Impact of Obesity on Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping in Patients with Endometrial Intraepithelial Neoplasia Undergoing Robotic Surgery: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
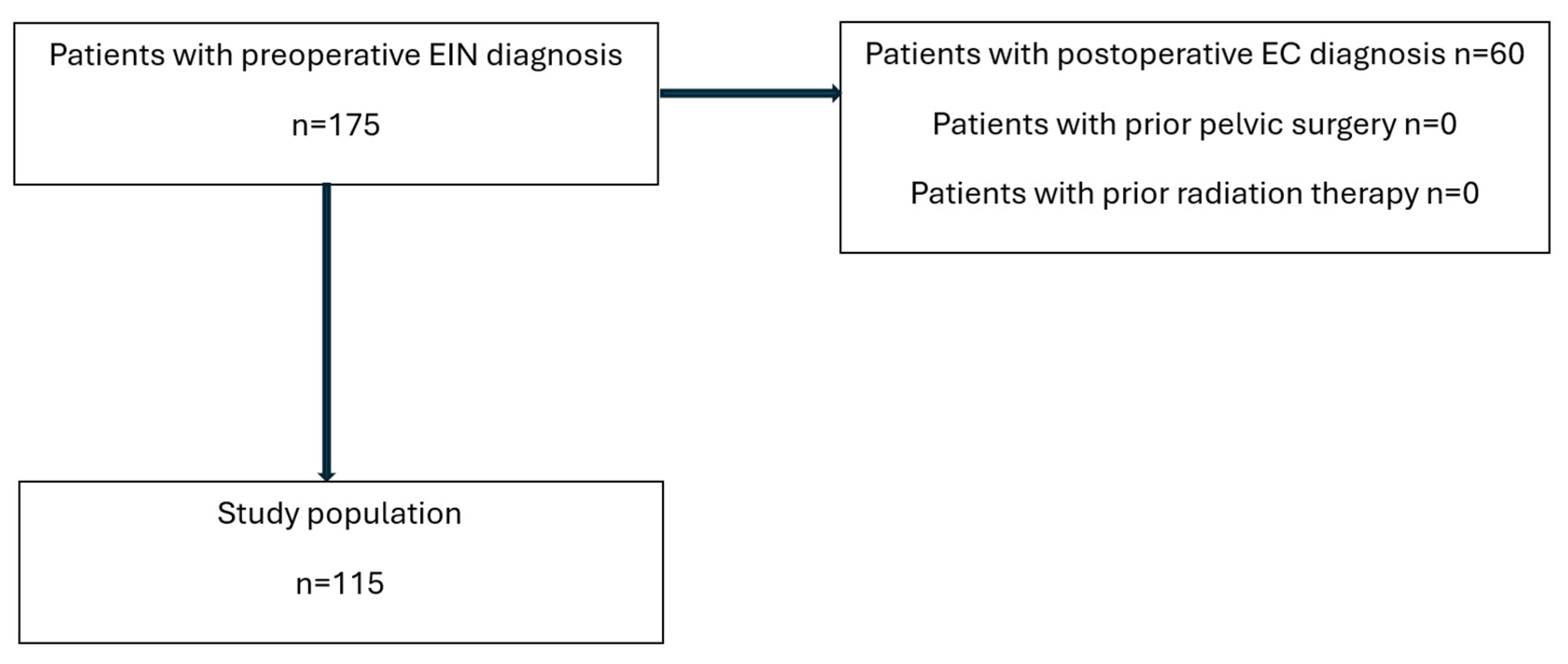
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. SLN Procedure
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
BMI Subgroup Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMI | Body-mass index |
| DR | Detection rate |
| EC | Endometrial carcinoma |
| EIN | Endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia |
| ICG | Indocyanine green |
| LN | Lymph node |
| LND | Lymph node dissection |
| NIR | Near-infrared |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SLN | Sentinel lymph node |
Appendix A
References
- Kurman, R.J.; Kaminski, P.F.; Norris, H.J. The behavior of endometrial hyperplasia. A long-term study of “untreated” hyperplasia in 170 patients. Cancer 1985, 56, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaino, R.J.; Kauderer, J.; Trimble, C.L.; Silverberg, S.G.; Curtin, J.P.; Lim, P.C.; Gallup, D.G. Reproducibility of the diagnosis of atypical endometrial hyperplasia: A Gynecologic Oncology Group study. Cancer 2006, 106, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parkash, V.; Fadare, O.; Tornos, C.; McCluggage, W.G. Committee Opinion No. 631: Endometrial Intraepithelial Neoplasia. Obstet. Gynecol. 2015, 126, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetter, M.H.; Smith, B.; Benedict, J.; Hade, E.M.; Bixel, K.; Copeland, L.J.; Cohn, D.E.; Fowler, J.M.; O’Malley, D.; Salani, R.; et al. Preoperative predictors of endometrial cancer at time of hysterectomy for endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia or complex atypical hyperplasia. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 2020, 222, 60.e1–60.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimble, C.L.; Kauderer, J.; Zaino, R.; Silverberg, S.; Lim, P.C.; Burke, J.J., 2nd; Alberts, D.; Curtin, J. Concurrent endometrial carcinoma in women with a biopsy diagnosis of atypical endometrial hyperplasia: A Gynecologic Oncology Group study. Cancer 2006, 106, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touhami, O.; Gregoire, J.; Renaud, M.C.; Sebastianelli, A.; Grondin, K.; Plante, M. The utility of sentinel lymph node mapping in the management of endometrial atypical hyperplasia. Gynecol. Oncol. 2018, 148, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costales, A.B.; Schmeler, K.M.; Broaddus, R.; Soliman, P.T.; Westin, S.N.; Ramirez, P.T.; Frumovitz, M. Clinically significant endometrial cancer risk following a diagnosis of complex atypical hyperplasia. Gynecol. Oncol. 2014, 135, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitao, M.M., Jr.; Han, G.; Lee, L.X.; Abu-Rustum, N.R.; Brown, C.L.; Chi, D.S.; Sonoda, Y.; Levine, D.A.; Gardner, G.J.; Jewell, E.E.; et al. Complex atypical hyperplasia of the uterus: Characteristics and prediction of underlying carcinoma risk. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 203, 349.e1–349.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti Panici, P.; Basile, S.; Maneschi, F.; Alberto Lissoni, A.; Signorelli, M.; Scambia, G.; Angioli, R.; Tateo, S.; Mangili, G.; Katsaros, D.; et al. Systematic pelvic lymphadenectomy vs. no lymphadenectomy in early-stage endometrial carcinoma: Randomized clinical trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2008, 100, 1707–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, E.C.; Kowalski, L.D.; Scalici, J.; Cantrell, L.; Schuler, K.; Hanna, R.K.; Method, M.; Ade, M.; Ivanova, A.; Boggess, J.F. A comparison of sentinel lymph node biopsy to lymphadenectomy for endometrial cancer staging (FIRES trial): A multicentre, prospective, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogan, L.; Matanes, E.; Wissing, M.; Mitric, C.; How, J.; Amajoud, Z.; Abitbol, J.; Yasmeen, A.; Lopez-Ozuna, V.; Eisenberg, N.; et al. The added value of sentinel node mapping in endometrial cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2020, 158, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sozzi, G.; Fanfani, F.; Berretta, R.; Capozzi, V.A.; Uccella, S.; Buono, N.; Giallombardo, V.; Di Donna, M.C.; Monterossi, G.; Restaino, S.; et al. Laparoscopic sentinel node mapping with intracervical indocyanine green injection for endometrial cancer: The SENTIFAIL study—A multicentric analysis of predictors of failed mapping. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2020, 30, 1713–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tortorella, L.; Casarin, J.; Multinu, F.; Cappuccio, S.; McGree, M.E.; Weaver, A.L.; Langstraat, C.L.; Keeney, G.L.; Kumar, A.; Melis, G.B.; et al. Sentinel lymph node biopsy with cervical injection of indocyanine green in apparent early-stage endometrial cancer: Predictors of unsuccessful mapping. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 155, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, E.J.; Sinno, A.K.; Stone, R.L.; Levinson, K.L.; Long, K.C.; Fader, A.N. Factors associated with successful bilateral sentinel lymph node mapping in endometrial cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2015, 138, 542–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, A.G.; Montovano, M.; Beavis, A.; Soslow, R.A.; Zhou, Q.; Abu-Rustum, N.R.; Gardner, G.J.; Zivanovic, O.; Barakat, R.R.; Brown, C.L.; et al. Impact of Obesity on Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Uterine Cancer Undergoing Robotic Surgery. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 23, 2522–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matanes, E.; Amajoud, Z.; Kogan, L.; Mitric, C.; Ismail, S.; Raban, O.; Knigin, D.; Levin, G.; Bahoric, B.; Ferenczy, A.; et al. Is sentinel lymph node assessment useful in patients with a preoperative diagnosis of endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia? Gynecol. Oncol. 2023, 168, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matanes, E.; Eisenberg, N.; Amajoud, Z.; Gupta, V.; Yasmeen, A.; Ismail, S.; Racovitan, F.; Raban, O.; Lau, S.; Salvador, S.; et al. Sentinel Lymph Node Sampling as an Alternative to Lymphadenectomy in Patients With Endometrial Cancer and Obesity. J. Obs. Gynaecol. Can. 2021, 43, 1136–1144.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matanes, E.; Eisenberg, N.; Mitric, C.; Yasmeen, A.; Ismail, S.; Raban, O.; Cantor, T.; Knigin, D.; Lau, S.; Salvador, S.; et al. Surgical and oncological outcomes of sentinel lymph node sampling in elderly patients with intermediate to high-risk endometrial carcinoma. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2022, 32, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.K.; Kwok, S.T.; Wang, Y.; Luk, H.M.; Chan, A.H.Y.; Tse, K.Y. Applications and Safety of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Endometrial Cancer. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, M.W.; Philp, L.; Kanbergs, A.N.; Safdar, N.; Oliva, E.; Bregar, A.; Del Carmen, M.G.; Eisenhauer, E.L.; Goodman, A.; Muto, M.; et al. Lymph node assessment at the time of hysterectomy has limited clinical utility for patients with pre-cancerous endometrial lesions. Gynecol. Oncol. 2021, 162, 613–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Body, N.; Gregoire, J.; Renaud, M.C.; Sebastianelli, A.; Grondin, K.; Plante, M. Tips and tricks to improve sentinel lymph node mapping with Indocyanin green in endometrial cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2018, 150, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodurtha Smith, A.J.; Fader, A.N.; Tanner, E.J. Sentinel lymph node assessment in endometrial cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 2017, 216, 459–476.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargiu, V.; Rosati, A.; Capozzi, V.A.; Sozzi, G.; Gioe, A.; Berretta, R.; Chiantera, V.; Scambia, G.; Fanfani, F.; Cosentino, F. Impact of Obesity on Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping in Patients with apparent Early-Stage Endometrial Cancer: The ObeLyX study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2022, 165, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iavazzo, C.; Fotiou, A.; Kokkali, K.; Vorgias, G. “Iavazzo score”, a preoperative score to predict duration of robotic-assisted gynaecological surgeries. Int. J. Med. Robot. 2022, 18, e2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, L.; Cunningham, M.J. Morbid obesity increases the failure rate of sentinel lymph node mapping for endometrial carcinoma. J. Robot. Surg. 2023, 17, 2047–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dioun, S.; Chen, L.; Melamed, A.; Gockley, A.; St Clair, C.M.; Hou, J.Y.; Tergas, A.I.; Khoury-Collado, F.; Hur, C.; Hershman, D.L.; et al. Uptake and Outcomes of Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping in Women With Atypical Endometrial Hyperplasia. Obs. Gynecol. 2021, 137, 924–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calle, E.E.; Rodriguez, C.; Walker-Thurmond, K.; Thun, M.J. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of US adults. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1625–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollak, M. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor signalling in neoplasia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 915–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaaks, R.; Lukanova, A.; Kurzer, M.S. Obesity, endogenous hormones, and endometrial cancer risk: A synthetic review. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2002, 11, 1531–1543. [Google Scholar]
- Fortner, R.T.; Hüsing, A.; Kühn, T.; Konar, M.; Overvad, K.; Tjønneland, A.; Hansen, L.; Boutron-Ruault, M.-C.; Severi, G.; Fournier, A. Endometrial cancer risk prediction including serum-based biomarkers: Results from the EPIC cohort. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 140, 1317–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmandt, R.E.; Iglesias, D.A.; Co, N.N.; Lu, K.H. Understanding obesity and endometrial cancer risk: Opportunities for prevention. Am. J. Obs. Gynecol. 2011, 205, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, N.E.; Key, T.J.; Dossus, L.; Rinaldi, S.; Cust, A.; Lukanova, A.; Peeters, P.H.; Onland-Moret, N.C.; Lahmann, P.H.; Berrino, F.; et al. Endogenous sex hormones and endometrial cancer risk in women in the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC). Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2008, 15, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, K.; Macharia, A.; Furuya, R.; Manning, C.; Hacker, M.R.; Harris, D.A.; Esselen, K.; Dottino, J. Association of body mass index with early age at diagnosis of endometrial intraepithelial neoplasia. Gynecol. Oncol. 2023, 175, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Parameter | Value | Mean | Median | Min | Max | Range | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Number of Patients (n) | 115 | ||||||
| Age (years) | - | 61 | 61 | 40 | 86 | 46 | ±10 |
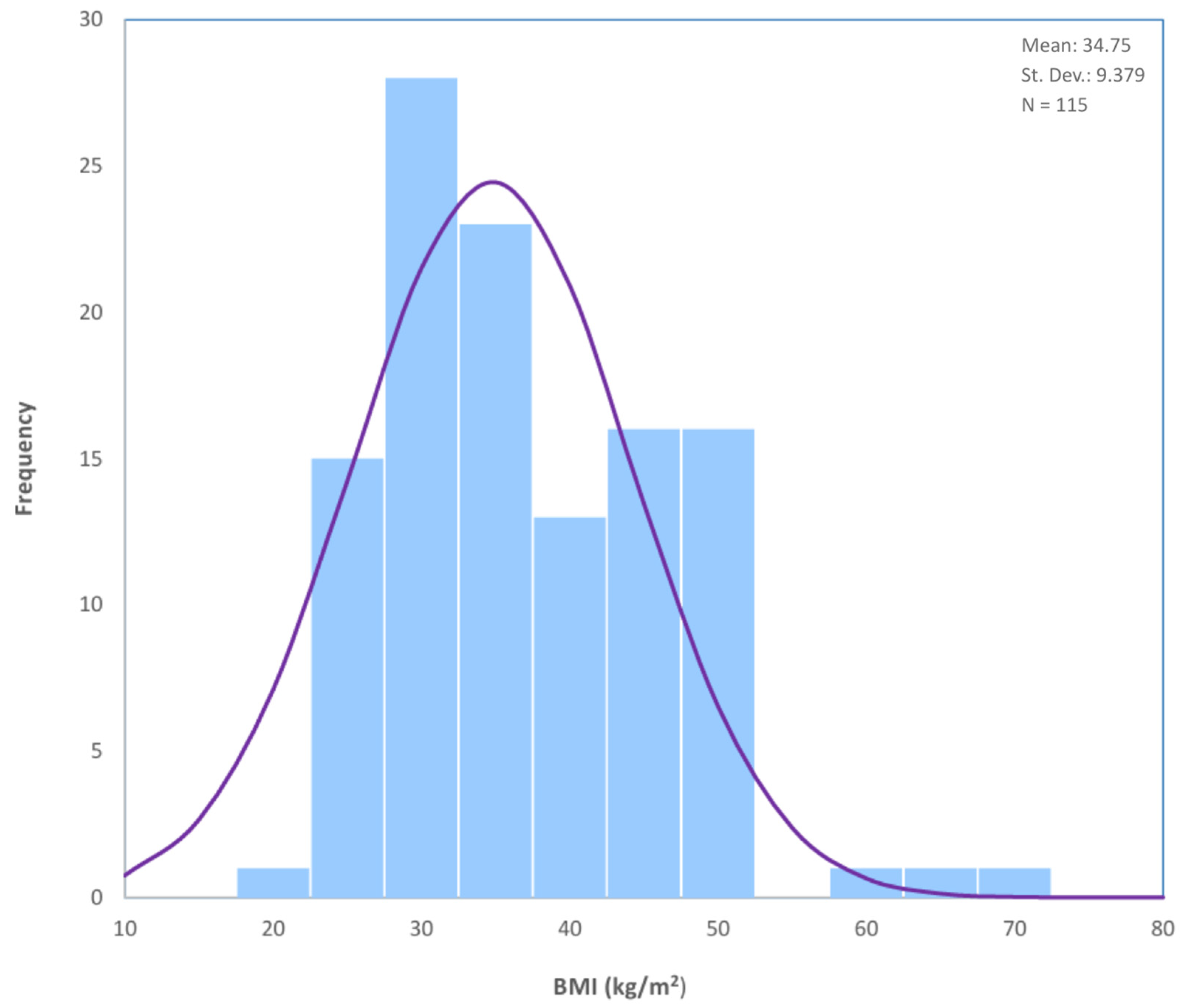
| BMI (kg/m2) | - | 34.75 | 33.0 | 18.9 | 67.0 | 48.1 | ±9.38 |
| BMI Categories (kg/m2) | |||||||
| Normal (24.9≥) | 16 (13.9%) | ||||||
| Overweight (25.0–29.9) | 25 (21.7%) | ||||||
| Obese Class I (30.0–34.9) | 25 (21.7%) | ||||||
| Obese Class II (35.0–39.9) | 12 (10.4%) | ||||||
| Obese Class III (≥40) | 37 (32.2%) | ||||||
| Diabetes Mellitus | 22 (19.3%) | ||||||
| Hypertension | 54 (47%) | ||||||
| ASA Score | |||||||
| ASA I | 20 (17.4%) | ||||||
| ASA II | 53 (46.1%) | ||||||
| ASA III | 41 (35.7%) | ||||||
| unavailable | 1 (0.9%) | ||||||
| Gravidity | |||||||
| 0 | 17 (14.8%) | ||||||
| 1 | 15 (13%) | ||||||
| 2 | 44 (38.3%) | ||||||
| 3 | 25 (21.7%) | ||||||
| >3 | 14 (12.2%) | ||||||
| Parity | |||||||
| 0 | 22 (19.1%) | ||||||
| 1 | 16 (13.9%) | ||||||
| 2 | 50 (43.5%) | ||||||
| 3 | 25 (21.7%) | ||||||
| >3 | 2 (1.8%) |
| BMI Group | Not Detected | Detected | Total | Non-Detection Rate (%) | Detection Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal (24.9≥) | 2 | 14 | 16 | 12.5 | 87.5 |
| Overweight (25.0–29.9) | 6 | 19 | 25 | 24 | 76 |
| Obese Class I (30.0–34.9) | 8 | 17 | 25 | 32 | 68 |
| Obese Class II (35.0–39.9) | 3 | 9 | 12 | 25 | 75 |
| Obese Class III (≥40) | 12 | 25 | 37 | 32.4 | 67.6 |
| Total | 31 | 84 | 115 | 27 | 73 |
| BMI Group | Not Detected | Detected | Total | Non-Detection Rate (%) | Detection Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal (24.9≥) | 0 | 16 | 16 | 0 | 100 |
| Overweight (25.0–29.9) | 1 | 24 | 25 | 4 | 96 |
| Obese Class I (30.0–34.9) | 4 | 21 | 25 | 16 | 84 |
| Obese Class II (35.0–39.9) | 1 | 11 | 12 | 8.3 | 91.7 |
| Obese Class III (≥40) | 6 | 31 | 37 | 16.2 | 83.8 |
| Total | 12 | 103 | 115 | 10.4 | 89.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bar-Noy, T.; Tzur, Y.; Brezinov, Y.; Matanes, E.; Lozano-Franco, R.; Salvador, S.; Brodeur, M.N.; Gotlieb, W.; Lau, S. Impact of Obesity on Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping in Patients with Endometrial Intraepithelial Neoplasia Undergoing Robotic Surgery: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Cancers 2025, 17, 2972. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182972
Bar-Noy T, Tzur Y, Brezinov Y, Matanes E, Lozano-Franco R, Salvador S, Brodeur MN, Gotlieb W, Lau S. Impact of Obesity on Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping in Patients with Endometrial Intraepithelial Neoplasia Undergoing Robotic Surgery: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Cancers. 2025; 17(18):2972. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182972
Chicago/Turabian StyleBar-Noy, Tomer, Yossi Tzur, Yoav Brezinov, Emad Matanes, Rebecca Lozano-Franco, Shannon Salvador, Melica Nourmoussavi Brodeur, Walter Gotlieb, and Susie Lau. 2025. "Impact of Obesity on Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping in Patients with Endometrial Intraepithelial Neoplasia Undergoing Robotic Surgery: A Retrospective Cohort Study" Cancers 17, no. 18: 2972. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182972
APA StyleBar-Noy, T., Tzur, Y., Brezinov, Y., Matanes, E., Lozano-Franco, R., Salvador, S., Brodeur, M. N., Gotlieb, W., & Lau, S. (2025). Impact of Obesity on Sentinel Lymph Node Mapping in Patients with Endometrial Intraepithelial Neoplasia Undergoing Robotic Surgery: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Cancers, 17(18), 2972. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17182972







