Discordance Between p16-Expression and HPV-Status in Sinonasal Carcinoma: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
2.2. Histopathological Evaluation and Immunohistochemistry
2.2.1. Site A
2.2.2. Site B
2.3. HPV-DNA Detection and Subtyping
2.3.1. Site A
2.3.2. Site B
2.4. Data Collection and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Tumor Characteristics
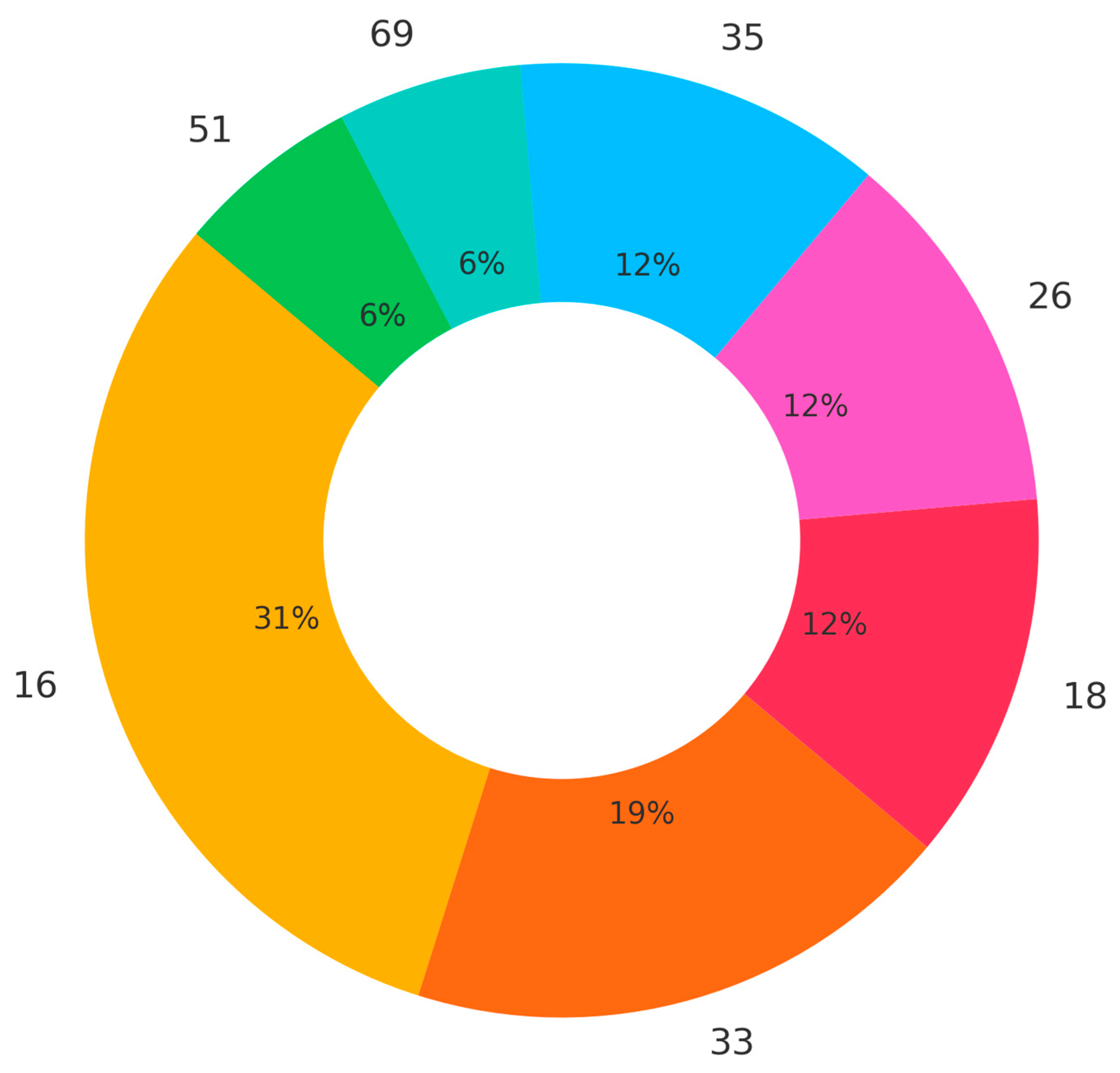
3.2. HPV-Subtype Analysis
3.3. Relation of p16 and HPV Status
4. Discussion
4.1. Relation of p16 and HPV Status
4.2. Demographics and Tumor Characteristics
4.3. HPV Subtypes
4.4. Limitations
4.5. Clinical Implications
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HMSC | HPV-related multiphenotypic sinonasal carcinoma |
| HNSCC | Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma |
| HPV | Human papillomavirus |
| IHC | Immunohistochemistry |
| ISH | In situ hybridization |
| NCCN | National Comprehensive Cancer Network |
| OPSCC | Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| SNSCC | Sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma |
| TMA | Tissue microarray |
References
- Lechner, M.; Liu, J. HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer: Epidemiology, molecular biology and clinical management. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 306–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amanian, A.; Maza, I. Epidemiologic Trends in Human Papillomavirus-Associated Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. JAMA Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2024, 150, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thawani, R.; Katabi, N.; Morris, L.G.T. The contemporary management of cancers of the sinonasal tract in adults. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 72–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prigge, E.S.; Arbyn, M. Diagnostic accuracy of p16INK4a immunohistochemistry in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 1186–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallus, R.; Näsman, A.; Iyer, M.K. Accuracy of p16 IHC in Classifying HPV-Driven OPSCC in Different Populations. Cancers 2023, 15, 656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Buchwald, C.; Jakobsen, K.K. TNM 8 staging system beyond p16: Double HPV/p16 status is superior to p16 alone in predicting outcome in oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 2024, 211, 114329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehanna, H.; Thomas, M.S.; Zafereo, M. Prognostic implications of p16 and HPV discordance in oropharyngeal cancer (HNCIG-EPIC-OPC): A multicentre, multinational, individual patient data analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiromaru, R.; Yamamoto, H.; Yasumatsu, R.; Hongo, T.; Nozaki, Y.; Hashimoto, K.; Taguchi, K.; Masuda, M.; Nakagawa, T.; Oda, Y. HPV-related Sinonasal Carcinoma: Clinicopathologic Features, Diagnostic Utility of p16 and Rb Immunohistochemistry, and EGFR Copy Number Alteration. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2020, 44, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Library of Medicine. GenBank Platform. Available online: http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi (accessed on 27 July 2025).
- Scott-Wittenborn, N.; Fakhry, C. Epidemiology of HPV Related Malignancies. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2021, 31, 286–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribb, J.P.; Wheelock, J.H.; Park, E.S. Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) and the Current State of Oropharyngeal Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Del. J. Public Health 2023, 9, 26–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutner, D.; Bevis, N.; Derad, C.; Asendorf, T.; Tostmann, R.; Iro, H.; Klussmann, J.P.; Guntinas-Lichius, O.; Collaborators. The multicenter registry “oropharyngeal cancer” of the German ENT Study Center—First Results. Laryngorhinootologie 2025, 104, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tawk, B.; Debus, J.; Abdollahi, A. Evolution of a Paradigm Switch in Diagnosis and Treatment of HPV-Driven Head and Neck Cancer-Striking the Balance Between Toxicity and Cure. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 12, 753387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sjostedt, S.; von Buchwald, C.; Agander, T.K.; Aanaes, K. Impact of human papillomavirus in sinonasal cancer-a systematic review. Acta Oncol. 2021, 60, 1175–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamuner, F.T.; Gunti, S.; Starrett, G.J.; Faraji, F.; Toni, T.; Saraswathula, A.; Vu, K.; Gupta, A.; Zhang, Y.; Faden, D.L.; et al. Molecular patterns and mechanisms of tumorigenesis in HPV-associated and HPV-independent sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2025, 16, 5285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Quan, H.; Yan, L.; Sun, J.; Lan, L.; Wang, S. Prevalence of human papillomavirus in sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma with and without association of inverted papilloma in Eastern China. Infect. Agents Cancer 2020, 15, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirakawa, H.; Ikegami, T.; Touyama, M.; Ooshiro, Y.; Higa, T.; Higa, T.; Agena, S.; Kinjyo, H.; Kondo, S.; Kise, N.; et al. p16 Overexpression in Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Association with Human Papillomavirus and Prediction of Survival Outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E.; Coviello, C.; Menaker, S.; Martinez-Duarte, E.; Gomez, C.; Lo, K.; Kerr, D.; Franzmann, E.; Leibowitz, J.; Sargi, Z. P16 and human papillomavirus in sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 2020, 42, 2021–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larque, A.B.; Hakim, S.; Ordi, J.; Nadal, A.; Diaz, A.; del Pino, M.; Marimon, L.; Alobid, I.; Cardesa, A.; Alos, L. High-risk human papillomavirus is transcriptionally active in a subset of sinonasal squamous cell carcinomas. Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tendron, A.; Classe, M.; Casiraghi, O.; Pere, H.; Even, C.; Gorphe, P.; Moya-Plana, A. Prognostic Analysis of HPV Status in Sinonasal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Quan, H.T.; Wang, J.; Tang, T.C.; Li, Y.; Song, X.M. Immunohistochemical p16 expression in the prognosis of patients with sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma. Neoplasma 2023, 70, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.S.; Zhang, H.; Ma, D.L.; Wan, H.F.; Li, Y.H.; Li, R.; Liu, H.G.; Piao, Y.S. Combined detection of p16 and Rb with high-risk human papilloma virus infection in non-oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 2025, 54, 612–617. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- London, N.R., Jr.; Windon, M.J.; Amanian, A.; Zamuner, F.T.; Bishop, J.; Fakhry, C.; Rooper, L.M. Evaluation of the Incidence of Human Papillomavirus-Associated Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Sinonasal Tract Among US Adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2255971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, J.R.; Lieberman, S.M.; Tam, M.M.; Liu, C.Z.; Li, Z.; Hu, K.S.; Morris, L.G.T.; Givi, B. Human papillomavirus and survival of patients with sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer 2020, 126, 1413–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabatabaeian, H.; Bai, Y.; Huang, R.; Chaurasia, A.; Darido, C. Navigating therapeutic strategies: HPV classification in head and neck cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2024, 131, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.A.; Andreasen, S.; Hang, J.F.; Bullock, M.J.; Chen, T.Y.; Franchi, A.; Garcia, J.J.; Gnepp, D.R.; Gomez-Fernandez, C.R.; Ihrler, S.; et al. HPV-related Multiphenotypic Sinonasal Carcinoma: An Expanded Series of 49 Cases of the Tumor Formerly Known as HPV-related Carcinoma With Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma-like Features. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 1690–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Lu, J.; Han, S. The correlation between multiple HPV infections and the occurrence, development, and prognosis of cervical cancer. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1220522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Querney, J.; Mendez, A.; Skinner, J.; Wihlidal, J.; Ramazani, F.; Biron, V.; Côté, D. Prognostic role of p16 overexpression in sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective analysis of Alberta patients. World J. Otorhinolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2024, 11, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlussel Markovic, E.; Marqueen, K.E.; Sindhu, K.K.; Lehrer, E.J.; Liu, J.; Miles, B.; Genden, E.; Sharma, S.; Gupta, V.; Westra, W.; et al. The prognostic significance of human papilloma virus in sinonasal squamous cell carcinoma. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2020, 5, 1070–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristics | HPV+ (n = 31) | HPV− (n = 80) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mean age (yrs) | 59.2 | 61.3 | 0.45 |
| Sex ratio (M/F) | 2.88 | 1.67 | 0.088 |
| Primary site | 0.93 | ||
| Maxillary | 3 (10%) | 10 (12.5%) | 1 |
| Ethmoid | 6 (19%) | 8(10%) | |
| Sphenoid | 1 (3%) | None | |
| Nasal cavity | 21 (68%) | 62 (78%) | |
| Pathological features | |||
| G1-G2:G3-G4 | 23 (74%):8 (26%) | 55 (69%):25 (31%) | 0.65 |
| History of inverted papilloma | 2 (6%) | 1 (1%) | |
| TNM stage | |||
| T1-T2:T3-T4 | 15 (48%):16 (52%) | 53 (66%):27 (34%) | 0.13 |
| N+ | 1 (3%) | 4 (5%) | 1 |
| M+ | None | 2 (2.5%) |
| Site | Cases | p16+ | p16− | HPV+ | HPV− | Discordance Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 56 | 27 | 29 | 24 | 32 | 44.6% |
| B | 55 | 7 | 48 | 7 | 48 | 14.5% |
| Total | 111 | 34 | 77 | 31 | 80 | 29.7% |
| Publication (Year) | Country | Patients (n) | Detection Method | p16+/ HPV+ | p16−/ HPV− | p16+/ HPV− | p16−/ HPV+ | HPV Subtypes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hu et al., 2020 [16] | China (Eastern) | 84 (de novo) 30 (inverted papilloma) | p16 IHC, HPV DNA PCR and genotyping | 2 (2.4%) 1 (3.3%) | 67 (79.8%) 23 (76.7%) | 14 (16.7%) 1 (3.3%) | 1 (1.2%) 5 (16.7%) | 16; 18 |
| Jiromaru et al., 2020 [8] | Japan | 101 | p16 IHC, HPV DNA ISH | 9 (8.9%) | 82 (81.2%) | 6 (5.9%) | 4 (4.0%) | 16; 18 |
| Hirakawa et al., 2023 [17] | Japan | 79 | p16 IHC, HPV DNA PCR and ISH | 10 (12.6%) | 69 (87.3%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 6; 18; 33; and 52 |
| Cohen et al., 2020 [18] | USA/ Florida | 47 | p16 IHC, HPV RNA ISH | 7 (14.9%) | 32 (68.1%) | 4 (8.5%) | 4 (8.5%) | Not specified |
| Larque et al., 2014 [19] | Spain | 70 | p16 IHC, HPV RNA | 14 (20%) | 56 (80%) | 0 | 0 | 16; 33 |
| Tendron et al., 2022 [20] | France | 59 | p16 IHC, HPV RNA ISH (RNAscope) PCR | 9 (15.3%) | 43 (72.9%) (“doubtful positive”: 5) | 2 (3.4%) | Not performed | 16; 18; 33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wenda, N.; Zech, H.B.; Barde, M.; Ramke, L.; Hoffmann, A.S.; Clauditz, T.; Wagner, S.; Gosepath, J.; Betz, C.S. Discordance Between p16-Expression and HPV-Status in Sinonasal Carcinoma: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Cancers 2025, 17, 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193135
Wenda N, Zech HB, Barde M, Ramke L, Hoffmann AS, Clauditz T, Wagner S, Gosepath J, Betz CS. Discordance Between p16-Expression and HPV-Status in Sinonasal Carcinoma: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Cancers. 2025; 17(19):3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193135
Chicago/Turabian StyleWenda, Nina, Henrike Barbara Zech, Marta Barde, Leoni Ramke, Anna Sophie Hoffmann, Till Clauditz, Sebastian Wagner, Jan Gosepath, and Christian Stephan Betz. 2025. "Discordance Between p16-Expression and HPV-Status in Sinonasal Carcinoma: A Multicenter Retrospective Study" Cancers 17, no. 19: 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193135
APA StyleWenda, N., Zech, H. B., Barde, M., Ramke, L., Hoffmann, A. S., Clauditz, T., Wagner, S., Gosepath, J., & Betz, C. S. (2025). Discordance Between p16-Expression and HPV-Status in Sinonasal Carcinoma: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Cancers, 17(19), 3135. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17193135







