Single-Cell Heterogeneity of Epigenetic Factor Regulation Deciphers Alteration of RNA Metabolism During Proliferative SHH-Medulloblastoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Open Pediatric Brain Tumor Atlas (PBTA) [15]
2.2. Williamson Cohort (RNA-seq)
2.3. sc-RNA Sequencing of Medulloblastoma Tumors (n = 28)
2.4. Bulk Transcriptome Analysis
2.5. Gene Expression Survival Analyses
2.6. Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Analyses
3. Results
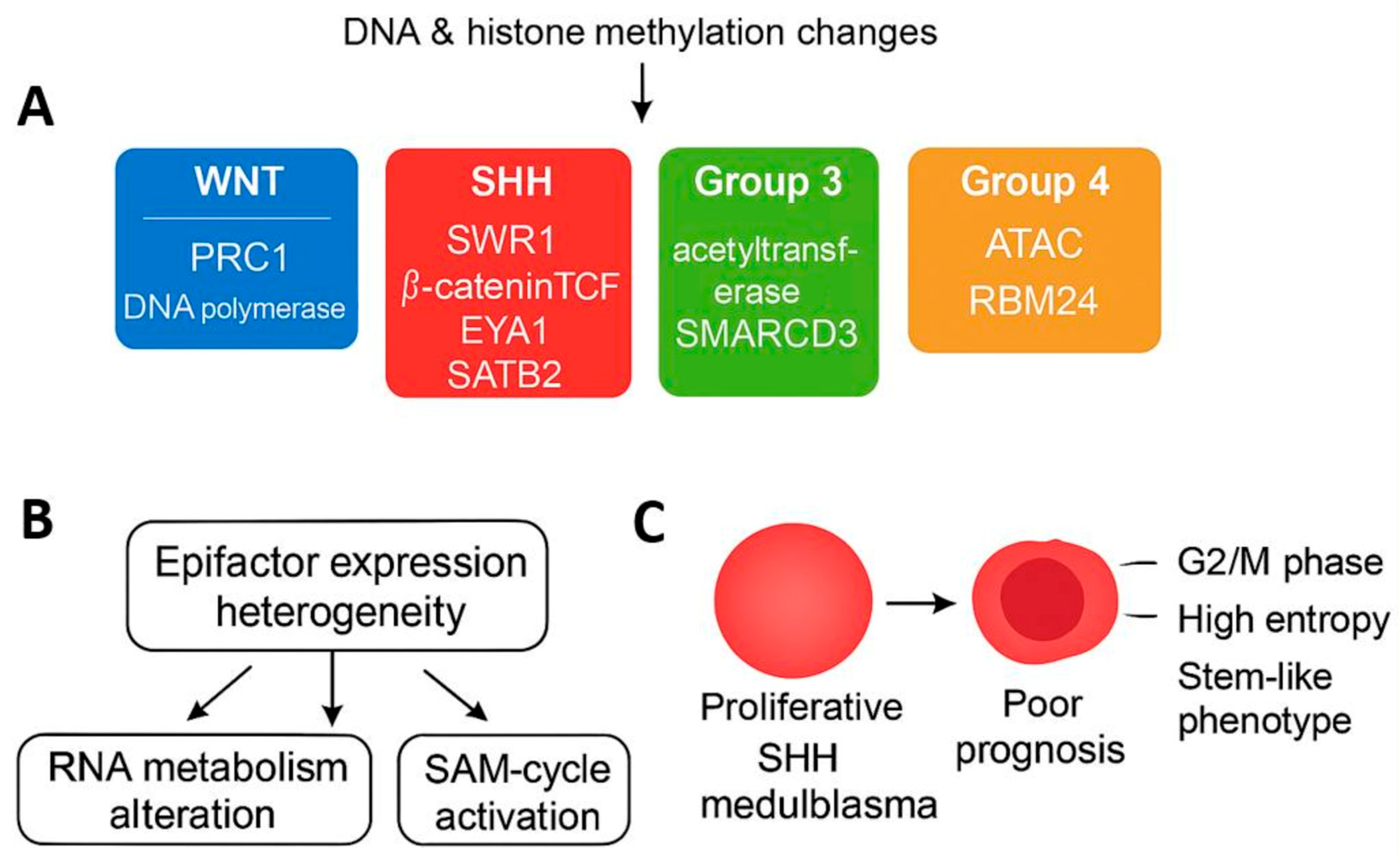
3.1. Epigenetic Factor Regulation Reflects Molecular Subtypes in Medulloblastoma
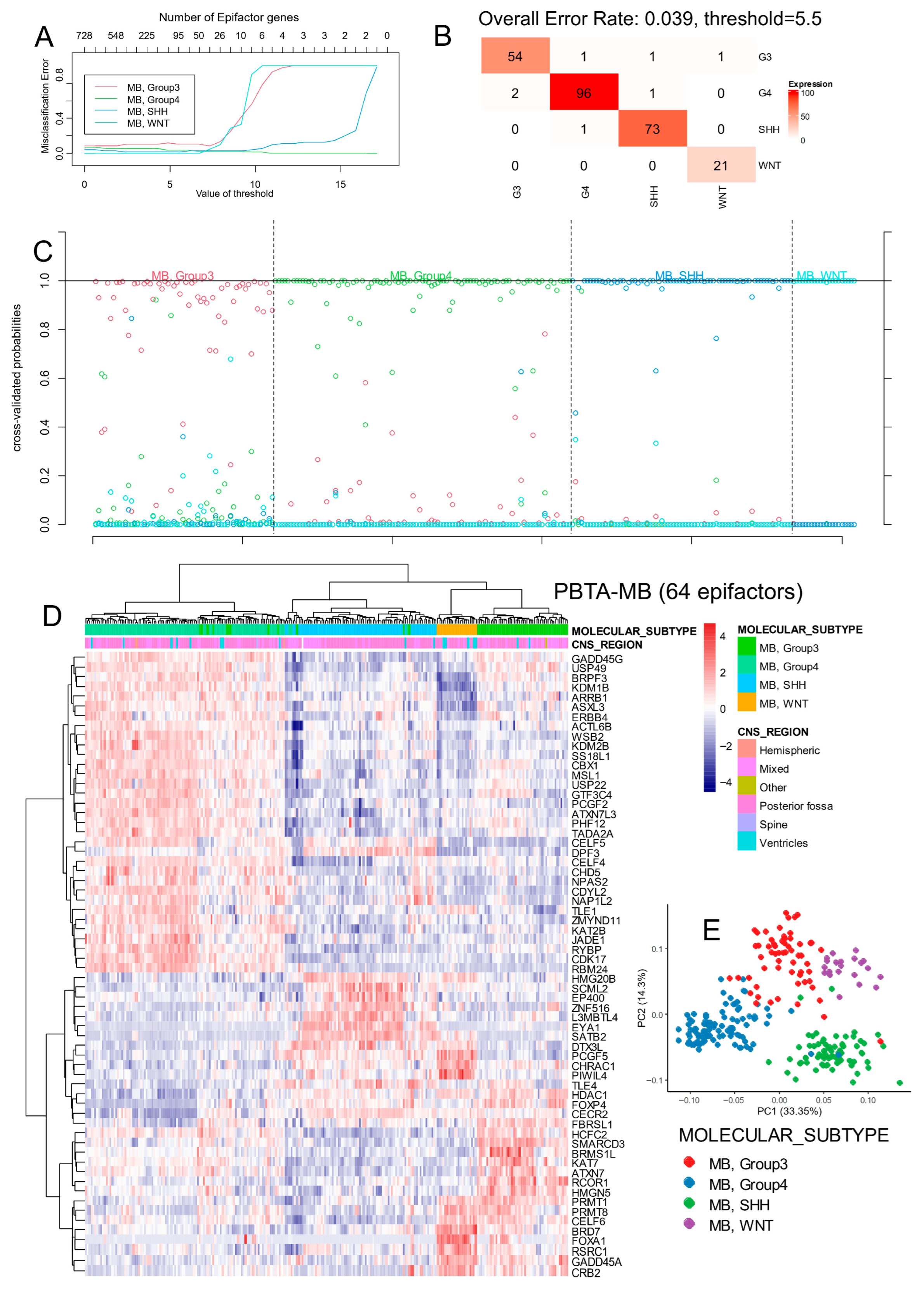
3.1.1. Epigenetic Factor Expression in the PBTA Bulk Transcriptome Cohort
3.1.2. Functional Characterization and Validation of Subtype-Specific Epigenetic Signatures

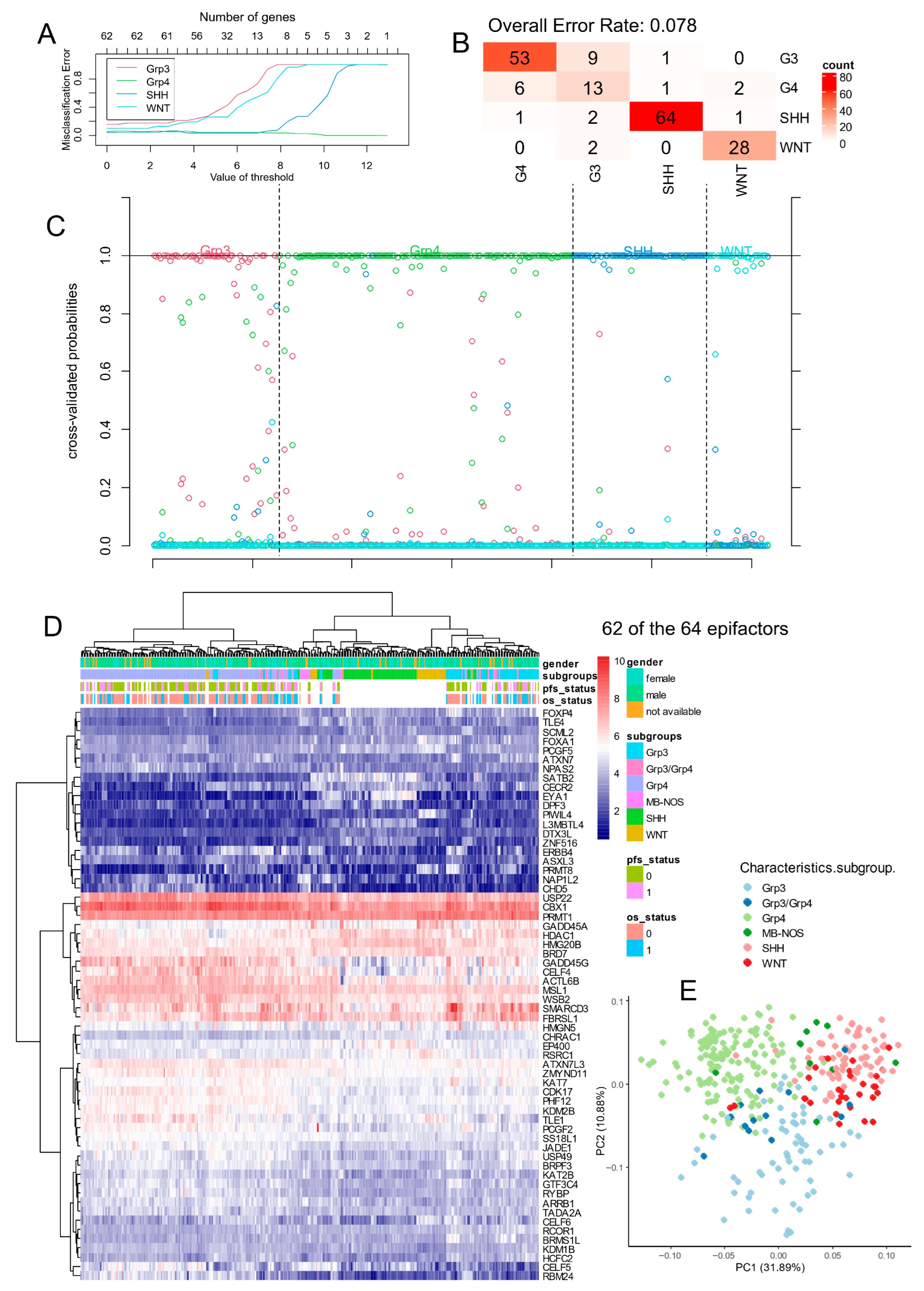
3.1.3. Epigenetic Factor Regulation in the Williamson Bulk Transcriptome Cohort
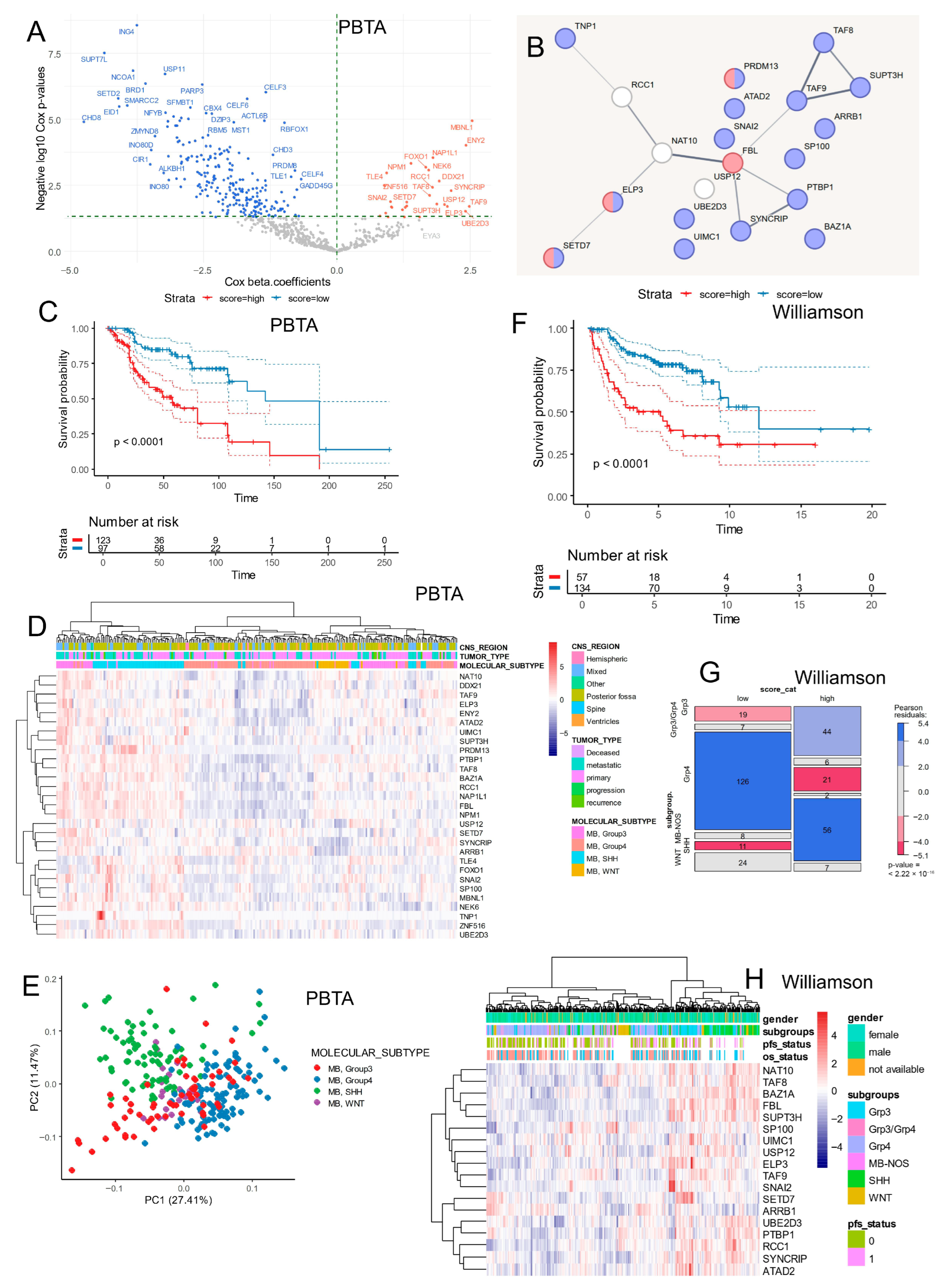
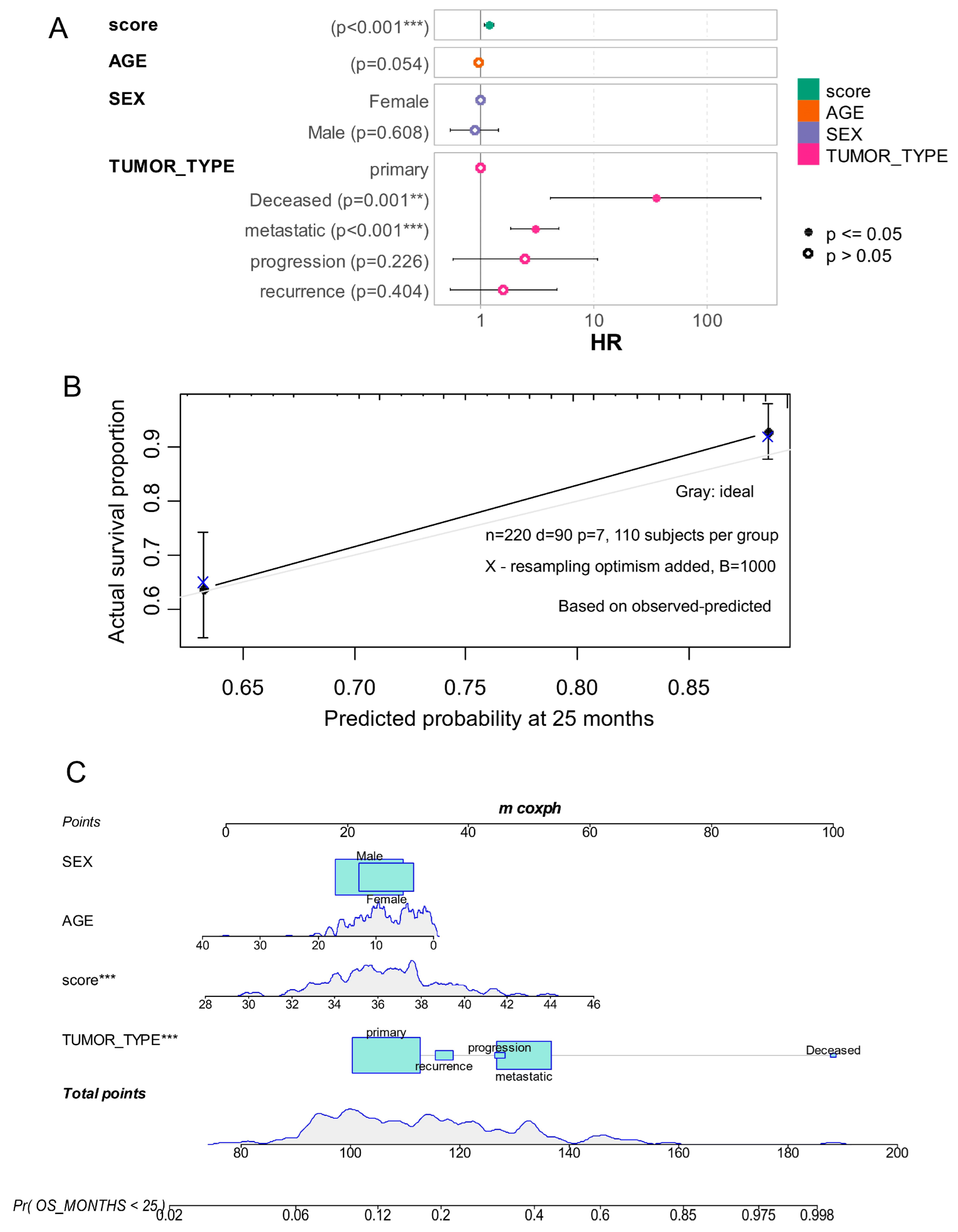
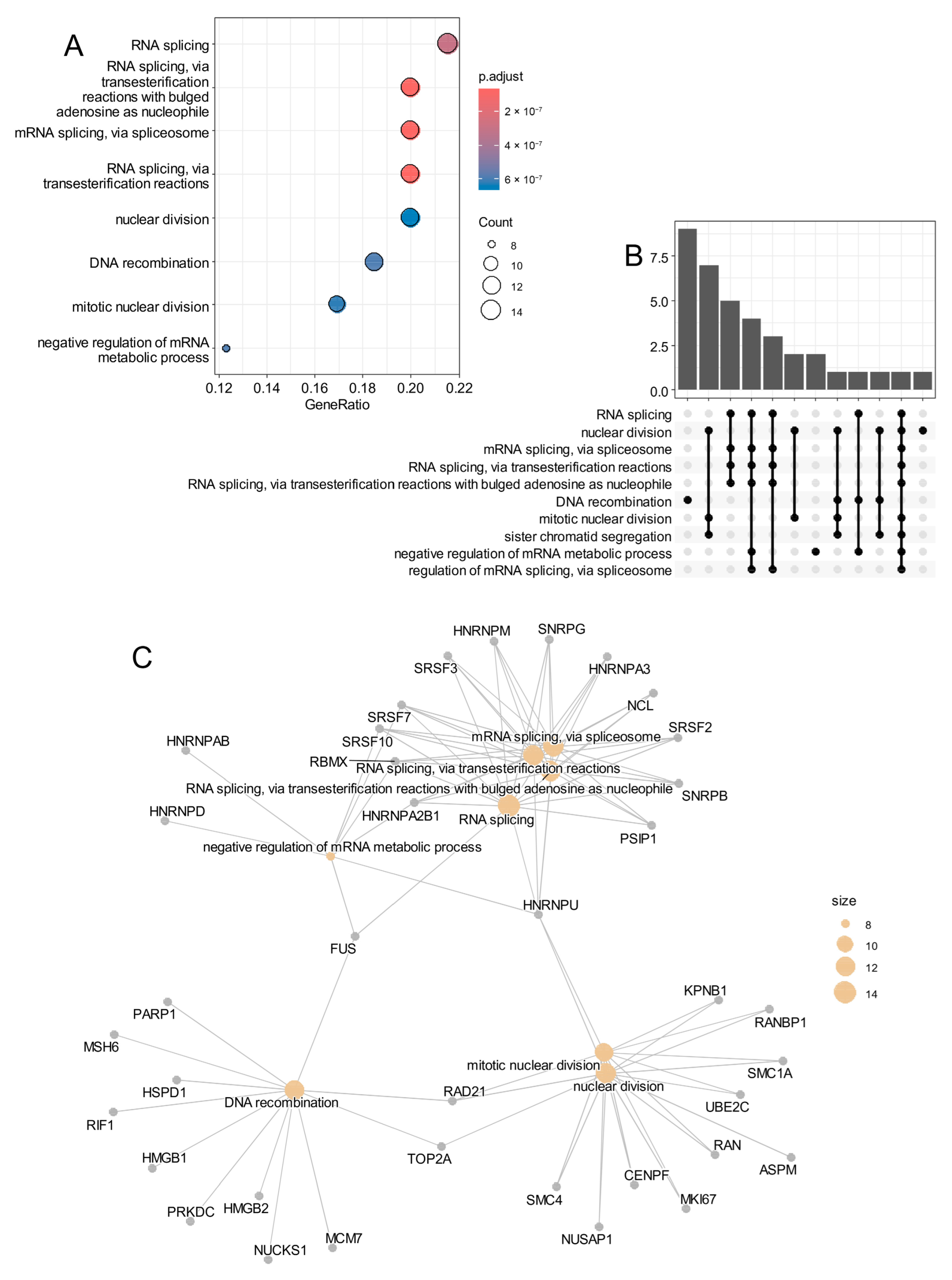
3.2. Epifactor Expression Score Related to RNA Metabolism Is Associated with Medulloblastoma Prognosis
- —
- Female sex (48% vs. 28%, p = 0.0025);
- —
- SHH subtype (46% vs. 10%, p < 1 × 10−4);
- —
- Group 3 subtype (30% vs. 15%, p < 1 × 10−4);
- —
- Metastatic tumors (38% vs. 27%, p = 0.04);
- —
- Recurrent tumors (6.5% vs. 1.7%, p = 0.04).
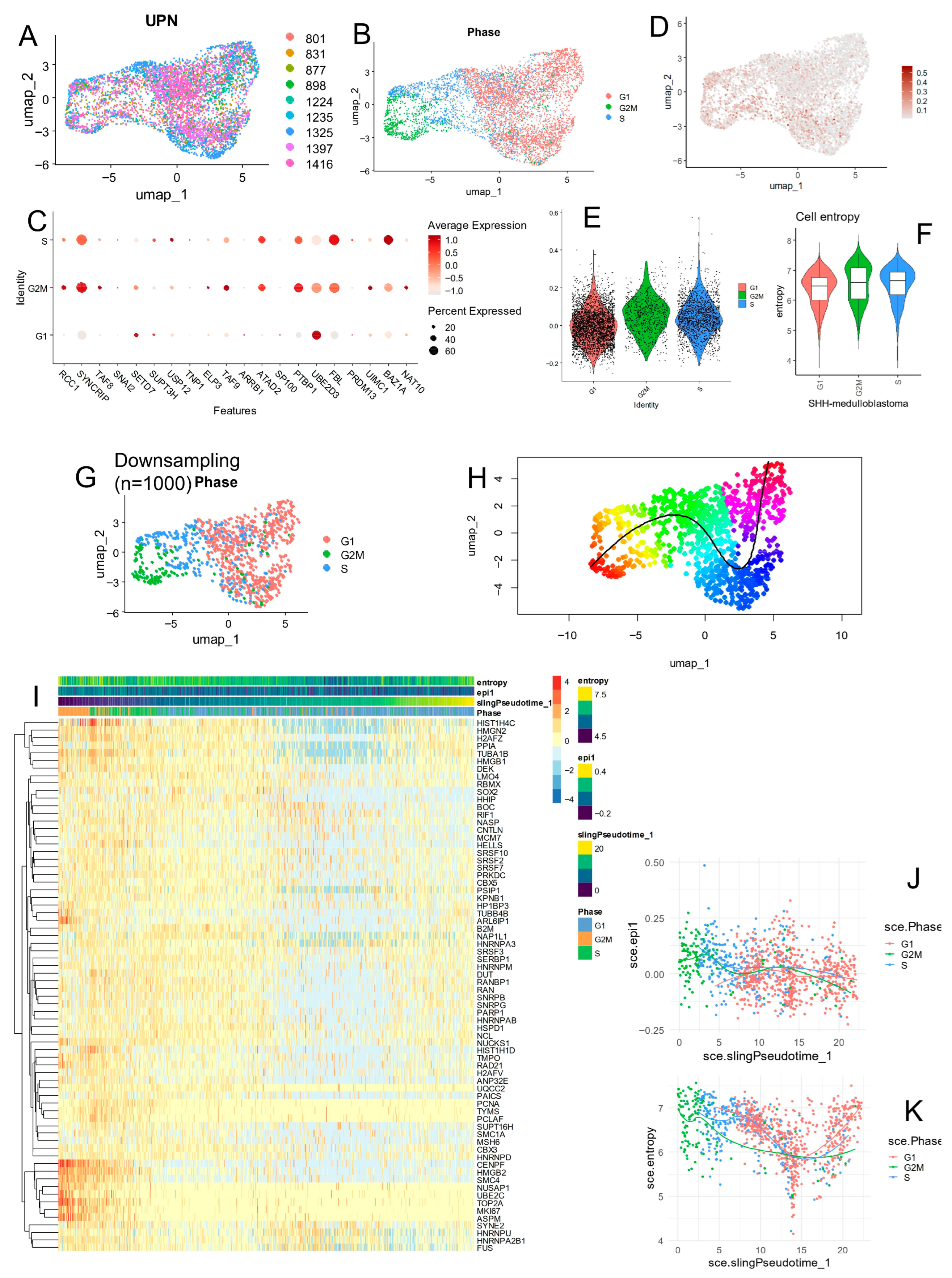
3.3. Epifactor Expression Score Is Elevated in Malignant Cells from the SHH Medulloblastoma Subtype at the Single-Cell Level
- —
- BAZ1A was highly expressed in malignant cells from the SHH subtype.
- —
- FBL showed widespread expression in WNT and SHH subtypes.
- —
- UBE2D3 was particularly enriched in malignant cells from Group 4.
- —
- SYNCRIP was highly expressed in malignant cells from Group 3.
3.4. SHH Medulloblastoma Malignant Cells Exhibit Elevated Epifactor Scores in Proliferative States with High Cellular Entropy
- —
- BAZ1A and FBL were predominantly expressed during the S phase;
- —
- UBE2D3 was mainly expressed in G1 phase;
- —
- SYNCRIP, PTBP1, and TAF9 were up-regulated during the G2/M phase.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MB | Medulloblastoma |
| SHH | Sonic Hedgehog |
| WNT | Wingless-Int1 |
| PPI | Protein–protein interaction |
References
- Kumar, L.P.; Deepa, S.F.A.J.; Moinca, I.; Suresh, P.; Naidu, K.V.J.R. Medulloblastoma: A Common Pediatric Tumor: Prognostic Factors and Predictors of Outcome. Asian J. Neurosurg. 2015, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwalbe, E.C.; Lindsey, J.C.; Nakjang, S.; Crosier, S.; Smith, A.J.; Hicks, D.; Rafiee, G.; Hill, R.M.; Iliasova, A.; Stone, T.; et al. Novel Molecular Subgroups for Clinical Classification and Outcome Prediction in Childhood Medulloblastoma: A Cohort Study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 958–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packer, R.J.; Gajjar, A.; Vezina, G.; Rorke-Adams, L.; Burger, P.C.; Robertson, P.L.; Bayer, L.; LaFond, D.; Donahue, B.R.; Marymont, M.H.; et al. Phase III Study of Craniospinal Radiation Therapy Followed by Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Newly Diagnosed Average-Risk Medulloblastoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 4202–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kijima, N.; Kanemura, Y. Molecular Classification of Medulloblastoma. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2016, 56, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, G.; Parker, M.; Kranenburg, T.A.; Lu, C.; Chen, X.; Ding, L.; Phoenix, T.N.; Hedlund, E.; Wei, L.; Zhu, X.; et al. Novel Mutations Target Distinct Subgroups of Medulloblastoma. Nature 2012, 488, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugh, T.J.; Weeraratne, S.D.; Archer, T.C.; Pomeranz Krummel, D.A.; Auclair, D.; Bochicchio, J.; Carneiro, M.O.; Carter, S.L.; Cibulskis, K.; Erlich, R.L.; et al. Medulloblastoma Exome Sequencing Uncovers Subtype-Specific Somatic Mutations. Nature 2012, 488, 106–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.T.W.; Jäger, N.; Kool, M.; Zichner, T.; Hutter, B.; Sultan, M.; Cho, Y.-J.; Pugh, T.J.; Hovestadt, V.; Stütz, A.M.; et al. Dissecting the Genomic Complexity Underlying Medulloblastoma. Nature 2012, 488, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubuc, A.M.; Remke, M.; Korshunov, A.; Northcott, P.A.; Zhan, S.H.; Mendez-Lago, M.; Kool, M.; Jones, D.T.W.; Un-terberger, A.; Morrissy, A.S.; et al. Aberrant Patterns of H3K4 and H3K27 Histone Lysine Methylation Occur Across Subgroups in Medulloblastoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 125, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalli, F.M.G.; Remke, M.; Rampasek, L.; Peacock, J.; Shih, D.J.H.; Luu, B.; Garzia, L.; Torchia, J.; Nor, C.; Morrissy, A.S.; et al. Intertumoral Heterogeneity Within Medulloblastoma Subgroups. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 737–754.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Liu, A.P.Y.; Northcott, P.A. Medulloblastoma Genomics in the Modern Molecular Era. Brain Pathol. 2020, 30, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovestadt, V.; Ayrault, O.; Swartling, F.J.; Robinson, G.W.; Pfister, S.M.; Northcott, P.A. Medulloblastomics Revisited: Biological and Clinical Insights from Thousands of Patients. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2020, 20, 42–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavalli, G.; Heard, E. Advances in Epigenetics Link Genetics to the Environment and Disease. Nature 2019, 571, 489–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medvedeva, Y.A.; Lennartsson, A.; Ehsani, R.; Kulakovskiy, I.V.; Vorontsov, I.E.; Panahandeh, P.; Khimulya, G.; Kasukawa, T.; The FANTOM Consortium; Drabløs, F. EpiFactors: A Comprehensive Database of Human Epigenetic Factors and Complexes. Database 2015, 2015, bav067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chmykhalo, V.K.; Deev, R.V.; Tokarev, A.T.; Polunina, Y.A.; Xue, L.; Shidlovskii, Y.V. SWI/SNF Complex Connects Signaling and Epigenetic State in Cells of Nervous System. Mol. Neurobiol. 2025, 62, 1536–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J.A.; Gaonkar, K.S.; Spielman, S.J.; Savonen, C.L.; Bethell, C.J.; Jin, R.; Rathi, K.S.; Zhu, Y.; Egolf, L.E.; Farrow, B.K.; et al. OpenPBTA: The Open Pediatric Brain Tumor Atlas. Cell Genomics 2023, 3, 100340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Z.; Wafula, E.; Corbett, R.J.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, R.; Gaonkar, K.S.; Shukla, S.; Rathi, K.S.; Hill, D.; Lahiri, A.; et al. The Open Pediatric Cancer Project 2024. bioRxiv 2025. bioRxiv:2024.07.09.599086. [Google Scholar]
- Leek, J.T.; Johnson, W.E.; Parker, H.S.; Jaffe, A.E.; Storey, J.D. The Sva Package for Removing Batch Effects and Other Unwanted Variation in High-Throughput Experiments. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 882–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, D.; Schwalbe, E.C.; Hicks, D.; Aldinger, K.A.; Lindsey, J.C.; Crosier, S.; Richardson, S.; Goddard, J.; Hill, R.M.; Castle, J.; et al. Medulloblastoma Group 3 and 4 Tumors Comprise a Clinically and Biologically Significant Expression Continuum Reflecting Human Cerebellar Development. Cell Rep. 2022, 40, 111162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riemondy, K.A.; Venkataraman, S.; Willard, N.; Nellan, A.; Sanford, B.; Griesinger, A.M.; Amani, V.; Mitra, S.; Hankinson, T.C.; Handler, M.H.; et al. Neoplastic and Immune Single-Cell Transcriptomics Define Subgroup-Specific Intra-Tumoral Heterogeneity of Childhood Medulloblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 24, 273–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.; Hoffman, P.; Smibert, P.; Papalexi, E.; Satija, R. Integrating Single-Cell Transcriptomic Data across Different Conditions, Technologies, and Species. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tibshirani, R.; Hastie, T.; Narasimhan, B.; Chu, G. Diagnosis of Multiple Cancer Types by Shrunken Centroids of Gene Expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6567–6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A Universal Enrichment Tool for Interpreting Omics Data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene Ontology: Tool for the Unification of Biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Nastou, K.; Koutrouli, M.; Kirsch, R.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Hu, D.; Peluso, M.E.; Huang, Q.; Fang, T.; et al. The STRING Database in 2025: Protein Networks with Directionality of Regulation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 53, D730–D737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: A Worldwide Hub of Protein Knowledge. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D506–D515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desterke, C.; Xiang, Y.; Elhage, R.; Duruel, C.; Chang, Y.; Hamaï, A. Ferroptosis Inducers Upregulate PD-L1 in Recurrent Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Cancers 2023, 16, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Therneau, T.M.; Grambsch, P.M. Modeling Survival Data: Extending the Cox Model; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Harrell, F.E., Jr. Multivariable Modeling Strategies. In Regression Modeling Strategies: With Applications to Linear Models, Logistic and Ordinal Regression, and Survival Analysis; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 63–102. ISBN 978-3-319-19425-7. [Google Scholar]
- Amezquita, R.A.; Lun, A.T.L.; Becht, E.; Carey, V.J.; Carpp, L.N.; Geistlinger, L.; Marini, F.; Rue-Albrecht, K.; Risso, D.; Soneson, C.; et al. Orchestrating Single-Cell Analysis with Bioconductor. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Ji, H. Pseudotime Reconstruction Using TSCAN. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1935, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Z.; Ji, H. TSCAN: Pseudo-Time Reconstruction and Evaluation in Single-Cell RNA-Seq Analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Street, K.; Risso, D.; Fletcher, R.B.; Das, D.; Ngai, J.; Yosef, N.; Purdom, E.; Dudoit, S. Slingshot: Cell Lineage and Pseudotime Inference for Single-Cell Transcriptomics. BMC Genomics 2018, 19, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Wei, G.; Liu, J.; Yang, F.; Sun, R.; Lu, H. Chemotherapy-induced adenosine A2B receptor expression mediates epigenetic regulation of pluripotency factors and promotes breast cancer stemness. Theranostics 2022, 12, 2598–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maassen, A.; Steciuk, J.; Wilga, M.; Szurmak, J.; Garbicz, D.; Sarnowska, E.; Sarnowski, T.J. SWI/SNF-Type Complexes-Transcription Factor Interplay: A Key Regulatory Interaction. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2025, 30, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahma, S.; Henikoff, S. The BAF Chromatin Remodeler Synergizes with RNA Polymerase II and Transcription Factors to Evict Nucleosomes. Nat. Genet. 2024, 56, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokpor, G.; Xie, Y.; Rosenbusch, J.; Tuoc, T. Chromatin Remodeling BAF (SWI/SNF) Complexes in Neural Development and Disorders. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfister, S.; Rea, S.; Taipale, M.; Mendrzyk, F.; Straub, B.; Ittrich, C.; Thuerigen, O.; Sinn, H.P.; Akhtar, A.; Lichter, P. The Histone Acetyltransferase hMOF Is Frequently Downregulated in Primary Breast Carcinoma and Medulloblastoma and Constitutes a Biomarker for Clinical Outcome in Medulloblastoma. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussel, M.F.; Stripay, J.L. Epigenetic Drivers in Pediatric Medulloblastoma. Cerebellum 2018, 17, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, H.; Poore, B.; Brown, E.E.; Qian, J.; Xie, B.; Asimakidou, E.; Razskazovskiy, V.; Ayrapetian, D.; Sharma, V.; Xia, S.; et al. A Neurodevelopmental Epigenetic Programme Mediated by SMARCD3–DAB1–Reelin Signalling Is Hijacked to Promote Medulloblastoma Metastasis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2023, 25, 493–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gershanov, S.; Madiwale, S.; Feinberg-Gorenshtein, G.; Vainer, I.; Nehushtan, T.; Michowiz, S.; Goldenberg-Cohen, N.; Birger, Y.; Toledano, H.; Salmon-Divon, M. Classifying Medulloblastoma Subgroups Based on Small, Clinically Achievable Gene Sets. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 637482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobor, M.S.; Venkatasubrahmanyam, S.; Meneghini, M.D.; Gin, J.W.; Jennings, J.L.; Link, A.J.; Madhani, H.D.; Rine, J. A Protein Complex Containing the Conserved Swi2/Snf2-Related ATPase Swr1p Deposits Histone Variant H2A.Z into Euchromatin. PLoS Biol. 2004, 2, E131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogan, N.J.; Baetz, K.; Keogh, M.-C.; Datta, N.; Sawa, C.; Kwok, T.C.Y.; Thompson, N.J.; Davey, M.G.; Pootoolal, J.; Hughes, T.R.; et al. Regulation of Chromosome Stability by the Histone H2A Variant Htz1, the Swr1 Chromatin Remodeling Complex, and the Histone Acetyltransferase NuA4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13513–13518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuguchi, G.; Shen, X.; Landry, J.; Wu, W.-H.; Sen, S.; Wu, C. ATP-Driven Exchange of Histone H2AZ Variant Catalyzed by SWR1 Chromatin Remodeling Complex. Science 2004, 303, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisner, A.; Pazyra-Murphy, M.F.; Durresi, E.; Zhou, P.; Zhao, X.; Chadwick, E.C.; Xu, P.-X.; Hillman, R.T.; Scott, M.P.; Greenberg, M.E.; et al. The Eya1 Phosphatase Promotes Shh Signaling During Hindbrain Development and Oncogenesis. Dev. Cell 2015, 33, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naik, R.; Galande, S. SATB Family Chromatin Organizers as Master Regulators of Tumor Progression. Oncogene 2019, 38, 1989–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, H.; Shi, L. Progress of Epigenetic Modification of SATB2 Gene in the Pathogenesis of Non-Syndromic Cleft Lip and Palate. Asian J. Surg. 2024, 47, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leone, D.P.; Srinivasan, K.; Chen, B.; Alcamo, E.; McConnell, S.K. The Determination of Projection Neuron Identity in the Developing Cerebral Cortex. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2008, 18, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Britanova, O.; Akopov, S.; Lukyanov, S.; Gruss, P.; Tarabykin, V. Novel Transcription Factor Satb2 Interacts with Matrix Attachment Region DNA Elements in a Tissuespecific Manner and Demonstrates Celltypedependent Expression in the Developing Mouse CNS. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 658–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subhramanyam, C.S.; Cao, Q.; Wang, C.; Heng, Z.S.L.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, Q. Role of PIWI-like 4 in Modulating Neuronal Differentiation from Human Embryonal Carcinoma Cells. RNA Biol. 2020, 17, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández-Ramos, D.; Lopitz-Otsoa, F.; Lu, S.C.; Mato, J.M. S-Adenosylmethionine: A Multifaceted Regulator in Cancer Pathogenesis and Therapy. Cancers 2025, 17, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccara, S.; Ries, R.J.; Jaffrey, S.R. Reading, Writing and Erasing mRNA Methylation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 608–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tassinari, V.; Jia, W.; Chen, W.-L.; Candi, E.; Melino, G. The Methionine Cycle and Its Cancer Implications. Oncogene 2024, 43, 3483–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, C.; Yang, H.; Zhu, L.; Chen, C.; Chen, C.; Zuo, Y.; Zheng, D. The Epigenetic Regulation of Nonhistone Proteins by SETD7: New Targets in Cancer. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 918509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.C.; Meredith, D.M.; Mayer, P.R.; Borromeo, M.D.; Lai, H.C.; Ou, Y.H.; Johnson, J.E. Prdm13 mediates the balance of inhibitory and excitatory neurons in somatosensory circuits. Dev. Cell 2013, 25, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A Summary. Neuro-Oncology 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteller, M. Epigenetics in Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 1148–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variable | Level | Low (n = 116) | High (n = 138) | Total (n = 254) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CANCER_TYPE_DETAILED | Medulloblastoma, WNT-activated | 13 (11.2) | 8 (5.8) | 21 (8.3) | |
| Medulloblastoma, SHH-activated | 11 (9.5) | 63 (45.7) | 74 (29.1) | ||
| Medulloblastoma, Group 4 | 74 (63.8) | 25 (18.1) | 99 (39.0) | ||
| Medulloblastoma, Group 3 | 18 (15.5) | 42 (30.4) | 60 (23.6) | <1 × 10−4 | |
| TUMOR_TYPE | Primary | 81 (69.8) | 74 (53.6) | 155 (61.0) | |
| Metastatic | 31 (26.7) | 53 (38.4) | 84 (33.1) | ||
| Recurrence | 2 (1.7) | 9 (6.5) | 11 (4.3) | ||
| Deceased | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.7) | 1 (0.4) | ||
| Progression | 2 (1.7) | 1 (0.7) | 3 (1.2) | 0.039831 | |
| EXTENT_OF_TUMOR_RESECTION | Gross/Near total resection | 71 (68.3) | 68 (58.6) | 139 (63.2) | |
| Partial resection | 22 (21.2) | 35 (30.2) | 57 (25.9) | ||
| Unavailable | 7 (6.7) | 6 (5.2) | 13 (5.9) | ||
| Biopsy only | 4 (3.8) | 7 (6.0) | 11 (5.0) | 0.350439 | |
| TUMOR_FRACTION | Mean (sd) | 0.7 (0.2) | 0.7 (0.3) | 0.7 (0.3) | 0.806818 |
| TUMOR_PLOIDY | Mean (sd) | 2.5 (0.8) | 2.4 (0.7) | 2.5 (0.7) | 0.384828 |
| CNS_REGION | Ventricles | 9 (7.8) | 8 (5.8) | 17 (6.7) | |
| Posterior fossa | 76 (65.5) | 89 (65.0) | 165 (65.2) | ||
| Mixed | 28 (24.1) | 38 (27.7) | 66 (26.1) | ||
| Spine | 1 (0.9) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.4) | ||
| Hemispheric | 2 (1.7) | 1 (0.7) | 3 (1.2) | ||
| Other | 0 (0.0) | 1 (0.7) | 1 (0.4) | 0.667556 | |
| SEX | Male | 83 (71.6) | 72 (52.2) | 155 (61.0) | |
| Female | 33 (28.4) | 66 (47.8) | 99 (39.0) | 0.002485 |
| Variable | Level | Low (n = 195) | High (n = 136) | Total (n = 331) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| gender | male | 123 (63.1) | 71 (52.2) | 194 (58.6) | |
| female | 54 (27.7) | 47 (34.6) | 101 (30.5) | 0.1329959 | |
| age | >16 | 3 (1.5) | 1 (0.7) | 4 (1.2) | |
| 0 to 3 | 18 (9.2) | 26 (19.1) | 44 (13.3) | ||
| 3 to 16 | 158 (81.0) | 88 (64.7) | 246 (74.3) | ||
| over 16 | 1 (0.5) | 4 (2.9) | 5 (1.5) | 0.0065849 | |
| developmental.stage | adult | 4 (2.1) | 5 (3.7) | 9 (2.7) | |
| infant | 18 (9.2) | 26 (19.1) | 44 (13.3) | ||
| child | 158 (81.0) | 88 (64.7) | 246 (74.3) | 0.0094959 | |
| subgroup | Grp4 | 126 (64.6) | 21 (15.4) | 147 (44.4) | |
| SHH | 11 (5.6) | 56 (41.2) | 67 (20.2) | ||
| MB-NOS | 8 (4.1) | 2 (1.5) | 10 (3.0) | ||
| Grp3 | 19 (9.7) | 44 (32.4) | 63 (19.0) | ||
| WNT | 24 (12.3) | 7 (5.1) | 31 (9.4) | ||
| Grp3/Grp4 | 7 (3.6) | 6 (4.4) | 13 (3.9) | <1 × 10−4 | |
| desmoplastic.nodular | TRUE | 11 (7.7) | 12 (12.6) | 23 (9.7) | |
| FALSE | 132 (92.3) | 83 (87.4) | 215 (90.3) | 0.2988058 | |
| large.cell.anaplastic | FALSE | 133 (93.0) | 75 (78.9) | 208 (87.4) | |
| TRUE | 10 (7.0) | 20 (21.1) | 30 (12.6) | 0.0026912 | |
| ctnnb1.mutation | FALSE | 129 (86.0) | 102 (95.3) | 231 (89.9) | |
| TRUE | 21 (14.0) | 5 (4.7) | 26 (10.1) | 0.0254499 | |
| tp53.mutation | FALSE | 189 (99.5) | 120 (89.6) | 309 (95.4) | |
| TRUE | 1 (0.5) | 14 (10.4) | 15 (4.6) | <1 × 10−4 | |
| tert.mutation | TRUE | 3 (2.1) | 15 (15.2) | 18 (7.4) | |
| FALSE | 140 (97.9) | 84 (84.8) | 224 (92.6) | 0.0003766 | |
| myc.amplification | FALSE | 155 (99.4) | 94 (88.7) | 249 (95.0) | |
| TRUE | 1 (0.6) | 12 (11.3) | 13 (5.0) | 0.0002977 | |
| mycn.amplification | FALSE | 151 (96.8) | 90 (84.1) | 241 (91.6) | |
| TRUE | 5 (3.2) | 17 (15.9) | 22 (8.4) | 0.0006199 | |
| gfi1.rearrangement | FALSE | 191 (97.9) | 131 (96.3) | 322 (97.3) | |
| TRUE | 4 (2.1) | 5 (3.7) | 9 (2.7) | 0.5816415 | |
| gfi1b.rearrangement | FALSE | 192 (98.5) | 136 (100.0) | 328 (99.1) | |
| TRUE | 3 (1.5) | 0 (0.0) | 3 (0.9) | 0.3877762 | |
| prdm6.rearrangement | FALSE | 170 (87.2) | 133 (97.8) | 303 (91.5) | |
| TRUE | 25 (12.8) | 3 (2.2) | 28 (8.5) | 0.0013109 |
| Identifiers | Beta Coefficients | Hazard Ratios | p-Values |
|---|---|---|---|
| MBNL1 | 2.536 | 12.629 | 1.13 × 10−5 |
| ENY2 | 2.427 | 11.32 | 9.42 × 10−5 |
| NAP1L1 | 1.801 | 6.055 | 2.75 × 10−4 |
| NPM1 | 1.39 | 4.015 | 4.65 × 10−4 |
| FOXO1 | 1.667 | 5.297 | 6.51 × 10−4 |
| NEK6 | 1.723 | 5.601 | 8.14 × 10−4 |
| TLE4 | 0.932 | 2.538 | 1.05 × 10−3 |
| DDX21 | 1.92 | 6.821 | 2.16 × 10−3 |
| ZNF516 | 0.893 | 2.443 | 3.10 × 10−3 |
| RCC1 | 1.791 | 5.997 | 3.68 × 10−3 |
| SYNCRIP | 2.145 | 8.546 | 4.85 × 10−3 |
| TAF8 | 1.737 | 5.679 | 7.57 × 10−3 |
| SNAI2 | 1.006 | 2.733 | 1.29 × 10−2 |
| SETD7 | 1.312 | 3.714 | 1.35 × 10−2 |
| SUPT3H | 1.879 | 6.548 | 1.56 × 10−2 |
| USP12 | 2.018 | 7.52 | 1.69 × 10−2 |
| TNP1 | 1.311 | 3.711 | 1.87 × 10−2 |
| ELP3 | 2.074 | 7.957 | 1.95 × 10−2 |
| TAF9 | 2.482 | 11.963 | 1.99 × 10−2 |
| ARRB1 | 1.022 | 2.778 | 2.07 × 10−2 |
| ATAD2 | 1.282 | 3.603 | 2.10 × 10−2 |
| SP100 | 1.032 | 2.806 | 2.16 × 10−2 |
| PTBP1 | 1.231 | 3.425 | 2.59 × 10−2 |
| UBE2D3 | 2.415 | 11.188 | 2.92 × 10−2 |
| FBL | 0.915 | 2.497 | 3.49 × 10−2 |
| PRDM13 | 0.81 | 2.248 | 4.54 × 10−2 |
| UIMC1 | 1.264 | 3.54 | 4.82 × 10−2 |
| BAZ1A | 0.962 | 2.616 | 4.87 × 10−2 |
| NAT10 | 1.554 | 4.729 | 4.95 × 10−2 |
| Term | Hazard Ratios | CI95.Low | CI95.High | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| score | 1.187 | 1.075 | 1.31 | 6.69 × 10−4 |
| AGE | 0.955 | 0.912 | 1.001 | 5.37 × 10−2 |
| SEXMale | 0.879 | 0.536 | 1.441 | 6.08 × 10−1 |
| TUMOR_TYPE: Deceased | 34.982 | 4.107 | 297.998 | 1.14 × 10−3 |
| TUMOR_TYPE: metastatic | 3.004 | 1.843 | 4.896 | 1.02 × 10−5 |
| TUMOR_TYPE: progression | 2.47 | 0.572 | 10.669 | 2.26 × 10−1 |
| TUMOR_TYPE: recurrence | 1.589 | 0.535 | 4.714 | 4.04 × 10−1 |
| Comparison | Mean Groupe 1 | Mean Groupe 2 | t-Test p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| GP4 versus SHH | −0.04 | 0.015 | 1.68 × 10−286 |
| GP4 versus GP3 | −0.04 | 0.001 | 1.57 × 10−195 |
| GP4 versus WNT | −0.04 | −0.026 | 1.55 × 10−5 |
| GP4 versus GP3/4 | −0.04 | −0.08 | 5.94 × 10−94 |
| SHH versus GP3 | 0.015 | 0.001 | 7.13 × 10−19 |
| SHH versus WNT | 0.015 | −0.026 | 5.24 × 10−33 |
| SHH versus GP3/4 | 0.015 | −0.08 | 0 |
| GP3 versus WNT | 0.001 | −0.026 | 9.79 × 10−16 |
| GP3 versus GP3/4 | 0.001 | −0.08 | 8.47 × 10−296 |
| WNT versus GP3/4 | −0.026 | −0.08 | 4.69 × 10−49 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Francés, R.; Bonifacio-Mundaca, J.; Casafont, Í.; Desterke, C.; Mata-Garrido, J. Single-Cell Heterogeneity of Epigenetic Factor Regulation Deciphers Alteration of RNA Metabolism During Proliferative SHH-Medulloblastoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213424
Francés R, Bonifacio-Mundaca J, Casafont Í, Desterke C, Mata-Garrido J. Single-Cell Heterogeneity of Epigenetic Factor Regulation Deciphers Alteration of RNA Metabolism During Proliferative SHH-Medulloblastoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(21):3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213424
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrancés, Raquel, Jenny Bonifacio-Mundaca, Íñigo Casafont, Christophe Desterke, and Jorge Mata-Garrido. 2025. "Single-Cell Heterogeneity of Epigenetic Factor Regulation Deciphers Alteration of RNA Metabolism During Proliferative SHH-Medulloblastoma" Cancers 17, no. 21: 3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213424
APA StyleFrancés, R., Bonifacio-Mundaca, J., Casafont, Í., Desterke, C., & Mata-Garrido, J. (2025). Single-Cell Heterogeneity of Epigenetic Factor Regulation Deciphers Alteration of RNA Metabolism During Proliferative SHH-Medulloblastoma. Cancers, 17(21), 3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17213424





