Brainstem Glioma Prognostication: Static FET PET/CT
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
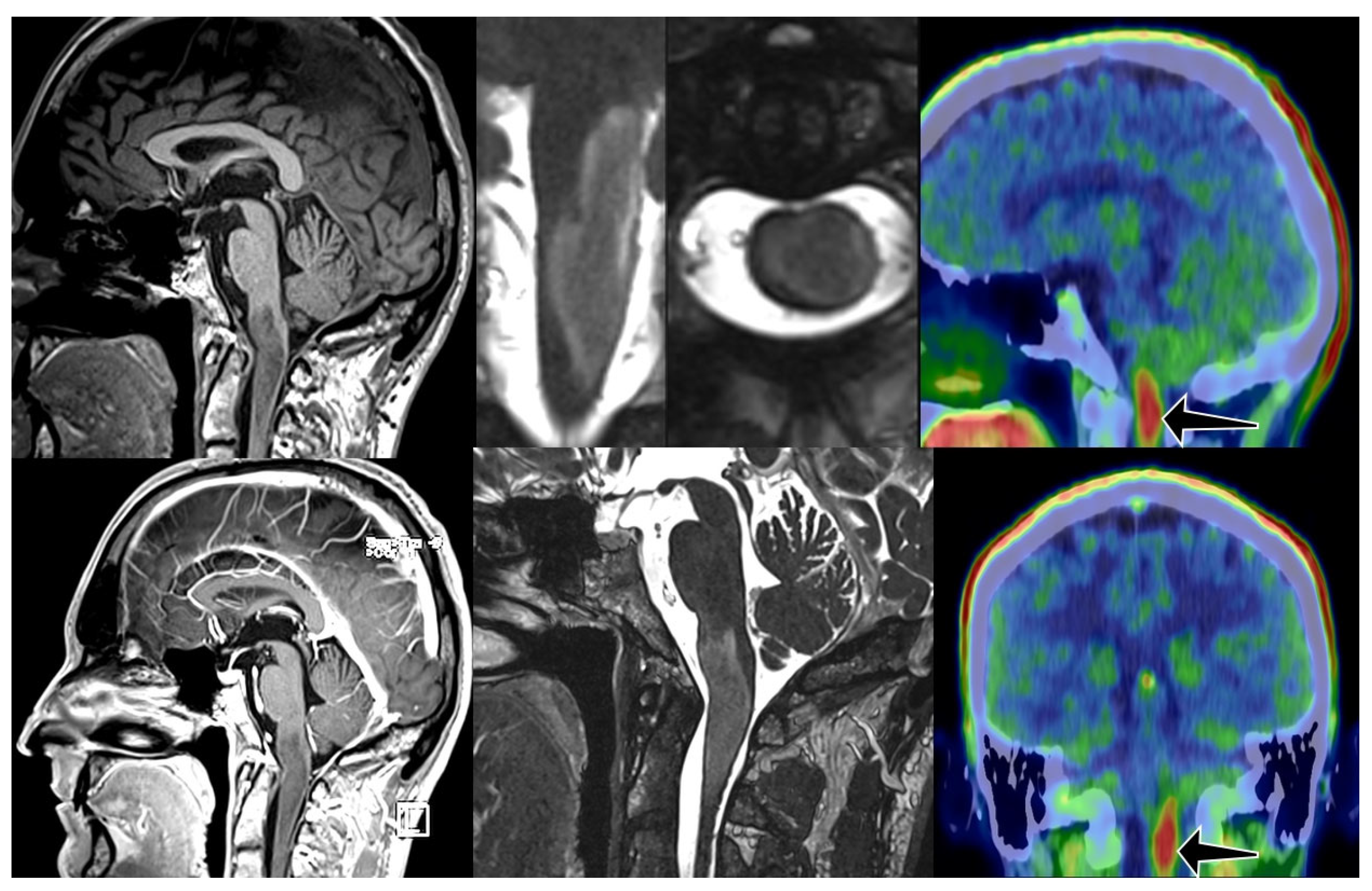
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A1 | astrocytoma grade 1 |
| ADC | apparent diffusion coefficient |
| BBB | blood brain barrier |
| BTV | biological tumor volume |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CT | computer tomography |
| DWI | Diffusion weighted imaging |
| EANO | European Association of Neuro-oncology |
| FDG | fluoro-deoxy-glucose |
| FET O | (2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine |
| FLAIR | fluid attenuated inversion recovery |
| GBM | glioblastoma |
| MET | L-[11C]methyl-methionine |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| MRS | magnetic resonance spectroscopy |
| NCCN | National Comprehensive Cancer Network |
| PET | positron emission tomography |
| PWI | perfusion weighted imaging |
| rCBV | relative cerebral blood volume |
| TBR | tumor brain ratio |
| TOF | time of flight |
| SUV | standardized uptake value |
References
- Reyes-Botero, G.; Mokhtari, K.; Martin-Duverneuil, N.; Delattre, J.-Y.; Laigle-Donadey, F. Adult brainstem gliomas. Oncologist 2012, 17, 388–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Western, S.; Kesari, S. Brainstem Glioma in Adults. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ius, T.; Montemurro, N.; Lombardi, G.; Berardinelli, J.; Romano, A.; Barresi, V.; Cerretti, G.; Guarnera, A.; Tel, A.; Cavallo, L.M.; et al. Decoding the puzzle: A multidisciplinary systematic review of adult brainstem glioma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2024, 196, 104261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisele, S.C.; Reardon, D.A. Adult brainstem gliomas. Cancer 2016, 122, 2799–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillamo, J.S.; Doz, F.; Delattre, J.Y. Brain stem gliomas. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2001, 14, 711–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.; van den Bent, M.; Preusser, M.; Le Rhun, E.; Tonn, J.C.; Minniti, G.; Bendszus, M.; Balana, C.; Chinot, O.; Dirven, L.; et al. EANO guidelines on the diagnosis and treatment of diffuse gliomas of adulthood. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 18, 170–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, A.P.; Sells, B.E.; Haque, S.J.; Chakravarti, A. Tumor Heterogeneity in Glioblastomas: From Light Microscopy to Molecular Pathology. Cancers 2021, 13, 761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, L.M.; DeWire, M.; Ryall, S.; Buczkowicz, P.; Leach, J.; Miles, L.; Ramani, A.; Brudno, M.; Kumar, S.S.; Drissi, R.; et al. Spatial genomic heterogeneity in diffuse intrinsic pontine and midline high-grade glioma: Implications for diagnostic biopsy and targeted therapeutics. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2016, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Broniscer, A.; McEachron, T.A.; Lu, C.; Paugh, B.S.; Becksfort, J.; Qu, C.; Ding, L.; Huether, R.; Parker, M.; et al. Somatic histone H3 alterations in pediatric diffuse intrinsic pontine gliomas and non-brainstem glioblastomas. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 251–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saratsis, A.A.-O.; Knowles, T.; Petrovic, A.; Nazarian, J. H3K27M mutant glioma: Disease definition and biological underpinnings. Neuro-Oncology 2023, 26, S92–S100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwahashi, H.; Nagashima, H.; Tanaka, K.; Uno, T.; Hashiguchi, M.; Maeyama, M.; Somiya, Y.; Komatsu, M.; Hirose, T.; Itoh, T.; et al. 2-Hydroxyglutarate magnetic resonance spectroscopy in adult brainstem glioma. J. Neurosurg. 2023, 139, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indoria, A.; Arora, A.; Garg, A.; Chauhan, R.S.; Chaturvedi, A.; Kumar, M.; Konar, S.; Sadashiva, N.; Rao, S.; Saini, J. Prediction of H3K27M alteration in midline gliomas of the brain using radiomics: A multi-institute study. Neuro-Oncol. Adv. 2024, 6, vdae153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, X.; Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Chen, N.; Sun, H.; Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Wan, X.; Tan, Q.; et al. Multimodal MR imaging signatures to identify brain diffuse midline gliomas with H3 K27M mutation. Cancer Med. 2021, 11, 1048–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Linera, J. Magnetic resonance techniques for the brainstem. Semin. Ultrasound CT MR 2010, 31, 230–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chourmouzi, D.; Papadopoulou, E.; Marias, K.; Drevelegas, A. Imaging of brain tumors. Surg. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 23, 629–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laprie, A.; Pirzkall, A.; Haas-Kogan, D.A.; Cha, S.; Banerjee, A.; Le, T.P.; Lu, Y.; Nelson, S.; McKnight, T.R. Longitudinal multivoxel MR spectroscopy study of pediatric diffuse brainstem gliomas treated with radiotherapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2005, 62, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meric, K.; Killeen, R.P.; Abi-Ghanem, A.S.; Soliman, F.; Novruzov, F.; Cakan, E.; Cayci, Z. The use of 18F-FDG PET ratios in the differential diagnosis of common malignant brain tumors. Clin. Imaging 2015, 39, 970–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccon, G.; Lohmann, P.; Werner, J.M.; Tscherpel, C.; Dunkl, V.; Stoffels, G.; Rosen, J.; Rapp, M.; Sabel, M.; Herrlinger, U.; et al. Early Treatment Response Assessment Using (18)F-FET PET Compared with Contrast-Enhanced MRI in Glioma Patients After Adjuvant Temozolomide Chemotherapy. J. Nucl. Med. 2021, 62, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galldiks, N.; Niyazi, M.; Grosu, A.L.; Kocher, M.; Langen, K.J.; Law, I.; Minniti, G.; Kim, M.M.; Tsien, C.; Dhermain, F.; et al. Contribution of PET imaging to radiotherapy planning and monitoring in glioma patients—A report of the PET/RANO group. Neuro Oncol. 2021, 23, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prather, K.Y.; O’Neal, C.M.; Westrup, A.M.; Tullos, H.J.; Hughes, K.L.; Conner, A.K.; Glenn, C.A.; Battiste, J.D. A systematic review of amino acid PET in assessing treatment response to temozolomide in glioma. Neurooncol. Adv. 2022, 4, vdac008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, D.G.; Fedorcsák, I.; Bagó, A.G.; Gáti, G.; Martos, J.; Szabó, P.; Rajnai, H.; Kenessey, I.; Borbély, K. Therapy Defining at Initial Diagnosis of Primary Brain Tumor-The Role of (18)F-FET PET/CT and MRI. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegmayr, C.; Stoffels, G.; Filß, C.; Heinzel, A.; Lohmann, P.; Willuweit, A.; Ermert, J.; Coenen, H.H.; Mottaghy, F.M.; Galldiks, N.; et al. Current trends in the use of O-(2-[18F] fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine ([18F] FET) in neurooncology. Nucl. Med. Biol. 2021, 92, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galldiks, N.; Stoffels, G.; Filss, C.; Rapp, M.; Blau, T.; Tscherpel, C.; Ceccon, G.; Dunkl, V.; Weinzierl, M.; Stoffel, M.; et al. The use of dynamic O-(2-18F-fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine PET in the diagnosis of patients with progressive and recurrent glioma. Neuro-Oncology 2015, 17, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rapp, M.; Heinzel, A.; Galldiks, N.; Stoffels, G.; Felsberg, J.; Ewelt, C.; Sabel, M.; Steiger, H.J.; Reifenberger, G.; Beez, T.; et al. Diagnostic performance of 18F-FET PET in newly diagnosed cerebral lesions suggestive of glioma. J. Nucl. Med. 2013, 54, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo Greco, M.C.; Milazzotto, R.; Liardo, R.L.; Acquaviva, G.; La Rocca, M.; Altieri, R.; Certo, F.; Barbagallo, G.M.; Basile, A.; Foti, P.V.; et al. Relapsing High—Grade Glioma from Peritumoral Zone: Critical Review of Radiotherapy Treatment Options. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dellaretti, M.; Touzet, G.; Reyns, N.; Dubois, F.; Gusmão, S.; Pereira, J.L.B.; Blond, S. Correlation among magnetic resonance imaging findings, prognostic factors for survival, and histological diagnosis of intrinsic brainstem lesions in children. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2011, 8, 539–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesari, S.; Kim, R.S.; Markos, V.; Drappatz, J.; Wen, P.Y.; Pruitt, A.A. Prognostic factors in adult brainstem gliomas: A multicenter, retrospective analysis of 101 cases. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2008, 88, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargrave, D.; Chuang, N.; Bouffet, E. Conventional MRI cannot predict survival in childhood diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2008, 86, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albatly, A.A.; Alsamarah, A.T.; Alhawas, A.; Veit-Haibach, P.; Buck, A.; Stolzmann, P.; Burger, I.A.; Kollias, S.S.; Huellner, M.W. Value of (18)F-FET PET in adult brainstem glioma. Clin. Imaging 2018, 51, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tscherpel, C.; Dunkl, V.; Ceccon, G.; Stoffels, G.; Judov, N.; Rapp, M.; Meyer, P.T.; Kops, E.R.; Ermert, J.; Fink, G.R.; et al. The use of O-(2-18F-fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET in the diagnosis of gliomas located in the brainstem and spinal cord. Neuro-Oncology 2016, 19, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kickingereder, P.; Willeit, P.; Simon, T.; Ruge, M.I. Diagnostic value and safety of stereotactic biopsy for brainstem tumors: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 1480 cases. Neurosurgery 2013, 72, 873–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faulkner, H.; Arnaout, O.; Hoshide, R.; Young, I.M.; Yeung, J.T.; Sughrue, M.E.; Teo, C. The Surgical Resection of Brainstem Glioma: Outcomes and Prognostic Factors. World Neurosurg. 2021, 146, e639–e650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mursch, K.; Halatsch, M.E.; Markakis, E.; Behnke-Mursch, J. Intrinsic brainstem tumours in adults: Results of microneurosurgical treatment of 16 consecutive patients. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2005, 19, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ius, T.; Lombardi, G.; Baiano, C.; Berardinelli, J.; Romano, A.; Montemurro, N.; Cavallo, L.M.; Pasqualetti, F.; Feletti, A. Surgical Management of Adult Brainstem Gliomas: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 9772–9785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Botero, G.; Laigle-Donadey, F.; Mokhtari, K.; Martin-Duverneuil, N.; Delattre, J.Y. Temozolomide after radiotherapy in recurrent “low grade” diffuse brainstem glioma in adults. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2014, 120, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Feng, S.; Li, J.; Cao, H.; Huang, J.; Fan, F.; Cheng, L.; Liu, Z.; Cheng, Q. The Survival Benefits of Surgical Resection and Adjuvant Therapy for Patients With Brainstem Glioma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 566972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Carlo, D.; Annereau, M.; Vignes, M.; Denis, L.; Epaillard, N.; Dumont, S.; Guyon, D.; Rieutord, A.; Jacobs, S.; Salomon, V.; et al. Real life data of ONC201 (dordaviprone) in pediatric and adult H3K27-altered recurrent diffuse midline glioma: Results of an international academia-driven compassionate use program. Eur. J. Cancer 2025, 216, 115165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venneti, S.; Kawakibi, A.R.; Ji, S.; Waszak, S.M.; Sweha, S.R.; Mota, M.; Pun, M.; Deogharkar, A.; Chung, C.; Tarapore, R.S.; et al. Clinical Efficacy of ONC201 in H3K27M-Mutant Diffuse Midline Gliomas Is Driven by Disruption of Integrated Metabolic and Epigenetic Pathways. Cancer Discov. 2023, 13, 2370–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauleit, D.; Floeth, F.; Hamacher, K.; Riemenschneider, M.J.; Reifenberger, G.; Müller, H.-W.; Zilles, K.; Coenen, H.H.; Langen, K.J. O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET combined with MRI improves the diagnostic assessment of cerebral gliomas. Brain 2005, 128, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langen, K.J.; Bartenstein, P.; Boecker, H.; Brust, P.; Coenen, H.H.; Drzezga, A.; Grünwald, F.; Krause, B.J.; Kuwert, T.; Sabri, O.; et al. [German guidelines for brain tumour imaging by PET and SPECT using labelled amino acids]. Nuklearmedizin 2011, 50, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Weckesser, M.; Langen, K.J.; Rickert, C.H.; Kloska, S.; Straeter, R.; Hamacher, K.; Kurlemann, G.; Wassmann, H.; Coenen, H.H.; Schober, O. O-(2-[18F]fluorethyl)-L-tyrosine PET in the clinical evaluation of primary brain tumours. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2005, 32, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Category | N | Mean | S.D. | Min | Median | Max |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Death cases | 8 | 2.30 | 1.00 | 1.2 | 2.14 | 3.9 |
| Survival cases | 12 | 2.07 | 0.82 | 1.1 | 2.10 | 3.9 |
| Overall | 20 | 2.16 | 0.88 | 1.1 | 2.10 | 3.9 |
| 95% CI | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Statistic | n/N | Estimate (%) | S.E. (%) | Lower Limit (%) | Upper Limit (%) |
| Sensitivity | 11/12 | 91.7 | 8.0 | 76.0 | 100.0 |
| Specificity | 3/8 | 37.5 | 17.1 | 4.0 | 71.0 |
| Positive Predictive Value | 11/16 | 68.8 | 11.6 | 46.0 | 91.5 |
| Negative Predictive Value | 3/4 | 75.0 | 21.7 | 32.6 | 100.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nagy, D.G.; Singer, J.; Borbély, K. Brainstem Glioma Prognostication: Static FET PET/CT. Cancers 2025, 17, 3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17183065
Nagy DG, Singer J, Borbély K. Brainstem Glioma Prognostication: Static FET PET/CT. Cancers. 2025; 17(18):3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17183065
Chicago/Turabian StyleNagy, Dávid Gergő, Júlia Singer, and Katalin Borbély. 2025. "Brainstem Glioma Prognostication: Static FET PET/CT" Cancers 17, no. 18: 3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17183065
APA StyleNagy, D. G., Singer, J., & Borbély, K. (2025). Brainstem Glioma Prognostication: Static FET PET/CT. Cancers, 17(18), 3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17183065





