Association of TP53 with Defective Long Chain 3-Hydroxy acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Induced Non-Cirrhotic Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study of cDNA Array of HCC Patients
2.2. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis
2.3. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. HADHA Transcript Levels in cDNA Array of HCC Patients
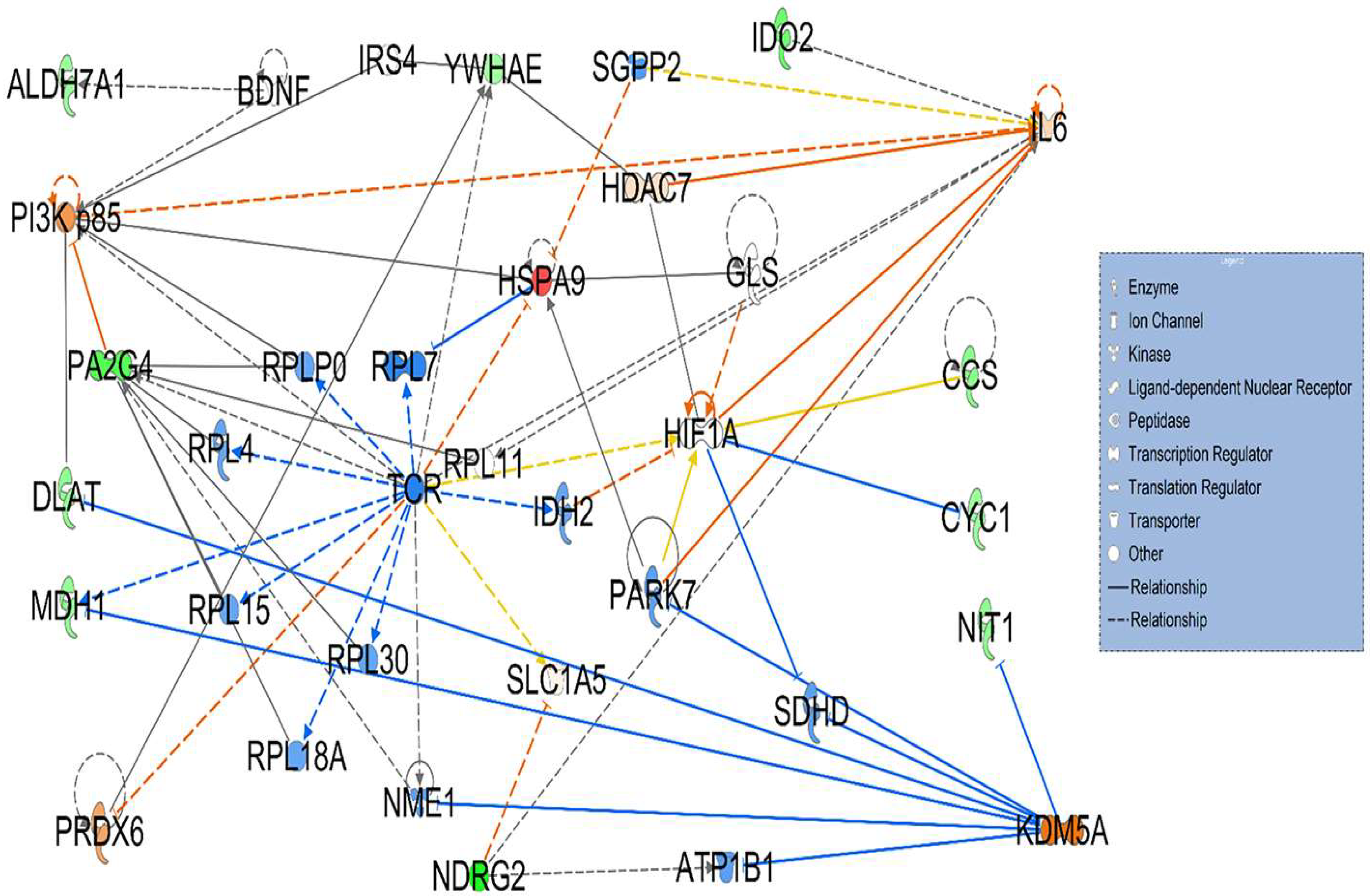
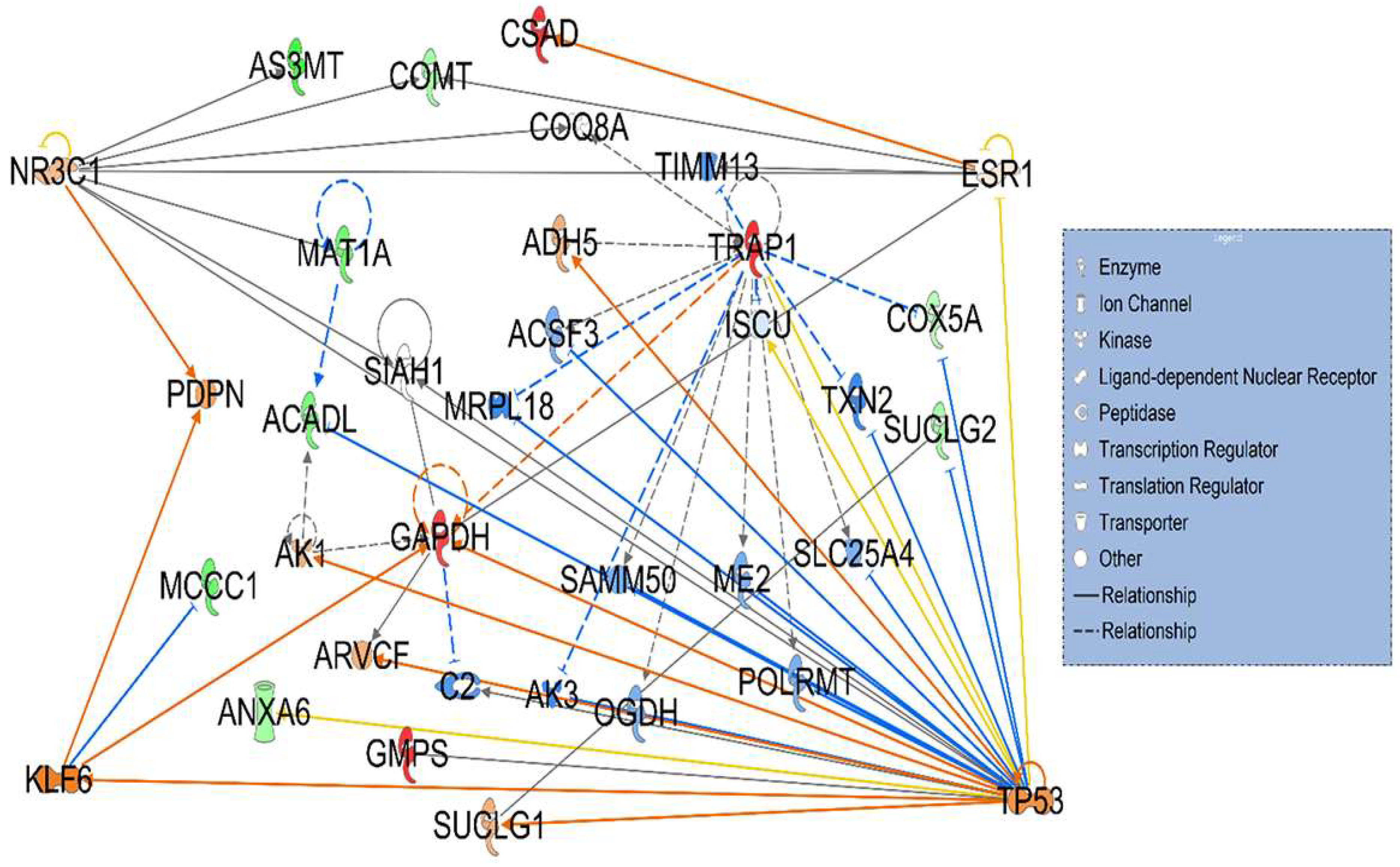
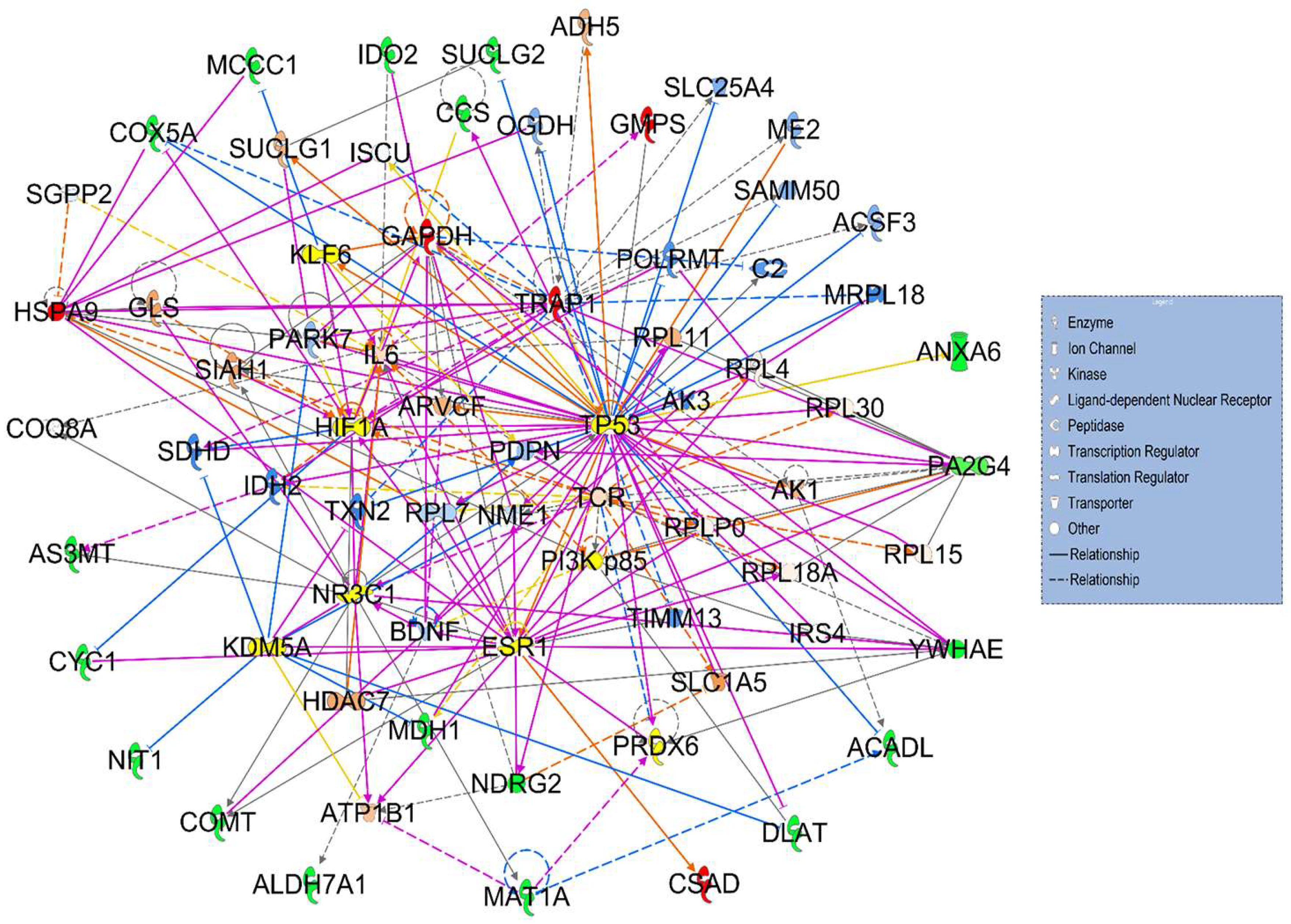
3.2. Signaling Networks Associated with Differentially Expressed Proteins Between HT (Heterozygous LCHAD Mice Without Cancer) and WT Mice
3.3. Hepatotoxicity Report and Identified Irregularities in Liver Function Related to Differentially Expressed Proteins Between HT (Heterozygous LCHAD Mice Without Cancer) and WT Mice
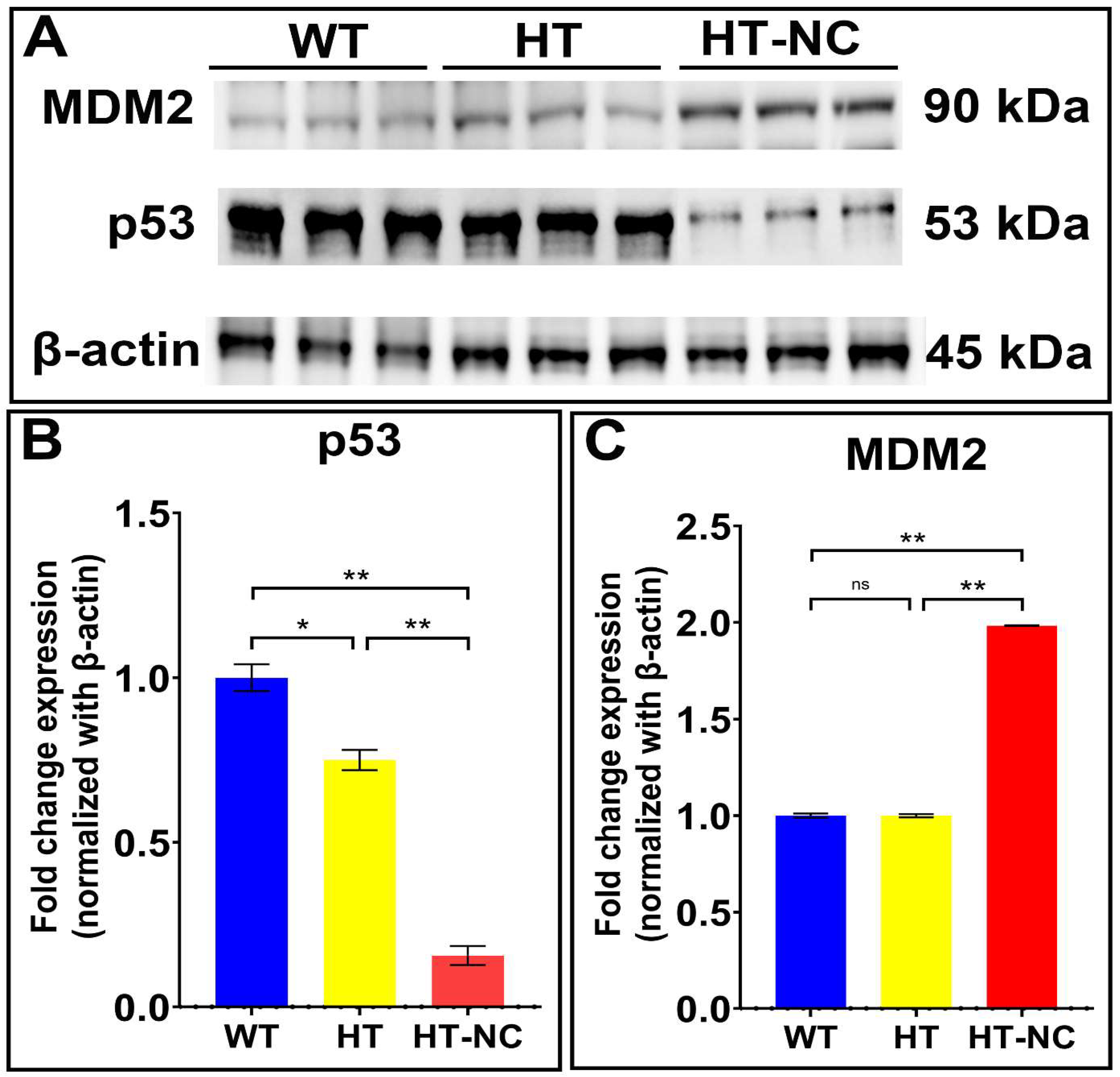
3.4. Differential Expression of p53 and MDM2 in WT, HT (Heterozygous LCHAD Mice Without Cancer) and HT-NC (Heterozygous LCHAD Mice with Non-Cirrhotic Cancer)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HCC | Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
| MASLD | Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease |
| HCC-NC | Non cirrhotic HCC |
| HCC-C | Cirrhotic HCC |
| HADHA | Hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase trifunctional multienzyme complex subunit alpha |
| LCHAD | Long chain 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase |
| IPA | Ingenuity pathway analysis |
| WT | Wild type mouse |
| HT | LCHAD-heterozygous mouse without cancer |
| HT-NC | LCHAD-heterozygous mouse with non-cirrhotic cancer |
References
- Rumgay, H.; Ferlay, J.; de Martel, C.; Georges, D.; Ibrahim, A.S.; Zheng, R.; Wei, W.; Lemmens, V.; Soerjomataram, I. Global, regional and national burden of primary liver cancer by subtype. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 161, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevisani, F.; Frigerio, M.; Santi, V.; Grignaschi, A.; Bernardi, M. Hepatocellular carcinoma in non-cirrhotic liver: A reappraisal. Dig. Liver Dis. 2010, 42, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkofer, B.; Lepennec, V.; Chiche, L. Hepatocellular cancer in the non-cirrhotic liver. J. Visc. Surg. 2011, 148, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, A.; Sandhu, S.; Lai, J.P.; Sandhu, D.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma in non-cirrhotic liver: A comprehensive review. World J. Hepatol. 2019, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.A.; Patil, R.; Harrison, S.A. NAFLD-related hepatocellular carcinoma: The growing challenge. Hepatology 2023, 77, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chan, K.W.; Wang, B.; Qiao, L. Fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 2617–2624; quiz 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, H.; Osaki, Y. Non-B, non-C hepatocellular carcinoma (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2013, 43, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Khare, T.; Khare, S.; Angdisen, J.J.; Zhang, Q.; Stuckel, A.; Mooney, B.P.; Ridenhour, S.E.; Gitan, R.S.; Hammoud, G.M.; Ibdah, J.A. Defects in long-chain 3-hydroxy acyl-CoA dehydrogenase lead to hepatocellular carcinoma: A novel etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 1461–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamad, B.; Shah, V.; Onyshchenko, M.; Elshamy, M.; Aucejo, F.; Lopez, R.; Hanouneh, I.A.; Alhaddad, R.; Alkhouri, N. Characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) patients without cirrhosis. Hepatol. Int. 2016, 10, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, R.; Bugianesi, E. Should we undertake surveillance for HCC in patients with NAFLD? J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddikeri, S.; McNeeley, M.F.; Wang, C.L.; Bhargava, P.; Dighe, M.K.; Yeh, M.M.; Dubinsky, T.J.; Kolokythas, O.; Lalwani, N. Hepatocellular carcinoma in the noncirrhotic liver. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2014, 203, W34–W47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Gouw, A.S.; van den Heuvel, M.C.; Molema, G.; Poppema, S.; van der Jagt, E.J.; de Jong, K.P. Hepatocellular carcinomas in cirrhotic and noncirrhotic human livers share angiogenic characteristics. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2010, 17, 1564–1571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamwal, R.; Krishnan, V.; Kushwaha, D.S.; Khurana, R. Hepatocellular carcinoma in non-cirrhotic versus cirrhotic liver: A clinico-radiological comparative analysis. Abdom. Radiol. 2020, 45, 2378–2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taie, D.; El-Wahed, M.; Badr, M.; Soliman, E.S.; Abdou, A. Hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic and noncirrhotic liver: Clinicopathological differences. Menoufia Med. J. 2015, 28, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, O.C.; Rosa, A.S.; Fernandes, A.; Niel, C.; Villela-Nogueira, C.A.; Pannain, V.; Araujo, N.M. RASSF1A and DOK1 Promoter Methylation Levels in Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Cirrhotic and Non-Cirrhotic Liver, and Correlation with Liver Cancer in Brazilian Patients. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Deger, T.; Boers, R.G.; Boers, J.B.; Doukas, M.; Gribnau, J.; Wilting, S.M.; Debes, J.D.; Boonstra, A. Hypermethylation of DNA Methylation Markers in Non-Cirrhotic Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2023, 15, 4784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Lou, W.; Liu, J.; Li, R.; Chen, J.; Fan, W. In silico analysis excavates potential biomarkers by constructing miRNA-mRNA networks between non-cirrhotic HCC and cirrhotic HCC. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.; Kler, R.S.; Bartlett, K.; Briggs, H.; Bindoff, L.A.; Pourfarzam, M.; Gardner-Medwin, D.; Turnbull, D.M. Combined enzyme defect of mitochondrial fatty acid oxidation. J. Clin. Investig. 1992, 90, 1219–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, Y.; Izai, K.; Orii, T.; Hashimoto, T. Novel fatty acid beta-oxidation enzymes in rat liver mitochondria. II. Purification and properties of enoyl-coenzyme A (CoA) hydratase/3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase/3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase trifunctional protein. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Giorgi, V.; Monaco, A.; Worchech, A.; Tornesello, M.; Izzo, F.; Buonaguro, L.; Marincola, F.M.; Wang, E.; Buonaguro, F.M. Gene profiling, biomarkers and pathways characterizing HCV-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Transl. Med. 2009, 7, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Han, J.; Xing, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Liang, L.; Li, C.; Dai, S.; Wu, M.; Shen, F.; et al. Dysregulated fatty acid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepat. Oncol. 2016, 3, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Masaki, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Miyazaki, M.; Kato, M.; Sugimoto, R.; Nakamura, K.; Aishima, S.; Shirabe, K.; Nakamuta, M.; et al. Reduction of fatty acid oxidation and responses to hypoxia correlate with the progression of de-differentiation in HCC. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013, 7, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Chen, X.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Xia, Q.; Zhang, W. The role of MDM2-p53 axis dysfunction in the hepatocellular carcinoma transformation. Cell Death Discov. 2020, 6, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Yang, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Hu, L.; Huang, D.; Xu, Q. Hypoxia-inducible factors in hepatocellular carcinoma (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2020, 43, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Jiang, C.; Wu, J. The role of hypoxia inducible factor-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 409272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Liu, S.; Ge, G.; Jiang, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, Q.; Jin, C.; Mo, J.; Li, J.; Wang, K.; et al. Roles of hypoxia-inducible factor in hepatocellular carcinoma under local ablation therapies. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1086813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Xu, Z.; Wang, J.; Cigliano, A.; Pilo, M.G.; Ribback, S.; Zhang, S.; Qiao, Y.; Che, L.; Pascale, R.M.; et al. Functional role of SGK3 in PI3K/Pten driven liver tumor development. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.J.; Zhu, M.H.; Lu, X.J.; Liu, Y.J.; Lu, J.F.; Leung, C.H.; Ma, D.L.; Chen, J. The emerging role of KDM5A in human cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Jablonowski, C.; Cheng, P.H.; AlTahan, A.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Palmer, L.; Lan, C.; Sun, B.; Abu-Zaid, A.; et al. KDM5A Regulates a Translational Program that Controls p53 Protein Expression. iScience 2018, 9, 84–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, K.M.; Themanns, M.; Friedbichler, K.; Kornfeld, J.W.; Esterbauer, H.; Tuckermann, J.P.; Moriggl, R. Hepatic growth hormone and glucocorticoid receptor signaling in body growth, steatosis and metabolic liver cancer development. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2012, 361, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.J.; Ding, H.; Chen, X.X.; Yang, L. Comprehensive Analysis of the Expression and Prognosis for Lipid Metabolism-Related Genes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. S. Asian J. Cancer 2023, 12, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabatino, M.E.; Castellaro, A.; Racca, A.C.; Carbajosa Gonzalez, S.; Pansa, M.F.; Soria, G.; Bocco, J.L. Kruppel-Like Factor 6 Is Required for Oxidative and Oncogene-Induced Cellular Senescence. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.H.; Wang, D.Y.; Zhang, J.K.; Wang, Z.H.; Pan, J.; Shi, X.Y.; Yang, H.; Zhang, S.J.; Guo, W.Z. Kruppel-like factor 6 suppresses growth and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2016, 29, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukocheva, O.A. Estrogen, estrogen receptors, and hepatocellular carcinoma: Are we there yet? World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.; Pasini, E.; Pastrello, C.; Angeli, M.; Baciu, C.; Abovsky, M.; Coffee, A.; Adeyi, O.; Kotlyar, M.; Jurisica, I. Estrogen Receptor 1 Inhibition of Wnt/beta-Catenin Signaling Contributes to Sex Differences in Hepatocarcinogenesis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 777834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.C.; Mato, J.M. Role of methionine adenosyltransferase and S-adenosylmethionine in alcohol-associated liver cancer. Alcohol 2005, 35, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Qin, W.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Z.; Yuan, B.; Dai, R.; Shen, H.; Chen, Y.; Fu, J.; Wang, H. ACADL plays a tumor-suppressor role by targeting Hippo/YAP signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2020, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzer, K.; Drucker, E.; Roessler, S.; Dauch, D.; Heinzmann, F.; Waldburger, N.; Eiteneuer, E.M.; Herpel, E.; Breuhahn, K.; Zender, L.; et al. Proteomic Analysis Reveals GMP Synthetase as p53 Repression Target in Liver Cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Liu, Q.; Shi, M.; Zhang, R.; Shi, H.; Ren, Q.; Ma, J.; Guo, H.; et al. NDRG2 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma adhesion, migration and invasion by regulating CD24 expression. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Li, T.; Ma, L.; Liu, G.; Wang, G.; Kang, J. NDRG2 inhibition facilitates angiogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Open Med. 2021, 16, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrejeva, D.; Kugler, J.M.; Nguyen, H.T.; Malmendal, A.; Holm, M.L.; Toft, B.G.; Loya, A.C.; Cohen, S.M. Metabolic control of PPAR activity by aldehyde dehydrogenase regulates invasive cell behavior and predicts survival in hepatocellular and renal clear cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.C.; Kang, Y.K.; Kim, W.H.; Jang, Y.J.; Kim, D.J.; Park, I.Y.; Sohn, B.H.; Sohn, H.A.; Lee, H.G.; Lim, J.S.; et al. Functional and clinical evidence for NDRG2 as a candidate suppressor of liver cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 4210–4220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Luk, J.M.; Lee, N.P.; Peng, J.; Leng, X.; Guan, X.Y.; Lau, G.K.; Beretta, L.; Fan, S.T. Association of mortalin (HSPA9) with liver cancer metastasis and prediction for early tumor recurrence. Mol. Cell Proteom. 2008, 7, 315–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, L.; Leveri, M.; Gritti, C.; De Silvestri, A.; Zavaglia, C.; Sonzogni, L.; Silvestri, L.; Civardi, E.; Mondelli, M.U.; Silini, E.M. Genetic polymorphisms of steroid hormone metabolizing enzymes and risk of liver cancer in hepatitis C-infected patients. J. Hepatol. 2003, 39, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hlady, R.A.; Sathyanarayan, A.; Thompson, J.J.; Zhou, D.; Wu, Q.; Pham, K.; Lee, J.H.; Liu, C.; Robertson, K.D. Integrating the Epigenome to Identify Drivers of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2019, 69, 639–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asghar, K.; Farooq, A.; Zulfiqar, B.; Rashid, M.U. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase: As a potential prognostic marker and immunotherapeutic target for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 23, 2286–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lob, S.; Konigsrainer, A.; Rammensee, H.G.; Opelz, G.; Terness, P. Inhibitors of indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase for cancer therapy: Can we see the wood for the trees? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, H.J.; Li, H.N.; Zhou, X.M.; Zhao, J.L.; Wan, D.F. Monitoring microarray-based gene expression profile changes in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2005, 11, 2811–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Zhu, X.; Lv, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, G. Glucometabolic Reprogramming in the Hepatocellular Carcinoma Microenvironment: Cause and Effect. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 5957–5974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elchuri, S.; Oberley, T.D.; Qi, W.; Eisenstein, R.S.; Jackson Roberts, L.; Van Remmen, H.; Epstein, C.J.; Huang, T.T. CuZnSOD deficiency leads to persistent and widespread oxidative damage and hepatocarcinogenesis later in life. Oncogene 2005, 24, 367–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, K.L.; Vorac, J.; Hofmann, K.; Meiser, P.; Unterweger, I.; Kuerschner, L.; Weighardt, H.; Forster, I.; Thiele, C. Kupffer Cells Sense Free Fatty Acids and Regulate Hepatic Lipid Metabolism in High-Fat Diet and Inflammation. Cells 2020, 9, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasenko, T.N.; Singh, L.N.; Chatterji-Len, M.; Zerfas, P.M.; Cusmano-Ozog, K.; McGuire, P.J. Kupffer cells modulate hepatic fatty acid oxidation during infection with PR8 influenza. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1852, 2391–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, P.; Wang, S.; Friedman, S.L. The Power of Plasticity-Metabolic Regulation of Hepatic Stellate Cells. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 242–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, D.; Jensen, J.E.R.; Andersen, C.A.T.; Jakobsgaard, P.R.; Havelund, J.; Lauritsen, L.; Mandacaru, S.; Siersbaek, M.; Shackleton, O.L.; Inoue, H.; et al. Hepatic stellate cells regulate liver fatty acid utilization via plasmalemma vesicle-associated protein. Cell Metab. 2025, 37, 971–986.e978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khare, T.; Stuckel, A.J.; Gupta, S.; Liu, K.; Hammoud, G.M.; Ibdah, J.A.; Khare, S. Association of TP53 with Defective Long Chain 3-Hydroxy acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Induced Non-Cirrhotic Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193241
Khare T, Stuckel AJ, Gupta S, Liu K, Hammoud GM, Ibdah JA, Khare S. Association of TP53 with Defective Long Chain 3-Hydroxy acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Induced Non-Cirrhotic Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193241
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhare, Tripti, Alexei J. Stuckel, Suneel Gupta, Karina Liu, Ghassan M. Hammoud, Jamal A. Ibdah, and Sharad Khare. 2025. "Association of TP53 with Defective Long Chain 3-Hydroxy acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Induced Non-Cirrhotic Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193241
APA StyleKhare, T., Stuckel, A. J., Gupta, S., Liu, K., Hammoud, G. M., Ibdah, J. A., & Khare, S. (2025). Association of TP53 with Defective Long Chain 3-Hydroxy acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase Induced Non-Cirrhotic Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers, 17(19), 3241. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193241






