The Cost of Breast Cancer: Economic and Social Perspective
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
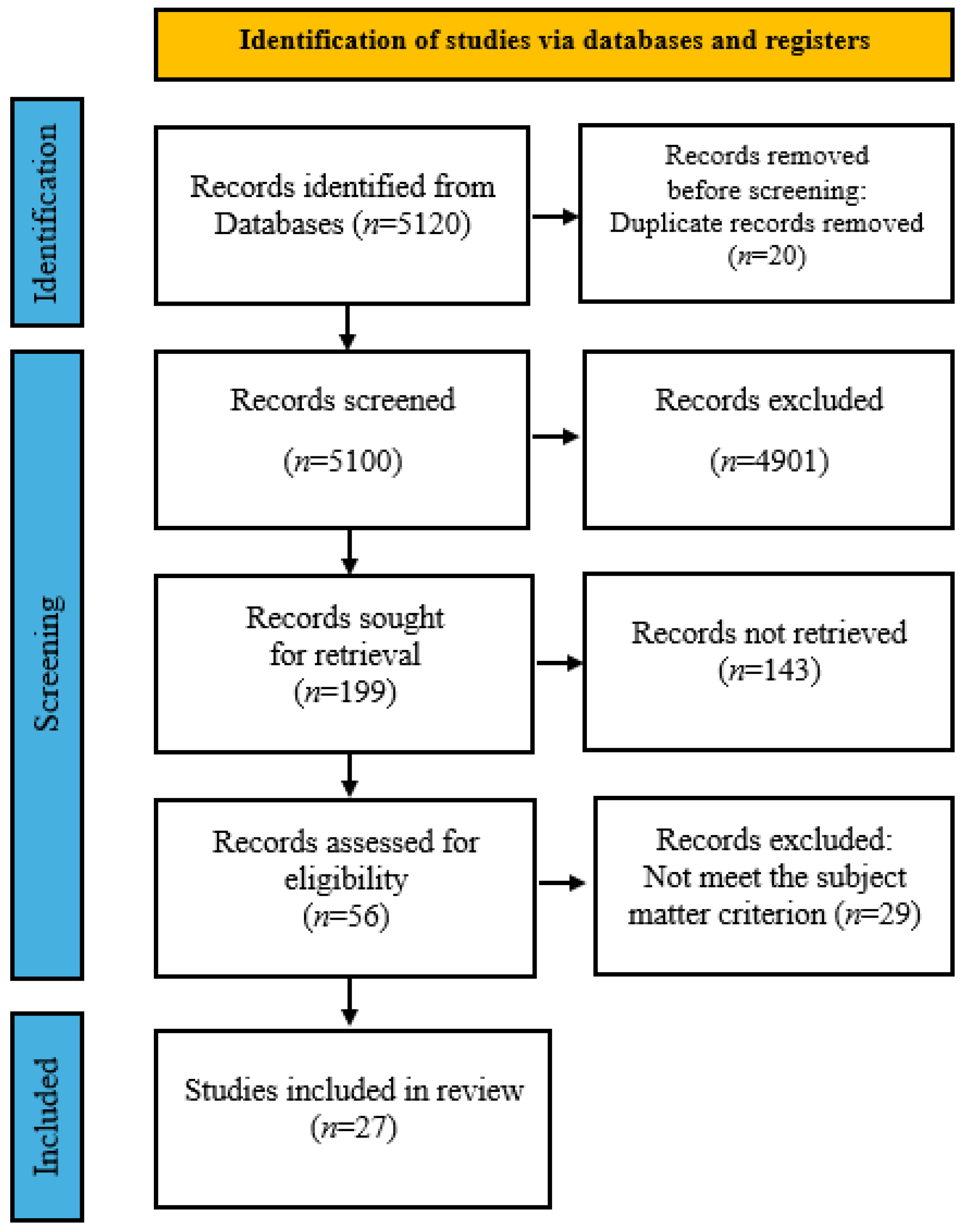
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
| Author/Year | Country | Unit of Measure | Methodology | Type of Costs | Group of Patients |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yaghoubi, N. et al., 2025 [14] | Iran | ICER, QALY | Cost-effectiveness analysis | Direct costs | Patients with metastatic breast cancer |
| Paulissen, J. et al., 2024 [15] | Finland | ICER, QALY | Assessment of the cost of the disease | Direct costs | Patients with HER2-positive (HER2+) unresectable and/or metastatic breast cancer |
| Heng, J. et al., 2024 [16] | Malaysia | USD | Cost-effectiveness analysis | Direct costs | Patients with breast cancer |
| Khoirunnisa, S.M. et al., 2024 [17] | Indonesia | USD | Cost-effectiveness analysis | Direct costs | Patients with HER2-positive (HER2+) breast cancer |
| Seyedifar, M. et al., 2024 [18] | IRAN | ICER, QALY | Cost-effectiveness analysis | Direct costs | Patients with HER2-positive (HER2+) breast cancer |
| Jia, C. et al., 2025 [19] | China | ICER, QALY | Cost-effectiveness analysis | Direct costs | Patients with Hormone receptor HR-positive/HER2-negative (HR+/HER2−) breast cancer |
| Nguyen, T.T.H et al., 2025 [20] | United States | ICER, QALY | Cost-effectiveness analysis | Direct costs | Patients with HER2-positive (HER2+) breast cancer |
| Chang, S. et al., 2024 [21] | United States | ICER, QALY | Cost-effectiveness analysis | Direct costs | Patients with Hormone receptor HR-positive/HER2-negative (HR+/HER2−) breast cancer |
| Sra, M. et al., 2024 [22] | India | ICER, QALY | Cost-effectiveness analysis | Direct costs | Patients with Hormone receptor HR-positive/HER2-negative (HR+/HER2−) breast cancer |
| Pan, J. et al., 2024 [23] | United States, China | ICER, QALY | Assessment of the cost of the disease | Direct costs | Patients with HER2-negative (HER2−) breast cancer |
| Xu, C. et al., 2025 [24] | United States, China | QALY | Cost-effectiveness analysis | Direct costs | Patients with HER2-negative (HER2−) breast cancer |
| Wang, L. et al., 2024 [25] | China | ICER, QALY | Cost-effectiveness analysis | Direct costs | Patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer |
| Cai, H. et al., 2024 [26] | China | ICER, QALY | Cost-effectiveness analysis | Direct costs | Patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer |
| Chen, P. et al., 2025 [27] | United States | ICER, QALY | Cost-effectiveness analysis | Direct costs | Patients with metastatic triple-negative breast cancer |
| Tseng, T. et al., 2024 [28] | Taiwan | ICER, QALY | Cost-effectiveness analysis | Direct costs | Patients with breast cancer |
| Mok, C. et al., 2025 [29] | Singapore | ICER, QALY | Cost-effectiveness analysis | Direct costs | Patients with metastatic breast cancer |
| Kim, Y. et al., 2024 [30] | United States | USD | Assessment of the cost of the disease | Direct costs | Patients with breast cancer who underwent breast-conserving surgery |
| Reddy, K. et al., 2025 [31] | United States | USD | Assessment of the cost of the disease | Direct costs | Patients with breast cancer |
| Teli, B. et al., 2025 [32] | Iran | USD | Assessment of the cost of the disease | Direct and indirect costs | Patients with breast cancer |
| Irandoust, K. et al., 2025 [33] | Iran | USD | Assessment of the cost of the disease | Direct costs | Patients with breast cancer |
| Hamza, D. et al., 2024 [34] | United Arab Emirates | USD | Assessment of the cost of the disease | Direct costs | Patients with breast cancer |
| Mittmann, N. et al., 2024 [35] | Canada | USD | Assessment of the cost of the disease | Direct costs | Patients with breast cancer |
| Malhan, S. et al., 2024 [36] | Turkey | USD | Assessment of the cost of the disease | Direct and indirect costs | Patients with breast cancer |
| Gunasekara, A. et al., 2024 [37] | Sri Lanka | ICER | Cost-effectiveness analysis | Direct costs | Patients with HER2-positive (HER2+) breast cancer |
| Fenix-Caballero, S. et al., 2025 [38] | Spain | USD, QALY | Cost-effectiveness analysis | Direct costs | Patients with HER2-positive (HER2+) breast cancer |
| Crafoord, M. et al., 2025 [39] | Sweden | ICER, QALY | Cost-effectiveness analysis | Direct costs | Patients with breast cancer undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy |
| Franklin, M. et al., 2024 [40] | United States | USD | Assessment of the cost of the disease | Indirect costs | Patients with breast cancer |
3.1. Direct Costs
3.1.1. Treatment of Breast Cancer
3.1.2. Adjuvant and Neoadjuvant Treatment
3.1.3. Supportive Care
3.2. Indirect Costs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. International Agency for Research on Cancer. Available online: https://gco.iarc.who.int/media/globocan/factsheets/cancers/20-breast-fact-sheet.pdf (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- WHO. Cancer Tomorrow. Available online: https://gco.iarc.fr/tomorrow/en/dataviz/tables?years=2030&cancers=20 (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/breast-cancer/risk-factors/index.html (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- National Cancer Institute. Breast Cancer Treatment (PDQ®)—Health Professional Version. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/types/breast/hp/breast-treatment-pdq (accessed on 10 July 2025).
- Loibl, S.; André, F.; Bachelot, T.; Barrios, C.; Bergh, J.; Burstein, H.; Cardoso, M.; Carey, L.; Dawood, S.; Del Mastro, L.; et al. Early breast cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2024, 35, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology (NCCN Guidelines®). Breast Cancer Version 4.2025. Available online: https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-detail?category=1&id=1419 (accessed on 17 April 2025).
- Seweryn, M.; Banaś, T.; Streb, J.; Matkowski, R.; Wysocki, W.; Augustyńska, J.; Kopel, J.; Kizińska, O. Discrepancies in breast cancer management. J. Health Inequalities 2021, 7, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semin, J.N.; Palm, D.; Smith, L.M.; Ruttle, S. Understanding breast cancer survivors’ financial burden and distress after financial assistance. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 4241–4248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudali, K.; Sagan, K.; Kwiatkowska, E.; Kosendiak, A. The impact of the early period of the COVID-19 pandemic on screening programmes of breast, colorectal and cervical cancer. J. Health Inequalities 2023, 9, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akobundu, E.; Ju, J.; Blatt, L.; Mullins, C.D. Cost-of-Illness Studies. PharmacoEconomics 2006, 24, 869–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.; Pauker, S.G. The Markov Process in Medical Prognosis. Med. Decis. Mak. 1983, 3, 419–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, B.S.; Sideris, E.; Palmer, S.; Latimer, N.; Soares, M. Partitioned Survival and State Transition Models for Healthcare Decision Making in Oncology: Where Are We Now? Value Health 2020, 23, 1613–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Treasury. UN Operational Rates of Exchange. Available online: https://treasury.un.org/operationalrates/OperationalRates.php (accessed on 12 July 2025).
- Yaghoubi, N.; Fatemi, B.; Ahmadi, R.; Metghalchi, Y.; Shahrami, B.; Vaezi, M.; Rezaei, S. Trastuzumab deruxtecan versus trastuzumab emtansine for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 positive metastatic breast cancer: Cost-effectiveness analysis from Iranian experience. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2025, 25, 711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paulissen, J.H.J.; Seddik, A.H.; Dunton, K.J.; Livings, C.J.; van Hulst, M.; Postma, M.J.; de Jong, L.A.; Freriks, R.D. Cost-effectiveness model of trastuzumab deruxtecan as second-line treatment in HER2-positive unresectable and/or metastatic breast cancer in Finland. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2023, 25, 689–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, J.E.; Raman, S.; Wong, Z.Y.; Nin Beh, V.J. Cost minimization analysis of subcutaneous trastuzumab versus intravenous biosimilar trastuzumab: Policy recommendations for breast cancer treatment in Malaysia. DARU J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 32, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoirunnisa, S.M.; Suryanegara, F.D.A.; Setiawan, D.; Postma, M.J.; de Jong, L.A.; Omar, N.E.E.A. Economic evaluation of trastuzumab in HER2-positive early breast cancer in Indonesia: A cost-effectiveness analysis. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0304483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemati, H.; Nosrati, M.; Seyedifar, M. Cost-Utility Analysis of Trastuzumab-Emtansine Versus Trastuzumab for the Treatment of Residual Invasive HER-2-Positive Breast Cancer in Iran. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2024, 23, e153452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Feng, B.; Shi, F.; Wang, M.; Li, S.; Xu, H.; Wang, M. Cost-effectiveness of CDK4/6 inhibitors for second-line HR+/HER2− advanced or metastatic breast cancer in China. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 12765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.T.H.; Mital, S. Cost-Effectiveness of Capivasertib as a Second-Line Therapy for Advanced Breast Cancer. PharmacoEconomics 2024, 43, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.-H.; Svensson, M.; Wang, G.H.-M.; Wang, Y.; Kang, H.-R.; Park, H. Cost-effectiveness of early vs delayed use of abemaciclib combination therapy for patients with high-risk hormone receptor–positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2–negative early breast cancer. J. Manag. Care Spéc. Pharm. 2024, 30, 942–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sra, M.S.; Sasi, A.; Batra, A.; Bakhshi, S.; Ganguly, S. Cost-Effectiveness of Adjuvant Abemaciclib and Ribociclib in High-Risk Hormone Receptor–Positive Early Breast Cancer: An Indian Perspective. JCO Glob. Oncol. 2024, 10, e2300433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Ren, N.; Ren, L.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Q. Cost-effectiveness of talazoparib for patients with germline BRCA1/2 mutated HER2-negative advanced breast cancer in China and the US. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 13935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhuang, J.; Shen, J.; Sun, H.; Cai, J.; Wei, X. Cost-utility analysis of olaparib assisted targeted therapy for BRCA mutation HER2-negative early breast cancer in China and in the United States. Cost Eff. Resour. Alloc. 2025, 23, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, F.; Ruan, Y.; He, Y.; Huang, J.; Zheng, X. Cost-effectiveness of Sacituzumab Govitecan versus Single-agent Chemotherapy for Patients with Metastatic Triple-Negative Breast Cancer in China. Clin. Breast Cancer 2024, 24, e545–e553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Huang, L.; Zheng, Z. Toripalimab plus chemotherapy in the treatment of metastatic triple-negative breast cancer: A cost-effectiveness analysis. Front. Public Health 2024, 12, 1421826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Qiao, D.; Xiao, L.; Deng, G.; Yang, Q.; Tian, R.; Wang, R. Cost-effectiveness analysis of toripalimab combined with nab-paclitaxel as a first-line treatment for advanced TNBC in the US. PLoS ONE 2025, 20, e0320727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, T.-H.; Chiang, S.-C.; Hsu, J.C.; Ko, Y. Cost-effectiveness analysis of granulocyte colony-stimulating factors for the prophylaxis of chemotherapy-induced febrile neutropenia in patients with breast cancer in Taiwan. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0303294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, C.W. Cost-effectiveness of robotic mastectomy vs. conventional mastectomy: A long-term economic evaluation from a Singapore healthcare perspective. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2025, 51, 109608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.; Ganduglia-Cazaban, C.; Tamirisa, N.; Lucci, A.; Krause, T.M. Contemporary Analysis of Reexcision and Conversion to Mastectomy Rates and Associated Healthcare Costs for Women Undergoing Breast-Conserving Surgery. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2024, 31, 3649–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.P.; Jarrell, K.; Berkowitz, C.; Hulse, S.; Elmore, L.C.; Fishman, R.; Greenup, R.A.; Mateo, A.M.; Rothman, J.D.; Sataloff, D.M.; et al. Association Between Delayed/Forgone Medical Care and Resource Utilization Among Women with Breast Cancer in the United States. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2025, 32, 2534–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teli, B.D.; Behzadifar, M.; Beiranvand, M.; Rezapour, A.; Ehsanzadeh, S.J.; Azari, S.; Bakhtiari, A.; Haghighatfard, P.; Martini, M.; Saran, M.; et al. The economic burden of breast cancer in western Iran: A cross-sectional cost-of-illness study. J. Health Popul. Nutr. 2025, 44, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irandoust, K.; Alipour, V.; Arabloo, J.; Nahvijou, A.; Akbari, A. Economic burden of five common cancers in Iran: A systematic review of cost-of-illness with a focus on healthcare resource utilization. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2025, 25, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamza, D.; Zayed, M.; Tahoun, N.; Farghaly, M.; Kumaresan, S.; Ramachandrachar, B.; Ali, A. A retrospective cohort study to evaluate disease burden, health care resource utilization, and costs in patients with breast cancer in Dubai, UAE. BMC Health Serv. Res. 2024, 24, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittmann, N.; Seung, S.J.; Ante, Z.; Liu, N.; Yong, J.H.E.; Yusuf, A.; Chiarelli, A.M.; Earle, C.C. Updated breast cancer costs for women by disease stage and phase of care using population-based databases. Health Rep. 2024, 35, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhan, S.; Akinci, M.B.; Akyürek, N.; Bilici, A.; Demirci, U.; Geredeli, Ç.; Karabulut, B.; Karadurmuş, N.; Özsüzoğlu, B.; Şendur, M.A.; et al. A Cost-of-illness Study on The Economic Burden of Breast Cancer in Türkiye: A Delphi Panel-based Analysis of Direct and Indirect Costs. Turk. J. Oncol. 2024, 39, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunasekara, A.D.M.; Youngkong, S.; Anothaisintawee, T.; Dejthevaporn, T.; Fernandopulle, R.; Chaikledkaew, U. Cost-utility and budget impact analysis of neoadjuvant dual HER2 targeted therapy for HER2-positive breast cancer in Sri Lanka. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 16736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenix-Caballero, S.; Sanchez-Vegas, A.; Del-Rey, E.J.A.; Epstein, D.; Garcia-Mochon, L.; Lima, A.O.d.L. Economic assessment of abemaciclib for the adjuvant treatment of luminal HER2- breast cancer from the perspective of the Spanish health system. Eur. J. Health Econ. 2025, 26, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crafoord, M.-T.; Ekstrand, J.; Sundberg, K.; Nilsson, M.I.; Fjell, M.; Langius-Eklöf, A. Mobile Electronic Patient-Reported Outcomes and Interactive Support During Breast and Prostate Cancer Treatment: Health Economic Evaluation from Two Randomized Controlled Trials. JMIR Cancer 2025, 11, e53539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, M.; Pollard, D.; Sah, J.; Rayner, A.; Sun, Y.; Dube, F.; Sutton, A.; Qin, L. Direct and Indirect Costs of Breast Cancer and Associated Implications: A Systematic Review. Adv. Ther. 2024, 41, 2700–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neto, F.L.; de Melo, M.A.Z.; Filho, C.M.T.H.; Mathias-Machado, M.C.; Testa, L.; Campolina, A.G. Global representativeness and impact of funding sources in cost-effectiveness research on systemic therapies for advanced breast cancer: A systematic review. Breast 2024, 75, 103727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Health Expenditure Database. Available online: https://apps.who.int/nha/database (accessed on 14 July 2025).
- Rose, L.; Rajasekar, G.; Nambiar, A.; Pohl, A.; Ruddy, K.J.; Arnow, K.; Patel, M.; Morris, A.M. Estimated Out-of-Pocket Costs for Patients with Common Cancers and Private Insurance. JAMA Netw. Open 2025, 8, e2521575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breastcancer.org. Special Report: The Cost of Breast Cancer Care. Available online: https://www.breastcancer.org/managing-life/covering-cost-of-care/cost-of-care-report (accessed on 30 May 2025).
| Population (P) | Patients diagnosed with breast cancer |
| Intervention (I) | Economic factors, including costs and economic impact |
| Comparator (C) | Any comparator or no comparator |
| Outcomes (O) | Direct costs of breast cancer treatment, indirect costs, and the overall economic burden of breast cancer |
| Studies (S) | Case studies, prospective studies, retrospective studies, systematic review, and randomized controlled trials (RCTs) |
| Limitations | Publications in English that assess the impact of breast cancer on quality of life, with a publication date range from January 1, 2024, to May 30, 2025 |
| Exclusion | Non-English publications and studies not directly related to breast cancer |
| Publication Number * | Diagnosis | Stage | Mechanism of Action | Treatment | Cost-Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [14] | (HER2)-positive metastatic breast cancer | Second line treatment | Antibody that inhibits the growth of cancer cells by interfering with the HER2 receptor | Trastuzumab deruxtecan | + |
| [15] | (HER2)-positive unspecified or metastatic breast cancer | Second line treatment | Antibody that inhibits the growth of cancer cells by interfering with the HER2 receptor | Trastuzumab deruxtecan | + |
| [16] | (HER2)-positive breast cancer | All HER2+ breast cancer patients | Antibody that inhibits the growth of cancer cells by interfering with the HER2 receptor | biosimilar intravenous Trastuzumab | + |
| [17] | HER2-positive early breast cancer | Early | Antibody that inhibits the growth of cancer cells by interfering with the HER2 receptor | Trastuzumab + chemotherapy | + |
| [18] | (HER2)-positive breast cancer | Residual | Antibody that inhibits the growth of cancer cells by interfering with the HER2 receptor | Trastuzumab-emtansine | +/− |
| [19] | HR+/HER2- breast cancer | Advanced or metastatic | Inhibiting the phosphorylation of tumor suppressor retinoblastoma protein by preventing CDK4/6 from binding to cyclin D | CDK4/6 inhibitors | + |
| [20] | HR+/HER2- breast cancer | Advanced | Inhibiting AKT (protein kinase B) isoforms | Capivasertib + Fulvestrant | − |
| [21] | HR+/HER2- breast cancer | Early | Inhibiting the phosphorylation of tumor suppressor retinoblastoma protein by preventing CDK4/6 from binding to cyclin D | abemaciclib | + |
| [22] | HR+/HER2- breast cancer | Early | Inhibiting the phosphorylation of tumor suppressor retinoblastoma protein by preventing CDK4/6 from binding to cyclin D | Abemaciclib, Ribociclib | − |
| [23] | Germline BRCA1/2 mutated HER2− | Advanced | Inhibiting adenosine diphosphate ribose polymerase | Talazoparib | + |
| [24] | HR+/HER2− breast cancer | Early | Inhibiting adenosine diphosphate ribose polymerase | Olaparib | − |
| [25] | Triple-negative breast cancer | 3 health states | Antibodies targeting trophoblast cell-surface antigen 2 | Sacituzumab govitecan | − |
| [26] | Triple-negative breast cancer | Second line treatment | Immune checkpoint inhibitor regulating immune responses | Toripalimab + chemotherapy | + |
| [27] | Triple-negative breast cancer | 3 health states | Immune checkpoint inhibitor regulating immune responses | Toripalimab + chemotherapy | − |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gąska, I.; Czerw, A.; Pajewska, M.; Partyka, O.; Deptała, A.; Badowska-Kozakiewicz, A.; Budzik, M.; Sygit, K.; Wojtyła-Buciora, P.; Drobnik, J.; et al. The Cost of Breast Cancer: Economic and Social Perspective. Cancers 2025, 17, 3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17183012
Gąska I, Czerw A, Pajewska M, Partyka O, Deptała A, Badowska-Kozakiewicz A, Budzik M, Sygit K, Wojtyła-Buciora P, Drobnik J, et al. The Cost of Breast Cancer: Economic and Social Perspective. Cancers. 2025; 17(18):3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17183012
Chicago/Turabian StyleGąska, Izabela, Aleksandra Czerw, Monika Pajewska, Olga Partyka, Andrzej Deptała, Anna Badowska-Kozakiewicz, Michał Budzik, Katarzyna Sygit, Paulina Wojtyła-Buciora, Jarosław Drobnik, and et al. 2025. "The Cost of Breast Cancer: Economic and Social Perspective" Cancers 17, no. 18: 3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17183012
APA StyleGąska, I., Czerw, A., Pajewska, M., Partyka, O., Deptała, A., Badowska-Kozakiewicz, A., Budzik, M., Sygit, K., Wojtyła-Buciora, P., Drobnik, J., Pobrotyn, P., Waśko-Czopnik, D., Pobrotyn, J., Bandurska, E., Ciećko, W., Grochans, E., Cybulska, A. M., Schneider-Matyka, D., Rachubińska, K., ... Kozlowski, R. (2025). The Cost of Breast Cancer: Economic and Social Perspective. Cancers, 17(18), 3012. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17183012









