Transcriptional Analysis of Effusion-Based Lymphoma Supports a Post-Germinal Center Origin and Specific Inflammatory Signal Background
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Samples
2.2. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
2.3. Expression Datasets and Cancer Subtypes
2.4. Immune Set Enrichment Analysis
3. Results
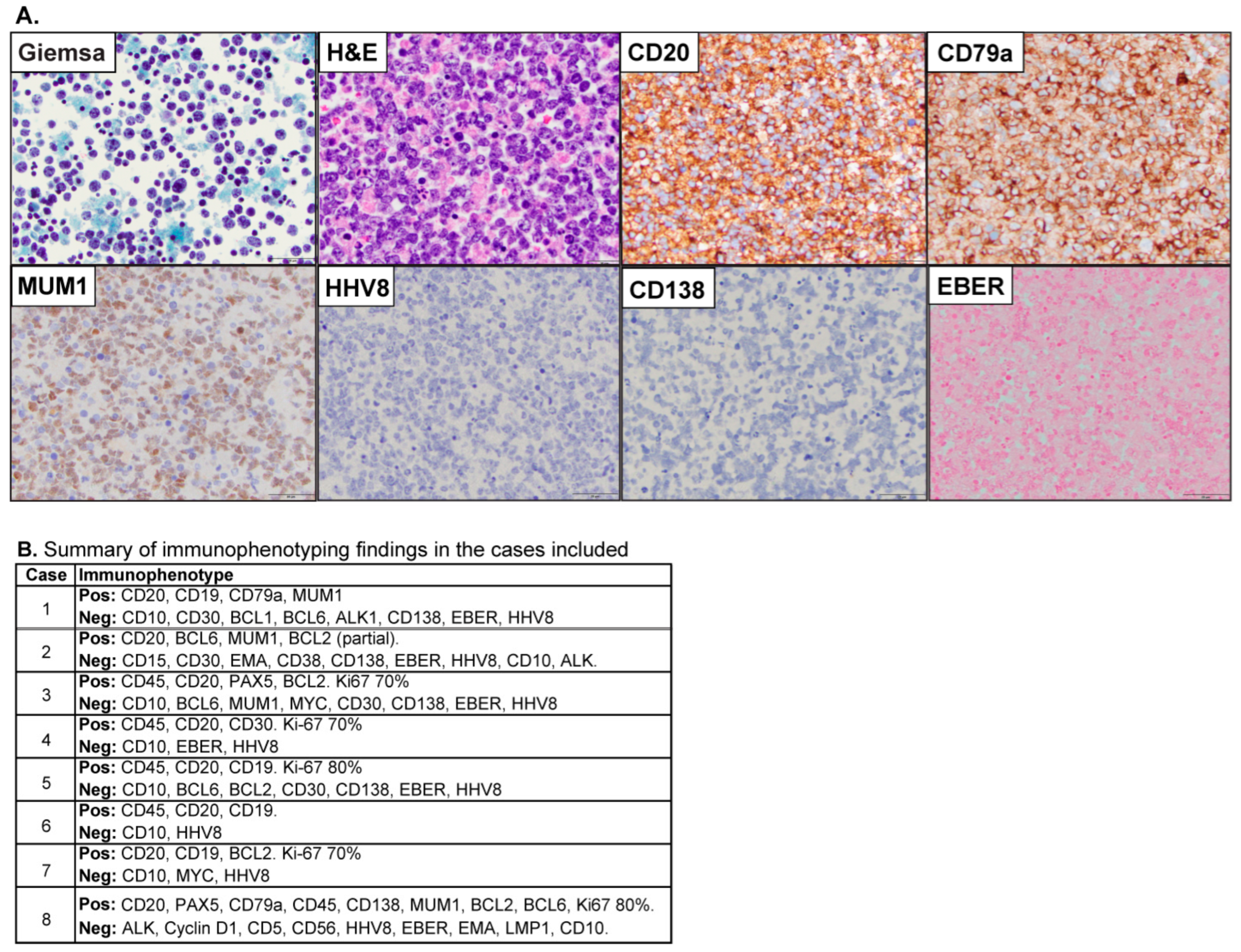
3.1. Patient Characteristics
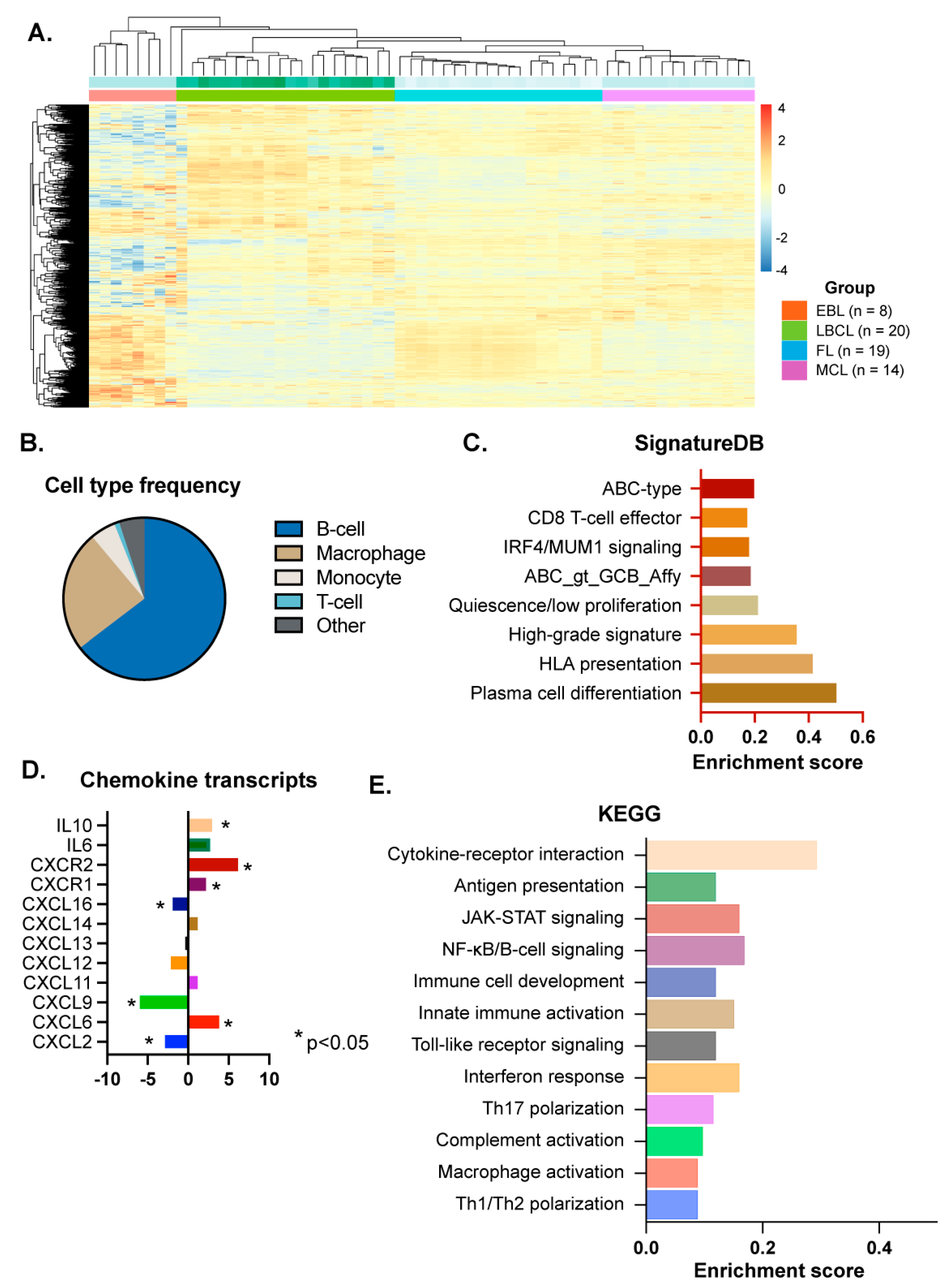
3.2. B-Cell Lymphoma-Specific Gene Expression Profiling
3.3. Inflammation-Related Signaling Pathway Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gisriel, S.D.; Yuan, J.; Braunberger, R.C.; Maracaja, D.L.; Chen, X.; Wu, X.; McCracken, J.; Chen, M.; Xie, Y.; Brown, L.E.; et al. Human herpesvirus 8-negative effusion-based large B-cell lymphoma: A distinct entity with unique clinicopathologic characteristics. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 35, 1411–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usmani, A.; Walts, A.E.; Patel, S.; Alkan, S.; Kitahara, S. HHV8-negative effusion based lymphoma: A series of 17 cases at a single institution. J. Am. Soc. Cytopathol. 2015, 4, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.W.; Wright, G.W.; Williams, P.M.; Lih, C.-J.; Walsh, W.; Jaffe, E.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Campo, E.; Chan, W.C.; Connors, J.M.; et al. Determining cell-of-origin subtypes of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using gene expression in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Blood 2014, 123, 1214–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Kamitsuji, Y.; Kuroda, J.; Tsunoda, S.; Uoshima, N.; Kimura, S.; Wada, K.; Matsumoto, Y.; Nomura, K.; Horiike, S.; et al. Comparison of Human Herpes Virus 8 Related Primary Effusion Lymphoma with Human Herpes Virus 8 Unrelated Primary Effusion Lymphoma-Like Lymphoma on the Basis of HIV: Report of 2 Cases and Review of 212 Cases in the Literature. Acta Haematol. 2006, 117, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaji, D.; Ota, Y.; Sato, Y.; Nagafuji, K.; Ueda, Y.; Okamoto, M.; Terasaki, Y.; Tsuyama, N.; Matsue, K.; Kinoshita, T.; et al. Primary human herpesvirus 8–negative effusion-based lymphoma: A large B-cell lymphoma with favorable prognosis. Blood Adv. 2020, 4, 4442–4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Shiozawa, E.; Takimoto, M.; Hishima, T.; Chong, J.-M. Age and CD20 Expression Are Significant Prognostic Factors in Human Herpes Virus-8-negative Effusion-based Lymphoma. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 1607–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Youm, W.; Rezk, S.A.; Zhao, X. Human Herpesvirus 8–Unrelated Primary Effusion Lymphoma–Like Lymphoma. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2013, 140, 258–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexanian, S.; Said, J.; Lones, M.; Pullarkat, S.T. KSHV/HHV8-negative Effusion-based Lymphoma, a Distinct Entity Associated With Fluid Overload States. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2013, 37, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendeville, M.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Hout, M.F.C.M.v.D.; Vries, G.T.L.-D.; Bladergroen, R.; Stathi, P.; Hijmering, N.J.; Rosenwald, A.; Ylstra, B.; de Jong, D. Aggressive genomic features in clinically indolent primary HHV8-negative effusion-based lymphoma. Blood 2019, 133, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troppan, K.; Wenzl, K.; Neumeister, P.; Deutsch, A. Molecular Pathogenesis of MALT Lymphoma. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2015, 2015, 102656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bende, R.J.; van Maldegem, F.; van Noesel, C.J. Chronic inflammatory disease, lymphoid tissue neogenesis and extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphomas. Haematologica 2009, 94, 1109–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Euler, N.; Hellbacher, E.; Klint, E.A.; Hansson, M.; Larsson, A.; Enblad, G.; Malmström, V.; Baecklund, E.; Grönwall, C. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma in rheumatoid arthritis patients is associated with elevated B-cell driving factors including CXCL13. Clin. Immunol. 2025, 275, 110476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baecklund, E.; Backlin, C.; Iliadou, A.; Granath, F.; Ekbom, A.; Amini, R.; Feltelius, N.; Enblad, G.; Sundström, C.; Klareskog, L.; et al. Characteristics of diffuse large B cell lymphomas in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 3774–3781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baecklund, E.; Iliadou, A.; Askling, J.; Ekbom, A.; Backlin, C.; Granath, F.; Catrina, A.I.; Rosenquist, R.; Feltelius, N.; Sundström, C.; et al. Association of chronic inflammation, not its treatment, with increased lymphoma risk in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006, 54, 692–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, C.; Gu, J.; Huang, X.; You, L.; Zhou, Z.; Jin, J. Cytokine profiles in patients with newly diagnosed diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: IL-6 and IL-10 levels are associated with adverse clinical features and poor outcomes. Cytokine 2023, 169, 156289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Romaguera, J.E.; Katz, R.L.; Said, J.; Cabanillas, F. Primary Effusion Lymphoma in an Hiv-Negative Patient with No Serologic Evidence of Kaposi's Sarcoma Virus. Leuk. Lymphoma 2001, 41, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashihara, E.; Shimazaki, C.; Hirai, H.; Inaba, T.; Hasegawa, G.; Mori, S.; Nakagawaa, M. Human Herpes Virus 8-Negative Primary Effusion Lymphoma in a Patient With a Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Tube. Int. J. Hematol. 2001, 74, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.; Zhang, J.; Davis, N.S.; Moffitt, A.; Love, C.L.; Waldrop, A.; Leppä, S.; Pasanen, A.; Meriranta, L.; Karjalainen-Lindsberg, M.-L.; et al. Genetic and Functional Drivers of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Cell 2017, 171, 481–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ennishi, D.; Jiang, A.; Boyle, M.; Collinge, B.; Grande, B.M.; Ben-Neriah, S.; Rushton, C.; Tang, J.; Thomas, N.; Slack, G.W.; et al. Double-Hit Gene Expression Signature Defines a Distinct Subgroup of Germinal Center B-Cell-Like Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Phelan, J.D.; Coulibaly, Z.A.; Roulland, S.; Young, R.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; Morin, R.D.; Tang, J.; et al. A Probabilistic Classification Tool for Genetic Subtypes of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma with Therapeutic Implications. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 551–568.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, W.; Wan, H.; Own, S.A.; Berglund, M.; Wang, X.; Yang, M.; Li, X.; Liu, D.; Ye, X.; Sonnevi, K.; et al. Genetic and transcriptomic analyses of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients with poor outcomes within two years of diagnosis. Leukemia 2023, 38, 610–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, G.; Tan, B.; Rosenwald, A.; Hurt, E.H.; Wiestner, A.; Staudt, L.M. A gene expression-based method to diagnose clinically distinct subgroups of diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 9991–9996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. EdgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’aNgelo, A.; Kilili, H.; Chapman, R.; Generali, D.; Tinhofer, I.; Luminari, S.; Donati, B.; Ciarrocchi, A.; Giannini, R.; Moretto, R.; et al. Immune-related pan-cancer gene expression signatures of patient survival revealed by NanoString-based analyses. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Hu, E.; Cai, Y.; Xie, Z.; Luo, X.; Zhan, L.; Tang, W.; Wang, Q.; Liu, B.; Wang, R.; et al. Using clusterProfiler to characterize multiomics data. Nat. Protoc. 2024, 19, 3292–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Q.; Yi, H.-M.; Qian, Y.; Xu, H.-M.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Au, K.; Tian, S.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, J.; Fu, D.; et al. Practical microenvironment classification in diffuse large B cell lymphoma using digital pathology. Cell Rep. Med. 2025, 6, 102030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balsas, P.; Veloza, L.; Clot, G.; Sureda-Gómez, M.; Rodríguez, M.-L.; Masaoutis, C.; Frigola, G.; Navarro, A.; Beà, S.; Nadeu, F.; et al. SOX11, CD70, and Treg cells configure the tumor immune microenvironment of aggressive mantle cell lymphoma. Blood 2021, 138, 2202–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Care, M.A.; Barrans, S.; Worrillow, L.; Jack, A.; Westhead, D.R.; Tooze, R.M.; Richards, K.L. A Microarray Platform-Independent Classification Tool for Cell of Origin Class Allows Comparative Analysis of Gene Expression in Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturutti, L.; Rivas, M.A.; Pelzer, B.W.; Flümann, R.; Hansen, J.; Karagiannidis, I.; Xia, M.; McNally, D.R.; Isshiki, Y.; Lytle, A.; et al. An Aged/Autoimmune B-cell Program Defines the Early Transformation of Extranodal Lymphomas. Cancer Discov. 2022, 13, 216–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Guo, S.; Shi, Y. Comprehensive analysis of the expression and significance of CXCLs in human diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Registry, U.P.S.S.; Traianos, E.Y.; Locke, J.; Lendrem, D.; Bowman, S.; Hargreaves, B.; Macrae, V.; Tarn, J.R.; Ng, W.-F. Serum CXCL13 levels are associated with lymphoma risk and lymphoma occurrence in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheumatol. Int. 2020, 40, 541–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiduo, C.; Ying, D.; Qiwei, W. CXCL9 promotes the progression of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma through up-regulating β-catenin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Tang, B.; Hu, J.; Fang, X.; Bian, H.; Han, J.; Hou, C.; Sun, F. Neutrophils correlate with hypoxia microenvironment and promote progression of non-small-cell lung cancer. Bioengineered 2021, 12, 8872–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.-L.; Yang, H.-X.; Liu, Q.-P.; Rahman, K.; Zhang, H. CXCL6: A potential therapeutic target for inflammation and cancer. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023, 23, 4413–4427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfroi, B.; McKee, T.; Mayol, J.F.; Tabruyn, S.; Moret, S.; Villiers, C.; Righini, C.; Dyer, M.; Callanan, M.; Schneider, P.; et al. CXCL-8/IL8 Produced by Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphomas Recruits Neutrophils Expressing a Proliferation-Inducing Ligand APRIL. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfroi, B.; Moreaux, J.; Righini, C.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Sturm, N.; Huard, B. Tumor-associated neutrophils correlate with poor prognosis in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients. Blood Cancer J. 2018, 8, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.; Gibbons, K.; Ehyaee, V.; Perez-Silos, V.; Zevallos, A.; Maienschein-Cline, M.; Brister, E.; Sverdlov, M.; Shah, E.; Balakrishna, J.; et al. Specific Polo-Like Kinase 1 Expression in Nodular Lymphocyte-Predominant Hodgkin Lymphoma Suggests an Intact Immune Surveillance Program. Am. J. Pathol. 2023, 194, 165–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissell, M.J.; Hines, W.C. Why don't we get more cancer? A proposed role of the microenvironment in restraining cancer progression. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| n = 8 | |
|---|---|
| Median age (Years) | 86 |
| Male/Female | 6/2 |
| HIV | 1/6 (14%) |
| HCV | 0/6 (0%) |
| Risk of fluid overload | 6/8 (75%) |
| Effusion sites | |
| Pleural total | 6/8 (75%) |
| Pericardial total | 4/8 (50%) |
| Pleural/Pericardial | 2/8 (25%) |
| Management | |
| None (+/− Drainage) | 4/7 (57%) |
| Chemotherapy | 3/7 (42%) |
| Responses | |
| Complete remission | 3/7 (50%) |
| Persistent or progressive | 4/7 (57%) |
| Follow up (Median, Months) | 5.3 |
| Outcome (Deceased) | 6/7 (85%) |
| Survival (Median, Months) | 5.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perez-Silos, V.; Kim, H.; Wang, C.; Zevallos-Morales, A.; Tipton, A.; Danos-Diaz, P.; Wilcox, R.; Bailey, N.; Aggarwal, N.; Gisriel, S.D.; et al. Transcriptional Analysis of Effusion-Based Lymphoma Supports a Post-Germinal Center Origin and Specific Inflammatory Signal Background. Cancers 2025, 17, 2978. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182978
Perez-Silos V, Kim H, Wang C, Zevallos-Morales A, Tipton A, Danos-Diaz P, Wilcox R, Bailey N, Aggarwal N, Gisriel SD, et al. Transcriptional Analysis of Effusion-Based Lymphoma Supports a Post-Germinal Center Origin and Specific Inflammatory Signal Background. Cancers. 2025; 17(18):2978. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182978
Chicago/Turabian StylePerez-Silos, Vanessa, Hojung Kim, Chenguang Wang, Alejandro Zevallos-Morales, Anthony Tipton, Pierina Danos-Diaz, Ryan Wilcox, Nathanael Bailey, Nidhi Aggarwal, Savanah Dior Gisriel, and et al. 2025. "Transcriptional Analysis of Effusion-Based Lymphoma Supports a Post-Germinal Center Origin and Specific Inflammatory Signal Background" Cancers 17, no. 18: 2978. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182978
APA StylePerez-Silos, V., Kim, H., Wang, C., Zevallos-Morales, A., Tipton, A., Danos-Diaz, P., Wilcox, R., Bailey, N., Aggarwal, N., Gisriel, S. D., Smith-Hannah, A., Xu, M., Frederiksen, J. K., & Murga-Zamalloa, C. (2025). Transcriptional Analysis of Effusion-Based Lymphoma Supports a Post-Germinal Center Origin and Specific Inflammatory Signal Background. Cancers, 17(18), 2978. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182978






