Analysis of the Role of the SRC Tyrosine Kinase and Podoplanin in the Process of Entosis
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines
2.2. Gene Silencing Using Small Interfering RNA (siRNA)
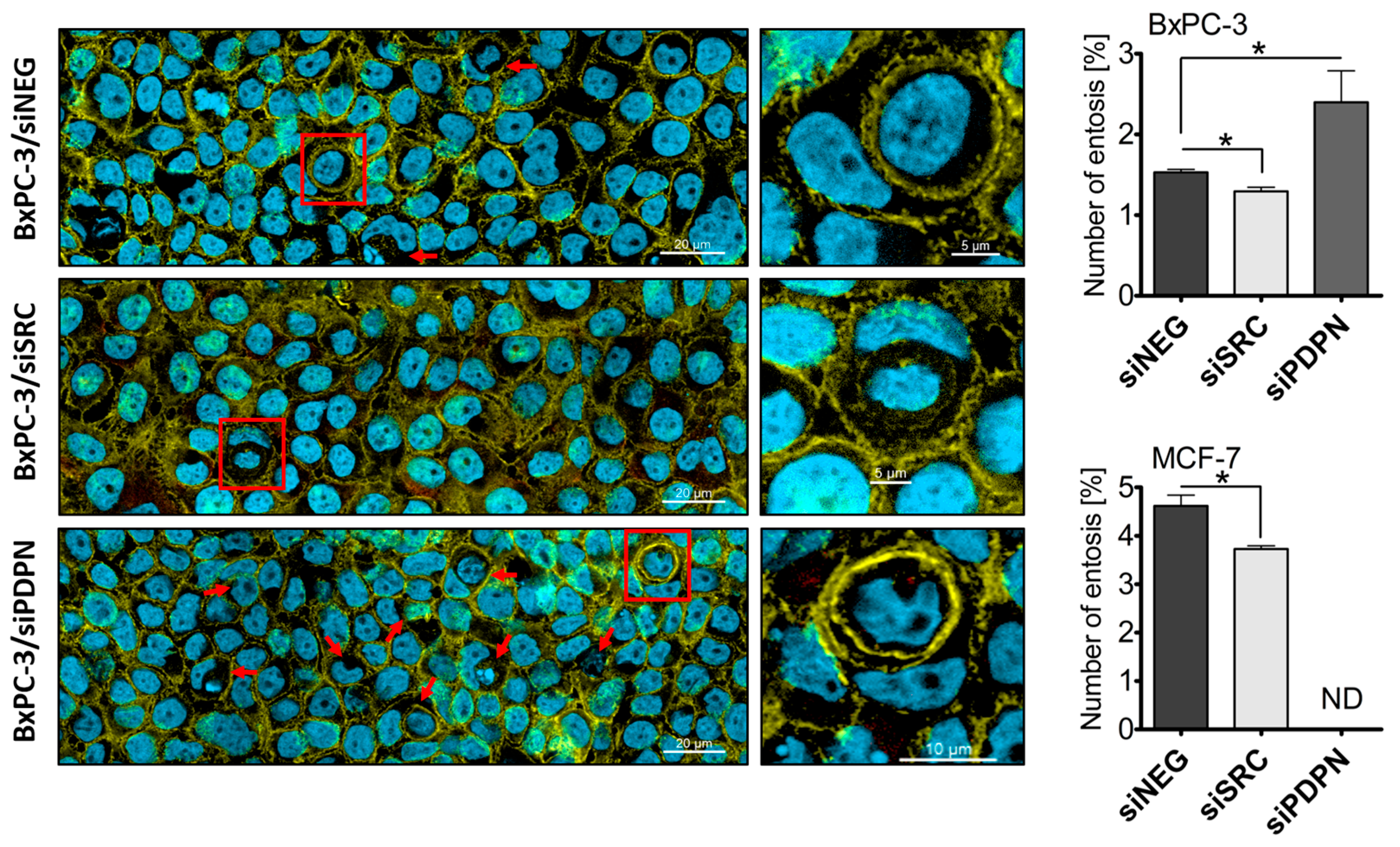
2.3. Analysis of Entotic Figures Using Confocal Microscopy
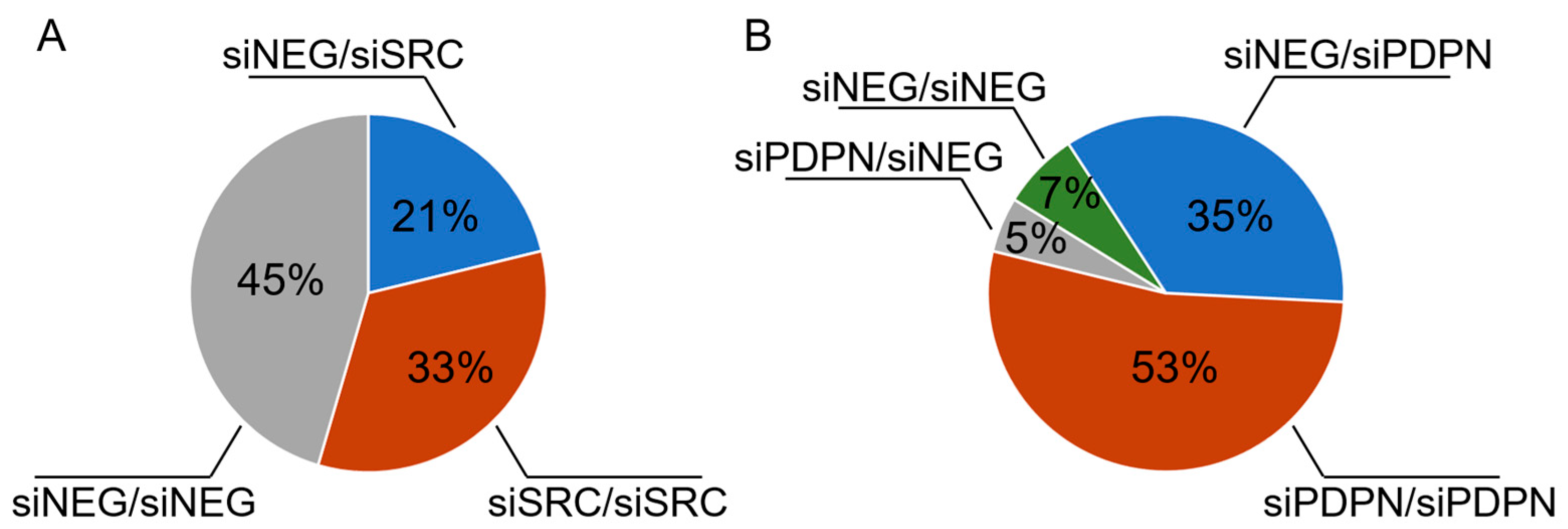
2.4. Co-Culture Experiment for the Evaluation of Entotic Structures
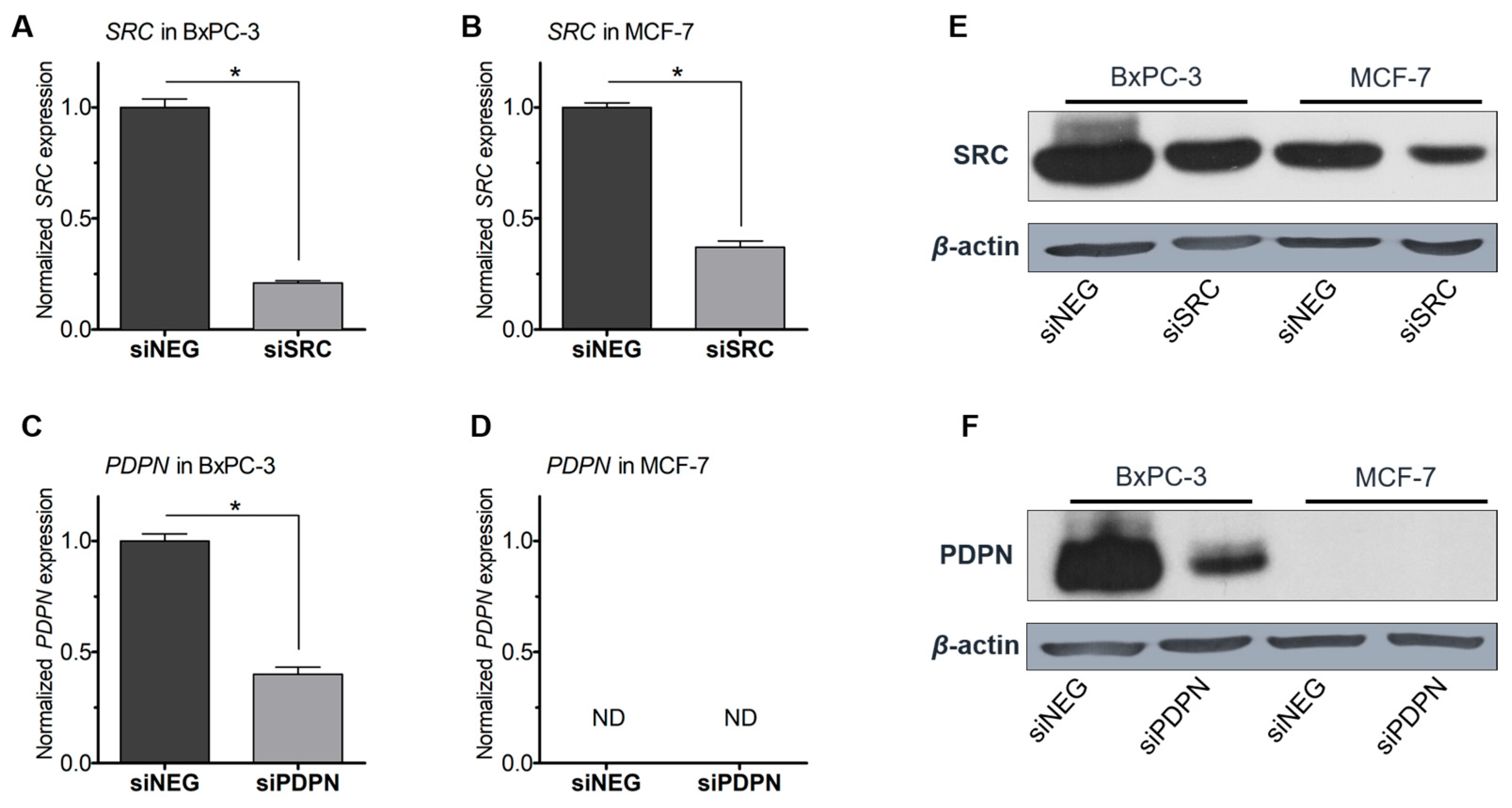
2.5. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription, and RT-qPCR
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
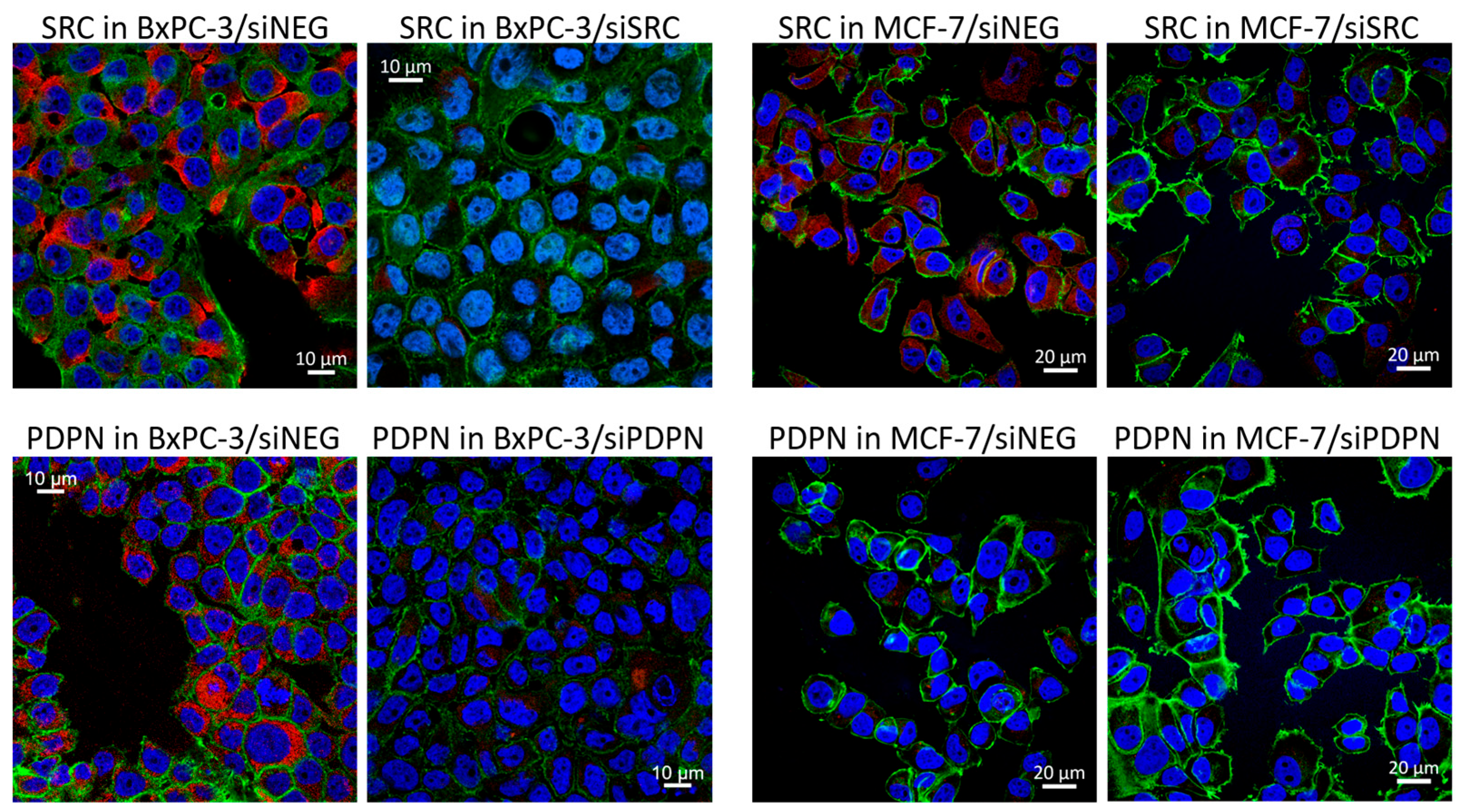
2.7. Immunocytochemistry Analysis
2.8. Cell Viability Assay
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Silencing of the Expression of SRC Tyrosine Kinase and Podoplanin in Pancreatic and Breast Cancer-Derived Cells
3.2. Depletion of SRC and PDPN Does Not Affect Cell Viability
3.3. Knockdown of SRC Reduces the Number of Entoses, While PDPN-Deficient Cells Are Entoses-Competent
3.4. PDPN-Deficient Cells Act as the Engulfing Cell in an Entotic Figure Formed of BxPC-3 Cells
3.5. Knockdown of SRC Increases the Expression of Podoplanin in BxPC-3 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATCC | American Type Culture Collection |
| BSA | Bovine serum albumin |
| CIC | Cell-in-cell |
| DAPI | 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| D-PBS | Dulbecco’s PBS |
| HRP | Horseradish peroxidase |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| FITC | Fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| NEG | Negative |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PDPN | Podoplanin |
| pERM | Phosphorylated ezrin-radixin-moesin proteins |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| RIPA | Radioimmunoprecipitation assay |
| ROCK | Rho/Rho-associated protein kinase |
| RPMI-1640 | Roswell Park Memorial Institute medium 1640 |
| siRNA | Small interfering RNA |
| SRC | SRC tyrosine kinase |
| TBST | Tris-buffered saline Tween 20 |
References
- Okuyama, K.; Fukushima, H.; Naruse, T.; Yanamoto, S. Cell-in-cell structure in cancer: Evading strategies from anti-cancer therapies. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1248097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Lee, D.; Kim, S.E.; Overholtzer, M. Entosis: The core mechanism and crosstalk with other cell death programs. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 870–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackay, H.L.; Muller, P.A.J. Biological relevance of cell-in-cell in cancers. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2019, 47, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziuba, I.; Gawel, A.M.; Tyrna, P.; Rybczynska, J.; Bialy, L.P.; Mlynarczuk-Bialy, I. Fate of Entosis: From the Beginning to the End in Untreated Advanced Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dziuba, I.; Gawel, A.M.; Tyrna, P.; Machtyl, J.; Olszanecka, M.; Pawlik, A.; Wojcik, C.; Bialy, L.P.; Mlynarczuk-Bialy, I. Homotypic Entosis as a Potential Novel Diagnostic Marker in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 6819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, H.L.; Moore, D.; Hall, C.; Birkbak, N.J.; Jamal-Hanjani, M.; Karim, S.A.; Phatak, V.M.; Pinon, L.; Morton, J.P.; Swanton, C.; et al. Genomic instability in mutant p53 cancer cells upon entotic engulfment. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, A.; Yavas, A.; McIntyre, C.A.; Ho, Y.J.; Erakky, A.; Wong, W.; Varghese, A.M.; Melchor, J.P.; Overholtzer, M.; O’Reilly, E.M.; et al. Genetic and clinical correlates of entosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2020, 33, 1822–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mlynarczuk-Bialy, I.; Dziuba, I.; Sarnecka, A.; Platos, E.; Kowalczyk, M.; Pels, K.K.; Wilczynski, G.M.; Wojcik, C.; Bialy, L.P. Entosis: From Cell Biology to Clinical Cancer Pathology. Cancers 2020, 12, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaptulbarova, K.A.; Tsydenova, I.A.; Dolgasheva, D.S.; Kravtsova, E.A.; Ibragimova, M.K.; Vtorushin, S.V.; Litviakov, N.V. Mechanisms and significance of entosis for tumour growth and progression. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Shang, Z.; Zhu, S.; Chang, C.; Niu, Y. Androgen receptor enhances entosis, a non-apoptotic cell death, through modulation of Rho/ROCK pathway in prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2013, 73, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Sun, F.; Wang, G.; Yang, T.; Wei, D.; Guo, L.; Xiao, H. Induction of entosis in prostate cancer cells by nintedanib and its therapeutic implications. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 3151–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overholtzer, M.; Mailleux, A.A.; Mouneimne, G.; Normand, G.; Schnitt, S.J.; King, R.W.; Cibas, E.S.; Brugge, J.S. A nonapoptotic cell death process, entosis, that occurs by cell-in-cell invasion. Cell 2007, 131, 966–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, H.; Kaneko, M.K.; Kato, Y. Roles of Podoplanin in Malignant Progression of Tumor. Cells 2022, 11, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sikorska, J.; Gawel, D.; Domek, H.; Rudzinska, M.; Czarnocka, B. Podoplanin (PDPN) affects the invasiveness of thyroid carcinoma cells by inducing ezrin, radixin and moesin (E/R/M) phosphorylation in association with matrix metalloproteinases. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielecki, D.; Gajda, E.; Sikorska, J.; Betkowska, A.; Rozwadowski, M.; Gawel, A.M.; Kulecka, M.; Zeber-Lubecka, N.; Godlewska, M.; Gawel, D. Resolving the role of podoplanin in the motility of papillary thyroid carcinoma-derived cells using RNA sequencing. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2023, 21, 3810–3826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, C.D.; Burridge, K. The on-off relationship of Rho and Rac during integrin-mediated adhesion and cell migration. Small GTPases 2014, 5, e27958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huveneers, S.; Danen, E.H. Adhesion signaling–crosstalk between integrins, Src and Rho. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 1059–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martellucci, S.; Clementi, L.; Sabetta, S.; Mattei, V.; Botta, L.; Angelucci, A. Src Family Kinases as Therapeutic Targets in Advanced Solid Tumors: What We Have Learned so Far. Cancers 2020, 12, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Zou, H.; Guo, Y.; Tong, T.; Ye, L.; Zhu, C.; Deng, L.; Wang, B.; Pan, Y.; Li, P. SRC kinase-mediated signaling pathways and targeted therapies in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2022, 24, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeatman, T.J. A renaissance for SRC. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 470–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Je, D.W.; Moon, O.Y.; Ji, Y.G.; Cho, Y.; Lee, D.H. The inhibition of SRC family kinase suppresses pancreatic cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Pancreas 2014, 43, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwietzer, M.F.; Tholmann, S.; Kummer, D.; Kaschler, A.; Greune, L.; Thuring, E.M.; Schmidt, M.A.; Gerke, V.; Ebnet, K. Loss of contact inhibition of locomotion in the absence of JAM-A promotes entotic cell engulfment. iScience 2022, 25, 105144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Chen, C.S.; Ichikawa, H.; Goldberg, G.S. SRC induces podoplanin expression to promote cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 9649–9656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retzbach, E.P.; Sheehan, S.A.; Krishnan, H.; Zheng, H.; Zhao, C.; Goldberg, G.S. Independent effects of Src kinase and podoplanin on anchorage independent cell growth and migration. Mol. Carcinog. 2022, 61, 677–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudzinska, M.; Gawel, D.; Sikorska, J.; Karpinska, K.M.; Kiedrowski, M.; Stepien, T.; Marchlewska, M.; Czarnocka, B. The role of podoplanin in the biology of differentiated thyroid cancers. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gawel, A.M.; Ratajczak, M.; Gajda, E.; Grzanka, M.; Paziewska, A.; Cieslicka, M.; Kulecka, M.; Oczko-Wojciechowska, M.; Godlewska, M. Analysis of the Role of FRMD5 in the Biology of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, S.; Overholtzer, M. Mechanisms and consequences of entosis. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 2379–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, C.; Zeng, B.; Dong, C.; Liu, J.; Xing, F. Rho-ROCK signaling mediates entotic cell death in tumor. Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oi, M.; Kushibiki, R.; Kanehira, Y.; Nishijima, Y.; Kobayashi, S.; Saio, M. ROCK signaling is involved in the entosis of both nonepithelial and epithelial tumors, whereas N-cadherin is involved in the entosis of nonepithelial tumors. Exp. Ther. Med. 2025, 29, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinojosa, L.S.; Holst, M.; Baarlink, C.; Grosse, R. MRTF transcription and Ezrin-dependent plasma membrane blebbing are required for entotic invasion. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 3087–3095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arpin, M.; Chirivino, D.; Naba, A.; Zwaenepoel, I. Emerging role for ERM proteins in cell adhesion and migration. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2011, 5, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clucas, J.; Valderrama, F. ERM proteins in cancer progression. J. Cell Sci. 2014, 127, 267–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Antigen | Catalog No. | Type/ Clone (Symbol) | Dilution/ Blocking Agent | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-actin | 3700 | Mouse monoclonal (IgG2b)/ 8H10D10 | 1:2000/ 5% skimmed milk | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. (Beverly, MA, USA) |
| pERM (T567/Ezrin, T564/Radixin, T558/Moesin) | ab76247 | Rabbit monoclonal (IgG)/ EP2122Y | 1:2000/ 5% BSA | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) |
| tERM | 3142 | Rabbit polyclonal | 1:1000/ 5% BSA | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. |
| PDPN | MCA2543 | Mouse mococlonal (IgG1)/ D2-40 | 1:1000/ 5% skimmed milk | Bio-Rad (Hercules, CA, USA) |
| pSRC (Y416) | 2101 | Rabbit polyclonal | 1:1000/ 5% BSA | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. |
| tSRC | 2110 | Mouse mococlonal (IgG1)/ L4A1 | 1:1000/ 5% skimmed milk | Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. |
| anti-mouse secondary immunoglobulins | 115-035-146 | Goat polyclonal | 1:10,000/ 1% skimmed milk | Jackson ImmunoResearch (West Grove, PA, USA) |
| anti-rabbit secondary immunoglobulins | P0448 | Goat polyclonal | 1:5000/ 1% skimmed milk | Dako (Carpinteria, CA, USA) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gawel, A.M.; Godlewska, M.; Biały, L.P.; Mlynarczuk-Bialy, I. Analysis of the Role of the SRC Tyrosine Kinase and Podoplanin in the Process of Entosis. Cancers 2025, 17, 3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193173
Gawel AM, Godlewska M, Biały LP, Mlynarczuk-Bialy I. Analysis of the Role of the SRC Tyrosine Kinase and Podoplanin in the Process of Entosis. Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193173
Chicago/Turabian StyleGawel, Agata M., Marlena Godlewska, Lukasz P. Biały, and Izabela Mlynarczuk-Bialy. 2025. "Analysis of the Role of the SRC Tyrosine Kinase and Podoplanin in the Process of Entosis" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193173
APA StyleGawel, A. M., Godlewska, M., Biały, L. P., & Mlynarczuk-Bialy, I. (2025). Analysis of the Role of the SRC Tyrosine Kinase and Podoplanin in the Process of Entosis. Cancers, 17(19), 3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193173





