Hippocampal-Avoidance Whole-Brain Radiotherapy: Dosimetric Comparison of 3D-CRT, IMRT, and VMAT for Brain Metastases from Lung Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Equipment
2.3. Methodology
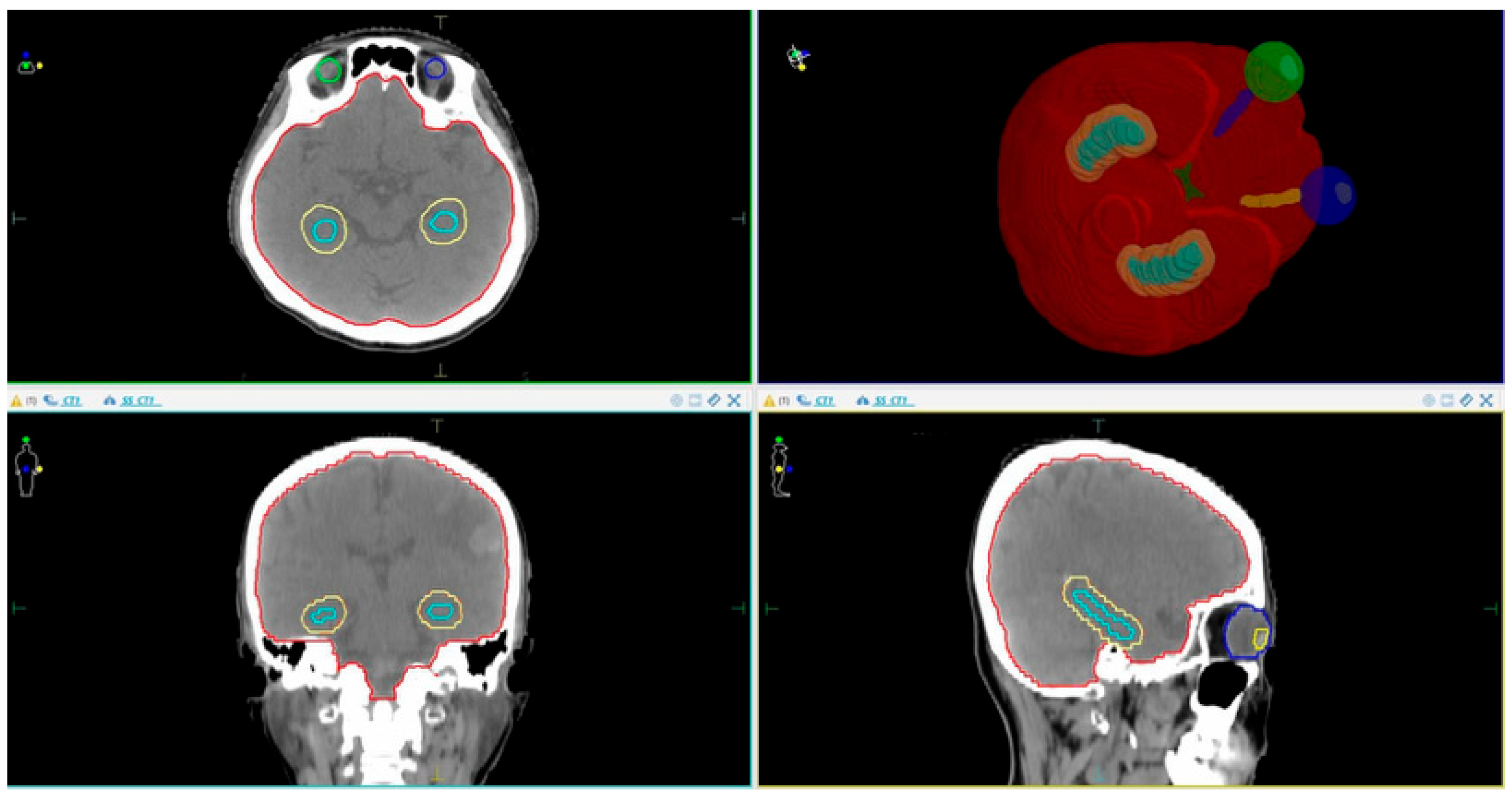
2.3.1. Patient Simulation CT Imaging and Volume Delineation Data
- CTV (Clinical Target Volume): This covers the entire brain up to C1 if there is no posterior fossa metastasis, or up to C2 if posterior fossa metastasis is present.
- PTV (Planning Target Volume): This is defined as the CTV + 3 mm, excluding the hippocampal margin.
- OARs (Organs at Risk): These include the eyeballs, lenses, optic nerves (left and right), optic chiasm, hippocampus, and hippocampal avoidance zone (hippocampus + 5 mm margin).
2.3.2. Radiotherapy Dose Prescription
2.3.3. Treatment Planning
- 3D-CRT Planning: Designed with two opposed lateral fields at gantry angles of 90° and 270°, with a collimator rotation of 5° to optimize eye shielding. The field size was extended to cover the entire PTV. The Collapsed Cone algorithm was used for dose calculation.
- HA-WBRT using IMRT: This plan utilized nine fields, each with a collimator angle of 45°. In our study, the 45° collimator angle was selected because this practice is consistent with the literature [15,16], helping to reduce the tongue-and-groove effect and facilitating dose modulation in concave anatomical regions such as the hippocampus. The Monte Carlo algorithm was applied.
- HA-WBRT using VMAT: The plan incorporated a single beam consisting of three full arcs (360° rotation), the collimator being set to 45°.
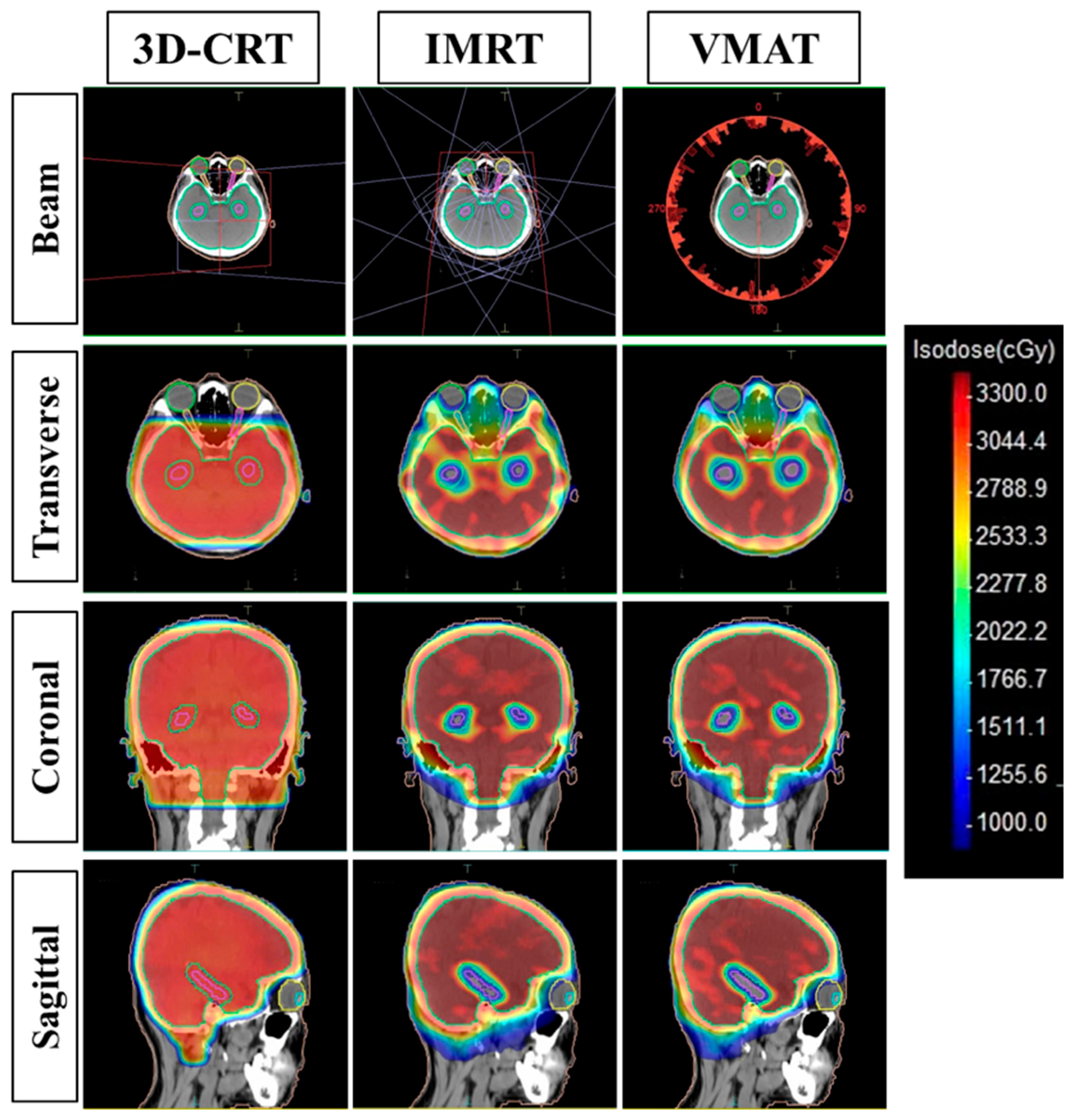
2.3.4. Treatment Plan Evaluation Criteria
- D2% is the absorbed dose value close to the Dmax, received by 2% of the PTV volume;
- D98% is the absorbed dose value close to the Dmin, received by 98% of the PTV volume;
- Drx is the prescribed dose to the PTV volume.
- Vri is the volume enclosed by the reference isodose line;
- TV is the PTV volume.
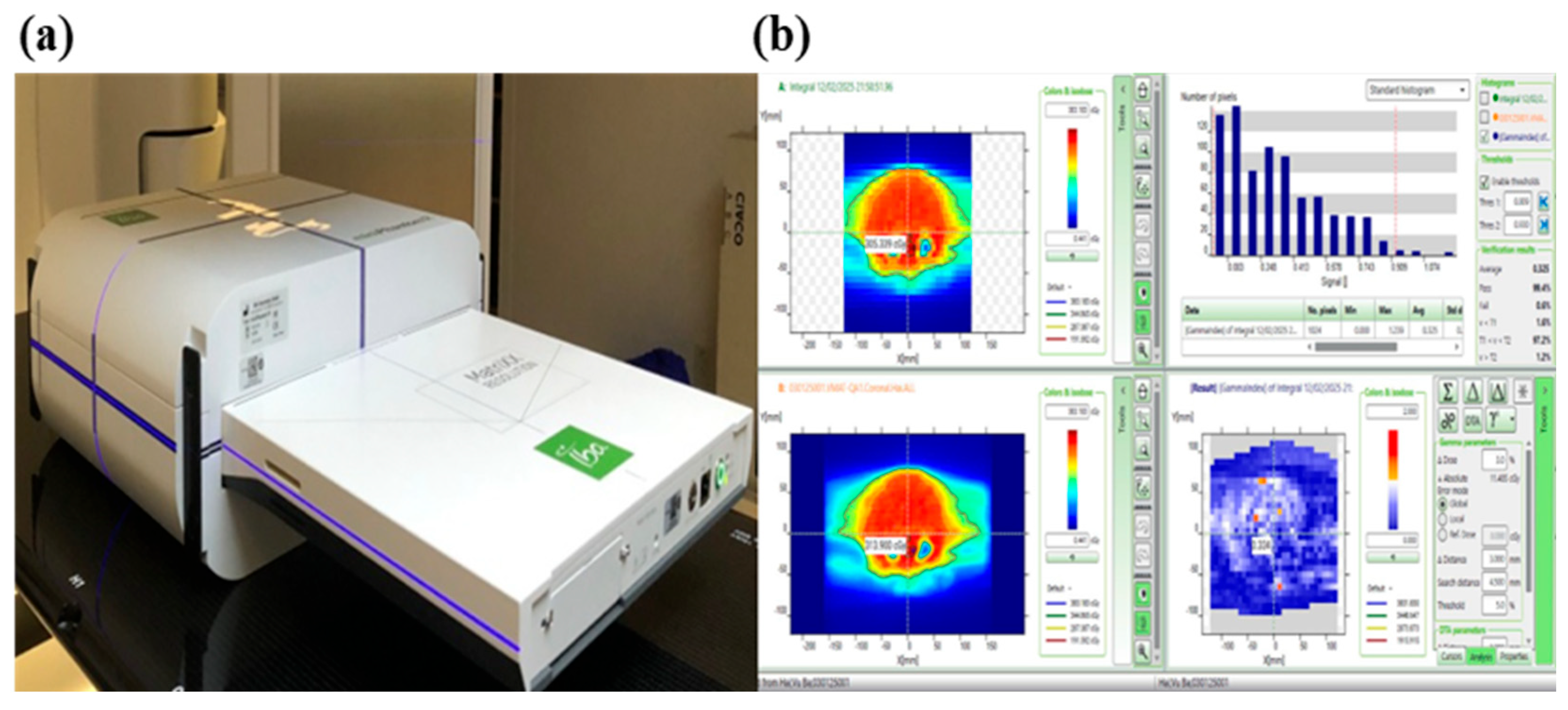
2.3.5. Treatment Plan Quality Assurance (QA Plan)
2.3.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
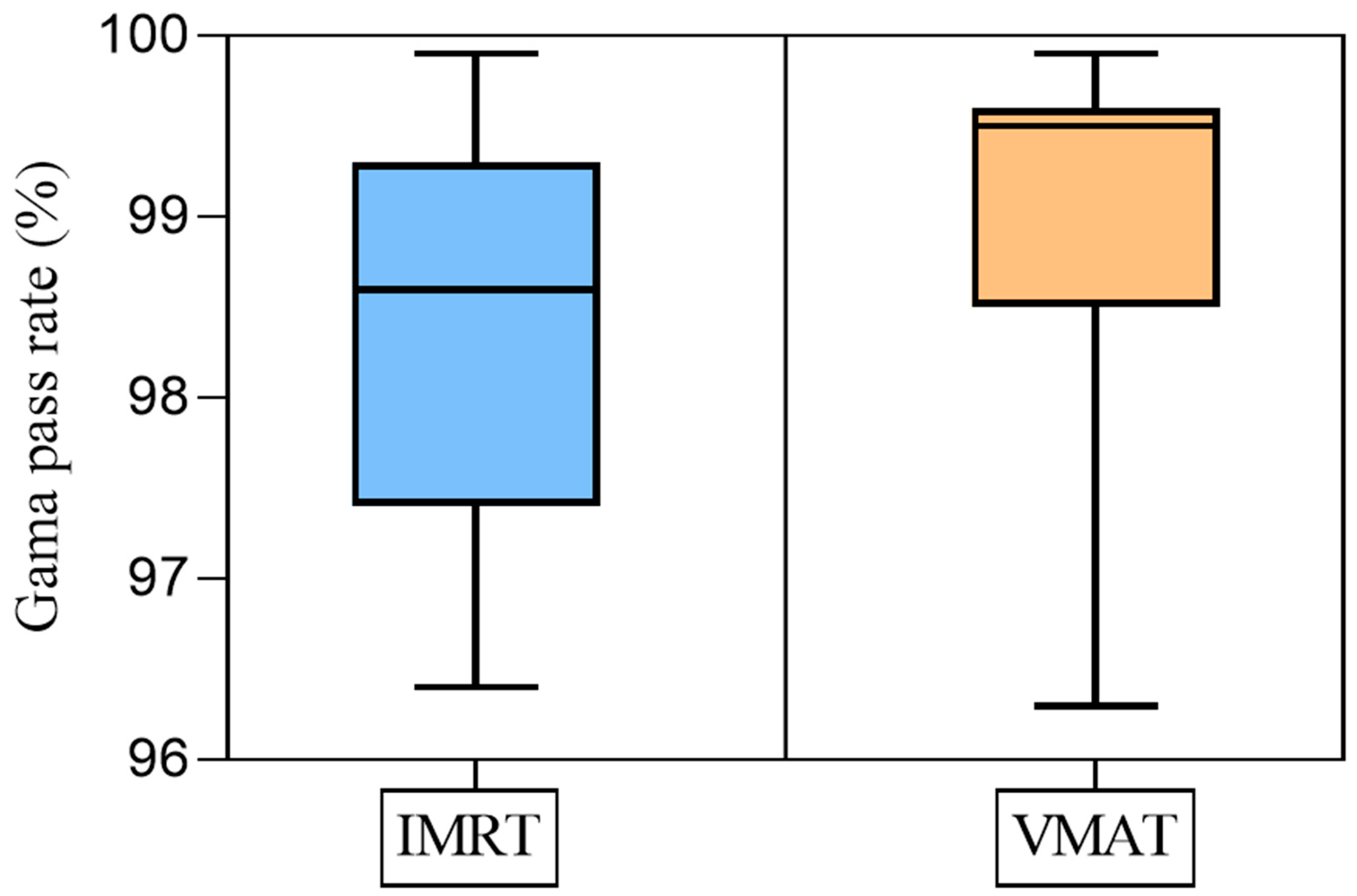
3.1. QA Plan
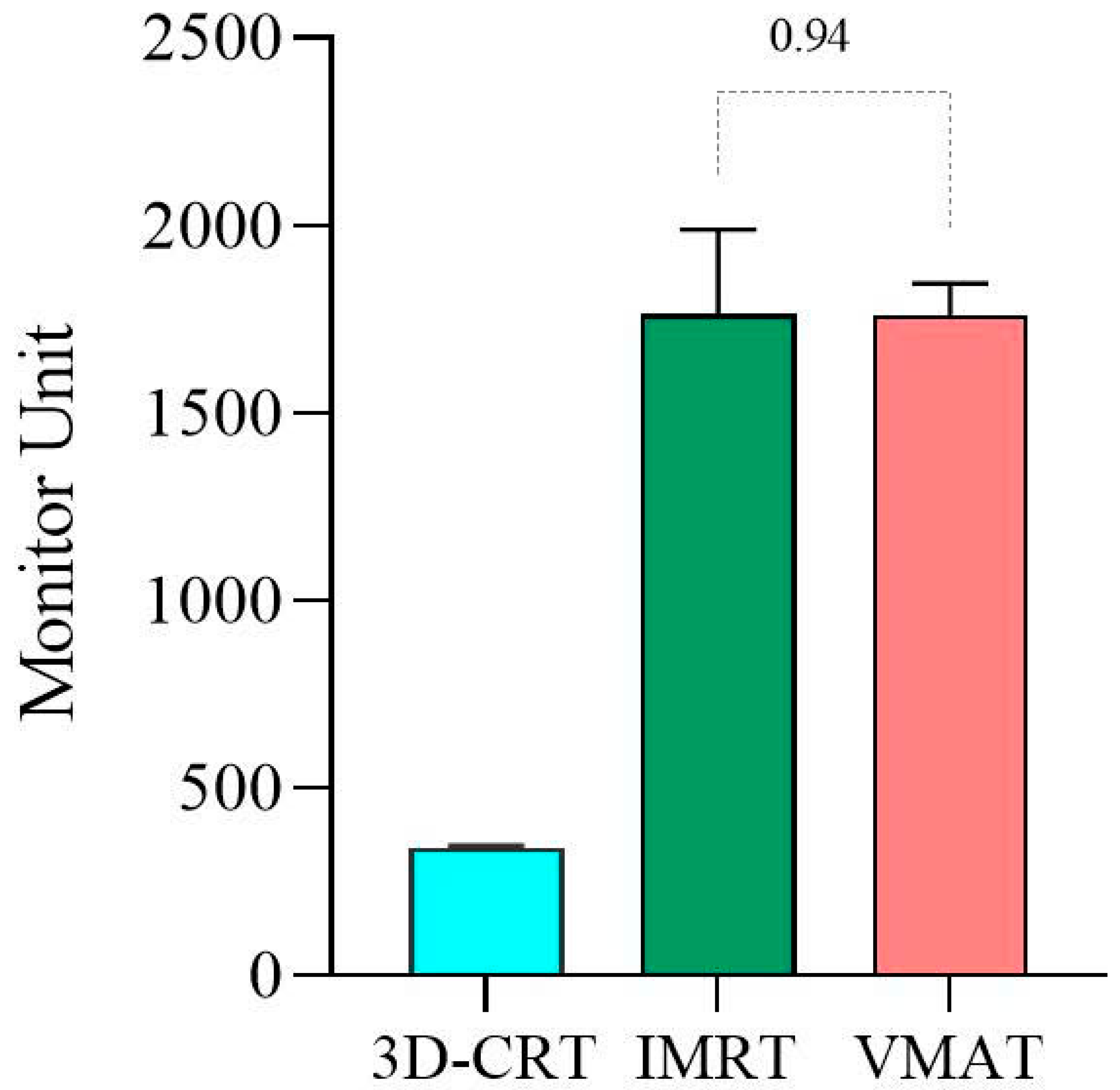
3.2. Dosimetric Evaluation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sas-Korczynska, B.; Rucinska, M. WBRT for brain metastases from non-small cell lung cancer: For whom and when?—Contemporary point of view. J. Thorac Dis. 2021, 13, 3246–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondi, V.; Pugh, S.L.; Tome, W.A.; Caine, C.; Corn, B.; Kanner, A.; Rowley, H.; Kundapur, V.; DeNittis, A.; Greenspoon, J.N.; et al. Preservation of Memory with Conformal Avoidance of the Hippocampal Neural Stem-Cell Compartment During Whole-Brain Radiotherapy for Brain Metastases (RTOG 0933): A Phase II Multi-Institutional Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3810–3816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondi, V.; Hermann, B.P.; Mehta, M.P.; Tomé, W.A. Hippocampal dosimetry predicts neurocognitive function impairment after fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy for benign or low-grade adult brain tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 83, e487–e493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monje, M.L.; Mizumatsu, S.; Fike, J.R.; Palmer, T.D. Irradiation induces neural precursor-cell dysfunction. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 955–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondi, V.; Tomé, W.A.; Mehta, M.P. Why avoid the hippocampus? A comprehensive review. Radiother. Oncol. J. Eur. Soc. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2010, 97, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Pugh, S.; Laack, N.N.; Wefel, J.S.; Khuntia, D.; Meyers, C.; Choucair, A.; Fox, S.; Suh, J.H.; Roberge, D.; et al. Memantine for the prevention of cognitive dysfunction in patients receiving whole-brain radiotherapy: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, P.D.; Gondi, V.; Pugh, S.; Tome, W.A.; Wefel, J.S.; Armstrong, T.S.; Bovi, J.A.; Robinson, C.; Konski, A.; Khuntia, D.; et al. Hippocampal Avoidance During Whole-Brain Radiotherapy Plus Memantine for Patients With Brain Metastases: Phase III Trial NRG Oncology CC001. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1019–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, P.D.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Khan, O.H.; Asher, A.L.; Wefel, J.S.; Gondi, V. Whole-Brain Radiotherapy for Brain Metastases: Evolution or Revolution? J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 483–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sood, S.; Pokhrel, D.; McClinton, C.; Lominska, C.; Badkul, R.; Jiang, H.; Wang, F. Volumetric-modulated arc therapy (VMAT) for whole brain radiotherapy: Not only for hippocampal sparing, but also for reduction of dose to organs at risk. Med. Dosim. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Med. Dosim. 2017, 42, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Gong, G.; Meng, K.; Du, S.; Yin, Y. Hippocampal sparing in whole-brain radiotherapy for brain metastases: Controversy, technology and the future. Front Oncol 2024, 14, 1342669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Jin, S.; Zhang, H.; Zou, K.; Sheng, J.; Tang, J.; Zhao, W.; Yang, P.; Tang, L.; Lv, X.; et al. A simplified non-coplanar volumetric modulated arc therapy for the whole brain radiotherapy with hippocampus avoidance. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1143564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, D.T.; Oanh, L.T.; Son, N.D.; Loan, T.T.H.; Chow, J.C.L. Dosimetric and Monte Carlo verification of jaws-only IMRT plans calculated by the Collapsed Cone Convolution algorithm for head and neck cancers. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2019, 24, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thi Oanh, L.; Thanh Tai, D.; Thi Hong Loan, T.; Chow, J.C. Calculation of Jaws-only IMRT (JO-IMRT) dose distributions based on the AAPM TG-119 test cases using Monte Carlo simulation and Prowess Panther treatment planning system. Nucl. Eng. Technol. 2021, 53, 4098–4105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, D.T.; Son, N.D.; Loan, T.T.H.; Anson, H.P.W. Quality assurance of the jaws only-intensity modulated radiation therapy plans for head-and-neck cancer. Phys. Medica PM Int. J. Devoted Appl. Phys. Med. Biol. Off. J. Ital. Assoc. Biomed. Phys. AIFB 2017, 38, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nevelsky, A.; Ieumwananonthachai, N.; Kaidar-Person, O.; Bar-Deroma, R.; Nasrallah, H.; Ben-Yosef, R.; Kuten, A. Hippocampal-sparing whole-brain radiotherapy using the Elekta equipment. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2013, 14, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.-J.; Li, M.-H.; Cheng, H.-W.; Kuo, C.-Y.; Sun, W.-L.; Tsai, J.-T. Hippocampus-sparing whole-brain radiotherapy: Dosimetric comparison between non-coplanar and coplanar planning. Ther. Radiol. Oncol. 2021, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, D.T.; Phat, L.T.; Ngoc Anh, N.; Sang, H.V.T.; Loc, T.M.; Hai, N.X.; Sandwall, P.A.; Bradley, D.; Chow, J.C.L. Dosimetric and radiobiological comparison between conventional and hypofractionated breast treatment plans using the Halcyon system. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1259416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, D.T.; Oanh, L.T.; Phuong, P.H.; Sulieman, A.; Abolaban, F.A.; Omer, H.; Chow, J.C. Dosimetric and radiobiological comparison in head-and-neck radiotherapy using JO-IMRT and 3D-CRT. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 29, 103336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paddick, I. A simple scoring ratio to index the conformity of radiosurgical treatment plans. Tech. Note J. Neurosurg. 2000, 93 (Suppl. 3), 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ICRU Report 83, Prescribing, Recording, and Reporting Intensity-Modulated Photon-Beam Therapy (IMRT)—ICRU n.d. Available online: https://www.icru.org/report/prescribing-recording-and-reporting-intensity-modulated-photon-beam-therapy-imrticru-report-83/ (accessed on 22 April 2025).
- Tai, D.T.; Omer, H.; Quoc, L.C.; Hai, N.X.; Minh, T.V.; Sulieman, A.; Mattar, E.; Toufig, H.; Tamam, N.; Bradley, D.A. An open-source software for calculating 1D gamma index in radiation therapy. J. King Saud. Univ.-Sci. 2023, 35, 102937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzell, G.A.; Burmeister, J.W.; Dogan, N.; LoSasso, T.J.; Mechalakos, J.G.; Mihailidis, D.; Molineu, A.; Palta, J.R.; Ramsey, C.R.; Salter, B.J. IMRT commissioning: Multiple institution planning and dosimetry comparisons, a report from AAPM Task Group 119. Med. Phys. 2009, 36, 5359–5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.; Lenards, N.; Holson, J. Whole-brain hippocampal sparing radiation therapy: Volume-modulated arc therapy vs intensity-modulated radiation therapy case study. Med. Dosim. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Med. Dosim. 2016, 41, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondi, V.; Tolakanahalli, R.; Mehta, M.P.; Tewatia, D.; Rowley, H.; Kuo, J.S.; Khuntia, D.; Tomé, W.A. Hippocampal-sparing whole-brain radiotherapy: A “how-to” technique using helical tomotherapy and linear accelerator-based intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 78, 1244–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, R.; Kong, W.; Shang, J.; Zhe, H.; Wang, Y.-Y. Hippocampal-Sparing Whole-Brain Radiotherapy for Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2017, 18, 127–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goss, M.D.; Rowles, R.; Spanovich, L.; Wegner, R.E.; Hasan, S.; Horne, Z.D. Hippocampal-sparing whole brain volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) planning in Monaco: A “How-to” not pull your hair out. Med. Dosim. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Med. Dosim. 2021, 46, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, J.; Pawlicki, T.; Chen, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, S.B.; Ma, C.M. The MLC tongue-and-groove effect on IMRT dose distributions. Phys. Med. Biol. 2001, 46, 1039–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Khac, P.; Doanh, V.T.; Thao, M.T.; Tai, D.T.; Sandwall, P.; Sulieman, A.; Chow, J.C. Optimizing intensity-modulated radiation therapy for stage II nasopharyngeal cancer: A comparative study of 7-field and 9-field treatment plans. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2025, 236, 112700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phat, L.T.; Thao, M.T.; Kien, T.T.; Tai, D.T.; Sandwall, P.; Sulieman, A.; Tamam, N.; Yani, S.; Chow, J.C.L. Dosimetric analysis of beam number variations in IMRT for head-and-neck, breast, and pelvic cancers using Halcyon. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2025, 236, 112755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, F.; Carolan, H.; Nichol, A.; Cao, F.; Nuraney, N.; Lee, R.; Gete, E.; Wong, F.; Schmuland, M.; Heran, M.; et al. Whole Brain Radiotherapy With Hippocampal Avoidance and Simultaneous Integrated Boost for 1–3 Brain Metastases: A Feasibility Study Using Volumetric Modulated Arc Therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 76, 1480–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokic, V.; Wiedenmann, N.; Fels, F.; Schmucker, M.; Nieder, C.; Grosu, A.-L. Whole brain irradiation with hippocampal sparing and dose escalation on multiple brain metastases: A planning study on treatment concepts. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 85, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Per Protocol | Variation Acceptable |
|---|---|---|
| PTV | D2% ≤ 37.5 Gy | D2% > 37.5 Gy, ≤ 40 Gy |
| D98% ≥ 25 Gy | D98% < 25 Gy | |
| Hippocampus | D100% ≤ 9 Gy | D100% ≤ 10 Gy |
| Maximum dose ≤ 16 Gy | Maximum dose ≤ 17 Gy | |
| Optic Nerves and Chiasm | Maximum dose ≤ 37.5 Gy | Maximum dose ≤ 37.5 Gy |
| Structure | NRG-CC001 Dose Constraints | NRG-CC001 Dose Constraints–Variation Acceptable |
|---|---|---|
| PTV | D2% ≤ 37.5 Gy | D2% ≤ 37.5 to 40 Gy |
| D98% ≥ 25 Gy | D98% 22.5 to 25.0 Gy | |
| V30Gy ≥ 95% | V30Gy 90 to 95% | |
| Hippocampus, Right | D100% ≤ 9 Gy | D100% ≤ 9 Gy to 10 Gy |
| D0.03cc ≤ 16 Gy | D0.03cc ≤ 16 to 17 Gy | |
| Hippocampus, Left | D100% ≤ 9 Gy | D100% ≤ 9 Gy to 10 Gy |
| D0.03cc ≤ 16 Gy | D0.03cc ≤ 16 to 17 Gy | |
| Optic Nerve, Right | D0.03cc ≤ 30 Gy | D0.03cc ≤ 30 to 37.5 Gy |
| Optic Nerve, Left | D0.03cc ≤ 30 Gy | D0.03cc ≤ 30 to 37.5 Gy |
| Optic Chiasm | D0.03cc ≤ 30 Gy | D0.03cc ≤ 30 to 37.5 Gy |
| Dose Index | 3D-CRT | IMRT | VMAT | p1 | p2 | p3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D2% (Gy) | 32.0 ± 0.4 | 35.5 ± 0.4 | 35.1 ± 0.3 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0072 |
| D98% (Gy) | 29.3 ± 0.5 | 25.1 ± 0.7 | 25.8 ± 0.6 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0014 |
| V30Gy (%) | 95.5 ± 1.5 | 93.9 ± 0.6 | 95.3 ± 0.6 | 0.0007 | 0.5209 | <0.0001 |
| 3D-CRT | IMRT | VMAT | p1 | p2 | p3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HI | 0.11 ± 0.06 | 0.35 ± 0.02 | 0.31 ± 0.02 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0011 |
| CI | 0.98 ± 0.02 | 0.96 ± 0.01 | 0.96 ± 0.01 | 0.0007 | <0.0001 | 0.8275 |
| OARs | Dose Index | 3D-CRT | IMRT | VMAT | p1 | p2 | p3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
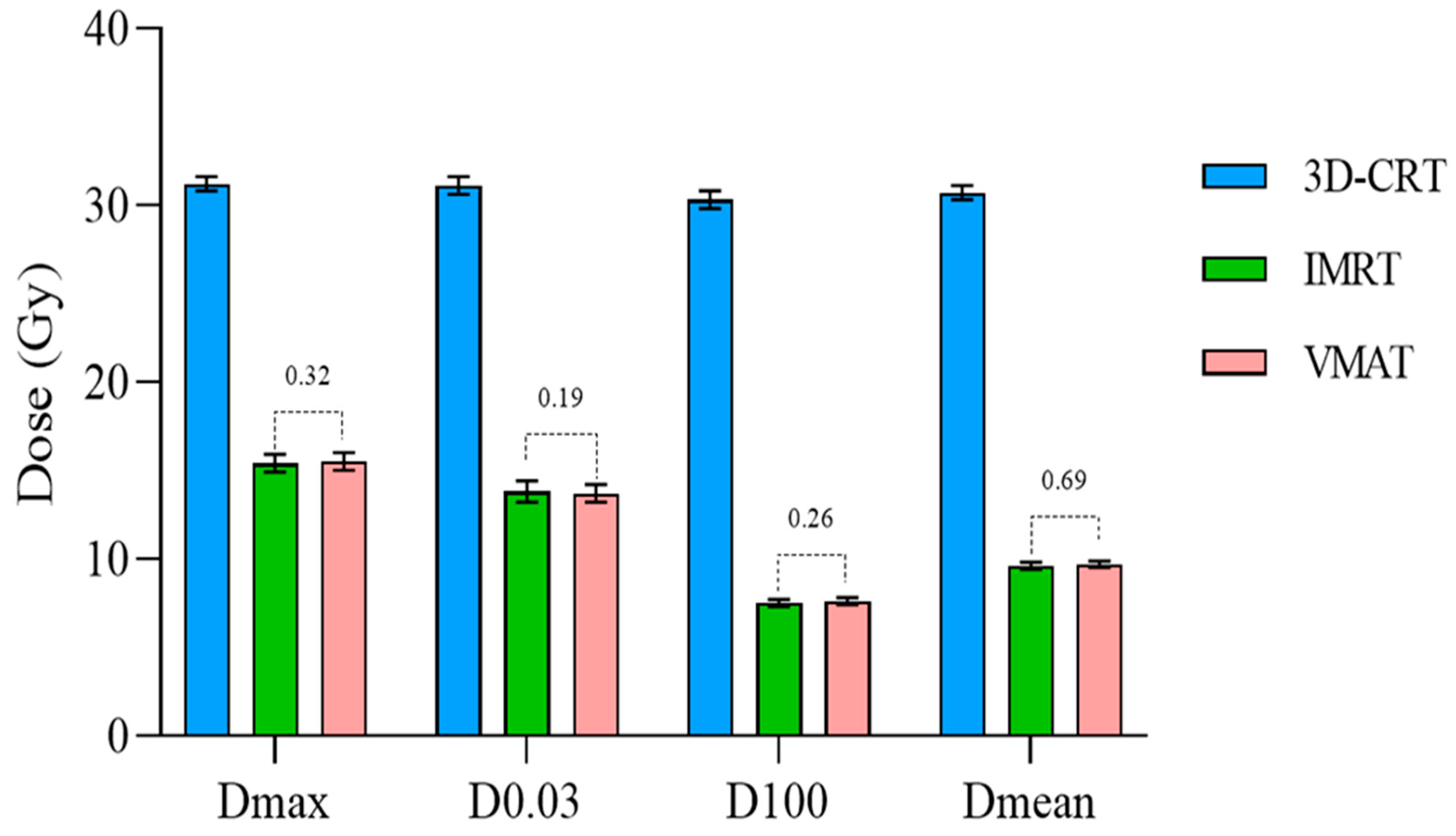
| Hippocampus | Dmax (Gy) | 31.2 ± 0.4 | 15.4 ± 0.5 | 15.5 ± 0.5 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.3200 |
| D0.03 cm3 (Gy) | 31.1 ± 0.5 | 13.8 ± 0.6 | 13.7 ± 0.5 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.1875 | |
| D100% (Gy) | 30.3 ± 0.5 | 7.5 ± 0.2 | 7.6 ± 0.2 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.2654 | |
| Dmean (Gy) | 30.7 ± 0.4 | 9.6 ± 0.2 | 9.7 ± 0.2 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.6927 | |
| Chiasm | Dmax (Gy) | 30.8 ± 0.5 | 29.0 ± 0.5 | 29.0 ± 0.8 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.6852 |
| D0.03 cm3 (Gy) | 30.8 ± 0.4 | 28.7 ± 0.3 | 28.0 ± 1.2 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0531 | |
| Left Lens | Dmax (Gy) | 2.7 ± 0.4 | 4.6 ± 0.2 | 4.7 ± 0.1 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.2843 |
| Right Lens | Dmax (Gy) | 2.8 ± 0.5 | 4.6 ± 0.1 | 4.6 ± 0.1 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.6578 |
| Left Optic Nerve | Dmax (Gy) | 30.8 ± 0.5 | 27.8 ± 1.3 | 28.2 ± 0.5 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.3341 |
| D0.03 cm3 (Gy) | 30.5 ± 0.3 | 26.5 ± 1.5 | 26.9 ± 1.2 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0349 | |
| Right Optic Nerve | Dmax (Gy) | 31.0 ± 0.3 | 27.7 ± 1.4 | 28.0 ± 1.3 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.3013 |
| D0.03 cm3 (Gy) | 30.6 ± 0.4 | 26.2 ± 1.9 | 26.8 ± 1.6 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.0542 | |
| Left Eye | Dmax (Gy) | 11.2 ± 1.3 | 21.1 ± 1.0 | 21.1 ± 0.7 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.8741 |
| Right Eye | Dmax (Gy) | 11.8 ± 1.9 | 20.6 ± 1.0 | 21.0 ± 1.1 | <0.0001 | <0.0001 | 0.2854 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thach, L.B.; Thao, M.T.; Nghia, N.V.; My, T.N.; Tai, D.T.; Tamam, N.; Sulieman, A.; Omer, H.; Toufig, H.; Bradley, D. Hippocampal-Avoidance Whole-Brain Radiotherapy: Dosimetric Comparison of 3D-CRT, IMRT, and VMAT for Brain Metastases from Lung Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17233744
Thach LB, Thao MT, Nghia NV, My TN, Tai DT, Tamam N, Sulieman A, Omer H, Toufig H, Bradley D. Hippocampal-Avoidance Whole-Brain Radiotherapy: Dosimetric Comparison of 3D-CRT, IMRT, and VMAT for Brain Metastases from Lung Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(23):3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17233744
Chicago/Turabian StyleThach, Le Ba, Mai Thi Thao, Nguyen Viet Nghia, Tran Nhat My, Duong Thanh Tai, Nissren Tamam, Abdelmoneim Sulieman, Hiba Omer, Hind Toufig, and David Bradley. 2025. "Hippocampal-Avoidance Whole-Brain Radiotherapy: Dosimetric Comparison of 3D-CRT, IMRT, and VMAT for Brain Metastases from Lung Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 23: 3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17233744
APA StyleThach, L. B., Thao, M. T., Nghia, N. V., My, T. N., Tai, D. T., Tamam, N., Sulieman, A., Omer, H., Toufig, H., & Bradley, D. (2025). Hippocampal-Avoidance Whole-Brain Radiotherapy: Dosimetric Comparison of 3D-CRT, IMRT, and VMAT for Brain Metastases from Lung Cancer. Cancers, 17(23), 3744. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17233744







