Lesion Conspicuity in Contrast-Enhanced Mammography: A Retrospective Analysis of Tumor Characteristics
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients’ Population
2.2. Histology
2.3. CEM Protocol
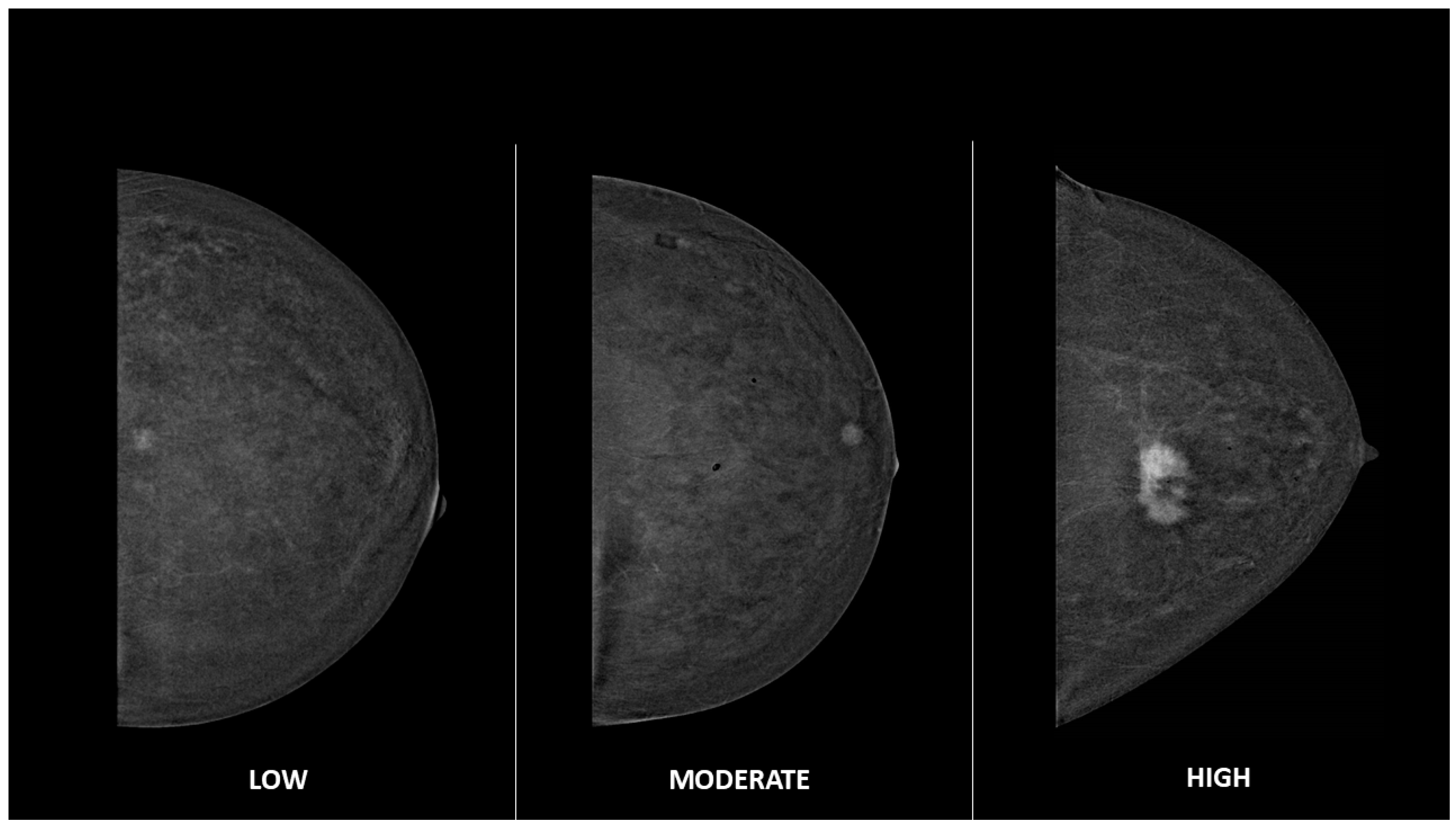
2.4. Image Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lima, S.M.; Kehm, R.D.; Terry, M.B. Global Breast Cancer Incidence and Mortality Trends by Region, Age-Groups, and Fertility Patterns. eClinicalMedicine 2021, 38, 100985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogani, J.; Mango, V.L.; Keating, D.; Sung, J.S.; Jochelson, M.S. Contrast-Enhanced Mammography: Past, Present, and Future. Clin. Imaging 2021, 69, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiaffino, S.; Cozzi, A.; Clauser, P.; Giannotti, E.; Marino, M.A.; van Nijnatten, T.J.A.; Baltzer, P.A.T.; Lobbes, M.B.I.; Mann, R.M.; Pinker, K.; et al. Current Use and Future Perspectives of Contrast-Enhanced Mammography (CEM): A Survey by the European Society of Breast Imaging (EUSOBI). Eur. Radiol. 2024, 34, 5439–5450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, B.K.; Gray, R.J.; Pockaj, B.A. Potential Cost Savings of Contrast-Enhanced Digital Mammography. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2017, 208, W231–W237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochelson, M.S.; Lobbes, M.B.I. Contrast-Enhanced Mammography: State of the Art. Radiology 2021, 299, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, C.; Bicchierai, G.; Amato, F.; Savi, E.; De Benedetto, D.; Di Naro, F.; Boeri, C.; Vanzi, E.; Miele, V.; Nori, J. Comparison between Second-Look Ultrasound and Second-Look Digital Breast Tomosynthesis in the Detection of Additional Lesions with Presurgical CESM. Br. J. Radiol. 2022, 95, 20210927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, Y.; Chou, C.-P.; Chan, C.W.; Buhari, S.A.; Hartman, M.; Tang, S.W.; Ng, C.W.Q.; Pillay, P.; Chua, W.; Jagmohan, P.; et al. Impact of Contrast-Enhanced Mammography in Surgical Management of Breast Cancers for Women with Dense Breasts: A Dual-Center, Multi-Disciplinary Study in Asia. Eur. Radiol. 2022, 32, 8226–8237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzini, A.; Nicosia, L.; Pruneri, G.; Maisonneuve, P.; Meneghetti, L.; Renne, G.; Vingiani, A.; Cassano, E.; Mastropasqua, M.G. Clinical Performance of Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography in Pre-Surgical Evaluation of Breast Malignant Lesions in Dense Breasts: A Single Center Study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2020, 184, 723–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicchierai, G.; Tonelli, P.; Piacenti, A.; De Benedetto, D.; Boeri, C.; Vanzi, E.; Bianchi, S.; Cirone, D.; Kaur Gill, M.; Miele, V.; et al. Evaluation of Contrast-Enhanced Digital Mammography (CEDM) in the Preoperative Staging of Breast Cancer: Large-Scale Single-Center Experience. Breast J. 2020, 26, 1276–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knogler, T.; Homolka, P.; Hoernig, M.; Leithner, R.; Langs, G.; Waitzbauer, M.; Pinker, K.; Leitner, S.; Helbich, T.H. Application of BI-RADS Descriptors in Contrast-Enhanced Dual-Energy Mammography: Comparison with MRI. Breast Care 2017, 12, 212–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, R.M.; Helal, M.H.; Mansour, S.M.; Haggag, M.A.; Nada, O.M.; Farahat, I.G.; Alieldin, N.H. Can We Apply the MRI BI-RADS Lexicon Morphology Descriptors on Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography? Br. J. Radiol. 2016, 89, 20160157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Phillips, J.; Sung, J.S.; Lewin, J.M.; Newell, M.S. ACR BI-RADS. In ACR BI-RADS Contrast Enhanced Mammography (CEM) (A Supplement to ACR BIRADS Mammography 2013) Atlas, Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System; American College of Radiology: Reston, VA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Dietzel, M.; Baltzer, P.A.T. How to Use the Kaiser Score as a Clinical Decision Rule for Diagnosis in Multiparametric Breast MRI: A Pictorial Essay. Insights Imaging 2018, 9, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.J.; Hwangbo, L.; Suh, H.B.; Kim, S.; Choo, K.S.; Nam, K.J.; Kang, T. Kinetic Heterogeneity of Breast Cancer Determined Using Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Preoperative MRI Scans: Relationship to Distant Metastasis-Free Survival. Radiology 2020, 295, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dharmalingam, P.; Jagannathan, D. Lesion Conspicuity and Contrast Kinetics as Predictors to Differentiate Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions in Contrast-Enhanced Mammogram. Egypt. J. Radiol. Nucl. Med. 2024, 55, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicosia, L.; Bozzini, A.C.; Palma, S.; Pesapane, F.; Meneghetti, L.; Pizzamiglio, M.; Abbate, F.; Latronico, A.; Bagnardi, V.; Frassoni, S.; et al. Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System and Contrast Enhancement Mammography: Lesion Conspicuity Likelihood of Malignancy and Relationship with Breast Tumor Receptor Status. Acad. Radiol. 2023, 30, 2243–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellini, C.; Pugliese, F.; Bicchierai, G.; Amato, F.; De Benedetto, D.; Di Naro, F.; Boeri, C.; Vanzi, E.; Migliaro, G.; Incardona, L.; et al. Contrast-Enhanced Mammography in the Management of Breast Architectural Distortions and Avoidance of Unnecessary Biopsies. Breast Cancer Tokyo Jpn. 2024, 31, 851–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łuczyńska, E.; Niemiec, J.; Hendrick, E.; Heinze, S.; Jaszczyński, J.; Jakubowicz, J.; Sas-Korczyńska, B.; Rys, J. Degree of Enhancement on Contrast Enhanced Spectral Mammography (CESM) and Lesion Type on Mammography (MG): Comparison Based on Histological Results. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 3886–3893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnicki, W.; Heinze, S.; Piegza, T.; Pawlak, M.; Kojs, Z.; Łuczyńska, E. Correlation Between Enhancement Intensity in Contrast Enhancement Spectral Mammography and Types of Kinetic Curves in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2020, 26, e920742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Gong, W.; Xie, Y.; Sheng, L. Correlation between the CEM Imaging Characteristics and Different Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer. Breast 2023, 72, 103595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marzogi, A.; Baltzer, P.A.T.; Kapetas, P.; Milos, R.I.; Bernathova, M.; Helbich, T.H.; Clauser, P. Is the Level of Contrast Enhancement on Contrast-Enhanced Mammography (CEM) Associated with the Presence and Biological Aggressiveness of Breast Cancer? Diagnostics 2023, 13, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, C.-Y.; Juan, Y.-H.; Cheung, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Lo, Y.-F.; Lin, G.; Chen, S.-C.; Ng, S.-H. Quantitative Analysis of Enhanced Malignant and Benign Lesions on Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography. Br. J. Radiol. 2018, 91, 20170605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Chi, X.; Sun, B.; Lin, S.; Xing, D. Diagnostic Value of Quantitative Gray-Scale Analysis of Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography for Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2020, 44, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zheng, B.; Chen, W.; Wen, C.; Zeng, H.; He, Z.; Qin, G.; Li, Y. Can the Delayed Phase of Quantitative Contrast-Enhanced Mammography Improve the Diagnostic Performance on Breast Masses? Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2021, 11, 3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bicchierai, G.; Amato, F.; Vanzi, B.; De Benedetto, D.; Boeri, C.; Vanzi, E.; Di Naro, F.; Bianchi, S.; Cirone, D.; Cozzi, D.; et al. Which Clinical, Radiological, Histological, and Molecular Parameters Are Associated with the Absence of Enhancement of Known Breast Cancers with Contrast Enhanced Digital Mammography (CEDM)? Breast 2020, 54, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzi, A.; Magni, V.; Zanardo, M.; Schiaffino, S.; Sardanelli, F. Contrast-Enhanced Mammography: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Diagnostic Performance. Radiology 2022, 302, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalji, U.C.; Jeukens, C.R.L.P.N.; Houben, I.; Nelemans, P.J.; van Engen, R.E.; van Wylick, E.; Beets-Tan, R.G.H.; Wildberger, J.E.; Paulis, L.E.; Lobbes, M.B.I. Evaluation of Low-Energy Contrast-Enhanced Spectral Mammography Images by Comparing Them to Full-Field Digital Mammography Using EUREF Image Quality Criteria. Eur. Radiol. 2015, 25, 2813–2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francescone, M.A.; Jochelson, M.S.; Dershaw, D.D.; Sung, J.S.; Hughes, M.C.; Zheng, J.; Moskowitz, C.; Morris, E.A. Low Energy Mammogram Obtained in Contrast-Enhanced Digital Mammography (CEDM) Is Comparable to Routine Full-Field Digital Mammography (FFDM). Eur. J. Radiol. 2014, 83, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Variable | n (%), [IQR 1] |
|---|---|
| Age (years, median) | 62.3 [20.4] |
| Enhancement type on CEM | |
| EA | 6 (1.1) |
| Mass | 431 (78.1) |
| Mass + NME | 22 (4.0) |
| NME | 93 (16.8) |
| Dimensions (mm, median) | 17 [13] |
| ER (positive) | 515 (93.3) |
| PgR (positive) | 489 (88.6) |
| HER2 (positive) | 100 (19.9) |
| Grade of differentiation | |
| G1 | 122 (22.1) |
| G2 | 260 (47.1) |
| G3 | 170 (30.8) |
| Molecular subtype | |
| Luminal A | 224 (44.5) |
| Luminal B | 158 (31.4) |
| HER2-positive | 100 (19.9) |
| TNBC | 21 (4.2) |
| Histology | |
| Mixed ductal and lobular carcinoma | 39 (7.1) |
| Invasive ductal carcinoma | 311 (56.3) |
| Invasive lobular carcinoma | 66 (12.0) |
| DCIS | 46 (8.3) |
| Other | 90 (16.3) |
| Variables | Lesion Conspicuity | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 n = 105 | 2 n = 276 | 3 n = 171 | ||
| n (%) [IQR] | n (%) [IQR] | n (%) [IQR] | ||
| Enhancement type on CEM | <0.001 | |||
| EA | 0 (-) | 1 (0.4) | 5 (2.9) | |
| Mass | 70 (66.7) | 216 (78.3) | 145 (84.8) | |
| Mass + NME | 1 (1.0) | 13 (4.7) | 8 (4.7) | |
| NME | 34 (32.4) | 46 (16.7) | 13 (7.6) | |
| Dimensions (mm, median) | 12 [8] | 16 [15] | 20 [15] | <0.001 |
| ER (positive) | 96 (91.4) | 262 (94.9) | 157 (91.8) | 0.307 |
| PgR (positive) | 92 (87.6) | 249 (90.2) | 148 (86.5) | 0.467 |
| HER2 (positive) | 12 (13.5) | 47 (19.2) | 41 (24.3) | 0.111 |
| Grade of differentiation | 0.770 | |||
| G1 | 26 (24.8) | 61 (22.1) | 35 (20.5) | |
| G2 | 51 (48.6) | 131 (47.5) | 78 (45.6) | |
| G3 | 28 (26.7) | 84 (30.4) | 58 (33.9) | |
| Ki67 index (%) | 0.019 | |||
| <20% | 36 (40.4) | 75 (30.6) | 40 (23.7) | |
| ≥20% | 53 (59.6) | 170 (69.4) | 129 (76.3) | |
| Molecular subtype | 0.025 | |||
| HER2-positive | 12 (13.5) | 47 (19.2) | 41 (24.3) | |
| Luminal A | 50 (56.2) | 112 (45.7) | 62 (36.7) | |
| Luminal B | 21 (23.6) | 80 (32.7) | 57 (33.7) | |
| TNBC | 6 (6.7) | 6 (2.4) | 9 (5.3) | |
| Histology | 0.001 | |||
| Mixed ductal and lobular carcinoma | 5 (4.8) | 16 (5.8) | 18 (10.5) | |
| Invasive ductal carcinoma | 53 (50.5) | 148 (53.6) | 110 (64.3) | |
| Invasive lobular carcinoma | 12 (11.4) | 35 (12.7) | 19 (11.1) | |
| DCIS | 14 (13.3) | 30 (10.9) | 2 (1.2) | |
| Other | 21 (20.0) | 47 (17.0) | 22 (12.9) | |
| Variable | β | Std. Error | Wald | df | Sig. | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||||
| Dimensions (mm) | 0.064 | 0.008 | 58.637 | 1 | 0.000 | 0.048 | 0.081 |
| Enhancement type on CEM | |||||||
| EA | 4.819 | 1.192 | 16.344 | 1 | 0.000 | 2.482 | 7.155 |
| Mass | 2.234 | 0.336 | 44.141 | 1 | 0.000 | 1.575 | 2.893 |
| Mass + NME | 1.541 | 0.512 | 9.049 | 1 | 0.003 | 0.537 | 2.544 |
| NME = ref | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Ki67 index (%) | |||||||
| <20% | −0.172 | 0.0251 | 0.473 | 1 | 0.492 | −0.664 | 0.319 |
| ≥20% = ref | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Histology | |||||||
| Mixed ductal and lobular carcinoma | 0.325 | 0.349 | 0.866 | 1 | 0.352 | −0.359 | 1.009 |
| Invasive lobular carcinoma | −0.124 | 0.286 | 0.188 | 1 | 0.665 | −0.685 | 0.437 |
| Other | −0.175 | 0.252 | 0.480 | 1 | 0.488 | −0.669 | 0.320 |
| DCIS | −0.585 | 1.959 | 0.089 | 1 | 0.765 | −4.424 | 3.254 |
| Invasive ductal carcinoma = ref | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Molecular subtype | |||||||
| Luminal B | 0.059 | 0.253 | 0.055 | 1 | 0.815 | −0.436 | 0.555 |
| HER2-positive | 0.417 | 0.266 | 2.465 | 1 | 0.116 | −0.104 | 0.938 |
| TNBC | −0.418 | 0.474 | 0.777 | 1 | 0.378 | −1.348 | 0.512 |
| Luminal A = ref | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bellini, C.; Susini, T.; Toncelli, K.; Pandolfi, M.; Migliaro, G.; Pugliese, F.; Vanzi, B.; Incardona, L.; Bicchierai, G.; di Naro, F.; et al. Lesion Conspicuity in Contrast-Enhanced Mammography: A Retrospective Analysis of Tumor Characteristics. Cancers 2025, 17, 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030501
Bellini C, Susini T, Toncelli K, Pandolfi M, Migliaro G, Pugliese F, Vanzi B, Incardona L, Bicchierai G, di Naro F, et al. Lesion Conspicuity in Contrast-Enhanced Mammography: A Retrospective Analysis of Tumor Characteristics. Cancers. 2025; 17(3):501. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030501
Chicago/Turabian StyleBellini, Chiara, Tommaso Susini, Kassandra Toncelli, Martina Pandolfi, Giuliano Migliaro, Francesca Pugliese, Bianca Vanzi, Ludovica Incardona, Giulia Bicchierai, Federica di Naro, and et al. 2025. "Lesion Conspicuity in Contrast-Enhanced Mammography: A Retrospective Analysis of Tumor Characteristics" Cancers 17, no. 3: 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030501
APA StyleBellini, C., Susini, T., Toncelli, K., Pandolfi, M., Migliaro, G., Pugliese, F., Vanzi, B., Incardona, L., Bicchierai, G., di Naro, F., de Benedetto, D., Vidali, S., Pancani, S., Miele, V., & Nori Cucchiari, J. (2025). Lesion Conspicuity in Contrast-Enhanced Mammography: A Retrospective Analysis of Tumor Characteristics. Cancers, 17(3), 501. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17030501






