Targeting Mediator Kinase Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 8/19 Potentiates Chemotherapeutic Responses, Reverses Tumor Growth, and Prolongs Survival from Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines, Culture Conditions, and Reagents
2.2. Cell Proliferation and IC 50 Assays
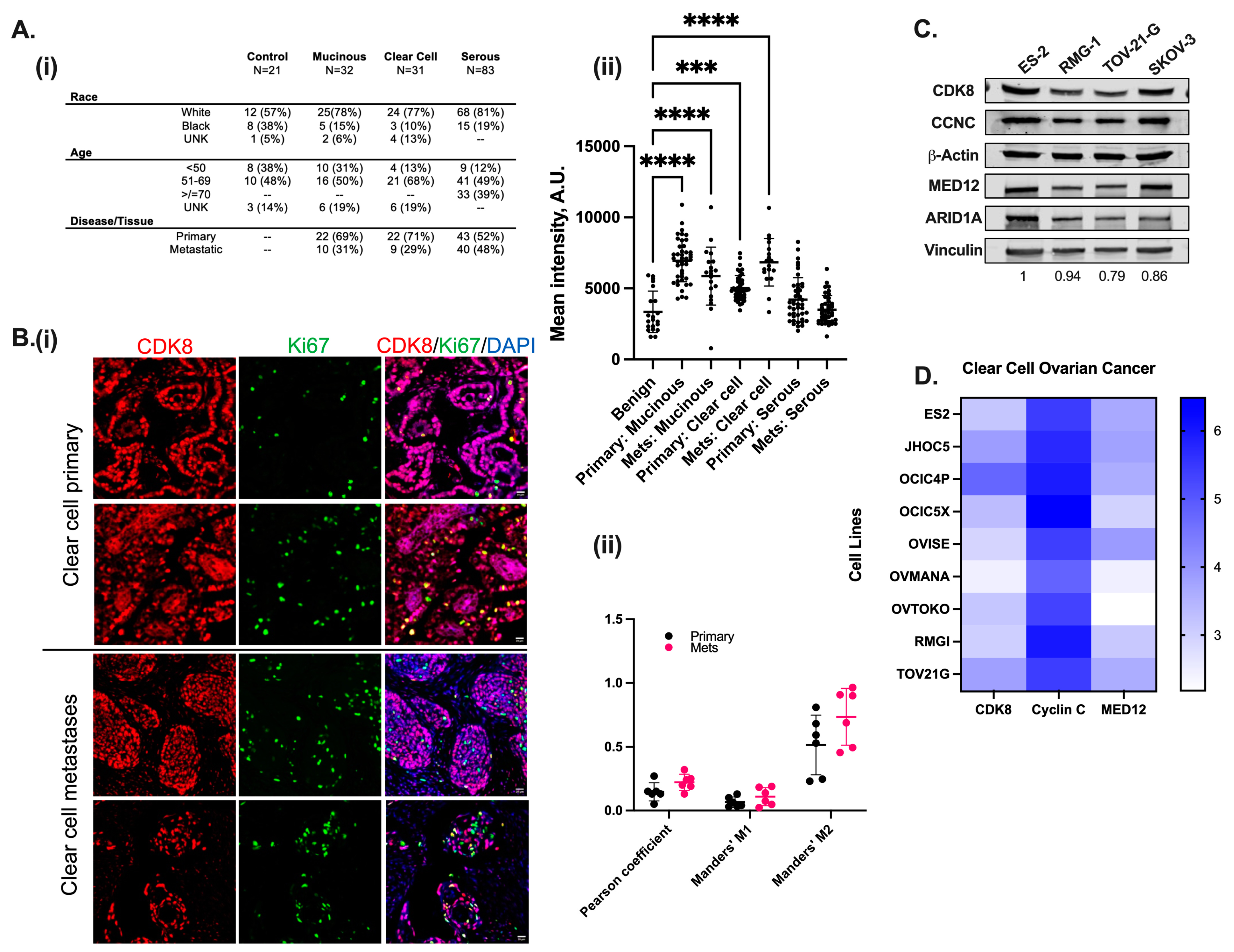
2.3. Tissue Specimen Collection
2.4. Immunoblotting
2.5. Immunohistochemistry (IHC), H&E Staining, Immunofluorescence (If) Labeling, and Analysis
2.6. CDK8/19 CRISPR Knock-Out Generation
2.7. Public Data Mining
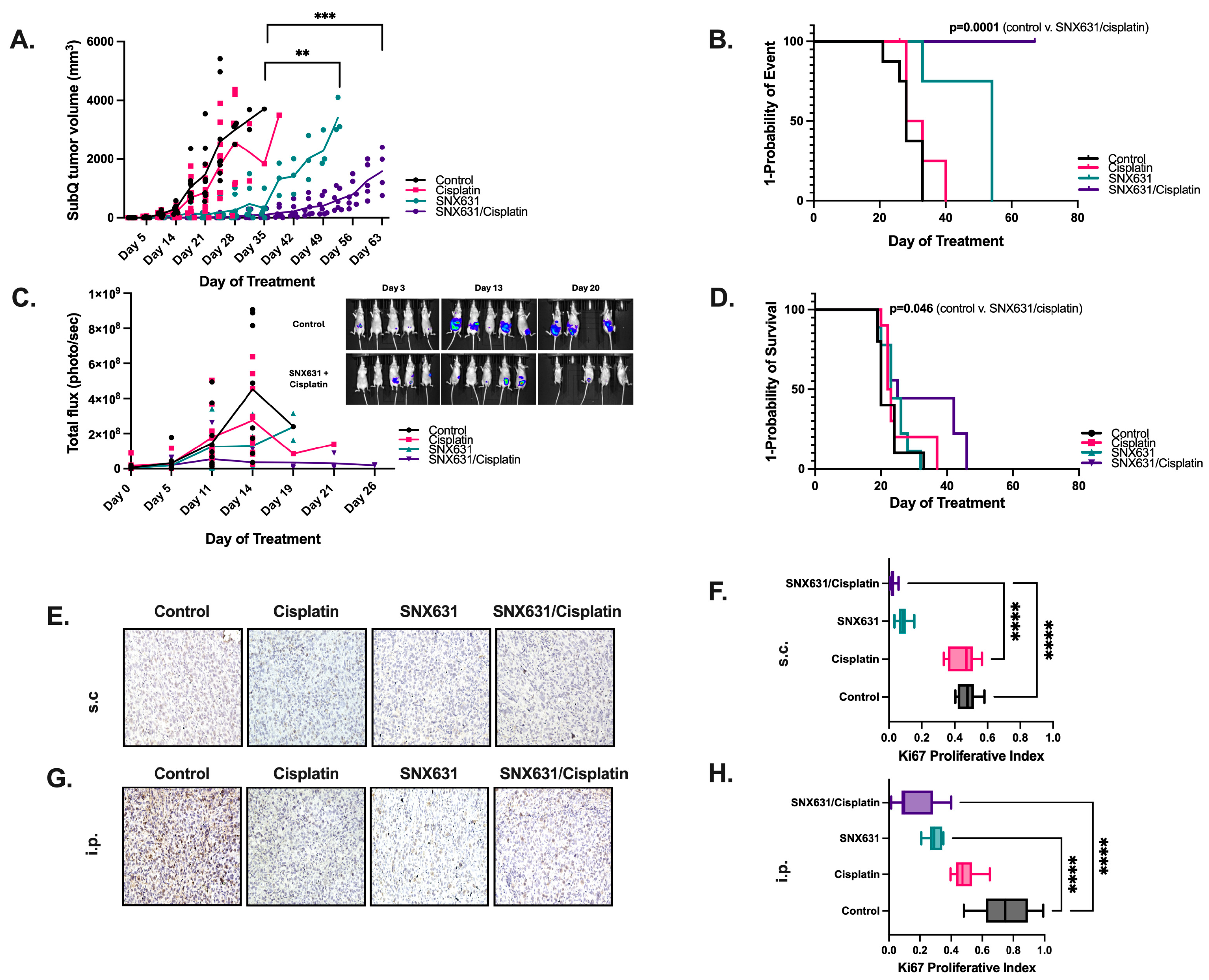
2.8. Mouse Xenograft Models
2.9. Animal Bioluminescent Imaging (BLI)
2.10. Anesthesia
2.11. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. CDK8/19 Is Significantly Expressed in Both Primary and Metastatic Clear Cell Ovarian Carcinoma and Correlates with Poor Prognosis
3.2. Targeting CDK8/19 Kinase Activity Is Not Independently Cytotoxic to Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines
3.3. CDK8 Inhibition Potentiates Cytotoxicity Towards Traditional Chemotherapeutics
3.4. CDK8/19 Inhibition Suppresses In Vivo Tumor Growth and Prolongs Overall Survival from Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma

4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDK | Cyclin-dependent kinase |
| OC | Ovarian cancer |
| OCCC | Ovarian clear cell carcinoma |
| CCNC | Cyclin-C |
| CDK8/19i | CDK8/19 inhibitor |
| CDK8/19is | CDK8/19 inhibitors |
| dKO | Double knock-out |
| IC50 | Inhibitory concentration 50 |
References
- Miller, K.D.; Nogueira, L.; Devasia, T.; Mariotto, A.B.; Yabroff, K.R.; Jemal, A.; Kramer, J.; Siegel, R.L. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 409–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Xu, Y.; Ji, J.; Dong, R.; Qiu, H.; Dai, X. Prognosis of ovarian clear cell cancer compared with other epithelial cancer types: A population-based analysis. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 1947–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackay, H.J.; Brady, M.F.; Oza, A.M.; Reuss, A.; Pujade-Lauraine, E.; Swart, A.M.; Siddiqui, N.; Colombo, N.; Bookman, M.A.; Pfisterer, J.; et al. Prognostic relevance of uncommon ovarian histology in women with stage III/IV epithelial ovarian cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2010, 20, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Chao, T.C.; Tsai, K.L. Structures and compositional dynamics of Mediator in transcription regulation. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2024, 88, 102892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyties, O.; Taatjes, D.J. The Mediator kinase module: An interface between cell signaling and transcription. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2022, 47, 314–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, S.; Mohammad, E.; Lidschreiber, M.; Stuetzer, A.; Bazso, F.L.; Maier, K.C.; Urlaub, H.; Cramer, P. The Cdk8 kinase module regulates interaction of the mediator complex with RNA polymerase II. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, P.A.; Makley, T.A.; Werling, K. Cerebro-rhino-orbital phycomycosis: A case report. Ann. Ophthalmol. 1980, 12, 459–463. [Google Scholar]
- Fant, C.B.; Taatjes, D.J. Regulatory functions of the Mediator kinases CDK8 and CDK19. Transcription 2019, 10, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Cheng, C.; Ji, H.; Altilia, S.; Ding, X.; Cai, G.; Altomare, D.; et al. CDK8 and CDK19: Positive regulators of signal-induced transcription and negative regulators of Mediator complex proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, 7288–7313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Liang, J.; Ji, H.; Yang, Z.; Altilia, S.; Hu, B.; Schronce, A.; McDermott, M.S.J.; Schools, G.P.; Lim, C.U.; et al. CDK8/19 Mediator kinases potentiate induction of transcription by NFkappaB. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10208–10213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clopper, K.C.; Taatjes, D.J. Chemical inhibitors of transcription-associated kinases. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2022, 70, 102186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hilimire, T.A.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Liang, J.; Gyorffy, B.; Sikirzhytski, V.; Ji, H.; Zhang, L.; Cheng, C.; et al. Mediator kinase inhibition reverses castration resistance of advanced prostate cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e176709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ji, H.; Porter, D.C.; Broude, E.V.; Roninson, I.B.; Chen, M. Characterizing CDK8/19 Inhibitors through a NFkappaB-Dependent Cell-Based Assay. Cells 2019, 8, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, P.A.; Ortiz-Ruiz, M.J.; TePoele, R.; Adeniji-Popoola, O.; Box, G.; Court, W.; Czasch, S.; El Bawab, S.; Esdar, C.; Ewan, K.; et al. Assessing the mechanism and therapeutic potential of modulators of the human Mediator complex-associated protein kinases. Elife 2016, 5, 20722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, J.; Liang, J.; Thompson, Z.S.; Kathrein, K.; Broude, E.V.; Roninson, I.B. Systemic Toxicity Reported for CDK8/19 Inhibitors CCT251921 and MSC2530818 Is Not Due to Target Inhibition. Cells 2019, 8, 1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stany, M.P.; Vathipadiekal, V.; Ozbun, L.; Stone, R.L.; Mok, S.C.; Xue, H.; Kagami, T.; Wang, Y.; McAlpine, J.N.; Bowtell, D.; et al. Identification of novel therapeutic targets in microdissected clear cell ovarian cancers. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Sharko, A.C.; McDermott, M.S.J.; Schools, G.P.; Chumanevich, A.; Ji, H.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Mack, Z.T.; Sikirzhytski, V.; et al. Inhibition of CDK8/19 Mediator kinase potentiates HER2-targeting drugs and bypasses resistance to these agents in vitro and in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2201073119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tae, K.; El-Naggar, A.K.; Yoo, E.; Feng, L.; Lee, J.J.; Hong, W.K.; Hittelman, W.N.; Shin, D.M. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and microvessel density in head and neck tumorigenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 2821–2828. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, S.; Wang, T.L.; Shih Ie, M.; Mao, T.L.; Nakayama, K.; Roden, R.; Glas, R.; Slamon, D.; Diaz, L.A., Jr.; Vogelstein, B.; et al. Frequent mutations of chromatin remodeling gene ARID1A in ovarian clear cell carcinoma. Science 2010, 330, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, J.; Kato, S.; Sicklick, J.K.; Kurzrock, R. Targeting ARID1A mutations in cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2021, 100, 102287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stubbs, F.E.; Birnie, M.T.; Biddie, S.C.; Lightman, S.L.; Conway-Campbell, B.L. SKOV3 cells containing a truncated ARID1a protein have a restricted genome-wide response to glucocorticoids. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 461, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domcke, S.; Sinha, R.; Levine, D.A.; Sander, C.; Schultz, N. Evaluating cell lines as tumour models by comparison of genomic profiles. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anglesio, M.S.; Wiegand, K.C.; Melnyk, N.; Chow, C.; Salamanca, C.; Prentice, L.M.; Senz, J.; Yang, W.; Spillman, M.A.; Cochrane, D.R.; et al. Type-specific cell line models for type-specific ovarian cancer research. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelish, H.E.; Liau, B.B.; Nitulescu, I.I.; Tangpeerachaikul, A.; Poss, Z.C.; Da Silva, D.H.; Caruso, B.T.; Arefolov, A.; Fadeyi, O.; Christie, A.L.; et al. Mediator kinase inhibition further activates super-enhancer-associated genes in AML. Nature 2015, 526, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDermott, M.S.; Chumanevich, A.A.; Lim, C.U.; Liang, J.; Chen, M.; Altilia, S.; Oliver, D.; Rae, J.M.; Shtutman, M.; Kiaris, H.; et al. Inhibition of CDK8 mediator kinase suppresses estrogen dependent transcription and the growth of estrogen receptor positive breast cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 12558–12575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Chen, M.; Hughes, D.; Chumanevich, A.A.; Altilia, S.; Kaza, V.; Lim, C.U.; Kiaris, H.; Mythreye, K.; Pena, M.M.; et al. CDK8 Selectively Promotes the Growth of Colon Cancer Metastases in the Liver by Regulating Gene Expression of TIMP3 and Matrix Metalloproteinases. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 6594–6606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Nakata, D.; Kakoi, Y.; Kunitomo, M.; Murai, S.; Ebara, S.; Hata, A.; Hara, T. CDK8/19 inhibition induces premature G1/S transition and ATR-dependent cell death in prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 13474–13487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.Y.; Sung, T.Y.; Pan, S.L.; Huang, W.J.; Hsu, K.C.; Hsu, J.Y.; Lin, T.E.; Hsu, C.M.; Yang, C.R. The study of a novel CDK8 inhibitor E966-0530-45418 that inhibits prostate cancer metastasis in vitro and in vivo. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 162, 114667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, K.; Zhu, Y.L.; Lin, Z.P.; Penketh, P.G.; Shyam, K.; Zhu, R.; Baumann, R.P.; Sartorelli, A.C.; Rutherford, T.J.; Ratner, E.S. Cataloging antineoplastic agents according to their effectiveness against platinum-resistant and platinum-sensitive ovarian carcinoma cell lines. J. Transl. Sci. 2016, 2, 117–124. [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur, M.N.; Simeone, K.; Leclerc-Deslauniers, K.; Fleury, H.; Carmona, E.; Provencher, D.M.; Mes-Masson, A.M. Carboplatin response in preclinical models for ovarian cancer: Comparison of 2D monolayers, spheroids, ex vivo tumors and in vivo models. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 18183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bancerek, J.; Poss, Z.C.; Steinparzer, I.; Sedlyarov, V.; Pfaffenwimmer, T.; Mikulic, I.; Dolken, L.; Strobl, B.; Muller, M.; Taatjes, D.J.; et al. CDK8 kinase phosphorylates transcription factor STAT1 to selectively regulate the interferon response. Immunity 2013, 38, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.Y.; Tang, D.S.; Zhang, Y.N.; Wang, K.Y.; Ao, M.; Luo, H.X.; Li, B. Antitumor effects of redox-responsive nanoparticles containing platinum (IV) in ovarian cancer. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 2024, 46, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roninson, I.B.; Gyorffy, B.; Mack, Z.T.; Shtil, A.A.; Shtutman, M.S.; Chen, M.; Broude, E.V. Identifying Cancers Impacted by CDK8/19. Cells 2019, 8, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porter, D.C.; Farmaki, E.; Altilia, S.; Schools, G.P.; West, D.K.; Chen, M.; Chang, B.D.; Puzyrev, A.T.; Lim, C.U.; Rokow-Kittell, R.; et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase 8 mediates chemotherapy-induced tumor-promoting paracrine activities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 13799–13804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrao, A.; Jenkins, L.M.; Chumanevich, A.A.; Horst, B.; Liang, J.; Gatza, M.L.; Lee, N.Y.; Roninson, I.B.; Broude, E.V.; Mythreye, K. Mediator kinase CDK8/CDK19 drives YAP1-dependent BMP4-induced EMT in cancer. Oncogene 2018, 37, 4792–4808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniak, N.; Fadare, O.; Kobel, M.; DeCoteau, J.; Parkash, V.; Hecht, J.L.; Hanley, K.Z.; Gwin, K.; Zheng, W.; Quick, C.M.; et al. Targeted Molecular and Immunohistochemical Analyses of Endometrial Clear Cell Carcinoma Show that POLE Mutations and DNA Mismatch Repair Protein Deficiencies Are Uncommon. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2019, 43, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiegand, K.C.; Shah, S.P.; Al-Agha, O.M.; Zhao, Y.; Tse, K.; Zeng, T.; Senz, J.; McConechy, M.K.; Anglesio, M.S.; Kalloger, S.E.; et al. ARID1A mutations in endometriosis-associated ovarian carcinomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1532–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crotzer, D.R.; Sun, C.C.; Coleman, R.L.; Wolf, J.K.; Levenback, C.F.; Gershenson, D.M. Lack of effective systemic therapy for recurrent clear cell carcinoma of the ovary. Gynecol. Oncol. 2007, 105, 404–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, M.; Tsuda, H.; Sugiyama, T. Clear cell carcinoma of the ovary: Is there a role of histology-specific treatment? J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 31, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eppinger, M.G.; Craig, P.L.; Adams, R.L.; Parsons, O.A. The WAIS-R index for estimating premorbid intelligence: Cross-validation and clinical utility. J. Consult. Clin. Psychol. 1987, 55, 86–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dannappel, M.V.; Sooraj, D.; Loh, J.J.; Firestein, R. Molecular and in vivo Functions of the CDK8 and CDK19 Kinase Modules. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 6, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCleland, M.L.; Soukup, T.M.; Liu, S.D.; Esensten, J.H.; de Sousa e Melo, F.; Yaylaoglu, M.; Warming, S.; Roose-Girma, M.; Firestein, R. Cdk8 deletion in the Apc(Min) murine tumour model represses EZH2 activity and accelerates tumourigenesis. J. Pathol. 2015, 237, 508–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Wen, P.; Hu, G.; Gao, Y.; Qi, X.; Zhu, K.; Chen, S.; Wu, L.; Xu, A.; Zhao, G. Antagonizing CDK8 Sensitizes Colorectal Cancer to Radiation Through Potentiating the Transcription of e2f1 Target Gene apaf1. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofmann, M.H.; Mani, R.; Engelhardt, H.; Impagnatiello, M.A.; Carotta, S.; Kerenyi, M.; Lorenzo-Herrero, S.; Böttcher, J.; Scharn, D.; Arnhof, H.; et al. Selective and Potent CDK8/19 Inhibitors Enhance NK-Cell Activity and Promote Tumor Surveillance. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2020, 19, 1018–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharko, A.C.; Lim, C.U.; McDermott, M.S.J.; Hennes, C.; Philavong, K.P.; Aiken, T.; Tatarskiy, V.V.; Roninson, I.B.; Broude, E.V. The Inhibition of CDK8/19 Mediator Kinases Prevents the Development of Resistance to EGFR-Targeting Drugs. Cells 2021, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas, K.A.; Belk, J.A.; Sotillo, E.; Quinn, P.J.; Ramello, M.C.; Malipatlolla, M.; Daniel, B.; Sandor, K.; Klysz, D.; Bjelajac, J.; et al. Enhanced T cell effector activity by targeting the Mediator kinase module. Science 2022, 378, eabn5647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, C.F.; Kim, M.; Alexe, G.; Engel, K.; Forman, A.B.; Robichaud, A.; Conway, A.S.; Goodale, A.; Meyer, A.; Khalid, D.; et al. Transcriptional Antagonism by CDK8 Inhibition Improves Therapeutic Efficacy of MEK Inhibitors. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 285–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Kong, L.; Xiao, Y.; Yuan, H.; Song, Y.; Wang, J.; Yu, H.; Mao, S.; Xu, W. CDK8 regulates the angiogenesis of pancreatic cancer cells in part via the CDK8-beta-catenin-KLF2 signal axis. Exp. Cell Res. 2018, 369, 304–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Cell Line | Initial Cell Density (Cell/Well) |
|---|---|
| ES-2 Luc | 2000 |
| TOV-21-G | 2000 |
| RMG-1 | 2500 |
| SKOV-3 | 1500 |
| SKOV-3 CDK 8/19 KO | 1500 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barton, W.C.; Kumari, A.; Mack, Z.T.; Schools, G.P.; Quintero, L.M.; Choi, A.S.; Rangavajhula, K.; Arend, R.C.; Broude, E.V.; Mythreye, K. Targeting Mediator Kinase Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 8/19 Potentiates Chemotherapeutic Responses, Reverses Tumor Growth, and Prolongs Survival from Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17060941
Barton WC, Kumari A, Mack ZT, Schools GP, Quintero LM, Choi AS, Rangavajhula K, Arend RC, Broude EV, Mythreye K. Targeting Mediator Kinase Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 8/19 Potentiates Chemotherapeutic Responses, Reverses Tumor Growth, and Prolongs Survival from Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(6):941. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17060941
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarton, Wade C., Asha Kumari, Zachary T. Mack, Gary P. Schools, Liz Macias Quintero, Alex Seok Choi, Karthik Rangavajhula, Rebecca C. Arend, Eugenia V. Broude, and Karthikeyan Mythreye. 2025. "Targeting Mediator Kinase Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 8/19 Potentiates Chemotherapeutic Responses, Reverses Tumor Growth, and Prolongs Survival from Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma" Cancers 17, no. 6: 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17060941
APA StyleBarton, W. C., Kumari, A., Mack, Z. T., Schools, G. P., Quintero, L. M., Choi, A. S., Rangavajhula, K., Arend, R. C., Broude, E. V., & Mythreye, K. (2025). Targeting Mediator Kinase Cyclin-Dependent Kinases 8/19 Potentiates Chemotherapeutic Responses, Reverses Tumor Growth, and Prolongs Survival from Ovarian Clear Cell Carcinoma. Cancers, 17(6), 941. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17060941







