Mesothelin as a Signal Pathways and Epigenetic Target in Cancer Therapy
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction to Mesothelin
2. Mesothelin in Normal and Cancer Cells
3. MSLN in Epigenetics and Signal Pathways
4. MSLN-Targeted Therapies
5. Clinical Trials Involving MSLN-Targeted Treatments
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATM | Ataxia telangiectasia mutated |
| ATR | Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad-3-related protein |
| DNA-PK | DNA-dependent protein kinase |
| ADC | Antibody-drug conjugate |
| MDSCs | Myeloid-derived suppressor cells |
| MCAT | Muscle-CAT binding site |
| MMP-7 | Matrix metalloproteinase-7 |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| NSCLC | Non-small-cell lung cancer |
| PE | Pseudomonas exotoxin A |
| RARG | Retinoic acid receptor gamma |
| RT | Proton radiation therapy |
| SP1 | Specificity Protein 1 |
| STAT 3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| TNBC | Triple-negative breast cancer |
| TNK2 | Kinase non-receptor 2 |
References
- Shen, J.; Sun, X.; Zhou, J. Insights into the Role of Mesothelin as a Diagnostic and Therapeutic Target in Ovarian Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, J.; Lin, D.; Watson, N.; Esser, L.; Tang, W.K.; Zhang, A.; Liu, X.; Hassan, R.; Gleinich, A.; Shajahan, A.; et al. Structures of Cancer Antigen Mesothelin and Its Complexes with Therapeutic Antibodies. Cancer Res. Commun. 2023, 3, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joseph, S.; Zhang, X.; Smith, L.K.; Alewine, C. Furin is not required for processing of mesothelin precursor protein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2021, 1868, 118967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Tang, Z.; Jiang, B.; Chen, J.; Fu, Z. miR-198 functions as a tumor suppressor in breast cancer by targeting CUB domain-containing protein 1. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 1753–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagerty, B.L.; Takabe, K. Biology of Mesothelin and Clinical Implications: A Review of Existing Literature. World J. Oncol. 2023, 14, 340–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrick, S.E.; Mutsaers, S.E. Mesothelial progenitor cells and their potential in tissue engineering. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2004, 36, 621–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledda, C.; Loreto, C.; Lombardo, C.; Cardile, V.; Rapisarda, V. Mesothelin methylation, soluble mesothelin related protein levels and inflammation profiling in workers chronically exposed to naturally occurring asbestos fibers. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 40, 101872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Fan, Q.; Li, X.; Li, K.; Wang, Z.; Liang, S.; Amin, B.; Zhang, N.; et al. MSLN induced EMT, cancer stem cell traits and chemotherapy resistance of pancreatic cancer cells. Heliyon 2024, 10, e29210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, L.; Riedel, H.; Wang, K.; Yang, Y.; Dinu, C.Z.; Rojanasakul, Y. Mesothelin promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and tumorigenicity of human lung cancer and mesothelioma cells. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Q.; Xu, C.; Shao, Y.; Yu, Q.; Huang, L.; Liu, Y.; Bao, H. Free CA125 promotes ovarian cancer cell migration and tumor metastasis by binding Mesothelin to reduce DKK1 expression and activate the SGK3/FOXO3 pathway. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 574–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.F.; Onda, M.; Schlomer, J.; Bassel, L.; Kozlov, S.; Tai, C.H.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, W.; Tsao, H.E.; Hassan, R.; et al. Tumor resistance to anti-mesothelin CAR-T cells caused by binding to shed mesothelin is overcome by targeting a juxtamembrane epitope. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2317283121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Despeaux, E.; Stueckle, T.A.; Chi, A.; Castranova, V.; Dinu, C.Z.; Wang, L.; Rojanasakul, Y. Role of mesothelin in carbon nanotube-induced carcinogenic transformation of human bronchial epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2016, 311, L538–L549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadzada, T.; Reid, G.; Kao, S. Biomarkers in malignant pleural mesothelioma: Current status and future directions. J. Thorac. Dis. 2018, 10 (Suppl. S9), S1003–S1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandenhoeck, J.; Ibrahim, J.; De Meulenaere, N.; Peeters, D.; Raskin, J.; Hendriks, J.M.H.; Van Schil, P.; van Meerbeeck, J.; Van Camp, G.; Op de Beeck, K. Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis reveals a unique methylation pattern for pleural mesothelioma compared to healthy pleura and other lung diseases. Clin. Epigenet. 2024, 16, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Muller, C.; Li, D.; Bharadwaj, U.; Li, M.; Chen, C.; Hodges, S.E.; Fisher, W.E.; Mo, Q.; Hung, M.C.; Yao, Q. A tumorigenic factor interactome connected through tumor suppressor microRNA-198 in human pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 5901–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, G.J.; Linton, A.; Kao, S.; Klebe, S.; Adelstein, S.; Yeo, D.; Rasko, J.E.J.; Cooper, W.A. High mesothelin expression by immunohistochemistry predicts improved survival in pleural mesothelioma. Histopathology 2023, 83, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieve, M.G.; Moon, R.T. Stromelysin-1 and mesothelin are differentially regulated by Wnt-5a and Wnt-1 in C57mg mouse mammary epithelial cells. BMC Dev. Biol. 2003, 3, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, J.R.; Hamill, D.; Kolb, E.A.; Gopalakrishnapillai, A.; Barwe, S.P. Mesothelin: An Immunotherapeutic Target beyond Solid Tumors. Cancers 2022, 14, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Liu, M.; Wang, L.; Liang, B.; Feng, Y.; Chen, X.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ye, X.; Tian, Y.; et al. Use of chimeric antigen receptor NK-92 cells to target mesothelin in ovarian cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 524, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickstroem, K.; Hagemann, U.B.; Cruciani, V.; Wengner, A.M.; Kristian, A.; Ellingsen, C.; Siemeister, G.; Bjerke, R.M.; Karlsson, J.; Ryan, O.B.; et al. Synergistic Effect of a Mesothelin-Targeted (227)Th Conjugate in Combination with DNA Damage Response Inhibitors in Ovarian Cancer Xenograft Models. J. Nucl. Med. 2019, 60, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Einama, T.; Kawamata, F.; Kamachi, H.; Nishihara, H.; Homma, S.; Matsuzawa, F.; Mizukami, T.; Konishi, Y.; Tahara, M.; Kamiyama, T.; et al. Clinical impacts of mesothelin expression in gastrointestinal carcinomas. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2016, 7, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amit, U.; Uslu, U.; Verginadis, I.I.; Kim, M.M.; Motlagh, S.A.O.; Diffenderfer, E.S.; Assenmacher, C.A.; Bicher, S.; Atoche, S.J.; Ben-Josef, E.; et al. Proton radiation boosts the efficacy of mesothelin-targeting chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy in pancreatic cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2403002121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Wang, F.; Meng, X.; Li, D.; Ding, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, H.; Yang, Z. Construction of a (124)I-Labeled Specific Antibody for the Noninvasive Detection of Mesothelin-Overexpressing Tumors. Mol. Pharm. 2022, 19, 3623–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, G.; Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Gu, Z.; Tian, H.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, X. Disruption of adenosine 2A receptor improves the anti-tumor function of anti-mesothelin CAR T cells both in vitro and in vivo. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 409, 112886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Li, D.; Zhang, L.; Gu, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, G.; Yang, M.; Gu, J.; Cui, X.; et al. PD-1 silencing improves anti-tumor activities of human mesothelin-targeted CAR T cells. Hum. Immunol. 2021, 82, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, S.; Tsunoda, T.; Riku, M.; Ito, H.; Inoko, A.; Murakami, H.; Ebi, M.; Ogasawara, N.; Pastan, I.; Kasugai, K.; et al. Diffuse mesothelin expression leads to worse prognosis through enhanced cellular proliferation in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, T.; Shinto, E.; Nearchou, I.P.; Tsuda, H.; Kajiwara, Y.; Einama, T.; Caie, P.D.; Kishi, Y.; Ueno, H. Prognostic significance of mesothelin expression in colorectal cancer disclosed by area-specific four-point tissue microarrays. Virchows Arch. 2020, 477, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.J.; Sharon, E.; Pastan, I.; Hassan, R. Mesothelin-targeted agents in clinical trials and in preclinical development. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weldon, J.E.; Pastan, I. A guide to taming a toxin--recombinant immunotoxins constructed from Pseudomonas exotoxin A for the treatment of cancer. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 4683–4700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Ebel, W.; Routhier, E.L.; Patel, R.; Kline, J.B.; Zhang, J.; Chao, Q.; Jacob, S.; Turchin, H.; Gibbs, L.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of MORAb-009, a chimeric antibody targeting tumor-associated mesothelin. Cancer Immun. 2007, 7, 20. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Xiao, X.; Zhu, Z.; Streaker, E.; Ho, M.; Pastan, I.; Dimitrov, D.S. A novel human monoclonal antibody that binds with high affinity to mesothelin-expressing cells and kills them by antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 1113–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rottey, S.; Clarke, J.; Aung, K.; Machiels, J.P.; Markman, B.; Heinhuis, K.M.; Millward, M.; Lolkema, M.; Patel, S.P.; de Souza, P.; et al. Phase I/IIa Trial of BMS-986148, an Anti-mesothelin Antibody-drug Conjugate, Alone or in Combination with Nivolumab in Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klampatsa, A.; Dimou, V.; Albelda, S.M. Mesothelin-targeted CAR-T cell therapy for solid tumors. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2021, 21, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Dong, J.; Yang, N.; Li, S.D.; Yang, Z.Y.; Huang, R.; Li, F.J.; Wang, W.T.; Ren, J.K.; Lei, J.; et al. Tandem CAR-T cells targeting FOLR1 and MSLN enhance the antitumor effects in ovarian cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 4365–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Melero, S.; Hassouneh, F.; Vallejo-Bermúdez, I.M.; Agüera-Morales, E.; Solana, R.; Caballero-Villarraso, J. Tandem CAR-T cell therapy: Recent advances and current challenges. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1546172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Yang, J.; Lu, P.; Zhao, L.; Li, B.; Pan, H.; Jiang, Z.; Shen, X.; et al. Chemokine Receptor CCR2b Enhanced Anti-tumor Function of Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells Targeting Mesothelin in a Non-small-cell Lung Carcinoma Model. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 628906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molloy, M.E.; Austin, R.J.; Lemon, B.D.; Aaron, W.H.; Ganti, V.; Jones, A.; Jones, S.D.; Strobel, K.L.; Patnaik, P.; Sexton, K.; et al. Preclinical Characterization of HPN536, a Trispecific, T-Cell-Activating Protein Construct for the Treatment of Mesothelin-Expressing Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 1452–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Batra, S.K. Understanding the Unique Attributes of MUC16 (CA125): Potential Implications in Targeted Therapy. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4669–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aithal, A.; Rauth, S.; Kshirsagar, P.; Shah, A.; Lakshmanan, I.; Junker, W.M.; Jain, M.; Ponnusamy, M.P.; Batra, S.K. MUC16 as a novel target for cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2018, 22, 675–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Alley, E.; Kindler, H.; Antonia, S.; Jahan, T.; Honarmand, S.; Nair, N.; Whiting, C.C.; Enstrom, A.; Lemmens, E.; et al. Clinical Response of Live-Attenuated, Listeria monocytogenes Expressing Mesothelin (CRS-207) with Chemotherapy in Patients with Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5787–5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cutri-French, C.; Nasioudis, D.; George, E.; Tanyi, J.L. CAR-T Cell Therapy in Ovarian Cancer: Where Are We Now? Diagnostics 2024, 14, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, H. Advances in Targeted Therapy for Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi 2024, 27, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, K.; Yue, L.; Zuo, D.; Sheng, J.; Lan, S.; Zhao, Z.; Dong, S.; Hu, S.; Chen, X.; et al. Mesothelin CAR-T cells expressing tumor-targeted immunocytokine IL-12 yield durable efficacy and fewer side effects. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 203, 107186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kronig, M.N.; Wehrli, M.; Salas-Benito, D.; Maus, M.V. Hurdles race for CAR T-cell therapy in digestive tract cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2023, 320, 100–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Sharon, E.; Thomas, A.; Zhang, J.; Ling, A.; Miettinen, M.; Kreitman, R.J.; Steinberg, S.M.; Hollevoet, K.; Pastan, I. Phase 1 study of the antimesothelin immunotoxin SS1P in combination with pemetrexed and cisplatin for front-line therapy of pleural mesothelioma and correlation of tumor response with serum mesothelin, megakaryocyte potentiating factor and cancer antigen 125. Cancer 2014, 120, 3311–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldo, P.; Cecco, S. Amatuximab and novel agents targeting mesothelin for solid tumors. OncoTargets Ther. 2017, 10, 5337–5353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, C.; Lutz, E.; Nair, N.; Chang, S.; Lemmens, E.; Chen, S.-Y.; Solt, S.; Ferber, S.; Maecker, H.; Murphy, A.; et al. Phase II, randomized study of GVAX pancreas and CRS-207 immunotherapy in patients with metastatic pancreatic cancer: Clinical update on long term survival and biomarker correlates to overall survival. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33 (Suppl. S3), 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Blumenschein, G.R., Jr.; Moore, K.N.; Santin, A.D.; Kindler, H.L.; Nemunaitis, J.J.; Seward, S.M.; Thomas, A.; Kim, S.K.; Rajagopalan, P.; et al. First-in-Human, Multicenter, Phase I Dose-Escalation and Expansion Study of Anti-Mesothelin Antibody-Drug Conjugate Anetumab Ravtansine in Advanced or Metastatic Solid Tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1824–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betof Warner, A.; Corrie, P.G.; Hamid, O. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocyte Therapy in Melanoma: Facts to the Future. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 29, 1835–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, R.; Alewine, C.; Mian, I.; Spreafico, A.; Siu, L.L.; Gomez-Roca, C.; Delord, J.P.; Italiano, A.; Lassen, U.; Soria, J.C.; et al. Phase 1 study of the immunotoxin LMB-100 in patients with mesothelioma and other solid tumors expressing mesothelin. Cancer 2020, 126, 4936–4947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, A.R.; Tanyi, J.L.; O’Hara, M.H.; Gladney, W.L.; Lacey, S.F.; Torigian, D.A.; Soulen, M.C.; Tian, L.; McGarvey, M.; Nelson, A.M.; et al. Phase I Study of Lentiviral-Transduced Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified T Cells Recognizing Mesothelin in Advanced Solid Cancers. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terenziani, R.; Zoppi, S.; Fumarola, C.; Alfieri, R.; Bonelli, M. Immunotherapeutic Approaches in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. Cancers 2021, 13, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
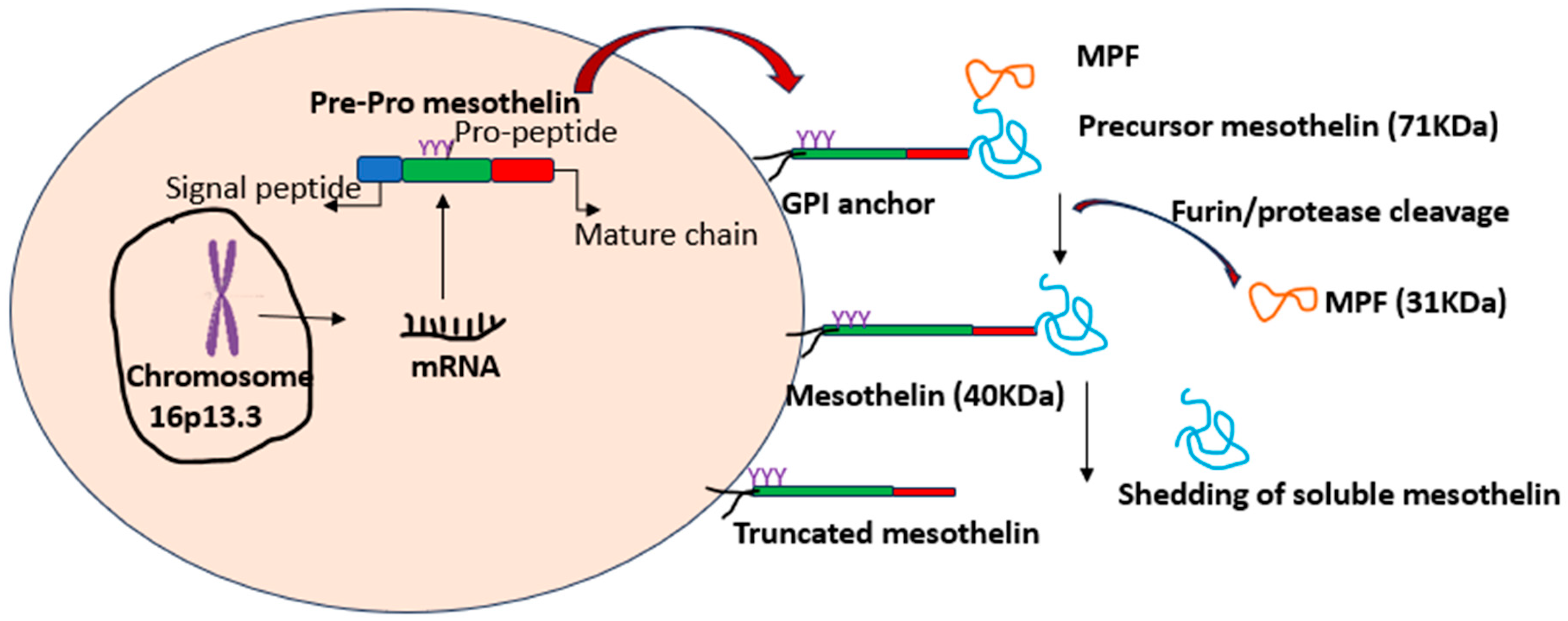
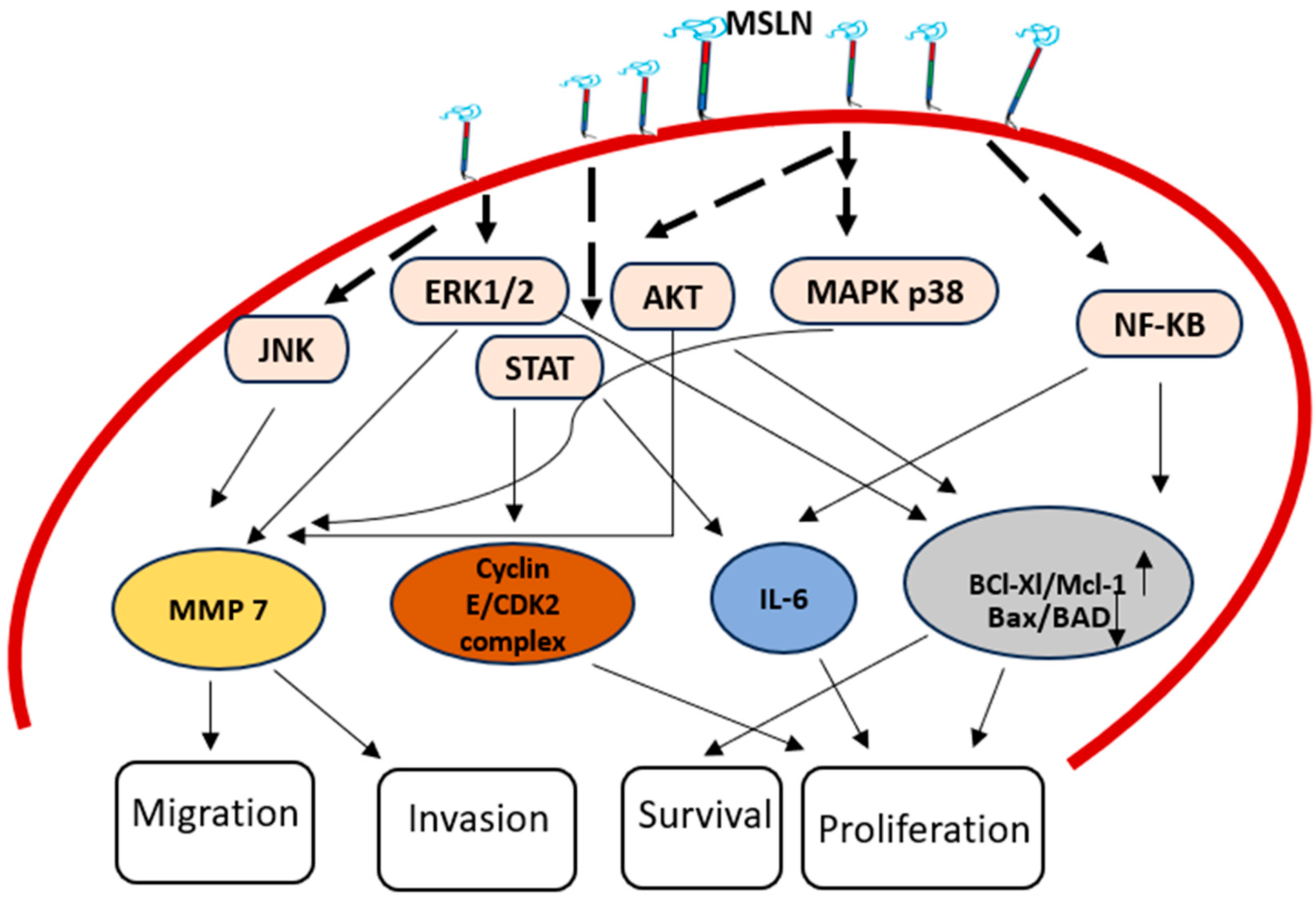
| Signal Pathways | Mechanism |
|---|---|
| NF-κB Pathway | Augmented expression of MSLN triggers NF-κB, causing augmented expression of IL-6, which in turn promotes cancer survival and proliferation |
| IL-6/sIL-6R Trans-Signaling Pathway | MSLN helps formation of an extracellular complex between IL-6 and sIL-6R, which triggers trans-signal pathway called the IL-6/sIL-6R pathway which in turn increases the survival and growth of cancer. |
| Stat3 Pathway | MSLN activates Stat3, increasing cyclin E expression and accelerating cell cycle advancement from G1 to S phase |
| ERK1/2 Pathway | Pro-apoptotic factor Bim is repressed by MSLN’s persistent ERK1/2 activation, which cause anoikis insensitivity. |
| MAPK Pathways (p38 MAPK, ERK and JNK) | MMP-7 and MMP-9 expression are triggered by MSLN, causing increased cancer invasion and migration. |
| p53 Pathway | Inhibiting apoptosis and promoting cell proliferation, MSLN modifies the p53-dependent regulation of apoptosis-related proteins. |
| β-Catenin Pathway | Reducing MSLN expression has an impact on invasion and EMT by lowering β-catenin expression. |
| Trial Number | Status/Year | MSLN-Based Therapy | Clinical Trials | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05779917 | Active/2024 | mesothelin-targeted chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells. Engineered to express a fusion protein of IL21 and scFv against PD1. | A Phase I study to evaluate the safety, tolerance and preliminary efficacy of second-generation mesothelin-targeted CAR-T cells, engineered to secrete a fusion protein of IL21 and scFv against PD1, for the immunotherapy of mesothelin-expressing cancers. | [44] |
| NCT01445392 | Terminated/2011 | SS1P (recombinant immunotoxin) | Phase I trials showed safety and anti-tumor efficacy, leading to a new trial combining SS1P with chemotherapy. | [45] |
| NCT00325494 | Completed/2009 | MORAb-009 (amatuximab, chimeric antibody) | Phase I trial demonstrated stable disease in 11 patients, with ongoing Phase II trials | [46] |
| NCT01417000 | Completed/2014 | GVAX | Presents MSLN to immune cells via MHC elicits an immune response | [47] |
| NCT01439152 | Completed/2019 | BMS-986148 | Phase 1 clinical trials. MSLN-directed antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), alone or with nivolumab, in 126 patients with selected tumors | [48] |
| NCT05397093 | Active/2022 | FOLR1 | Targeting multiple antigens and modulating gene expression | [49] |
| NCT02810418 | Completed/2016 | LMB-100 | LMB-100 is given in combination with tofacitinib to patients with pancreatic adenocarcinoma, extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and other MSLN-positive solid tumors | [50] |
| NCT02639091 | Completed/2020 | Anetumab Ravtansine in Combination With Pemetrexed and Cisplatin | In Phase 1b, BAY 94-9343 in combination with pemetrexed and cisplatin was administered to the patient with metastatic epithelial mesothelioma or nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC). To study was to assess the assessing the safety, tolerability and efficacy of the drug regimen. Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) is directed against the cancer antigen MSLN on tumor cells. | [48] |
| NCT02159716 | Completed/2014 | CART-meso in Mesothelin Expressing Cancers | Phase I Study of Chimeric Antigen Receptor Modified T Cells in Patients With Mesothelin Expressing Cancers | [51] |
| NCT03872206 | Completed/2023 | HPN536 | Phase 1/2a study of HPN536 as monotherapy to assess the safety, tolerability and PK in patients with advanced cancers associated with mesothelin expression | [37] |
| NCT05372692 | Completed/2023 | Mesothelin-specific Chimeric antigen Receptor T Cells (LD013) | Chimeric antigen receptor T cells (LD013) in patients with refractory or relapsed mesothelin-positive ovarian cancer | [41] |
| NCT02884726 | Completed/2020 | BMS 986148 | Phase 1 Study of Mesothelin-ADC Study is to assess the safety and tolerability of Mesothelin-ADC in subjects with advanced and/or metastatic solid tumors | [32] |
| NCT01675765 | Completed/2018 | CRS-207 attenuated form of Listeria monocytogenes | Clinical trial assesses the safety and immune response of CRS-207, a modified Listeria monocytogenes cancer vaccine targeting mesothelin, given with or without cyclophosphamide, followed by pemetrexed and cisplatin. | [52] |
| NCT02341625 | Terminated/2020 | BMS-986148 a drug | Combination treatment of BMS-986148 (a drug) with or without nivolumab an immune checkpoint inhibitor a safe and tolerable. Some patients experienced long-lasting positive responses to the treatment. | [32] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumari, S. Mesothelin as a Signal Pathways and Epigenetic Target in Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2025, 17, 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071118
Kumari S. Mesothelin as a Signal Pathways and Epigenetic Target in Cancer Therapy. Cancers. 2025; 17(7):1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071118
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumari, Seema. 2025. "Mesothelin as a Signal Pathways and Epigenetic Target in Cancer Therapy" Cancers 17, no. 7: 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071118
APA StyleKumari, S. (2025). Mesothelin as a Signal Pathways and Epigenetic Target in Cancer Therapy. Cancers, 17(7), 1118. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071118






