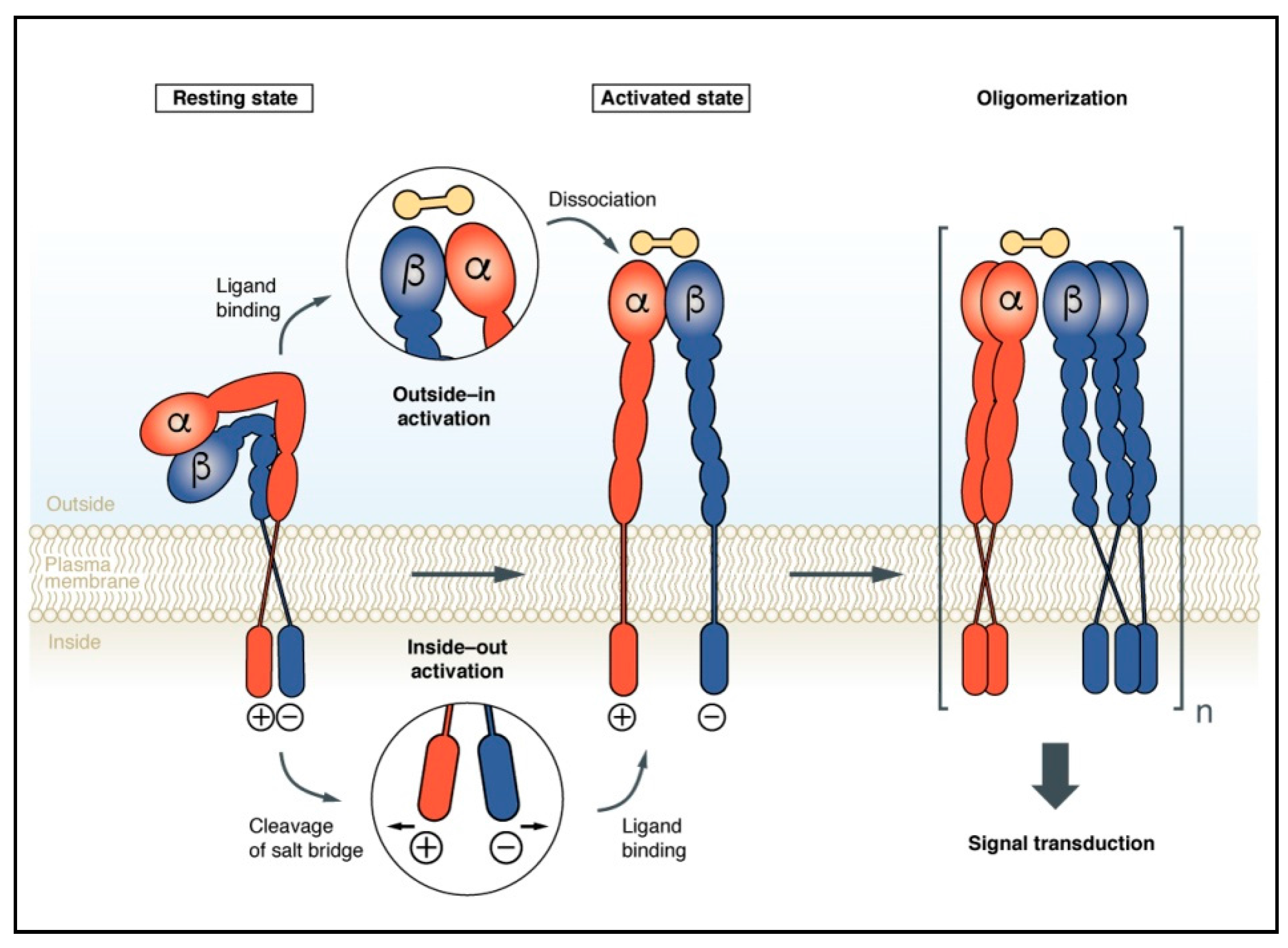
2. Integrin Activation upon Conformational Rearrangements
3. Integrins in Cancer Progression and Metastasis
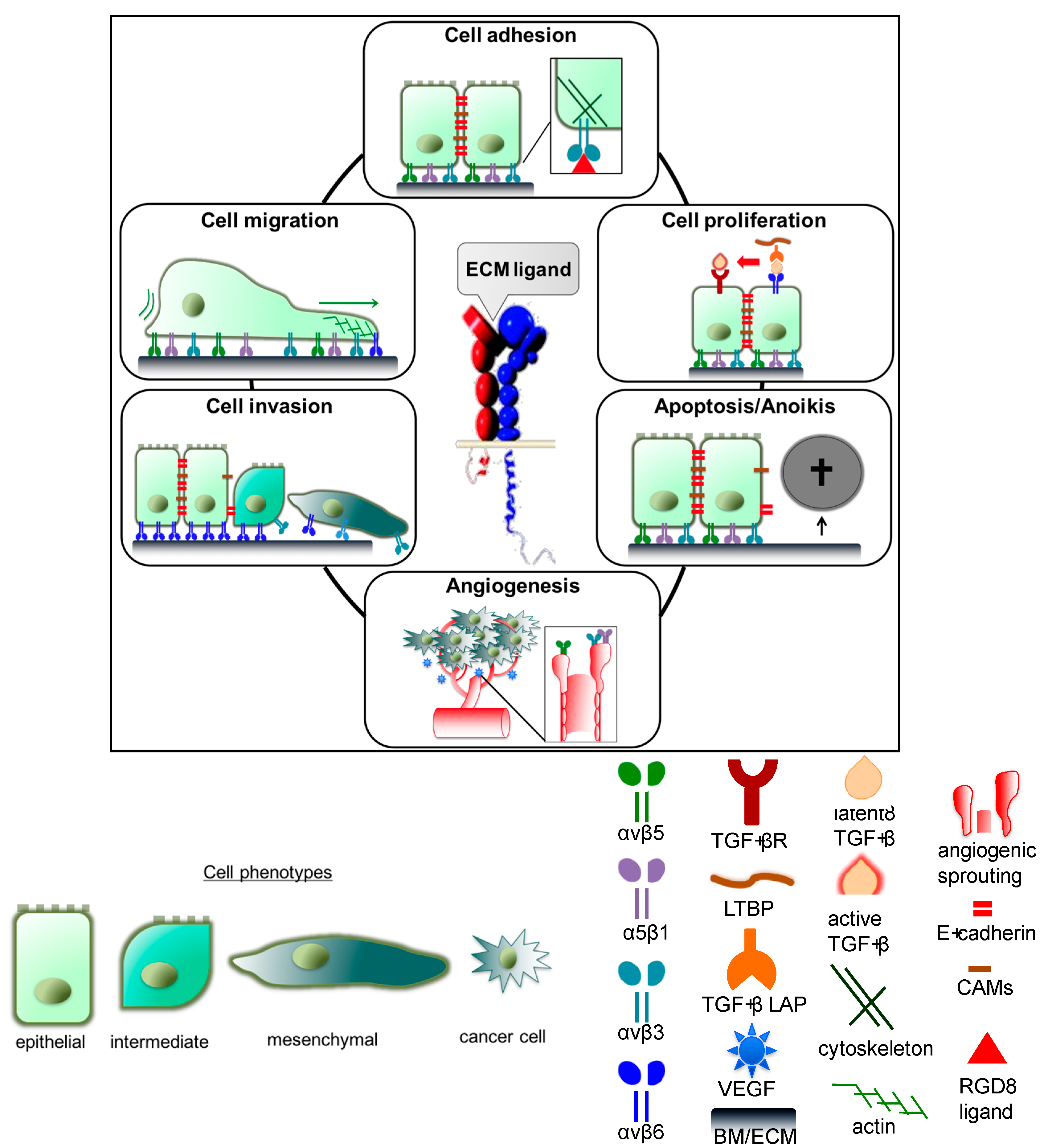
3.1. Integrin-Mediated Cell Adhesion, Migration, and Invasion
3.1.1. Integrin αvβ3 and α5β1
3.1.2. Integrin αvβ6
3.1.3. Integrin αvβ8
3.2. Impact of Integrins on Cellular Proliferation
3.2.1. Integrin αvβ3
3.2.2. Integrin αvβ6
3.2.3. Integrin αvβ8
3.3. Integrin Effects on Cell Survival and Apoptosis
3.4. Integrins αvβ3, αvβ5, and α5β1 in Tumor Angiogenesis
3.5. TGF-β1 and Its Integration with Integrin Signaling
4. Challenges for the Design of Novel Integrin Ligands and Their Translation into Clinical Applications
5. Improving the Activity and Selectivity of Integrin Ligands
6. In Vivo Targeting of Integrins for Cancer Imaging and Therapy
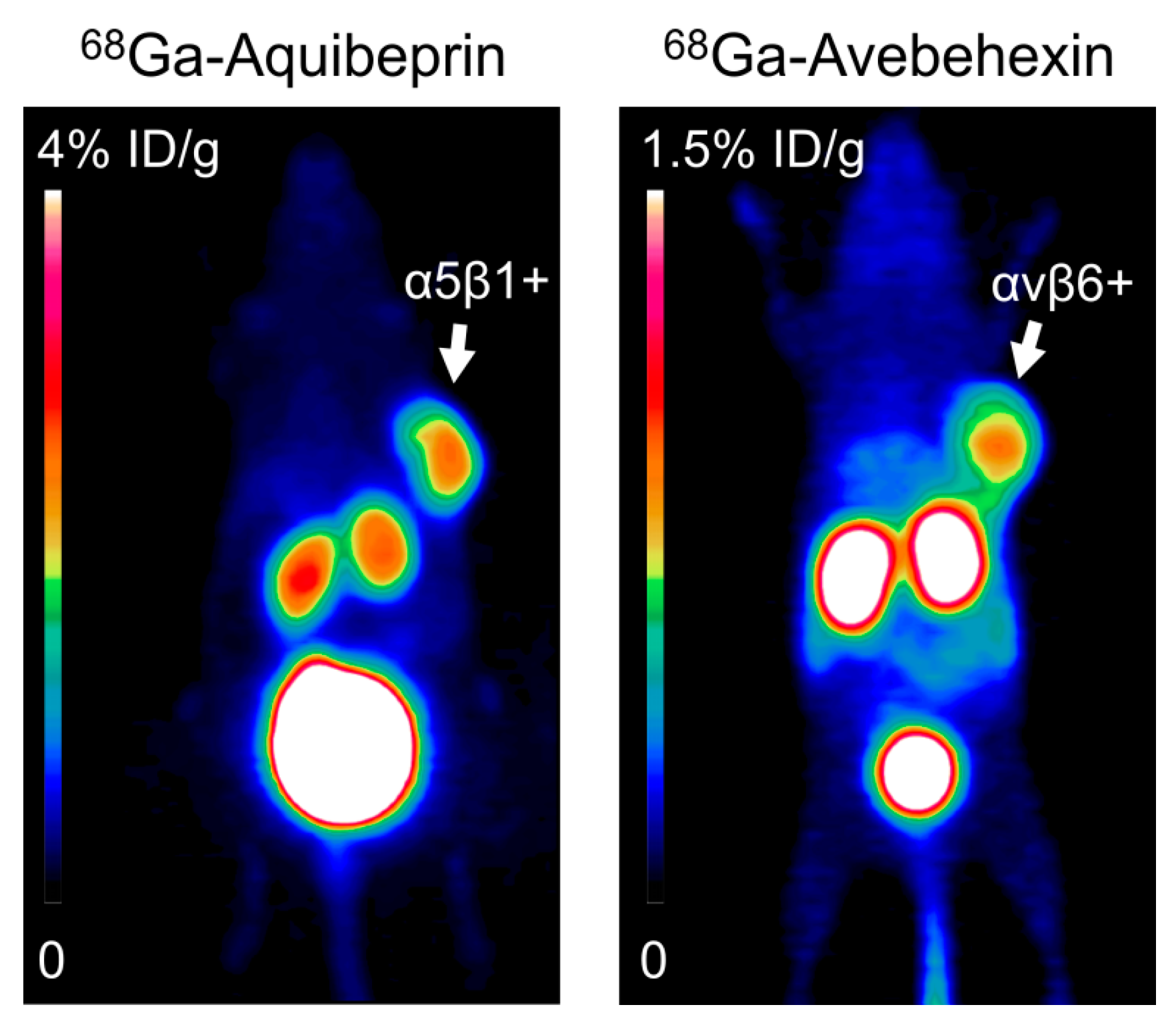
6.1. Integrin αvβ3 and α5β1
6.2. Integrin αvβ6
7. Integrins in Cancer Therapy
8. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RGD | Arg-Gly-Asp |
| BM | Basement membrane |
| BMP | Bone morphogenetic protein |
| CAM | Cell adhesion molecule |
| CD | Crohn’s disease |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| DC | Dendritic cells |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| ERK | Extracellular signal regulated kinase |
| FA | Focal adhesion |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factors-β |
| MAP | Mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide kinase |
| GTP | Guanosine-5′-triphosphate |
| EGF-R | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| PDGF-R | Platelet-derived growth factor |
| FAK | Focal adhesion kinase |
| CAS | Crk-associated substrate |
| LAP | Latency-associated peptide |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteases |
| uPA | Urokinase-type plasminogen activator |
| HREs | Hypoxia response elements |
| HAX-1 | Hematopoietic lineage cell-specific protein-1 (HS1) associated protein |
| HIF | Hypoxia-inducible factor |
| OSCC | Oral squamous cell carcinoma |
| BCC | Basal cell carcinomas |
| Shh | Sonic hedgehog |
| SPECT | Single-photon emission computed tomography |
| tTregs | T regulatory cells |
| SLC | Small latent complex |
| LLC | Large latent complex |
| LTBP | Latent TGF- β binding proteins |
| FMDV | Foot-and-mouth disease virus |
| HNSCC | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| NSCLC | Non-small-cell lung carcinoma |
| PDAC | Pancreatic carcinoma |
| SPECT | Single photon emission computed tomography |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
References
- Horwitz, A.R. The origins of the molecular era of adhesion research. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, J.; Springer, T.A. Complete integrin headpiece opening in eight steps. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 201, 1053–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Calderwood, D.A. Integrin activation. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mould, A.P.; Barton, S.J.; Askari, J.A.; Craig, S.E.; Humphries, M.J. Role of ADMIDAS cation-binding site in ligand recognition by integrin α5β1. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 51622–51629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Agthoven, J.F.; Xiong, J.-P.; Alonso, J.L.; Rui, X.; Adair, B.D.; Goodman, S.L.; Arnaout, M.A. Structural basis for pure antagonism of integrin αvβ3 by a high-affinity form of fibronectin. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rahmouni, S.; Lindner, A.; Rechenmacher, F.; Neubauer, S.; Sobahi, T.R.; Kessler, H.; Cavalcanti-Adam, E.A.; Spatz, J.P. Hydrogel micropillars with integrin selective peptidomimetic functionalized nanopatterned tops for the separate measurement of cell traction forces transmitted through αvβ3- or α5β1-integrins. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 5869–5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Zhao, B.; Iacob, R.E.; Zhu, J.; Koksal, A.C.; Lu, C.; Engen, J.R.; Springer, T.A. Force interacts with macromolecular structure in activation of TGF-β. Nature 2017, 542, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierschbacher, M.D.; Ruoslahti, E. Cell attachment activity of fibronectin can be duplicated by small synthetic fragments of the molecule. Nature 1984, 309, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, S.; Oldberg, A.; Hayman, E.G.; Pierschbacher, M.D.; Ruoslahti, E. Complete amino acid sequence of human vitronectin deduced from cDNA. Similarity of cell attachment sites in vitronectin and fibronectin. EMBO J. 1985, 4, 2519–2524. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plow, E.F.; Pierschbacher, M.D.; Ruoslahti, E.; Marguerie, G.A.; Ginsberg, M.H. The effect of Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptides on fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor binding to platelets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 8057–8061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oldberg, A.; Franzén, D.; Heinegård, D. Cloning and sequence analysis of rat bone sialoprotein (osteopontin) cDNA reveals an Arg-Gly-Asp cell-binding sequence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 8819–8823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, D.S.; Tashiro, K.-I.; Segui-Real, B.; Yamada, Y.; Martin, G.R.; Kleinman, H.K. Two different laminin domains mediate the differentiation of human endothelial cells into capillary-like structures in vitro. Cell 1989, 58, 933–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aota, S.; Nomizu, M.; Yamada, K.M. The short amino acid sequence Pro-His-Ser-Arg-Asn in human fibronectin enhances cell-adhesive function. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 24756–24761. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pierschbacher, M.D.; Ruoslahti, E. Arg-Gly-Asp: A versatile cell recognition signal. Cell 1986, 44, 517–518. [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti, E.; Pierschbacher, M.D. New perspectives in cell adhesion: RGD and integrins. Science 1987, 238, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schittenhelm, J.; Klein, A.; Tatagiba, M.S.; Meyermann, R.; Fend, F.; Goodman, S.L.; Sipos, B. Comparing the expression of integrins αvβ3, αvβ5, αvβ6, αvβ8, fibronectin and fibrinogen in human brain metastases and their corresponding primary tumors. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2013, 6, 2719–2732. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huveneers, S.; Danen, E.H.J. Adhesion signaling-crosstalk between integrins, Src and Rho. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, B.; Spatz, J.; Bershadsky, A.D. Environmental sensing through focal adhesions. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, J.; Li, Z. The roles of integrin αvβ6 in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017, 403, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.; Varner, J. Integrins: Roles in cancer development and as treatment targets. Br. J. Cancer 2004, 90, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desgrosellier, J.S.; Cheresh, D.A. Integrins in cancer: Biological implications and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrake, H.M.; Patterson, L.H. Strategies to inhibit tumor associated integrin receptors: Rationale for dual and multi-antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 6310–6315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niland, S.; Eble, J.A. Integrin-mediated cell-matrix interaction in physiological and pathological blood vessel formation. J. Oncol. 2012, 125278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, S.L.; Picard, M. Integrins as therapeutic targets. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2012, 33, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, S. Importance of integrin receptors in the field of pharmaceutical and medical science. Adv. Biol. Chem. 2013, 3, 224–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran Marelli, U.; Rechenmacher, F.; Ali Sobahi, T.R.; Mas-Moruno, C.; Kessler, H. Tumor targeting via integrin ligands. Front. Pharmacol. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meyer, A.; Auernheimer, J.; Modlinger, A.; Kessler, H. Targeting RGD recognizing integrins: Drug development, biomaterial research, tumor imaging and targeting. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 2723–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arndt, T.; Arndt, U.; Reuning, U.; Kessler, H. Integrins in angiogenesis: Implications for tumor therapy. In Cancer Therapy. Molecular Targets in Tumor-Host Interactions; Weber, G.F., Ed.; Horizon Bioscience: Norfolk, UK, 2005; pp. 93–141. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.P.; Stehle, T.; Diefenbach, B.; Zhang, R.; Dunker, R.; Scott, D.L.; Joachimiak, A.; Goodman, S.L.; Arnaout, M.A. Crystal structure of the extracellular segment of integrin αvβ3. Science 2001, 294, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, J.P.; Stehle, T.; Zhang, R.; Joachimiak, A.; Frech, M.; Goodman, S.L.; Arnaout, M.A. Crystal structure of the extracellular segment of integrin αvβ3 in complex with an Arg-Gly-Asp ligand. Science 2002, 296, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.A.; Opfer, J.; Volkhardt, L.A.; Brunie, L.; Sinner, E.-K.; Boettiger, D.; Bochen, A.; Kessler, H.; Gottschalk, K.-E.; Reuning, U. The glycophorin A transmembrane sequence within integrin αvβ3 creates a non-signalling integrin with low basal affinity that is strongly adhesive under force. J. Mol. Biol. 2013, 425, 2988–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschalk, K.-E.; Kessler, H. The structures of integrins and integrin-ligand complexes: Implications for drug design and signal transduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 3767–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, K.-E.; Adams, P.D.; Brunger, A.T.; Kessler, H. Transmembrane signal transduction of the αIIbβ3 integrin. Protein Sci. 2002, 11, 1800–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moser, M.; Legate, K.R.; Zent, R.; Faessler, R. The tail of integrins, talin, and kindlins. Science 2009, 324, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mas-Moruno, C.; Fraioli, R.; Rechenmacher, F.; Neubauer, S.; Kapp, T.G.; Kessler, H. αvβ3- or α5β1-integrin-selective peptidomimetics for surface coating. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 7048–7067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askari, J.A.; Buckley, P.A.; Mould, A.P.; Humphries, M.J. Linking integrin conformation to function. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoefling, M.; Kessler, H.; Gottschalk, K.-E. The transmembrane structure of integrin αIIbβ3—Significance to signal transduction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 6590–6593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottschalk, K.-E.; Kessler, H. A computational model of transmembrane integrin clustering. Structure 2004, 12, 1109–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, M.A.; Brunie, L.; Bächer, A.S.; Kessler, H.; Gottschalk, K.-E.; Reuning, U. Cytoplasmic salt bridge formation in integrin αvβ3 stabilizes its inactive state affecting integrin-mediated cell biological effects. Cell Signal. 2014, 11, 2493–2503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiller, H.B.; Hermann, M.R.; Polleux, J.; Vignaud, T.; Zanivan, S.; Friedel, C.C.; Sun, Z.Q.; Raducanu, A.; Gottschalk, K.E.; Thery, M.; et al. β1- and αv-class integrins cooperate to regulate myosin II during rigidity sensing of fibronectin-based microenvironments. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stucci, S.; Tucci, M.; Passarelli, A.; Silvestris, F. αvβ3 integrin: Pathogenetic role in osteotropic tumors. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2015, 96, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janes, S.M.; Watt, F.M. Switch from αvβ1 to αvβ6 integrin expression protects squamous cell carcinomas from anoikis. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 166, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takayama, S.; Ishii, S.; Ikeda, T.; Masamura, S.; Doi, M.; Kitajima, M. The relationship between bone metastasis from human breast cancer and integrin αvβ3 expression. Anticancer Res. 2005, 25, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Furger, K.A.; Allan, A.L.; Wilson, S.M.; Hota, C.; Vantyghem, S.A.; Postenka, C.O.; Al-Katib, W.; Chambers, A.F.; Tuck, A.B. β3 integrin expression increases breast carcinoma cell responsiveness to the malignancy-enhancing effects of osteopontin. Mol. Cancer Res. 2003, 1, 810–819. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ju, J.A.; Godet, I.; Ye, I.C.; Byun, J.; Jayatilaka, H.; Lee, S.J.; Xiang, L.; Samanta, D.; Lee, M.H.; Wu, P.H.; et al. Hypoxia selectively enhances integrin α5β1 receptor expression in breast cancer to promote metastasis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, R.C.; Bellovin, D.I.; Brown, C.; Maynard, E.; Wu, B.; Kawakatsu, H.; Sheppard, D.; Oettgen, P.; Mercurio, A.M. Transcriptional activation of integrin beta6 during the epithelial-mesenchymal transition defines a novel prognostic indicator of aggressive colon carcinoma. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Raghavan, S. Defining the role of integrin αvβ6 in cancer. Curr. Drug Targets 2009, 10, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, A.; Tsugawa, S.; Boku, A.; Kobayashi, M.; Minamoto, T.; Nakanishi, I.; Oda, Y. Expression of αv integrin family in gastric carcinomas: Increased αvβ6 is associated with lymph node metastasis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2003, 199, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.; Pansino, F.; Clyde, R.; Murthi, P.; Quinn, M.A.; Rice, G.E.; Agrez, M.V.; Mok, S.; Baker, M.S. Overexpression of alpha(v)beta6 integrin in serous epithelial ovarian cancer regulates extracellular matrix degradation via the plasminogen activation cascade. Carcinogenesis 2002, 23, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, D.M.; But, M.; Regezi, J.; Schmidt, B.L.; Atakilit, A.; Dang, D.; Ellis, D.; Jordan, R.; Li, X. Expression of integrin beta 6 enhances invasive behavior in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Matrix Biol. J. Int. Soc. Matrix Biol. 2002, 21, 297–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipos, B.; Hahn, D.; Carceller, A.; Piulats, J.; Hedderich, J.; Kalthoff, H.; Goodman, S.L.; Kosmahl, M.; Kloppel, G. Immunohistochemical screening for beta6-integrin subunit expression in adenocarcinomas using a novel monoclonal antibody reveals strong up-regulation in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinomas in vivo and in vitro. Histopathology 2004, 45, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patsenker, E.; Wilkens, L.; Banz, V.; Osterreicher, C.H.; Weimann, R.; Eisele, S.; Keogh, A.; Stroka, D.; Zimmermann, A.; Stickel, F. The αvβ6 integrin is a highly specific immunohistochemical marker for cholangiocarcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.Y.; Xu, K.S.; Wang, J.S.; Yang, G.Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.Y.; Niu, W.B.; Liu, E.Y.; Mi, Y.T.; Niu, J. Integrin αvβ6 acts as a prognostic indicator in gastric carcinoma. Clin. Oncol. R. Coll. Radiol. 2008, 20, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arihiro, K.; Kaneko, M.; Fujii, S.; Inai, K.; Yokosaki, Y. Significance of α9β1 and αvβ6 integrin expression in breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer 2000, 7, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.; Riley, C.; Rice, G.E.; Quinn, M.A.; Baker, M.S. αvβ6 integrin—A marker for the malignant potential of epithelial ovarian cancer. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2002, 50, 1371–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, R.C. Colorectal cancer progression: Integrin αvβ6 and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Cell Cycle 2005, 4, 1350–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, R.C.; Mercurio, A.M. The epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and colorectal cancer progression. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2005, 4, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, D.M.; Dang, D.; Sadler, S. The role of the integrin αvβ6 in regulating the epithelial to mesenchymal transition in oral cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Munshi, H.G.; Stack, M.S. Reciprocal interactions between adhesion receptor signaling and MMP regulation. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2006, 25, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böger, C.; Warneke, V.S.; Behrens, H.M.; Kalthoff, H.; Goodman, S.L.; Becker, T.; Röcken, C. Integrins αvβ3 and αvβ5 as prognostic, diagnostic, and therapeutic targets in gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer 2015, 18, 784–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnell, O.; Krebs, B.; Wagner, E.; Romagna, A.; Beer, A.J.; Grau, S.J.; Thon, N.; Goetz, C.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Tonn, J.C.; et al. Expression of integrin αvβ3 in gliomas correlates with tumor grade and is not restricted to tumor vasculature. Brain Pathol. 2008, 18, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berghoff, A.S.; Kovanda, A.K.; Melchardt, T.; Bartsch, R.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Sipos, B.; Schittenhelm, J.; Zielinski, C.C.; Widhalm, G.; Dieckmann, K.; et al. αvβ3, αvβ5 and αvβ6 integrins in brain metastases of lung cancer. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2014, 31, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böger, C.; Kalthoff, H.; Goodman, S.L.; Behrens, H.M.; Röcken, C. Integrins and their ligands are expressed in non-small cell lung cancer but not correlated with parameters of disease progression. Virchows Arch. 2014, 464, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabricius, E.M.; Wildner, G.P.; Kruse-Boitschenko, U.; Hoffmeister, B.; Goodman, S.L.; Raguse, J.D. Immunohistochemical analysis of integrins αvβ3, αvβ5 and α5β1, and their ligands, fibrinogen, fibronectin, osteopontin and vitronectin, in frozen sections of human oral head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Exp. Ther. Med. 2011, 2, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosotani, R.; Kawaguchi, M.; Masui, T.; Koshiba, T.; Ida, J.; Fujimoto, K.; Wada, M.; Doi, R.; Imamura, M. Expression of integrin αvβ3 in pancreatic carcinoma: Relation to MMP-2 activation and lymph node metastasis. Pancreas 2002, 25, e30–e35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heß, K.; Böger, C.; Behrens, H.M.; Röcken, C. Correlation between the expression of integrins in prostate cancer and clinical outcome in 1284 patients. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2014, 18, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, D.; Dickinson, S.; Neill, G.W.; Marshall, J.F.; Hart, I.R.; Thomas, G.J. αvβ6 integrin promotes the invasion of morphoeic basal cell carcinoma through stromal modulation. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 3295–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, K.M.; Thomas, G.J.; Duffy, S.W.; Warwick, J.; Gabe, R.; Chou, P.; Ellis, I.O.; Green, A.R.; Haider, S.; Brouilette, K.; et al. Therapeutic targeting of integrin αvβ6 in breast cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.Y.; Guo, S.; Dong, C.Y.; Wang, X.Q.; Hu, B.Y.; Liu, Y.F.; Chen, Y.W.; Niu, J.; Dong, J.H. Integrin αvβ6 sustains and promotes tumor invasive growth in colon cancer progression. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 7457–7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecht, J.L.; Dolinski, B.M.; Gardner, H.A.; Violette, S.M.; Weinreb, P.H. Overexpression of the αvβ6 integrin in endometrial cancer. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2008, 16, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elayadi, A.N.; Samli, K.N.; Prudkin, L.; Liu, Y.H.; Bian, A.; Xie, X.J.; Wistuba, I.I.; Roth, J.A.; McGuire, M.J.; Brown, K.C. A peptide selected by biopanning identifies the integrin αvβ6 as a prognostic biomarker for nonsmall cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 5889–5895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Impola, U.; Uitto, V.J.; Hietanen, J.; Hakkinen, L.; Zhang, L.; Larjava, H.; Isaka, K.; Saarialho-Kere, U. Differential expression of matrilysin-1 (MMP-7), 92 kd gelatinase (MMP-9), and metalloelastase (MMP-12) in oral verrucous and squamous cell cancer. J. Pathol. 2004, 202, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steiger, K.; Schlitter, A.M.; Weichert, W.; Esposito, I.; Wester, H.J.; Notni, J. Perspective of αvβ6-integrin imaging for clinical management of pancreatic carcinoma and its precursor lesions. Mol. Imaging 2017, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawada, K.; Mitra, A.K.; Radjabi, A.R.; Bhaskar, V.; Kistner, E.O.; Tretiakova, M.; Jagadeeswaran, S.; Montag, A.; Becker, A.; Kenny, H.A.; et al. Loss of E-cadherin promotes ovarian cancer metastasis via α5-integrin, which is a therapeutic target. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 2329–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daley, W.P.; Peters, S.B.; Larsen, M. Extracellular matrix dynamics in development and regenerative medicine. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, C.T.; Guzman, M.L.; Noble, M. Cancer stem cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taipale, J.; Beachy, P.A. The Hedgehog and Wnt signalling pathways in cancer. Nature 2001, 411, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurt, E.M.; Chan, K.; Serrat, M.A.; Thomas, S.B.; Veenstra, T.D.; Farrar, W.L. Identification of vitronectin as an extrinsic inducer of cancer stem cell differentiation and tumor formation. Stem Cells 2010, 28, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seguin, L.; Kato, S.; Franovic, A.; Camargo, M.F.; Lesperance, J.; Elliott, K.C.; Yebra, M.; Mielgo, A.; Lowy, A.M.; Husain, H.; et al. An integrin β3-KRAS-RalB complex drives tumour stemness and resistance to EGFR inhibition. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vellon, L.; Menendez, J.A.; Liu, H.; Lupu, R. Upregulation of αvβ3 integrin expression is a novel molecular response to chemotherapy-induced cell damage in a heregulin-dependent manner. Differentiation 2007, 75, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheldrake, H.M.; Patterson, L.H. Function and antagonism of β3 integrins in the development of cancer therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2009, 9, 519–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gianni, T.; Massaro, R.; Campadelli-Fiume, G. Dissociation of HSV gL from gH by αvβ6- or αvβ8-integrin promotes gH activation and virus entry. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E3901–E3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesnokova, L.S.; Nishimura, S.L.; Hutt-Fletcher, L.M. Fusion of epithelial cells by Epstein-Barr Virus proteins is triggered by binding of viral glycoproteins gHgL to integrins αvβ6 or αvβ8. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20464–20469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutt-Fletcher, L.M.; Chesnokova, L.S. Integrins as triggers of Epstein-barr virus fusion and epithelial cell infection. Virulence 2010, 1, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bear, J.E.; Haugh, J.M. Directed migration of mesenchymal cells: Where signaling and the cytoskeleton meet. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2014, 30, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, J.T.; Horwitz, A.R.; Schwartz, M.A. Cell adhesion: Integrating cytoskeletal dynamics and cellular tension. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missirlis, D.; Haraszti, T.; Scheele, C.; Wiegand, T.; Diaz, C.; Neubauer, S.; Rechenmacher, F.; Kessler, H.; Spatz, J.P. Substrate engagement of integrins α5β1 and αvβ3 is necessary, but not sufficient, for high directional persistence in migration on fibronectin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganguly, K.K.; Pal, S.; Moulik, S.; Chatterjee, A. Integrins and metastasis. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2013, 7, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, C.D.; Burridge, K. The on-off relationship of Rho and Rac during integrin-mediated adhesion and cell migration. Small GTPases 2014, 5, e27958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Z.; Livas, T.; Kyprianou, N. Anoikis and EMT: Lethal “liaisons” during cancer progression. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2016, 21, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartsch, J.E.; Staren, E.D.; Appert, H.E. Adhesion and migration of extracellular matrix-stimulated breast cancer. J. Surg. Res. 2003, 110, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pytela, R.; Pierschbacher, M.D.; Ruoslahti, E. Identification and isolation of a 140 kd cell surface glycoprotein with properties expected of a fibronectin receptor. Cell 1985, 40, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefansson, S.; Lawrence, D.A. The serpin PAI-1 inhibits cell migration by blocking integrin αvβ3 binding to vitronectin. Nature 1996, 383, 441–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, J.; Guoping, C.; Shapiro, S.S.; Tran, L.P.; Beacham, D.A. Glycoprotein Ibα can mediate endothelial cell migration on von Willebrand factor-containing substrata. Exp. Cell Res. 1999, 252, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamidi, H.; Pietilä, M.; Ivaska, J. The complexity of integrins in cancer and new scopes for therapeutic targeting. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 1017–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehler, S.; Ponik, S.M.; Riching, K.M.; Keely, P.J. Bi-directional signaling: Extracellular matrix and integrin regulation of breast tumor progression. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2013, 23, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Upheber, S.; Karle, A.; Miller, J.; Schlaugk, S.; Gross, E.; Reuning, U. Alternative splicing of KAI1 abrogates its tumor-suppressive effects on integrin αvβ3-mediated ovarian cancer biology. Cell Signal. 2015, 27, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hapke, S.; Kessler, H.; Luber, B.; Benge, A.; Hutzler, P.; Höfler, H.; Schmitt, M.; Reuning, U. Ovarian cancer cell proliferation and motility is induced by engagement of integrin αvβ3/vitronectin interaction. Biol. Chem. 2003, 384, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Löffek, S.; Franzke, C.W.; Helfrich, I. Tension in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, M.R.; Byron, A.; Humphries, M.J.; Bass, M.D. Giving off mixed signals-distinct functions of α5β1 and αvβ3 integrins in regulating cell behaviour. IUBMB Life 2009, 61, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca-Cusachs, P.; Iskratsch, T.; Sheetz, M.P. Finding the weakest link: Exploring integrin-mediated mechanical molecular pathways. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 3025–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCabe, N.P.; De, S.; Vasanji, A.; Brainard, J.; Byzova, T.V. Prostate cancer specific integrin αvβ3 modulates bone metastatic growth and tissue remodeling. Oncogene 2007, 26, 6238–6243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mierke, C.T.; Frey, B.; Fellner, M.; Herrmann, M.; Fabry, B. Integrin α5β1 facilitates cancer cell invasion through enhanced contractile forces. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 369–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paul, N.R.; Allen, J.L.; Chapman, A.; Morlan-Mairal, M.; Zindy, E.; Jacquemet, G.; Fernandez del Ama, L.; Ferizovic, N.; Green, D.M.; Howe, J.D.; et al. α5β1 integrin recycling promotes Arp2/3-independent cancer cell invasion via the formin FHOD3. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 210, 1013–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuss, J.M.; Gillett, N.; Lu, L.; Sheppard, D.; Pytela, R. Restricted distribution of integrin beta 6 mRNA in primate epithelial tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1993, 41, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, G.; Chen, X. Why integrin as a primary target for imaging and therapy. Theranostics 2011, 1, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breuss, J.M.; Gallo, J.; DeLisser, H.M.; Klimanskaya, I.V.; Folkesson, H.G.; Pittet, J.F.; Nishimura, S.L.; Aldape, K.; Landers, D.V.; Carpenter, W. Expression of the beta 6 integrin subunit in development, neoplasia and tissue repair suggests a role in epithelial remodeling. J. Cell Sci. 1995, 108, 2241–2251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Zong, X. Aberrant cancer metabolism in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer metastasis: Mechanisms in cancer progression. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 115, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Teng, M.; Guo, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Huang, Y. Switch from αvβ5 to αvβ6 integrin is required for CD9-regulated keratinocyte migration and MMP-9 activation. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 4044–4052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Giancotti, F.G. Integrin signalling during tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balzac, F.; Avolio, M.; Degani, S.; Kaverina, I.; Torti, M.; Silengo, L.; Small, J.V.; Retta, S.F. E-cadherin endocytosis regulates the activity of Rap1: A traffic light GTPase at the crossroads between cadherin and integrin function. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 4765–4783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oloumi, A.; McPhee, T.; Dedhar, S. Regulation of E-cadherin expression and beta-catenin/Tcf transcriptional activity by the integrin-linked kinase. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1691, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.Y.; Xu, K.S.; Pan, Z.Q.; Zhang, Z.Y.; Mi, Y.T.; Wang, J.S.; Chen, R.; Niu, J. Integrin αvβ6 mediates the potential for colon cancer cells to colonize in and metastasize to the liver. Cancer Sci. 2008, 99, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldanha, R.G.; Molloy, M.P.; Bdeir, K.; Cines, D.B.; Song, X.; Uitto, P.M.; Weinreb, P.H.; Violette, S.M.; Baker, M.S. Proteomic identification of lynchpin urokinase plasminogen activator receptor protein interactions associated with epithelial cancer malignancy. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 1016–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Dang, D.; Regezi, J.; Schmidt, B.L.; Atakilit, A.; Chen, B.; Ellis, D.; Ramos, D.M. Alphavbeta6-fyn signaling promotes oral cancer progression. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 41646–41653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hazmi, N.; Thomas, G.J.; Speight, P.M.; Whawell, S.A. The 120 kDa cell-binding fragment of fibronectin up-regulates migration of αvβ6-expressing cells by increasing matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 secretion. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2007, 115, 454–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, M.R.; Thomas, G.J.; Russell, A.; Hart, I.R.; Marshall, J.F. The integrin cytoplasmic-tail motif ekqkvdlstdc is sufficient to promote tumor cell invasion mediated by matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 or MMP-9. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 26533–26539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, G.J.; Hart, I.R.; Speight, P.M.; Marshall, J.F. Binding of TGF-β1 latency-associated peptide (LAP) to αvβ6 integrin modulates behaviour of squamous carcinoma cells. Br. J. Cancer 2002, 87, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, G.J.; Lewis, M.P.; Hart, I.R.; Marshall, J.F.; Speight, P.M. αvβ6 integrin promotes invasion of squamous carcinoma cells through up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 92, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Dorahy, D.J.; Gu, X.; Scott, R.J.; Draganic, B.; Ahmed, N.; Agrez, M.V. Integrin expression in colon cancer cells is regulated by the cytoplasmic domain of the β6 integrin subunit. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 99, 529–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsay, A.G.; Keppler, M.D.; Jazayeri, M.; Thomas, G.J.; Parsons, M.; Violette, S.; Weinreb, P.; Hart, I.R.; Marshall, J.F. HS1-associated protein X-1 regulates carcinoma cell migration and invasion via clathrin-mediated endocytosis of integrin αvβ6. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 5275–5284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanzetti, L.; Di Fiore, P.P. Endocytosis and Cancer: An ‘Insider’ Network with Dangerous Liaisons. Traffic 2008, 9, 2011–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, S.L.; Sheppard, D.; Pytela, R. Integrin αvβ8. Interaction with vitronectin and functional divergence of the β8 cytoplasmic domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 28708–28715. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Worthington, J.J.; Klementowicz, J.E.; Travis, M.A. TGF-β: A sleeping giant awoken by integrins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aluwihare, P.; Mu, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Yu, D.; Weinreb, P.H.; Horan, G.S.; Violette, S.M.; Munger, J.S. Mice that lack activity of αvβ6- and αvβ8-integrins reproduce the abnormalities of TGF-β1- and TGF-β3-null mice. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozawa, A.; Sato, Y.; Imabayashi, T.; Uemura, T.; Takagi, J.; Sekiguchi, K. Molecular basis of the ligand binding specificity of αvβ8 integrin. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 11551–11565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, D.; Cambier, S.; Fjellbirkeland, L.; Baron, J.L.; Munger, J.S.; Kawakatsu, H.; Sheppard, D.; Broaddus, V.C.; Nishimura, S.L. The integrin αvβ8 mediates epithelial homeostasis through MT1-MMP-dependent activation of TGF-β1. J. Cell Biol. 2002, 157, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarty, J.H.; Cook, A.A.; Hynes, R.O. An interaction between αvβ8 integrin and band 4.1b via a highly conserved region of the band 4.1 c-terminal domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13479–13483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheerathodi, M.; Avci, N.G.; Guerrero, P.A.; Tang, L.K.; Popp, J.; Morales, J.E.; Chen, Z.; Carnero, A.; Lang, F.F.; Ballif, B.A.; et al. The cytoskeletal adapter protein spinophilin regulates invadopodia dynamics and tumor cell invasion in glioblastoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurohr, C.; Nishimura, S.L.; Sheppard, D. Activation of transforming growth factor-beta by the integrin αvβ8 delays epithelial wound closure. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 35, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, R.; Huang, X.; Wu, J.; Nishimura, S.; Pytela, R.; Sheppard, D.; Ffrench-Constant, C. Distinct roles for astrocyte a αvβ5 and αvβ8 integrins in adhesion and migration. J. Cell Sci. 1999, 112, 4271–4279. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cambier, S.; Gline, S.; Mu, D.; Collins, R.; Araya, J.; Dolganov, G.; Einheber, S.; Boudreau, N.; Nishimura, S.L. Integrin αvβ8-mediated activation of transforming growth factor-β by perivascular astrocytes: An angiogenic control switch. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 1883–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruet-Hennequart, S.; Maubant, S.; Luis, J.; Gauduchon, P.; Staedel, C.; Dedhar, S. αv integrins regulate cell proliferation through integrin-linked kinase (ILK) in ovarian cancer cells. Oncogene 2003, 22, 1688–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Q.; Pohl, T.L.; Seckinger, A.; Spatz, J.P.; Cavalcanti-Adam, E.A. Regulation of integrin and growth factor signaling in biomaterials for osteodifferentiation. Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2015, 11, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streuli, C.H.; Akhtar, N. Signal co-operation between integrins and other receptor systems. Biochem. J. 2009, 418, 491–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannigan, G.; Troussard, A.A.; Dedhar, S. Integrin-linked kinase. A cancer therapeutic target unique among its ILK. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupack, D.G.; Cheresh, D.A. Get a ligand, get a life: Integrins, signaling and cell survival. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 3729–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lössner, D.; Abou-Ajram, C.; Benge, A.; Reuning, U. Integrin αvβ3 mediates upregulation of epidermal growth-factor receptor expression and activity in human ovarian cancer cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2008, 40, 2746–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, M.A.; Assoian, R.K. Integrins and cell proliferation: Regulation of cyclin-dependent kinases via cytoplasmic signaling pathways. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 2553–2560. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Munger, J.S.; Huang, X.; Kawakatsu, H.; Griffiths, M.J.; Dalton, S.L.; Wu, J.; Pittet, J.F.; Kaminski, N.; Garat, C.; Matthay, M.A.; et al. The integrin αvβ6 binds and activates latent TGF-β1: A mechanism for regulating pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. Cell 1999, 96, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Xu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Tao, B.B. Study on the effect of Integrin αvβ6 on proliferation and apoptosis of cervical cancer cells. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 21, 2811–2815. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fjellbirkeland, L.; Cambier, S.; Broaddus, V.C.; Hill, A.; Brunetta, P.; Dolganov, G.; Jablons, D.; Nishimura, S.L. Integrin αvβ8-mediated activation of transforming growth factor-beta inhibits human airway epithelial proliferation in intact bronchial tissue. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambier, S.; Mu, D.Z.; O’Connell, D.; Boylen, K.; Travis, W.; Liu, W.H.; Broaddus, V.C.; Nishimura, S.L. A role for the integrin αvβ8 in the negative regulation of epithelial cell growth. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 7084–7093. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Giacotti, F.G.; Ruoslahti, E. Transduction-integrin signaling. Science 1999, 285, 1028–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashido, Y.; Kitano, H.; Sakaue, T.; Fujii, T.; Suematsu, M.; Sakurai, S.; Okamoto, T. Overexpression of integrin αv facilitates proliferation and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via MEK/ERK signaling pathway that is activated by interaction of integrin αvβ8 with type collagen. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 1875–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, M.; Yanagisawa, H.; Minagawa, S.; Sen, D.; Ma, R.; Murray, L.A.; Tsui, P.; Lou, J.; Marks, J.D.; Baron, J.L.; et al. TGF-β-dependent dendritic cell chemokinesis in murine models of airway disease. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 1182–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, O.J.; Somanath, S.; Moermans, C.; Yanagisawa, H.; Hashimoto, M.; Cambier, S.; Markovics, J.; Bondesson, A.J.; Hill, A.; Jablons, D.; et al. Transforming growth factor-β and interleukin-1β signaling pathways converge on the chemokine CCL20 promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 14717–14728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, H.; Cambier, S.; Somanath, S.; Barker, T.; Minagawa, S.; Markovics, J.; Goodsell, A.; Publicover, J.; Reichardt, L.; Jablons, D.; et al. Mouse and human lung fibroblasts regulate dendritic cell trafficking, airway inflammation, and fibrosis through integrin αvβ8-mediated activation of TGF-β. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2863–2875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worthington, J.J.; Kelly, A.; Smedley, C.; Bauche, D.; Campbell, S.; Marie, J.C.; Travis, M.A. Integrin αvβ8-mediated TGF-β activation by effector regulatory T cells is essential for suppression of T-cell-mediated inflammation. Immunity 2015, 42, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Edwards, J.P.; Thornton, A.M.; Shevach, E.M. Release of active TGF-β1 from the latent TGF-β1/GARP complex on T regulatory cells is mediated by integrin β8. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 2843–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheresh, D.A.; Stupack, D.G. Integrin-mediated death: An explanation of the integrin-knockout phenotype? Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 193–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, S.M.; Ruoslahti, E. Integrins and anoikis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1997, 9, 701–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchheit, C.L.; Weigel, K.J.; Schafer, Z.T. Cancer cell survival during detachment from the ECM: Multiple barriers to tumour progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teitz, T.; Wei, T.; Valentine, M.B.; Vanin, E.F.; Grenet, J.; Valentine, V.A.; Behm, F.G.; Look, A.T.; Lahti, J.M.; Kidd, V.J. Caspase 8 is deleted or silenced preferentially in childhood neuroblastomas with amplification of MYCN. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 529–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alanko, J.; Mai, A.; Jacquemet, G.; Schauer, K.; Kaukonen, R.; Saari, M.; Goud, B.; Ivaska, J. Integrin endosomal signalling suppresses anoikis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 1412–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plantefaber, L.C.; Hynes, R.O. Changes in integrin receptors on oncogenically transformed cells. Cell 1989, 56, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmeron-Sanchez, M.; Dalby, M.J. Synergistic growth factor microenvironments. Chem. Commun. Camb. 2016, 52, 13327–13336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reginato, M.J.; Mills, K.R.; Paulus, J.K.; Lynch, D.K.; Sgroi, D.C.; Debnath, J.; Muthuswamy, S.K.; Brugge, J.S. Integrins and EGFR coordinately regulate the pro-apoptotic protein BIM to prevent anoikis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2003, 5, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, A.-M.; Schaffner, F.; Janouskova, H.; Noulet, F.; Rognan, D.; Lelong-Rebel, I.; Choulier, L.; Blandin, A.-F.; Lehmann, M.; Martin, S.; et al. Single cell tracking assay reveals an opposite effect of selective small non-peptidic α5β1 or αvβ3/β5 integrins antagonists in U87MG glioma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 2978–2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renner, G.; Janouskova, H.; Noulet, F.; Guerin, E.; Bär, S.; Nuesch, J.; Rechenmacher, F.; Neubauer, S.; Kessler, H.; Choulier, L.; et al. Integrin α5β1 and p53 convergent pathways in the control of anti-apoptotic proteins PEA-15 and survivin in high grade glioma. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paoli, P.; Giannoni, E.; Chiarugi, P. Anoikis molecular pathways and its role in cancer progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 3481–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demircioglu, F.; Hodivala-Dilke, K. αvβ3 Integrin and tumour blood vessels-learning from the past to shape the future. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2016, 42, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avraamides, C.J.; Garmy-Susini, B.; Varner, J.A. Integrins in angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 604–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergers, G.; Benjamin, L.E. Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Bell, K.; Mousa, S.A.; Varner, J.A. Regulation of angiogenesis in vivo by ligation of integrin α5β1 with the central cell-binding domain of fibronectin. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 1345–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanidakis, M.; Koivunen, E. Cell-surface association between matrix metalloproteinases and integrins: Role of the complexes in leukocyte migration and cancer progression. Blood 2006, 108, 1441–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mengele, K.; Napieralski, R.; Magdolen, V.; Reuning, U.; Gkazepis, A.; Sweep, F.; Brunner, N.; Foekens, J.; Harbeck, N.; Schmitt, M. Characteristics of the level-of-evidence-1 disease forecast cancer biomarkers uPA and its inhibitor PAI-1. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2010, 10, 947–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.L.; Jiang, B.H.; Rue, E.A.; Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-pas heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 5510–5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krock, B.L.; Skuli, N.; Simon, M.C. Hypoxia-induced angiogenesis: Good and evil. Genes Cancer 2011, 2, 1117–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowden Dahl, K.D.; Robertson, S.E.; Weaver, V.M.; Simon, M.C. Hypoxia-inducible factor regulates αvβ3 integrin cell surface expression. Mol. Biol. Cell 2005, 16, 1901–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keely, S.; Glover, L.E.; MacManus, C.F.; Campbell, E.L.; Scully, M.M.; Furuta, G.T.; Colgan, S.P. Selective induction of integrin β1 by hypoxia-inducible factor: Implications for wound healing. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 1338–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, D.L.; Schwab, L.P.; Krutilina, R.; Parke, D.N.; Sethuraman, A.; Hoogewijs, D.; Schorg, A.; Gotwald, L.; Fan, M.; Wenger, R.H.; et al. Itga6 is directly regulated by hypoxia-inducible factors and enriches for cancer stem cell activity and invasion in metastatic breast cancer models. Mol. Cancer 2016, 15, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.C.; Chuang, H.C.; Salunke, S.B.; Kulp, S.K.; Chen, C.S. A novel HIF-1 alpha-integrin-linked kinase regulatory loop that facilitates hypoxia-induced HIF-1alpha expression and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 8271–8285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Shen, S.M.; Zhao, X.Y.; Chen, G.Q. Targeted genes and interacting proteins of hypoxia inducible factor-1. Int. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 3, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.B.; Ren, H.; Zhao, H.; Chi, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhou, B.; Liu, Y.J.; Zhang, L.; Xu, B.; Liu, B.; et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 alpha directly enhances the transcriptional activity of stem cell factor (scf) in response to hypoxia and epidermal growth factor (EGF). Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 1853–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, B.D.; Hackett, S.F.; Hirota, K.; Oshima, Y.; Cai, Z.; Berg-Dixon, S.; Rowan, A.; Yan, Z.; Campochiaro, P.A.; Semenza, G.L. Cell type-specific regulation of angiogenic growth factor gene expression and induction of angiogenesis in nonischemic tissue by a constitutively active form of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Circ. Res. 2003, 93, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikitenko, L.L.; Smith, D.M.; Bicknell, R.; Rees, M.C. Transcriptional regulation of the crlr gene in human microvascular endothelial cells by hypoxia. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 1499–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, S.M.; Cheresh, D.A. αV integrins in angiogenesis and cancer. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2011, 1, a006478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raguse, J.D.; Gath, H.J.; Bier, J.; Riess, H.; Oettle, H. Cilengitide (emd 121974) arrests the growth of a heavily pretreated highly vascularised head and neck tumour. Oral Oncol. 2004, 40, 228–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, A.R.; Hart, I.R.; Watson, A.R.; Welti, J.C.; Silva, R.G.; Robinson, S.D.; Da Violante, G.; Gourlaourou, V.; Salih, M.; Jones, M.C.; et al. Stimulation of tumor growth and angiogenesis by low concentrations of RGD-mimetic integrin inhibitors. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bader, B.L.; Rayburn, H.; Crowley, D.; Hynes, R.O. Extensive vasculogenesis, angiogenesis, and organogenesis precede lethality in mice lacking all αv integrins. Cell 1998, 95, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, L.E.; Wyder, L.; Lively, J.C.; Taverna, D.; Robinson, S.D.; Huang, X.; Sheppard, D.; Hynes, R.O.; Hodivala-Dilke, K.M. Enhanced pathological angiogenesis in mice lacking β3 integrin or β3 and β5 integrins. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Flier, A.; Badu-Nkansah, K.; Whittaker, C.A.; Crowley, D.; Bronson, R.T.; Lacy-Hulbert, A.; Hynes, R.O. Endothelial α5 and αv integrins cooperate in remodeling of the vasculature during development. Development 2010, 137, 2439–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, P.P.; Demircioglu, F.; Ghazaly, E.; Alrawashdeh, W.; Stratford, M.R.L.; Scudamore, C.L.; Cereser, B.; Crnogorac-Jurcevic, T.; McDonald, S.; Elia, G.; et al. Dual-action combination therapy enhances angiogenesis while reducing tumor growth and spread. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostourou, V.; Lechertier, T.; Reynolds, L.E.; Lees, D.M.; Baker, M.; Jones, D.T.; Tavora, B.; Ramjaun, A.R.; Birdsey, G.M.; Robinson, S.D.; et al. FAK-heterozygous mice display enhanced tumour angiogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, P.P.; Bodrug, N.; Hodivala-Dilke, K.M. Exploring Novel Methods for Modulating Tumor Blood Vessels in Cancer Treatment. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R1161–R1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnold, T.D.; Niaudet, C.; Pang, M.F.; Siegenthaler, J.; Gaengel, K.; Jung, B.; Ferrero, G.M.; Mukouyama, Y.S.; Fuxe, J.; Akhurst, R.; et al. Excessive vascular sprouting underlies cerebral hemorrhage in mice lacking αvβ8-TGFβ signaling in the brain. Development 2014, 141, 4489–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zeng, L.; Kennedy, R.M.; Gruenig, N.M.; Childs, S.J. βPix plays a dual role in cerebral vascular stability and angiogenesis, and interacts with integrin αvβ8. Dev. Biol. 2012, 363, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, S.; Liu, Q.; Lee, H.S.; Hossain, M.G.; Lacy-Hulbert, A.; McCarty, J.H. The astrocyte-expressed integrin αvβ8 governs blood vessel sprouting in the developing retina. Development 2011, 138, 5157–5166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tchaicha, J.H.; Mobley, A.K.; Hossain, M.G.; Aldape, K.D.; McCarty, J.H. A mosaic mouse model of astrocytoma identifies αvβ8 integrin as a negative regulator of tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4460–4472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, H.; Kim, H.; Pawlikowska, L.; Kitamura, H.; Shen, F.; Cambier, S.; Markovics, J.; Lawton, M.T.; Sidney, S.; Bollen, A.W.; et al. Reduced expression of integrin αvβ8 is associated with brain arteriovenous malformation pathogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 176, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, B.N.; Bhowmick, N.A. Role of EMT in metastasis and therapy resistance. J. Clin. Med. 2016, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.; Marshall, J.F. The role of integrins in TGF-β-activation in the tumour stroma. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 365, 657–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araki, K.; Shimura, T.; Suzuki, H.; Tsutsumi, S.; Wada, W.; Yajima, T.; Kobayahi, T.; Kubo, N.; Kuwano, H. E/N-cadherin switch mediates cancer progression via TGF-β-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 1885–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, C.M.; Laprise, M.H.; Blanchette, F.; Gentry, L.E.; Leduc, R. Processing of transforming growth factor β1 precursor by human furin convertase. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 10618–10624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrence, D.A.; Pircher, R.; Kryceve-Martinerie, C.; Jullien, P. Normal embryo fibroblasts release transforming growth factors in a latent form. J. Cell Physiol. 1984, 121, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wipff, P.J.; Hinz, B. Integrins and the activation of latent transforming growth factor beta1—An intimate relationship. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 87, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Zhu, J.; Wang, R.; Chen, X.; Mi, L.; Walz, T.; Springer, T.A. Latent TGF-β structure and activation. Nature 2011, 474, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, F.; Pereira, L. The fibrillins. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 1999, 31, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahamed, J.; Burg, N.; Yoshinaga, K.; Janczak, C.A.; Rifkin, D.B.; Coller, B.S. In vitro and in vivo evidence for shear-induced activation of latent transforming growth factor-β1. Blood 2008, 112, 3650–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annes, J.P.; Chen, Y.; Munger, J.S.; Rifkin, D.B. Integrin αvβ6-mediated activation of latent TGF-β requires the latent TGF-β binding protein-1. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 165, 723–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munger, J.S.; Harpel, J.G.; Giancotti, F.G.; Rifkin, D.B. Interactions between growth factors and integrins: Latent forms of transforming growth factor-β are ligands for the integrin αvβ1. Mol. Biol. Cell 1998, 9, 2627–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, I.B.; Rifkin, D.B. Regulation of the bioavailability of TGF-β and TGF-β-related proteins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2016, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eke, I.; Zscheppang, K.; Dickreuter, E.; Hickmann, L.; Mazzeo, E.; Unger, K.; Krause, M.; Cordes, N. Simultaneous β1 integrin-EGFR targeting and radiosensitization of human head and neck cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2015, 107, dju419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatler, A.L.; Goodwin, A.T.; Gbolahan, O.; Saini, G.; Porte, J.; John, A.E.; Clifford, R.L.; Violette, S.M.; Weinreb, P.H.; Parfrey, H.; et al. Amplification of TGF-β induced ITGB6 gene transcription may promote pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.Y.; Chiao, C.C.; Kuo, W.Y.; Hsiao, Y.C.; Chen, Y.J.; Wei, Y.Y.; Lai, T.H.; Fong, Y.C.; Tang, C.H. TGF-β1 increases motility and αvβ3 integrin up-regulation via PI3K, Akt and NF-κB-dependent pathway in human chondrosarcoma cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wendt, M.K.; Smith, J.A.; Schiemann, W.P. Transforming growth factor-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition facilitates epidermal growth factor-dependent breast cancer progression. Oncogene 2010, 29, 6485–6498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pechkovsky, D.V.; Scaffidi, A.K.; Hackett, T.L.; Ballard, J.; Shaheen, F.; Thompson, P.J.; Thannickal, V.J.; Knight, D.A. Transforming growth factor β1 induces αvβ3 integrin expression in human lung fibroblasts via a β3 integrin-, c-SRC-, and p38 MAPK-dependent pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 12898–12908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kracklauer, M.P.; Schmidt, C.; Sclabas, G.M. TGF-β1 signaling via αvβ6 integrin. Mol. Cancer 2003, 2, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mamuya, F.A.; Duncan, M.K. αv integrins and TGF-β-induced EMT: A circle of regulation. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 445–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckmann, D.; Kessler, H. Design and chemical synthesis of integrin ligands. Methods Enzymol. 2007, 426, 463–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapp, T.G.; Rechenmacher, F.; Neubauer, S.; Maltsev, O.V.; Cavalcanti-Adam, A.E.; Zarka, R.; Reuning, U.; Notni, J.; Wester, H.-J.; Mas-Moruno, C.; et al. A comprehensive evaluation of the activity and selectivity profile of ligands for RGD-binding integrins. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 39805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dechantsreiter, M.A.; Planker, E.; Mathä, B.; Lohof, E.; Hölzemann, G.; Jonczyk, A.; Goodman, S.L.; Kessler, H. N-Methylated cyclic RGD Peptides as highly active and selective αvβ3 integrin antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 1999, 42, 3033–3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mas-Moruno, C.; Rechenmacher, F.; Kessler, H. Cilengitide: The first anti-angiogenic small molecule drug candidate. Design, synthesis and clinical evaluation. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2010, 10, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reardon, D.A.; Neyns, B.; Weller, M.; Tonn, J.C.; Nabors, L.B.; Stupp, R. Cilengitide: An RGD pentapeptide αvβ3 and αvβ5 integrin inhibitor in development for glioblastoma and other malignancies. Future Oncol. 2011, 7, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nabors, L.B.; Fink, K.L.; Mikkelsen, T.; Grujicic, D.; Tarnawski, D.H.N.; Mazurkiewicz, M.; Salacz, M.; Ashby, L.; Zagonel, V.; Depenni, R.; et al. Two Cilengitide regimens in combination with standard treatment for patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma and unmethylated MGMT gene promoter: Results of the open-label, controlled, randomized phase II CORE study. Neuro-Oncology 2015, 17, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, W.P. End of the road: Confounding results of the CORE trial terminate the arduous journey of Cilengitide for glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2015, 17, 634–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heckmann, D.; Meyer, A.; Laufer, B.; Zahn, G.; Stragies, R.; Kessler, H. Rational design of highly active and selective ligands for the α5β1 integrin receptor. ChemBioChem 2008, 9, 1397–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubauer, S.; Rechenmacher, F.; Brimioulle, R.; Di Leva, F.S.; Bochen, A.; Sobahi, T.R.; Schottelius, M.; Novellino, E.; Mas-Moruno, C.; Marinelli, L.; et al. Pharmacophoric modifications lead to superpotent αvβ3 integrin ligands with suppressed α5β1 activity. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 3410–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stragies, R.; Osterkamp, F.; Zischinsky, G.; Vossmeyer, D.; Kalkhof, H.; Reimer, U.; Zahn, G. Design and Synthesis of a new class of selective integrin α5β1 antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 3786–3794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maltsev, O.V.; Marelli, U.K.; Kapp, T.G.; Di Leva, F.S.; Di Maro, S.; Nieberler, M.; Reuning, U.; Schwaiger, M.; Novellino, E.; Marinelli, L.; et al. Stable peptides instead of stapled peptides: Highly potent αvβ6-selective integrin ligands. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 1535–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indrevoll, B.; Kindberg, G.M.; Solbakken, M.; Bjurgert, E.; Johansen, J.H.; Karlsen, H.; Mendizabal, M.; Cuthbertson, A. NC-100717: A versatile RGD peptide scaffold for angiogenesis imaging. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 6190–6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, R.O. Integrins: Versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell 1992, 69, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumailley, M.; Gurrath, M.; Müller, G.; Calvete, J.; Timpl, R.; Kessler, H. Arg-Gly-Asp constrained within cyclic pentapeptides. Strong and selective inhibitors of cell adhesion to vitronectin and laminin fragment P1. FEBS Lett. 1991, 291, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubner, R.; Finsinger, D.; Kessler, H. Stereoisomeric Peptide Libraries and Peptidomimetics for designing selective inhibitors of the αvβ3 integrin for a new cancer therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1997, 36, 1374–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurrath, M.; Müller, G.; Kessler, H.; Aumailley, M.; Timpl, R. Conformation/activity studies of rationally designed potent anti-adhesive RGD peptides. Eur. J. Biochem. 1992, 210, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, J.; Rechenmacher, F.; Kessler, H. N-Methylation of peptides and proteins: An important element for modulating biological functions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 254–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coller, B.S.; Shattil, S.J. The GPIIb/IIIa (integrin αIIbβ3) odyssey: A technology-driven saga of a receptor with twists, turns, and even a bend. Blood 2008, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Luo, B.-H.; Xiao, T.; Zhang, C.; Nishida, N.; Springer, T.A. Structure of a complete integrin ectodomain in a physiologic resting state and activation and deactivation by applied forces. Mol. Cell 2008, 32, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagae, M.; Re, S.; Mihara, E.; Nogi, T.; Sugita, Y.; Tagaki, J. Crystal structure of α5β1 integrin ectodomain: Atomic details of the fibronectin receptor. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 187, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallarola, D.; Platzman, I.; Bochen, A.; Cavalcanti-Adam, E.A.; Axmann, M.; Kessler, H.; Geiger, B.; Spatz, J.P. Focal adhesion stabilization by enhanced integrin-cRGD binding affinity. BioNanoMaterials 2017, 18, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, K.; Rivera-Nieves, J.; Sandborn, W.J.; Shattil, S. Integrin-based therapeutics: Biological basis, clinical use and new drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2016, 15, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovlid, M.L.; Steinmetz, N.F.; Laufer, B.; Lau, J.L.; Kuzelka, J.; Wang QHyypiä, T.; Nemerow, G.R.; Kessler, H.; Manchester, M.; Finn, M.G. Guiding plant virus particles to integrin-displaying cells. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 3698–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shroff, K.; Kokkoli, E. PEGylated liposomal doxorubicin targeted to α5β1-expressing MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Langmuir 2012, 28, 4729–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, A.J.; Haubner, R.; Goebel, M.; Luderschmidt, S.; Spilker, M.E.; Wester, H.J.; Weber, W.A.; Schwaiger, M. Biodistribution and pharmacokinetics of the αvβ3-selective tracer 18F-galacto-RGD in cancer patients. J. Nucl. Med. 2005, 46, 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Beer, A.J.; Haubner, R.; Sarbia, M.; Goebel, M.; Luderschmidt, S.; Grosu, A.L.; Schnell, O.; Niemeyer, M.; Kessler, H.; Wester, H.J.; et al. Positron emission tomography using 18F-Galacto-RGD identifies the level of integrin αvβ3 expression in man. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 3942–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haubner, R.; Weber, W.A.; Beer, A.J.; Vabuliene, E.; Reim, D.; Sarbia, M.; Becker, K.F.; Goebel, M.; Hein, R.; Wester, H.J.; et al. Noninvasive visualization of the activated αvβ3 integrin in cancer patients by positron emission tomography and 18F-Galacto-RGD. PLoS Med. 2005, 2, e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.; Niu, G.; Wu, H.; Chen, X. Clinical application of radiolabeled RGD peptides for PET imaging of integrin αvβ3. Theranostics 2016, 6, 78–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, A.J.; Haubner, R.; Wolf, I.; Goebel, M.; Luderschmidt, S.; Niemeyer, M.; Grosu, A.-L.; Martinez, M.-J.; Wester, H.J.; Weber, W.A.; et al. PET-based human dosimetry of 18F-galacto-RGD, a new radiotracer for imaging αvβ3 expression. J. Nucl. Med. 2006, 47, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McParland, B.J.; Miller, M.P.; Spinks, T.J.; Kenny, L.M.; Osman, S.; Khela, M.K.; Aboagye, E.; Coombes, R.C.; Hui, A.M.; Cohen, P.S. The biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of the Arg-Gly-Asp peptide 18F-AH111585 in healthy volunteers. J. Nucl. Med. 2008, 49, 1664–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doss, M.; Kolb, H.C.; Zhang, J.J.; Belanger, M.J.; Stubbs, J.B.; Stabin, M.G.; Hostetler, E.D.; Alpaugh, R.K.; von Mehren, M.; Walsh, J.C.; et al. Biodistribution and radiation dosimetry of the integrin marker 18F-RGD-K5 determined from whole-body PET/CT in monkeys and humans. J. Nucl. Med. 2012, 53, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Kang, K.W.; Lee, H.Y.; Han, S.W.; Kim, T.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Jeong, J.M.; Lee, D.S. Whole-body distribution and radiation dosimetry of 68Ga-NOTA-RGD, a positron emission tomography agent for angiogenesis imaging. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2012, 27, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, W.; Guo, N.; Pan, D.; Yu, C.; Weng, Y.; Luo, S.; Ding, H.; Xu, Y.; Wang, L.; Lang, L.; et al. First experience of 18F-Alfatide in lung cancer patients using a new lyophilized kit for rapid radiofluorination. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittra, E.S.; Goris, M.L.; Iagaru, A.H.; Kardan, A.; Burton, L.; Berganos, R.; Chang, E.; Lui, S.; Shen, B.; Chin, F.T.; et al. Pilot pharmacokinetic and dosimetric studies of 18F-FPPRGD2: A PET radiopharmaceutical agent for imaging αvβ3 integrin levels. Radiology 2011, 260, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.; Pan, D.; Mi, B.; Xu, Y.; Lang, L.; Niu, G.; Yang, M.; Wan, W.; Chen, X. 18F-Alfatide II PET/CT in healthy human volunteers and patients with brain metastases. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 42, 2021–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, K.; Liang, N.; Zhang, J.; Lang, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Zhao, J.; Niu, G.; Li, F.; Zhu, Z.; et al. 68Ga-NOTA-PRGD2 PET/CT for integrin imaging in patients with lung cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 1823–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkinson, S.J.; Ellison, T.S.; Steri, V.; Gould, E.; Robinson, S.D. Redefining the role(s) of endothelial αvβ3-integrin in angiogenesis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2014, 42, 1590–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fässler, R.; Meyer, M. Consequences of lack of β1 integrin gene expression in mice. Genes Dev. 1995, 9, 1896–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanjore, H.; Zeisberg, E.M.; Gerami-Naini, B.; Kalluri, R. β1 integrin expression on endothelial cells is required for angiogenesis but not for vasculogenesis. Dev. Dyn. 2007, 237, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neubauer, S.; Rechenmacher, F.; Beer, A.J.; Curnis., F.; Pohle, K.; D’Alessandria, C.; Wester, H.J.; Reuning, U.; Corti, A.; Schwaiger, M.; et al. Selective imaging of the angiogenic relevant integrins α5β1 and αvβ3. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 11656–11659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alessandria, C.; Pohle., K.; Rechenmacher, S.; Neubauer, S.; Notni, J.; Wester, H.J.; Schwaiger, M.; Kessler, H.; Beer, A.J. In vivo biokinetic and metabolic characterization of the 68Ga-labeled α5β1-selective peptidomimetic FR366. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2016, 43, 953–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haubner, R.; Maschauer, S.; Einsiedel, J.; Eder, I.E.; Rangger, C.; Gmeiner, P.; Virgolini, I.; Prante, O. H-CRRETAWAC-OH, a lead structure for the development of radiotracer targeting integrin α5β1? Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 243185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.T.; Gao, H.N.; Zhai, L.P.; Liu, X.J.; Jia, B.; Shi, J.Y.; Wang, F. Tc-99m-HisoDGR as a Potential SPECT Probe for orthotopic glioma detection via targeting of integrin α5β1. Bioconjug. Chem. 2016, 27, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notni, J.; Steiger, K.; Hoffmann, F.; Reich, D.; Kapp, F.G.; Rechenmacher, T.; Neubauer, S.; Kessler, H.; Wester, H.J. Complementary, selective PET-Imaging of integrin subtypes α5β1 and αvβ3 using Ga-68-aquibeprin and Ga-68-avebetrin. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notni, J.; Steiger, K.; Hoffmann, F.; Reich, D.; Schwaiger, M.; Kessler, H.; Wester, H.J. Variation of specific activities of Ga-68-aquibeprin and Ga-68-avebetrin enables selective PET-imaging of different expression levels of integrins α5β1 and αvβ3. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 1618–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, Z. Molecular imaging of integrin αvβ6 expression in living subjects. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2014, 4, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yang, F.; Guo, J.; He, J.; Wu, Q.; Cao, W.; Lv, L.; Zheng, H.; Zhang, Z. Induction of partial protection against foot and mouth disease virus in guinea pigs by neutralization with the integrin β6-1 subunit. Viruses 2013, 5, 1114–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodman, S.L.; Hölzemann, G.; Sulyok, G.A.; Kessler, H. Nanomolar small molecule inhibitors for αvβ6, αvβ5, and αvβ3 integrins. J. Med. Chem. 2002, 45, 1045–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, S.; Diefenbach, B.; Mehta, R.; Jonczyk, A.; Luckenbach, G.A.; Goodman, S.L. Definition of an unexpected ligand recognition motif for αvβ6 integrin. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 1979–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausner, S.H.; DiCara, D.; Marik, J.; Marshall, J.F.; Sutcliffe, J.L. Use of a peptide derived from foot-and-mouth disease virus for the noninvasive imaging of human cancer: Generation and evaluation of 4-[18f]fluorobenzoyl a20fmdv2 for in vivo imaging of integrin αvβ6 expression with positron emission tomography. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 7833–7840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; McGuire, M.J.; Lin, M.; Liu, Y.H.; Oyama, T.; Sun, X.; Brown, K.C. Synthesis and characterization of a high-affinity αvβ6-specific ligand for in vitro and in vivo applications. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, R.H.; Teed, R.; Hackel, B.J.; Pysz, M.A.; Chuang, C.Z.; Sathirachinda, A.; Willmann, J.K.; Gambhir, S.S. Pharmacokinetically stabilized cystine knot peptides that bind αvβ6 integrin with single-digit nanomolar affinities for detection of pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmedah, H.T.; Patterson, L.H.; Shnyder, S.D.; Sheldrake, H.M. RGD-binding integrins in head and neck cancers. Cancers 2017, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- John, A.E.; Luckett, J.C.; Tatler, A.L.; Awais, R.O.; Desai, A.; Habgood, A.; Ludbrook, S.; Blanchard, A.D.; Perkins, A.C.; Jenkins, R.G.; et al. Preclinical SPECT/CT imaging of αvβ6 integrins for molecular stratification of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 2146–2152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Ma, T.; Sun, X.; Shi, J.; Jia, B.; Sun, Y.; Zhan, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Integrin αvβ6-targeted SPECT imaging for pancreatic cancer detection. J. Nucl. Med. 2014, 55, 989–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Li, J.; Hong, Y.; Kimura, R.H.; Ma, X.; Liu, H.; Qin, C.; Hu, X.; Hayes, T.R.; Benny, P.; et al. 99mTC-labeled cystine knot peptide targeting integrin αvβ6 for tumor SPECT imaging. Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausner, S.H.; Abbey, C.K.; Bold, R.J.; Gagnon, M.K.; Marik, J.; Marshall, J.F.; Stanecki, C.E.; Sutcliffe, J.L. Targeted in vivo imaging of integrin αvβ6 with an improved radiotracer and its relevance in a pancreatic tumor model. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5843–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.N.; McGuire, M.J.; Li, S.; Hao, G.; Kumar, A.; Sun, X.; Brown, K.C. Dimerization of a phage-display selected peptide for imaging of αvβ6-integrin: Two approaches to the multivalent effect. Theranostics 2014, 4, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausner, S.H.; Bauer, N.; Sutcliffe, J.L. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of the effects of aluminum [18F]fluoride radiolabeling on an integrin αvβ6-specific peptide. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2014, 41, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausner, S.H.; Bauer, N.; Hu, L.Y.; Knight, L.M.; Sutcliffe, J.L. The effect of bi-terminal PEGylation of an integrin αvβ6-targeted 18F peptide on pharmacokinetics and tumor uptake. J. Nucl. Med. 2015, 56, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hausner, S.H.; Carpenter, R.D.; Bauer, N.; Sutcliffe, J.L. Evaluation of an integrin αvβ6-specific peptide labeled with [18F]fluorine by copper-free, strain-promoted click chemistry. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2013, 40, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altmann, A.; Sauter, M.; Roesch, S.; Mier, W.; Warta, R.; Debus, J.; Dyckhoff, G.; Herold-Mende, C.; Haberkorn, U. Identification of a novel ITGαvβ6-binding peptide using protein separation and phage display. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notni, J.; Reich, D.; Maltsev, O.V.; Kapp, T.G.; Steiger, K.; Hoffmann, F.; Esposito, I.; Weichert, W.; Kessler, H.; Wester, H.J. In Vivo pet imaging of the “cancer integrin” alphavbeta6 using gallium-68 labelled cyclic RGD nonapeptides. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 58, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.-Y.; Xu, K.; He, Q.-S.; Niu, W.-B.; Wang, J.-Y.; Mi, Y.-T.; Wang, J.-S.; Wang, G.-Q.; Yang, G.-Y.; Niu, J. Signaling and regulatory mechanisms of integrin αvβ6 on the apoptosis of colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2008, 266, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogelberg, H.; Tolner, B.; Thomas, G.J.; Di Cara, D.; Minogue, S.; Ramesh, B.; Sodha, S.; Marsh, D.; Lowdell, M.W.; Meyer, T.; et al. Engineering a single-chain fv antibody to αvβ6 integrin using the specificity-determining loop of a foot-and-mouth disease virus. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 382, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Integrin Alpha-v-Beta and [18F]-R01-MG-F2 PET/CT in Measuring Response in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer and Healthy Volunteers. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02683824 (accessed on 7 August 2017).
- First-in-Human Positron Emission Tomography Study Using the 18F-αvβ6-Binding Peptide. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03164486 (accessed on 7 August 2017).
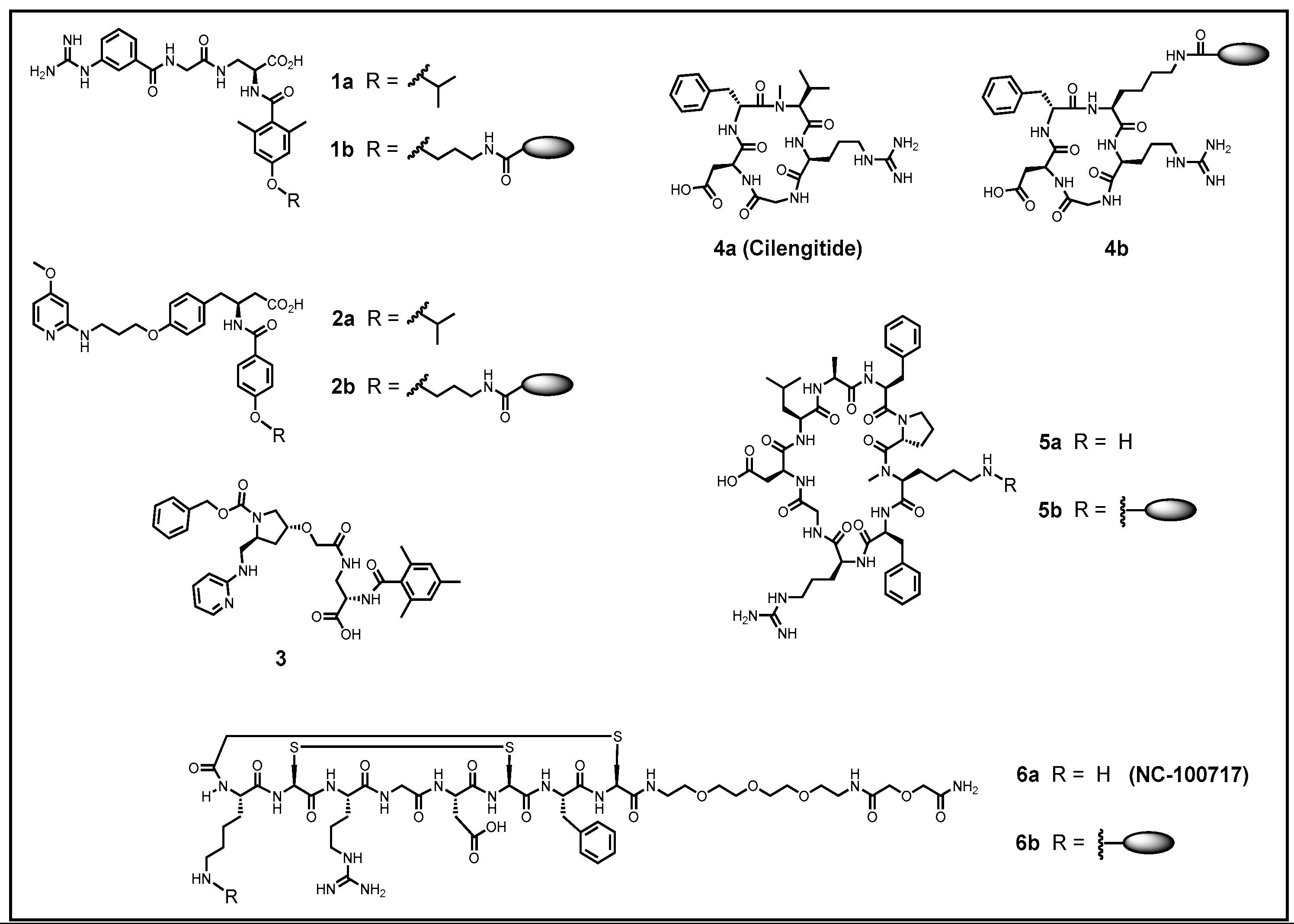
| αvβ3 [nM] | αvβ5 [nM] | αvβ6 [nM] | αvβ8 [nM] | α5β1 [nM] | αIIbβ3 [nM] | Ref. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1a | >10,000 | >10,000 | 433 ± 101 | 37 ± 3 | 2.3 ± 0.02 | >10,000 | [220] |
| 2a | 0.65 ± 0.05 | 199 ± 21 | >10,000 | >10,000 | 108 ± 27.5 | >10,000 | [221] |
| 3 | >10,000 | >10,000 | 23 ± 3.4 | 8.2 ± 0.52 | 2.5 ± 0.4 | >10,000 | [222] |
| 4a | 0.61 ± 0.06 | 8.4 ± 2.1 | 2050 ± 640 | 2350 ± 438 | 14.9 ± 3.1 | 5400 ± 814 | [216] |
| 5a | 1200 ± 240 | >10,000 | 0.28 ± 0.019 | 24 ± 3.1 | 73 ± 6 | >10,000 | [223] |
| 6a | 1.1 ± 0.1 | 16.7 ± 2.1 | >10,000 | >10,000 | 820 ± 156 | >10,000 | [224] |
| Integrin | Cancer Type | Cell Type | Main Expression Feature | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| αvβ3 | gastric cancer | tumor, endothelial and stromal cells | low to moderate expression frequency in tumor cells, high frequency in stroma and endothelia, correlates with phenotype, endothelial expression correlates with survival | [60] |
| glioma | endothelial and tumor cells | expression correlates with grade | [61] | |
| lung cancer brain metastases | endothelial and tumor cells | high expression frequency in endothelial, low frequency in tumor cells | [62] | |
| non small cell lung cancer | endothelial and tumor cells | high expression frequency in endothelia, low frequency in tumor cells, no correlation with survival | [63] | |
| oral squamous cell carcinoma | endothelial cells | higher expression in intratumoral endothelia compared with control tissue | [64] | |
| pancreatic cancer | tumor cells | moderate expression frequency, involved in lymph node metastasis | [65] | |
| prostate cancer | endothelial cells | high expression frequency peritumoral | [66] | |
| αvβ5 | gastric cancer | tumor, endothelial and stromal cells | moderate (to high) frequency in tumor cells, high frequency in stroma and endothelial cells, independent prognostic factor in intestinal-type | [60] |
| lung cancer (with brain metastases) | vessel endothelia and tumor cells | high expression frequency in endothelia, low frequency in tumor cells | [62] | |
| non small cell lung cancer | tumor cells and stroma | high frequency in tumor and stroma cells, no correlation with survival | [63] | |
| oral squamous cell carcinoma | tumor cells and stroma | [64] | ||
| prostate cancer | tumor cells | expression influenced by differentiation | [66] | |
| αvβ6 | basal cell carcinoma | tumor cells | higher expression frequency in infiltrative subtype | [67] |
| breast cancer | expression correlates with prognosis | [68] | ||
| colon cancer | upregulated at invasive front and in budding tumor cells | [69] | ||
| endometrial cancer | often overexpressed without correlation with occurrence of lymph node metastasis | [70] | ||
| gastric cancer | potential prognostic marker in early stage carcinoma | [53] | ||
| liver | differentiates cholangiocarcinoma from hepatocellular carcinoma | [52] | ||
| non small cell lung cancer | high expression frequency with intratumoral heterogeneity, no correlation with survival | [71] | ||
| lung cancer brain metastases | high expression frequency | [62] | ||
| oral squamous cell carcinoma | expression at invasive front | [72] | ||
| ovarian cancer | expression correlates with grade | [55] | ||
| pancreatic cancer | high expression frequency | [51] [73] | ||
| prostate cancer | not/weakly expressed | [66] | ||
| αvβ8 | non small cell lung cancer | tumor cells | low to moderate expression frequency, no correlation with survival | [63] |
| prostate cancer | not expressed | [66] | ||
| α5β1 | oral squamous cell carcinoma | tumor, endothelial cells, stroma | strong expression in stroma, expressed also in tumor and endothelial cells | [64] |
| ovarian cancer | tumor cells | moderate expression frequency, correlates with survival | [74] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nieberler, M.; Reuning, U.; Reichart, F.; Notni, J.; Wester, H.-J.; Schwaiger, M.; Weinmüller, M.; Räder, A.; Steiger, K.; Kessler, H. Exploring the Role of RGD-Recognizing Integrins in Cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9090116
Nieberler M, Reuning U, Reichart F, Notni J, Wester H-J, Schwaiger M, Weinmüller M, Räder A, Steiger K, Kessler H. Exploring the Role of RGD-Recognizing Integrins in Cancer. Cancers. 2017; 9(9):116. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9090116
Chicago/Turabian StyleNieberler, Markus, Ute Reuning, Florian Reichart, Johannes Notni, Hans-Jürgen Wester, Markus Schwaiger, Michael Weinmüller, Andreas Räder, Katja Steiger, and Horst Kessler. 2017. "Exploring the Role of RGD-Recognizing Integrins in Cancer" Cancers 9, no. 9: 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9090116
APA StyleNieberler, M., Reuning, U., Reichart, F., Notni, J., Wester, H.-J., Schwaiger, M., Weinmüller, M., Räder, A., Steiger, K., & Kessler, H. (2017). Exploring the Role of RGD-Recognizing Integrins in Cancer. Cancers, 9(9), 116. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9090116






