1. Introduction
DTC accounts for over 90% of thyroid malignancies and continues to rise in incidence globally. According to GLOBOCAN 2020 data, thyroid cancer ranks as the ninth-most common malignancy worldwide, with approximately 586,000 new cases annually, and the highest incidence in Eastern Asia and parts of Southern Europe. DTC includes papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC), follicular thyroid carcinoma (FTC), and Hürthle cell carcinoma (HCC), with PTC being the most prevalent subtype (~80–85%). Standard treatment for DTC includes total thyroidectomy followed by RAI therapy and thyroid-stimulating hormone suppression [
1,
2].
The role of postoperative radioactive iodine continues to expand due to the increasing incidence of DTC. However, transformation to RAIR-DTC reduces the therapeutic efficacy of RAI treatment and represents a significant cause of mortality and treatment failure [
3,
4], which is characterized by the loss of iodine avidity in metastatic lesions, progressive disease despite RAI uptake, or the presence of lesions that do not concentrate RAI on diagnostic or post-therapy scans. Clinically, RAIR-DTC is defined by any of the following: (1) absence of RAI uptake in all lesions, (2) disease progression within 12–16 months after RAI therapy, or (3) mixed uptake with progression in non-RAI–avid sites. RAIR-DTC accounts for approximately 10–15% of all DTC cases and is associated with poor prognosis, with a 10-year survival rate of <10% once distant metastases occur [
5,
6]. Emerging treatment strategies aim to address the challenges posed by RAIR-DTC [
7,
8]. Phase I/II clinical trials using MLN0128 (NCT02244463) and interventional trials using AZD6244 (NCT00970359) selectively target and restore iodine metabolism in the tumor microenvironment of RAIR-DTC. Modifications to the tumor microenvironment promote RAI reuptake by RAIR-DTC [
9,
10]. Moreover, BRAF
V600E and MEK inhibitors, such as dabrafenib and trametinib, enhance RAI uptake in RAIR-DTC patients by targeting the MAPK signaling pathway [
11,
12]. Despite their efficacy, these treatment strategies ultimately fail to resolve the fundamental challenges associated with RAIR-DTC, partly due to low structural and biochemical remission rates and unsatisfactory RAI uptake rates [
13,
14]. Consequently, further research is essential to elucidate the mechanisms underlying RAIR-DTC development and to identify precise targets and comprehensive treatment strategies.
Recent studies have implicated stress response genes, including the Gadd45 family, in modulating cancer cell survival, DNA repair, and metabolic adaptation—features potentially relevant to RAI resistance [
15]. Growth arrest and DNA damage protein 45 beta (Gadd45B) plays a crucial role in cellular stress responses by regulating the cell cycle, DNA repair, and apoptosis [
16]. Previous studies have shown that it may exert an inhibitory effect on cancer development and function as a tumor suppressor [
17,
18]. Specifically, low Gadd45B expression correlates with a more aggressive tumor phenotype and increased metastatic propensity in triple-negative breast cancer [
19]. By facilitating DNA repair and inhibiting cell cycle progression, Gadd45B suppresses clonogenic proliferation in breast cancer cells [
20,
21]. Moreover, the Gadd45 family can enhance breast cancer cell sensitivity to chemotherapeutic drugs, further inhibiting tumor growth [
22]. In non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), Gadd45B activates the p38 MAPK signaling pathway, inducing cell cycle arrest and inhibiting NSCLC cell proliferation [
23,
24]. Gadd45B also sensitizes NSCLC tumor cells to radiotherapy, thereby improving treatment efficacy [
25]. In colorectal cancer, Gadd45B expression closely correlates with tumor staging and patient survival rates [
26]. It inhibits colorectal cancer cell proliferation by promoting apoptosis and suppressing angiogenesis [
27]. Simultaneously, Gadd45B modulates the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [
28,
29]. The function of Gadd45B may vary across different cancer subtypes due to its interactions with specific cellular microenvironments, tumor genotypes, and signaling pathways [
30]. However, the role of Gadd45B in thyroid cancer physiology and its relationship with RAIR-DTC remains poorly understood.
In this study, we explored Gadd45B deficiency as a potential driver of RAI treatment resistance and characterized its mechanism of action in cell cycle progression. We collected clinical samples of BRAF
V600E-mutated RAIR-DTC and DTC for RNA sequencing. All samples exhibited BRAF
V600E mutation. Notably, Gadd45B expression in RAIR-DTC tissue was significantly lower than in DTC, potentially exacerbating abnormal MAPK signaling pathway activation and promoting RAIR-DTC development. At the molecular level, overexpression of Gadd45B reduced MAPK pathway activity [
31]. This reduction increased the expression of key iodine metabolic genes, including NIS, TPO, and Tg.
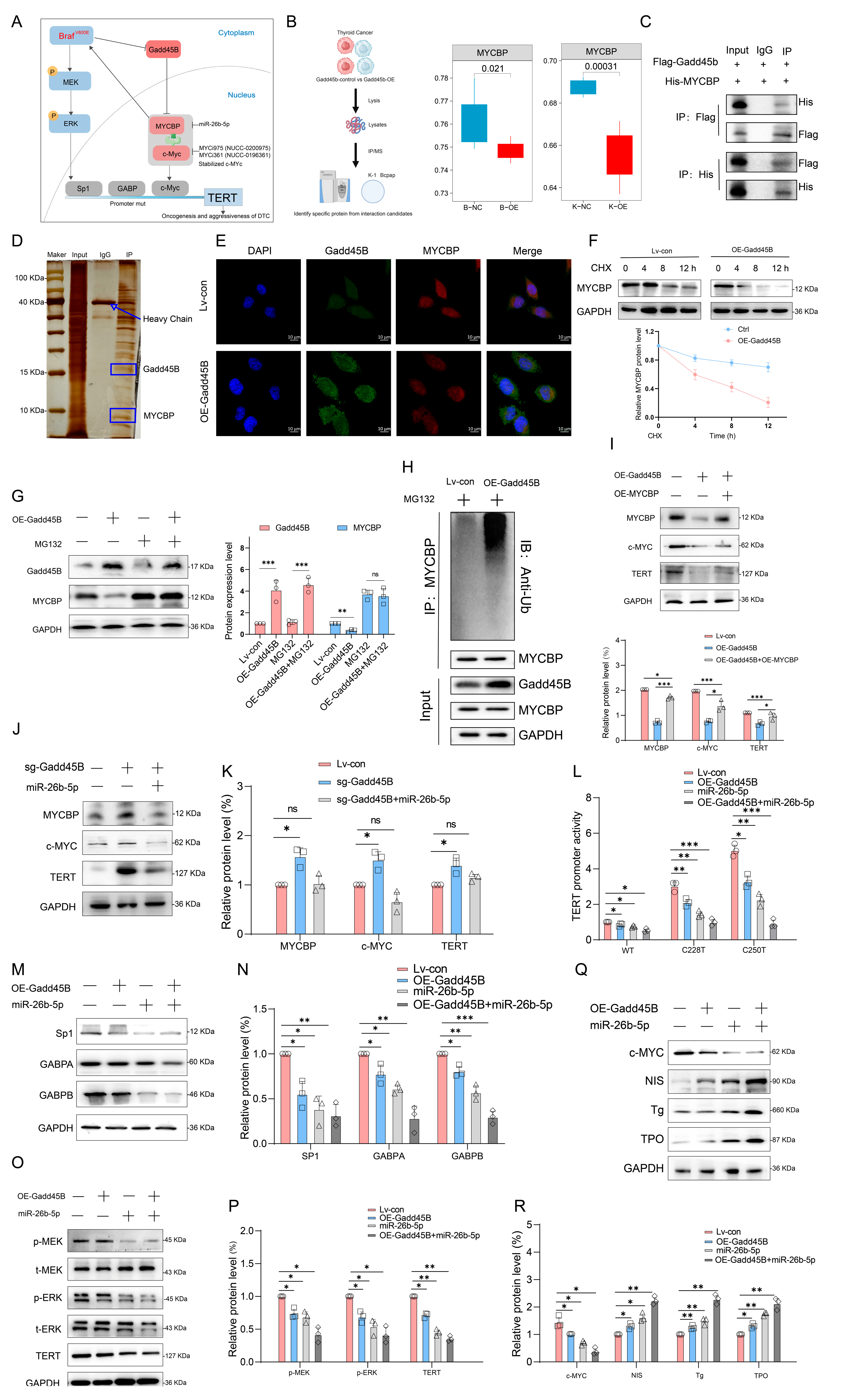
Furthermore, Gadd45B competed with MYCBP for c-Myc binding and mediated MYCBP ubiquitination and degradation. This disrupted the stability of the c-Myc–MYCBP complex, thereby reducing c-Myc oncogenic activity. Consequently, this process influenced TERT gene promoter activity and further enhanced iodine metabolism gene expression, aiding in reversing the dedifferentiated state of RAIR-DTC and restoring its ability to absorb radioactive iodine. A treatment strategy focused on Gadd45B could hold substantial clinical value and provide a scientific basis for translation into clinical practice.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
The objective of this study was to investigate the mechanism of dedifferentiation in radioactive iodine-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer (RAIR-DTC). We screened Gadd45B, a non-critical gene with the potential to affect key pathways, using sequencing technology (n = 16, next-generation sequencing, NSG). Its oncogenic effects were confirmed through analyses of various universal databases. Subsequently, phenotyping experiments were conducted to assess the oncogene-suppressive effects of Gadd45B in both BRAFV600E-mutated and wild-type thyroid cancer cells.
Furthermore, we evaluated the potential of Gadd45B to inhibit thyroid cancer dedifferentiation through its interacting factors, validated via in vivo experiments. All experiments in this study were repeated at least three times to demonstrate biological reproducibility and ensure sufficient statistical power for comparisons. The study was unblinded, and statistical methods were not employed to predetermine sample size. Details of the in vivo experiments, including the number of cells used, duration, and statistical tests, are described in the figure legends. No formal a priori sample size calculation was performed; however, sample sizes were determined based on previous studies in the field that yielded statistically robust results. Post hoc power analysis was conducted for the primary endpoints, confirming that the study was sufficiently powered (power > 0.8) to detect the observed effect sizes. Blinding of investigators was not feasible for all experiments due to the nature of the interventions; nevertheless, bias was minimized by random allocation of samples/animals to treatment groups, independent data acquisition by separate personnel, and blinded analysis of outcome measures where possible.
2.2. Human Thyroid Tissue
Two independent cohorts of patients with differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) who underwent thyroidectomy at the Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital Otorhinolaryngology Department were included in this study. In this study, RAIR-DTC was defined according to the criteria recommended by the 2015 American Thyroid Association (ATA) Guidelines [
32] and recent consensus statements
Normal thyroid tissue (N, n = 5): histologically normal thyroid tissue collected from patients diagnosed with DTC in whom the primary tumor was very small, allowing for the safe sampling of adjacent non-tumorous thyroid tissue during surgery.
DTC group (n = 6): primary tumor tissue obtained at initial thyroidectomy from patients diagnosed with DTC who had not received any prior therapy.
RAIR-DTC group (n = 5): tumor tissue obtained from patients initially diagnosed with DTC, who underwent total thyroidectomy followed by 131I treatment, and subsequently developed progressive disease characterized by either loss of radioiodine uptake or enlargement of metastatic lesions. These RAIR-DTC samples were obtained via surgical resection or core needle biopsy of recurrent or metastatic lesions.
All specimens were immediately snap-frozen in liquid nitrogen or fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde. Each sample was independently reviewed and graded by two board-certified pathologists. Transcriptome sequencing of these tissues was performed by Novogene Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China) to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) among the N, DTC, and RAIR-DTC groups.
Cohort 2 included tumor tissues and para-tumor tissues from 5 patients with DTC who underwent resection between January 2018 and January 2023.
Cohort 3 consisted of 176 pathological diagnosed with thyroid cancer who underwent surgical treatment in the Department of Head and Neck Surgery at Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital between May 2022 and October 2023. Clinical data included age, sex, tumor size, histological subtype, TNM stage, and radioactive iodine (RAI) treatment history. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants, and the study was approved by the institutional ethics committee.
Cohort 4 comprised 121 BRAFV600E-mutated DTC patients, selected from the 176 patients originally included in Cohort 3.
Patient-derived xenografts were established from freshly resected BRAFV600E-mutated RAIR-DTC tumor specimens obtained from patients who had undergone thyroidectomy and failed RAI therapy. Tumor donors included 5 females and 2 males, aged 38–65 years, with histological subtypes encompassing 5 papillary and 2 poorly differentiated carcinomas. All tumors exhibited reduced or absent NIS expression by IHC, and at least one iodine metabolism gene mutation (e.g., SLC5A5, TPO). The overall engraftment rate was 71% (5/7), with a median latency period of ~4 weeks before palpable tumors formed. Histopathological examination confirmed that the PDXs retained the original tumor’s morphological features, BRAFV600E mutation status, and heterogeneous expression of NIS, Tg, and TPO, indicating that these models faithfully recapitulate the molecular and phenotypic heterogeneity of the donor tumors.
2.3. Ethical Statement
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital (KY2024-94), and all tissue samples were obtained with informed consent.
2.4. Cell Line and Drug Treatment
Human thyroid cancer cell lines BCPAP, K1, and TPC-1 were obtained from Miaoling Biological Co., Ltd. (Dalian, China). All cell lines were routinely cultured at 37 °C in RPMI 1640 or DMEM medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum. For specific experiments, cells were treated with 1 μm BRAF kinase inhibitor PLX4720 (Selleck Chemicals, Houston, TX, USA), 1 μm MEK1/2 inhibitor AZD6244 (Selleck Chemicals, TX, USA), 100 mg/mL cycloheximide (HY-12320, MCE), Gadd45B recombinant protein (HY-P70212, MCE), or 10 nm MG-132 (HY-13259, MCE) for the specified durations. All inhibitors were dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), aliquoted, and stored at −80 °C until use. Equivalent DMSO volumes were used as controls.
According to the International Cell Line Authentication Committee (ICLAC) database, the K1 cell line is contaminated with the GLAG-66 cell line. While this contamination did not alter the BRAFV600E mutation status or the MAPK-dependency of the cells, we cannot exclude the possibility that transcriptional or functional heterogeneity introduced by GLAG-66 cells may have influenced some downstream analyses. All functional assays were repeated in an independently validated BRAFV600E-mutated DTC cell line (BCPAP) and results were concordant, supporting the robustness of our main conclusions. Nevertheless, readers should interpret the K1-derived data with this caveat in mind. Both lines originate from human papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC). Our genetic analysis confirmed that the BCPAP and K1 cell lines used in this study exhibited typical heterozygous BRAFV600E and TERT C228T mutations. Cells were authenticated via short tandem repeat (STR) analysis and tested for mycoplasma contamination. The K1 cell line met the purpose of this study to investigate the roles of BRAFV600E and TERT promoter mutations in human cancer.
RNA interference, lentivirus transfection, and expression plasmids were utilized. Control siRNAs and specific siRNAs targeting Gadd45B (human), MAP3K4 (human), MYCBP (human), and c-Myc (human) were obtained from Gene Pharma (Shanghai, China). Cells at ~50% confluence were transfected with 50 nM siRNAs using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen, NY, USA). Lentiviruses expressing shRNA targeting MAP3K4 and control lentiviruses were purchased from HanBio Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Shanghai, China). Cells were infected at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) ranging from 30% to 60% confluence, followed by selection with 2 μg/mL puromycin for one week and maintenance screening at 1 μg/mL for an additional week. Infection efficiency was validated using qRT-PCR was performed using an ABI 7500 Real-Time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA).and Western blotting. Recombinant human Gadd45B protein was applied at the indicated concentrations for 48 h in vitro or administered intraperitoneally every other day for 2 weeks in animal experiments. The purity of the recombinant Gadd45B protein (>95%) was confirmed by SDS–PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. Biological activity was validated by assessing its ability to modulate MAP3K4 phosphorylation in TPC-1 and BCPAP cells. Endotoxin levels were measured using the Limulus amebocyte lysate (LAL) assay and confirmed to be <0.1 EU/μg.
Gadd45B gene knockout and knockdown was performed using a CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing approach, following previously described protocols. Single-guide RNAs (sgRNAs) targeting human Gadd45B were designed and synthesized by Miaoling. The targeting sequences were described as follows: shGadd45B #H1: GACCTGTCTTTGCGAAAGCAA; sgRNA1: 5′-GGAGGCTGGGACGCTGCGGA-3′ The sgRNA was cloned into the PX459 vector (Addgene, Watertown, MA, USA) and transfected into thyroid cancer cells using Lipofectamine 3000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Overexpression pCMV-GADD45B-3×FLAG-Neo NM_015675.4 Forty-eight hours after transfection, cells were selected with puromycin (2 μg/mL) for 1–2 weeks to establish stable knockout lines. Successful gene disruption was confirmed by Sanger sequencing and Western blot analysis.
2.5. Mice
Four-week-old female BALB/c nude mice and four-week-old NOD SCID female mice were purchased from Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal Technologies. The mice were group-housed in specific pathogen-free (SPF) conditions with a 12 h light/12 h dark cycle (150–300 lux), an ambient temperature of 20–26 °C, and a humidity range of 40–70%, with air ventilation four times per hour. Mice were randomly assigned to experimental groups based on body weight and were fed a standard chow diet. All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital. For all animal experiments, investigators responsible for measuring tumor volume and assessing RAI uptake were blinded to the group allocation throughout the study period. Randomization codes were held by a separate technician not involved in data collection or analysis, and unblinding was performed only after completion of statistical analyses. Humane endpoints were set at 2000 mm3 tumor volume or 20% weight loss; buprenorphine (0.05 mg kg−1 s.c.) was given post-surgery, and animals were monitored daily with tumor size measured twice weekly.
To avoid physiological uptake by the native thyroid gland during the 131I uptake experiments in mice, the following procedure was applied. Mice received gastric perfusion of potassium iodide solution (200 μL/day) for three consecutive days prior to SPECT imaging, as previously described.
2.6. Data Collection and Processing
Gene expression data, clinical information, and single nucleotide variation data for thyroid carcinoma were obtained from multiple sources, including the Genomic Data Commons (
https://portal.gdc.cancer.gov/), GEO database (
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/), cBioPortal (
https://cbioportal.org/), and Timer2.0 (
http://timer.cistrome.org/) all accessed on 1 January 2000. Initial normalization and log2 conversion of the original data were performed using the Million Transcripts per Million (TPM) method. TCGA sample inclusion criteria were limited to type 01A (Primary Tumor) samples with complete survival information.
2.7. Silver Stain-Guided In-Gel Digestion and LC–MS/MS Identification
Protein complexes were immunoprecipitated using anti-Flag agarose from TPC-1 and Bcpap cells stably overexpressing Flag-Gadd45B. Eluates were resolved by SDS–PAGE and visualized by silver staining (Pierce Silver Stain Kit) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Bands of interest were excised with a sterile scalpel, destained (fresh 30 mM K3 [Fe(CN)6]/100 mM Na2S2O3, 1:1, 5–10 min), reduced with 10 mM DTT (56 °C, 45 min) and alkylated with 55 mM iodoacetamide (RT, dark, 30 min). In-gel digestion was performed overnight at 37 °C with sequencing-grade trypsin (Promega, Madison, WI, USA).
Peptides were extracted, dried, and reconstituted for nano-LC–MS/MS (EASY-nLC coupled to an Orbitrap-type mass spectrometer). Data-dependent acquisition was used (typical settings: MS1 resolution 60,000–120,000; HCD MS2; dynamic exclusion enabled). RAW files were searched in Proteome Discoverer (v2.x)/MaxQuant (v1.x) against the UniProt human reference proteome with the following parameters: enzyme trypsin, max 2 missed cleavages; carbamidomethyl-C fixed; oxidation-M and acetyl-protein N-term variable; precursor tolerance ±10 ppm; fragment tolerance 0.02 Da. Peptide-spectrum matches and protein IDs were filtered to FDR ≤ 1% (target–decoy). Proteins were reported only if supported by ≥2 unique peptides. Under these criteria, peptides mapped uniquely to GADD45B and MYCBP in the corresponding gel bands.
2.8. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from cultured cells using the TRIzol reagent (#15596-018; Ambion, Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and reverse-transcribed to cDNA using the SuperScript III First-Strand Synthesis System (#18080-051; Invitrogen, Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA). Gene expression analysis was performed in triplicate using FastStart Universal SYBR Green Master with ROX (#04913850001; Roche Applied Science, Indianapolis, IN, USA) on an Applied Biosystems 7900HT Fast Real-Time PCR System. Relative gene expression was calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method, with GAPDH used as the internal control for normalization. Primers of Gadd45B: (forward) 5′-TGTACGAGTCGGCCAAGTTG-3′ and 5′-ATTTGCAGGGCGATGTCATC-3′ (reverse). The TERT promoter region was amplified by PCR using the primers 5′-AGTGGATTCGCGGGCACAGA-3′ (forward) and 5′-CAGCGCTGCCTGAAACTC-3′ (reverse). The BRAFV600E mutation hotspot was amplified using the primers 5′- GGCAGAGTGCCTCAAAAAGAA-3′ (forward) and 5′- GCGGTGAATTTTTGGCAATG-3′ (reverse). The PCR products were subjected to Sanger sequencing to detect BRAFV600E and TERT promoter mutations.
2.9. Western Blotting
Proteins were extracted from thyroid cancer tissues and cells using a protein extraction kit (Beyotime, Shanghai, China). Extracted proteins were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE (Beyotime) and transferred to PVDF membranes (Roche, Shanghai, China). Membranes were blocked with blocking buffer (Beyotime) for 20 min, incubated overnight at 4 °C with primary antibodies diluted in buffer, and then incubated with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies (Agilent Technologies) for 1 h at room temperature. Protein bands were visualized using an ECL kit (YEASEN, Shanghai, China) and a chemiluminescent gel imaging system (Vilber, Paris, France). Antibodies used are presented in
Table S3. Densitometric analysis of Western blot bands was performed using ImageJ software (version 1.53 k, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA). Band intensities were normalized to the corresponding GAPDH (or other indicated loading control) signals. Background subtraction was applied using the “rolling ball” method in ImageJ to eliminate non-specific background. All values were expressed as relative intensity (arbitrary units) compared with control samples.
2.10. Cell Proliferation Assays
For the Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assays, transfected cells were seeded in 96-well plates (500 cells/well). At designated time points (1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and 6 days), 10 μL of CCK-8 solution was added to each well, followed by incubation at 37 °C for 2 h. Absorbance at 450 nm was measured using a Multiskan GO plate reader (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
For 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) assays, transfected cells were seeded in 96-well plates (20,000 cells/well) and cultured for 2 days. Subsequently, 50 μM EdU (RiboBio, Guangzhou, China) was added to each well, and cells were incubated at 37 °C for 2 h. Cells were then fixed, permeabilized, and stained with 400 μL Hoechst 33342 to visualize nuclei. The proportion of EdU-positive cells was determined by counting cells in five randomly selected areas per well.
For colony formation assays, transfected cells were seeded in 6-well plates (500 cells/well) and incubated in 2 mL of culture medium for 10 days. Colonies were fixed with alcohol, stained with crystal violet, and quantified.
2.11. Flow Cytometry
Tumor cells were cultured in serum-free basal medium for flow cytometry analysis. To detect cell apoptosis, cells were rinsed, resuspended in ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), and incubated with Annexin V-FITC and propidium iodide (PI) staining solution (apoptosis detection kit; Vazyme) at 37 °C for 20 min.
2.12. Transwell Assays
For Transwell migration assays, 200 μL of serum-free medium containing 2 × 104 transfected cells were seeded into the upper chamber of a Transwell plate (Corning, NY, USA), while 800 μL of serum-containing medium was added to the lower chamber. After 24 h of incubation, cells in the upper chamber were fixed, stained with crystal violet (Beyotime) for 20 min, and observed using an inverted optical microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). Cell counts were determined from three randomly selected fields of view. To evaluate cell invasion ability, Matrigel was applied to the Transwell plate surface prior to seeding.
2.13. Immunofluorescence Assays
Microarrays of thyroid cancer tissues and sections from mouse xenografts were prepared for immunohistochemical staining. Slides were incubated in 3% H2O2 for 5 min at room temperature to block endogenous peroxidase activity, followed by antigen retrieval in sodium citrate buffer for 15 min at 95 °C. After blocking with 5% normal goat serum for 10 min, slides were incubated overnight at 4 °C with primary antibodies. The following day, slides were incubated with appropriate secondary antibodies for 1 h at room temperature. Nuclei were visualized with DAPI (Beyotime, China) staining, and images were captured using a fluorescence microscope (Olympus, Japan).
For immunofluorescence, cells attached to slides were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and permeabilized using Immunostaining Permeabilization Buffer with Saponin (Beyotime, China). Slides were blocked with 5% bovine serum albumin (BSA) in PBS for 1 h at room temperature and incubated overnight at 4 °C with the appropriate primary antibody. Following three PBS washes, slides were incubated with corresponding secondary antibodies for 1 h at room temperature. Nuclei were stained with DAPI, and images were obtained using a fluorescence microscope.
2.14. RAI Uptake Assays
For in vitro assays, cells were seeded into 6-well plates, incubated with 1 μCi 125I for 2 h, washed twice with pre-cooled PBS, digested with trypsin, and collected for analysis. Cell radioactivity was measured using a gamma radioimmunoassay counter (GC-1500, ZONKIA, China).
For in vivo assays, mice were fed water containing 0.1% potassium iodide (Sangon, A100512) for 7 days before the 125I uptake experiments. Each mouse received a tail vein injection of 1 mCi 125I, and subcutaneous tumors were assessed for counts per minute using a gamma counter.
2.15. Dual-Luciferase Reporter Assay
The C228T/C250T-mutant and wild-type TERT-pGL4.10 luciferase reporter plasmids were purchased from Abxin (China). Luciferase activity was measured following standard protocols. Briefly, cells were seeded at 70% confluence and transfected with pRL-TK and either C228T-TERT-Luc or C250T-TERT-Luc plasmids using X-treme GENE HP DNA transfection reagent (Roche) in 12-well plates.
For siRNA experiments, cells were transfected with specific siRNAs 24 h before luciferase plasmid transfection. For trametinib treatment, cells were treated with 1 μM PLX4720 and AZD6244 or DMSO for 24 h after luciferase plasmid transfection. In overexpression experiments, cells were co-transfected with Sp1-WT or Sp1-T739A expression plasmids and luciferase plasmids.
Cells were collected 48 h post-treatment, and luminescence intensity was measured using an EnSpire Multimode Plate Reader (PerkinElmer) with the dual-luciferase reporter assay system (Promega), following the manufacturer’s instructions. Data were normalized to pRL-TK luciferase activity. All experiments were performed in triplicate.
2.16. Co-IP
Co-IP experiments were performed to investigate the interaction between Gadd45B and MAP3K4. TPC-1 and Bcpap thyroid cancer cells stably overexpressing Gadd45B were generated using lentiviral transduction of the pCMV-GADD45B-3×FLAG-Neo construct, followed by neomycin (G418) selection. For Co-IP, these stable cell lines were further transfected with pcDNA3.1-MAP3K4-His plasmid using Lipofectamine 3000 (Thermo Fisher Scientific) to achieve transient overexpression of His-tagged MAP3K4.
After 48 h, cells were lysed in IP lysis buffer (Beyotime, China) supplemented with protease and phosphatase inhibitors. Lysates were incubated overnight at 4 °C with either anti-Flag antibody (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) or anti-His antibody (Abcam, Cambridge, UK), followed by 2 h incubation with protein A/G agarose beads (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Immunoprecipitates were washed three times with lysis buffer and eluted by boiling in SDS loading buffer. Western blotting was then performed using reciprocal antibodies (anti-His for Flag-IP, anti-Flag for His-IP) to confirm the protein–protein interaction.
2.17. Molecular Docking Analysis
Molecular docking analysis was conducted using rigid protein–protein docking to investigate the interaction between Gadd45B and MAP3K4 using GRAMM-X (
http://gramm.compbio.ku.edu/). Structural domains of Gadd45B and MAP3K4 were sourced from the AlphaFold Protein Structure Database (
https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/). Protein–protein interactions were visualized and analyzed using PyMOL (Version 3.0) and PDBePISA (
https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbe/pisa/) all accessed on 1 January 2000. Docking parameters were set according to the software default scoring function, with the grid box centered on the predicted active site. The exhaustiveness parameter was set to 8, and all ligands were subjected to energy minimization before docking. The docking procedure followed best practice guidelines as described in previous research with binding poses ranked by predicted binding affinity (kcal/mol) and visually inspected for interaction plausibility.
2.18. IP-MS
Immunoprecipitation coupled with mass spectrometry (IP-MS) was performed to analyze proteins extracted from transfected cells. Immunoprecipitation was carried out using primary antibodies and Protein A/G agarose beads (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Shanghai, China). The isolated immunoprecipitates were subjected to mass spectrometry analysis using a Thermo Scientific mass spectrometer (Waltham, MA, USA). Peptide labeling was conducted using Tandem Mass Tag (TMT) 10-plex reagents according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Mass accuracy was set to ±10 ppm for precursor ions and ±0.02 Da for fragment ions. Peptide identification required at least one unique peptide per protein, and peptide-spectrum matches were filtered at a false discovery rate (FDR) of 1% using the target-decoy strategy. Database searching was performed against the UniProt human reference proteome using Proteome Discoverer software (version 2.5) with carbamidomethylation (C) as a fixed modification and oxidation (M) and TMT labeling as variable modifications.
2.19. Immunohistochemistry
Tissue sections were deparaffinized in xylene, dehydrated through a graded ethanol series, and subjected to antigen retrieval in sodium citrate solution (Servicebio, Wuhan, China) using a heater. The slides were incubated with the primary antibody overnight at 4 °C, followed by incubation with the secondary antibody at 25 °C for 2 h. Signals were developed using 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) solution (Servicebio).
The intensity and staining area were scored as follows:
Staining intensity scores: 0 (negative), 1 (weak), 2 (moderate), 3 (strong).
Staining area scores: 0 (0–10%), 1 (11–25%), 2 (26–50%), 3 (51–75%), 4 (76–100%).
The two scores were multiplied to calculate the IHC staining score.
2.20. Statistical Analysis
Data presentation and statistical rationale. All in vitro results are reported as mean ± standard deviation (SD) to reflect technical variability among replicates, whereas in vivo and ex vivo data are presented as mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) to estimate population-level precision. Normality was verified with the Shapiro–Wilk test; equal variances were checked with Levene’s test. For two-group comparisons we used two-tailed Student’s t-test; for three or more groups we applied one- or two-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Šídák’s multiple-comparison test because it preserves family-wise error rates without excessive loss of power. Kaplan–Meier survival curves were compared by the Mantel–Cox log-rank test, with Bonferroni correction applied when pairwise survival analyses exceeded two groups. Statistical significance is denoted by p * < 0.05, p ** < 0.01, p *** < 0.001 and p **** < 0.0001.
4. Discussion
RAI therapy has a long-standing history of successful application in the treatment of thyroid cancer. However, dedifferentiated thyroid cancer that does not respond to RAI therapy tends to have a poor prognosis. Modifying gene expression represents a promising strategy for converting RAI-refractory thyroid cancer into RAI-sensitive thyroid cancer. Currently, most studies have focused on individual signaling proteins rather than examining the broader spectrum of signaling pathways involved [
47]. As indicated by previous clinical trials (NCT04462471), single-agent treatment may be insufficient to achieve durable redifferentiation efficacy due to the reactivation of signaling pathways and the subsequent development of drug resistance. This underscores the potential benefits of combination therapies involving targeted agents and RAI. Additionally, a comprehensive investigation into the molecular mechanisms of thyroid cancer can facilitate the identification of novel targets and the development of innovative therapies, providing safer, more effective, and cost-efficient treatment options for RAIR-DTC patients.
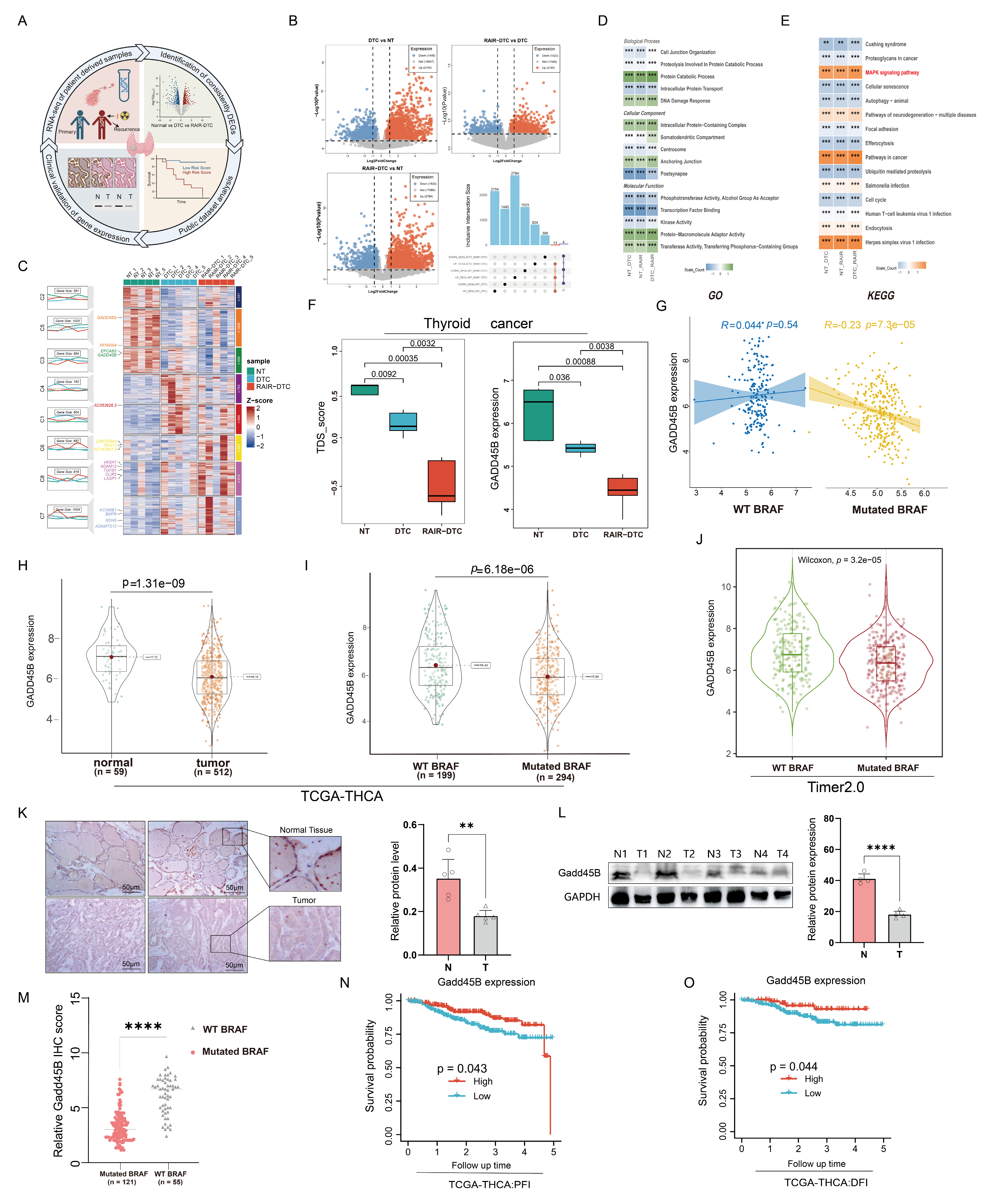
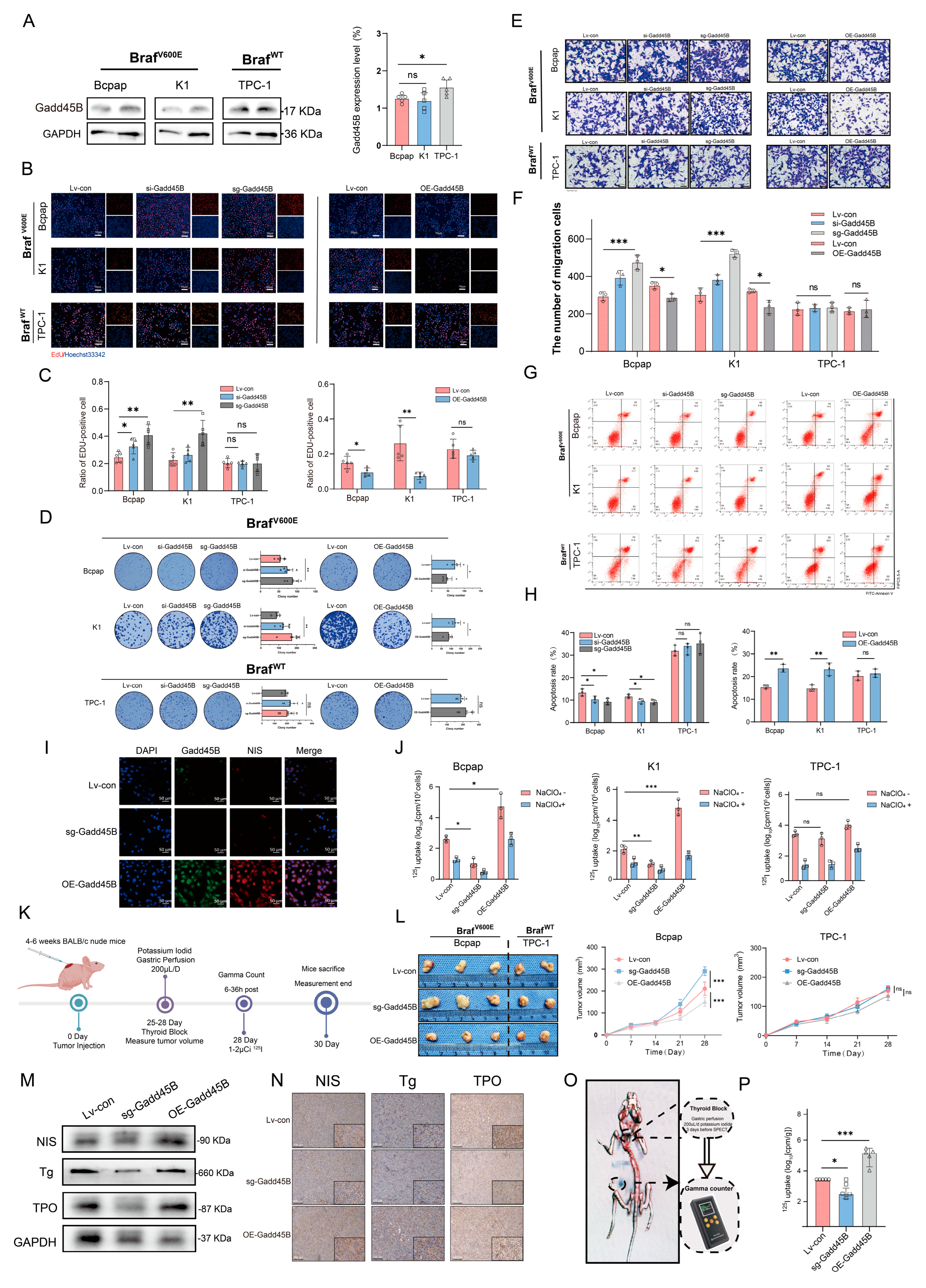
Our transcriptome sequencing of para-cancer tissue, DTC, and RAIR-DTC revealed a strong negative correlation between the BRAF
V600E mutation and Gadd45B expression (
Figure 1A–F). Reduced Gadd45B expression contributed to the progression from DTC to RAIR-DTC in the context of the BRAF
V600E mutation (
Figure 2J–P and
Figure 3M,N). The role of Gadd45B loss in promoting dedifferentiation suggests that a comprehensive investigation into the interplay between BRAF
V600E mutation and Gadd45B expression, as well as its underlying mechanisms, could enhance the development of targeted treatment strategies for RAIR-DTC.
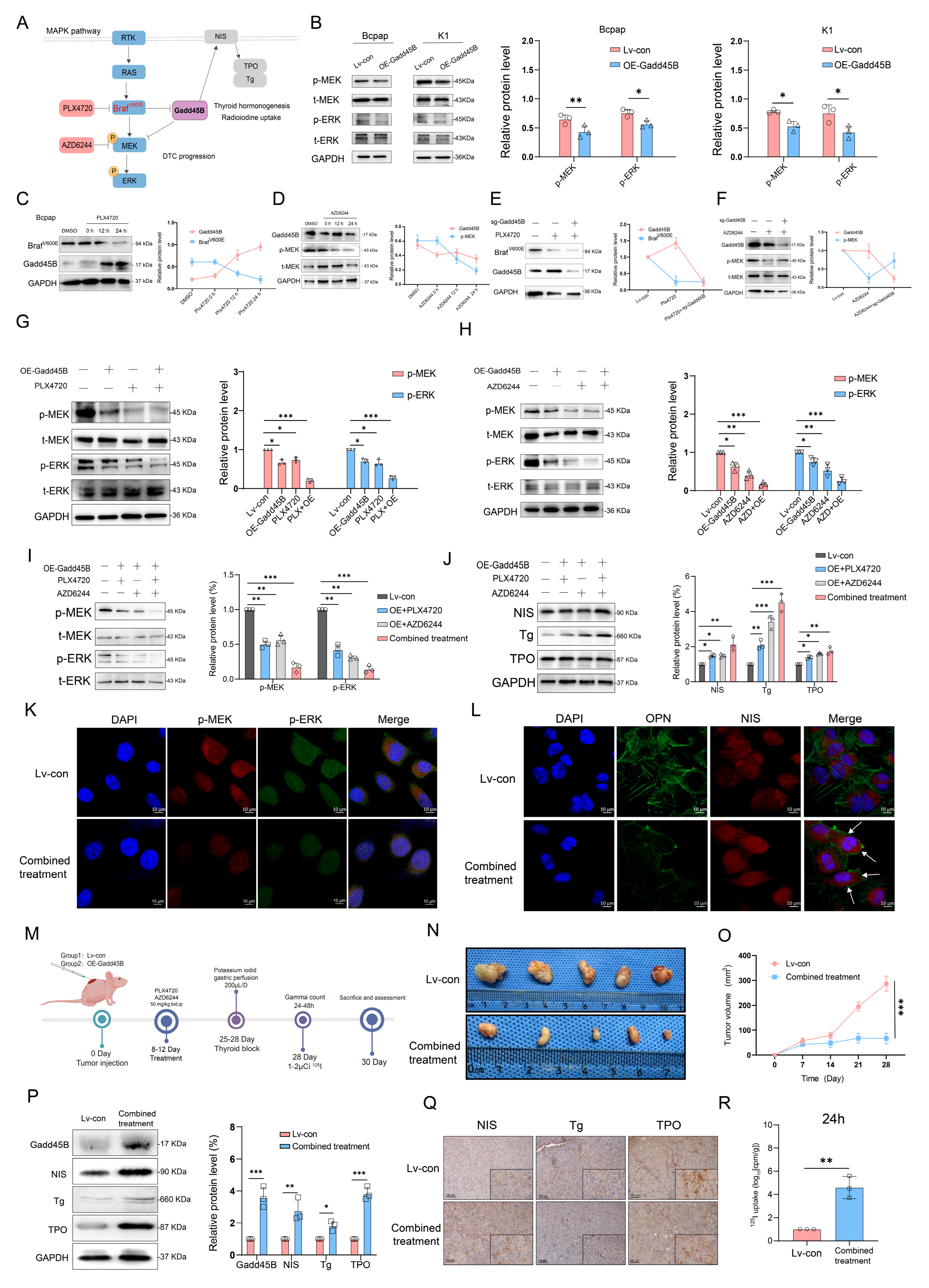
Initial results from a clinical trial indicated that GSK2118436 (Dabrafenib, a BRAF
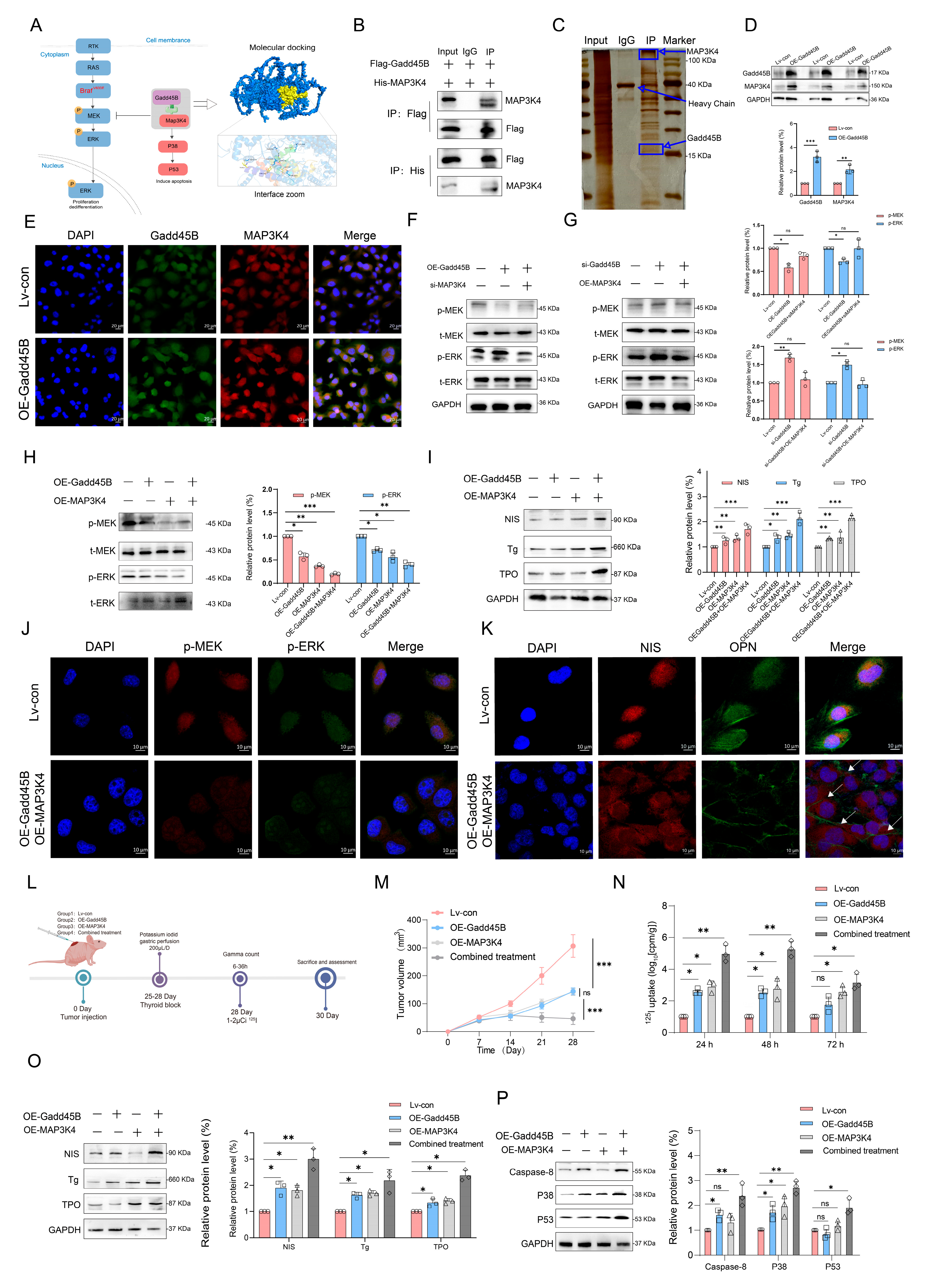
V600E inhibitor) improved the stable disease (SD) rate, achieving a 70% response based on RECIST criteria. However, thyroglobulin levels increased in 60% of participants (NCT04462471). In another clinical trial, the administration of AZD6244 resulted in a 60% increase in RAI uptake among patients. Nevertheless, this treatment did not achieve complete remission, with a partial response (PR) rate of only 62.5% (NCT00970359). Independent use of MAPK signaling pathway inhibitors may not fully restore RAI uptake in RAIR-DTC patients, as abnormal activation of alternative targets within the MAPK pathway can result in unfavorable outcomes. MAP3K4 is a critical molecule in this pathway. Interaction coefficients from docking analysis revealed a strong interaction between Gadd45B and MAP3K4 (
Figure 4A–D). This interaction was further validated through experiments demonstrating that Gadd45B and MAP3K4 collaborate to activate the p38-p53 pathway, leading to increased expression of iodine metabolic proteins. Furthermore, overexpression of Gadd45B in conjunction with MAP3K4 overexpression effectively restored iodine uptake (
Figure 4N). Recent studies have highlighted the involvement of the TERT promoter in the dedifferentiation process of thyroid cancer [
48]. To further investigate Gadd45B targets, we analyzed its interactions using IP-MS (
Figure 5B). Our study confirmed that Gadd45B overexpression enhanced MYCBP ubiquitination while suppressing c-MYC expression (
Figure 5H). It has been proposed that c-MYC exerts pro-oxidant functions in thyroid cancer by increasing the probability of TERT promoter mutations. Based on this theoretical framework, we investigated the effects of Gadd45B overexpression on c-MYC expression and TERT promoter activity. Our results showed that Gadd45B reduced MYCBP expression by increasing MYCBP ubiquitination, which diminished c-MYC’s impact on promoting TERT promoter mutations and thereby impeded thyroid cancer dedifferentiation (
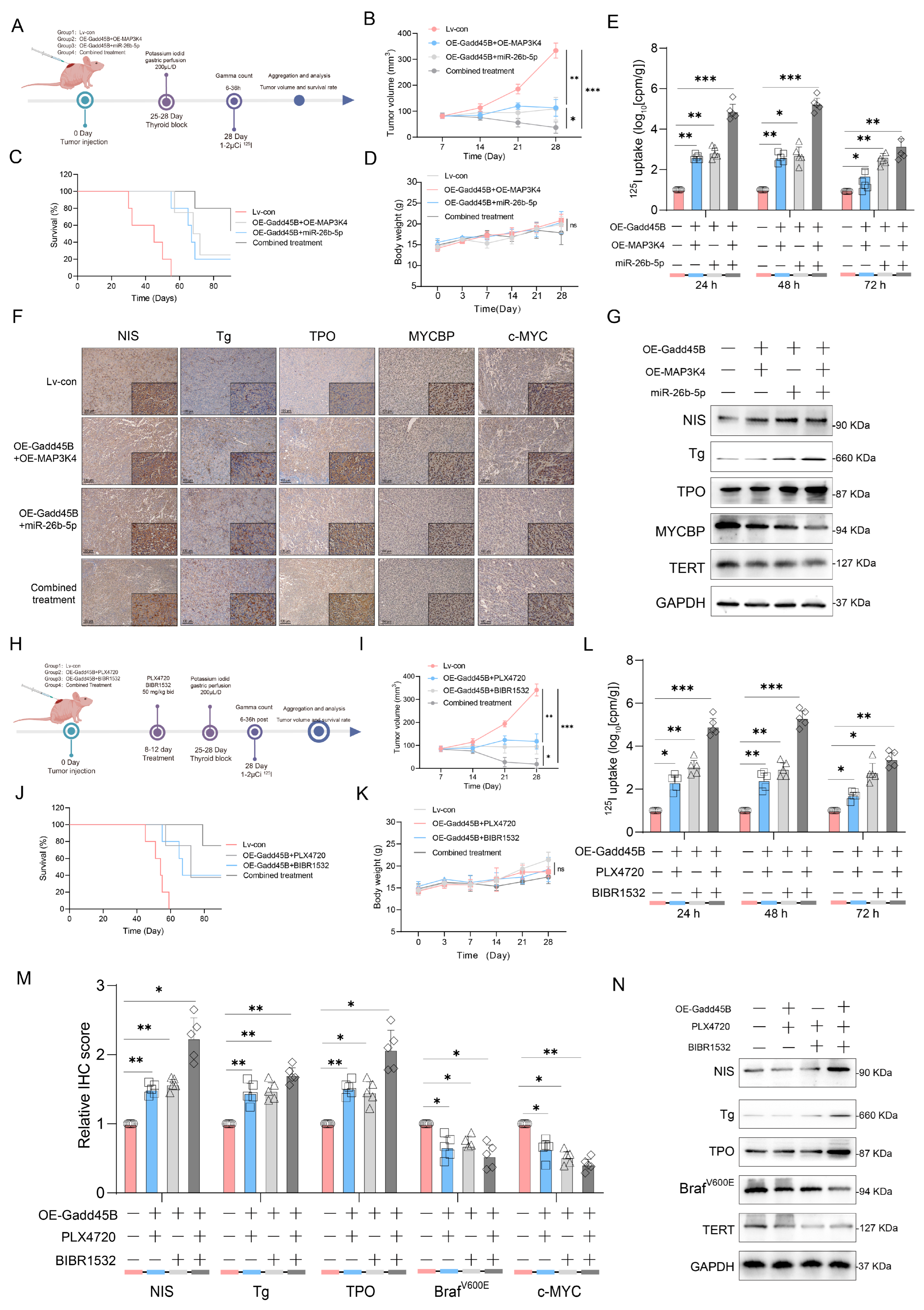
Figure 5L,Q). Subsequently, a tumor-burden mouse model validated the synergistic effects of Gadd45B overexpression with MAP3K4 overexpression and MYCBP inhibition (
Figure 6A–G), as well as with classical targeted drugs PLX4720 and BIBR1532 (
Figure 6H–N). Furthermore, PDX models of RAIR-DTC showed consistent results that supported our findings (
Figure 7H,I,L,M). Correlations between related markers and dedifferentiation status were further substantiated by evidence from cohort 4 (
Figure 7O–Q). These results suggest that Gadd45B could serve as a significant biomarker for predicting patients likely to benefit from RAI treatment and as a potential therapeutic target for synergistic treatment in RAIR-DTC. However, this study has several limitations. This study aimed to elucidate the mechanisms underlying Gadd45B function in RAIR-DTC and to determine whether regulating Gadd45B expression could reverse the dedifferentiation process. Notably, our study did not address Gadd45B’s role in cell cycle regulation during tumor initiation or mechanisms of tumor progression, including tumor cell autophagy, epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), immune escape, and drug resistance development. Future research is necessary to explore Gadd45B’s role in the immunotherapy microenvironment, potential synergistic functions of other Gadd45 family members, and strategies to safely and effectively enhance Gadd45B expression during immunotherapy. The expression of Gadd45B remains a fundamentally and clinically relevant question that warrants further investigation in RAIR-DTC. These modifications may impact tumor development and provide a potential adjuvant treatment strategy to synergize with RAI therapy. Based on our integrated functional, mechanistic, and preclinical data, the MAP3K4–MYCBP–c-MYC axis emerges as the most promising candidate for next-stage validation. This axis not only represents a downstream effector pathway of Gadd45B deficiency but also directly links MAPK signaling perturbations to impaired iodine metabolism and enhanced radio-resistance. Given that MAP3K4 restoration partially rescues NIS expression and sensitizes BRAFV600E-mutated RAIR-DTC cells to RAI therapy in vitro and in vivo, targeting this pathway—potentially in combination with recombinant Gadd45B protein or BRAF/TERT inhibition—may offer a rational translational strategy. Future work will focus on validating this axis in larger patient cohorts and assessing therapeutic efficacy in immunocompetent models. Although intratumoral administration of recombinant Gadd45B protein significantly enhanced RAI uptake and suppressed tumor growth in vivo, the precise mechanism by which the recombinant protein exerts its effects remains to be elucidated. As Gadd45B is not a secreted protein, the possibility of cellular internalization and its intracellular activity require further validation. In the present study, we did not perform direct assays, such as Western blotting or immunofluorescence, to confirm cellular uptake of the recombinant protein. Therefore, while our data support a therapeutic effect of recombinant Gadd45B, future studies should rigorously assess whether and how the exogenous protein penetrates tumor cells and mimics endogenous Gadd45B function.
In future studies, priority should be given to validating Gadd45B-based adjuvant strategies in preclinical immunotherapy models, given their strong mechanistic rationale and the urgent clinical need for effective radiosensitizers in RAIR-DTC. This will be followed by pilot clinical studies with safety and pharmacokinetic endpoints, enabling early translational assessment. Parallel efforts will explore the MAP3K4–MYCBP–c-MYC axis as a complementary target, with the goal of integrating molecular restoration strategies into multimodal treatment regimens. Such a phased approach will allow systematic evaluation from mechanistic insight to clinical applicability.