The Effects of PAK-Regulated Tumour Vasculature on Gemcitabine Response of Pancreatic Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.2. Animal Studies
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.4. Immunofluorescence
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Proteomics
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
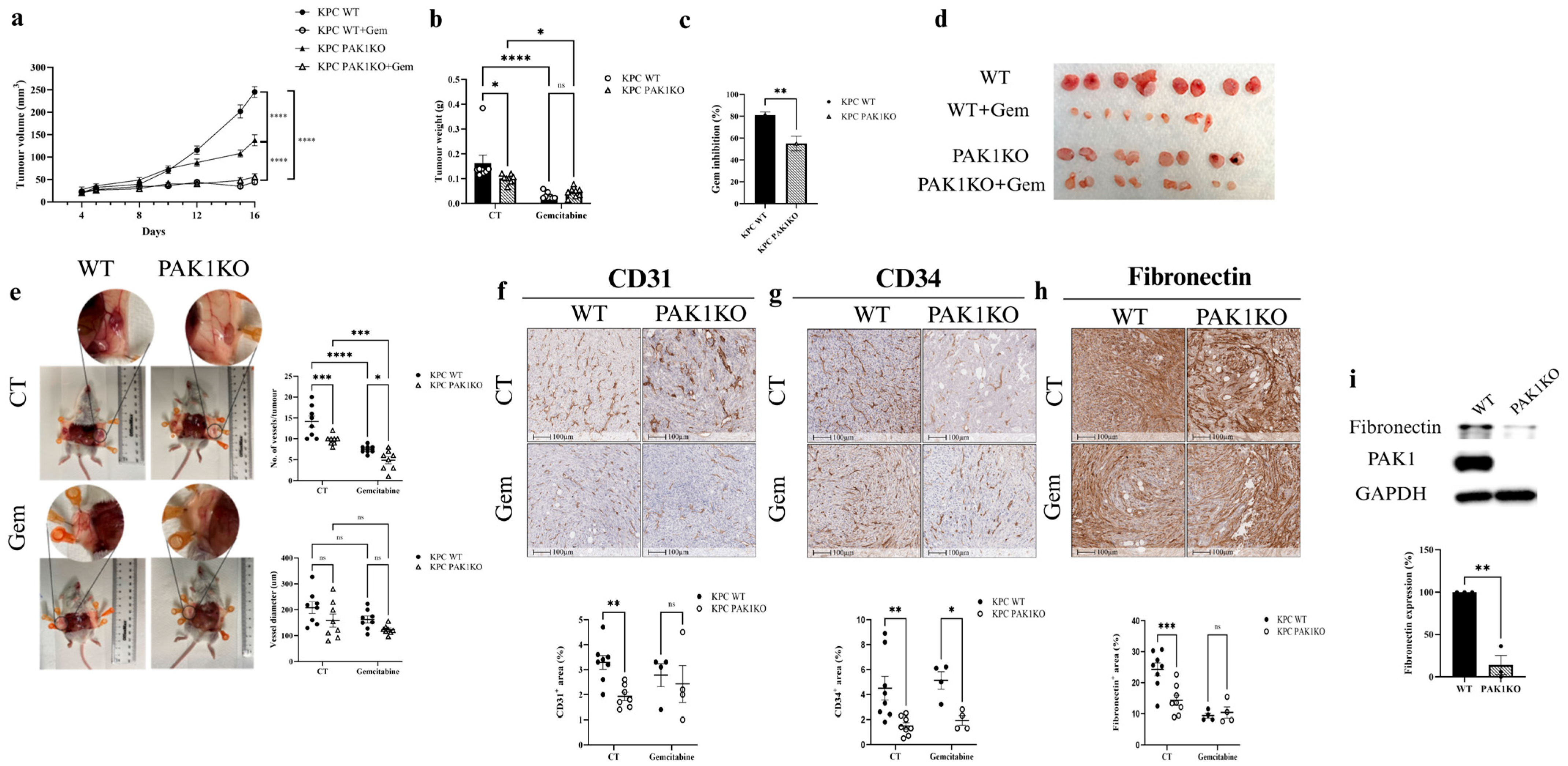
3.1. PAK1 Knockout Reduced Angiogenesis and Decreased the Effect of Gemcitabine on Pancreatic Cancer
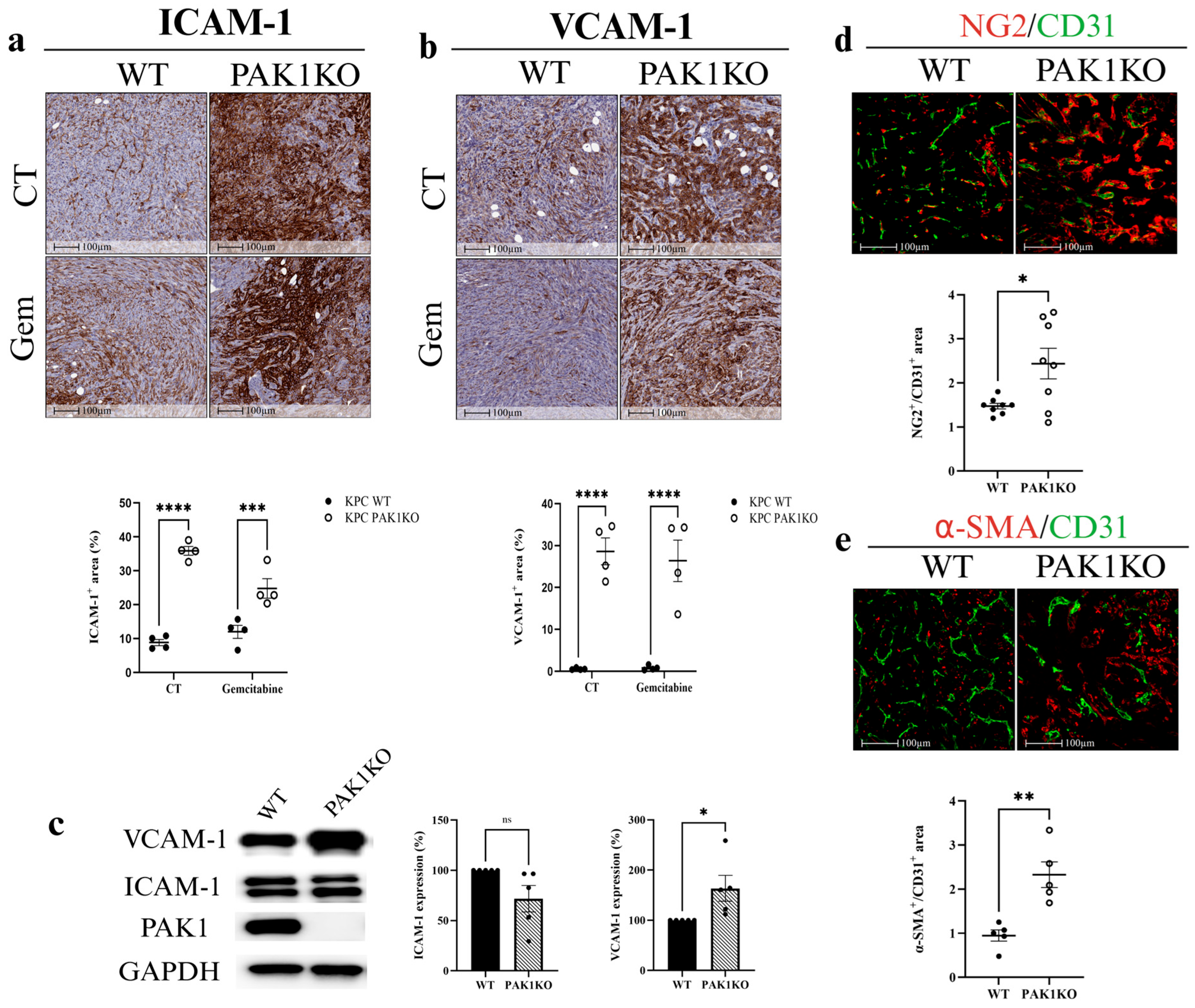
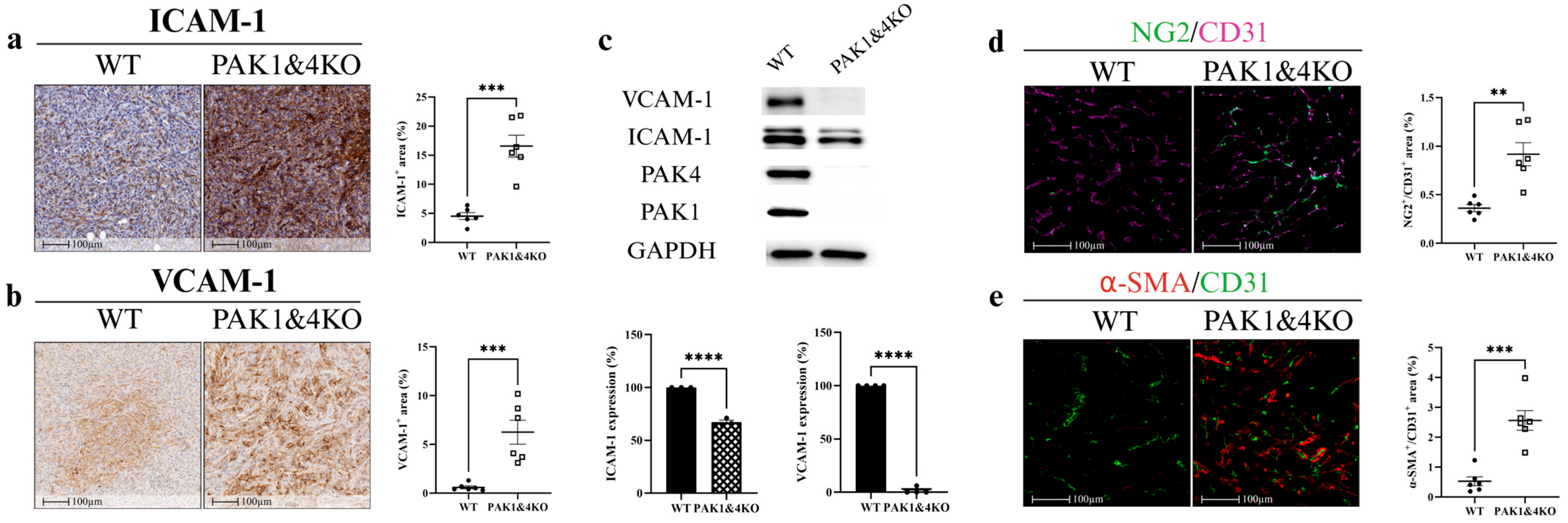
3.2. PAK1 Knockout Upregulated ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 and Promoted Vascular Normalisation
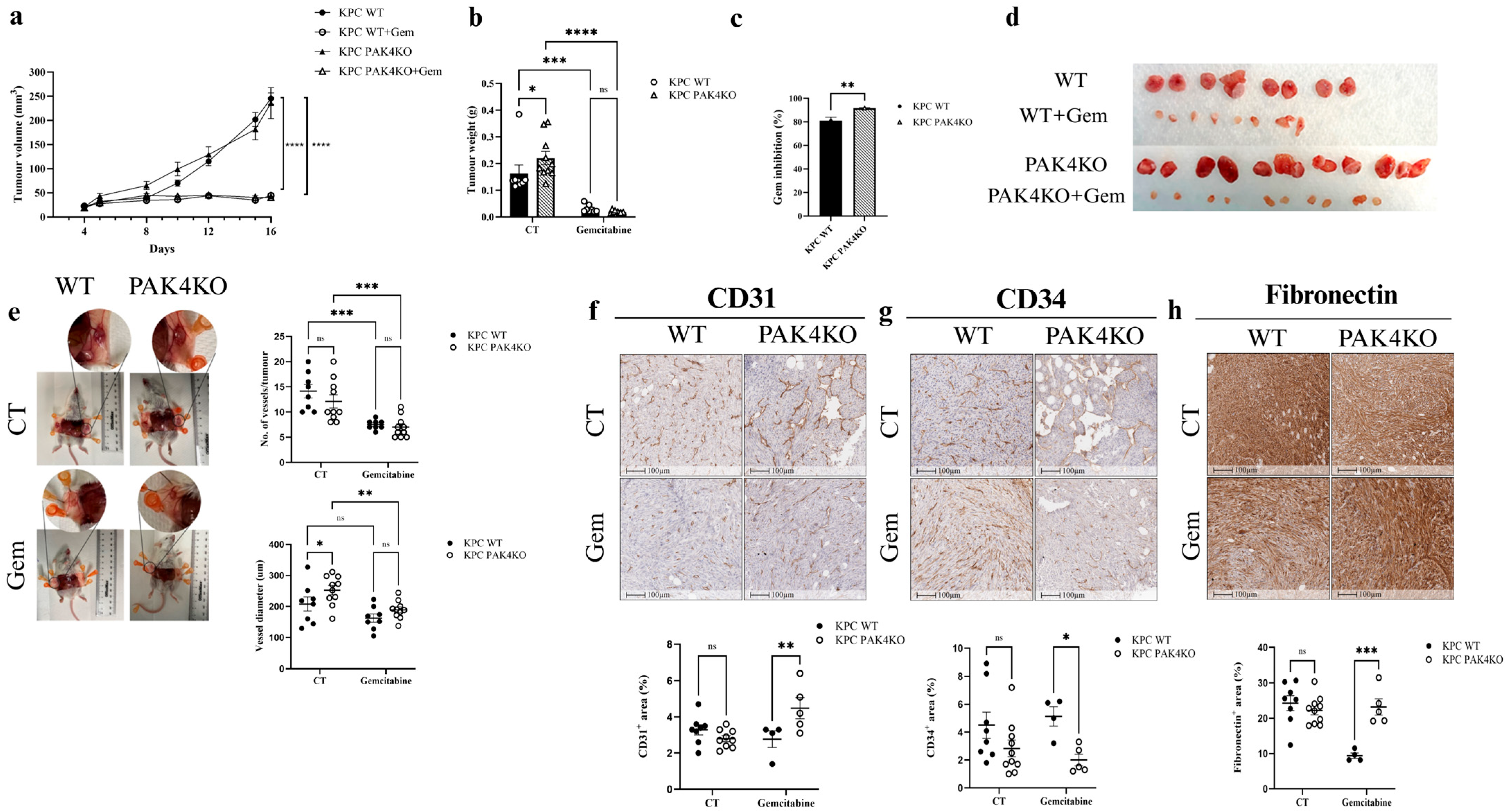
3.3. PAK4 Knockout Enhanced the Inhibitory Effects of Gemcitabine by Increasing Blood Vessel Diameter
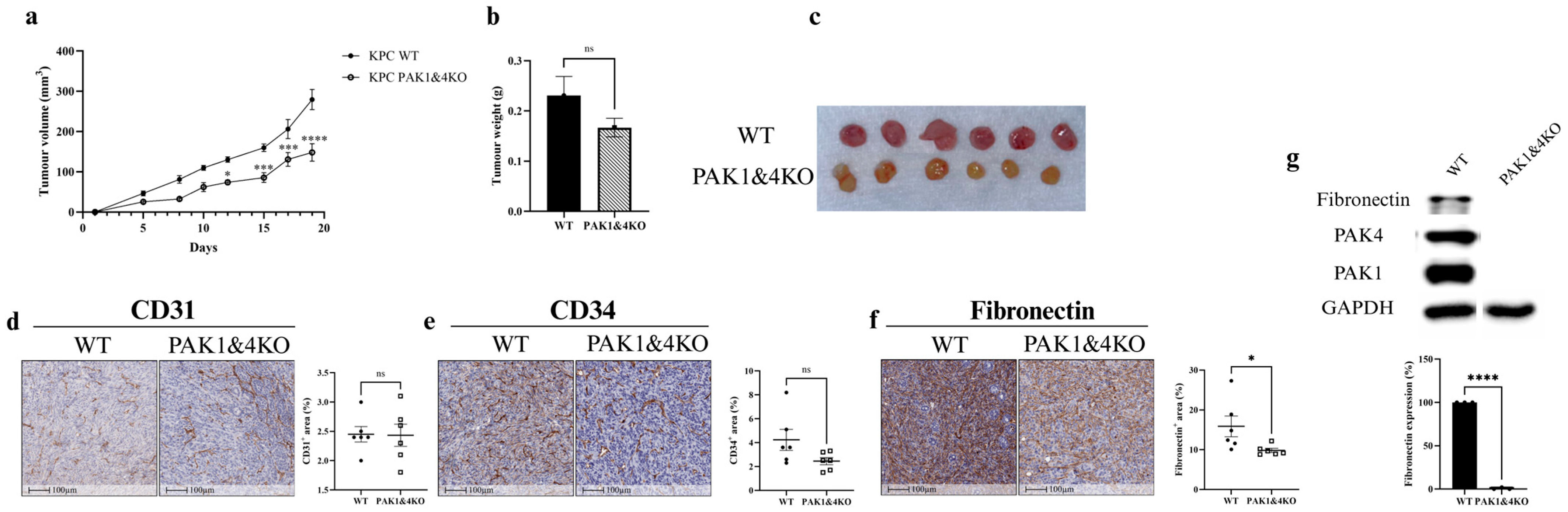
3.4. The Effects of Double Knockout of PAK1 and PAK4 on Pancreatic Tumour Growth and Tumour Vasculature
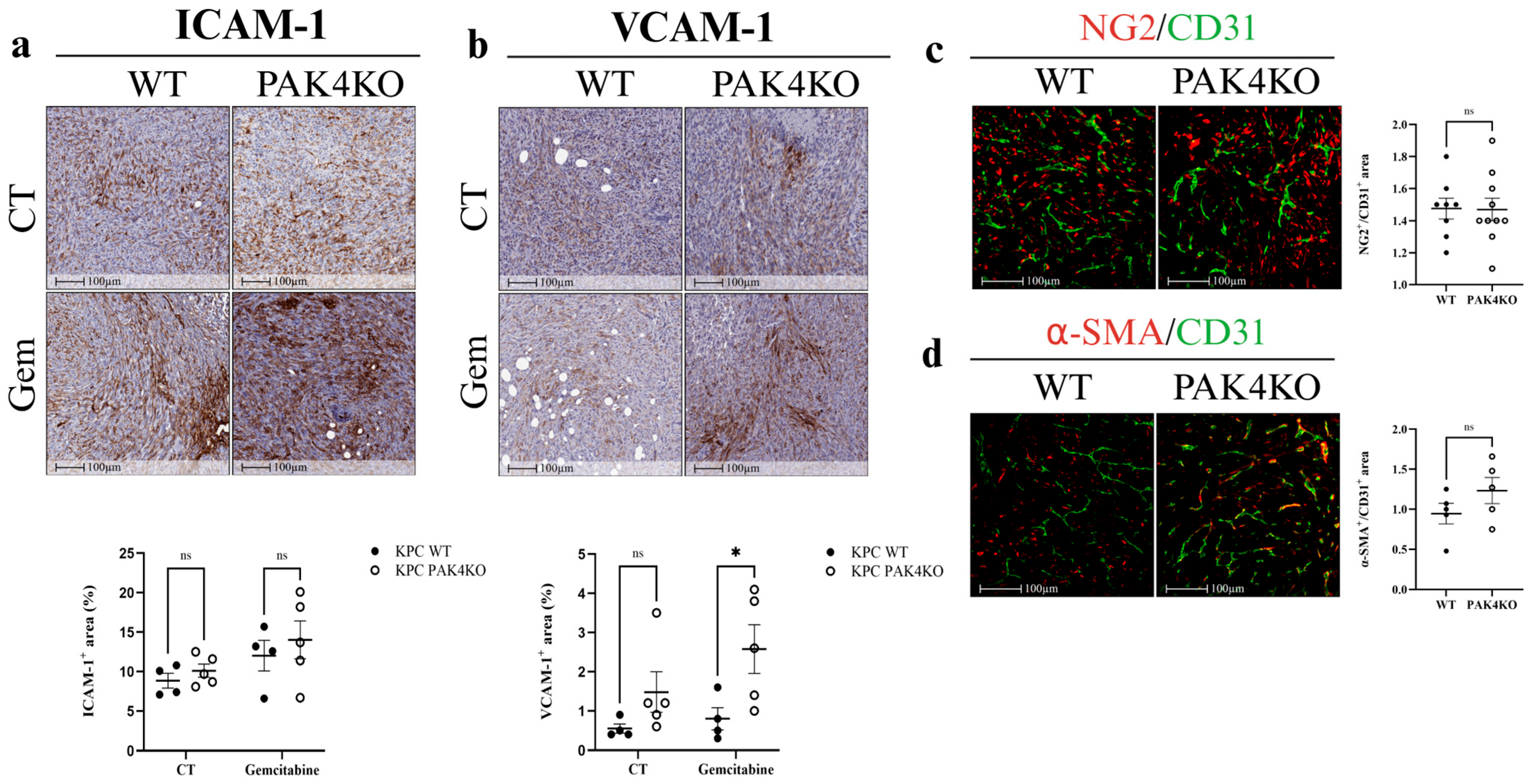
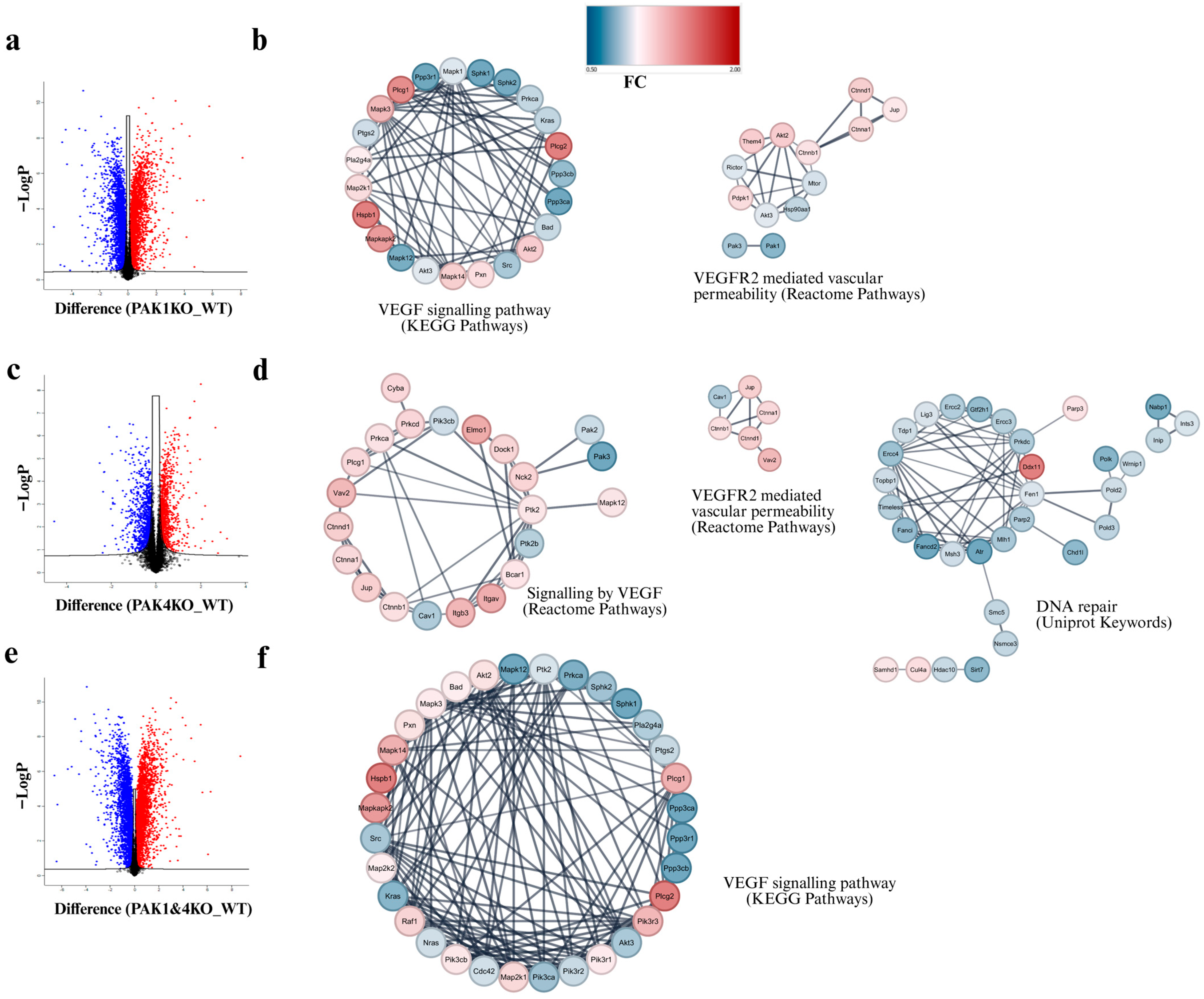
3.5. PAK1 and PAK4 Differentially Affected the Molecules Involved in Angiogenesis and Tumour Vasculature
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PDA | Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma |
| PAKs | P21-activated kinases |
| WT | Wild type |
| PAK1KO | PAK1 knockout |
| PC | Pancreatic cancer |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| NGS | Normal goat serum |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| CM | Conditioned media |
| LC | Liquid chromatography |
| MS | Mass spectrometry |
| DIA | Data-independent acquisition |
| ICAM-1 | Intercellular adhesion molecule-1 |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| PPI | Protein–protein interaction |
| VM | Vasculogenic mimicry |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Kratzer, T.B.; Giaquinto, A.N.; Sung, H.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2025. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2025, 75, 10–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahib, L.; Coffin, T.; Kenner, B. Factors Driving Pancreatic Cancer Survival Rates. Pancreas 2025, 54, e530–e536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.; Alqahtani, M.S.; Alshahrani, M.Y.; Alabdullh, K. Aggressive and Drug-resistant Pancreatic Cancer: Challenges and Novel Treatment Approaches. Discov. Med. 2022, 34, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Adel, N. Current treatment landscape and emerging therapies for pancreatic cancer. Am. J. Manag. Care 2019, 25, S3–S10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jamal, M.H.; Khan, M.N. Developments in pancreatic cancer emerging therapies, diagnostic methods, and epidemiology. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2025, 271, 156012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koltai, T.; Reshkin, S.J.; Carvalho, T.M.; Di Molfetta, D.; Greco, M.R.; Alfarouk, K.O.; Cardone, R.A. Resistance to gemcitabine in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: A physiopathologic and pharmacologic review. Cancers 2022, 14, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feig, C.; Gopinathan, A.; Neesse, A.; Chan, D.S.; Cook, N.; Tuveson, D.A. The pancreas cancer microenvironment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4266–4276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessmann, E.; Buchholz, S.M.; Demir, I.E.; Singh, S.K.; Gress, T.M.; Ellenrieder, V.; Neesse, A. Microenvironmental Determinants of Pancreatic Cancer. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 100, 1707–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.M.; Faix, P.H.; Schnitzer, J.E. Overcoming key biological barriers to cancer drug delivery and efficacy. J. Control. Release 2017, 267, 15–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, P.F.; Lutz, M.; Siveke, J.T. Immunotherapy and Combination Strategies in Pancreatic Cancer: Current Status and Emerging Trends. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2018, 41, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Xu, H.X.; Wu, C.T.; Wang, W.Q.; Jin, W.; Gao, H.L.; Li, H.; Zhang, S.R.; Xu, J.Z.; Qi, Z.H.; et al. Angiogenesis in pancreatic cancer: Current research status and clinical implications. Angiogenesis 2019, 22, 15–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shojaei, F. Anti-angiogenesis therapy in cancer: Current challenges and future perspectives. Cancer Lett. 2012, 320, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, B.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, Q. Progress in tumor vascular normalization for anticancer therapy: Challenges and perspectives. Front. Med. 2012, 6, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansardamavandi, A.; Nikfarjam, M.; He, H. PAK in Pancreatic Cancer-Associated Vasculature: Implications for Therapeutic Response. Cells 2023, 12, 2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rane, C.K.; Minden, A. P21 activated kinase signaling in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 54, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whale, A.; Hashim, F.N.; Fram, S.; Jones, G.E.; Wells, C.M. Signalling to cancer cell invasion through PAK family kinases. Front. Biosci. (Landmark Ed.) 2011, 16, 849–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockton, R.A.; Schaefer, E.; Schwartz, M.A. p21-activated kinase regulates endothelial permeability through modulation of contractility. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 46621–46630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, J.; Mocevicius, P.; Werner, J.; Ryschich, E. The role of the tumor endothelium in leukocyte recruitment in pancreatic cancer. Surgery 2012, 152, S89–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhan, Y.; Huynh, N.; Dumesny, C.; Wang, X.; Asadi, K.; Herrmann, D.; Timpson, P.; Yang, Y.; Walsh, K.; et al. Inhibition of PAK1 suppresses pancreatic cancer by stimulation of anti-tumour immunity through down-regulation of PD-L1. Cancer Lett. 2020, 472, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naїja, A.; Merhi, M.; Inchakalody, V.; Fernandes, Q.; Mestiri, S.; Prabhu, K.S.; Uddin, S.; Dermime, S. The role of PAK4 in the immune system and its potential implication in cancer immunotherapy. Cell. Immunol. 2021, 367, 104408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abril-Rodriguez, G.; Torrejon, D.Y.; Liu, W.; Zaretsky, J.M.; Nowicki, T.S.; Tsoi, J.; Puig-Saus, C.; Baselga-Carretero, I.; Medina, E.; Quist, M.J. PAK4 inhibition improves PD-1 blockade immunotherapy. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abril-Rodriguez, G.; Torrejon, D.Y.; Karin, D.; Campbell, K.M.; Medina, E.; Saco, J.D.; Galvez, M.; Champhekar, A.S.; Perez-Garcilazo, I.; Baselga-Carretero, I. Remodeling of the tumor microenvironment through PAK4 inhibition sensitizes tumors to immune checkpoint blockade. Cancer Res. Commun. 2022, 2, 1214–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, F.; Zhang, D.; Huang, M.; Zhang, L.; Dorsey, J.F.; Binder, Z.A.; O’Rourke, D.M. Targeting PAK4 to reprogram the vascular microenvironment and improve CAR-T immunotherapy for glioblastoma. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Zhang, J.; Pan, L.; He, J.; Zhu, M.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, W.; Xie, D.; Shen, X.; et al. Multi-omics analysis reveals RNA polymerase II degradation as a novel mechanism of PF-3758309’s anti-tumor activity. Cell Death Discov. 2025, 11, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Dumesny, C.; Ang, C.S.; Dong, L.; Ma, Y.; Zeng, J.; Nikfarjam, M. A novel PAK4 inhibitor suppresses pancreatic cancer growth and enhances the inhibitory effect of gemcitabine. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 16, 101329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboukameel, A.; Muqbil, I.; Senapedis, W.; Baloglu, E.; Landesman, Y.; Shacham, S.; Kauffman, M.; Philip, P.A.; Mohammad, R.M.; Azmi, A.S. Novel p21-Activated Kinase 4 (PAK4) Allosteric Modulators Overcome Drug Resistance and Stemness in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wu, Y.; Xing, D. New-generation advanced PROTACs as potential therapeutic agents in cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, X.; Huang, Z.; Pei, H.; Jia, Z.; Zheng, J. Molecular glue-mediated targeted protein degradation: A novel strategy in small-molecule drug development. iScience 2024, 27, 110712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neerasa, J.; Kim, B.; Chung, H. Novel dual-targeting PROTAC degraders of GSK-3β and CDK5: A promising approach for pancreatic cancer treatment. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2025, 120, 118085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansardamavandi, A.; Dumesny, C.; Ma, Y.; Dong, L.; Ellis, S.; Ang, C.-S.; Nikfarjam, M.; He, H. P-21 Kinase 1 or 4 Knockout Stimulated Anti-Tumour Immunity Against Pancreatic Cancer by Enhancing Vascular Normalisation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 8357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stockmann, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Klose, R.; Helfrich, I. The impact of the immune system on tumor: Angiogenesis and vascular remodeling. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Dumesny, C.; Dong, L.; Ang, C.-S.; Asadi, K.; Zhan, Y.; Nikfarjam, M.; He, H. Inhibition of P21-activated kinases 1 and 4 synergistically suppresses the growth of pancreatic cancer by stimulating anti-tumour immunity. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Huynh, N.; Wang, X.; Pajic, M.; Parkin, A.; Man, J.; Baldwin, G.S.; Nikfarjam, M.; He, H. PAK inhibition by PF-3758309 enhanced the sensitivity of multiple chemotherapeutic reagents in patient-derived pancreatic cancer cell lines. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 3353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bevilacqua, M.P. Endothelial-leukocyte adhesion molecules. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1993, 11, 767–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garmy-Susini, B.; Jin, H.; Zhu, Y.; Sung, R.-J.; Hwang, R.; Varner, J. Integrin α 4 β 1–VCAM-1–mediated adhesion between endothelial and mural cells is required for blood vessel maturation. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 1542–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, M.R.; Luscinskas, F.W. Leukocyte rolling and adhesion via ICAM-1 signals to endothelial permeability. Focus on “Leukocyte rolling and adhesion both contribute to regulation of microvascular permeability to albumin via ligation of ICAM-1”. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 301, C777–C779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Takahashi, R.; Ijichi, H.; Sano, M.; Miyabayashi, K.; Mohri, D.; Kim, J.; Kimura, G.; Nakatsuka, T.; Fujiwara, H.; Yamamoto, K. Soluble VCAM-1 promotes gemcitabine resistance via macrophage infiltration and predicts therapeutic response in pancreatic cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamzah, J.; Jugold, M.; Kiessling, F.; Rigby, P.; Manzur, M.; Marti, H.H.; Rabie, T.; Kaden, S.; Gröne, H.-J.; Hämmerling, G.J. Vascular normalization in Rgs5-deficient tumours promotes immune destruction. Nature 2008, 453, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Obberghen-Schilling, E.; Tucker, R.P.; Saupe, F.; Gasser, I.; Cseh, B.; Orend, G. Fibronectin and tenascin-C: Accomplices in vascular morphogenesis during development and tumor growth. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2011, 55, 511–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.; Sun, J.; Ye, L.; Jiang, T.; Li, W.; Su, C.; Ren, S.; Wu, F.; Zhou, C.; Gao, G. Fibronectin promotes tumor angiogenesis and progression of non-small-cell lung cancer by elevating WISP3 expression via FAK/MAPK/ HIF-1α axis and activating wnt signaling pathway. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 12, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalovski, M.; Brekken, R.A. Matrix control of pancreatic cancer: New insights into fibronectin signaling. Cancer Lett. 2016, 381, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Liu, K.; Dong, Z. The role of p21-activated kinases in cancer and beyond: Where are we heading? Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 641381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, D.; He, H.; Baldwin, G.S.; Nikfarjam, M. The role of p21-activated kinases in pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2015, 44, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, N.; Marimuthu, S.; Bhardwaj, A.; Deshmukh, S.K.; Srivastava, S.K.; Singh, A.P.; McClellan, S.; Carter, J.E.; Singh, S. p-21 activated kinase 4 (PAK4) maintains stem cell-like phenotypes in pancreatic cancer cells through activation of STAT3 signaling. Cancer Lett. 2016, 370, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicosia, R.F.; Bonanno, E.; Smith, M. Fibronectin promotes the elongation of microvessels during angiogenesis in vitro. J. Cell. Physiol. 1993, 154, 654–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, V.; Viji, R.; Kiran, M.; Sudhakaran, P.R. Angiogenic response of endothelial cells to fibronectin. In Biochemical Roles of Eukaryotic Cell Surface Macromolecules: 2011 ISCSM Proceedings; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijelath, E.S.; Rahman, S.; Murray, J.; Patel, Y.; Savidge, G.; Sobel, M. Fibronectin promotes VEGF-induced CD34+ cell differentiation into endothelial cells. J. Vasc. Surg. 2004, 39, 655–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Yang, C.; Tang, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Song, M.; Cheng, P.; Wei, Z.; Zhong, C. Pharmacological manipulation of Ezh2 with salvianolic acid B results in tumor vascular normalization and synergizes with cisplatin and T cell-mediated immunotherapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2022, 182, 106333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Kaur, R.; Kumari, P.; Pasricha, C.; Singh, R. ICAM-1 and VCAM-1: Gatekeepers in various inflammatory and cardiovascular disorders. Clin. Chim. Acta 2023, 548, 117487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppenheimer-Marks, N.; Davis, L.S.; Bogue, D.T.; Ramberg, J.; Lipsky, P.E. Differential utilization of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 during the adhesion and transendothelial migration of human T lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 1991, 147, 2913–2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Buul, J.D.; Van Rijssel, J.; Van Alphen, F.P.; van Stalborch, A.-M.; Mul, E.P.; Hordijk, P.L. ICAM-1 clustering on endothelial cells recruits VCAM-1. BioMed Res. Int. 2010, 2010, 120328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjunpää, H.; Llort Asens, M.; Guenther, C.; Fagerholm, S.C. Cell Adhesion Molecules and Their Roles and Regulation in the Immune and Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, M.; Chernoff, J. An in vivo assay to test blood vessel permeability. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 73, 50062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Bao, M.; Miele, L.; Sarkar, F.H.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Q. Tumour vasculogenic mimicry is associated with poor prognosis of human cancer patients: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 3914–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Liao, Y.; Mai, D.; Xie, P.; Qiang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Wang, M.; Mei, Y.; Meng, D.; Xu, L. Tumor vasculogenic mimicry predicts poor prognosis in cancer patients: A meta-analysis. Angiogenesis 2016, 19, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Bellido, D.; Serrano-Saenz, S.; Fernández-Cortés, M.; Oliver, F.J. Vasculogenic mimicry signaling revisited: Focus on non-vascular VE-cadherin. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisacane, A.; Picciotto, F.; Risio, M. CD31 and CD34 expression as immunohistochemical markers of endothelial transdifferentiation in human cutaneous melanoma. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2007, 29, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wang, C.-Y.; Liu, T.; Wu, B.; Zhou, F.; Xiong, J.-X.; Wu, H.-S.; Tao, J.; Zhao, G.; Yang, M. Persistence of side population cells with high drug efflux capacity in pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2008, 14, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huanwen, W.; Zhiyong, L.; Xiaohua, S.; Xinyu, R.; Kai, W.; Tonghua, L. Intrinsic chemoresistance to gemcitabine is associated with constitutive and laminin-induced phosphorylation of FAK in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Mol. Cancer 2009, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, F.; Luo, B.; Wang, X.; Sun, H.; Liu, S.; Cui, Y.; Xu, X. A side population of cells from a human pancreatic carcinoma cell line harbors cancer stem cell characteristics. Neoplasma 2009, 56, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ansardamavandi, A.; Dumesny, C.; Ma, Y.; Dong, L.; Ellis, S.; Ang, C.-S.; Nikfarjam, M.; He, H. The Effects of PAK-Regulated Tumour Vasculature on Gemcitabine Response of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 3434. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213434
Ansardamavandi A, Dumesny C, Ma Y, Dong L, Ellis S, Ang C-S, Nikfarjam M, He H. The Effects of PAK-Regulated Tumour Vasculature on Gemcitabine Response of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(21):3434. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213434
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnsardamavandi, Arian, Chelsea Dumesny, Yi Ma, Li Dong, Sarah Ellis, Ching-Seng Ang, Mehrdad Nikfarjam, and Hong He. 2025. "The Effects of PAK-Regulated Tumour Vasculature on Gemcitabine Response of Pancreatic Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 21: 3434. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213434
APA StyleAnsardamavandi, A., Dumesny, C., Ma, Y., Dong, L., Ellis, S., Ang, C.-S., Nikfarjam, M., & He, H. (2025). The Effects of PAK-Regulated Tumour Vasculature on Gemcitabine Response of Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers, 17(21), 3434. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213434






