Molecular Characterization of Polyomavirus-Positive and Negative Merkel Cell Carcinoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection from Participants
2.2. DNA Sequencing
2.3. Global Loss of Heterozygosity (gLoH)
2.4. COSMIC Mutational Signatures
2.5. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus Detection
2.6. RNA Sequencing
2.7. Immunotherapy-Related Biomarker Assessment
2.8. Immune Microenvironment
2.9. Real-World Survival Analysis
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
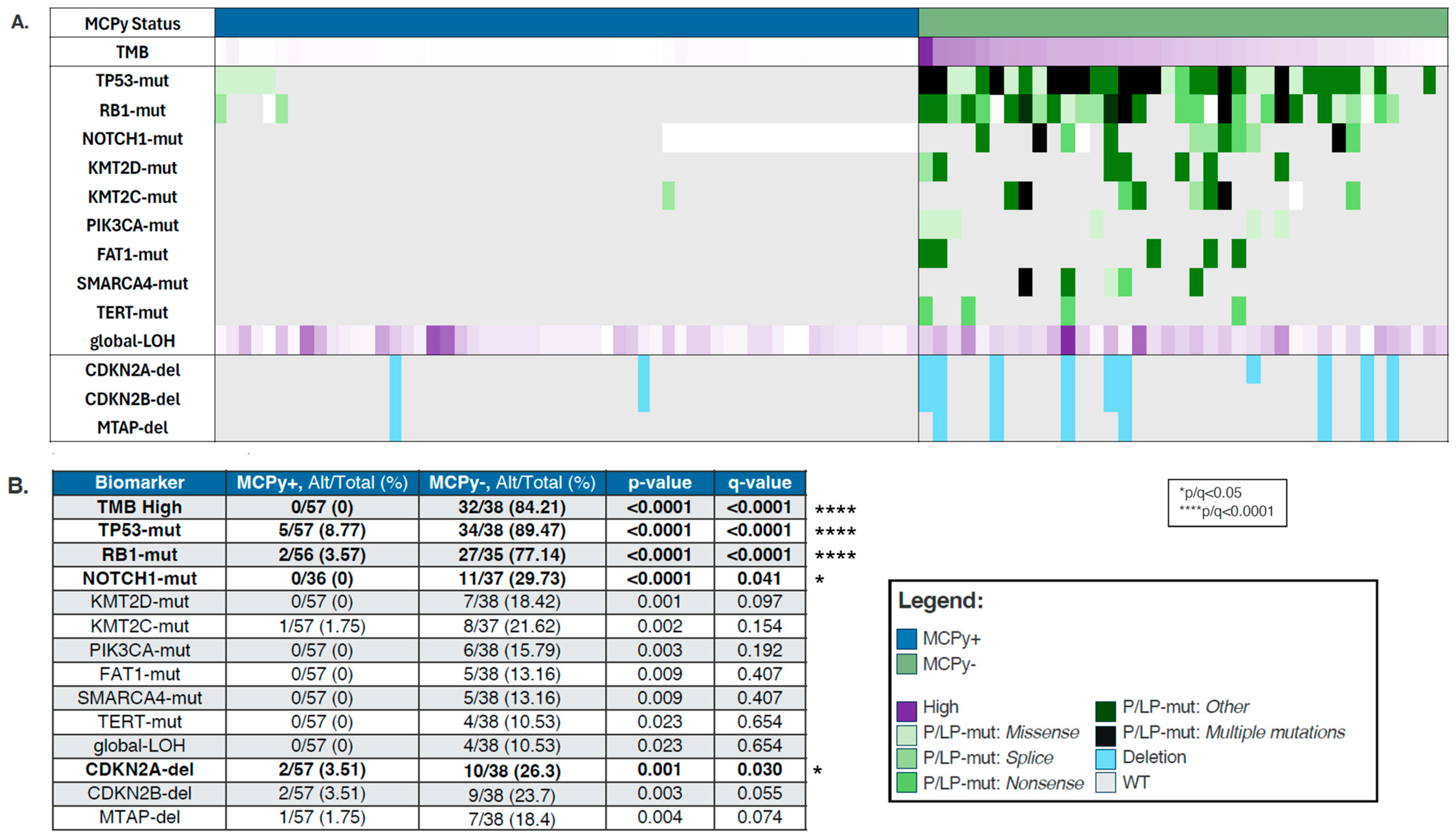
3.2. Mutational Differences
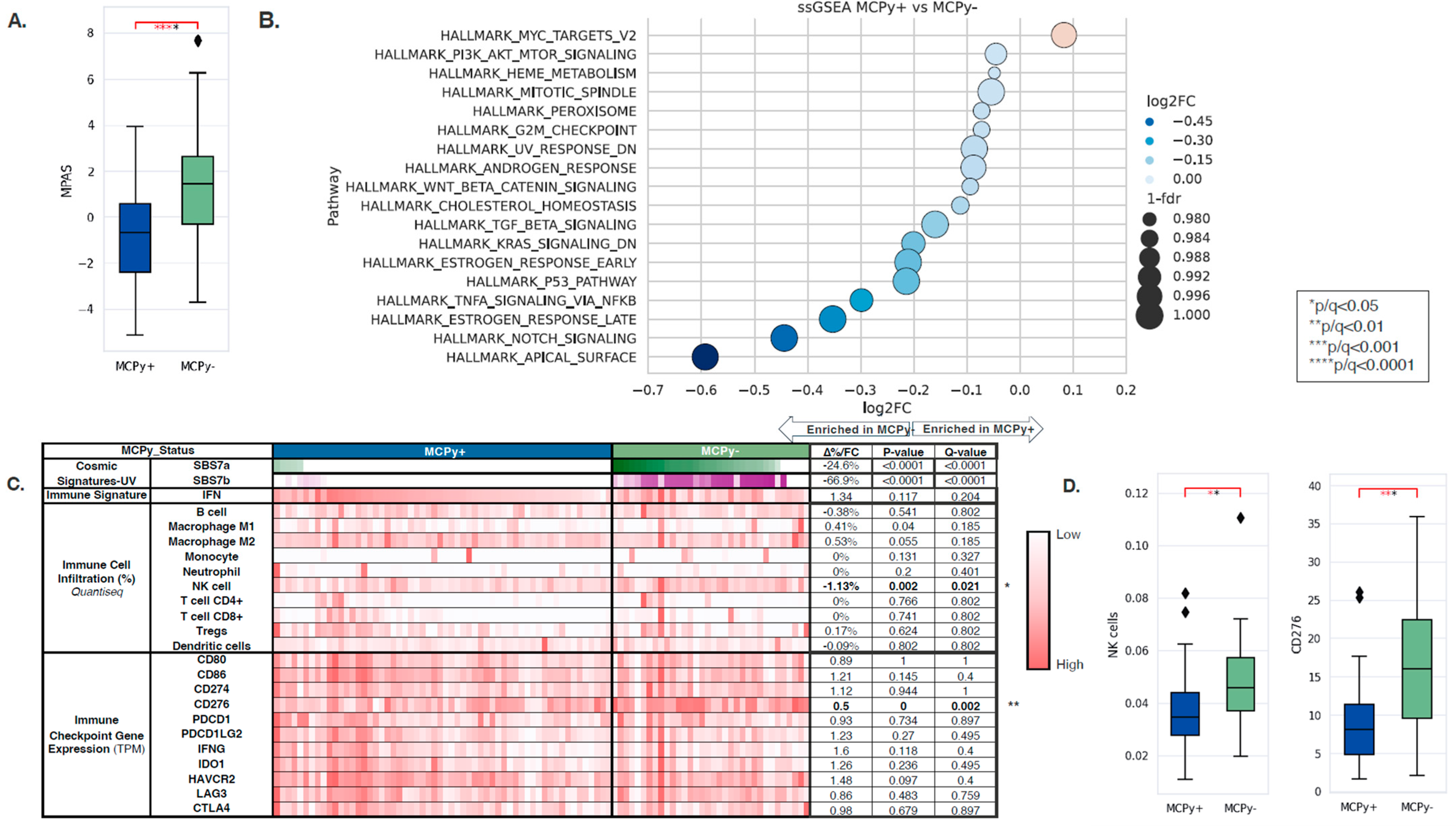
3.3. Transcriptomic Immune Signatures
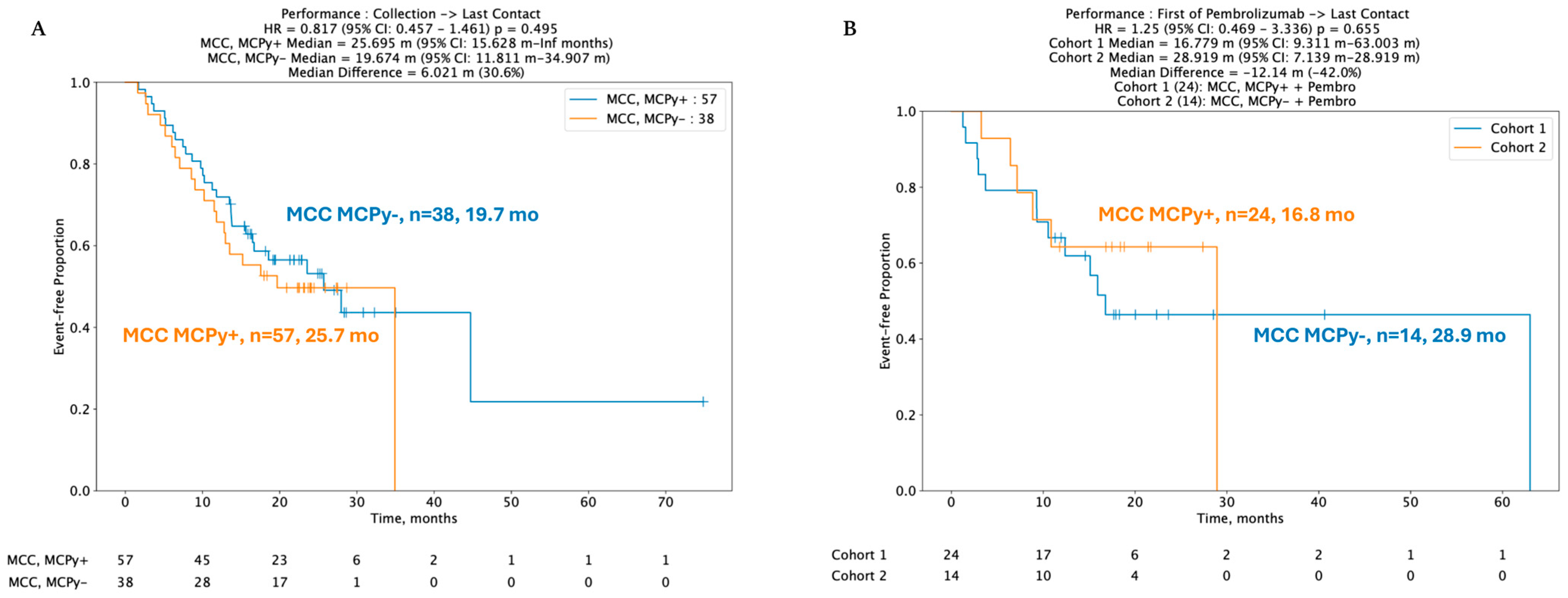
3.4. Clinical Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| dMMR | Mismatch Repair Deficient |
| ICI | Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor |
| MCC | Merkel Cell Carcinoma |
| MCPyV | Merkel Cell Polyomavirus |
| MMR | Mismatch Repair |
| MSI-H | Microsatellite Instability High |
| MSS | Microsatellite Stable |
| NGS | Next-Generation Sequencing |
| NK | Natural Killer |
| ORR | Objective Response Rate |
| PD-L1 | Programmed Cell Death Ligand 1 (PD-L1) |
| rwOS | Real-World Overall Survival |
| TIS | T-Cell Inflammation Scores |
| TMB | Tumor Mutational Burden |
| UVR | Ultraviolet Radiation |
| VN-MCC | Merkel Cell Polyomavirus-Negative Merkel Cell Carcinoma |
| VP-MCC | Merkel Cell Polyomavirus-Positive Merkel Cell Carcinoma |
| WES | Whole Exome Sequencing |
| WTS | Whole Transcriptome Sequencing |
References
- Harms, K.L.; Healy, M.A.; Nghiem, P.; Sober, A.J.; Johnson, T.M.; Bichakjian, C.K.; Wong, S.L. Analysis of Prognostic Factors from 9387 Merkel Cell Carcinoma Cases Forms the Basis for the New 8th Edition AJCC Staging System. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 3564–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, K.G.; Park, S.Y.; Vandeven, N.A.; Lachance, K.; Thomas, H.; Chapuis, A.G.; Harms, K.L.; Thompson, J.A.; Bhatia, S.; Stang, A.; et al. Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Current US Incidence and Projected Increases Based on Changing Demographics. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 457–463.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Shuda, M.; Chang, Y.; Moore, P.S. Clonal Integration of a Polyomavirus in Human Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Science 2008, 319, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strong, J.; Hallaert, P.; Brownell, I. Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Hematol./Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2024, 38, 1133–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iyer, J.G.; Blom, A.; Doumani, R.; Lewis, C.; Tarabadkar, E.S.; Anderson, A.; Ma, C.; Bestick, A.; Parvathaneni, U.; Bhatia, S.; et al. Response Rates and Durability of Chemotherapy among 62 Patients with Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 2294–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Chaudhury, H.; Wali, A.; Yasinzai, A.Q.K.; Iqbal, A.; Jain, H.; Brandi, L.; Karki, N.R.; Ullah, A. Survival Analysis of Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma Patients Pre- and Post-Immunotherapy Era in the US: A Retrospective Population-Based Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, e21515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, S.P.; Lebbé, C.; Mortier, L.; Brohl, A.S.; Fazio, N.; Grob, J.-J.; Prinzi, N.; Hanna, G.J.; Hassel, J.C.; Kiecker, F.; et al. First-Line Avelumab in a Cohort of 116 Patients with Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma (JAVELIN Merkel 200): Primary and Biomarker Analyses of a Phase II Study. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nghiem, P.T.; Bhatia, S.; Lipson, E.J.; Kudchadkar, R.R.; Miller, N.J.; Annamalai, L.; Berry, S.; Chartash, E.K.; Daud, A.; Fling, S.P.; et al. PD-1 Blockade with Pembrolizumab in Advanced Merkel-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2542–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulson, K.G.; Voillet, V.; McAfee, M.S.; Hunter, D.S.; Wagener, F.D.; Perdicchio, M.; Valente, W.J.; Koelle, S.J.; Church, C.D.; Vandeven, N.; et al. Acquired Cancer Resistance to Combination Immunotherapy from Transcriptional Loss of Class I HLA. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ch’en, P.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hippe, D.S.; Akaike, T.; Miller, N.J.; Church, C.; Lachance, K.; Finberg, A.; Gooley, T.; Hall, E.; et al. Real-World Outcomes of Patients Receiving Salvage Therapies for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Resistant Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Rationale for Future Clinical Trials. J. Immunother. Cancer 2025, 13, e012660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nammour, H.M.; Madrigal, K.; Starling, C.T.; Doan, H.Q. Advancing Treatment Options for Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Review of Tumor-Targeted Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 11055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaggana, E.; Konstantinou, M.P.; Krasagakis, G.H.; de Bree, E.; Kalpakis, K.; Mavroudis, D.; Krasagakis, K. Merkel Cell Carcinoma—Update on Diagnosis, Management and Future Perspectives. Cancers 2023, 15, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinstein, Z.Z.; Zhang, Y.; Ospina, O.E.; Nichols, M.D.; Chu, V.A.; de Mingo Pulido, A.; Prieto, K.; Nguyen, J.V.; Yin, R.; Moran Segura, C.; et al. Preexisting Skin-Resident CD8 and Γδ T-Cell Circuits Mediate Immune Response in Merkel Cell Carcinoma and Predict Immunotherapy Efficacy. Cancer Discov. 2024, 14, 1631–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spassova, I.; Ugurel, S.; Kubat, L.; Zimmer, L.; Terheyden, P.; Mohr, A.; Andtback, H.B.; Villabona, L.; Leiter, U.; Eigentler, T.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Characteristics Associated with Response to Therapeutic PD-1/PD-L1 Inhibition in Advanced Merkel Cell Carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e003198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundqvist, B.; Kilpinen, S.; Böhling, T.; Koljonen, V.; Sihto, H. Activation of Oncogenic and Immune-Response Pathways Is Linked to Disease-Specific Survival in Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 3591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gujar, H.; Mehta, A.; Li, H.-T.; Tsai, Y.C.; Qiu, X.; Weisenberger, D.J.; Jasiulionis, M.G.; In, G.K.; Liang, G. Characterizing DNA Methylation Signatures and Their Potential Functional Roles in Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starrett, G.J.; Thakuria, M.; Chen, T.; Marcelus, C.; Cheng, J.; Nomburg, J.; Thorner, A.R.; Slevin, M.K.; Powers, W.; Burns, R.T.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Characterization of Virus-Positive and Virus-Negative Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Genome Med. 2020, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chokwassanasakulkit, T.; McMillan, N.A.J. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus-Pathophysiology and Treatment in the Era of Gene-Targeted Therapies. Rev. Med. Virol. 2024, 34, e2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, K.; Zheng, D.X.; Agak, G.W. T-Cell Mediated Immunity in Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 6058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, L.B.; Kim, J.; Haradhvala, N.J.; Huang, M.N.; Tian Ng, A.W.; Wu, Y.; Boot, A.; Covington, K.R.; Gordenin, D.A.; Bergstrom, E.N.; et al. The Repertoire of Mutational Signatures in Human Cancer. Nature 2020, 578, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marabelle, A.; Le, D.T.; Ascierto, P.A.; Di Giacomo, A.M.; De Jesus-Acosta, A.; Delord, J.-P.; Geva, R.; Gottfried, M.; Penel, N.; Hansen, A.R.; et al. Efficacy of Pembrolizumab in Patients with Noncolorectal High Microsatellite Instability/Mismatch Repair–Deficient Cancer: Results from the Phase II KEYNOTE-158 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knepper, T.C.; Montesion, M.; Russell, J.S.; Sokol, E.S.; Frampton, G.M.; Miller, V.A.; Albacker, L.A.; McLeod, H.L.; Eroglu, Z.; Khushalani, N.I.; et al. The Genomic Landscape of Merkel Cell Carcinoma and Clinicogenomic Biomarkers of Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5961–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grignani, G.; Rutkowski, P.; Lebbe, C.; Prinzi, N.; Grob, J.; Tanda, E.T.; Guida, M.; Burgess, M.; Pulini, J.; Shankar, S.; et al. 545 A Phase 2 Study of Retifanlimab in Patients with Advanced or Metastatic Merkel Cell Carcinoma (MCC) (POD1UM-201). J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9 (Suppl. 2), A574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Han, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, H.; Wei, J.; Meng, L.; Xin, Y.; Jiang, X. Overcoming Acquired Resistance to Cancer Immune Checkpoint Therapy: Potential Strategies Based on Molecular Mechanisms. Cell Biosci. 2023, 13, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; McClure, E.M.; Akaike, T.; Park, S.Y.; Huynh, E.T.; Goff, P.H.; Nghiem, P. The Evolving Treatment Landscape of Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2023, 24, 1231–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glutsch, V.; Kneitz, H.; Gesierich, A.; Goebeler, M.; Haferkamp, S.; Becker, J.C.; Ugurel, S.; Schilling, B. Activity of Ipilimumab plus Nivolumab in Avelumab-Refractory Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2021, 70, 2087–2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, N.J.; Ambrazeviciute, G.; Bencomo, T.J.; Biese, K.; Chen, W.; Church, C.; Dakhil, S.N.; Kim, P.; Kiriluk, S.; Kulikauskas, R.; et al. Trick-MCC: Final Results from the Proof-of-Concept Investigator-Initiated Study of Combination Therapy with Anti–PD-1, Anti–LAG-3, and Anti–TIM-3 in Participants with Advanced or Metastatic PD-(L)1 Refractory Merkel Cell Carcinoma (NCT06056895). J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, 9531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakuni, R.; Hall, E.T.; Ansstas, G.; Bhatia, S.; Brohl, A.S.; Burgess, M.A.; Dimitrova, M.; Gao, L.; Ishizuka, J.J.; Lipson, E.J.; et al. The MATRiX Trial: A Multicenter, Randomized, Phase II Study of ATR Inhibition (via Tuvusertib) with or without Avelumab in Patients with Advanced Anti-PD-(L)1–Refractory Merkel Cell Carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2025, 43, TPS9598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulliam, T.; Jani, S.; Goff, P.H.; Bhakuni, R.; Tabachnick-Cherny, S.; Smythe, K.; Seaton, B.W.; Tachiki, L.; Kulikauskas, R.; Church, C.; et al. Intratumoral STING Agonist Reverses Immune Evasion in PD-(L)1-Refractory Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Mechanistic Insights from Detailed Biomarker Analyses. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e009803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, K.; Vromans, A.M.; Cheng, L.; Grant-Kels, J.M.; Katz, S.C.; Hadfield, M.J. Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Current Treatment Landscape and Emerging Therapeutic Targets. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2025, 27, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivier, E.; Rebuffet, L.; Narni-Mancinelli, E.; Cornen, S.; Igarashi, R.Y.; Fantin, V.R. Natural Killer Cell Therapies. Nature 2024, 626, 727–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- QUILT-3.063: A Study of N-803, haNK and Avelumab in Patients with Merkel Cell Carcinoma That Has Progressed After Checkpoint Therapy—NCI. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/research/participate/clinical-trials-search/v?id=NCI-2019-02908 (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- QUILT-3.009: Patients with Stage III (IIIB) or Stage (IV) Merkel Cell Carcinoma (MCC)—NCI. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/research/participate/clinical-trials-search/v?id=NCI-2015-01343 (accessed on 14 March 2025).
- Guo, C.; Figueiredo, I.; Gurel, B.; Neeb, A.; Seed, G.; Crespo, M.; Carreira, S.; Rekowski, J.; Buroni, L.; Welti, J.; et al. B7-H3 as a Therapeutic Target in Advanced Prostate Cancer. Eur. Urol. 2023, 83, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulido, R.; López, J.I.; Nunes-Xavier, C.E. B7-H3: A Robust Target for Immunotherapy in Prostate Cancer. Trends Cancer 2024, 10, 584–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Chen, L.; Qian, Z.; Zhang, Y. A Promising Target for Breast Cancer: B7-H3. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houben, R.; Michel, B.; Vetter-Kauczok, C.S.; Pföhler, C.; Laetsch, B.; Wolter, M.D.; Leonard, J.H.; Trefzer, U.; Ugurel, S.; Schrama, D.; et al. Absence of Classical MAP Kinase Pathway Signalling in Merkel Cell Carcinoma. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwasaki, T.; Hayashi, K.; Matsushita, M.; Nonaka, D.; Kohashi, K.; Kuwamoto, S.; Umekita, Y.; Oda, Y. Merkel Cell Polyomavirus–Negative Merkel Cell Carcinoma Is Associated with JAK-STAT and MEK-ERK Pathway Activation. Cancer Sci. 2022, 113, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantaraki, M.; Berdiaki, A.; Neagu, M.; Zurac, S.; Krasagakis, K.; Nikitovic, D. Understanding Merkel Cell Carcinoma: Pathogenic Signaling, Extracellular Matrix Dynamics, and Novel Treatment Approaches. Cancers 2025, 17, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Characteristic | MCPyV+ | MCPyV− | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | 57 (60) | 38 (40) | |
| Age, median (range) | 71 (22–90) | 75.5 (47–90) | 0.361 |
| TMB, median (range) | 1 (0–7) | 27.5 (2–98) | <0.0001 |
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Male | 41 (71.9) | 29 (76.3) | 0.793 |
| Female | 16 (28.1) | 9 (23.7) | |
| Biopsy Site, n (%) | |||
| Skin | 17 (28.1) | 19 (50) | 0.109 |
| Lymph Nodes | 17 (29.8) | 10 (26.3) | |
| Other Mets | 23 (40.4) | 9 (23.7) | |
| Race, n (%) | |||
| Asian American or Pacific Islander | 2 (4.08) | 0 (0) | 0.162 |
| Black or African American | 1 (2.04) | 2 (5.88) | |
| White | 42 (85.7) | 32 (94.1) | |
| Other | 4 (8.16) | 0 (0) | |
| Ethnicity, n (%) | |||
| Hispanic or Latino | 9 (17.7) | 1 (2.94) | 0.039 |
| Not Hispanic or Latino | 42 (82.4) | 33 (97.1) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaidya, P.; Wu, S.; Bryant, D.; Perry, C.J.; Prakash, V.; Lou, E.; Guo, T.; Brownell, I.; Darabi, S.; Gao, L.; et al. Molecular Characterization of Polyomavirus-Positive and Negative Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 3508. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213508
Vaidya P, Wu S, Bryant D, Perry CJ, Prakash V, Lou E, Guo T, Brownell I, Darabi S, Gao L, et al. Molecular Characterization of Polyomavirus-Positive and Negative Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(21):3508. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213508
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaidya, Poorva, Sharon Wu, Dave Bryant, Curtis J. Perry, Varsha Prakash, Emil Lou, Theresa Guo, Isaac Brownell, Sourat Darabi, Ling Gao, and et al. 2025. "Molecular Characterization of Polyomavirus-Positive and Negative Merkel Cell Carcinoma" Cancers 17, no. 21: 3508. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213508
APA StyleVaidya, P., Wu, S., Bryant, D., Perry, C. J., Prakash, V., Lou, E., Guo, T., Brownell, I., Darabi, S., Gao, L., Abdulla, F., & Park, S. J. (2025). Molecular Characterization of Polyomavirus-Positive and Negative Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Cancers, 17(21), 3508. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213508








