Imaging in Autologous Breast Reconstruction
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- Decreased operative time: Mapping the precise location, size, and course of each perforator streamlines flap design by allowing surgeons to know exactly which perforators to include before entering the operating room. This results in shorter operative times and decreased risk of complications associated with prolonged surgery.
- Fewer complications: Flap perfusion is critical to successfully transferring a soft and supple flap without undue amounts of fat necrosis. Preoperative and intraoperative assessment of each perforator and their perfusion allows for the development of a plan that minimizes the risk of such complications.
- Decreased donor-site morbidity: By delineating the subfascial and intramuscular courses of the perforators, surgeons can minimize the amount of healthy muscle and/or fascia that is sacrificed, thereby reducing donor-site morbidity.
- Efficient patient selection: Preoperative imaging can help surgeons assess the suitability of patients for abdominal-based free flaps, particularly if they have undergone previous abdominal surgery that may have threatened the flap’s perforators and/or pedicle.
2. Ultrasonography (US)
3. Computed Tomography Angiography (CTA)
4. Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA)
5. Dye-Based and Indocyanine Green (ICG) Angiography
6. 3D Surface Imaging
7. Current State-of-the-Art and Future Clinical Applications
7.1. Imaging in Stacked Flap Breast Reconstruction
7.2. Recipient Vessel Assessment
7.3. Robotic-Assisted DIEP Flap Harvest
8. Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Artificial Intelligence (AI)
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Society, A.C. Key Statistics for Breast Cancer. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/breast-cancer/about/how-common-is-breast-cancer.html (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Rainsbury, R.M. Surgery insight: Oncoplastic breast-conserving reconstruction—Indications; benefits; choices and outcomes. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2007, 4, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surgeons ASoP. 2022 ASPS. Procedural Statistics Release. Available online: https://www.plasticsurgery.org/documents/News/Statistics/2022/plastic-surgery-statistics-report-2022.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Khajuria, A.; Prokopenko, M.; Greenfield, M.; Smith, O.; Pusic, A.L.; Mosahebi, A. A Meta-analysis of Clinical; Patient-Reported Outcomes and Cost of DIEP versus Implant-based Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2019, 7, e2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartrampf, C.R.; Scheflan, M.; Black, P.W. Breast reconstruction with a transverse abdominal island flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1982, 69, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hidaka, T.; Mori, H.; Shimizu, H.; Takahashi, S.; Tanaka, K.; Okazaki, M. Comparison of Lumbar Artery and Superior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flaps for Breast Reconstruction: Multislice CT-Based Anatomical Study. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2022, 89, e39–e44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martineau, J.; Kalbermatten, D.F.; Oranges, C.M. Safety and efficacy of the superior gluteal artery perforator (SGAP) flap in autologous breast reconstruction: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, K.T.; Blondeel, P.N.; Lobo, F.; Van Landuyt, K. Early experience with the free lumbar artery perforator flap for breast reconstruction. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2015, 68, 1112–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weum, S. Imaging in plastic surgery. A clinical and experimental study with notes on the history of medical imaging. In Doktorgradsavhandlinger (Helsefak); UiT The Arctic University of Norway: Tromsø, Norway, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Corsi, F.; Sorrentino, L.; Bossi, D.; Sartani, A.; Foschi, D. Preoperative localization and surgical margins in conservative breast surgery. Int. J. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 2013, 793819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.G.; Burgess, E.M. The use of CAD/CAM technology in prosthetics and orthotics--current clinical models and a view to the future. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2001, 38, 327–334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Myers, P.L.; Nelson, J.A.; Rosen, E.B.; Allen, R.J., Jr.; Disa, J.J.; Matros, E. Virtual surgical planning for oncologic mandibular and maxillary reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2021, 9, e3672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodby, K.A.; Turin, S.; Jacobs, R.J.; Cruz, J.F.; Hassid, V.J.; Kolokythas, A.; Antony, A.K. Advances in oncologic head and neck reconstruction: Systematic review and future considerations of virtual surgical planning and computer aided design/computer aided modeling. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2014, 67, 1171–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J., Jr.; Nelson, J.A.; Polanco, T.O.; Shamsunder, M.G.; Ganly, I.; Boyle, J.; Evan, R.; Evan, M. Short-term Outcomes following Virtual Surgery Assisted Immediate Dental Implant Placement (IDIP) in Free Fibula Flaps for Oncologic Mandibular Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 146, 768e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egeberg, A.; Rasmussen, M.K.; Sørensen, J.A. Comparing the donor-site morbidity using DIEP; SIEA or MS-TRAM flaps for breast reconstructive surgery: A meta-analysis. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2012, 65, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paige, K.T.; Bostwick, J., III; Bried, J.T.; Jones, G. A comparison of morbidity from bilateral; unipedicled and unilateral; unipedicled TRAM flap breast reconstructions. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1998, 101, 1819–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrero, M.; Hilaire, H.S.; Allen, R. Modern Approaches to Abdominal-Based Breast Reconstruction. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2023, 50, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, P.L.; Nelson, J.A.; Allen, R.J., Jr. Alternative flaps in autologous breast reconstruction. Gland. Surg. 2021, 10, 444–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G.I.; Doyle, M.; McCarten, G. The Doppler probe for planning flaps: Anatomical study and clinical applications. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1990, 43, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinser, M.J.; Kroger, N.; Malter, W.; Schulz, T.; Puesken, M.; Mallmann, P.; Zirk, M.; Schröder, K.; Andree, C.; Seidenstuecker, K.; et al. Preoperative Perforator Mapping in DIEP Flaps for Breast Reconstruction. The Impact of New Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Techniques. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enriquez, J.L.; Wu, T.S. An introduction to ultrasound equipment and knobology. Crit. Care Clin. 2014, 30, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, J.L.; Hoffenberg, S.R.; Smith, R.S. History of emergency and critical care ultrasound: The evolution of a new imaging paradigm. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 35, S126–S130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallock, G.G. Attributes and shortcomings of acoustic Doppler sonography in identifying perforators for flaps from the lower extremity. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2009, 25, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitaker, I.S.; Rozen, W.M.; Chubb, D.; Acosta, R.; Kiil, B.J.; Birke-Sorensen, H.; Grinsell, D.; Ashton, M.W. Postoperative monitoring of free flaps in autologous breast reconstruction: A multicenter comparison of 398 flaps using clinical monitoring; microdialysis; and the implantable Doppler probe. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2010, 26, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallock, G.G. Evaluation of fasciocutaneous perforators using color duplex imaging. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1994, 94, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabegger, A.H.; Bodner, G.; Rieger, M.; Jaschke, W.R.; Ninkovic, M. Internal mammary vessels as a model for power Doppler imaging of recipient vessels in microsurgery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1999, 104, 1656–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numata, T.; Iida, Y.; Shiba, K.; Hanazawa, T.; Terada, N.; Nagata, H.; Konno, A. Usefulness of color Doppler sonography for assessing hemodynamics of free flaps for head and neck reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2002, 48, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.-M.; Huang, C.-C.; Hsu, H.; Chiu, C.-H.; Chien, S.-H. Advancements in free flap monitoring in the last decade: A critical review. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 126, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, L.; Levin, L.S.; Klitzman, B. Laser Doppler flowmeter monitoring of free-tissue transfers: Blood flow in normal and complicated cases. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2001, 107, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hallock, G.G. A “true” false-negative misadventure in free flap monitoring using laser Doppler flowmetry. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2002, 110, 1609–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanzonico, P.; Rothenberg, L.N.; Strauss, H.W. Radiation exposure of computed tomography and direct intracoronary angiography: Risk has its reward. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 47, 1846–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrik, V.; Apok, V.; Britton, J.A.; Bell, B.A.; Papadopoulos, M.C. Godfrey Hounsfield and the dawn of computed tomography. Neurosurgery 2006, 58, 780–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, C.R.; Koolen, P.G.; Ho, O.A.; Tobias, A.M.; Lin, S.J.; Lee, B.T. Preoperative CT-angiography in autologous breast reconstruction. Microsurgery 2016, 36, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hembd, A.; Teotia, S.S.; Zhu, H.; Haddock, N.T. Optimizing perforator selection: A multivariable analysis of predictors for fat necrosis and abdominal morbidity in DIEP flap breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 142, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cina, A.; Barone-Adesi, L.; Rinaldi, P.; Cipriani, A.; Salgarello, M.; Masetti, R.; Bonomo, L. Planning deep inferior epigastric perforator flaps for breast reconstruction: A comparison between multidetector computed tomography and magnetic resonance angiography. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 2333–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozen, W.M.; Phillips, T.J.; Ashton, M.W.; Stella, D.L.; Gibson, R.N.; Taylor, G.I. Preoperative imaging for DIEA perforator flaps: A comparative study of computed tomographic angiography and Doppler ultrasound. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 121, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, A.; Chhaya, N.; Nsiah-Sarbeng, P.; Mosahebi, A. CT-guided deep inferior epigastric perforator (DIEP) flap localization—Better for the patient; the surgeon; and the hospital. Clin. Radiol. 2013, 68, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozen, W.M.; Whitaker, I.S.; Stella, D.L.; Phillips, T.J.; Einsiedel, P.F.; Acosta, R.; Ashton, M.W. The radiation exposure of Computed Tomographic Angiography (CTA) in DIEP flap planning: Low dose but high impact. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2009, 62, e654–e655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sergesketter, A.R.; Pyfer, B.J.; Phillips, B.T.; Zhao, R.; Hollenbeck, S.T. Check the Record: Remote CT Scans for Breast Flap Perforator Mapping. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2018, 34, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, A.; Cina, A.; Macrì, G.; Belli, P.; Mercogliano, S.; Barbieri, P.; Grippo, C.; Franceschini, G.; D’Archi, S.; Mason, E.J.; et al. Conventional CT versus Dedicated CT Angiography in DIEP Flap Planning: A Feasibility Study. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seth, A.K.; Allen, R.J., Jr. Modern techniques and alternative flaps in microsurgical breast reconstruction. J. Surg. Oncol. 2018, 118, 768–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, A.; Marston, A. Ascaris infection. Br. Med. J. 1977, 1, 776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neil-Dwyer, J.G.; Ludman, C.N.; Schaverien, M.; McCulley, S.J.; Perks, A.G. Magnetic resonance angiography in preoperative planning of deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flaps. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2009, 62, 1661–1665. [Google Scholar]
- Rozen, W.M.; Stella, D.L.; Bowden, J.; Taylor, G.I.; Ashton, M.W. Advances in the pre-operative planning of deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flaps: Magnetic resonance angiography. Microsurgery 2009, 29, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, A. Magnetic resonance imaging. BMJ 2002, 324, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibelli, T.J.; Chennareddy, S.; Mandelbaum, M.; Henderson, P.W. Vascular Mapping for Abdominal-Based Breast Reconstruction: A Comprehensive Review of Current and Upcoming Imaging Modalities. Eplasty 2023, 23, e44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yazdy, A.M.; Tomashefski, J.F., Jr.; Yagan, R.; Kleinerman, J. Regional alveolar damage (RAD). A localized counterpart of diffuse alveolar damage. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1989, 92, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olenczak, J.B.; Martinovic, M.; Martin, J.P.; Campbell, C.A. Prone liver phase MRA demonstrates improved intramuscular vascular detail compared to CTA in preoperative perforator mapping for free autologous abdominally-based breast reconstruction. Ann. Breast Surg. 2018, 2, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimmappa, N.D. MRA for Preoperative Planning and Postoperative Management of Perforator Flap Surgeries: A Review. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2023, 59, 797–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Miller, M.J.; Friel, H.T.; Slijepcevic, A.; Knopp, M.V. Perforator Phase Contrast Angiography of Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforators: A Better Preoperative Imaging Tool for Flap Surgery than Computed Tomographic Angiography? Investig. Radiol. 2017, 52, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J., Jr.; Lee, Z.-H.; Mayo, J.L.; Levine, J.; Ahn, C.; Allen, R.J., Sr. The profunda artery perforator flap experience for breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 138, 968–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddock, N.T.; Suszynski, T.M.; Teotia, S.S. Consecutive Bilateral Breast Reconstruction Using Stacked Abdominally Based and Posterior Thigh Free Flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 147, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momeni, A.; Kanchwala, S. Delayed-immediate hybrid breast reconstruction-Increasing patient input and precision in breast reconstruction. Breast J. 2019, 25, 898–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummelink, S.; Hameeteman, M.; Hoogeveen, Y.; Slump, C.; Ulrich, D.; Kool, L.S. Preliminary results using a newly developed projection method to visualize vascular anatomy prior to DIEP flap breast reconstruction. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2015, 68, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shan, T.; Han, J.; Pan, W.; Gu, C.; Xu, R. Three-dimensional image fusion of CTA and angiography for real-time guidance during neurointerventional procedures. J. NeuroInterventional Surg. 2017, 9, 302–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellerano, C.; Savini, L. [9-Hydrazinoacridine derivatives and 9-hydrazino-1;2;3;4-tetrahydroacridines: Preparation and biological activity]. Boll. Chim. Farm. 1983, 122, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stryker. About Us. Available online: https://www.stryker.com/us/en/endoscopy/systems/aim-platform/plastic-recon.html#:~:text=Launched%20for%20use%20in%20plastic;and%20other%20reconstructive%20surgical%20procedures (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Stryker. SPY Portable Handheld Imaging System Operator’s Manual. Novadaq Technologies ULC. Available online: https://www.stryker.com/content/dam/stryker/about/our-locations/apac/ifus/4-8-22/4-0003045G_SPY_PHI_System_Operators_Manual_en-INTL_printing_template.pdf (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- Momeni, A.; Sheckter, C. Intraoperative laser-assisted indocyanine green imaging can reduce the rate of fat necrosis in microsurgical breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 145, 507e–513e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anker, A.M.; Prantl, L.; Strauss, C.; Brébant, V.; Baringer, M.; Ruewe, M.; Vykoukal, J.; Klein, S.M. Clinical impact of DIEP flap perforator characteristics–a prospective indocyanine green fluorescence imaging study. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2020, 73, 1526–1533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girard, N.; Delomenie, M.; Malhaire, C.; Sebbag, D.; Roulot, A.; Sabaila, A.; Couturaud, B.; Feron, J.-G.; Reyal, F. Innovative DIEP flap perfusion evaluation tool: Qualitative and quantitative analysis of indocyanine green-based fluorescence angiography with the SPY-Q proprietary software. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0217698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, C.; Mayr, M.; Hofter, E.; Ninkovic, M. Perfusion zones of the DIEP flap revisited: A clinical study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 117, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moo, T.-A.; Nelson, J.A.; Sevilimedu, V.; Charyn, J.; Le, T.V.; Allen, R.J.; Mehrara, B.J.; Barrio, A.V.; Capko, D.M.; Pilewskie, M.; et al. Strategies to avoid mastectomy skin-flap necrosis during nipple-sparing mastectomy. Br. J. Surg. 2023, 110, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nykiel, M.; Sayid, Z.; Wong, R.; Lee, G.K. Management of mastectomy skin flap necrosis in autologous breast reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2014, 72, S31–S34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eder, M.; Raith, S.; Jalali, J.; Müller, D.; Harder, Y.; Dobritz, M.; Papadopulos, N.A.; Machens, H.-G.; Kovacs, L. Three-dimensional prediction of free-flap volume in autologous breast reconstruction by CT angiography imaging. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2014, 9, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, C.S.; Plotsker, E.L.; Rubenstein, R.; Mehrara, E.; Haglich, K.; Zoghbi, Y.; Mehrara, B.J.; Nelson, J.A. Three-Dimensional Surface Analysis for Preoperative Prediction of Breast Volume: A Validation Study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 152, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissler, J.M.; Stern, C.S.; Schreiber, J.E.; Amirlak, B.; Tepper, O.M. The evolution of photography and three-dimensional imaging in plastic surgery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 139, 761–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, M.P.; Rozen, W.M.; Patel, N.G.; Hunter-Smith, D.J.; Ramakrishnan, V. Enhancing breast projection in autologous reconstruction using the St Andrew’s coning technique and 3D volumetric analysis. Gland Surg. 2017, 6, 706–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canfield. VECTRA. Available online: https://www.canfieldsci.com/imaging-systems/vectra-xt-3d-imaging-system/ (accessed on 1 January 2024).
- Tomita, K.; Yano, K.; Hata, Y.; Nishibayashi, A.; Hosokawa, K. DIEP flap breast reconstruction using 3-dimensional surface imaging and a printed mold. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2015, 3, e316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozen, W.M.; Patel, N.G.; Ramakrishnan, V.V. Increasing options in autologous microsurgical breast reconstruction: Four free flaps for ‘stacked’ bilateral breast reconstruction. Gland Surg. 2016, 5, 255. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boyd, C.J.; Sorenson, T.J.; Hemal, K.; Karp, N.S. Maximizing volume in autologous breast reconstruction: Stacked/conjoined free flaps. Gland Surg. 2023, 12, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evgeniou, E.; Teotia, S.S.; Haddock, N.T. Asymmetric Four-Flap Breast Reconstruction with DIEP Flaps and PAP Flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 150, 1236e–1239e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coriddi, M.; Dayan, J.; Bloomfield, E.; McGrath, L.; Diwan, R.; Monge, J.; Julia, G.; Stav, B.; Lillian, B.; Babak, M. Efficacy of Immediate Lymphatic Reconstruction to Decrease Incidence of Breast Cancer-related Lymphedema: Preliminary Results of Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Surg. 2023, 278, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fansa, H.; Schirmer, S.; Cervelli, A.; Gehl, H.B. Computed tomographic angiography imaging and clinical implications of internal mammary artery perforator vessels as recipient vessels in autologous breast reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2013, 71, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.T.A.; Won, B.W.; Baumgardner, K.; Lue, M.; Montorfano, L.; Hosein, R.C.; Wang, H.T.; Martinez, R.A. Literature Review: Robotic-Assisted Harvest of Deep Inferior Epigastric Flap for Breast Reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2022, 89, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selber, J.C. The Robotic DIEP Flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2020, 145, 340–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, S.N.; Asaad, M.; Liu, J.; Chu, C.K.M.; Clemens, M.W.; Kapur, S.S.; Largo, R.D.; Selber, J.C.M. Robotic harvest of the deep inferior epigastric perforator flap for breast reconstruction: A case series. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 149, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daar, D.A.; Anzai, L.M.; Vranis, N.M.; Schulster, M.L.; Frey, J.D.; Jun, M.; Zhao, L.C.; Levine, J.P. Robotic deep inferior epigastric perforator flap harvest in breast reconstruction. Microsurgery 2022, 42, 319–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurlander, D.E.; Le-Petross, H.T.; Shuck, J.W.; Butler, C.E.; Selber, J.C. Robotic DIEP Patient Selection: Analysis of CT Angiography. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2021, 9, e3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitoussi, A.; Tacher, V.; Pigneur, F.; Heranney, J.; Sawan, D.; Dao, T.H.; Hersant, B.; Meningaud, J.-P.; Bosc, R. Augmented reality-assisted deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap harvesting. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2021, 74, 1931–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, I.; Lindhardt, J.; Jakobsen, A.; Thomsen, J.B.; Kiil, B.J.; Rozen, W.M.; Kenney, P.S. Improving Visualization of Intramuscular Perforator Course: Augmented Reality Headsets for DIEP Flap Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg.-Glob. Open 2023, 11, e5282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholok, D.J.; Fischer, M.J.; Leuze, C.W.; Januszyk, M.; Daniel, B.L.; Momeni, A. Spatial Fidelity of Microvascular Perforating Vessels as Perceived by Augmented Reality Virtual Projections. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2023, 153, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cevik, J.; Seth, I.; Rozen, W.M. Transforming breast reconstruction: The pioneering role of artificial intelligence in preoperative planning. Gland Surg. 2023, 12, 1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavioso, C.; Araújo, R.J.; Oliveira, H.P.; Anacleto, J.C.; Vasconcelos, M.A.; Pinto, D.; Gouveia, P.F.; Alves, C.; Cardoso, F.; Cardoso, J.S.; et al. Automatic detection of perforators for microsurgical reconstruction. Breast 2020, 50, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DellaCroce, F.J.; Sullivan, S.K.; Trahan, C. Stacked deep inferior epigastric perforator flap breast reconstruction: A review of 110 flaps in 55 cases over 3 years. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 127, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pusic, A.L.; Klassen, A.F.; Scott, A.M.; Klok, J.A.; Cordeiro, P.G.; Cano, S.J. Development of a new patient-reported outcome measure for breast surgery: The BREAST-Q. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 124, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
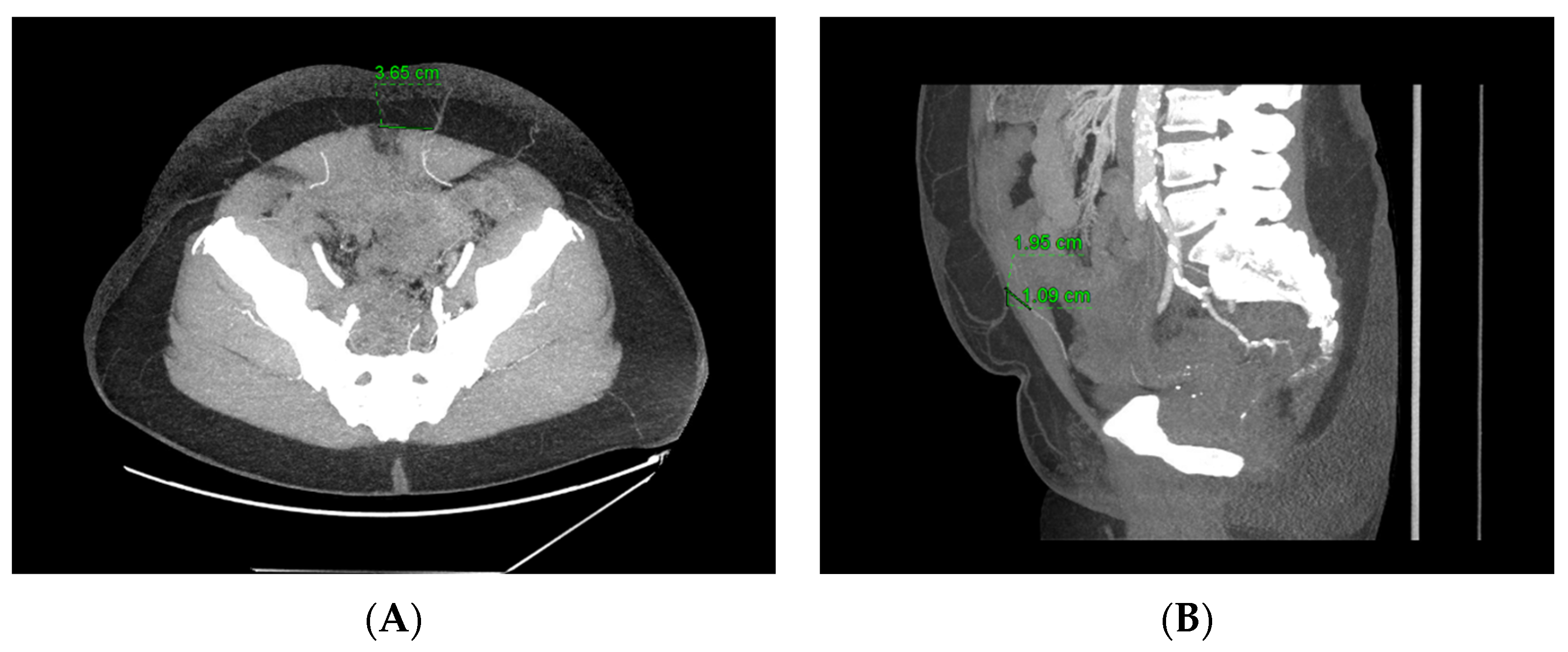
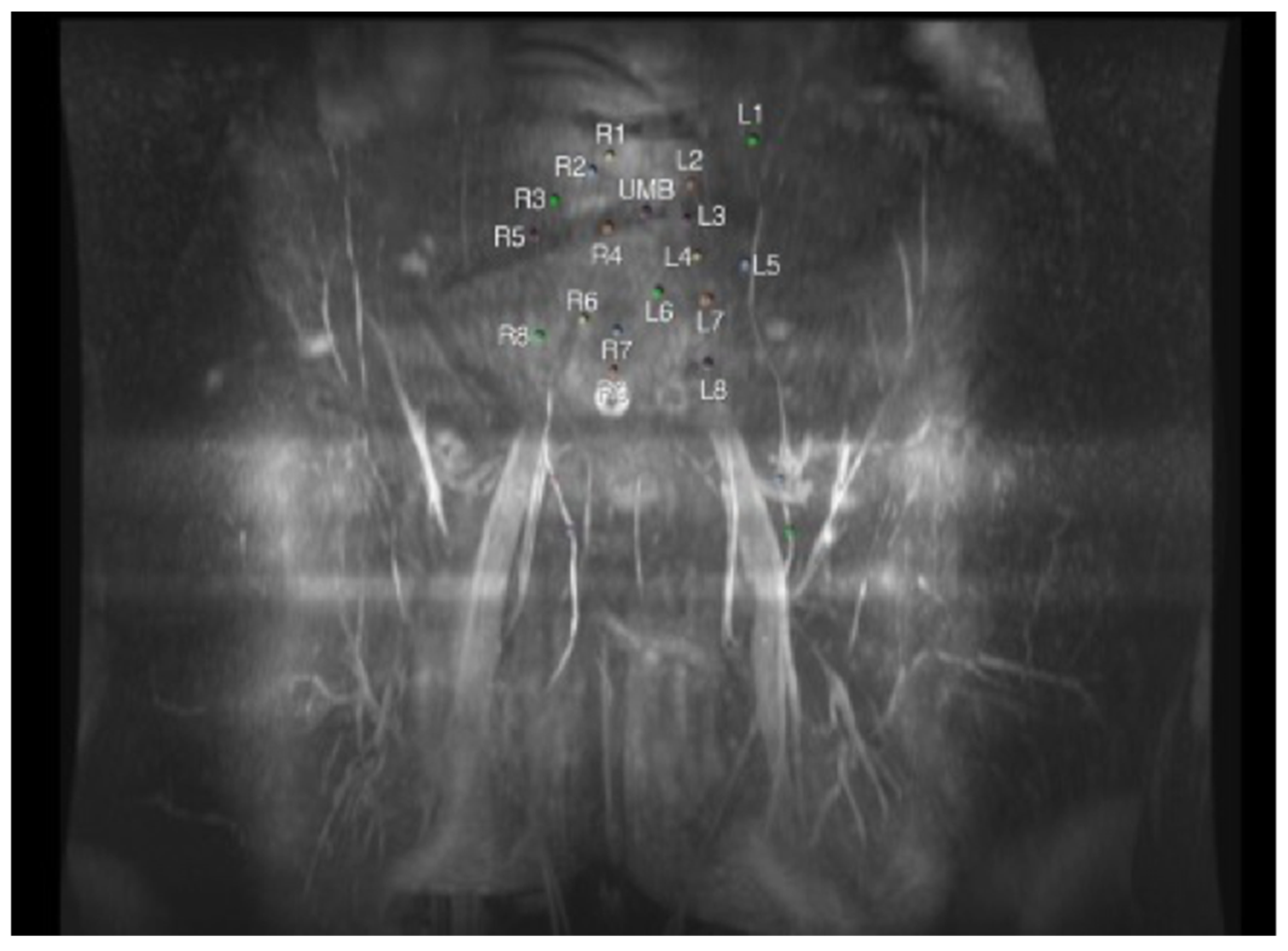
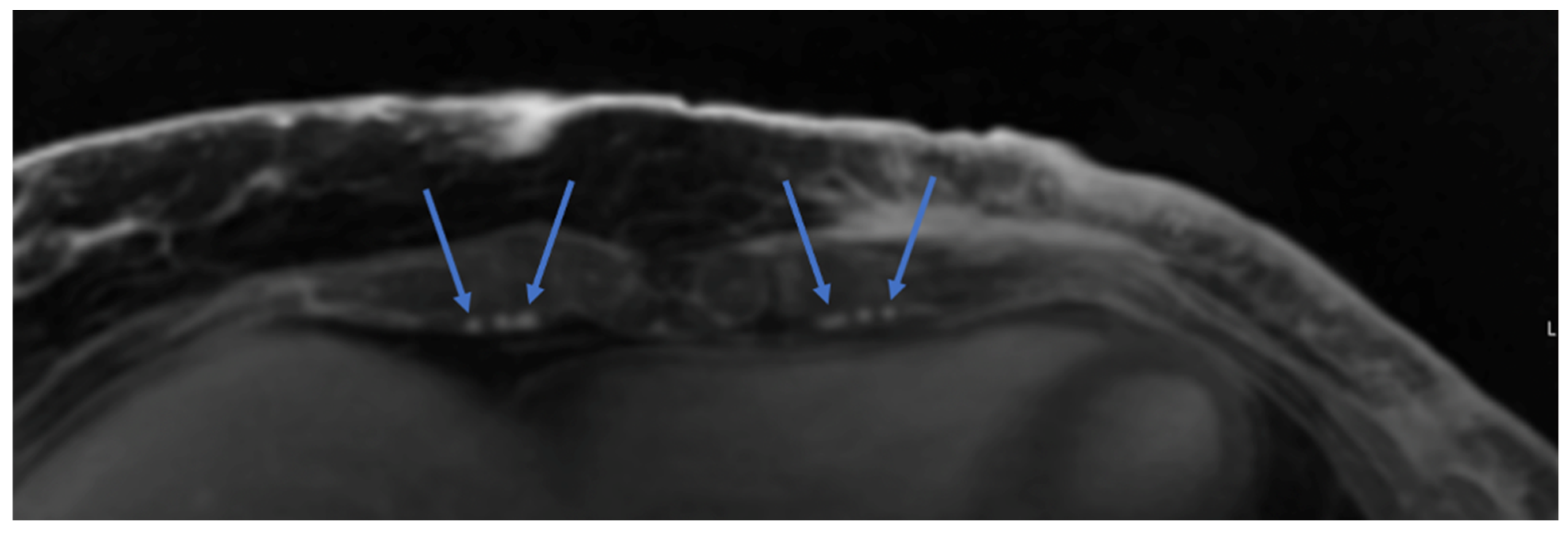
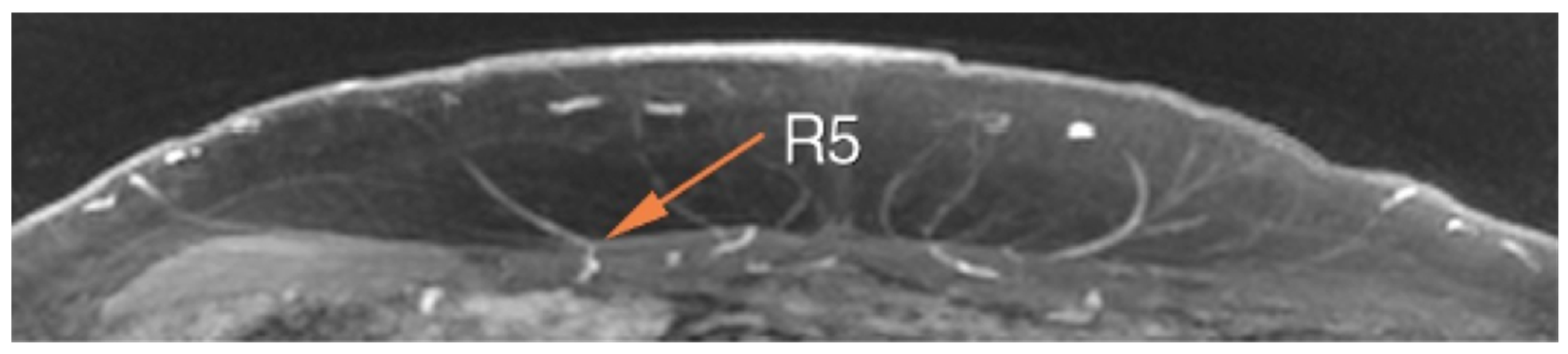


| Imaging Modality | Perforator Location | Perforator Size | Intramuscular Anatomy | Subcutaneous Branching | Superficial System | Recipient Vessels | Flow Assessment | Perfusion Assessment | Downsides |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasound | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | No | Operator dependent |
| CTA | Yes | Yes | Variable | Variable | Yes | Yes | No | No | Ionizing radiation |
| MRA | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Costly |
| Dye-based angiography | Yes | No | No | No | No | No | No | Yes | Limited to surface |
| 3D surface imaging | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | Software limitations |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Coleman-Belin, J.C.; Barnett, J.; Khavanin, N.; Nelson, J.A.; Stern, C.S.; Allen, R.J., Jr. Imaging in Autologous Breast Reconstruction. Cancers 2024, 16, 2851. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162851
Coleman-Belin JC, Barnett J, Khavanin N, Nelson JA, Stern CS, Allen RJ Jr. Imaging in Autologous Breast Reconstruction. Cancers. 2024; 16(16):2851. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162851
Chicago/Turabian StyleColeman-Belin, Janet C., Joshua Barnett, Nima Khavanin, Jonas A. Nelson, Carrie S. Stern, and Robert J. Allen, Jr. 2024. "Imaging in Autologous Breast Reconstruction" Cancers 16, no. 16: 2851. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162851
APA StyleColeman-Belin, J. C., Barnett, J., Khavanin, N., Nelson, J. A., Stern, C. S., & Allen, R. J., Jr. (2024). Imaging in Autologous Breast Reconstruction. Cancers, 16(16), 2851. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16162851







