Alternative Splicing at the Crossroad of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Cancer Risk in Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease
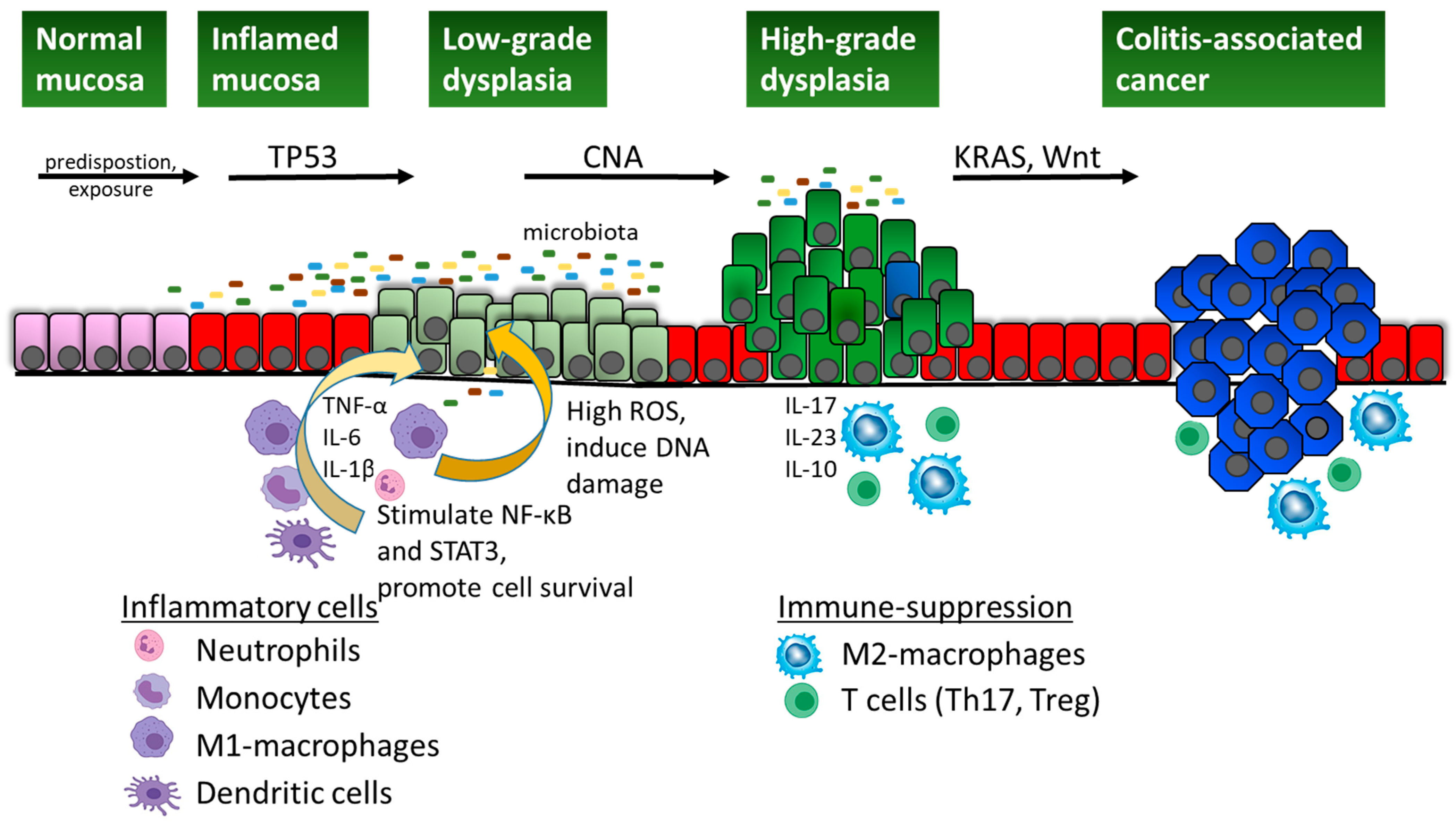
3. Specificities of Colitis-Associated Cancer
4. Molecular Pathways in Colitis-Associated Cancer
4.1. NF-κB Activation
4.2. IL-6/STAT3 Signalling
4.3. WNT Pathway
4.4. Other Pathways
5. Transcriptomic Reprogramming Through Alternative Splicing
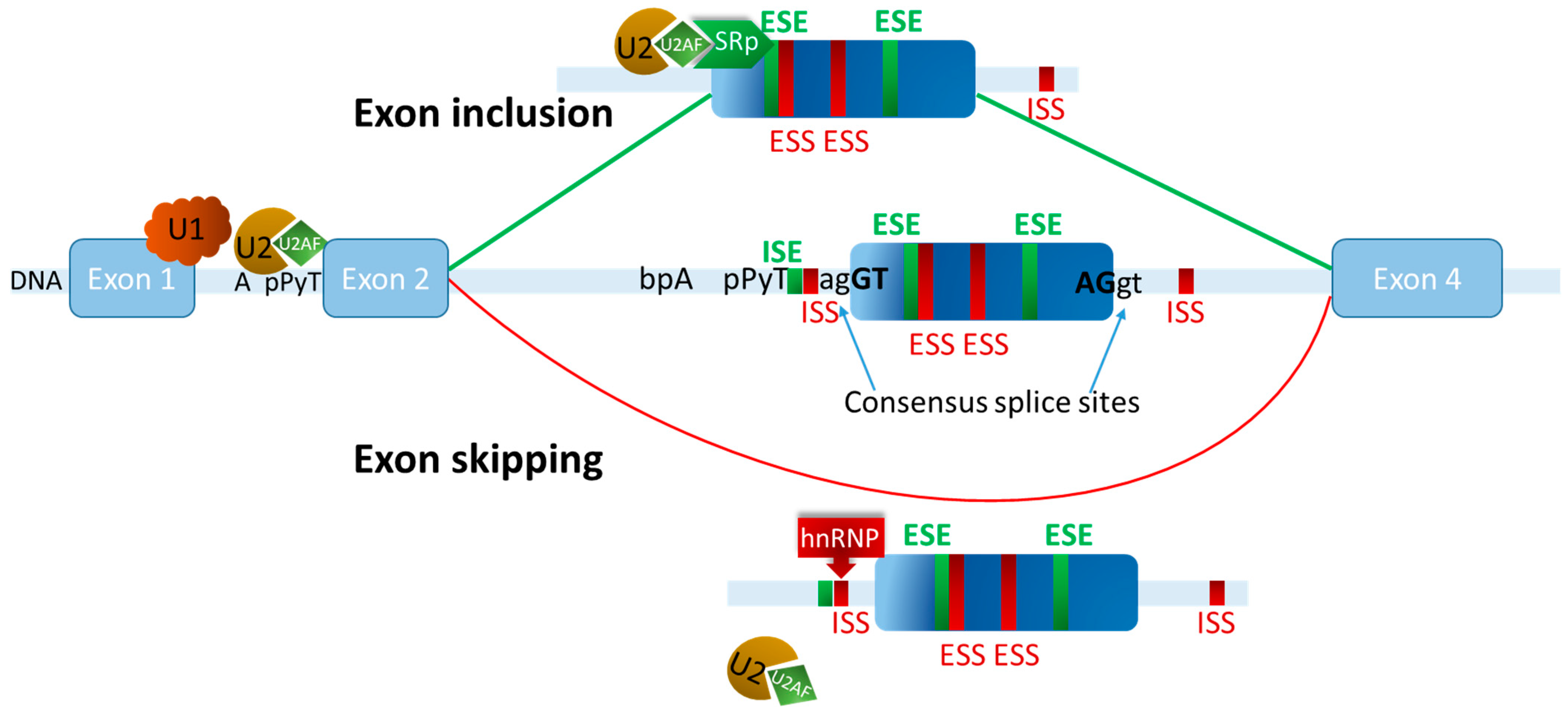
6. Exon Definition Governs Alternative Splicing Decisions
7. The Role of Alternative Splicing in CAC Development
7.1. Splicing Variants Associated with CAC
7.2. Splicing Factors Associated with CAC
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Souza, H.S.P.; Fiocchi, C. Immunopathogenesis of IBD: Current State of the Art. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bamias, G.; Cominelli, F. Exploring the Early Phase of Crohn’s Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 19, 2469–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, T.; Lim, S.S.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi, M.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global Burden of 369 Diseases and Injuries in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990–2019: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Zhang, D. Global, Regional and National Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in 204 Countries and Territories from 1990 to 2019: A Systematic Analysis Based on the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e065186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, J.D.; Parlett, L.E.; Jonsson Funk, M.L.; Brensinger, C.; Pate, V.; Wu, Q.; Dawwas, G.K.; Weiss, A.; Constant, B.D.; McCauley, M.; et al. Incidence, Prevalence, and Racial and Ethnic Distribution of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in the United States. Gastroenterology 2023, 165, 1197–1205.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasvol, T.J.; Horsfall, L.; Bloom, S.; Segal, A.W.; Sabin, C.; Field, N.; Rait, G. Incidence and Prevalence of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in UK Primary Care: A Population-Based Cohort Study. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e036584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Gönczi, L.; Lakatos, P.L.; Burisch, J. The Burden of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Europe in 2020. J. Crohns Colitis 2021, 15, 1573–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, S.-W.; Yen, H.-H.; Chen, Y.-Y. Chemoprevention of Colitis-Associated Dysplasia or Cancer in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Gut Liver 2022, 16, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, S.K.; Kuenzig, M.E.; Windsor, J.W.; Matthews, P.; Tandon, P.; Benchimol, E.I.; Bernstein, C.N.; Bitton, A.; Coward, S.; Jones, J.L.; et al. The 2023 Impact of Inflammatory Bowel Disease in Canada: Cancer and IBD. J. Can. Assoc. Gastroenterol. 2023, 6, S83–S96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bopanna, S.; Ananthakrishnan, A.N.; Kedia, S.; Yajnik, V.; Ahuja, V. Risk of Colorectal Cancer in Asian Patients with Ulcerative Colitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 2, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eaden, J.A. The Risk of Colorectal Cancer in Ulcerative Colitis: A Meta-Analysis. Gut 2001, 48, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadder, N.J.; Valentine, J.F.; Guthery, S.; Singh, H.; Bernstein, C.N.; Leighton, J.A.; Wan, Y.; Wong, J.; Boucher, K.; Pappas, L.; et al. Family History Associates With Increased Risk of Colorectal Cancer in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 17, 1807–1813.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annese, V.; Beaugerie, L.; Egan, L.; Biancone, L.; Bolling, C.; Brandts, C.; Dierickx, D.; Dummer, R.; Fiorino, G.; Gornet, J.M.; et al. European Evidence-Based Consensus: Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Malignancies. J. Crohns Colitis 2015, 9, 945–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and Cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehart, H.; Clevers, H. Tales from the Crypt: New Insights into Intestinal Stem Cells. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patankar, J.V.; Becker, C. Cell Death in the Gut Epithelium and Implications for Chronic Inflammation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.R. Colorectal Cancer in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: The Risk, Pathogenesis, Prevention and Diagnosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 9872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, A.-M.; Cross, W.; Curtius, K.; Al Bakir, I.; Choi, C.-H.R.; Davis, H.L.; Temko, D.; Biswas, S.; Martinez, P.; Williams, M.J.; et al. Evolutionary History of Human Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer. Gut 2019, 68, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olafsson, S.; McIntyre, R.E.; Coorens, T.; Butler, T.; Jung, H.; Robinson, P.S.; Lee-Six, H.; Sanders, M.A.; Arestang, K.; Dawson, C.; et al. Somatic Evolution in Non-Neoplastic IBD-Affected Colon. Cell 2020, 182, 672–684.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanki, K.; Fujii, M.; Shimokawa, M.; Matano, M.; Nishikori, S.; Date, S.; Takano, A.; Toshimitsu, K.; Ohta, Y.; Takahashi, S.; et al. Somatic Inflammatory Gene Mutations in Human Ulcerative Colitis Epithelium. Nature 2020, 577, 254–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakiuchi, N.; Yoshida, K.; Uchino, M.; Kihara, T.; Akaki, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kawada, K.; Nagayama, S.; Yokoyama, A.; Yamamoto, S.; et al. Frequent Mutations That Converge on the NFKBIZ Pathway in Ulcerative Colitis. Nature 2020, 577, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, S.; Norgard, R.J.; Stanger, B.Z. Cellular Plasticity in Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 837–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.C.; Itzkowitz, S.H. Colorectal Cancer in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Mechanisms and Management. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 715–730.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhao, T.; Wu, D.; Li, J.; Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; Hou, S. Colorectal Cancer in Ulcerative Colitis: Mechanisms, Surveillance and Chemoprevention. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 6091–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galandiuk, S.; Rodriguez–Justo, M.; Jeffery, R.; Nicholson, A.M.; Cheng, Y.; Oukrif, D.; Elia, G.; Leedham, S.J.; McDonald, S.A.C.; Wright, N.A.; et al. Field Cancerization in the Intestinal Epithelium of Patients With Crohn’s Ileocolitis. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 855–864.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.W.; Harpaz, N.; Itzkowitz, S.H.; Parsons, R.E. Molecular Mechanisms in Colitis-Associated Colorectal Cancer. Oncogenesis 2023, 12, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajamäki, K.; Taira, A.; Katainen, R.; Välimäki, N.; Kuosmanen, A.; Plaketti, R.-M.; Seppälä, T.T.; Ahtiainen, M.; Wirta, E.-V.; Vartiainen, E.; et al. Genetic and Epigenetic Characteristics of Inflammatory Bowel Disease–Associated Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology 2021, 161, 592–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinchen, J.; Chen, H.H.; Parikh, K.; Antanaviciute, A.; Jagielowicz, M.; Fawkner-Corbett, D.; Ashley, N.; Cubitt, L.; Mellado-Gomez, E.; Attar, M.; et al. Structural Remodeling of the Human Colonic Mesenchyme in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Cell 2018, 175, 372–386.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatila, W.K.; Walch, H.; Hechtman, J.F.; Moyer, S.M.; Sgambati, V.; Faleck, D.M.; Srivastava, A.; Tang, L.; Benhamida, J.; Ismailgeci, D.; et al. Integrated Clinical and Genomic Analysis Identifies Driver Events and Molecular Evolution of Colitis-Associated Cancers. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles, A.I.; Traverso, G.; Zhang, M.; Roberts, N.J.; Khan, M.A.; Joseph, C.; Lauwers, G.Y.; Selaru, F.M.; Popoli, M.; Pittman, M.E.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing Analyses of Inflammatory Bowel Disease−Associated Colorectal Cancers. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 931–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, M.; Oshima, M. Mutant P53 in Colon Cancer. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 11, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirbel, J.; Pyl, P.T.; Kartal, E.; Zych, K.; Kashani, A.; Milanese, A.; Fleck, J.S.; Voigt, A.Y.; Palleja, A.; Ponnudurai, R.; et al. Meta-Analysis of Fecal Metagenomes Reveals Global Microbial Signatures That Are Specific for Colorectal Cancer. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 679–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glassner, K.L.; Abraham, B.P.; Quigley, E.M.M. The Microbiome and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 145, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, J.C.; Perez-Chanona, E.; Mühlbauer, M.; Tomkovich, S.; Uronis, J.M.; Fan, T.-J.; Campbell, B.J.; Abujamel, T.; Dogan, B.; Rogers, A.B.; et al. Intestinal Inflammation Targets Cancer-Inducing Activity of the Microbiota. Science 2012, 338, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zackular, J.P.; Baxter, N.T.; Iverson, K.D.; Sadler, W.D.; Petrosino, J.F.; Chen, G.Y.; Schloss, P.D. The Gut Microbiome Modulates Colon Tumorigenesis. mBio 2013, 4, e00692-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karin, M.; Clevers, H. Reparative Inflammation Takes Charge of Tissue Regeneration. Nature 2016, 529, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T.; Hirayama, D.; Wagatsuma, K.; Yamakawa, T.; Yokoyama, Y.; Nakase, H. Immunological Mechanisms in Inflammation-Associated Colon Carcinogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M. Nuclear Factor-κB in Cancer Development and Progression. Nature 2006, 441, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, B.; Peng, J.; Tang, H.; Wang, S.; Peng, S.; Ye, F.; Wang, J.; Ouyang, K.; Li, J.; et al. Inhibition of NF-κB Signaling Unveils Novel Strategies to Overcome Drug Resistance in Cancers. Drug Resist. Updates 2024, 73, 101042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neurath, M.F.; Finotto, S.; Glimcher, L.H. The Role of Th1/Th2 Polarization in Mucosal Immunity. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschen, A.R.; Tilg, H.; Raine, T. IL-12, IL-23 and IL-17 in IBD: Immunobiology and Therapeutic Targeting. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-W.; Egan, L.; Li, Z.-W.; Greten, F.R.; Kagnoff, M.F.; Karin, M. The Two Faces of IKK and NF-κB Inhibition: Prevention of Systemic Inflammation but Increased Local Injury Following Intestinal Ischemia-Reperfusion. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greten, F.R.; Eckmann, L.; Greten, T.F.; Park, J.M.; Li, Z.-W.; Egan, L.J.; Kagnoff, M.F.; Karin, M. IKKβ Links Inflammation and Tumorigenesis in a Mouse Model of Colitis-Associated Cancer. Cell 2004, 118, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, I.C.; Wilson, J.E.; Schneider, M.; Lich, J.D.; Roberts, R.A.; Arthur, J.C.; Woodford, R.-M.T.; Davis, B.K.; Uronis, J.M.; Herfarth, H.H.; et al. NLRP12 Suppresses Colon Inflammation and Tumorigenesis through the Negative Regulation of Noncanonical NF-κB Signaling. Immunity 2012, 36, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwitalla, S.; Fingerle, A.A.; Cammareri, P.; Nebelsiek, T.; Göktuna, S.I.; Ziegler, P.K.; Canli, O.; Heijmans, J.; Huels, D.J.; Moreaux, G.; et al. Intestinal Tumorigenesis Initiated by Dedifferentiation and Acquisition of Stem-Cell-like Properties. Cell 2013, 152, 25–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooks, T.; Pateras, I.S.; Tarcic, O.; Solomon, H.; Schetter, A.J.; Wilder, S.; Lozano, G.; Pikarsky, E.; Forshew, T.; Rozenfeld, N.; et al. Mutant P53 Prolongs NF-κB Activation and Promotes Chronic Inflammation and Inflammation-Associated Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahini, A.; Shahini, A. Role of Interleukin-6-Mediated Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Focus on the Available Therapeutic Approaches and Gut Microbiome. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2023, 17, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marafini, I.; Sedda, S.; Dinallo, V.; Monteleone, G. Inflammatory Cytokines: From Discoveries to Therapies in IBD. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2019, 19, 1207–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galizia, G.; Orditura, M.; Romano, C.; Lieto, E.; Castellano, P.; Pelosio, L.; Imperatore, V.; Catalano, G.; Pignatelli, C.; De Vita, F. Prognostic Significance of Circulating IL-10 and IL-6 Serum Levels in Colon Cancer Patients Undergoing Surgery. Clin. Immunol. 2002, 102, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, Y.; Chang, Y. Serum Interleukin-6 Levels Reflect the Disease Status of Colorectal Cancer. J. Surg. Oncol. 2003, 83, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogler, G.; Biedermann, L.; Scharl, M. Anti-Cytokine Strategies beyond Anti-Tumour Necrosis Factor-α Therapy: Pathophysiology and Clinical Implications. Dig. Dis. 2017, 35, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; De Haar, C.; Chen, M.; Deuring, J.; Gerrits, M.M.; Smits, R.; Xia, B.; Kuipers, E.J.; Van Der Woude, C.J. Disease-Related Expression of the IL6/STAT3/SOCS3 Signalling Pathway in Ulcerative Colitis and Ulcerative Colitis-Related Carcinogenesis. Gut 2010, 59, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, S.; Hara, T.; Mitsuyama, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Tsuruta, O.; Sata, M.; Scheller, J.; Rose-John, S.; Kado, S.; Takada, T. Essential Roles of IL-6 Trans-Signaling in Colonic Epithelial Cells, Induced by the IL-6/Soluble–IL-6 Receptor Derived from Lamina Propria Macrophages, on the Development of Colitis-Associated Premalignant Cancer in a Murine Model. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 1543–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldner, M.J.; Neurath, M.F. Master Regulator of Intestinal Disease: IL-6 in Chronic Inflammation and Cancer Development. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turano, M.; Cammarota, F.; Duraturo, F.; Izzo, P.; De Rosa, M. A Potential Role of IL-6/IL-6R in the Development and Management of Colon Cancer. Membranes 2021, 11, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalaris, A.; Garbers, C.; Rabe, B.; Rose-John, S.; Scheller, J. The Soluble Interleukin 6 Receptor: Generation and Role in Inflammation and Cancer. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 90, 484–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose-John, S.; Jenkins, B.J.; Garbers, C.; Moll, J.M.; Scheller, J. Targeting IL-6 Trans-Signalling: Past, Present and Future Prospects. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsuyama, K.; Toyonaga, A.; Sasaki, E.; Ishida, O.; Ikeda, H.; Tsuruta, O.; Harada, K.; Tateishi, H.; Nishiyama, T.; Tanikawa, K. Soluble Interleukin-6 Receptors in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Relation to Circulating Interleukin-6. Gut 1995, 36, 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose-John, S.; Mitsuyama, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Thaiss, W.; Scheller, J. Interleukin-6 Trans-Signaling and Colonic Cancer Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2009, 15, 2095–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 Signalling Axis in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhendi, A.; Naser, S.A. The Dual Role of Interleukin-6 in Crohn’s Disease Pathophysiology. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1295230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Chen, M.; Wei, Y.; Ma, X.; Shi, H. Signaling Pathways in Colorectal Cancer: Implications for the Target Therapies. Mol. Biomed. 2024, 5, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grivennikov, S.; Karin, E.; Terzic, J.; Mucida, D.; Yu, G.-Y.; Vallabhapurapu, S.; Scheller, J.; Rose-John, S.; Cheroutre, H.; Eckmann, L.; et al. IL-6 and Stat3 Are Required for Survival of Intestinal Epithelial Cells and Development of Colitis-Associated Cancer. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Lee, H.; Herrmann, A.; Buettner, R.; Jove, R. Revisiting STAT3 Signalling in Cancer: New and Unexpected Biological Functions. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; He, Z.; Ye, J.; Liu, Z.; She, X.; Gao, X.; Liang, R. Progress in Understanding the IL-6/STAT3 Pathway in Colorectal Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 13023–13032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Herrmann, A.; Deng, J.-H.; Kujawski, M.; Niu, G.; Li, Z.; Forman, S.; Jove, R.; Pardoll, D.M.; Yu, H. Persistently Activated Stat3 Maintains Constitutive NF-κB Activity in Tumors. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusse, R.; Clevers, H. Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling, Disease, and Emerging Therapeutic Modalities. Cell 2017, 169, 985–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsukiyama, T.; Fukui, A.; Terai, S.; Fujioka, Y.; Shinada, K.; Takahashi, H.; Yamaguchi, T.P.; Ohba, Y.; Hatakeyama, S. Molecular Role of RNF43 in Canonical and Noncanonical Wnt Signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2015, 35, 2007–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Li, X. Advances of Wnt Signalling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer. Cells 2023, 12, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhir, M.; Montgomery, E.A.; Glöckner, S.C.; Schuebel, K.E.; Hooker, C.M.; Herman, J.G.; Baylin, S.B.; Gearhart, S.L.; Ahuja, N. Epigenetic Regulation of WNT Signaling Pathway Genes in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) Associated Neoplasia. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2008, 12, 1745–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claessen, M.M.H.; Schipper, M.E.I.; Oldenburg, B.; Siersema, P.D.; Offerhaus, G.J.A.; Vleggaar, F.P. WNT-Pathway Activation in IBD-Associated Colorectal Carcinogenesis: Potential Biomarkers for Colonic Surveillance. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2010, 32, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenoy, A.K.; Fisher, R.C.; Butterworth, E.A.; Pi, L.; Chang, L.-J.; Appelman, H.D.; Chang, M.; Scott, E.W.; Huang, E.H. Transition from Colitis to Cancer: High Wnt Activity Sustains the Tumor-Initiating Potential of Colon Cancer Stem Cell Precursors. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 5091–5100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Q.; Geller, D. Cross-Regulation Between WNT and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Forum Immunopathol. Dis. Ther. 2010, 1, 155–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.J.; DuBois, R.N. Role of Prostaglandin E2 in the Progression of Gastrointestinal Cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. 2022, 15, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Rhee, K.-J.; Albesiano, E.; Rabizadeh, S.; Wu, X.; Yen, H.-R.; Huso, D.L.; Brancati, F.L.; Wick, E.; McAllister, F.; et al. A Human Colonic Commensal Promotes Colon Tumorigenesis via Activation of T Helper Type 17 T Cell Responses. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1016–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabijak, L.; Attencourt, C.; Guignant, C.; Chatelain, D.; Marcelo, P.; Marolleau, J.-P.; Treiner, E. Increased Tumor Infiltration by Mucosal-Associated Invariant T Cells Correlates with Poor Survival in Colorectal Cancer Patients. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2015, 64, 1601–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldner, M.J.; Neurath, M.F. Mechanisms of Immune Signaling in Colitis-Associated Cancer. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 1, 6–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kastner, B.; Will, C.L.; Stark, H.; Lührmann, R. Structural Insights into Nuclear Pre-mRNA Splicing in Higher Eukaryotes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2019, 11, a032417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkinson, M.E.; Charenton, C.; Nagai, K. RNA Splicing by the Spliceosome. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2020, 89, 359–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasawa, C.K.; Garcia-Blanco, M.A. Early Splicing Complexes and Human Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blencowe, B.J.; Ahmad, S.; Lee, L.J. Current-Generation High-Throughput Sequencing: Deepening Insights into Mammalian Transcriptomes. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 1379–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keren, H.; Lev-Maor, G.; Ast, G. Alternative Splicing and Evolution: Diversification, Exon Definition and Function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braunschweig, U.; Barbosa-Morais, N.L.; Pan, Q.; Nachman, E.N.; Alipanahi, B.; Gonatopoulos-Pournatzis, T.; Frey, B.; Irimia, M.; Blencowe, B.J. Widespread Intron Retention in Mammals Functionally Tunes Transcriptomes. Genome Res. 2014, 24, 1774–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, H.; Lee, D.; Lee, J.; Park, D.; Kim, Y.J.; Park, W.-Y.; Hong, D.; Park, P.J.; Lee, E. Intron Retention Is a Widespread Mechanism of Tumor-Suppressor Inactivation. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1242–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oltean, S.; Bates, D.O. Hallmarks of Alternative Splicing in Cancer. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5311–5318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnal, S.C.; López-Oreja, I.; Valcárcel, J. Roles and Mechanisms of Alternative Splicing in Cancer—Implications for Care. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 17, 457–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Krainer, A.R.; Abdel-Wahab, O. SnapShot: Splicing Alterations in Cancer. Cell 2020, 180, 208–208.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, R.K.; Anczuków, O. RNA Splicing Dysregulation and the Hallmarks of Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2023, 23, 135–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Zhong, G.; He, C.; Li, M. Targeted Splicing Therapy: New Strategies for Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1222932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertel, K.J. Combinatorial Control of Exon Recognition. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 1211–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartegni, L.; Chew, S.L.; Krainer, A.R. Listening to Silence and Understanding Nonsense: Exonic Mutations That Affect Splicing. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2002, 3, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.C.; Caceres, J.F. The SR Protein Family of Splicing Factors: Master Regulators of Gene Expression. Biochem. J. 2009, 417, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piñol-Roma, S.; Choi, Y.D.; Matunis, M.J.; Dreyfuss, G. Immunopurification of Heterogeneous Nuclear Ribonucleoprotein Particles Reveals an Assortment of RNA-Binding Proteins. Genes Dev. 1988, 2, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Wen, M.; Gao, F.; Wang, Y.; Wei, G.; Duan, Y. Regulation of HNRNP Family by Post-Translational Modifications in Cancer. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matlin, A.J.; Clark, F.; Smith, C.W.J. Understanding Alternative Splicing: Towards a Cellular Code. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 386–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Morais, N.L.; Carmo-Fonseca, M.; Aparício, S. Systematic Genome-Wide Annotation of Spliceosomal Proteins Reveals Differential Gene Family Expansion. Genome Res. 2006, 16, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papasaikas, P.; Tejedor, J.R.; Vigevani, L.; Valcárcel, J. Functional Splicing Network Reveals Extensive Regulatory Potential of the Core Spliceosomal Machinery. Mol. Cell 2015, 57, 7–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ule, J.; Blencowe, B.J. Alternative Splicing Regulatory Networks: Functions, Mechanisms, and Evolution. Mol. Cell 2019, 76, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, V.; Pereira, J.F.S.; Jordan, P. Signaling Pathways Driving Aberrant Splicing in Cancer Cells. Genes 2017, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blencowe, B.J. Alternative Splicing: New Insights from Global Analyses. Cell 2006, 126, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grosso, A.R.; Gomes, A.Q.; Barbosa-Morais, N.L.; Caldeira, S.; Thorne, N.P.; Grech, G.; Von Lindern, M.; Carmo-Fonseca, M. Tissue-Specific Splicing Factor Gene Expression Signatures. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 4823–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallego-Paez, L.M.; Bordone, M.C.; Leote, A.C.; Saraiva-Agostinho, N.; Ascensão-Ferreira, M.; Barbosa-Morais, N.L. Alternative Splicing: The Pledge, the Turn, and the Prestige: The Key Role of Alternative Splicing in Human Biological Systems. Hum. Genet. 2017, 136, 1015–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.W.; Valcárcel, J. Alternative Pre-mRNA Splicing: The Logic of Combinatorial Control. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2000, 25, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.-D.; Ares, M. Context-Dependent Control of Alternative Splicing by RNA-Binding Proteins. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2014, 15, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luco, R.F.; Pan, Q.; Tominaga, K.; Blencowe, B.J.; Pereira-Smith, O.M.; Misteli, T. Regulation of Alternative Splicing by Histone Modifications. Science 2010, 327, 996–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Jiang, J.; Duan, C.-G. The Crosstalk Between Epigenetic Mechanisms and Alternative RNA Processing Regulation. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Mata, M.; Alonso, C.R.; Kadener, S.; Fededa, J.P.; Blaustein, M.; Pelisch, F.; Cramer, P.; Bentley, D.; Kornblihtt, A.R. A Slow RNA Polymerase II Affects Alternative Splicing in Vivo. Mol. Cell 2003, 12, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häsler, R.; Kerick, M.; Mah, N.; Hultschig, C.; Richter, G.; Bretz, F.; Sina, C.; Lehrach, H.; Nietfeld, W.; Schreiber, S.; et al. Alterations of Pre-mRNA Splicing in Human Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 90, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, V.; Henriques, A.F.A.; Matos, P.; Jordan, P. Ibuprofen Disrupts a WNK1/GSK3β/SRPK1 Protein Complex Required for Expression of Tumor-Related Splicing Variant RAC1B in Colorectal Cells. Oncotarget 2020, 11, 4421–4437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, K.; Somineni, H.; Prince, J.; Kugathasan, S.; Gibson, G. Altered Splicing Associated with the Pathology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Hum. Genomics 2021, 15, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Song, Y.; Leng, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Z. The Regulatory Role of Alternative Splicing in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1095267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díez-Obrero, V.; Dampier, C.H.; Moratalla-Navarro, F.; Devall, M.; Plummer, S.J.; Díez-Villanueva, A.; Peters, U.; Bien, S.; Huyghe, J.R.; Kundaje, A.; et al. Genetic Effects on Transcriptome Profiles in Colon Epithelium Provide Functional Insights for Genetic Risk Loci. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 12, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, C.A. Apoptosis Inhibiting Factor Bcl-xL Might Be the Crucial Member of the Bcl-2 Gene Family in Colorectal Cancer. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1998, 43, 2641–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bielli, P.; Bordi, M.; Biasio, V.D.; Sette, C. Regulation of BCL-X Splicing Reveals a Role for the Polypyrimidine Tract Binding Protein (PTBP1/hnRNP I) in Alternative 5′ Splice Site Selection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 12070–12081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shultz, J.C.; Goehe, R.W.; Wijesinghe, D.S.; Murudkar, C.; Hawkins, A.J.; Shay, J.W.; Minna, J.D.; Chalfant, C.E. Alternative Splicing of Caspase 9 Is Modulated by the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Akt Pathway via Phosphorylation of SRp30a. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9185–9196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Su, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, S.; Lei, H.; Ma, F.; Shi, M.; Shi, W.; Xie, X.; Di, C. Aberrant Cyclin D1 Splicing in Cancer: From Molecular Mechanism to Therapeutic Modulation. Cell Death Dis. 2023, 14, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeilstra, J.; Joosten, S.P.J.; Van Andel, H.; Tolg, C.; Berns, A.; Snoek, M.; Van De Wetering, M.; Spaargaren, M.; Clevers, H.; Pals, S.T. Stem Cell CD44v Isoforms Promote Intestinal Cancer Formation in Apc(Min) Mice Downstream of Wnt Signaling. Oncogene 2014, 33, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todaro, M.; Gaggianesi, M.; Catalano, V.; Benfante, A.; Iovino, F.; Biffoni, M.; Apuzzo, T.; Sperduti, I.; Volpe, S.; Cocorullo, G.; et al. CD44v6 Is a Marker of Constitutive and Reprogrammed Cancer Stem Cells Driving Colon Cancer Metastasis. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 342–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ieda, J.; Yokoyama, S.; Tamura, K.; Takifuji, K.; Hotta, T.; Matsuda, K.; Oku, Y.; Nasu, T.; Kiriyama, S.; Yamamoto, N.; et al. Re-expression of CEACAM1 Long Cytoplasmic Domain Isoform Is Associated with Invasion and Migration of Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 1351–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Xu, L.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, L. Aberrant FAM135B Attenuates the Efficacy of Chemotherapy in Colorectal Cancer by Modulating SRSF1-Mediated Alternative Splicing. Oncogene 2024, 43, 3532–3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vilys, L.; Peciuliene, I.; Jakubauskiene, E.; Zinkeviciute, R.; Makino, Y.; Kanopka, A. U2AF—Hypoxia-Induced Fas Alternative Splicing Regulator. Exp. Cell Res. 2021, 399, 112444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mager, L.F.; Koelzer, V.H.; Stuber, R.; Thoo, L.; Keller, I.; Koeck, I.; Langenegger, M.; Simillion, C.; Pfister, S.P.; Faderl, M.; et al. The ESRP1-GPR137 Axis Contributes to Intestinal Pathogenesis. eLife 2017, 6, e28366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groulx, J.-F.; Giroux, V.; Beauséjour, M.; Boudjadi, S.; Basora, N.; Carrier, J.C.; Beaulieu, J.-F. Integrin α6A Splice Variant Regulates Proliferation and the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Human Colorectal Cancer Cells. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 1217–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maimon, A.; Mogilevsky, M.; Shilo, A.; Golan-Gerstl, R.; Obiedat, A.; Ben-Hur, V.; Lebenthal-Loinger, I.; Stein, I.; Reich, R.; Beenstock, J.; et al. Mnk2 Alternative Splicing Modulates the P38-MAPK Pathway and Impacts Ras-Induced Transformation. Cell Rep. 2014, 7, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Li, X.; Zhao, W.; Wang, X.; Jin, L.; Feng, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, M.; Tian, Y.; Hu, G.; et al. SF3B3-Regulated mTOR Alternative Splicing Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression and Metastasis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2024, 43, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, J.; Hassan, W.; Xu, D.; Wang, X.; Huang, Z. Sam68 Promotes Aerobic Glycolysis in Colorectal Cancer by Regulating PKM2 Alternative Splicing. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, P.; Collard, J.G.; Jordan, P. Tumor-Related Alternatively Spliced Rac1b Is Not Regulated by Rho-GDP Dissociation Inhibitors and Exhibits Selective Downstream Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 50442–50448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghigna, C.; Giordano, S.; Shen, H.; Benvenuto, F.; Castiglioni, F.; Comoglio, P.M.; Green, M.R.; Riva, S.; Biamonti, G. Cell Motility Is Controlled by SF2/ASF through Alternative Splicing of the Ron Protooncogene. Mol. Cell 2005, 20, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karni, R.; de Stanchina, E.; Lowe, S.W.; Sinha, R.; Mu, D.; Krainer, A.R. The Gene Encoding the Splicing Factor SF2/ASF Is a Proto-Oncogene. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, E.; Leeman, S.E.; Watts, L.A.; Coukos, J.A.; O’Brien, M.J.; Cerda, S.R.; Farraye, F.A.; Stucchi, A.F.; Becker, J.M. Truncated Neurokinin-1 Receptor Is Increased in Colonic Epithelial Cells from Patients with Colitis-Associated Cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17420–17425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.-E.; Won, M.; Lee, S.-G.; Park, C.; Song, C.-H.; Kim, K.K. RBM47-Regulated Alternative Splicing of TJP1 Promotes Actin Stress Fiber Assembly during Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. Oncogene 2019, 38, 6521–6536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, R.; Peña, C.; Silva, J.; Lorenzo, Y.; García, V.; García, J.M.; Sánchez, A.; Espinosa, P.; Yuste, R.; Bonilla, F.; et al. P73 Isoforms Affect VEGF, VEGF165 b and PEDF Expression in Human Colorectal Tumors: VEGF165 b Downregulation as a Marker of Poor Prognosis. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 1060–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Luo, Y.; Guo, R.; Zhan, Z.; Wei, N.; Xie, Z.; Shen, L.; et al. U2-related Proteins CHERP and SR140 Contribute to Colorectal Tumorigenesis via Alternative Splicing Regulation. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 2728–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, E.N.D.; Mokhtar, N.M.; Wong, Z.; Raja Ali, R.A. Colonic Mucosal Transcriptomic Changes in Patients with Long-Duration Ulcerative Colitis Revealed Colitis-Associated Cancer Pathways. J. Crohns Colitis 2019, 13, 755–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, J.F.S.; Bessa, C.; Matos, P.; Jordan, P. Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Trigger the Overexpression of Tumour-Related Splice Variant RAC1B in Polarized Colorectal Cells. Cancers 2022, 14, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, P.; Brazão, R.; Boavida, M.G.; Gespach, C.; Chastre, E. Cloning of a Novel Human Rac1b Splice Variant with Increased Expression in Colorectal Tumors. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6835–6839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, P.; Kotelevets, L.; Goncalves, V.; Henriques, A.; Zerbib, P.; Moyer, M.P.; Chastre, E.; Jordan, P. Ibuprofen Inhibits Colitis-Induced Overexpression of Tumor-Related Rac1b. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, P.; Oliveira, C.; Velho, S.; Gonçalves, V.; da Costa, L.T.; Moyer, M.P.; Seruca, R.; Jordan, P. B-Raf(V600E) Cooperates with Alternative Spliced Rac1b to Sustain Colorectal Cancer Cell Survival. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 899–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotelevets, L.; Chastre, E. Rac1 Signaling: From Intestinal Homeostasis to Colorectal Cancer Metastasis. Cancers 2020, 12, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriques, A.; Barros, P.; Moyer, M.P.; Matos, P.; Jordan, P. Expression of Tumour-Related Rac1b Antagonizes B-Raf-Induced Senescence in Colorectal Cells. Cancer Lett. 2015, 369, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Ying, L.; Wang, H.; Wei, S.-S.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y.-H.; Xu, W.-P.; Jie, Q.-Q.; Zhou, Q.; Li, Y.-G.; et al. Rac1b Enhances Cell Survival through Activation of the JNK2/c-JUN/Cyclin-D1 and AKT2/MCL1 Pathways. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 17970–17985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotelevets, L.; Walker, F.; Mamadou, G.; Lehy, T.; Jordan, P.; Chastre, E. The Rac1 Splice Form Rac1b Favors Mouse Colonic Mucosa Regeneration and Contributes to Intestinal Cancer Progression. Oncogene 2018, 37, 6054–6068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goka, E.T.; Chaturvedi, P.; Lopez, D.T.M.; Garza, A.D.L.; Lippman, M.E. RAC1b Overexpression Confers Resistance to Chemotherapy Treatment in Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radisky, D.C.; Levy, D.D.; Littlepage, L.E.; Liu, H.; Nelson, C.M.; Fata, J.E.; Leake, D.; Godden, E.L.; Albertson, D.G.; Nieto, M.A.; et al. Rac1b and Reactive Oxygen Species Mediate MMP-3-Induced EMT and Genomic Instability. Nature 2005, 436, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.K.; Lee, K.; Radisky, D.C.; Nelson, C.M. Extracellular Matrix Proteins Regulate Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Mammary Epithelial Cells. Differentiation 2013, 86, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melzer, C.; Hass, R.; Lehnert, H.; Ungefroren, H. RAC1B: A Rho GTPase with Versatile Functions in Malignant Transformation and Tumor Progression. Cells 2019, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungefroren, H.; Wellner, U.F.; Keck, T.; Lehnert, H.; Marquardt, J.-U. The Small GTPase RAC1B: A Potent Negative Regulator of-and Useful Tool to Study-TGFβ Signaling. Cancers 2020, 12, 3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pethe, V.V.; Charames, G.S.; Bapat, B. Rac1b Recruits Dishevelled and β-Catenin to Wnt Target Gene Promoters Independent of Wnt3A Stimulation. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 39, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.; Chen, Q.K.; Lui, C.; Cichon, M.A.; Radisky, D.C.; Nelson, C.M. Matrix Compliance Regulates Rac1b Localization, NADPH Oxidase Assembly, and Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition. Mol. Biol. Cell 2012, 23, 4097–4108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Aranda, M.; Téllez, T.; McKenna, L.; Redondo, M. Neurokinin-1 Receptor (NK-1R) Antagonists as a New Strategy to Overcome Cancer Resistance. Cancers 2022, 14, 2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goode, T. Neurokinin-1 Receptor Expression in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Molecular Quantitation and Localisation. Gut 2000, 47, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Renzi, D.; Pellegrini, B.; Tonelli, F.; Surrenti, C.; Calabrò, A. Substance P (Neurokinin-1) and Neurokinin A (Neurokinin-2) Receptor Gene and Protein Expression in the Healthy and Inflamed Human Intestine. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 1511–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Valaiyaduppu Subas, S.; Ghani, M.R.; Busa, V.; Dardeir, A.; Marudhai, S.; Cancarevic, I. Role of Substance P in the Pathophysiology of Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Its Correlation With the Degree of Inflammation. Cureus 2020, 12, e11027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.; Coveñas, R. Neurokinin-1 Receptor Antagonists as Antitumor Drugs in Gastrointestinal Cancer: A New Approach. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coveñas, R.; Muñoz, M. Involvement of the Substance P/Neurokinin-1 Receptor System in Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, S.J.; Morris, J.L.; Gibbins, I.L. Cloning of a C-Terminally Truncated NK-1 Receptor from Guinea-Pig Nervous System. Mol. Brain Res. 2003, 111, 136–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, S.D.; Leeman, S.E. Neurokinin-1 Receptor: Functional Significance in the Immune System in Reference to Selected Infections and Inflammation. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2011, 1217, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, J.-P.; Lai, S.; Tuluc, F.; Tansky, M.F.; Kilpatrick, L.E.; Leeman, S.E.; Douglas, S.D. Differences in the Length of the Carboxyl Terminus Mediate Functional Properties of Neurokinin-1 Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 12605–12610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitsin, S.; Pappa, V.; Douglas, S.D. Truncation of Neurokinin-1 Receptor—Negative Regulation of Substance P Signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2018, 103, 1043–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, A.; Lal, G. Neurokinin Receptors and Their Implications in Various Autoimmune Diseases. Curr. Res. Immunol. 2021, 2, 66–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Wang, Z. Difference in Expression of Two Neurokinin-1 Receptors in Adenoma and Carcinoma from Patients That Underwent Radical Surgery for Colorectal Carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 3729–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kretova, M.; Selicky, T.; Cipakova, I.; Cipak, L. Regulation of Pre-mRNA Splicing: Indispensable Role of Post-Translational Modifications of Splicing Factors. Life 2023, 13, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, V.; Matos, P.; Jordan, P. Antagonistic SR Proteins Regulate Alternative Splicing of Tumor-Related Rac1b Downstream of the PI3-Kinase and Wnt Pathways. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 3696–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, V.; Henriques, A.; Pereira, J.; Neves Costa, A.; Moyer, M.P.; Moita, L.F.; Gama-Carvalho, M.; Matos, P.; Jordan, P. Phosphorylation of SRSF1 by SRPK1 Regulates Alternative Splicing of Tumor-Related Rac1b in Colorectal Cells. RNA 2014, 20, 474–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, V.; Jordan, P. Posttranscriptional Regulation of Splicing Factor SRSF1 and Its Role in Cancer Cell Biology. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 287048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Zhao, J.; Xu, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y. Bioinformatics Analysis of SRSF1-controlled Gene Networks in Colorectal Cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 5393–5399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Paz, S.; Ritchie, A.; Mauer, C.; Caputi, M. The RNA Binding Protein SRSF1 Is a Master Switch of Gene Expression and Regulation in the Immune System. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021, 57, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassidy, M.F.; Herbert, Z.T.; Moulton, V.R. Splicing Factor SRSF1 Controls Distinct Molecular Programs in Regulatory and Effector T Cells Implicated in Systemic Autoimmune Disease. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 141, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Qiu, J.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Plocinik, R.M.; Li, H.; Hu, Q.; Ghosh, G.; Adams, J.A.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; et al. The Akt-SRPK-SR Axis Constitutes a Major Pathway in Transducing EGF Signaling to Regulate Alternative Splicing in the Nucleus. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weg-Remers, S.; Ponta, H.; Herrlich, P.; König, H. Regulation of Alternative Pre-mRNA Splicing by the ERK MAP-Kinase Pathway. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 4194–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matter, N.; Herrlich, P.; König, H. Signal-Dependent Regulation of Splicing via Phosphorylation of Sam68. Nature 2002, 420, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisserant, A.; König, H. Signal-Regulated Pre-mRNA Occupancy by the General Splicing Factor U2AF. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manco, M.; Ala, U.; Cantarella, D.; Tolosano, E.; Medico, E.; Altruda, F.; Fagoonee, S. The RNA-Binding Protein ESRP1 Modulates the Expression of RAC1b in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Cancers 2021, 13, 4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleymanjahi, S.; Blanc, V.; Molitor, E.A.; Alvarado, D.M.; Xie, Y.; Gazit, V.; Brown, J.W.; Byrnes, K.; Liu, T.-C.; Mills, J.C.; et al. RBM47 Regulates Intestinal Injury and Tumorigenesis by Modifying Proliferation, Oxidative Response, and Inflammatory Pathways. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e161118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokavec, M.; Kaller, M.; Horst, D.; Hermeking, H. Pan-Cancer EMT-Signature Identifies RBM47 down-Regulation during Colorectal Cancer Progression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Wang, Z.; Luo, L.; Chen, Y.; Han, G.; Wang, R.; Xiao, H.; Li, X.; Hou, C.; Feng, J.; et al. Spliceosome Protein Eftud2 Promotes Colitis-Associated Tumorigenesis by Modulating Inflammatory Response of Macrophage. Mucosal Immunol. 2019, 12, 1164–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.; Zan, X.; Jia, Z.; Zheng, L.; Gu, Y.; Liu, F.; Han, Y.; Xu, C.; Wu, A.; Zhi, Q. Crosstalk between Alternative Splicing and Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Basic Mechanisms, Biotechnological Progresses and Future Perspectives. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mata-Garrido, J.; Xiang, Y.; Chang-Marchand, Y.; Reisacher, C.; Ageron, E.; Guerrera, I.C.; Casafont, I.; Bruneau, A.; Cherbuy, C.; Treton, X.; et al. The Heterochromatin Protein 1 Is a Regulator in RNA Splicing Precision Deficient in Ulcerative Colitis. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batsché, E.; Yi, J.; Mauger, O.; Kornobis, E.; Hopkins, B.; Hanmer-Lloyd, C.; Muchardt, C. CD44 Alternative Splicing Senses Intragenic DNA Methylation in Tumors via Direct and Indirect Mechanisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 6213–6237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessa, C.; Matos, P.; Jordan, P.; Gonçalves, V. Alternative Splicing: Expanding the Landscape of Cancer Biomarkers and Therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancamelbeke, M.; Vanuytsel, T.; Farré, R.; Verstockt, S.; Ferrante, M.; Van Assche, G.; Rutgeerts, P.; Schuit, F.; Vermeire, S.; Arijs, I.; et al. Genetic and Transcriptomic Bases of Intestinal Epithelial Barrier Dysfunction in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2017, 23, 1718–1729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiser, M.; Simon, J.M.; Kochar, B.; Tovar, A.; Israel, J.W.; Robinson, A.; Gipson, G.R.; Schaner, M.S.; Herfarth, H.H.; Sartor, R.B.; et al. Molecular Classification of Crohn’s Disease Reveals Two Clinically Relevant Subtypes. Gut 2018, 67, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, J.; Waetzig, G.H.; Chalaris, A.; Reinheimer, T.M.; Wege, H.; Rose-John, S.; Garbers, C. Different Soluble Forms of the Interleukin-6 Family Signal Transducer Gp130 Fine-Tune the Blockade of Interleukin-6 Trans-Signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 16186–16196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Marotte, H.; Kwan, K.; Ruth, J.H.; Campbell, P.L.; Rabquer, B.J.; Pakozdi, A.; Koch, A.E. Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Inhibits IL-6 Synthesis and Suppresses Transsignaling by Enhancing Soluble Gp130 Production. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14692–14697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, P.; Lu, L.; Cai, S.; Chen, J.; Lin, W.; Han, F. Alternative Splicing: A New Cause and Potential Therapeutic Target in Autoimmune Disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 713540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Name | Colon Cancer-related Variant | Splicing Event | Functional Properties | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCL2L1 | BCL-xL | Alternative 5′ splice site usage in exon 2 | Anti-apoptotic effect at mitochondria | [113,114] |
| CASP 9 | Caspase 9b | Skipping of exons 3–6 | Anti-apoptotic effect in caspase cascade | [115] |
| CCND1 | CCND1b | Intron 4 retention creates alternative C-terminus | Cyclin D variant for cell cycle progression | [116] |
| CD44 | CD44 v4–10 | Inclusion of variable exons 4–10 | Increased interaction with HGF stimulates proliferation | [117] |
| CD44 v6 | Inclusion of exon v6 | Enhances EMT, cell motility, and invasion | [118] | |
| CEACAM1 | CEACAM1-S | Skipping of exon 7 | Promotes migration and invasion | [119] |
| FAAD20 | FAAD20-t | Exon 4 inclusion | Enhanced binding to Fanconi anemia group A protein improves DNA repair | [120] |
| FAS (CD95) | sFAS | Skipping of exon 6 | Anti-apoptotic soluble Fas isoform | [121] |
| GPR137 | GPR137-L | Exon 4 inclusion | WNT signalling activation | [122] |
| IL6R | sIL-6R | Skipping of exon 10 | Lacks transmembrane domain and is secreted as soluble protein | [55] |
| ITGA6 | ITGA6A | Skipping of exon 25 | Integrin α6 variant that activates the WNT/β-catenin pathway | [123] |
| MKNK2 | MNK2b | Skipping of exon 14a | Pro-oncogenic variant lacking a domain capable of activating p38α–MAPK-mediated cell death | [124] |
| MTOR | fl-mTOR | Exon 8 inclusion | Increased pro-proliferative signalling | [125] |
| PKM | PKM2 | Inclusion of exon 10 instead of exon 9 | Increased aerobic glycolysis and lactate generation for metabolic adaptation | [126] |
| RAC1 | RAC1B | Inclusion of exon 3b | Promotes NF-κB signalling and cell survival | [127] |
| RON (MST1R) | deltaRON | Skipping of exon 11 | Enhances EMT, cell motility, and invasion | [128] |
| RPS6KB1 | S6K-p31 (isoform 2) | Alternative C-terminal cassette exons (6a, 6b, and 7a) | S6-kinase variant activates mTORC1 activity and cell growth | [129] |
| TACE1 | tr-NK-1R | Intron 4 retention | Different ligand affinity and signalling outcomes | [130] |
| TJP1 (ZO1) | TJP1-E20 | Skipping of exon 20 | Promotes EMT and cell proliferation | [131] |
| VEGF | VEGF165a | Proximal splice site usage in exon 8 | Promotes angiogenesis | [132] |
| UPF3A | UPF3A-S | Skipping of exon 4 | Promotes proliferation | [133] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Matos, P.; Jordan, P. Alternative Splicing at the Crossroad of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer. Cancers 2025, 17, 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17020219
Matos P, Jordan P. Alternative Splicing at the Crossroad of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer. Cancers. 2025; 17(2):219. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17020219
Chicago/Turabian StyleMatos, Paulo, and Peter Jordan. 2025. "Alternative Splicing at the Crossroad of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer" Cancers 17, no. 2: 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17020219
APA StyleMatos, P., & Jordan, P. (2025). Alternative Splicing at the Crossroad of Inflammatory Bowel Diseases and Colitis-Associated Colon Cancer. Cancers, 17(2), 219. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17020219






