Recent Research on Role of p53 Family in Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structural and Functional Insights into the p53 Family Proteins
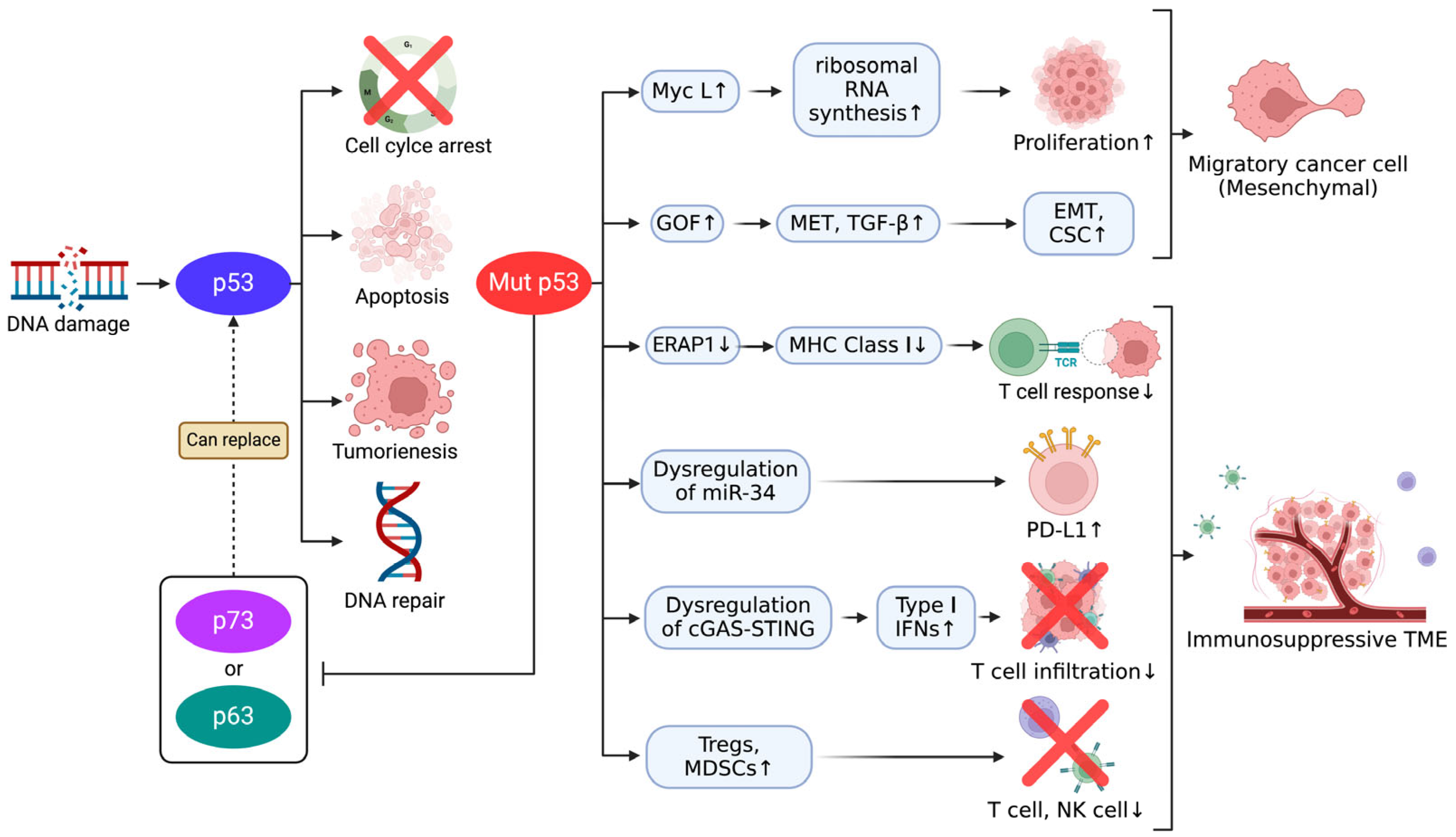
3. Mechanism of Tumor Suppression and Immune Modulation by p53 Family
3.1. p53-Mediated Apoptosis and Cell Cycle Regulation
3.2. The General Roles of p73 and p63 in Tumor Suppression
3.3. Functional Synergy Within the p53 Family
4. The Specific Roles of p53, p73, and p63 in SCLC Tumor Suppression
4.1. Inactivation of p53 and Its Consequences in SCLC
4.2. p73 as a Compensatory Mechanism for p53 Loss in SCLC
4.3. The Minimal Role of p63 in SCLC
5. The Role of the p53 Family in Immune Evasion and EMT in Cancer
5.1. Immune Evasion Mediated by p53 Family
5.2. Mutant p53-Induced EMT and Its Implications for Therapeutic Resistance
6. Therapeutic Strategies Targeting the p53 Family in SCLC
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, H.; Shan, J.; Zhang, H.; Song, G.; Li, Q.; Xu, C.-X. Targeting the epigenetic processes to enhance antitumor immunity in small cell lung cancer. In Seminars in Cancer Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2022; pp. 960–970. [Google Scholar]
- Raso, M.G.; Bota-Rabassedas, N.; Wistuba, I.I. Pathology and classification of SCLC. Cancers 2021, 13, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Zou, J.; Xu, F. The molecular subtypes of small cell lung cancer defined by key transcription factors and their clinical significance. Lung Cancer 2024, 198, 108033. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rudin, C.M.; Brambilla, E.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Sage, J. Small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gazdar, A.F.; Bunn, P.A.; Minna, J.D. Small-cell lung cancer: What we know, what we need to know and the path forward. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 725–737. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-W.; Kim, K.-C.; Kim, K.-B.; Dunn, C.T.; Park, K.-S. Transcriptional deregulation underlying the pathogenesis of small cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2018, 7, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Denninghoff, V.; Russo, A.; de Miguel-Pérez, D.; Malapelle, U.; Benyounes, A.; Gittens, A.; Cardona, A.F.; Rolfo, C. Small cell lung cancer: State of the art of the molecular and genetic landscape and novel perspective. Cancers 2021, 13, 1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattuca-Truc, M.; Timsit, J.-F.; Levra, M.G.; Ruckly, S.; Villa, J.; Dumas, I.; Pinsolle, J.; Ferrer, L.; Guillem, P.; Moro-Sibilot, D. Trends in response rate and survival in small-cell lung cancer patients between 1997 and 2017. Lung Cancer 2019, 131, 122–127. [Google Scholar]
- Doshita, K.; Kenmotsu, H.; Omori, S.; Tabuchi, Y.; Kawabata, T.; Kodama, H.; Nishioka, N.; Miyawaki, E.; Iida, Y.; Miyawaki, T.; et al. Long-Term Survival Data of Patients with Limited Disease Small Cell Lung Cancer: A retrospective analysis. Investig. New Drugs 2022, 40, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, A.J. p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 1997, 88, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastenhuber, E.R.; Lowe, S.W. Putting p53 in context. Cell 2017, 170, 1062–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Strubel, A.; Münick, P.; Hartmann, O.; Chaikuad, A.; Dreier, B.; Schaefer, J.V.; Gebel, J.; Osterburg, C.; Tuppi, M.; Schäfer, B. DARPins detect the formation of hetero-tetramers of p63 and p73 in epithelial tissues and in squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 674. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hassin, O.; Oren, M. Drugging p53 in cancer: One protein, many targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2023, 22, 127–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Papavassiliou, K.A.; Sofianidi, A.A.; Gogou, V.A.; Anagnostopoulos, N.; Papavassiliou, A.G. P53 and Rb Aberrations in Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC): From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Modulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, J.; Lim, J.S.; Jang, S.J.; Cun, Y.; Ozretić, L.; Kong, G.; Leenders, F.; Lu, X.; Fernández-Cuesta, L.; Bosco, G. Comprehensive genomic profiles of small cell lung cancer. Nature 2015, 524, 47–53. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.; McKeon, F. p63 and p73: p53 mimics, menaces and more. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2000, 1, 199–207. [Google Scholar]
- King, N.; Westbrook, M.J.; Young, S.L.; Kuo, A.; Abedin, M.; Chapman, J.; Fairclough, S.; Hellsten, U.; Isogai, Y.; Letunic, I. The genome of the choanoflagellate Monosiga brevicollis and the origin of metazoans. Nature 2008, 451, 783–788. [Google Scholar]
- Åberg, E.; Saccoccia, F.; Grabherr, M.; Ore, W.Y.J.; Jemth, P.; Hultqvist, G. Evolution of the p53-MDM2 pathway. BMC Evol. Biol. 2017, 17, 177. [Google Scholar]
- Dos Santos, H.G.; Nunez-Castilla, J.; Siltberg-Liberles, J. Functional diversification after gene duplication: Paralog specific regions of structural disorder and phosphorylation in p53, p63, and p73. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vousden, K.H.; Lane, D.P. p53 in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 275–283. [Google Scholar]
- Deyoung, M.; Ellisen, L. p63 and p73 in human cancer: Defining the network. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5169–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenberg, J.M.; Rogovaya, O.S.; Melino, G.; Barlev, N.A.; Kagansky, A. Distinct p63 and p73 protein interactions predict specific functions in mRNA splicing and polyploidy control in Epithelia. Cells 2020, 10, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belyi, V.A.; Levine, A.J. One billion years of p53/p63/p73 evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 17609–17610. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Levine, A.J. p53: 800 million years of evolution and 40 years of discovery. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Wu, H.; Wiesmüller, L.; Chen, M. Canonical and non-canonical functions of p53 isoforms: Potentiating the complexity of tumor development and therapy resistance. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 412. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, J.; Qi, R.; Tang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wei, G.; Nussinov, R.; Ma, B. Conformational stability and dynamics of the cancer-associated isoform Δ133p53β are modulated by p53 peptides and p53-specific DNA. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 4225. [Google Scholar]
- Neely, V.; Manchikalapudi, A.; Nguyen, K.; Dalton, K.; Hu, B.; Koblinski, J.E.; Faber, A.C.; Deb, S.; Harada, H. Targeting Oncogenic Mutant p53 and BCL-2 for Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logotheti, S.; Pavlopoulou, A.; Marquardt, S.; Takan, I.; Georgakilas, A.G.; Stiewe, T. p73 isoforms meet evolution of metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2022, 41, 853–869. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos, H.; Raimundo, L.; Saraiva, L. p73: From the p53 shadow to a major pharmacological target in anticancer therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 162, 105245. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, X.; Yan, W.; Sun, W.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, H.J.; Chen, M.; Chen, H.; de Vere White, R.W.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. Isoform-specific disruption of the TP73 gene reveals a critical role for TAp73γ in tumorigenesis via leptin. elife 2023, 12, e82115. [Google Scholar]
- Cicero, D.O.; Falconi, M.; Candi, E.; Mele, S.; Cadot, B.; Di Venere, A.; Rufini, S.; Melino, G.; Desideri, A. NMR structure of the p63 SAM domain and dynamical properties of G534V and T537P pathological mutants, identified in the AEC syndrome. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2006, 44, 475–489. [Google Scholar]
- Chi, S.W.; Ayed, A.; Arrowsmith, C.H. Solution structure of a conserved C-terminal domain of p73 with structural homology to the SAM domain. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 4438–4445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.K.; Bycroft, M.; Foster, N.W.; Buckle, A.M.; Fersht, A.R.; Chen, Y.W. Structure of the C-terminal sterile α-motif (SAM) domain of human p73α. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2001, 57, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marshall, C.B.; Beeler, J.S.; Lehmann, B.D.; Gonzalez-Ericsson, P.; Sanchez, V.; Sanders, M.E.; Boyd, K.L.; Pietenpol, J.A. Tissue-specific expression of p73 and p63 isoforms in human tissues. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neira, J.L.; Díaz-García, C.; Prieto, M.; Coutinho, A. The C-terminal SAM domain of p73 binds to the N terminus of MDM2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, A.M.; Biderman, L.; Tong, D.; Alaghebandan, B.; Plumber, S.A.; Mueller, H.S.; van Vlimmeren, A.; Katz, C.; Prives, C. MDM2, MDMX, and p73 regulate cell-cycle progression in the absence of wild-type p53. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2102420118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabow, Z.; Laubach, K.; Kong, X.; Shen, T.; Mohibi, S.; Zhang, J.; Fiehn, O.; Chen, X. P73α1, an isoform of the p73 tumor suppressor, modulates lipid metabolism and cancer cell growth via stearoyl-coa desaturase-1. Cells 2022, 11, 2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laubach, K.N.; Yan, W.; Kong, X.; Sun, W.; Chen, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. p73α1, a p73 C-terminal isoform, regulates tumor suppression and the inflammatory response via Notch1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2123202119. [Google Scholar]
- Prives, C.; Hall, P.A. The p53 pathway. J. Pathol. 1999, 187, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Pei, F.; Yang, F.; Li, L.; Amin, A.D.; Liu, S.; Buchan, J.R.; Cho, W.C. Role of autophagy and apoptosis in non-small-cell lung cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vousden, K.H.; Prives, C. Blinded by the light: The growing complexity of p53. Cell 2009, 137, 413–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hensel, C.H.; Hsieh, C.-L.; Gazdar, A.F.; Johnson, B.E.; Sakaguchi, A.Y.; Naylor, S.L.; Lee, W.-H.; Lee, E.Y.P. Altered structure and expression of the human retinoblastoma susceptibility gene in small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 1990, 50, 3067–3072. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, T.; Nau, M.M.; Chiba, I.; Birrer, M.J.; Rosenberg, R.K.; Vinocour, M.; Levitt, M.; Pass, H.; Gazdar, A.F.; Minna, J.D. p53: A frequent target for genetic abnormalities in lung cancer. Science 1989, 246, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moll, U.M.; Slade, N. p63 and p73: Roles in development and tumor formation. Mol. Cancer Res. 2004, 2, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dabiri, Y.; Kalman, S.; Gürth, C.-M.; Kim, J.Y.; Mayer, V.; Cheng, X. The essential role of TAp73 in bortezomib-induced apoptosis in p53-deficient colorectal cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5423. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, A.; Kaghad, M.; Caput, D.; McKeon, F. On the shoulders of giants: p63, p73 and the rise of p53. Trends Genet. 2002, 18, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, M.; Schleithoff, E.S.; Stremmel, W.; Melino, G.; Krammer, P.H.; Schilling, T. One, two, three—p53, p63, p73 and chemosensitivity. Drug Resist. Updates 2006, 9, 288–306. [Google Scholar]
- Zangen, R.; Ratovitski, E.A.; Sidransky, D. ΔNp63α levels correlate with clinical tumor response to cisplatin. Cell Cycle 2005, 4, 1313–1315. [Google Scholar]
- Petronilho, E.C.; de Andrade, G.C.; dos Santos de Sousa, G.; Almeida, F.P.; Mota, M.F.; dos Santos Gomes, A.V.; Pinheiro, C.H.S.; da Silva, M.C.; Arruda, H.R.; Marques, M.A. Oncogenic p53 triggers amyloid aggregation of p63 and p73 liquid droplets. Commun. Chem. 2024, 7, 207. [Google Scholar]
- Petronilho, E.C.; Pedrote, M.M.; Marques, M.A.; Passos, Y.M.; Mota, M.F.; Jakobus, B.; dos Santos de Sousa, G.; da Costa, F.P.; Felix, A.L.; Ferretti, G.D. Phase separation of p53 precedes aggregation and is affected by oncogenic mutations and ligands. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 7334–7349. [Google Scholar]
- Benitez, D.A.; Cumplido-Laso, G.; Olivera-Gómez, M.; Del Valle-Del Pino, N.; Díaz-Pizarro, A.; Mulero-Navarro, S.; Román-García, A.; Carvajal-Gonzalez, J.M. p53 genetics and biology in lung carcinomas: Insights, implications and clinical applications. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudin, C.M.; Durinck, S.; Stawiski, E.W.; Poirier, J.T.; Modrusan, Z.; Shames, D.S.; Bergbower, E.A.; Guan, Y.; Shin, J.; Guillory, J. Comprehensive genomic analysis identifies SOX2 as a frequently amplified gene in small-cell lung cancer. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1111–1116. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Melino, G.; Bernassola, F.; Ranalli, M.; Yee, K.; Zong, W.X.; Corazzari, M.; Knight, R.A.; Green, D.R.; Thompson, C.; Vousden, K.H. p73 Induces apoptosis via PUMA transactivation and Bax mitochondrial translocation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 8076–8083. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vikhreva, P.; Petrova, V.; Gokbulut, T.; Pestlikis, I.; Mancini, M.; Di Daniele, N.; Knight, R.A.; Melino, G.; Amelio, I. TAp73 upregulates IL-1β in cancer cells: Potential biomarker in lung and breast cancer? Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Amelio, I.; Inoue, S.; Markert, E.K.; Levine, A.J.; Knight, R.A.; Mak, T.W.; Melino, G. TAp73 opposes tumor angiogenesis by promoting hypoxia-inducible factor 1α degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 226–231. [Google Scholar]
- Nyman, U.; Sobczak-Pluta, A.; Vlachos, P.; Perlmann, T.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Joseph, B. Full-length p73α represses drug-induced apoptosis in small cell lung carcinoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 34159–34169. [Google Scholar]
- Tong, J.; Tan, X.; Song, X.; Gao, M.; Risnik, D.; Hao, S.; Ermine, K.; Wang, P.; Li, H.; Huang, Y. CDK4/6 inhibition suppresses p73 phosphorylation and activates DR5 to potentiate chemotherapy and immune checkpoint blockade. Cancer Res. 2022, 82, 1340–1352. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, W.; Yan, W.; Kong, X.; Shen, T.; Laubach, K.; Chen, M.; Chen, X. TP73 Isoform-specific disruption reveals a critical role of TAp73beta in growth suppression and inflammatory response. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 14. [Google Scholar]
- Rozenberg, J.M.; Zvereva, S.; Dalina, A.; Blatov, I.; Zubarev, I.; Luppov, D.; Bessmertnyi, A.; Romanishin, A.; Alsoulaiman, L.; Kumeiko, V. The p53 family member p73 in the regulation of cell stress response. Biol. Direct 2021, 16, 23. [Google Scholar]
- Urist, M.; Tanaka, T.; Poyurovsky, M.V.; Prives, C. p73 induction after DNA damage is regulated by checkpoint kinases Chk1 and Chk2. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 3041–3054. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Wang, B.; Gil, J.; Sabo, E.; Miller, L.; Gan, L.; Burstein, D.E. p63 and TTF-1 immunostaining: A useful marker panel for distinguishing small cell carcinoma of lung from poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma of lung. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2003, 119, 696–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordi, P.; Tiseo, M.; Barbieri, F.; Bavieri, M.; Sartori, G.; Marchetti, A.; Buttitta, F.; Bortesi, B.; Ambrosini-Spaltro, A.; Gnetti, L. Gene mutations in small-cell lung cancer (SCLC): Results of a panel of 6 genes in a cohort of Italian patients. Lung Cancer 2014, 86, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.Y.; Gil, J.; Kaufman, D.; Gan, L.; Kohtz, D.S.; Burstein, D.E. P63 in pulmonary epithelium, pulmonary squamous neoplasms, and other pulmonary tumors. Hum. Pathol. 2002, 33, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, G.; Pasini, F.; Olsen Stenholm, C.; Pastorino, U.; Maisonneuve, P.; Sonzogni, A.; Maffini, F.; Pruneri, G.; Fraggetta, F.; Cavallon, A. p63 immunoreactivity in lung cancer: Yet another player in the development of squamous cell carcinomas? J. Pathol. J. Pathol. Soc. G. B. Irel. 2002, 198, 100–109. [Google Scholar]
- Rowshanravan, B.; Halliday, N.; Sansom, D.M. CTLA-4: A moving target in immunotherapy. Blood J. Am. Soc. Hematol. 2018, 131, 58–67. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.; Mezzadra, R.; Schumacher, T.N. Regulation and function of the PD-L1 checkpoint. Immunity 2018, 48, 434–452. [Google Scholar]
- Acheampong, E.; Abed, A.; Morici, M.; Bowyer, S.; Amanuel, B.; Lin, W.; Millward, M.; Gray, E.S. Tumour PD-L1 expression in small-cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cells 2020, 9, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Dai, Z.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, W.-J.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Q. Regulatory mechanisms of immune checkpoints PD-L1 and CTLA-4 in cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 184. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Ling, S.; Hong, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, W.; Yin, L.; Xu, S.; Que, Q.; Wu, Y.; Zhan, Q. TP53/mTORC1-mediated bidirectional regulation of PD-L1 modulates immune evasion in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e007479. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Tan, J.Y.M.; Chitkara, N.; Bhatt, S. TP53 Mutation-Mediated Immune Evasion in Cancer: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications. Cancers 2024, 16, 3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozenberg, J.M.; Zvereva, S.; Dalina, A.; Blatov, I.; Zubarev, I.; Luppov, D.; Bessmertnyi, A.; Romanishin, A.; Alsoulaiman, L.; Kumeiko, V. Dual role of p73 in cancer microenvironment and DNA damage response. Cells 2021, 10, 3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logotheti, S.; Richter, C.; Murr, N.; Spitschak, A.; Marquardt, S.; Pützer, B.M. Mechanisms of functional pleiotropy of p73 in cancer and beyond. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 737735. [Google Scholar]
- Carlsen, L.; Zhang, S.; Tian, X.; De La Cruz, A.; George, A.; Arnoff, T.E.; El-Deiry, W.S. The role of p53 in anti-tumor immunity and response to immunotherapy. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1148389. [Google Scholar]
- Mathur, A.; Bareja, C.; Mittal, M.; Singh, A.; Saluja, D. Targeting Cellular Plasticity: Esculetin-Driven Reversion of Stemness and EMT Phenotype in Transforming Cells with Sequential p53/p73 Knockdowns; University of Delhi: New Delhi, India, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, P.A.; Vousden, K.H. Mutant p53 in cancer: New functions and therapeutic opportunities. Cancer Cell 2014, 25, 304–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dittmer, D.; Pati, S.; Zambetti, G.; Chu, S.; Teresky, A.K.; Moore, M.; Finlay, C.; Levine, A.J. Gain of function mutations in p53. Nat. Genet. 1993, 4, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- George, J.; Maas, L.; Abedpour, N.; Cartolano, M.; Kaiser, L.; Fischer, R.N.; Scheel, A.H.; Weber, J.-P.; Hellmich, M.; Bosco, G. Evolutionary trajectories of small cell lung cancer under therapy. Nature 2024, 627, 880–889. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.-W.; Wu, N.; Kim, Y.-C.; Cheng, P.F.; Basom, R.; Kim, D.; Dunn, C.T.; Lee, A.Y.; Kim, K.; Lee, C.S. Genetic requirement for Mycl and efficacy of RNA Pol I inhibition in mouse models of small cell lung cancer. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 1289–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Drygin, D.; Lin, A.; Bliesath, J.; Ho, C.B.; O’Brien, S.E.; Proffitt, C.; Omori, M.; Haddach, M.; Schwaebe, M.K.; Siddiqui-Jain, A. Targeting RNA polymerase I with an oral small molecule CX-5461 inhibits ribosomal RNA synthesis and solid tumor growth. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 1418–1430. [Google Scholar]
- Khot, A.; Brajanovski, N.; Cameron, D.P.; Hein, N.; Maclachlan, K.H.; Sanij, E.; Lim, J.; Soong, J.; Link, E.; Blombery, P. First-in-human RNA polymerase I transcription inhibitor CX-5461 in patients with advanced hematologic cancers: Results of a phase I dose-escalation study. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1036–1049. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, M.; Zhao, Y.; Arkenau, H.-T.; Lao, T.; Chu, L.; Xu, Q. Signal pathways and precision therapy of small-cell lung cancer. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 187. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, T.; Tong, P.; Stewart, C.A.; Cristea, S.; Valliani, A.; Shames, D.S.; Redwood, A.B.; Fan, Y.H.; Li, L.; Glisson, B.S. CHK1 inhibition in small-cell lung cancer produces single-agent activity in biomarker-defined disease subsets and combination activity with cisplatin or olaparib. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 3870–3884. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Cao, J.; Topatana, W.; Juengpanich, S.; Li, S.; Zhang, B.; Shen, J.; Cai, L.; Cai, X.; Chen, M. Targeting mutant p53 for cancer therapy: Direct and indirect strategies. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 157. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Chang, Y.; Li, Y.; Butler, W.; Jin, E.; Wang, A.; Tao, Y.; Chen, X.; Liang, C. Therapeutic potential of ReACp53 targeting mutant p53 protein in CRPC. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2020, 23, 160–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serrano, M.; Lin, A.W.; McCurrach, M.E.; Beach, D.; Lowe, S.W. Oncogenic ras provokes premature cell senescence associated with accumulation of p53 and p16INK4a. Cell 1997, 88, 593–602. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moyer, S.M.; Wasylishen, A.R.; Qi, Y.; Fowlkes, N.; Su, X.; Lozano, G. p53 drives a transcriptional program that elicits a non-cell-autonomous response and alters cell state in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 23663–23673. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta, J.; Li, Q.; Freeburg, N.F.; Murali, N.; Indeglia, A.; Grothusen, G.P.; Cicchini, M.; Mai, H.; Gladstein, A.C.; Adler, K.M. p53 restoration in small cell lung cancer identifies a latent cyclophilin-dependent necrosis mechanism. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfaye, E.; Martinez-Terroba, E.; Bendor, J.; Winkler, L.; Olivero, C.; Chen, K.; Feldser, D.M.; Zamudio, J.R.; Dimitrova, N. The p53 transcriptional response across tumor types reveals core and senescence-specific signatures modulated by long noncoding RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2025539118. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Zaika, E.; Zaika, A. p53 family: Role of protein isoforms in human cancer. J. Nucleic Acids 2012, 2012, 687359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name | Target | Mechanism of Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ganetespib | HSP90 | Degrades mutant p53 and induces BIM expression | [46] |
| Venetoclax | BCL-2 | Inhibits BCL-2 to induce apoptosis | [46,66,67] |
| Cisplatin | DNA crosslinking | Induces DNA damage, leading to apoptosis in cancer cells | [66,68] |
| Olaparib | PARP | Inhibits PARP, preventing DNA repair and causing cell death in p53-deficient tumors | [66,67,68] |
| Talazoparib | Strong PARP inhibition and DNA damage enhancement, causing cancer cell death | [67] | |
| Prexasertib | CHK1 | Inhibits CHK1, leading to increased DNA damage and apoptosis in p53-deficient cells | [67,68] |
| SRA-737 | Targets CHK1 to enhance DNA damage effects in cancer cells | [67] | |
| Nutlin-3a | MDM2 | Inhibits the interaction between p53 and MDM2, reactivating wild-type p53 | [69,70,71,72,73] |
| RG7112 | Prevents p53 degradation by inhibiting MDM2 | [69] | |
| APR-246 | Mutant p53 | Restores the wild-type conformation of mutant p53 and induces apoptosis | [69,73] |
| COTI-2 | Converts mutant p53 into its wild-type form and targets additional oncogenic pathways | [69,73] | |
| Disulfiram | Promotes the degradation of wild-type and mutant p53 via the proteasome pathway | [69,73] | |
| PRIMA-1 | Restores the DNA-binding ability and wild-type conformation of mutant p53 | [69] | |
| HDAC inhibitors | Mutant p53/HDACs | Disrupts HDAC6/Hsp90/mutant p53 complexes and destabilizes mutant p53 proteins | [69,73] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, M.; Kim, K.-B. Recent Research on Role of p53 Family in Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071110
Jeong M, Kim K-B. Recent Research on Role of p53 Family in Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(7):1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071110
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Minho, and Kee-Beom Kim. 2025. "Recent Research on Role of p53 Family in Small-Cell Lung Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 7: 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071110
APA StyleJeong, M., & Kim, K.-B. (2025). Recent Research on Role of p53 Family in Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers, 17(7), 1110. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17071110





