Impact of Serum Albumin Levels on Prognosis and Recurrence in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Group A (albumin-preserved group): Alb ≥ 3.5 g/dL and Bil ≥ 1.0 mg/dL (n = 42)
- Group T (bilirubin-preserved group): Alb < 3.5 g/dL and Bil < 1.0 mg/dL (n = 36)
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Background in Groups a and T with the Same Liver Function
3.2. Clinical Background and OS After Propensity Score Matching
3.3. Clincal Background and OS in Groups a and T After Curative Treatment
3.4. Clinical Background and OS in Groups a and T After RFA
3.5. Comparison of Recurrence-Free Survival and Recurrence Patterns in 44 Patients Receiving Curative Treatment (Surgical Resection or Radiofrequency Ablation)
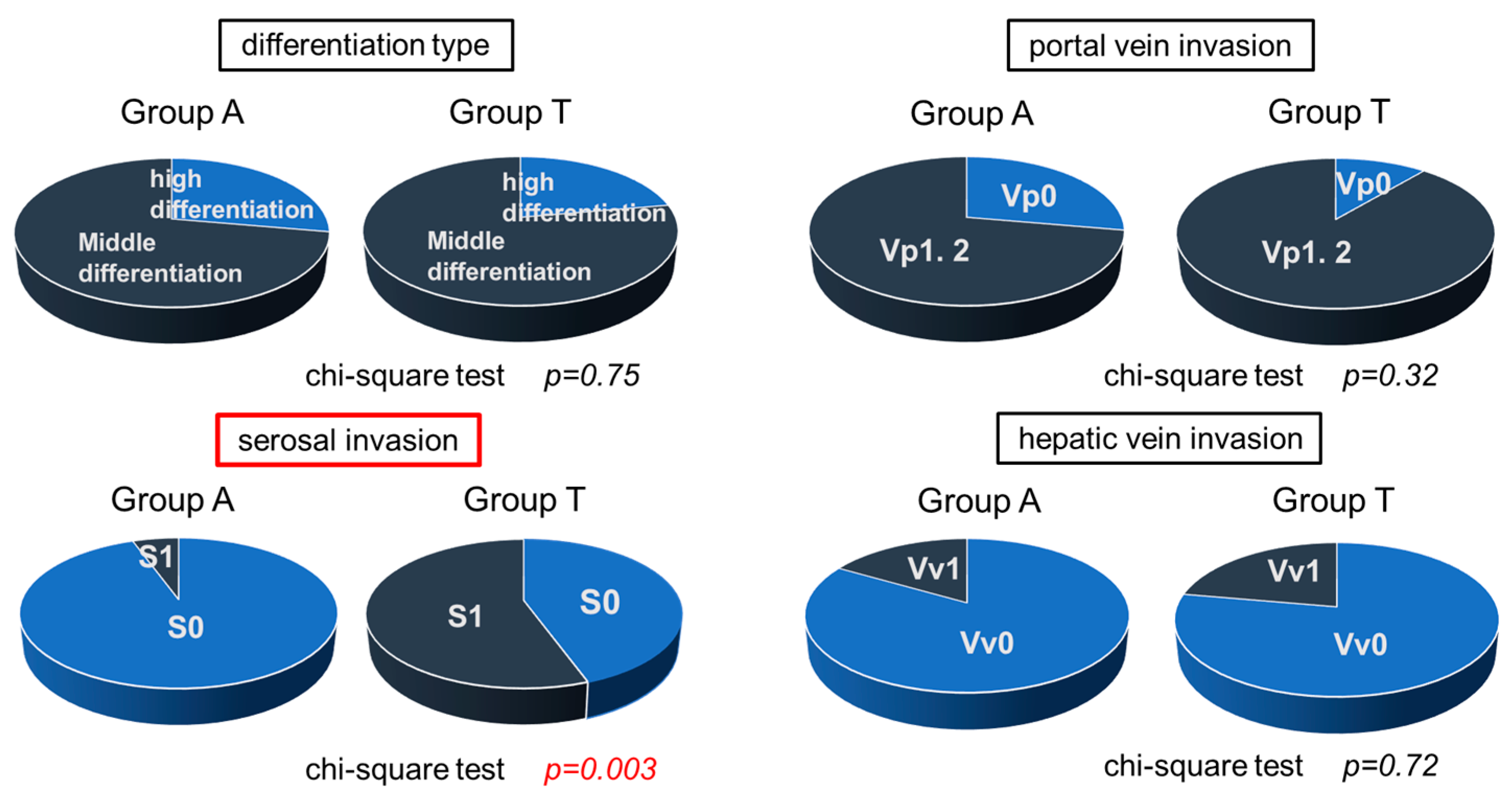
3.6. Histological Study in Surgical Specimens in Group A and T
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| Alb | Albumin |
| Bil | Bilirubin |
| OS | Overall survival |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| ALBI | albumin-bilirubin |
| PS | Performance status |
| CT | computed tomography |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| TMN | the Tumor-Node-Metastasis |
| UICC | the Union for International Cancer Control |
| BCLC | the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer |
| AASLD | the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases |
| JSH | the Japan Society of Hepatology |
| Ope | surgical resection |
| RFA | radiofrequency ablation |
| TACE | transarterial chemoembolization |
| PSM | propensity score matching |
| BCAA | branched-chain amino acids |
| uPA | urokinase-type plasminogen activator |
| MMPs | matrix metalloproteinases |
| EMT | epithelial–mesenchymal transition |
References
- Child, C.G. Surgery and Portal Hypertension; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1964; pp. 50–64. [Google Scholar]
- Pugh, R.N.; Murray-Lyon, I.M.; Dawson, J.L.; Pietroni, M.C.; Williams, R. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br. J. Surg. 1973, 60, 646–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, P.J.; Berhane, S.; Kagebayashi, C.; Satomura, S.; Teng, M.; Reeves, H.L.; O’Beirne, J.; Fox, R.; Skowronska, A.; Palmer, D.; et al. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: A new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamana, H.; Imai, S.; Yamasaki, K.; Horiguchi, H.; Ario, K.; Komatsu, T.; Sugimoto, R.; Katsushima, S.; Naganuma, A.; Mano, Y.; et al. Prognosis of patients with liver cirrhosis: A multi-center retrospective observational study. Hepatol. Res. 2021, 51, 1196–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M. Newly Developed Modified ALBI Grade Shows Better Prognostic and Predictive Value for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2022, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraoka, A.; Kumada, T.; Tsuji, K.; Takaguchi, K.; Itobayashi, E.; Kariyama, K.; Ochi, H.; Tajiri, K.; Hirooka, M.; Shimada, N.; et al. Validation of Modified ALBI Grade for More Detailed Assessment of Hepatic Function in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients: A Multicenter Analysis. Liver Cancer. 2019, 8, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanali, G.; di Masi, A.; Trezza, V.; Marino, M.; Fasano, M.; Ascenzi, P. Human serum albumin: From bench to bedside. Mol. Asp. Med. 2012, 33, 209–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiselius, A. A new apparatus for electrophoretic analysis of colloidal mixtures. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1937, 33, 524–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, G.J.; Martin, G.S.; Evans, T.W. Albumin: Biochemical properties and therapeutic potential. Hepatology 2005, 41, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starling, E.H. On the absorption of fluids from the connective tissue spaces. J. Physiol. 1896, 19, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caraceni, P.; O’Brien, A.; Gines, P. Long-term albumin treatment in patients with cirrhosis and ascites. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 1306–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudlow, G.; Birkett, D.J.; Wade, D.N. The characterization of two specific drug binding sites on human serum albumin. Mol. Pharmacol. 1975, 11, 824–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghuman, J.; Zunszain, P.A.; Petitpas, I.; Otagiri, M.; Curry, S. Structural basis of the drug-binding specificity of human serum albumin. J. Mol. Biol. 2005, 353, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran-Güel, M. Albumin protects the liver from TNF-α-induced immunopathology. FASEB J. 2021, 35, e21365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.S. The immunomodulatory effects of albumin in vitro and in vivo. Mediat. Inflamm. 2011, 2011, 691928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caraceni, P.; Riggio, O.; Angeli, P.; Alessandria, C.; Neri, S.; Foschi, F.G.; Levantesi, F.; Airoldi, A.; Boccia, S.; Svegliati-Baroni, G.; et al. ANSWER Study Investigators. an open-label randomized trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 2417–2429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, F.; Yixuan, Y.; Dazhi, Z. Molecular mechanism of albumin in suppressing invasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver. Int. 2022, 42, 696–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, S.M.; Jonas, O.; Keibler, M.A.; Hou, H.W.; Luengo, A.; Mayers, J.R.; Wyckoff, J.; Rosario, A.M.D.; Whitman, M.; Chin, C.R. Direct evidence for cancer-cell-autonomous extracellular protein catabolism in pancreatic tumors. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardi, M.; Angeli, P.; Clària, J.; Moreau, R.; Ginès, P.; Jalan, R.; Caraceni, P.; Fernandez, J.; Gerbes, A.L.; O’Brien, A.J.; et al. Albumin in Decompensated Cirrhosis: New Concepts and Perspectives. Gut 2020, 69, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldassarre, M.; Domenicali, M.; Naldi, M.; Laggetta, M.; Giannone, F.A.; Biselli, M.; Zaccherini, G.; Trevisani, F.; Bernardi, M. Albumin Homodimers in Patients with Cirrhosis: Clinical and Prognostic Relevance of a Novel Identified Structural Alteration of the Molecule. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, I.F.; Miranda, R.G.; Dorta, D.J.; Rolo, A.P.; Palmeira, C.M. Targeting Oxidative Stress with Polyphenols to Fight Liver Diseases. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romanelli, R.; Villa, G.L.; Barletta, G.; Vizzutti, F.; Lanini, F.; Arena, U.; Boddi, V.; Tarquini, R.; Pantaleo, P.; Gentilini, P.; et al. Long-term albumin infusion improves survival in patients with cirrhosis and ascites: An unblinded randomized trial. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 1403–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sort, P.; Navasa, M.; Arroyo, V.; Aldeguer, X.; Planas, R.; Ruiz del Arbol, L.; Castells, L.; Vargas, V.; Soriano, G.; Guevara, M.; et al. Effect of intravenous albumin on renal impairment and mortality in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muto, Y.; Sato, S.; Watanabe, A.; Moriwaki, H.; Suzuki, K.; Kato, A.; Kato, M.; Nakamura, T.; Higuchi, K.; Nishiguchi, S.; et al. Long-Term Survival Study Group. Effects of oral branched-chain amino acid granules on event-free survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 3, 705–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muto, Y.; Sato, S.; Watanabe, A.; Moriwaki, H.; Suzuki, K.; Kato, A.; Kato, M.; Nakamura, T.; Higuchi, K.; Nishiguchi, S.; et al. Overweight and obesity increase the risk for liver cancer in patients with liver cirrhosis and long-term oral supplementation with branched-chain amino acid granules inhibits liver carcinogenesis in heavier patients with liver cirrhosis. Hepatol. Res. 2006, 35, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, M.; Ikeda, K.; Arase, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Suzuki, F.; Akuta, N.; Hosaka, T.; Murashima, N.; Saitoh, S.; Someya, T.; et al. Inhibitory effect of branched chain amino acid granules on progression of compensated liver cirrhosis due to hepatitis C virus. J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 43, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, B.I.; Guerra, V. Serum Albumin Levels in Relation to Tumor Parameters in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2017, 32, e391–e396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D.; Lis, C.G. Pretreatment serum albumin as a predictor of cancer survival: A systematic review of the epidemiological literature. Nutr. J. 2010, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onate-Ocaña, L.F.; Aiello-Crocifoglio, V.; Gallardo-Rincón, D.; Herrera-Goepfert, R.; Brom-Valladares, R.; Carrillo, J.F.; Cervera, E.; Mohar-Betancourt, A. Serum albumin as a significant prognostic factor for patients with gastric carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 14, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.C.; You, J.F.; Yeh, C.Y.; Chen, J.S.; Tang, R.; Wang, J.Y.; Chin, C.C. Low preoperative serum albumin in colon cancer: A risk factor for poor outcome. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2011, 26, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonpipattanapong, T.; Chewatanakornkul, S. Preoperative carcinoembryonic antigen and albumin in predicting survival in patients with colon and rectal carcinomas. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2006, 40, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.C.; Chu, K.S.; Cheng, S.C.; Lu, C.Y.; Kuo, C.H.; Hsieh, J.S.; Shih, Y.L.; Chang, S.J.; Wang, J.Y. Preoperative serum carcinoembryonic antigen, albumin and age are supplementary to UICC staging systems in predicting survival for colorectal cancer patients undergoing surgical treatment. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz Tovar, J.; Martin Perez, E.; Fernandez Contreras, M.E.; Reguero Callejas, M.E.; Gamallo Amat, C. Impact of preoperative levels of hemoglobin and albumin on the survival of pancreatic carcinoma. Rev. Esp. Enferm. Dig. 2010, 102, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lis, C.G.; Grutsch, J.F.; Vashi, P.G.; Lammersfeld, C.A. Is serum albumin an independent predictor of survival in patients with breast cancer? J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 2003, 27, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, O.; Michel Ortega, R.M.; Villanueva-Rodríguez, G.; Serna-Thomé, M.G.; Flores-Estrada, D.; Díaz-Romero, C.; Rodríguez, C.M.; Martínez, L.; Sánchez-Lara, K. Association of nutritional status and serum albumin levels with development of toxicity in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer treated with paclitaxel-cisplatin chemotherapy: A prospective study. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, O.; Zhang, J.; Lu, J. A novel prognostic scoring model based on albumin and γ-Glutamyltransferase for hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 10685–10694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Li, H.; Chen, L.; Qui, X. Prognostic value of albumin-bilirubin grade in lung cancer: A meta-analysis. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2024, 19, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haskins, I.N.; Baginsky, M.; Amdur, R.L.; Agarwal, S. Preoperative hypoalbuminemia is associated with worse outcomes in colon cancer patients. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1333–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mignatti, P.; Rifkin, D.B. Biology and biochemistry of proteinases in tumor invasion. Physiol. Rev. 1993, 73, 161–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nojiri, S.; Joh, T. Albumin suppresses human hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and the cell cycle. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5163–5174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, B.I.; Guerra, V. Validation of a liver index and its significance for HCC aggressiveness. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2017, 48, 262–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonohara, F.; Nomoto, S.; Inokawa, Y.; Kanda, M.; Yamada, S.; Fujii, T.; Sugimoto, H.; Kodera, Y. Serosal Invasion Strongly Associated with Recurrence After Curative Hepatic Resection of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Medicine 2015, 94, e602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohi, M.; Mori, K.; Toiyama, Y.; Mohri, Y.; Okigami, M.; Yasuda, H.; Saigusa, S.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Kusunoki, M. Preoperative prediction of peritoneal metastasis in gastric cancer as an indicator for neoadjuvant treatment. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 3511–3518. [Google Scholar]
- Toiyama, Y.; Yasuda, H.; Ohi, M.; Yoshiyama, S.; Araki, T.; Tanaka, K.; Inoue, Y.; Mohri, Y.; Kusunoki, M. Clinical impact of preoperative albumin to globulin ratio in gastric cancer patients with curative intent. Am. J. Surg. 2017, 213, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitsu, H.; Okuda, K.; Yoshida, K.; Nonaka, M.; Sato, M.; Nakagoshi, K.; Hamasaki, K.; Yoshida, H.; Miyoshi, A.; Nakayama, Y.; et al. Confirmation of the presence of lymph channels in hepatoma nodes for use in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Kanzo 1986, 27, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Shenglong, L.; Qinghong, G.; Xinran, L.; Zhenyu, Y.; Yingwei, X.; Fujing, W. Extent of Serosal Changes Predicts Peritoneal Recurrence and Poor Prognosis After Curative Surgery for Gastric Cancer. Medicine 2015, 94, e1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Ulíbarri, J.I.; González-Madroño, A.; de Villar, N.G.P.; González, P.; González, B.; Mancha, A.; Rodríguez, F.; Fernández, G. CONUT: A tool for controlling nutritional status. First validation in a hospital population. Nutr. Hosp. 2005, 20, 38–45. [Google Scholar]
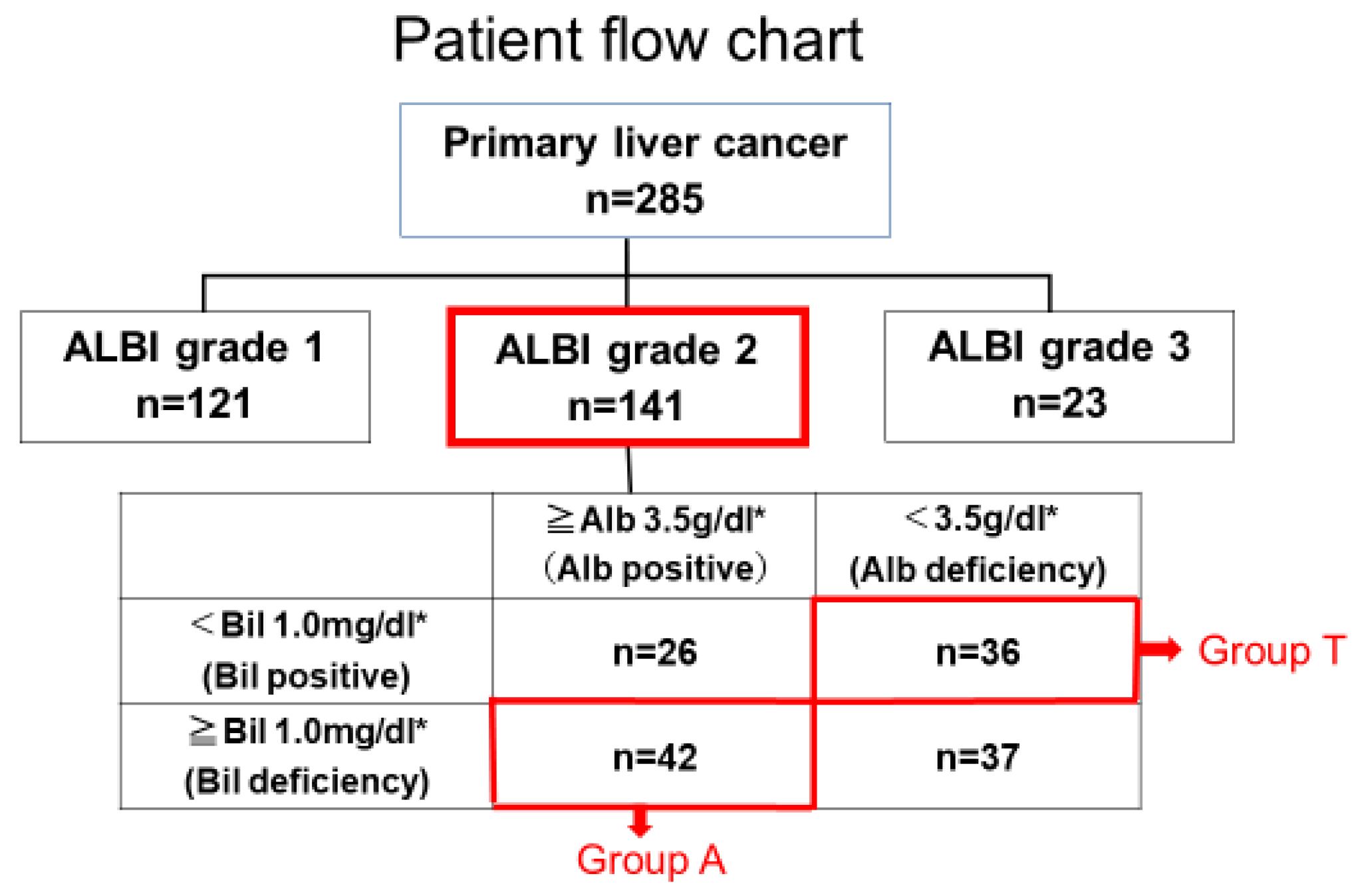
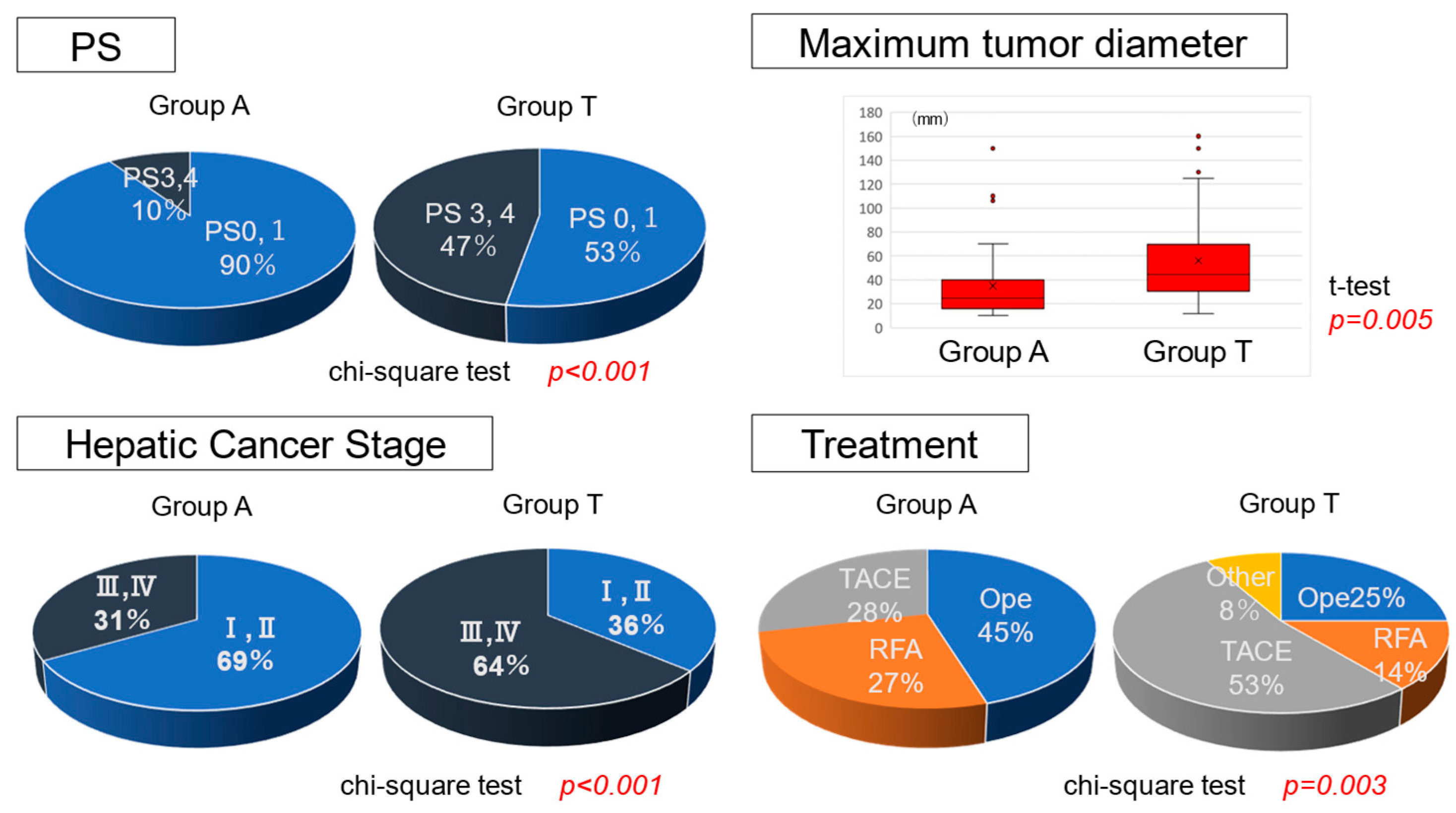
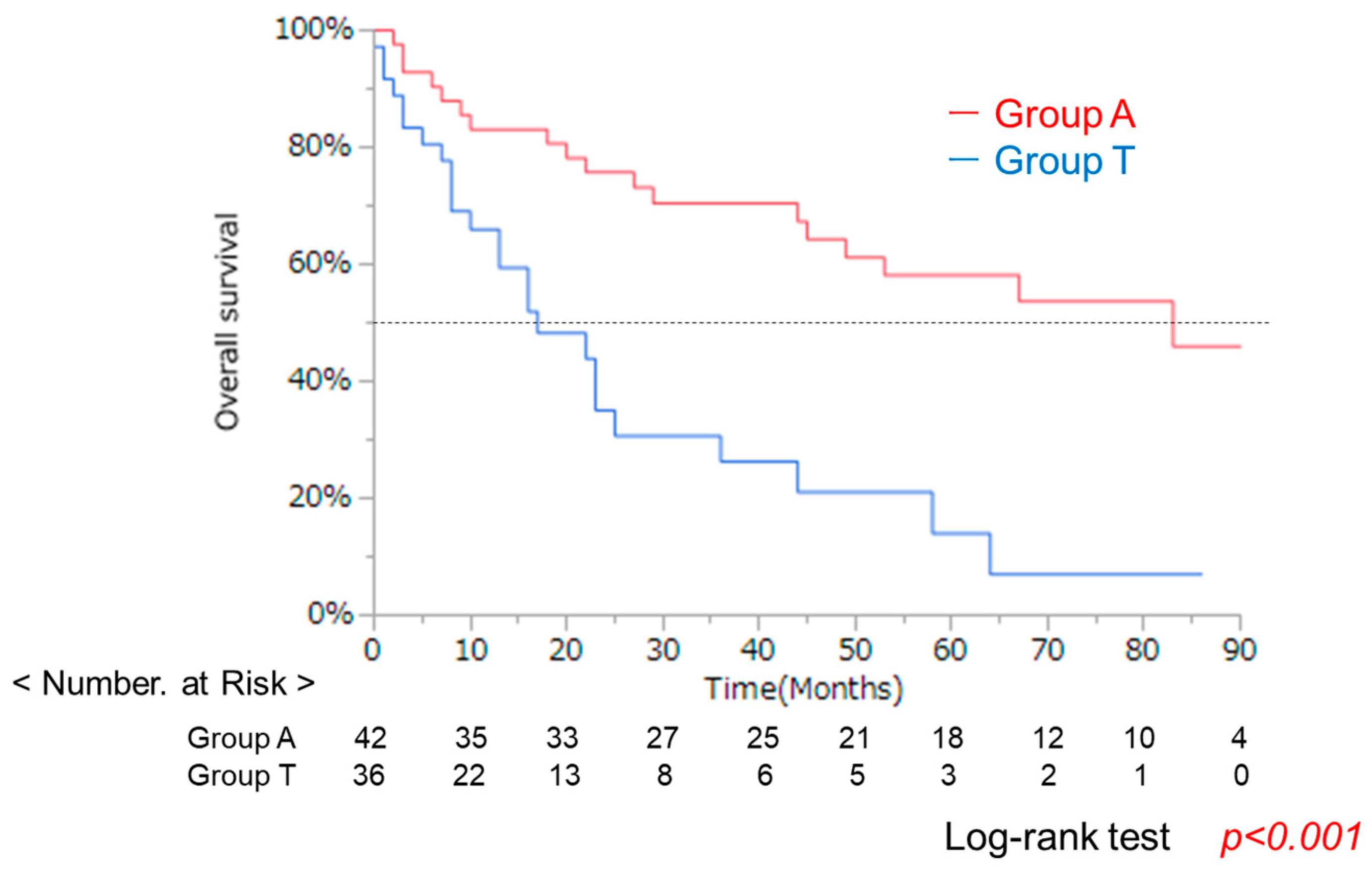
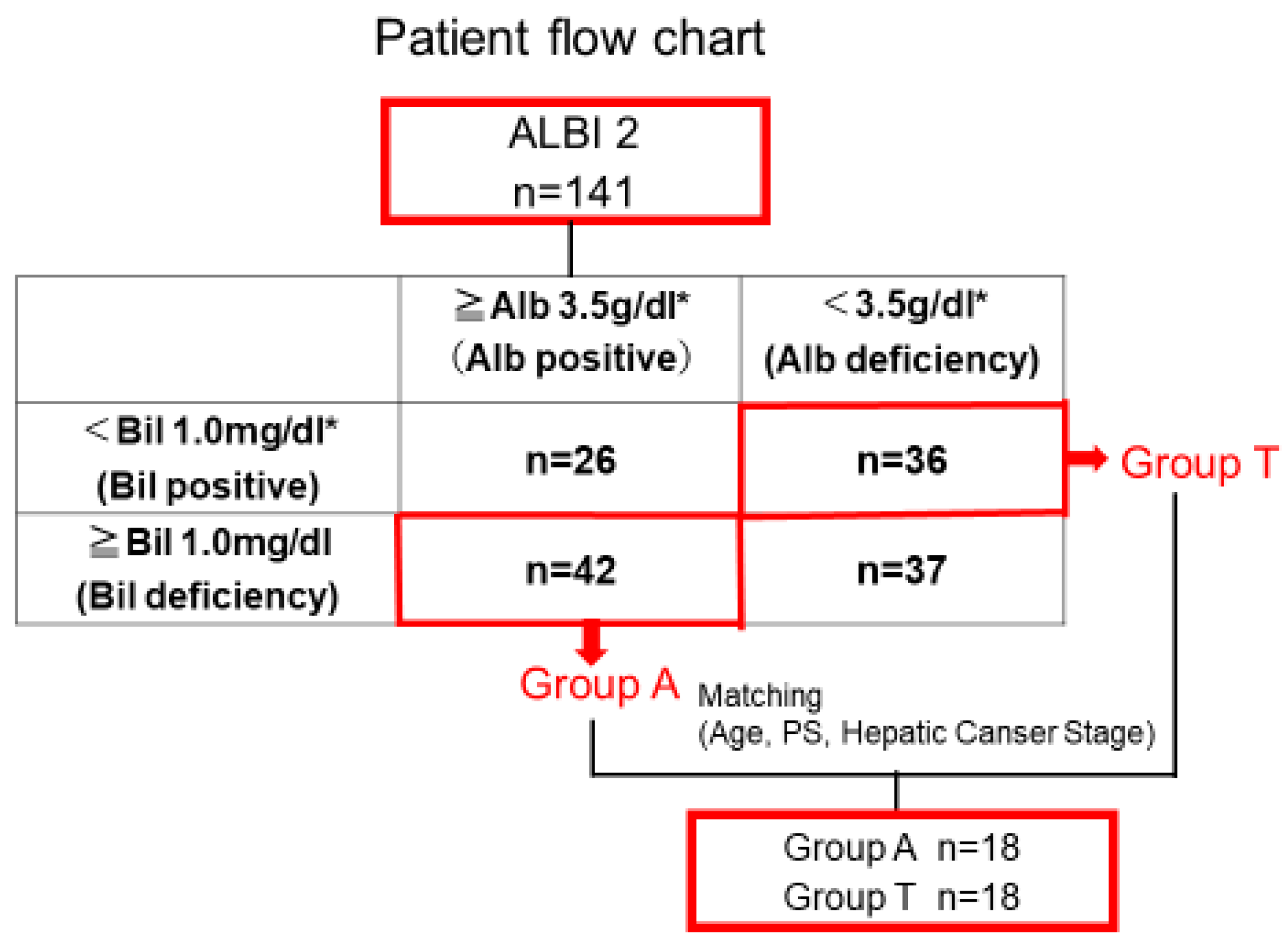
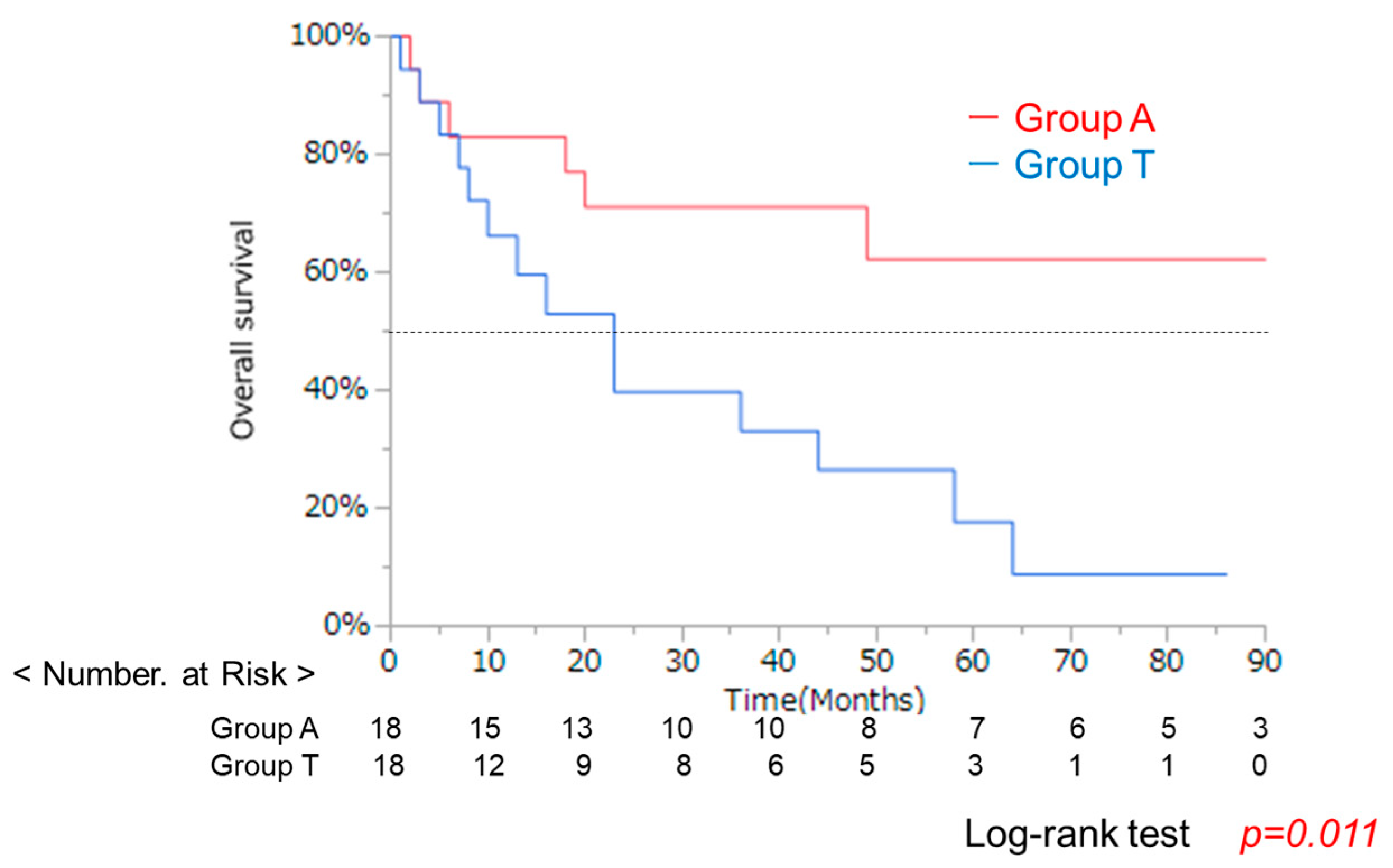
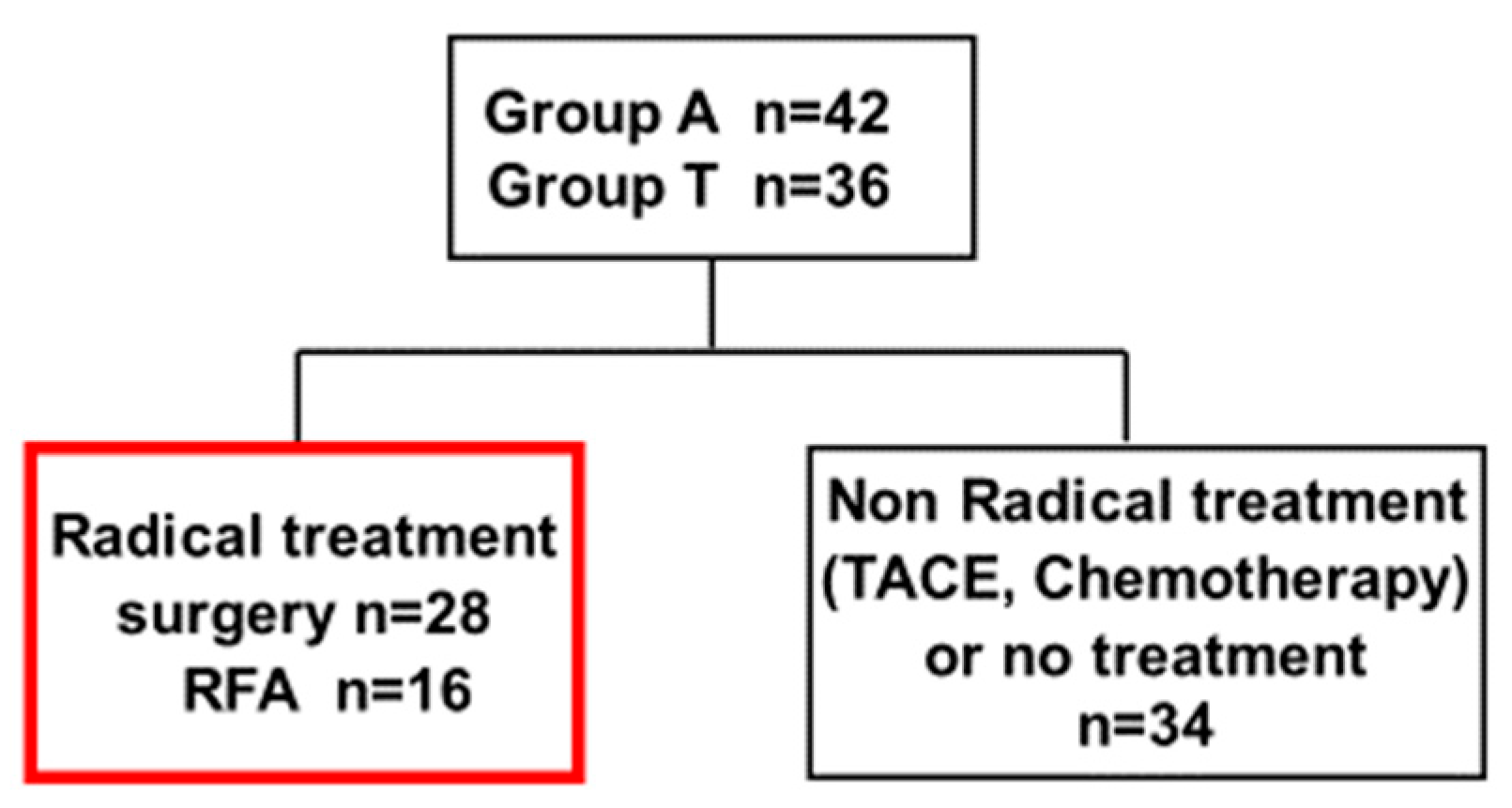
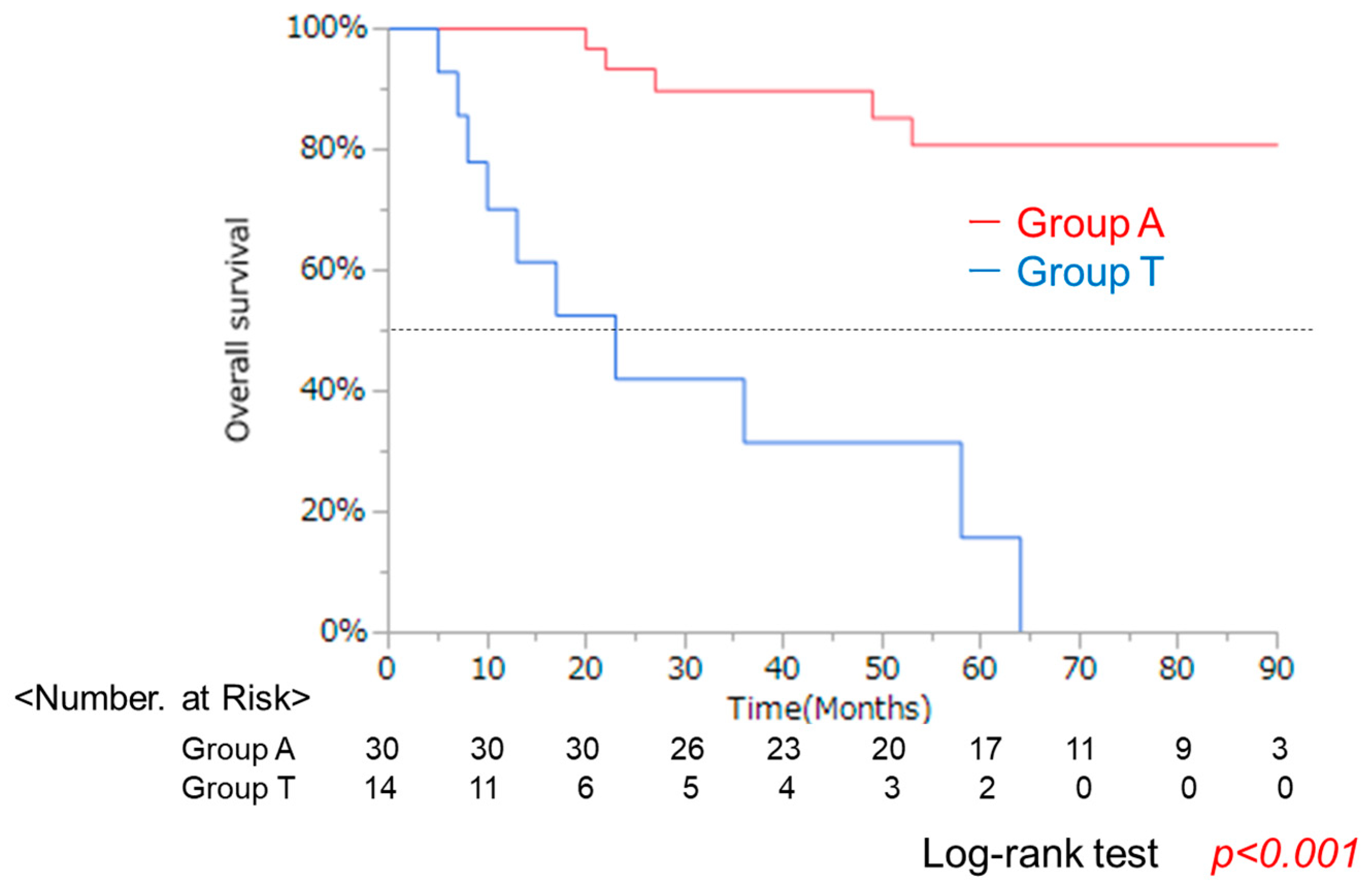
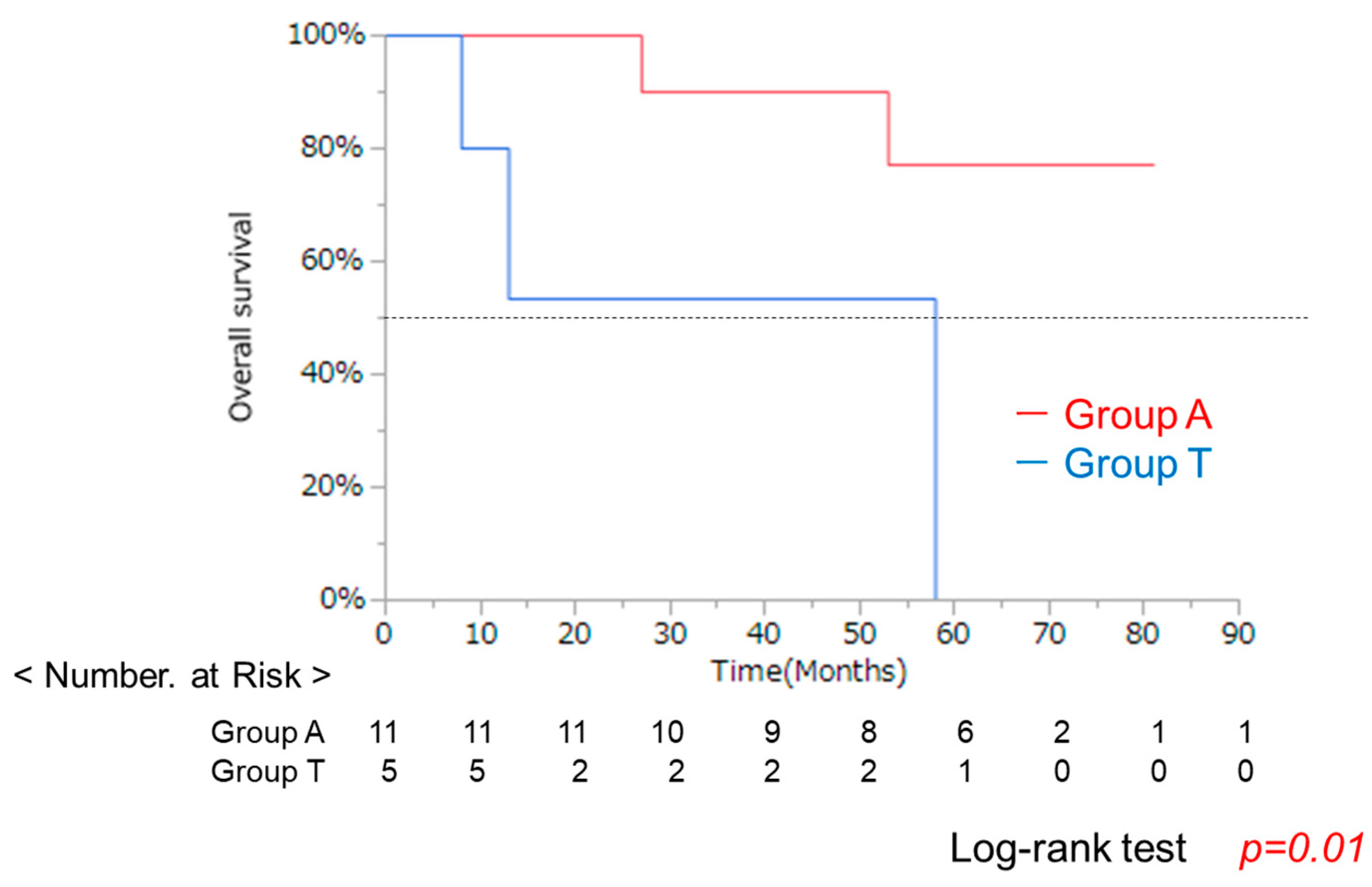

| Characteristic | A Group (n = 42) | T Group (n = 36) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 70.5 ± 8.5 | 75.6 ± 7.6 | 0.006 |
| Sex (M/F) | 30/12 | 25/11 | 0.38 |
| Etiology of HCC | |||
| HCV/HBV/Alcohol/NASH/AIH /Unknown | 15/6/12/4/1/4 | 16/5/7/0/1/7 | 0.15 |
| † PS (0/1/2/3/4) | 31/7/3/1/0 | 12/7/5/12/0 | <0.001 |
| †† HCC Stage (I/II/III/IV) | 11/18/10/3 | 3/10/15/8 | <0.001 |
| Maximum tumor diameter (mm) | 34.8 ± 28.5 | 56.6 ± 36.7 | 0.005 |
| ††† Treatment modality | |||
| Ope/RFA/TACE/Chemo/None | 19/11/12/0/0 | 9/5/19/1/2 | 0.003 |
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.3 ± 0.3 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.0001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.8 ± 0.2 | 3.1 ± 0.3 | 0.0001 |
| Platelet count (×104/μL) | 17.2 ± 28.2 | 20.7 ± 11.1 | 0.46 |
| Prothrombin time (%) | 75.2 ± 12.2 | 79.2 ± 15.0 | 0.18 |
| Characteristic | A Group (n = 18) | T Group (n = 18) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 75.0 ± 6.0 | 72.5 ± 6.9 | 0.77 |
| Sex (M/F) | 7/11 | 4/14 | 0.28 |
| Etiology of HCC | |||
| HCV/HBV/Alcohol/NASH/AIH /Unknown | 9/1/1/2/1/3 | 7/2/4/0/1/4 | 0.74 |
| † Performance Status (0/1/2/3/4) | 11/4/2/1/0 | 12/3/2/1/0 | 1.0 |
| †† HCC Stage (I/II/III/IV) | 2/9/6/1 | 2/8/6/2 | 0.41 |
| Maximum tumor diameter (mm) | 27.0 ± 34.5 | 50.0 ± 38.9 | 0.20 |
| Treatment modality | |||
| ††† Ope/RFA/TACE/Chemo/None | 9/3/6/0/0 | 7/4/6/1/0 | 0.73 |
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.2 ± 0.22 | 0.6 ± 0.20 | <0.001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.8 ± 0.15 | 3.2 ± 0.27 | <0.001 |
| Platelet count (×104/μL) | 11.6 ± 41.7 | 19.9 ± 12.2 | 0.87 |
| Prothrombin time (%) | 74.3 ± 10.9 | 84.3 ± 11.7 | 0.03 |
| Characteristic | A Group (n = 30) | T Group (n = 14) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 70 ± 7.9 | 73 ± 5.7 | 0.2 |
| Sex (M/F) | 20/10 | 11/3 | 0.46 |
| Etiology of HCC | |||
| HCV/HBV/Alcohol/NASH/AIH /Unknown | 9/5/9/3/1/3 | 6/2/3/0/1/2 | 0.52 |
| † Performance Status (0/1/2/3/4) | 24/3/3/0/0 | 9/1/1/3/0 | 0.11 |
| †† HCC Stage (I/II/III/IV) | 10/15/5/0 | 3/6/5/0 | 0.16 |
| Maximum tumor diameter (mm) | 24.3 ± 10.6 | 37.1 ± 22.3 | 0.06 |
| ††† Treatment modality | |||
| Ope/RFA | 19/11 | 9/5 | 0.95 |
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 0.6 ± 0.2 | 0.0001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.8 ± 0.2 | 3.1 ± 0.2 | 0.0001 |
| Platelet count (×104/μL) | 13.1 ± 6.7 | 19.3 ± 12.4 | 0.10 |
| Prothrombin time (%) | 75.4 ± 12.5 | 76.5 ± 13.0 | 0.80 |
| Characteristic | A Group (n = 11) | T Group (n = 5) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 69 ± 6.4 | 75 ± 6.4 | 0.28 |
| Sex (M/F) | 8/3 | 0/5 | 0.007 |
| Etiology of HCC | |||
| HCV/HBV/Alcohol/NASH/AIH /Unknown | 2/3/4/2/0/0 | 2/1/1/0/0/1 | 0.59 |
| † Performance Status (0/1/2/3/4) | 7/2/2/0/0 | 2/1/1/1/0 | 0.35 |
| †† HCC Stage (I/II/III/IV) | 7/4/0/0 | 1/3/1/0 | 0.13 |
| Maximum tumor diameter (mm) | 15 ± 6.3 | 23 ± 5.9 | 0.44 |
| Total Bilirubin (mg/dL) | 1.1 ± 0.14 | 0.6 ± 0.19 | 0.0001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.8 ± 0.12 | 2.9 ± 0.2 | 0.0001 |
| Platelet count (×104/μL) | 13.1 ± 6.7 | 19.3 ± 12.4 | 0.74 |
| Prothrombin time (%) | 74.3 ± 13.6 | 78.3 ± 12.6 | 0.38 |
| Characteristic | A Group (n = 19) | T Group (n = 9) | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 71.0 ± 7.2 | 72.0 ± 5.3 | 0.49 |
| Sex (M/F) | 12/7 | 6/3 | 0.86 |
| † Etiology of HCC | |||
| HCV/HBV/Alcohol/NASH/AIH /Unknown | 6/3/5/1/1/3 | 4/1/2/1/0/1 | 0.69 |
| †† Performance Status (0/1/2/3/4) | 17/1/1/0/0 | 7/0/0/2/0 | 0.18 |
| ††† HCC Stage (I/II/III/IV) | 3/10/6/0 | 2/5/2/0 | 0.61 |
| Maximum tumor diameter (mm) | 28 ± 10.6 | 45 ± 23.3 | 0.07 |
| Total Bilirubin(mg/dL) | 1.3 ± 0.22 | 0.7 ± 0.15 | <0.001 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.9 ± 0.17 | 3.2 ± 0.23 | <0.001 |
| Platelet count (×104/μL) | 73.3 ± 11.8 | 11.6 ± 6.4 | 0.56 |
| Prothrombin time (%) | 76.2 ± 12.8 | 16.4 ± 12.3 | 0.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hayata, N.; Hosui, A.; Kurahashi, T.; Suemura, S.; Namiki, A.; Okamoto, A.; Tanimoto, T.; Murai, H.; Ohnishi, K.; Hirao, M.; et al. Impact of Serum Albumin Levels on Prognosis and Recurrence in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 2971. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182971
Hayata N, Hosui A, Kurahashi T, Suemura S, Namiki A, Okamoto A, Tanimoto T, Murai H, Ohnishi K, Hirao M, et al. Impact of Serum Albumin Levels on Prognosis and Recurrence in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(18):2971. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182971
Chicago/Turabian StyleHayata, Naoko, Atsushi Hosui, Tomohide Kurahashi, Shigeki Suemura, Akane Namiki, Akino Okamoto, Takafumi Tanimoto, Hiroki Murai, Kohsaku Ohnishi, Motohiro Hirao, and et al. 2025. "Impact of Serum Albumin Levels on Prognosis and Recurrence in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Cancers 17, no. 18: 2971. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182971
APA StyleHayata, N., Hosui, A., Kurahashi, T., Suemura, S., Namiki, A., Okamoto, A., Tanimoto, T., Murai, H., Ohnishi, K., Hirao, M., Yamada, T., & Hiramatsu, N. (2025). Impact of Serum Albumin Levels on Prognosis and Recurrence in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers, 17(18), 2971. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182971








