Applicability of Radiomics for Differentiation of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma from Healthy Tissue of Pancreas by Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Machine Learning
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. MRI Scanning Protocol
2.3. MRI Analysis
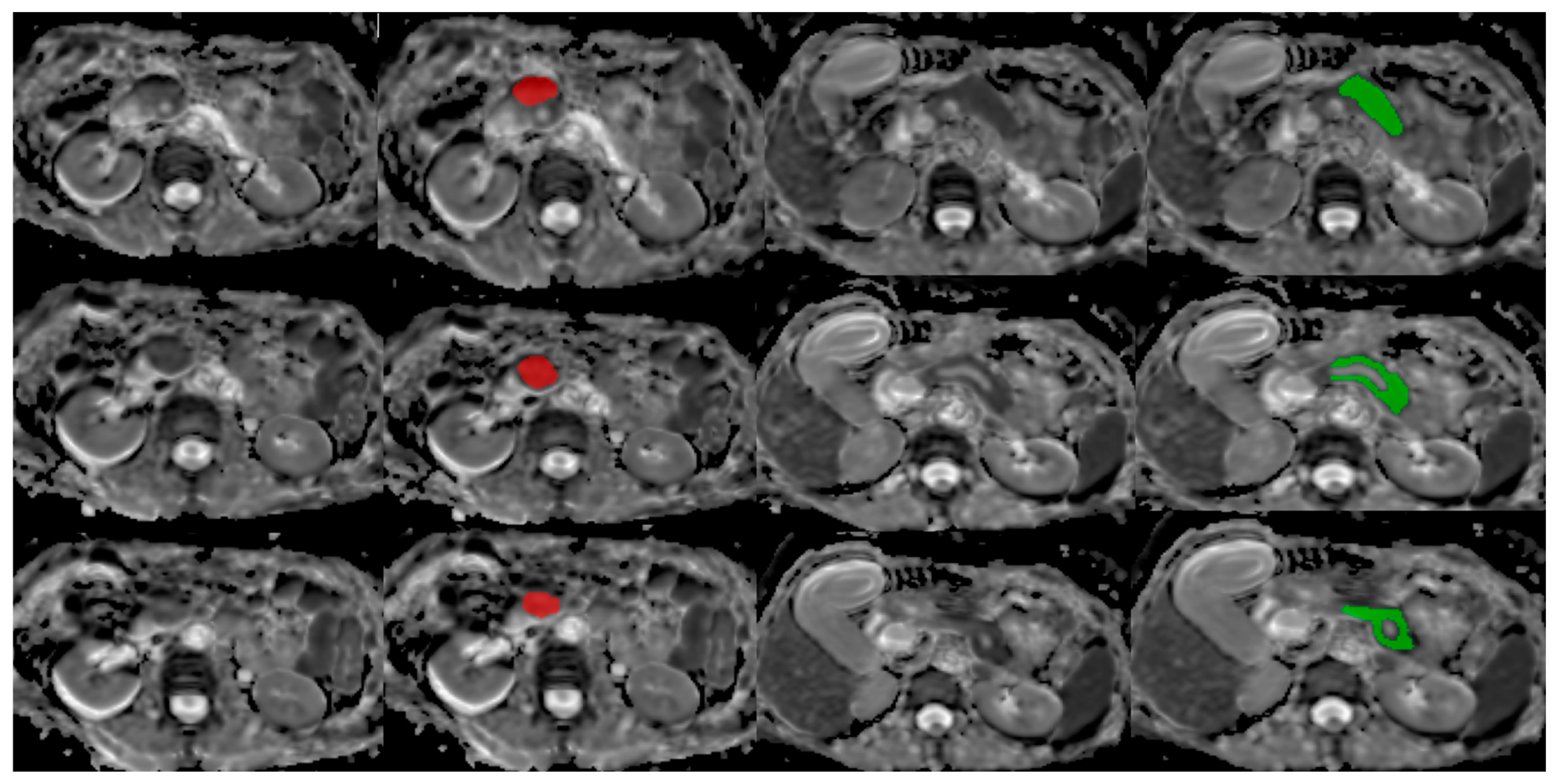
2.3.1. Database
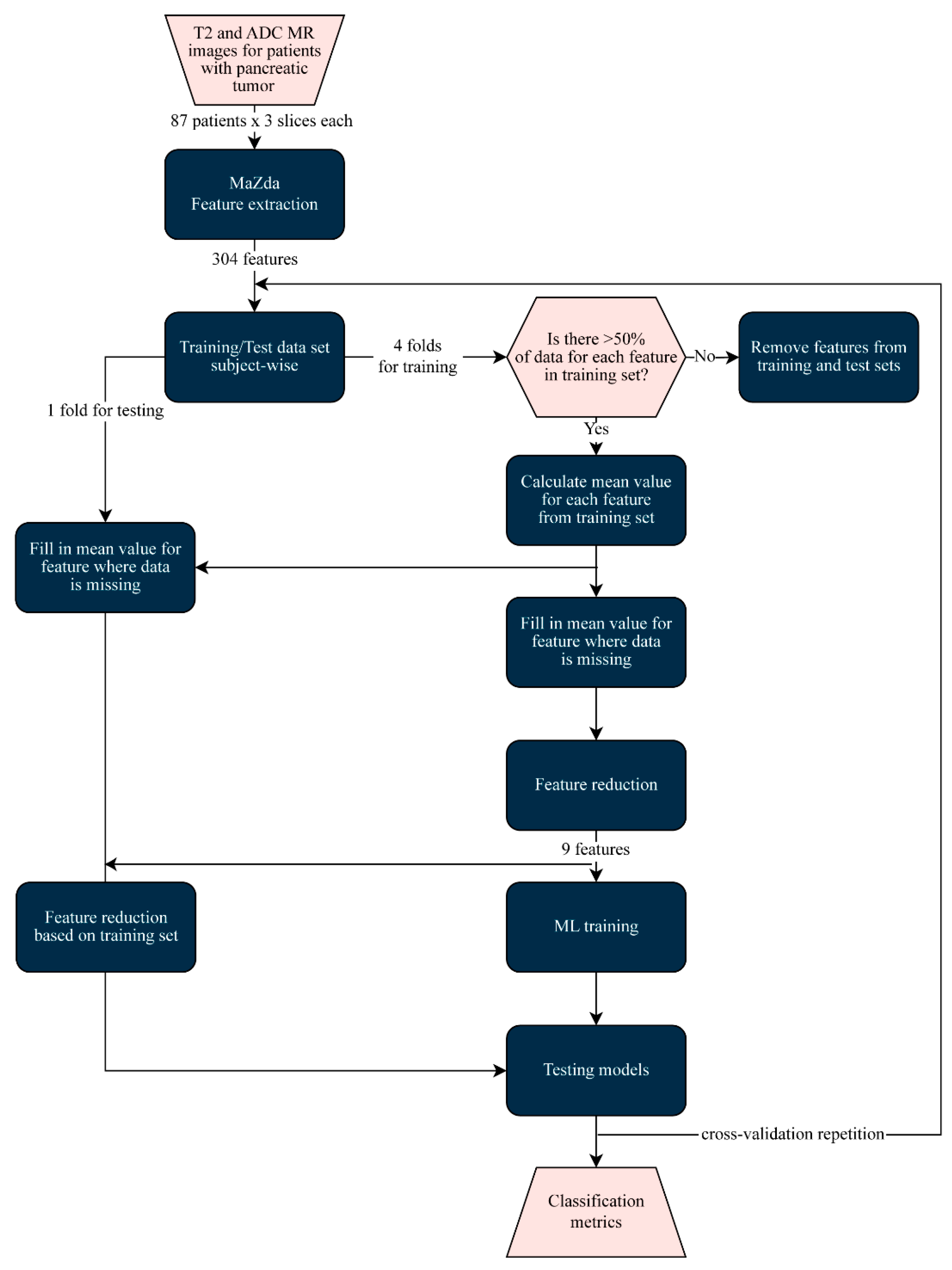
2.3.2. Image Processing
2.3.3. Machine Learning Classification
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
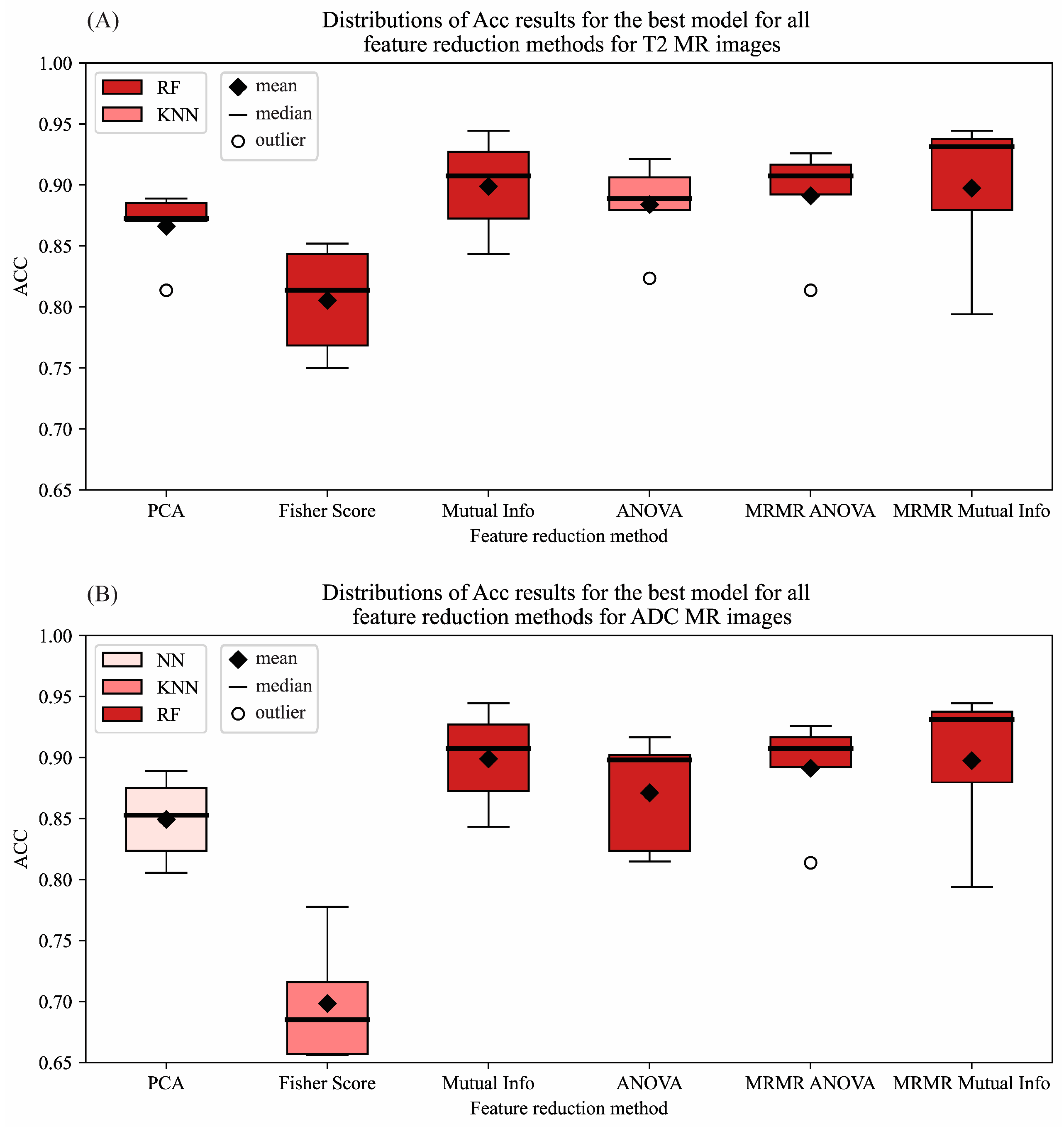
3.1. Machine Learning Classification Results
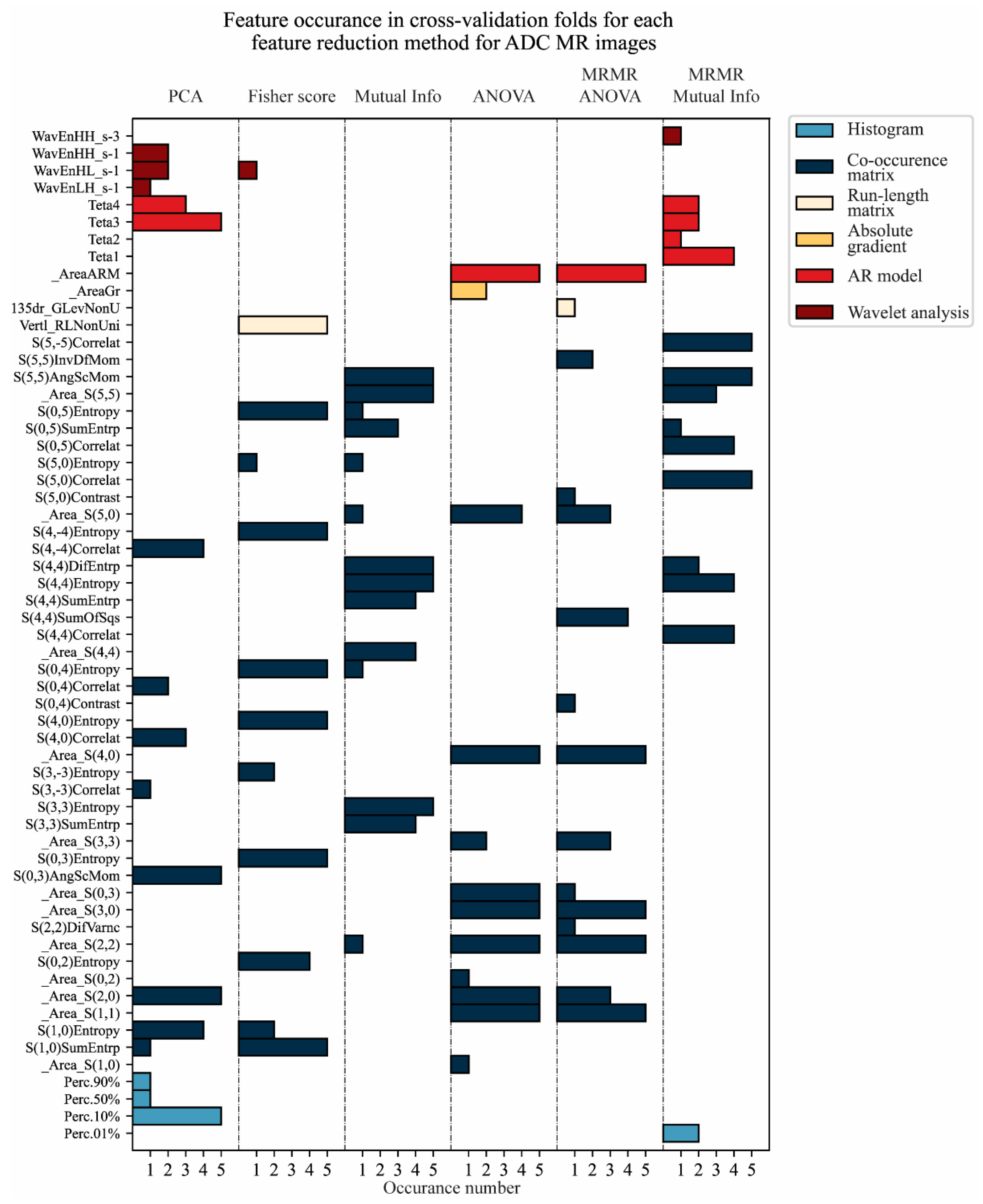
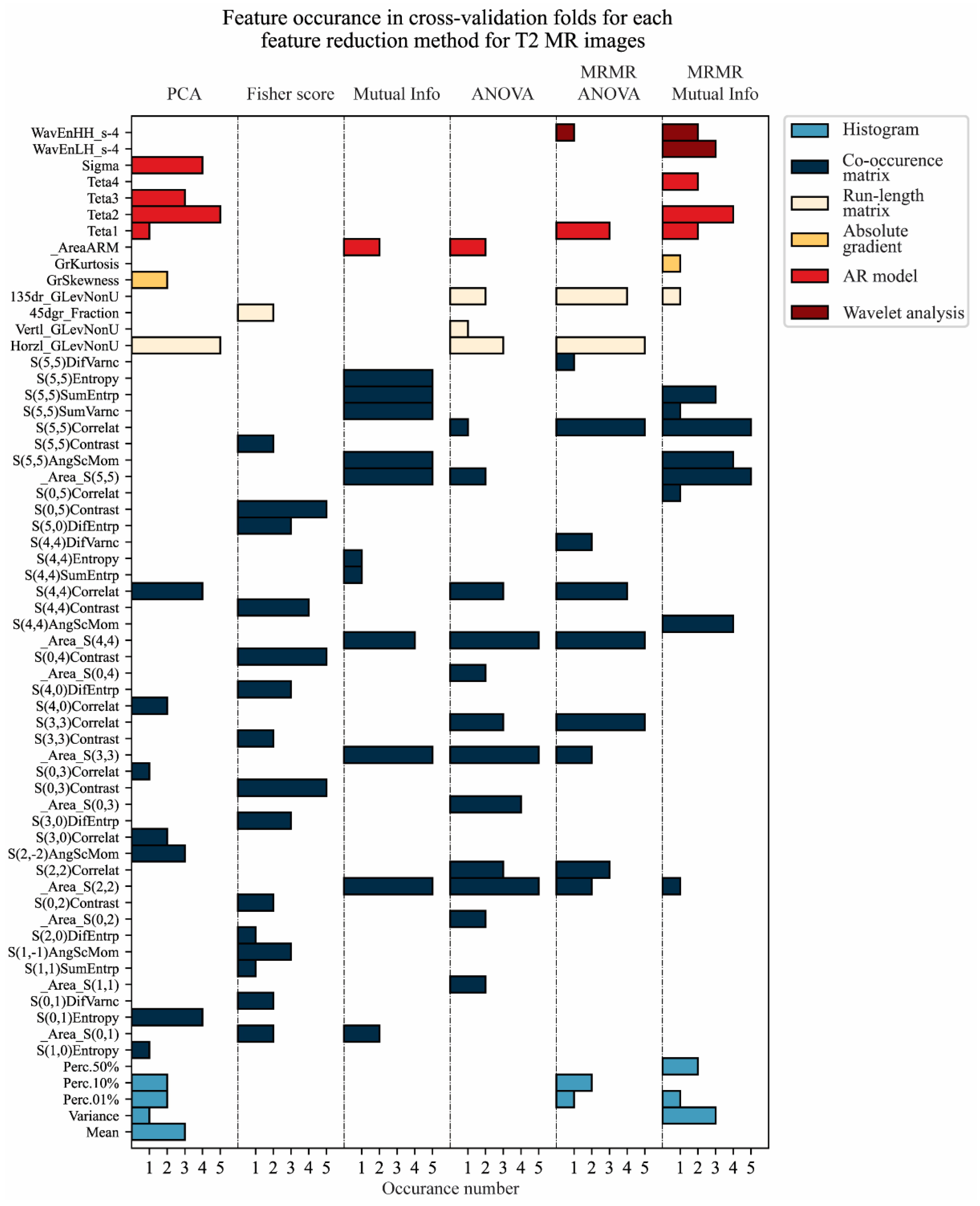
3.2. Feature Reduction
3.3. Classification Model of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma
3.4. Testing of Classification Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- GLOBOCAN. The Global Cancer Observatory. 2022. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/today (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Chu, L.; Goggins, M.G.; Fishman, E. Diagnosis and Detection of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer. J. 2017, 23, 333–342. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.S.; Lee, J.M. Imaging diagnosis of pancreatic cancer: A state-of-the-art review. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 7864–7877. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, S.H.; Lee, J.M.; Cho, J.Y.; Lee, K.B.; Kim, J.E.; Moon, S.K.; Kim, S.J.; Baek, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.H.; et al. Small (≤20 mm) pancreatic adenocarcinomas: Analysis of enhancement patterns and secondary signs with multiphasic multidetector CT. Radiology 2011, 259, 442–452. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, K.M.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Park, M.J.; Lee, M.H.; Hwang, J.; Rhim, H. Imaging features of small (≤3 cm) pancreatic solid tumors on gadoxetic-acid-enhanced MR imaging and diffusion-weighted imaging: An initial experience. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 916–925. [Google Scholar]
- Kowada, A. Cost-effectiveness of abdominal ultrasound versus magnetic resonance imaging for pancreatic cancer screening in familial high-risk individuals in Japan. Pancreas 2020, 49, 1052–1056. [Google Scholar]
- Preuss, K.; Thach, N.; Liang, X.; Baine, M.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z.; Du, H.; Yu, H.; Lin, C.; Hollingsworth, M.A.; et al. Imaging for personalized medicine in pancreatic cancer: A review of radiomics and deep learning applications. Cancers 2022, 14, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Keles, E.; Yazici, C.; Tirkes, T.; Bagci, U. A review of deep learning and radiomics approaches for pancreatic cancer diagnosis from medical imaging. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2023, 39, 436–447. [Google Scholar]
- Anghel, C.; Grasu, M.C.; Anghel, D.A.; Rusu-Munteanu, G.I.; Dumitru, R.L.; Lupescu, I.G. Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: Imaging Modalities and the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Analyzing CT and MRI Images. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strzelecki, M.; Szczypinski, P.; Materka, A. MaZda 4.00 MR Analysis Software: User’s Manual. Available online: https://qmazda.p.lodz.pl/ (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, L.C.; Park, S.; Kawamoto, S.; Fouladi, D.; Shayesteh, S.; Zinreich, E.S.; Graves, J.S.; Horton, K.M.; Hruban, R.H.; Yuille, A.L.; et al. Utility of CT radiomics features in differentiation of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma from normal pancreatic tissue. Am. J. Roendgenol. AJR 2019, 213, 349–357. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, P.T.; Chang, D.; Yen, H.; Liu, K.L.; Huang, S.Y.; Roth, H.; Wu, M.-S.; Liao, W.-C.; Wang, W. Radiomic features at CT can distinguish pancreatic cancer from noncancerous pancreas. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2021, 3, e21001020. [Google Scholar]
- Mukherjee, S.; Patra, A.; Khasawneh, H.; Korfiatis, P.; Rajamohan, N.; Suman, G.; Majumder, S.; Panda, A.; Johnson, M.P.; Larson, N.B.; et al. Radiomics-based Machine-learning Models Can Detect Pancreatic Cancer on Prediagnostic Computed Tomography Scans at a Substantial Lead Time Before Clinical Diagnosis. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 1435–1446.e3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Liang, H.; Yan, G.; Liu, Y. Comparison of Multiple Radiomics Models for Identifying Histological Grade of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Preoperatively Based on Multiphasic Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography: A Two-Center Study in Southwest China. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Ming, B.; Zhou, T.; Wu, J.L.; Chen, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.Y.; Chen, T.W.; Zhang, X.M. Radiomics Model Based on MR Images to Discriminate Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Mass-Forming Chronic Pancreatitis Lesions. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 620981. [Google Scholar]
- Podina, N.; Gheorghe, E.C.; Constantin, A.; Cazacu, I.; Croitoru, V.; Gheorghe, C.; Balaban, D.V.; Jinga, M.; Tieranu, C.G.; Saftoiu, A. Artificial Intelligence in Pancreatic Imaging: A Systematic Review. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2025, 13, 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaissis, G.; Ziegelmayer, S.; Lohofer, F.; Algul, H.; Eiber, M.; Weichert, W.; Schmid, R.; Friess, H.; Rummeny, E.; Ankerst, D.; et al. A machine learning model for the prediction of survival and tumor subtype in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma from preoperative diffusion-weighted imaging. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2019, 3, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, N.; Fan, X.; Chen, D.; Chen, J.; Yu, H.; He, M.; Liu, H.; Yin, X.; Li, B.; Wang, H. Peritumoral and Intratumoral Texture Features Based on Multiparametric MRI and Multiple Machine Learning Methods to Preoperatively Evaluate the Pathological Outcomes of Pancreatic Cancer. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 58, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Shu, Z.; Peng, J.; Wang, W.; Hou, J.; Han, L.; Zheng, G.; Wei, Y.; Zhong, J. Prediction of postoperative liver metastasis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma based on multiparametric magnetic resonance radiomics combined with serological markers: A cohort study of machine learning. Abdom. Radiol. 2024, 49, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, T.; Zhang, Q.W.; Duan, S.F.; Bian, Y.; Hao, Q.; Xing, P.Y.; Wang, T.G.; Chen, L.G.; Ma, C.; Lu, J.P. MRI-based radiomics approach for differentiation of hypovascular non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and solid pseudopapillary neoplasms of the pancreas. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 21, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lainez Ramos-Bossini, A.J.; Gamez Martinez, A.; Luengo Gomez, D.; Valverde-Lopez, F.; Morillo Gil, A.J.; Gonzalez Flores, E.; Salmeron Ruiz, A.; Jimenez Gutierrez, P.M.; Melguizo, C.; Prados, J. Computed Tomography-Based Sarcopenia and Pancreatic Cancer Survival-A Comprehensive Meta-Analysis Exploring the Influence of Definition Criteria, Prevalence, and Treatment Intention. Cancers 2025, 17, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Cao, B.; Xia, T.; Zhu, L.; Yu, Y.; Lu, C.; Tang, T.; Wang, Y.; Ju, S. Multiparametric MRI for Assessment of the Biological Invasiveness and Prognosis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma in the Era of Artificial Intelligence. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging, 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocak, B.; Baessler, B.; Bakas, S.; Cuocolo, R.; Fedorov, A.; Maier-Hein, L.; Mercaldo, N.; Muller, H.; Orlhac, F.; Pinto Dos Santos, D.; et al. CheckList for EvaluAtion of Radiomics research (CLEAR): A step-by-step reporting guideline for authors and reviewers endorsed by ESR and EuSoMII. Insights Imaging 2023, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, K.; Xia, Y.; Yao, J.; Han, X.; Lambert, L.; Zhang, T.; Tang, W.; Jin, G.; Jiang, H.; Fang, X.; et al. Large-Scale Pancreatic Cancer Detection via Non-Contrast CT and Deep Learning. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 3033–3043. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Alves, N.; Schuurmans, M.; Litjens, G.; Bosma, J.S.; Hermans, J.; Huisman, H. Fully Automatic Deep Learning Framework for Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Detection on Computed Tomography. Cancers 2022, 14, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.L.; Wu, T.; Chen, P.T.; Tsai, Y.M.; Roth, H.; Wu, M.S.; Liao, W.-C.; Wang, W. Deep learning to distinguish pancreatic cancer tissue from non-cancerous pancreatic tissue: A retrospective study with cross-racial external validation. Lancet Digit. Health 2020, 2, e303–e313. [Google Scholar]

| Parameter | T2-Weighted Single Shot FSE | T2-Weighted FS | T1-Weighted in-Phase | T1-Weighted out of Phase | T1-Weighted 3D-GRE | DW SSSE EPI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TR (ms) | 1200 | 1200 | 160 | 160 | 6.7 | 5000 |
| TE (ms) | 90 | 90 | 2 | 2 | 4.3 | 52 |
| Flip angle | 90 | 90 | 80 | 80 | 15 | 180 |
| BW/pixel (Hz) | 62.5 | 62.5 | 62.5 | 62.5 | 83.33 | 250 |
| Matrix (phase × frequency) | 224 × 288 | 224 × 288 | 192 × 256 | 192 × 256 | 192 × 320 | 136 × 136 |
| FOV (mm) | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 40 | 36 |
| Section thickness (mm) | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 4.4 | 7 |
| Intersectional gap (%) | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 50 | 0 |
| No. of signal acquisition | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Fat suppression | None | Fat sat | None | None | Fat sat | None |
| Respiratory control | BH | BH | BH | BH | BH | RT |
| Logistic Regression | Penalty ∈ {l1, l2} C ∈ {0.1, 0.5, 1, 2} Solver ∈ {newton-cg, lbfgs, liblinear, sag, saga} |
| k-Nearest Neighbors | N neighbors ∈ {2, 5, 10, 20} Weights ∈ {uniform, distance} Algorithm ∈ {ball tree, kd tree, brute} |
| Support Vector Machine | C ∈ {0.1, 0.5, 1, 2} Kernel ∈ {linear, poly, rbf, sigmoid} |
| Neural Network | Hidden layer sizes ∈ {50, 100, 200, [200, 100], [200, 50], [100, 50], [50, 50], [200, 150, 100, 50], [200, 100, 50]} Batch size ∈ {16, 32, 64} Solver ∈ {lbfgs, adam} |
| Random Forest | N estimators ∈ {200, 400, 600, 800, 1500, 3000} Criterion ∈ {gini, entropy} Max depth ∈ {10, 20, 30, 40, 50, None} Max features ∈ {sqrt, log2} |
| Gaussian Naïve Bayes | / |
| Training–Validation Group (n = 87) | Test Group (n = 58) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (median) | 63 | 63.5 | 0.913 |
| Gender (Male/Female) | 45/42 | 26/32 | 0.416 |
| Location of tumor (Head/Body/Tail) | 68/15/4 | 44/12/2 | 0.836 |
| Diameter of tumor (median) | 3.3 cm | 2.7 cm | 0.001 ** |
| Diameter of tumor (<2 cm/≥2 cm) | 7/80 | 14/44 | 0.009 ** |
| Acc | Se | Sp | F1-Score | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR | 87.04% | 85.19% | 88.89% | 86.79% | 87.04% |
| KNN | 89.81% | 90.74% | 88.89% | 89.91% | 89.81% |
| SVM | 90.74% | 88.89% | 92.59% | 90.57% | 90.74% |
| RF | 94.44% | 94.44% | 94.44% | 94.44% | 94.44% |
| NN | 89.81% | 85.19% | 94.44% | 89.32% | 89.81% |
| GNB | 75.00% | 61.11% | 88.89% | 70.97% | 75.00% |
| Acc | Se | Sp | F1-Score | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCA | 88.89% | 90.74% | 87.04% | 89.09% | 88.89% |
| Fisher Score | 76.85% | 83.33% | 70.37% | 78.26% | 76.85% |
| Mutual Information | 94.44% | 94.44% | 94.44% | 94.44% | 94.44% |
| ANOVA | 89.81% | 90.74% | 88.89% | 89.91% | 89.81% |
| MRMR ANOVA | 92.59% | 90.74% | 94.44% | 92.45% | 92.59% |
| MRMR Mutual Information | 94.44% | 96.30% | 92.59% | 94.55% | 94.44% |
| Acc | Se | Sp | F1-Score | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LR | 95.37% | 94.44% | 96.30% | 95.33% | 95.37% |
| KNN | 99.07% | 100% | 98.15% | 99.08% | 99.07% |
| SVM | 96.30% | 96.30% | 96.30% | 96.30% | 96.30% |
| RF | 98.15% | 98.15% | 98.15% | 98.15% | 98.15% |
| NN | 91.67% | 98.15% | 85.19% | 92.18% | 91.67% |
| GNB | 91.67% | 92.59% | 90.74% | 91.74% | 91.67% |
| Acc | Se | Sp | F1-Score | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCA | 88.89% | 96.30% | 81.48% | 89.66% | 88.89% |
| Fisher Score | 91.67% | 98.15% | 85.19% | 92.18% | 91.67% |
| Mutual Information | 98.15% | 98.15% | 98.15% | 98.15% | 98.15% |
| ANOVA | 91.67% | 92.59% | 90.74% | 91.74% | 91.67% |
| MRMR ANOVA | 92.59% | 94.44% | 90.74% | 92.72% | 92.59% |
| MRMR Mutual Information | 97.22% | 98.15% | 96.30% | 97.25% | 97.22% |
| T2W-FS | ADC | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| RF hyperparameters | N estimators = 200 Criterion = entropy Max depth = 10 Max features = sqrt | RF hyperparameters | N estimators = 200 Criterion = gini Max depth = 10 Max features = sqrt |
| Features | _Area_S(0,1) _Area_S(2,2) _Area_S(3,3) _Area_S(4,4) _Area_S(5,5) S(5,5)AngScMom S(5,5)SumVarnc S(5,5)SumEntrp S(5,5)Entropy | Features | S(3,3)SumEntrp S(3,3)Entropy _Area_S(4,4) S(4,4)SumEntrp S(4,4)Entropy S(4,4)DifEntrp S(0,5)SumEntrp _Area_S(5,5) S(5,5)AngScMom |
| Acc | Se | Sp | F1-Score | AUC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| T2W-FS | 69.25% | 86.21% | 52.30% | 73.71% | 69.25% |
| ADC | 81.32% | 92.53% | 70.10% | 83.21% | 81.32% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sarac, D.; Badza Atanasijevic, M.; Mitrovic Jovanovic, M.; Kovac, J.; Lazic, L.; Jankovic, A.; Saponjski, D.J.; Milosevic, S.; Stosic, K.; Masulovic, D.; et al. Applicability of Radiomics for Differentiation of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma from Healthy Tissue of Pancreas by Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Machine Learning. Cancers 2025, 17, 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071119
Sarac D, Badza Atanasijevic M, Mitrovic Jovanovic M, Kovac J, Lazic L, Jankovic A, Saponjski DJ, Milosevic S, Stosic K, Masulovic D, et al. Applicability of Radiomics for Differentiation of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma from Healthy Tissue of Pancreas by Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Machine Learning. Cancers. 2025; 17(7):1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071119
Chicago/Turabian StyleSarac, Dimitrije, Milica Badza Atanasijevic, Milica Mitrovic Jovanovic, Jelena Kovac, Ljubica Lazic, Aleksandra Jankovic, Dusan J. Saponjski, Stefan Milosevic, Katarina Stosic, Dragan Masulovic, and et al. 2025. "Applicability of Radiomics for Differentiation of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma from Healthy Tissue of Pancreas by Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Machine Learning" Cancers 17, no. 7: 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071119
APA StyleSarac, D., Badza Atanasijevic, M., Mitrovic Jovanovic, M., Kovac, J., Lazic, L., Jankovic, A., Saponjski, D. J., Milosevic, S., Stosic, K., Masulovic, D., Radenkovic, D., Papic, V., & Djuric-Stefanovic, A. (2025). Applicability of Radiomics for Differentiation of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma from Healthy Tissue of Pancreas by Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Machine Learning. Cancers, 17(7), 1119. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071119