18F-FDG PET/CT Radiomics for Predicting Therapy Response in Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma: A Bi-Centric Pilot Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
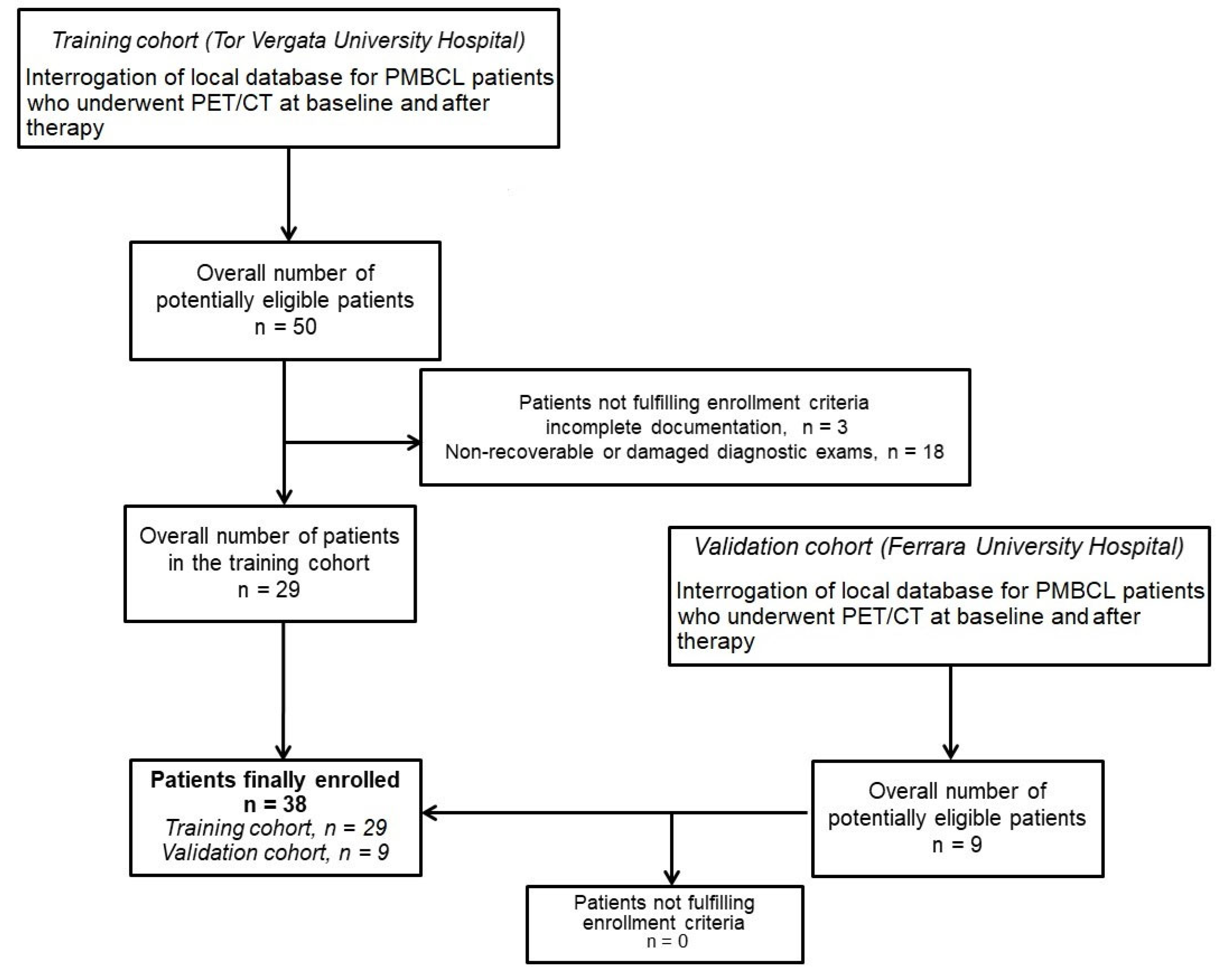
2.1. Study Design
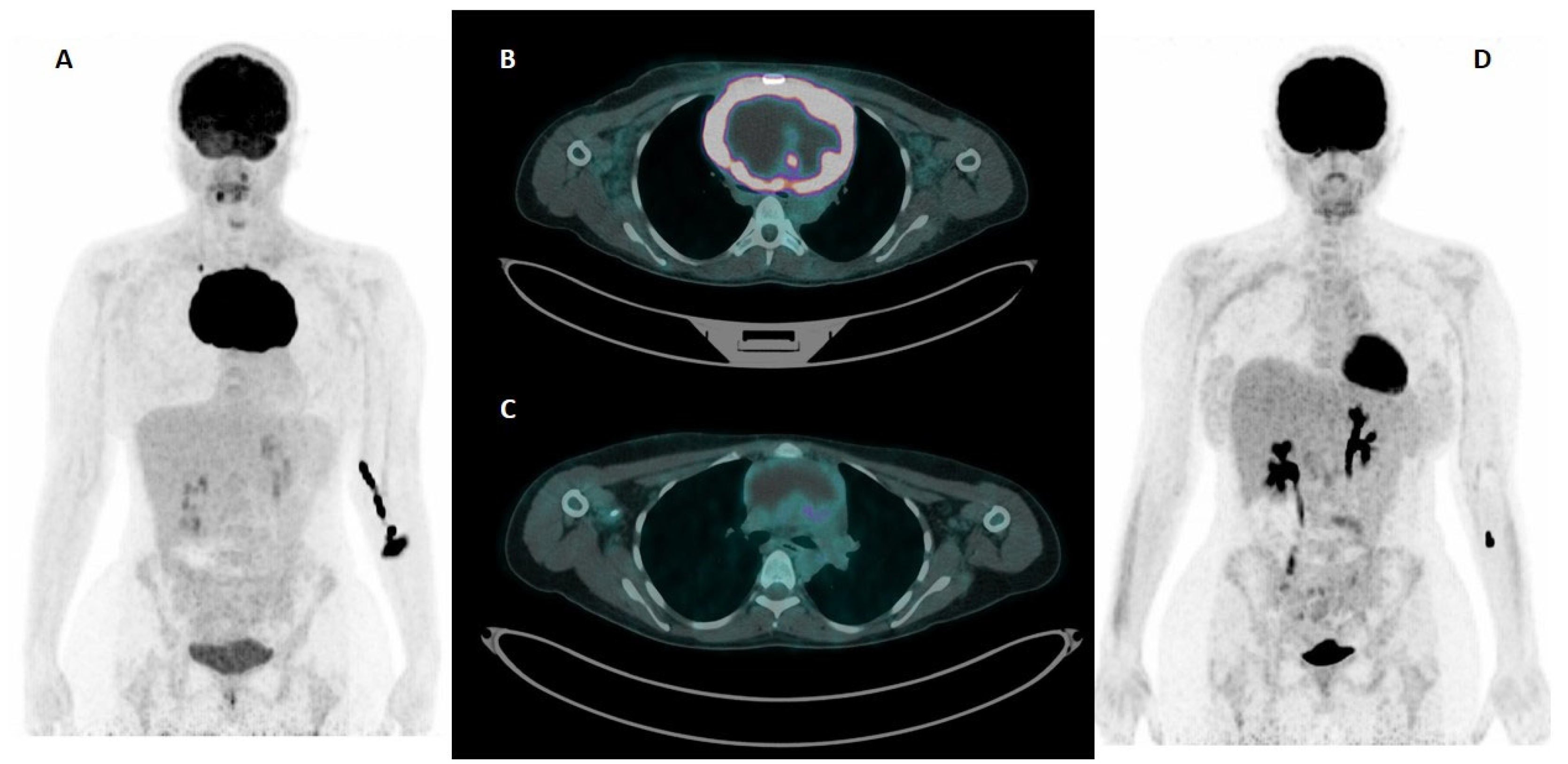
2.2. [18F]FDG PET/CT Imaging
2.3. Feature Extraction
2.4. Data Preprocessing and Balancing Strategy
2.5. Statistical Analysis and Model Construction
3. Results
3.1. Cohorts’ Composition, Characteristics, and Outcome
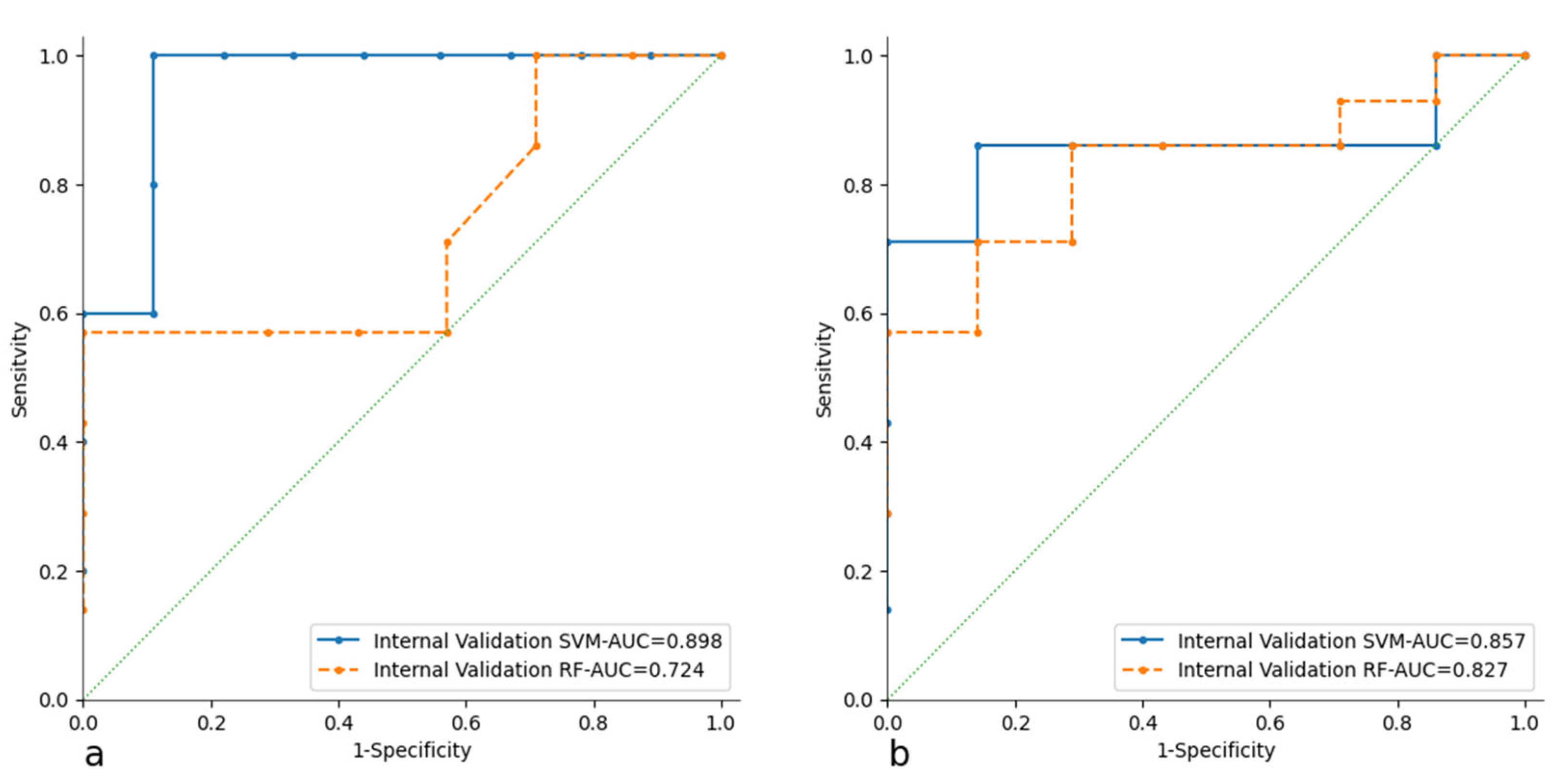
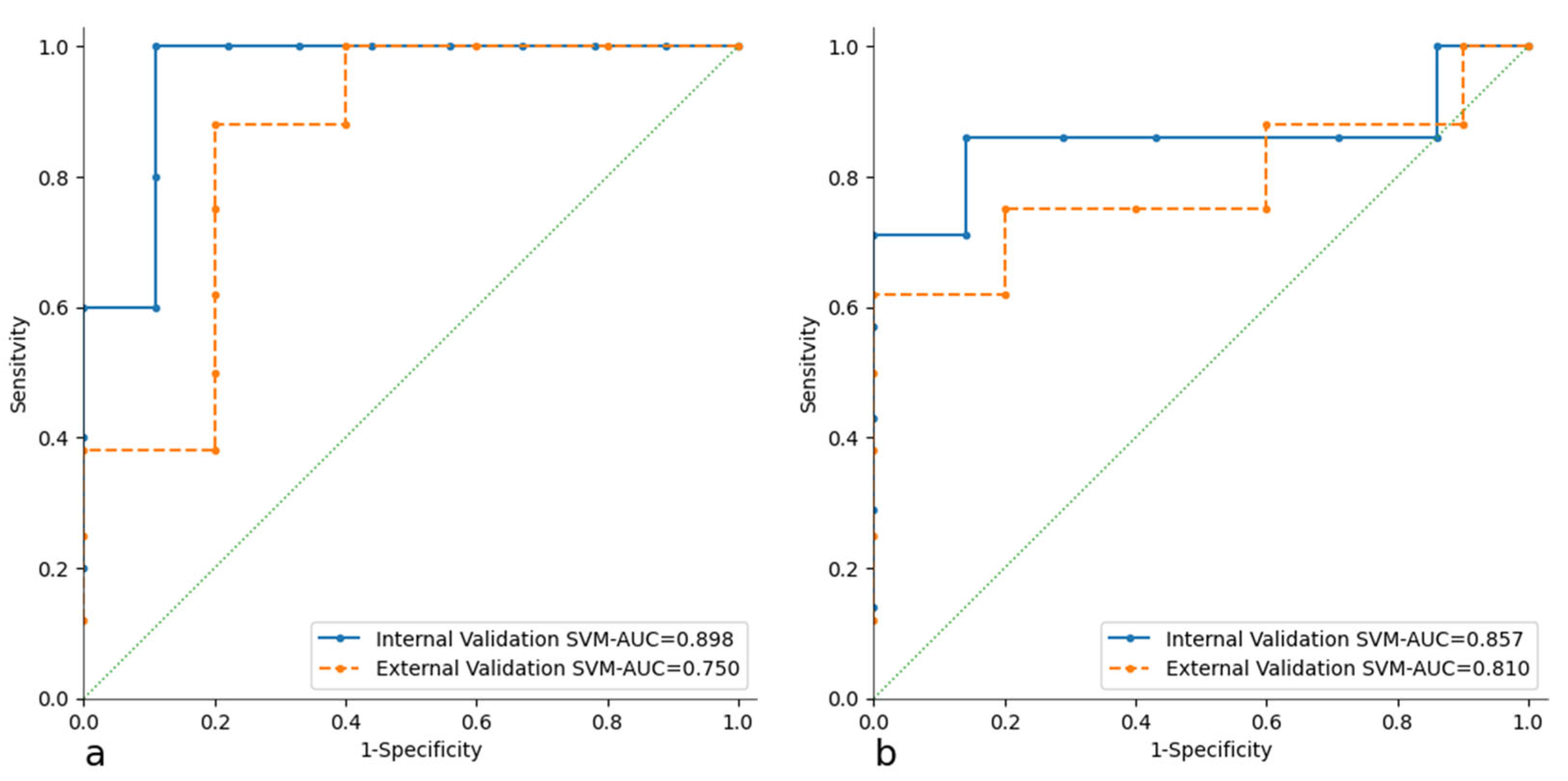
3.2. Radiomic Analysis and Model Building
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, Y.; Dong, X.; Tu, M.; Wang, H. Primary Mediastinal Large B Cell Lymphoma. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 2831–2837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenwald, A.; Wright, G.; Leroy, K.; Yu, X.; Gaulard, P.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Chan, W.C.; Zhao, T.; Haioun, C.; Greiner, T.C.; et al. Molecular Diagnosis of Primary Mediastinal B Cell Lymphoma Identifies a Clinically Favorable Subgroup of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Related to Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 851–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martelli, M.; Ferreri, A.; Di Rocco, A.; Ansuinelli, M.; Johnson, P.W.M. Primary Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2017, 113, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.D.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th Edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.W.M.; Davies, A.J. Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma. Hematology 2008, 2008, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinzani, P.L.; Martelli, M.; Poletti, V.; Vitolo, U.; Gobbi, P.G.; Chisesi, T.; Barosi, G.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; Marchetti, M.; Pimpinelli, N.; et al. Practice Guidelines for the Management of Extranodal Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphomas of Adult Non-Immunodeficient Patients. Part I: Primary Lung and Mediastinal Lymphomas. A Project of the Italian Society of Hematology, the Italian Society of Experimental Hematology and the Italian Group for Bone Marrow Transplantation. Haematologica 2008, 93, 1364–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, W.; Nakamura, N.; Tomita, N.; Ishii, Y.; Takasaki, H.; Hashimoto, C.; Motomura, S.; Yamazaki, E.; Ohshima, R.; Numata, A.; et al. Clinicopathological Analysis of Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma and Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma of the Mediastinum. Leuk. Lymphoma 2013, 54, 967–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donzelli, L.; Rocco, A.D.; Petrucci, L.; Martelli, M. Primary Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Biological Features, Clinical Characteristics and Current Treatment Strategies. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2025, 134, 102898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunleavy, K.; Pittaluga, S.; Maeda, L.S.; Advani, R.; Chen, C.C.; Hessler, J.; Steinberg, S.M.; Grant, C.; Wright, G.; Varma, G.; et al. Dose-Adjusted EPOCH-Rituximab Therapy in Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanishyna, Y.; Skrypets, T.; Novosad, O.; Pastushenko, I.; Kryachok, I. DA-EPOCH-R vs. R-CHOP in Patients with Primary Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Results of Prospective Randomized Ukrainian Multicenter Study. Blood 2020, 136, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, M.; Hawkes, E.A.; Cunningham, D.; Chadwick, N.; Counsell, N.; Lawrie, A.; Jack, A.; Smith, P.; Mouncey, P.; Pocock, C.; et al. Rituximab, Cyclophosphamide, Doxorubicin, Vincristine and Prednisolone (R- CHOP) in the Management of Primary Mediastinal B-cell Lymphoma: A Subgroup Analysis of the UK NCRI R- CHOP 14 versus 21 Trial. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 175, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malenda, A.; Kołkowska-Leśniak, A.; Puła, B.; Długosz-Danecka, M.; Chełstowska, M.; Końska, A.; Giza, A.; Lech-Marańda, E.; Jurczak, W.; Warzocha, K. Outcomes of Treatment with Dose-adjusted EPOCH-R or R-CHOP in Primary Mediastinal Large B-cell Lymphoma. Eur. J. Haematol. 2020, 104, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, M.R.; Williams, L.S.; Dorris, C.S.; Luo, Y.; Makambi, K.; Dunleavy, K. Improved Survival for Dose-Intensive Chemotherapy in Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 4068 Patients. Haematologica 2023, 109, 846–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, M.; Zucca, E.; Botto, B.; Kryachok, I.; Ceriani, L.; Balzarotti, M.; Tucci, A.; Cabras, M.G.; Zilioli, V.R.; Rusconi, C.; et al. Impact of Different Induction Regimens on the Outcome of Primary Mediastinal B Cell Lymphoma in the Prospective Ielsg 37 Trial. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39, hon.49_2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vardhana, S.; Hamlin, P.A.; Yang, J.; Zelenetz, A.; Sauter, C.S.; Matasar, M.J.; Ni, A.; Yahalom, J.; Moskowitz, C.H. Outcomes of Relapsed and Refractory Primary Mediastinal (Thymic) Large B Cell Lymphoma Treated with Second-Line Therapy and Intent to Transplant. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2018, 24, 2133–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzola, R.; Giaj Levra, N.; Alongi, F. Radiation Dose-Response Relationship for Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Survivors of Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2940–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Leeuwen, F.E.; Ng, A.K. Long-Term Risk of Second Malignancy and Cardiovascular Disease after Hodgkin Lymphoma Treatment. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2016, 2016, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassi, L.; De Sanctis, V.; Loseto, G.; Gerardi, C.; Allocati, E.; Ciavarella, S.; Minoia, C.; Guarini, A.; Bari, A. Second Cancers in Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma and Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: A Systematic Review by the Fondazione Italiana Linfomi. Cancers 2022, 14, 519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, M.; Ceriani, L.; Ciccone, G.; Ricardi, U.; Kriachok, I.; Botto, B.; Balzarotti, M.; Tucci, A.; Usai, S.V.; Zilioli, V.R.; et al. Omission of Radiotherapy in Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma: IELSG37 Trial Results. J. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 42, 4071–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, M.; Ceriani, L.; Zucca, E.; Zinzani, P.L.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; Vitolo, U.; Stelitano, C.; Brusamolino, E.; Cabras, M.G.; Rigacci, L.; et al. [18F]Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography Predicts Survival After Chemoimmunotherapy for Primary Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Results of the International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group IELSG-26 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 1769–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheson, B.D.; Fisher, R.I.; Barrington, S.F.; Cavalli, F.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zucca, E.; Lister, T.A. Recommendations for Initial Evaluation, Staging, and Response Assessment of Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: The Lugano Classification. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3059–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melani, C.; Advani, R.; Roschewski, M.; Walters, K.M.; Chen, C.C.; Baratto, L.; Ahlman, M.A.; Miljkovic, M.D.; Steinberg, S.M.; Lam, J.; et al. End-of-Treatment and Serial PET Imaging in Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma Following Dose-Adjusted EPOCH-R: A Paradigm Shift in Clinical Decision Making. Haematologica 2018, 103, 1337–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, H.J.A.; Kwee, T.C. Unproven Value of End-of-Treatment and Serial Follow-up FDG-PET in Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma. Haematologica 2018, 103, e380–e381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillies, R.J.; Kinahan, P.E.; Hricak, H. Radiomics: Images Are More than Pictures, They Are Data. Radiology 2016, 278, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albano, D.; Ravanelli, M.; Durmo, R.; Versari, A.; Filice, A.; Rizzo, A.; Racca, M.; Pizzuto, D.A.; Bertagna, F.; Annunziata, S. Semiquantitative 2-[18F]FDG PET/CT-Based Parameters Role in Lymphoma. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1515040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, L.; Ferrari, C.; Nuvoli, S.; Bianconi, F.; Donner, D.; Marongiu, A.; Mammucci, P.; Vultaggio, V.; Chierichetti, F.; Rubini, G.; et al. Pet-Radiomics in Lymphoma and Multiple Myeloma: Update of Current Literature. Clin. Transl. Imaging 2023, 12, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abenavoli, E.M.; Barbetti, M.; Linguanti, F.; Mungai, F.; Nassi, L.; Puccini, B.; Romano, I.; Sordi, B.; Santi, R.; Passeri, A.; et al. Characterization of Mediastinal Bulky Lymphomas with FDG-PET-Based Radiomics and Machine Learning Techniques. Cancers 2023, 15, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousefirizi, F.; Gowdy, C.; Klyuzhin, I.S.; Sabouri, M.; Tonseth, P.; Hayden, A.R.; Wilson, D.; Sehn, L.H.; Scott, D.W.; Steidl, C.; et al. Evaluating Outcome Prediction via Baseline, End-of-Treatment, and Delta Radiomics on PET-CT Images of Primary Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Cancers 2024, 16, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boellaard, R.; Delgado-Bolton, R.; Oyen, W.J.G.; Giammarile, F.; Tatsch, K.; Eschner, W.; Verzijlbergen, F.J.; Barrington, S.F.; Pike, L.C.; Weber, W.A.; et al. FDG PET/CT: EANM Procedure Guidelines for Tumour Imaging: Version 2.0. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 42, 328–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippi, L.; Proietti, I.; Morea, S.; Potenza, C. Concomitant Thyroiditis and Orchitis Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors Detected on [18F]FDG PET/CT. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2024, 55, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urso, L.; Panareo, S.; Castello, A.; Ambrosio, M.R.; Zatelli, M.C.; Caracciolo, M.; Tonini, E.; Valpiani, G.; Boschi, A.; Uccelli, L.; et al. Glucose Metabolism Modification Induced by Radioligand Therapy with [177Lu]Lu/[90Y]Y-DOTATOC in Advanced Neuroendocrine Neoplasms: A Prospective Pilot Study within FENET-2016 Trial. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, A.; Beichel, R.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Finet, J.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pujol, S.; Bauer, C.; Jennings, D.; Fennessy, F.; Sonka, M.; et al. 3D Slicer as an Image Computing Platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behdenna, A.; Colange, M.; Haziza, J.; Gema, A.; Appé, G.; Azencott, C.-A.; Nordor, A. pyComBat, a Python Tool for Batch Effects Correction in High-Throughput Molecular Data Using Empirical Bayes Methods. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, N.V.; Bowyer, K.W.; Hall, L.O.; Kegelmeyer, W.P. SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-Sampling Technique. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 2002, 16, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceriani, L.; Milan, L.; Johnson, P.W.M.; Martelli, M.; Presilla, S.; Giovanella, L.; Zucca, E. Baseline PET Features to Predict Prognosis in Primary Mediastinal B Cell Lymphoma: A Comparative Analysis of Different Methods for Measuring Baseline Metabolic Tumour Volume. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2019, 46, 1334–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melani, C.; Wilson, W.H.; Roschewski, M. What Is the Standard of Care for Primary Mediastinal B-cell Lymphoma; R- CHOP or DA-EPOCH-R? Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 184, 836–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.N.; Szabo, A.; Huntington, S.F.; Epperla, N.; Reddy, N.; Ganguly, S.; Vose, J.; Obiozor, C.; Faruqi, F.; Kovach, A.E.; et al. R- CHOP versus Dose-adjusted R- EPOCH in Frontline Management of Primary Mediastinal B-cell Lymphoma: A Multi-centre Analysis. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 180, 534–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Liu, L.; Wang, Z.; Yu, B.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, D.; Liu, X.; Lv, F.; et al. Prognostic Significance of Clinical Characteristics and18 Fluorodeoxyglucose-Positron Emission Tomography/Computed Tomography Quantitative Parameters in Patients with Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Int. Med. Res. 2022, 50, 03000605211063027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, E.H.L.; Koh, L.P.; Lee, J.; De Mel, S.; Jeyasekharan, A.; Liu, X.; Tang, T.; Lim, S.T.; Tao, M.; Quek, R.; et al. Real World Experience of R-CHOP with or without Consolidative Radiotherapy vs. DA-EPOCH-R in the First-line Treatment of Primary Mediastinal B-cell Lymphoma. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 4626–4632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, N.L.; Wilson, W.H.; Jung, S.-H.; Hsi, E.D.; Maurer, M.J.; Pederson, L.D.; Polley, M.-Y.C.; Pitcher, B.N.; Cheson, B.D.; Kahl, B.S.; et al. Dose-Adjusted EPOCH-R Compared With R-CHOP as Frontline Therapy for Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Clinical Outcomes of the Phase III Intergroup Trial Alliance/CALGB 50303. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 1790–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceriani, L.; Milan, L.; Pirosa, M.C.; Martelli, M.; Ruberto, T.; Cascione, L.; Johnson, P.W.M.; Davies, A.J.; Ciccone, G.; Zucca, E. PET-Based Risk Stratification in Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma: A Comparative Analysis of Different Segmentation Methods in the IELSG37 Trial Patient Cohort. J. Nucl. Med. 2025, 66, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceriani, L.; Milan, L.; Martelli, M.; Ferreri, A.J.M.; Cascione, L.; Zinzani, P.L.; Di Rocco, A.; Conconi, A.; Stathis, A.; Cavalli, F.; et al. Metabolic Heterogeneity on Baseline 18FDG-PET/CT Scan Is a Predictor of Outcome in Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2018, 132, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senjo, H.; Hirata, K.; Izumiyama, K.; Minauchi, K.; Tsukamoto, E.; Itoh, K.; Kanaya, M.; Mori, A.; Ota, S.; Hashimoto, D.; et al. High Metabolic Heterogeneity on Baseline 18FDG-PET/CT Scan as a Poor Prognostic Factor for Newly Diagnosed Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 2286–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Ren, Q.; Xiao, H.; Li, S.; Zheng, L.; Yang, X.; Feng, L.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, J.; et al. Whole-Tumoral Metabolic Heterogeneity in 18F-FDG PET/CT Is a Novel Prognostic Marker for Neuroblastoma. Cancer Imaging 2024, 24, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanli, Y.; Leake, J.; Odu, A.; Xi, Y.; Subramaniam, R.M. Tumor Heterogeneity on FDG PET/CT and Immunotherapy: An Imaging Biomarker for Predicting Treatment Response in Patients With Metastatic Melanoma. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 212, 1318–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostakoglu, L.; Chauvie, S. PET-Derived Quantitative Metrics for Response and Prognosis in Lymphoma. PET Clin. 2019, 14, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, J.; Frood, R.; Patel, C.; Scarsbrook, A. The Role of AI in Lymphoma: An Update. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2025, 55, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista, L.; Fiz, F.; Laudicella, R.; Bianconi, F.; Castello, A.; Guglielmo, P.; Liberini, V.; Manco, L.; Frantellizzi, V.; Giordano, A.; et al. PET Radiomics and Response to Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Cancers 2023, 15, 3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, T.; Sun, R.; Lerousseau, M.; Estienne, T.; Robert, C.; Besse, B.; Robert, C.; Paragios, N.; Deutsch, E. Investigation of Radiomics Based Intra-Patient Inter-Tumor Heterogeneity and the Impact of Tumor Subsampling Strategies. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veziroglu, E.M.; Farhadi, F.; Hasani, N.; Nikpanah, M.; Roschewski, M.; Summers, R.M.; Saboury, B. Role of Artificial Intelligence in PET/CT Imaging for Management of Lymphoma. Semin. Nucl. Med. 2023, 53, 426–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urso, L.; Manco, L.; Cittanti, C.; Adamantiadis, S.; Szilagyi, K.E.; Scribano, G.; Mindicini, N.; Carnevale, A.; Bartolomei, M.; Giganti, M. 18F-FDG PET/CT Radiomic Analysis and Artificial Intelligence to Predict Pathological Complete Response after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Breast Cancer Patients. Radiol. Med. 2025, 130, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlhac, F.; Eertink, J.J.; Cottereau, A.-S.; Zijlstra, J.M.; Thieblemont, C.; Meignan, M.; Boellaard, R.; Buvat, I. A Guide to ComBat Harmonization of Imaging Biomarkers in Multicenter Studies. J. Nucl. Med. 2022, 63, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genta, S.; Ghilardi, G.; Cascione, L.; Juskevicius, D.; Tzankov, A.; Schär, S.; Milan, L.; Pirosa, M.C.; Esposito, F.; Ruberto, T.; et al. Integration of Baseline Metabolic Parameters and Mutational Profiles Predicts Long-Term Response to First-Line Therapy in DLBCL Patients: A Post Hoc Analysis of the SAKK38/07 Study. Cancers 2022, 14, 1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceriani, L.; Milan, L.; Cascione, L.; Gritti, G.; Dalmasso, F.; Esposito, F.; Pirosa, M.C.; Schär, S.; Bruno, A.; Dirnhofer, S.; et al. Generation and Validation of a PET Radiomics Model That Predicts Survival in Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Treated with R-CHOP14: A SAKK 38/07 Trial Post-hoc Analysis. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 40, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, C.; Anconina, R.; Joshi, S.; Metser, U.; Prica, A.; Johnson, S.; Liu, Z.A.; Keshavarzi, S.; Veit-Haibach, P. Combination of FDG PET/CT Radiomics and Clinical Parameters for Outcome Prediction in Patients with Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2024, 45, 1039–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Training Cohort (Rome) N (%) | Validation Cohort (Ferrara) N (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Patients | 29 | 9 |
| Male sex | 9 (31%) | 4 (44.4%) |
| Median age years (range) | 35(18–58) | 39.5(25–58) |
| IPI score | ||
| 1 | 11 (37.9%) | 7 (77.8%) |
| 2 | 10 (34.5%) | 1 (0.1%) |
| 3 | 3 (10.3%) | 1 (0.1%) |
| 4 | 1 (3.4%) | 0 (0%) |
| >4 | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| B symptoms | 9 (31%) | 0 (0%) |
| LDH | ||
| ≤225 U/L | 19 (65.5%) | 0 (0%) |
| >225 U/L | 10 (34.5%) | 9 (100%) |
| ECOG | ||
| 0–1 | 19 (65.5%) | 9 (100%) |
| ≥2 | 10 (34.5%) | 0 (0%) |
| Bulky presentation | 25 (86.2%) | 8 (88.9%) |
| Extranodal localization | 3 (10.3%) | 0 (0%) |
| R-based regimen | ||
| R-CHOP | 4 (13.8%) | 9 (100%) |
| R-MACOP-B | 22 (75.9%) | 0 (0%) |
| R-MACOP-B + autoTMO | 2 (6.9%) | 0 (0%) |
| R-MACOP-B + surgery | 1 (3.4%) | 0 (0%) |
| EoT PET response | ||
| Responders (DS 1–3) | 23 (79.3%) | 4 (44.4%) |
| Not-responders (DS 4–5) | 6 (20.7%) | 5 (55.6%) |
| Consolidative RT | ||
| Yes | 18 (62.1%) | 8 (88.9%) |
| No | 11 (37.9%) | 1 (11.1%) |
| Relapse | ||
| Yes | 2 (6.9%) | 0 (0%) |
| Not | 27 (93.1%) | 9 (100%) |
| Patient status at last follow-up | ||
| Alive with NED | 28 (96.6%) | 9 (100%) |
| Progressive | 1 (3.4%) | 0 (0%) |
| Median follow-up (years) | 4.66 | 3.64 |
| Training 10FoldCV | AUC | CA | PRE | SEN | SPE | TP | TN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT Model | RF | 0.92 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 88.90% | 86.70% |
| SVM | 0.97 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 84.60% | 75.00% | |
| PET Model | RF | 0.83 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 77.30% | 90.90% |
| SVM | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.86 | 83.30% | 61.90% |
| Internal Validation | AUC | CA | PRE | SEN | SPE | TP | TN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CT Model | RF | 0.72 | 0.64 | 0.65 | 0.64 | 0.64 | 88.90% | 66.70% |
| SVM | 0.90 | 0.93 | 0.94 | 0.93 | 0.93 | 84.60% | 75.00% | |
| PET Model | RF | 0.83 | 0.71 | 0.73 | 0.71 | 0.71 | 77.30% | 80.00% |
| SVM | 0.86 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.84 | 0.85 | 83.30% | 85.70% | |
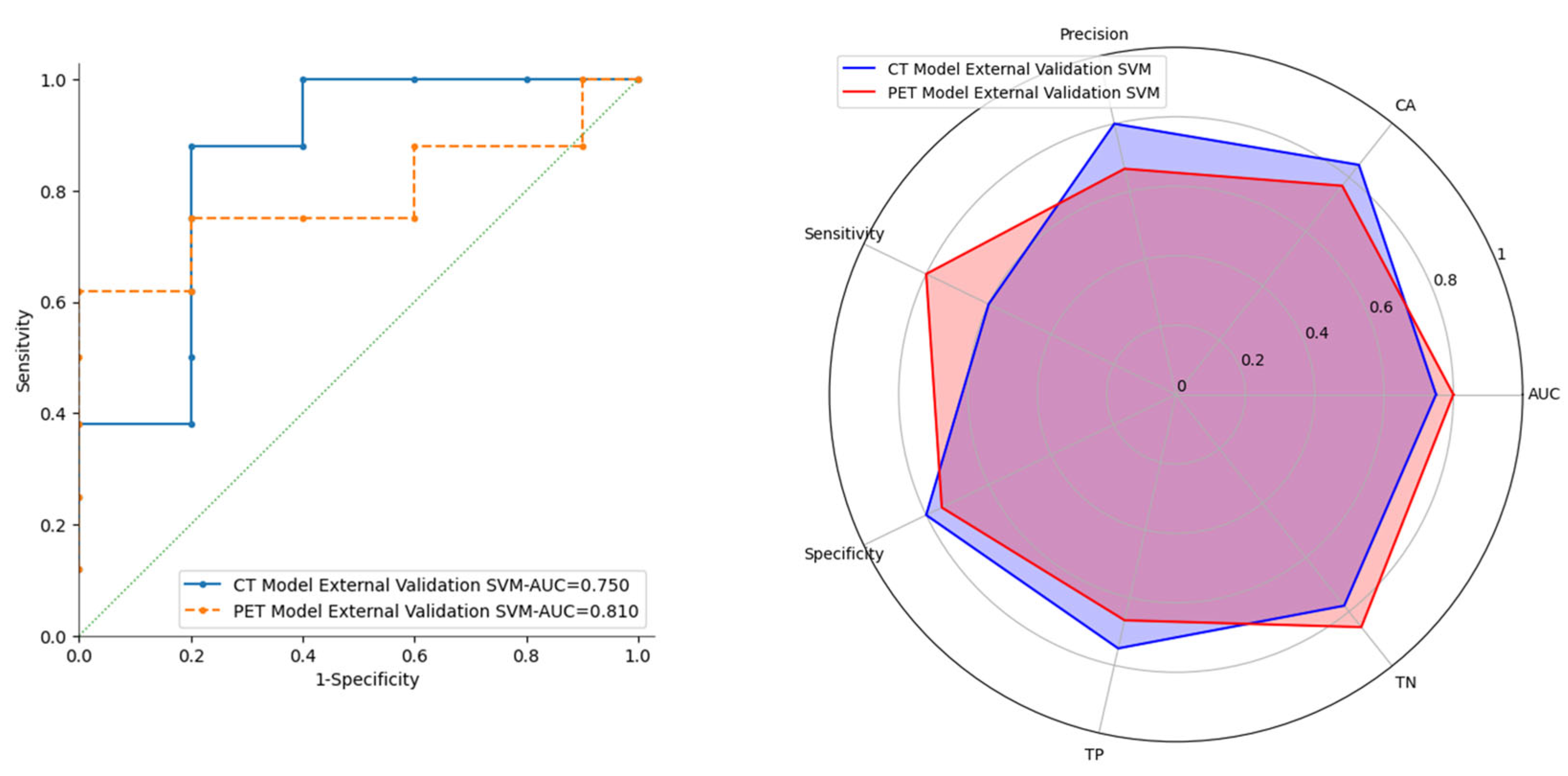
| External Validation | AUC | CA | PRE | SEN | SPE | TP | TN | |
| CT Model | RF | 0.85 | 0.69 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.75 | 60.00% | 75.00% |
| SVM | 0.75 | 0.85 | 0.97 | 0.60 | 0.98 | 75.00% | 77.80% | |
| PET Model | RF | 0.74 | 0.69 | 0.57 | 0.80 | 0.63 | 57.10% | 83.30% |
| SVM | 0.81 | 0.77 | 0.67 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 66.70% | 85.70% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Esposito, F.; Manco, L.; Urso, L.; Adamantiadis, S.; Scribano, G.; De Marchi, L.; Venditti, A.; Postorino, M.; Urbano, N.; Gafà, R.; et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT Radiomics for Predicting Therapy Response in Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma: A Bi-Centric Pilot Study. Cancers 2025, 17, 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111827
Esposito F, Manco L, Urso L, Adamantiadis S, Scribano G, De Marchi L, Venditti A, Postorino M, Urbano N, Gafà R, et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT Radiomics for Predicting Therapy Response in Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma: A Bi-Centric Pilot Study. Cancers. 2025; 17(11):1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111827
Chicago/Turabian StyleEsposito, Fabiana, Luigi Manco, Luca Urso, Sara Adamantiadis, Giovanni Scribano, Lucrezia De Marchi, Adriano Venditti, Massimiliano Postorino, Nicoletta Urbano, Roberta Gafà, and et al. 2025. "18F-FDG PET/CT Radiomics for Predicting Therapy Response in Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma: A Bi-Centric Pilot Study" Cancers 17, no. 11: 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111827
APA StyleEsposito, F., Manco, L., Urso, L., Adamantiadis, S., Scribano, G., De Marchi, L., Venditti, A., Postorino, M., Urbano, N., Gafà, R., Cuneo, A., Chiaravalloti, A., Bartolomei, M., & Filippi, L. (2025). 18F-FDG PET/CT Radiomics for Predicting Therapy Response in Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma: A Bi-Centric Pilot Study. Cancers, 17(11), 1827. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17111827









