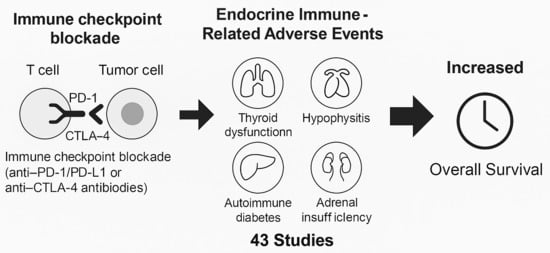
Prognostic Significance of Endocrine-Related Adverse Events in Patients with Melanoma, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Urothelial Cancer After Treatment with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Objective
2.2. Search Strategy and Data Sources
2.3. Eligibility Criteria
2.4. Data Selection and Analysis
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
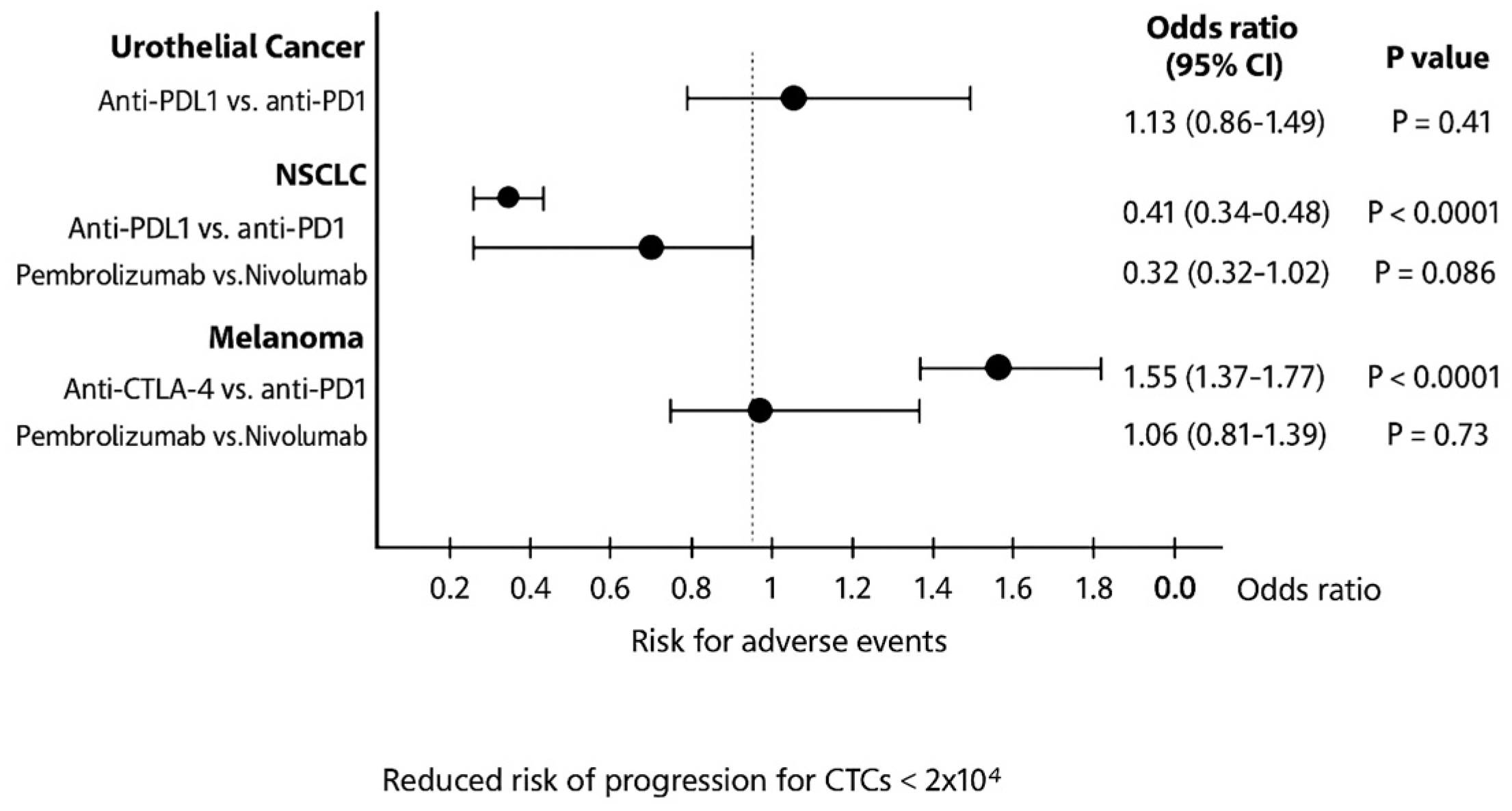
3.1. Stratification by ICI Class (PD-1/PD-L1 vs. CTLA-4)
3.2. Stratification by Adverse Events and Therapeutic Agent
3.3. Stratification by Adverse-Event Onset
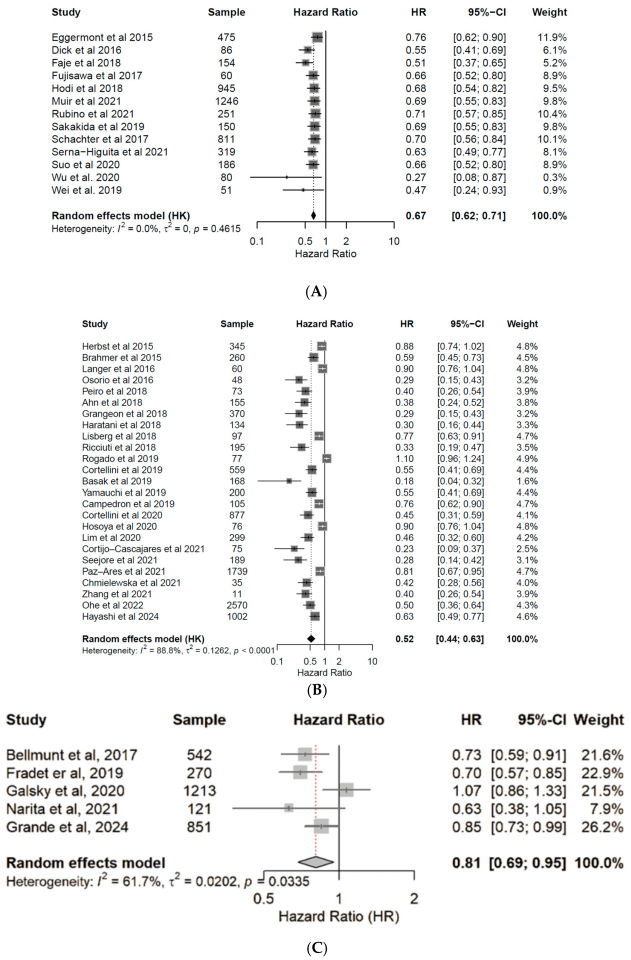
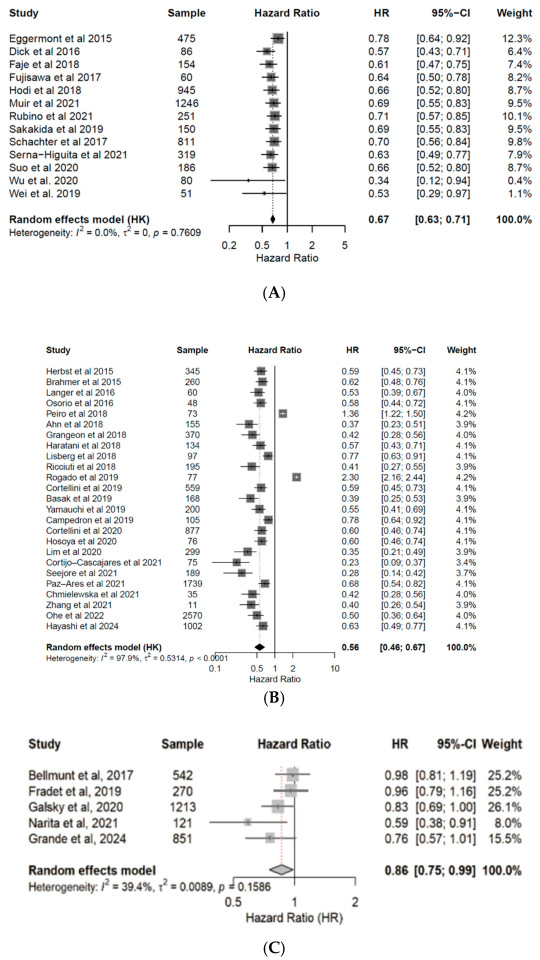
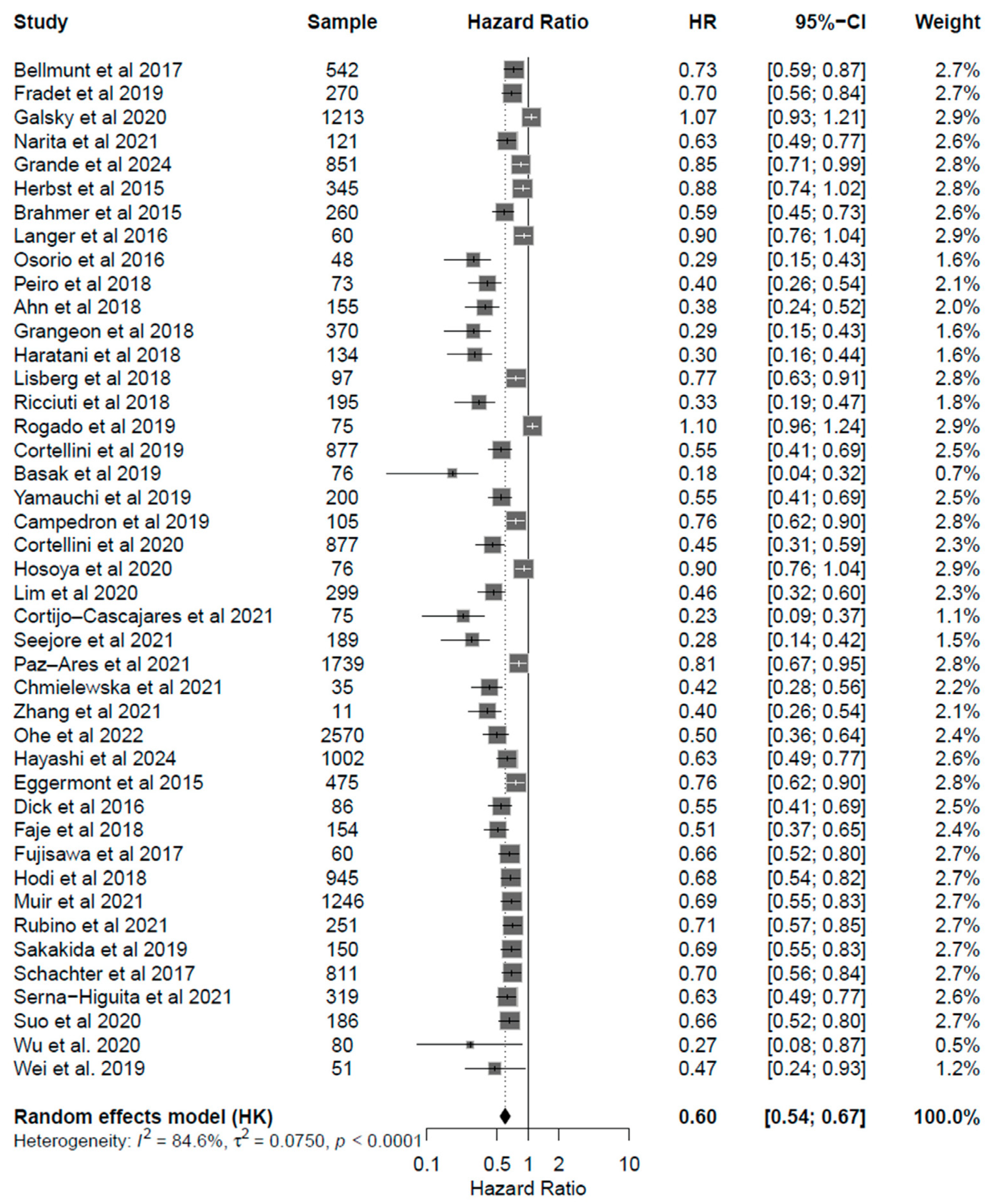
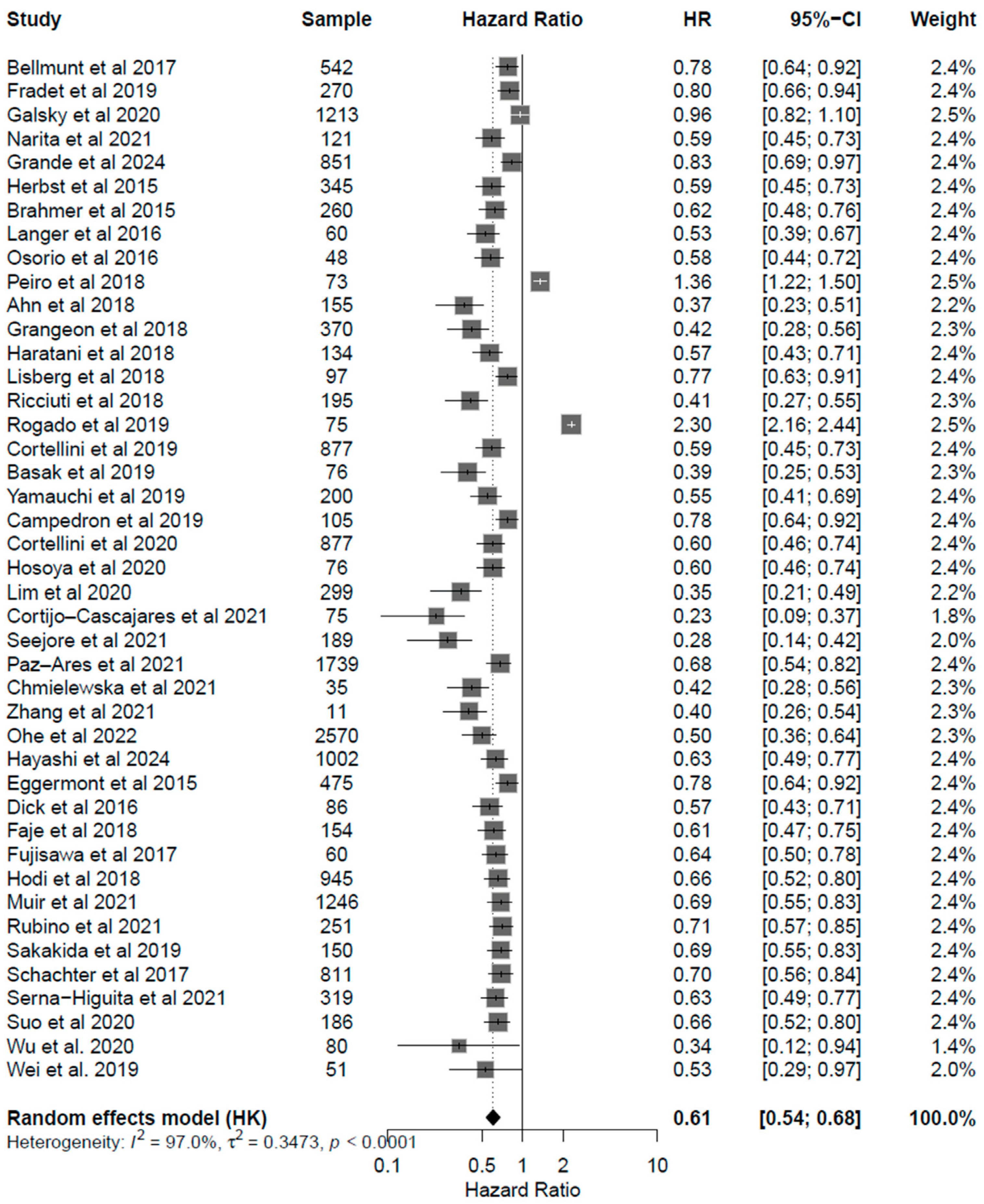
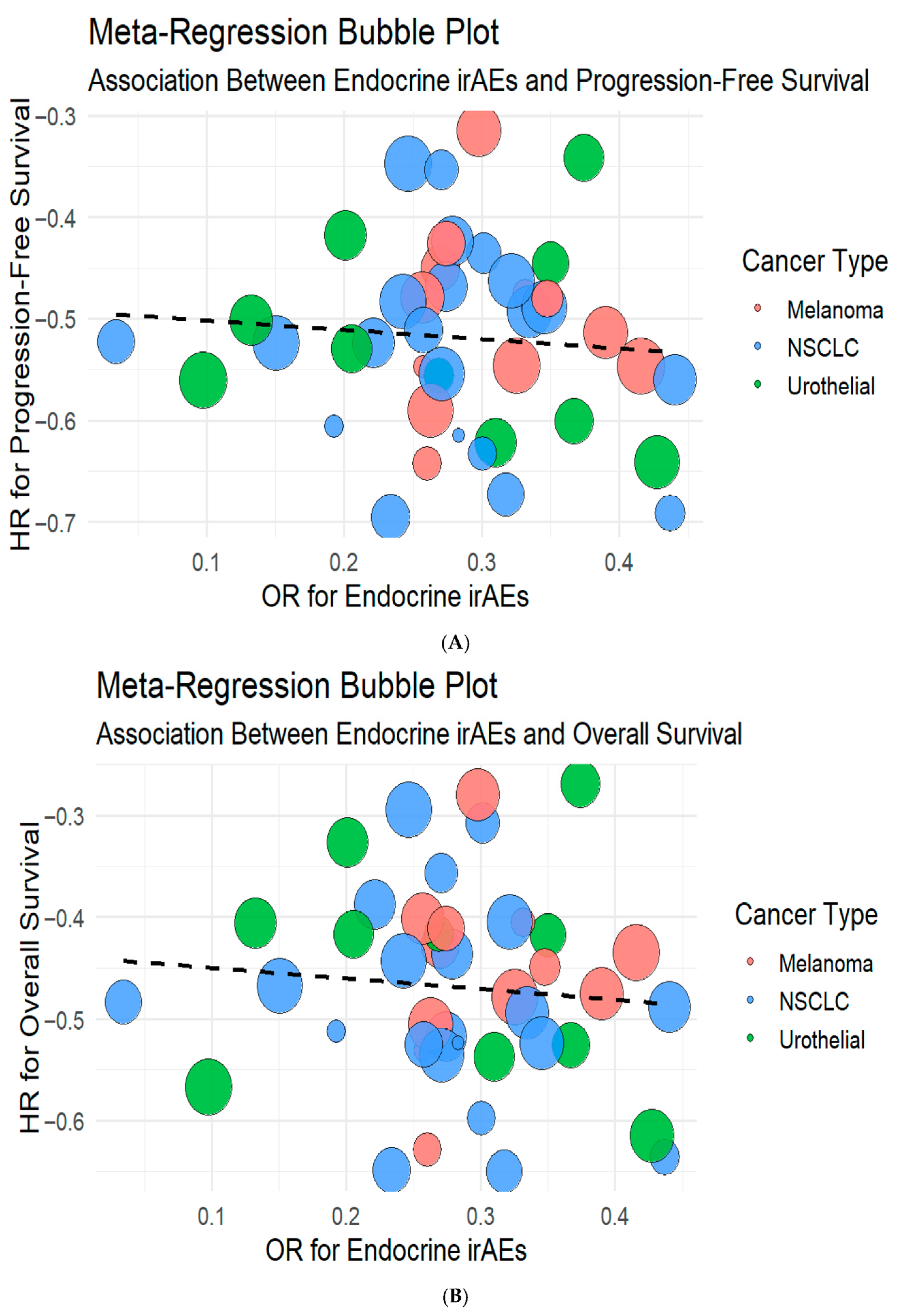
3.4. Correlation of Endocrine irAEs with ICI Response and Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ICIs | Immune checkpoint inhibitors |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| HR | Hazard ratio |
| OR | Odds ratio |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| PD-1 | Programmed cell death protein 1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed death-ligand 1 |
| CTLA-4 | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte–associated antigen 4 |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| CIADM | Checkpoint inhibitor-associated autoimmune diabetes mellitus |
| irAEs | Immune-related adverse events |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance |
| HbA1c | Hemoglobin A1c |
| FSH | follicle stimulating hormone |
| LH | luteinizing hormone |
| CRH | corticotropin-releasing hormone |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichtenstein, P.; Holm, N.V.; Verkasalo, P.K.; Iliadou, A.; Kaprio, J.; Koskenvuo, M.; Pukkala, E.; Skytthe, A.; Hemminki, K. Environmental and heritable factors in the causation of cancer—analyses of cohorts of twins from Sweden, Denmark, and Finland. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, R.L.; Kratzer, T.B.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2025. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2025, 75, 10–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchbinder, E.I.; Desai, A. CTLA-4 and PD-1 Pathways: Similarities, Differences, and Implications of Their Inhibition. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 39, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooksley, T.; Girotra, M.; Ginex, P.; Gordon, R.A.; Anderson, R.; Blidner, A.; Choi, J.; Dougan, M.; Glezerman, I.; Gupta, D.; et al. Multinational Association of Supportive Care in Cancer (MASCC) 2020 clinical practice recommendations for the management of immune checkpoint inhibitor endocrinopathies and the role of advanced practice providers in the management of immune-mediated toxicities. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 6175–6181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A.; Wolchok, J.D. Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science 2018, 359, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.S.; Barroso-Sousa, R.; Tolaney, S.M.; Hodi, F.S.; Kaiser, U.B.; Min, L. Endocrine toxicity of cancer immunotherapy targeting immune checkpoints. Endocr. Rev. 2018, 40, 17–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allouchery, M.; Lombard, T.; Martin, M.; Rouby, F.; Sassier, M.; Bertin, C.; Atzenhoffer, M.; Miremont-Salame, G.; Perault-Pochat, M.C.; Puyade, M. Safety of immune checkpoint inhibitor rechallenge after discontinuation for grade ≥ 2 immune-related adverse events in patients with cancer. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouhlel, L.; Doyen, J.; Chamorey, E.; Poudenx, M.; Ilie, M.; Gal, J.; Guigay, J.; Benzaquen, J.; Marquette, C.H.; Berthet, J.P.; et al. Occurrence and number of immune-related adverse events are independently associated with survival in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer treated by nivolumab. Bull. Cancer 2020, 107, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chera, A.; Stancu, A.L.; Bucur, O. Thyroid-related adverse events induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1010279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, X.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Lin, X. Immune checkpoint inhibitor-associated thyroid dysfunction: A disproportionality analysis using the WHO Adverse Drug Reaction Database, VigiBase. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 182, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garon-Czmil, J.; Petitpain, N.; Rouby, F.; Sassier, M.; Babai, S.; Yelehe-Okouma, M.; Weryha, G.; Klein, M.; Gillet, P. Thyroiditis and immune check point inhibitors: The post-marketing experience using the French National Pharmacovigilance database. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 2019, 33, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, P.B.; Coelho, M.C.A.; Arruda, M.; Gadelha, M.R.; Neto, L.V. Ipilimumab-induced hypophysitis: Review of the literature. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2015, 38, 1159–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castillero, F.; Castillo-Fernández, O.; Jiménez-Jiménez, G.; Fallas-Ramírez, J.; Peralta-Álvarez, M.P.; Arrieta, O. Cancer immunotherapy-associated hypophysitis. Futur. Oncol. 2019, 15, 3159–3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanie, K.; Iguchi, G.; Bando, H.; Fujita, Y.; Odake, Y.; Yoshida, K.; Matsumoto, R.; Fukuoka, R.; Ogawa, W.; Takahasi, Y. Two Cases of Atezolizumab-Induced Hypophysitis. J. Endocr. Soc. 2018, 2, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.; Varlamov, E.V.; McCartney, S.; Fleseriu, M. A Novel Etiology of Hypophysitis: Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 49, 387–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okano, Y.; Satoh, T.; Horiguchi, K.; Toyoda, M.; Osaki, A.; Matsumoto, S.; Tomaru, T.; Nakajima, Y.; Ishii, S.; Ozawa, A.; et al. Nivolumab-induced hypophysitis in a patient with advanced malignant melanoma. Endocr. J. 2016, 63, 905–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee. 2. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2025. Diabetes Care 2025, 48, S27–S49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Tsang, V.; Menzies, A.M.; Sasson, S.C.; Carlino, M.S.; Brown, D.A.; Clifton-Bligh, R.; Gunton, J.E. Risk Factors and Characteristics of Checkpoint Inhibitor-Associated Autoimmune Diabetes Mellitus (CIADM): A Systematic Review and Delineation From Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 1292–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martella, S.; Lucas, M.; Porcu, M.; Perra, L.; Denaro, N.; Pretta, A.; Deias, G.; Willard-Gallo, K.; Sotto Parra, H.; Saba, L.; et al. Primary adrenal insufficiency induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors: Biological, clinical, and radiological aspects. Semin. Oncol. 2023, 50, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorlund, K.; Imberger, G.; Johnston, B.C.; Walsh, M.; Awad, T.; Thabane, L.; Gluud, C.; Devereaux, P.J.; Wetterslev, J. Evolution of Heterogeneity (I2) Estimates and Their 95% Confidence Intervals in Large Meta-Analyses. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e39471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Chu, H. Quantifying Publication Bias in Meta-Analysis. Biometrics 2017, 74, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campredon, P.; Mouly, C.; Lusque, A.; Bigay-Game, L.; Bousquet, E.; Mazières, J.; Caron, P. Incidence of thyroid dysfunctions during treatment with nivolumab for non-small cell lung cancer: Retrospective study of 105 patients. Presse Medi. 2019, 48, e197–e207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggermont, A.M.M.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Grob, J.J.; Dummer, R.; Wolchok, J.D.; Schmidt, H.; Hamid, O.; Robert, C.; Ascierto, P.A.; Richards, J.M.; et al. Adjuvant ipilimumab versus placebo after complete resection of high-risk stage III melanoma (EORTC 18071): A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 522–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faje, A. Immunotherapy and hypophysitis: Clinical presentation, treatment, and biologic insights. Pituitary 2016, 19, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisawa, Y.; Yoshino, K.; Otsuka, A.; Funakoshi, T.; Uchi, H.; Fujimura, T.; Matsushita, S.; Hata, H.; Okuhira, H.; Tanaka, R.; et al. Retrospective study of advanced melanoma patients treated with ipilimumab after nivolumab: Analysis of 60 Japanese patients. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 89, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodi, F.S.; Chiarion-Sileni, V.; Gonzalez, R.; Grob, J.J.; Rutkowski, P.; Cowey, C.L.; Lao, C.D.; Schadendorf, D.; Wagstaff, J.; Dummer, R.; et al. Nivolumab plus ipilimumab or nivolumab alone versus ipilimumab alone in advanced melanoma (CheckMate 067): 4-year outcomes of a multicentre, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 1480–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muir, C.A.; Clifton-Bligh, R.J.; Long, G.V.; Scolyer, R.A.; Lo, S.N.; Carlino, M.S.; Tsang, V.H.M.; Menzies, A.M. Thyroid Immune-related Adverse Events Following Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 106, e3704–e3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubino, R.; Marini, A.; Roviello, G.; Presotto, E.M.; Desideri, I.; Ciardetti, I.; Brugia, M.; Pimpinelli, N.; Antonuzzo, L.; Mini, E.; et al. Endocrine-related adverse events in a large series of cancer patients treated with anti-PD1 therapy. Endocrine 2021, 74, 172–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakamuri, D.; Glitza, I.C.; Cuellar, S.L.B.; Subbiah, V.; Fu, S.; Tsimberidou, A.M.; Wheler, J.J.; Hong, D.S.; Naing, A.; Falchook, G.S.; et al. Phase I Dose-Escalation Study of Anti-CTLA-4 Antibody Ipilimumab and Lenalidomide in Patients with Advanced Cancers. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schachter, J.; Ribas, A.; Long, G.V.; Arance, A.; Grob, J.J.; Mortier, L.; Daud, A.; Carlino, M.S.; McNeil, C.; Lotem, M.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab for advanced melanoma: Final overall survival results of a multicentre, randomised, open-label phase 3 study (KEYNOTE-006). Lancet 2017, 390, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Bai, H.; Gao, Y. Thyroid dysfunction during PD-1 inhibitor treatment in patients with cancer: Incidence and association with progression-free survival. Oncol. Lett. 2022, 24, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Xu, Y.; Wang, X.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhao, H.; Liu, H.; Chai, X.; et al. Thyroid dysfunction after immune checkpoint inhibitor treatment in a single-center Chinese cohort: A retrospective study. Endocrine 2023, 81, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serna-Higuita, L.M.; Amaral, T.; Forschner, A.; Leiter, U.; Flatz, L.; Seeber, O.; Thomas, I.; Garbe, C.; Eigentler, T.K.; Martus, P. Association between Immune-Related Adverse Events and Survival in 319 Stage IV Melanoma Patients Treated with PD-1-Based Immunotherapy: An Approach Based on Clinical Chemistry. Cancers 2021, 13, 6141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahn, A.W.; Gill, D.M.; Agarwal, N.; Maughan, B.L. PD-1 checkpoint inhibition: Toxicities and management. Urol Oncol Semin Orig Investig. 2017, 35, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zheng, J.; Ren, C.; Ye, C.; Wu, X.; Lv, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, J. Risk factors of immune-related endocrine toxicities in non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with pembrolizumab and its impact on patient outcomes: A multicenter retrospective study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2025, 25, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrelli, F.; Grizzi, G.; Ghidini, M.; Ghidini, A.; Ratti, M.; Panni, S.; Cabiddu, M.; Ghilardi, M.; Borgonovo, K.; Parati, M.C.; et al. Immune-related Adverse Events and Survival in Solid Tumors Treated With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Immunother. 2020, 43, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, E.A.; Meer, J.W.M.V.D.; Hurkmans, D.P.; Schreurs, M.W.J.; Hoop, E.O.D.; Veldt, A.A.M.V.D.; Bins, S.; Joosse, A.; Koolen, S.L.W.; Debets, R.; et al. Overt Thyroid Dysfunction and Anti-Thyroid Antibodies Predict Response to Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy in Cancer Patients. Thyroid 2020, 30, 966–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, J.E.; Hoffman-Censits, J.; Powles, T.; Heijden, M.S.V.D.; Balar, A.V.; Necchi, A.; Dawson, N.; O’Donnell, P.H.; Balmanoukian, A.; Loriot, Y.; et al. Atezolizumab in patients with locally advanced and metastatic urothelial carcinoma who have progressed following treatment with platinum-based chemotherapy: A single-arm, multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1909–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Lee, J.S.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Caro, R.B.; Nishio, M.; Urban, L.; Audigier-Valette, C.; Lupinacci, L.; Sangha, R.; Pluzanski, A.; et al. Five-Year Survival Outcomes With Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab Versus Chemotherapy as First-Line Treatment for Metastatic Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer in CheckMate 227. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1200–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortellini, A.; Friedlaender, A.; Banna, G.L.; Porzio, G.; Bersanelli, M.; Cappuzzo, F.; Aerts, J.G.J.V.; Giusti, R.; Bria, E.; Cortinovis, D.; et al. Immune-related Adverse Events of Pembrolizumab in a Large Real-world Cohort of Patients With NSCLC With a PD-L1 Expression ≥ 50% and Their Relationship With Clinical Outcomes. Clin. Lung Cancer 2020, 21, 498–508.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortellini, A.; Chiari, R.; Ricciuti, B.; Metro, G.; Perrone, F.; Tiseo, M.; Bersanelli, M.; Bordi, P.; Santini, D.; Giusti, R.; et al. Correlations Between the Immune-related Adverse Events Spectrum and Efficacy of Anti-PD1 Immunotherapy in NSCLC Patients. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, 237–247.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortijo-Cascajares, S.; Cercós-Lletí, A.C.; Ortiz-Pérez, S.; Caro-Teller, J.M.; Ferrari-Piquero, J.M. Analysis of immune-mediated reactions in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with nivolumab and its association with effectiveness. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2023, 29, 290–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grangeon, M.; Tomasini, P.; Chaleat, S.; Jeanson, A.; Souquet-Bressand, M.; Khobta, N.; Bermudez, J.; Trigui, Y.; Greillier, L.; Blanchon, M.; et al. Association Between Immune-related Adverse Events and Efficacy of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Non–small-cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Lung Cancer 2019, 20, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haratani, K.; Hayashi, H.; Chiba, Y.; Kudo, K.; Yonesaka, K.; Kato, R.; Kaneda, H.; Hasegawa, Y.; Tanaka, T.; Takeda, M.; et al. Association of immune-related adverse events with nivolumab efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2018, 4, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, H.; Nishio, M.; Akamatsu, H.; Goto, Y.; Miura, S.; Gemma, A.; Yoshino, I.; Misumi, T.; Kijima, T.; Takase, N.; et al. Association between Immune-Related Adverse Events and Atezolizumab in Previously Treated Patients with Unresectable Advanced or Recurrent Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. Commun. 2024, 4, 2858–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbst, R.S.; Baas, P.; Kim, D.W.; Felip, E.; Pérez-Gracia, J.L.; Han, J.Y.; Molina, J.; Kim, J.H.; Dubos Arvis, C.; Ahn, M.J.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus docetaxel for previously treated, PD-L1-positive, advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-010): A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, C.J. Emerging Immunotherapies in the Treatment of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC): The Role of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 38, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narita, T.; Hatakeyama, S.; Numakura, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Muto, Y.; Saito, M.; Narita, S.; Tanaka, T.; Noro, D.; Tokui, N.; et al. Comparison of pembrolizumab with conventional chemotherapy after first-line platinum-based chemotherapy for advanced urothelial carcinoma in real-world practice: A multicenter retrospective study. Int. J. Urol. 2021, 28, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohe, Y.; Yamazaki, N.; Yamamoto, N.; Murakami, H.; Yoh, K.; Kitano, S.; Hashimoto, H.; Murayama, A.; Nakane, S.; Gemma, A. The real-world safety of atezolizumab as second-line or later treatment in Japanese patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: A post-marketing surveillance study. Jpn J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 52, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, J.C.; Ni, A.; Chaft, J.E.; Pollina, R.; Kasler, M.K.; Stephens, D.; Rodriguez, C.; Cambridge, L.; Rizvi, H.; Wolchok, J.D.; et al. Antibody-mediated thyroid dysfunction during T-cell checkpoint blockade in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol. 2017, 28, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.G.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Lee, J.S.; Urban, L.; Caro, R.B.; Park, K.; Sakai, H.; Ohe, Y.; Nishio, M.; et al. First-Line Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in Advanced NSCLC: 4-Year Outcomes From the Randomized, Open-Label, Phase 3 CheckMate 227 Part 1 Trial. J Thorac Oncol. 2022, 17, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peiró, I.; Palmero, R.; Iglesias, P.; Díez, J.J.; Simó-Servat, A.; Marín, J.A.; Jiménez, L.; Domingo-Domenech, E.; Mancho-Fora, N.; Nadal, E.; et al. Thyroid dysfunction induced by nivolumab: Searching for disease patterns and outcomes. Endocrine 2019, 64, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Levi, A.M.; Rogado, J.; Sanchez-Torres, J.M.; Colomer, R.; Marazuela, M. Nivolumab-induced thyroid dysfunction in patients with lung cancer. Endocrinol. Diabetes Nutr. 2019, 66, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogado, J.; Sánchez-Torres, J.M.; Romero-Laorden, N.; Ballesteros, A.I.; Pacheco-Barcia, V.; Ramos-Leví, A.; Arranz, R.; Gullón, P.; Donnay, O.; Adrados, M.; et al. Immune-related adverse events predict the therapeutic efficacy of anti–PD-1 antibodies in cancer patients. Eur. J. Cancer. 2019, 109, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seejore, K.; Giannoudi, M.; Osborn, D.; Lynch, J.M.; Al-Qaissi, A.; Dunwoodie, E.; Hook, J.; Marples, M.; Murray, R.D. Characterisation of the onset and severity of adrenal and thyroid dysfunction associated with CTLA4-related hypophysitis. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2021, 186, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonia, S.J.; Villegas, A.; Daniel, D.; Vicente, D.; Murakami, S.; Hui, R.; Yokoi, T.; Chiappori, A.; Lee, K.H.; de Wit, M.; et al. Durvalumab after Chemoradiotherapy in Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.K.; Wu, Y.L.; Kudaba, I.; Kowalski, D.M.; Cho, B.C.; Turna, H.Z.; Castro, G., Jr.; Srimuninnimit, V.; Laktionov, K.K.; Bondarenko, I.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for previously untreated, PD-L1-expressing, locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (KEYNOTE-042): A randomised, open-label, controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 1819–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, I.; Yasoda, A.; Matsumoto, S.; Sakamori, Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Nomura, M.; Otsuka, A.; Yamasaki, T.; Saito, R.; Kitamura, M.; et al. Incidence, features, and prognosis of immune-related adverse events involving the thyroid gland induced by nivolumab. PloS ONE 2019, 14, e0216954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chmielewska, I.; Dudzinska, M.; Szczyrek, M.; Swirska, J.; Wojas-Krawczyk, K.; Zwolak, A. Do endocrine adverse events predict longer progression-free survival among patients with non-small-cell lung cancer receiving nivolumab? PloS ONE 2021, 16, e0257484. [Google Scholar]
- Fradet, Y.; Bellmunt, J.; Vaughn, D.J.; Lee, J.L.; Fong, L.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Climent, M.A.; Petrylak, D.P.; Choueiri, T.K.; Necchi, A.; et al. Randomized phase III KEYNOTE-045 trial of pembrolizumab versus paclitaxel, docetaxel, or vinflunine in recurrent advanced urothelial cancer: Results of >2 years of follow-up. Ann. Oncol. Off. 2019, 30, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, S.K.; Hoffman-Censits, J.; Zheng, H.; Kaiser, C.; Tayama, D.; Bellmunt, J. Atezolizumab in Platinum-treated Locally Advanced or Metastatic Urothelial Carcinoma: Clinical Experience from an Expanded Access Study in the United States. Eur. Urol. 2018, 73, 800–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweis, R.F.; Galsky, M.D. Emerging role of immunotherapy in urothelial carcinoma—Immunobiology/biomarkers. Urol. Oncol. 2016, 34, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grande, E.; Arranz, J.; Santis, M.D.; Bamias, A.; Kikuchi, E.; Del Muro, X.G.; Park, S.H.; De Giorgi, U.; Alekseev, B.; Mencinger, M.; et al. Atezolizumab plus chemotherapy versus placebo plus chemotherapy in untreated locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma (IMvigor130): Final overall survival analysis results from a randomised, controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zezza, M.; Kosinski, C.; Mekoguem, C.; Marino, L.; Chtioui, H.; Pitteloud, N.; Lamine, F. Combined immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy with nivolumab and ipilimumab causing acute-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus following a single administration: Two case reports. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2019, 19, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karaviti, D.; Kani, E.R.; Karaviti, E.; Gerontiti, E.; Michalopoulou, O.; Stefanaki, K.; Kazakou, P.; Vasileiou, V.; Psaltopoulou, T.; Paschou, S. Thyroid disorders induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors. Endocrine 2024, 85, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, R.; Imbimbo, M.; Malouf, R.; Paget-Bailly, S.; Calais, F.; Marchal, C.; Westeel, V. Single or combined immune checkpoint inhibitors compared to first-line platinum-based chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for people with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 2021, CD013257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukushima, S. A review of adverse events caused by immune checkpoint inhibitors. Jpn. J. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 39, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoli, M.; Kaltsas, G.; Angelousi, A.; Alexandraki, K.; Randeva, H.; Kassi, E. Managing Ipilimumab-Induced Hypophysitis: Challenges and Current Therapeutic Strategies. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 9551–9561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fameli, A.; Nardone, V.; Azgomi, M.S.; Bianco, G.; Gandolfo, C.; Oliva, B.M.; Monoriti, M.; Saladino, R.E.; Falzea, A.; Romeo, C.; et al. PD-1/PD-L1 immune-checkpoint blockade induces immune effector cell modulation in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients: A single-cell flow cytometry approach. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 911579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, X.; Qu, J.; Zuo, W.; Tang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Chen, X. Immune-Related Adverse Events Associated With Outcomes in Patients With NSCLC Treated With Anti-PD-1 Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 708195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.B.; Friedman, D.L.; Berry, E.; Decker, I.; Ye, F.; Zhao, S.; Morgans, A.K.; Puzanov, I.; Sosman, J.A.; Lovly, C.M. Survivorship in Immune Therapy: Assessing Chronic Immune Toxicities, Health Outcomes, and Functional Status among Long-term Ipilimumab Survivors at a Single Referral Center. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppolzer, I.A.; Riester, J.; Büttner, R.; Burger, M.; Schnabel, M.J. Endocrine immune-related adverse events in patients with metastatic renal and urothelial cancer treated with immune checkpoint-inhibitors. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2023, 55, 1943–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassi, E.; Angelousi, A.; Asonitis, N.; Diamantopoulos, P.; Anastasopoulou, A.; Papaxoinis, G.; Kokkinos, M.; Giovanopoulos, I.; Kyriakakis, G.; Petychaki, F.; et al. Endocrine-related adverse events associated with immune-checkpoint inhibitors in patients with melanoma. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 6585–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, Y.M.M.; Wang, W.; McGregor, B.; Hamnvik, O.P.R. Associations between immune-related thyroid dysfunction and efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 71, 1795–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indini, A.; Guardo, L.D.; Cimminiello, C.; Prisciandaro, M.; Randon, G.; Braud, F.D.; Del Vecchio, M. Immune-related adverse events correlate with improved survival in patients undergoing anti-PD1 immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 145, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| P(opulation) | Patients with melanoma, NSCLC and urothelial cancer |
| I(ntervention) | Measurement of endocrine adverse events during patients’ follow-up |
| C(omparator) | Immune checkpoint inhibitors (anti-PD-(L)1 or anti-CTLA-4 agents) |
| O(utcome) | Progression Free Survival (PFS), Overall Survival (OS) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kopanos, S.; Filippatos, C.; Rousakis, P.; Kostopoulos, I.V.; Baxevanis, C.N.; Tentolouris, A.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Tsitsilonis, O.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I. Prognostic Significance of Endocrine-Related Adverse Events in Patients with Melanoma, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Urothelial Cancer After Treatment with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2025, 17, 3675. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17223675
Kopanos S, Filippatos C, Rousakis P, Kostopoulos IV, Baxevanis CN, Tentolouris A, Gavriatopoulou M, Tsitsilonis O, Ntanasis-Stathopoulos I. Prognostic Significance of Endocrine-Related Adverse Events in Patients with Melanoma, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Urothelial Cancer After Treatment with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers. 2025; 17(22):3675. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17223675
Chicago/Turabian StyleKopanos, Stylianos, Charalampos Filippatos, Pantelis Rousakis, Ioannis V. Kostopoulos, Constantin N. Baxevanis, Anastasios Tentolouris, Maria Gavriatopoulou, Ourania Tsitsilonis, and Ioannis Ntanasis-Stathopoulos. 2025. "Prognostic Significance of Endocrine-Related Adverse Events in Patients with Melanoma, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Urothelial Cancer After Treatment with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Cancers 17, no. 22: 3675. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17223675
APA StyleKopanos, S., Filippatos, C., Rousakis, P., Kostopoulos, I. V., Baxevanis, C. N., Tentolouris, A., Gavriatopoulou, M., Tsitsilonis, O., & Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I. (2025). Prognostic Significance of Endocrine-Related Adverse Events in Patients with Melanoma, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Urothelial Cancer After Treatment with Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers, 17(22), 3675. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17223675