Elevated Likelihood of Infectious Complications Related to Oral Mucositis After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Outcomes and Risk Factors
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
- (1)
- Identify risk factors associated with OM across HSCT modalities from multivariate analyses.
- (2)
- Quantify the risk of infectious complications associated with OM.
2. Methods
2.1. Search and Screening Protocol
| Inclusion Criteria for Risk Analysis | Exclusion Criteria for Risk Analysis |
|
|
| Inclusion Criteria for Infection Outcomes | Exclusion Criteria for Infection Outcomes |
|
|
2.2. Data Extraction and Assessment of Studies
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
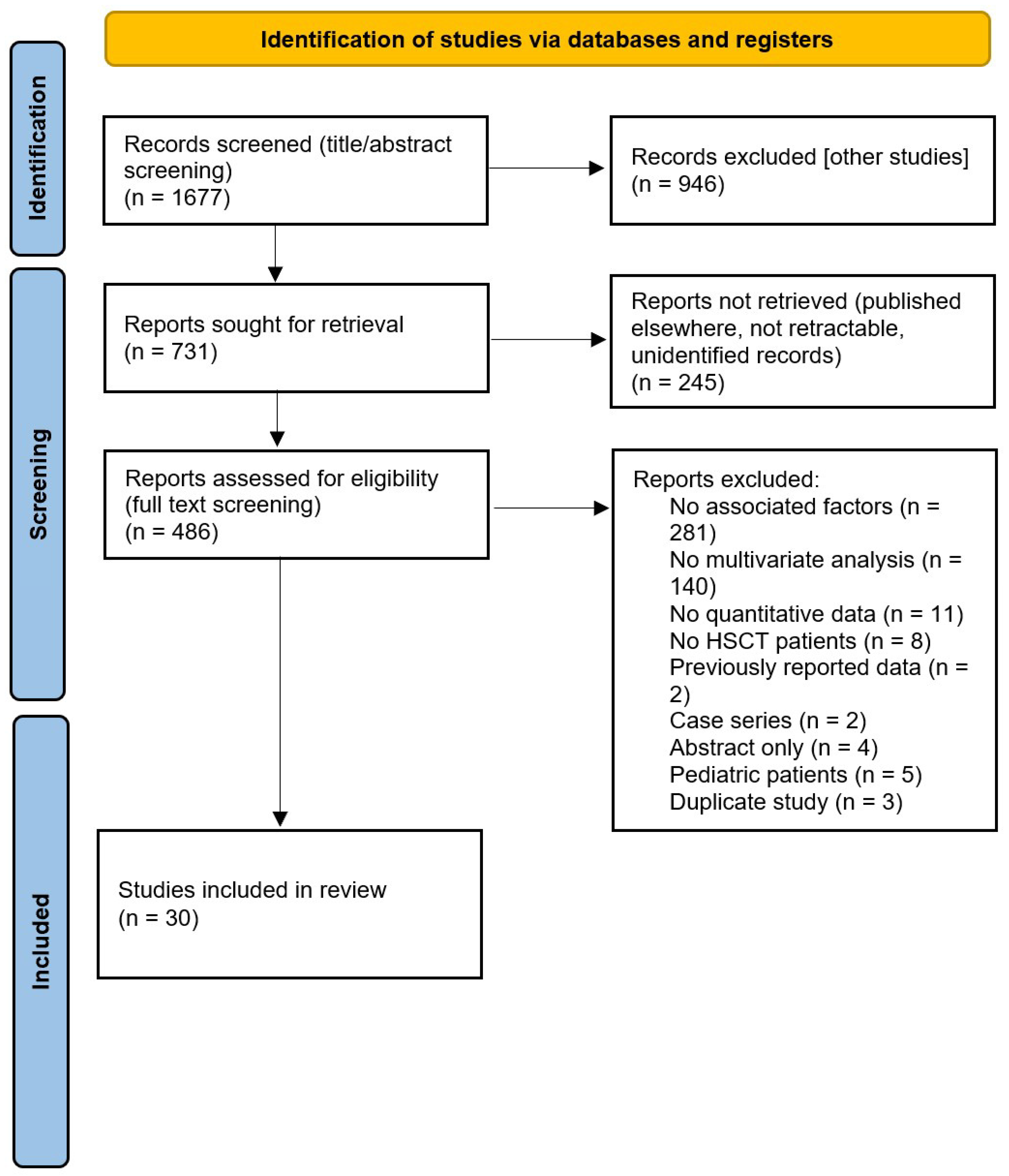
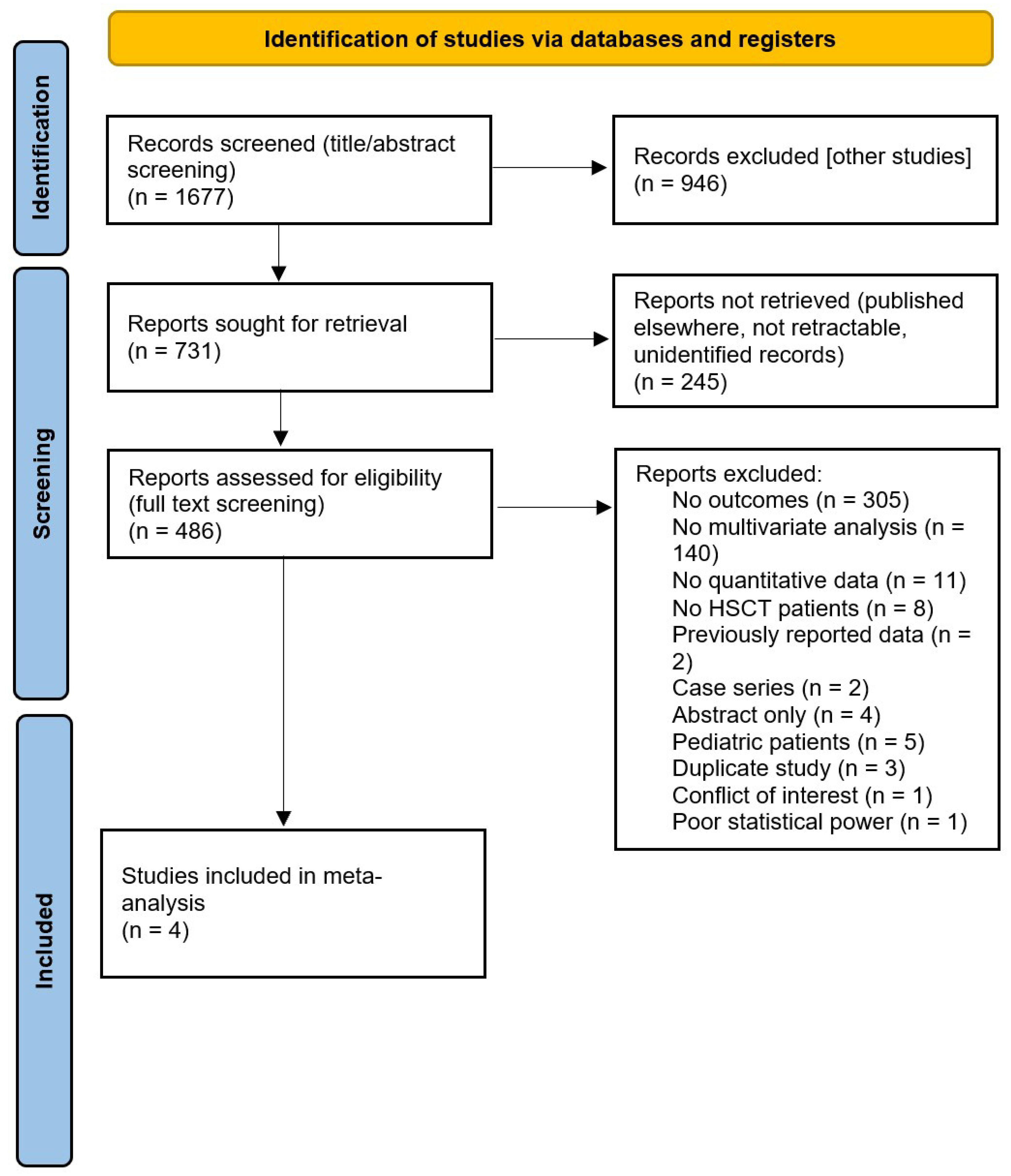
3.1. Search Results
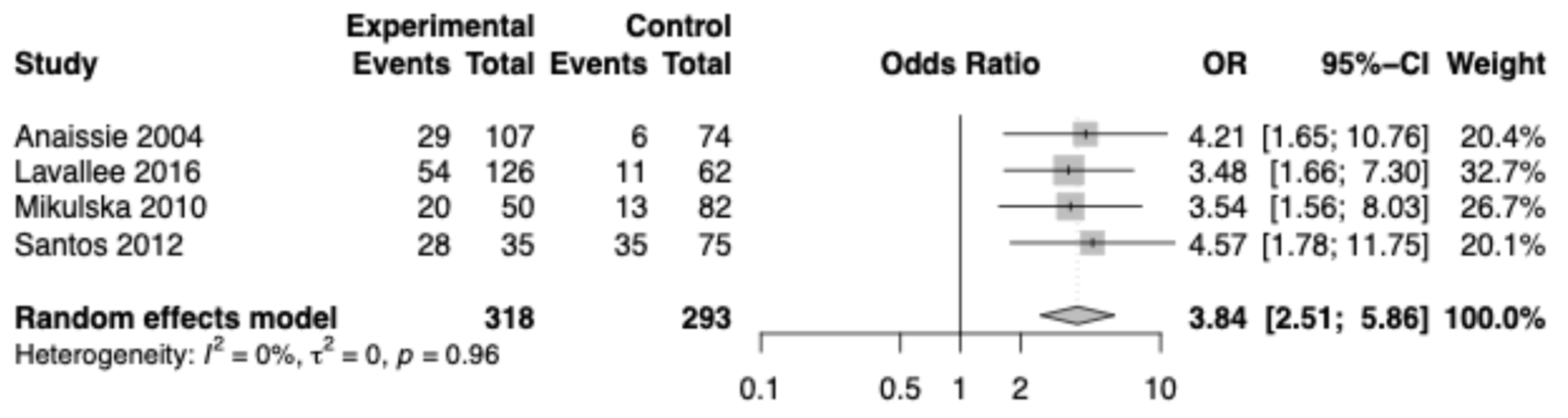
3.2. Meta-Analysis of Effect of Oral Mucositis on Developing Infectious Complications
3.3. Oral Mucositis Risk Factors Across HSCT Recipients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OM | oral mucositis |
| RCT | randomized controlled trial |
| HSCT | hematopoietic stem cell transplant |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| GVHD | graft-versus-host disease |
| HL | Hodgkin lymphoma |
| NHL | non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma |
| MAC | myeloablative conditioning |
| BEAM | BCNU, etoposide (VP-16), and cytarabine |
| BUCY(2) | busulfan and cyclophosphamide |
| CYTBI | cyclophosphamide and total body irradiation |
| FLUBU | fludarabine and busulfan |
| THIOFLUBU | thiotepa, fludarabine, and busulfan |
| RIC | reduced intensity conditioning |
| FLAMZA | fludarabine, cytarabine, and idarubicin |
| FLUCYTBI | fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and total body irradiation |
| FLUCY | fludarabine and cyclophosphamide |
| FLUTBI | fludarabine and total body irradiation |
| CTC (AE) | Common Terminology Criteria (for adverse events) |
| NCI | National Cancer Institute |
| MM | multiple myeloma |
| HSV | herpes simplex virus |
| HDM | high dose melphalan |
| RSV | respiratory syncytial virus |
| FLUMEL | fludarabine and melphalan |
| GLIM | Global Leadership Initiative on Malnutrition |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-α |
| IL-6 | Interleukin 6 |
| IL-1β | Interleukin 1β |
References
- Lalla, R.V.; Saunders, D.P.; Peterson, D.E. Chemotherapy or radiation-induced oral mucositis. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2014, 58, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curra, M.; Soares Junior, L.A.V.; Martins, M.D.; Santos, P.S.D.S. Chemotherapy protocols and incidence of oral mucositis. An integrative review. Einstein (Sao Paulo) 2018, 16, eRW4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satheeshkumar, P.S.; Blijlevens, N.; Sonis, S.T. Application of big data analyses to compare the impact of oral and gastrointestinal mucositis on risks and outcomes of febrile neutropenia and septicemia among patients hospitalized for the treatment of leukemia or multiple myeloma. Support. Care Cancer 2023, 31, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khaddour, K.; Hana, C.K.; Mewawalla, P. Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30725636/ (accessed on 23 July 2025).
- Kennedy, V.E.; Olin, R.L. Haematopoietic Stem-Cell Transplantation in Older Adults: Geriatric Assessment, Donor Considerations, and Optimization of Care. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e853–e861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorror, M.L.; Storb, R.F.; Sandmaier, B.M.; Maziarz, R.T.; Pulsipher, M.A.; Maris, M.B.; Bhatia, S.; Ostronoff, F.; Deeg, H.J.; Syrjala, K.L.; et al. Comorbidity-age index: A clinical measure of biologic age before allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 3249–3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, H.; Arıkan, F.; Çil Kazan, S.; Atay Turan, S.; Ören, R. Evaluation of the Incidence and Stage of Oral Mucositis in Patients Undergoing Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Retrospective Study. Florence Nightingale J. Nurs. 2024, 32, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Handbook for Reporting Results of Cancer Treatment; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 1979.
- Pulito, C.; Cristaudo, A.; Porta, C.; Zapperi, S.; Blandino, G.; Morrone, A.; Strano, S. Oral mucositis: The hidden side of cancer therapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elad, S.; Cheng, K.K.F.; Lalla, R.V.; Yarom, N.; Hong, C.; Logan, R.M.; Bowen, J.; Gibson, R.; Saunders, D.P.; Zadik, Y.; et al. MASCC/ISOO clinical practice guidelines for the management of mucositis secondary to cancer therapy. Cancer 2020, 126, 4423–4431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonis, S.T. The pathobiology of mucositis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balletto, E.; Mikulska, M. Bacterial Infections in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2015, 7, e2015045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Leeuwen, L.P.M.; du Toit, J.; McMillan, B.; Tadzimirwa, G.Y.; Oosthuizen, J.; Brown, K.; Doornekamp, L.; van Gorp, E.C.M.; Prentice, E.; Papavarnavas, N.S.; et al. Bloodstream Infections and Colonization in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients at a South African Center: A Retrospective Analysis. Transplant. Cell Ther. 2025, 31, 269.e1–269.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawiec, K.M.; Czemerska, M.; Stelmach, P.; Wierzbowska, A.; Pluta, A. Assessment of Colonization and Infection Epidemiology in Patients Undergoing Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Single-Center Study. Acta Haematol. Pol. 2022, 53, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, C.; Wang, Q.; Ding, Y.; Hu, X. Incidence and Risk Factors for Radiotherapy-Induced Oral Mucositis Among Patients With Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: A Meta-Analysis. Asian Nurs. Res. (Korean Soc. Nurs. Sci.) 2023, 17, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coracin, F.L.; Santos, P.S.; Gallottini, M.H.; Saboya, R.; Musqueira, P.T.; Barban, A.; Chamone, D.d.e.A.; Dulley, F.L.; Nunes, F.D. Oral health as a predictive factor for oral mucositis. Clinics 2013, 68, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardill, H.R.; Sonis, S.T.; Blijlevens, N.M.A.; Van Sebille, Y.Z.A.; Ciorba, M.A.; Loeffen, E.A.H.; Cheng, K.K.F.; Bossi, P.; Porcello, L.; Castillo, D.A.; et al. Prediction of mucositis risk secondary to cancer therapy: A systematic review of current evidence and call to action. Support. Care Cancer 2020, 28, 5059–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, E.A.; Lee, J.Y.; Erickson, S.W.; Goodwin, J.A.; Sanathkumar, N.; Raj, V.R.; Zhou, D.; McKelvey, K.D.; Apewokin, S.; Stephens, O.; et al. GWAS of 972 autologous stem cell recipients with multiple myeloma identifies 11 genetic variants associated with chemotherapy-induced oral mucositis. Support. Care Cancer 2015, 23, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhry, H.M.; Bruce, A.J.; Wolf, R.C.; Litzow, M.R.; Hogan, W.J.; Patnaik, M.S.; Kremers, W.K.; Phillips, G.L.; Hashmi, S.K. The Incidence and Severity of Oral Mucositis among Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Patients: A Systematic Review. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2016, 22, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, B.E.; Steinberg, J.R.; Weeks, B.T.; Rodriguez, F.; Cullen, M.R. Race/ethnicity reporting and representation in US clinical trials: A cohort study. Lancet Reg. Health Am. 2022, 11, 100252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daitch, V.; Turjeman, A.; Poran, I.; Tau, N.; Ayalon-Dangur, I.; Nashashibi, J.; Yahav, D.; Paul, M.; Leibovici, L. Underrepresentation of women in randomized controlled trials: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Trials 2022, 23, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, T.C.; Huang, M.S.; Lu, P.L.; Huang, S.T.; Lin, Y.C. The effect of oral care intervention on pneumonia hospitalization, Staphylococcus aureus distribution, and salivary bacterial concentration in Taiwan nursing home residents: A pilot study. BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Moher, D.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. PRISMA 2020 explanation and elaboration: Updated guidance and exemplars for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, G.; Shea, B.; O’Connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomised Studies in Meta-Analyses. Available online: https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp (accessed on 20 June 2021).
- Higgins, J.P.; Altman, D.G.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Jüni, P.; Moher, D.; Oxman, A.D.; Savovic, J.; Schulz, K.F.; Weeks, L.; Sterne, J.A. The Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d5928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anaissie, E.J.; Mahfouz, T.H.; Aslan, T.; Pouli, A.; Desikan, R.; Fassas, A.; Barlogie, B. The natural history of respiratory syncytial virus infection in cancer and transplant patients: Implications for management. Blood 2004, 103, 1611–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deveci, B.; Kublashvili, G.; Yilmaz, S.; Özcan, B.; Korkmaz, H.F.; Gürsoy, O.; Toptaş, T.; Döşemeci, L.; Saba, R. Investigation of typhlitis in bone marrow transplant patients in a stem cell transplant unit. Medicine 2022, 101, e30104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavallée, C.; Labbé, A.C.; Talbot, J.D.; Alonso, C.D.; Marr, K.A.; Cohen, S.; Laverdière, M.; Dufresne, S.F. Risk factors for the development of Clostridium difficile infection in adult allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients: A single-center study in Québec, Canada. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2017, 19, e12648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikulska, M.; Del Bono, V.; Prinapori, R.; Boni, L.; Raiola, A.M.; Gualandi, F.; Van Lint, M.T.; Dominietto, A.; Lamparelli, T.; Cappellano, P.; et al. Risk factors for enterococcal bacteremia in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2010, 12, 505–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, K.B.; Neto, A.E.; Silva, G.A.; Atalla, A.; Abreu, M.M.; Ribeiro, L.C. Infection profile of patients undergoing autologous bone marrow transplantation in a Brazilian institution. Sao Paulo Med. J. 2012, 130, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altes, A.; Remacha, A.F.; Sarda, P.; Baiget, M.; Sureda, A.; Martino, R.; Briones, J.; Brunet, S.; Canals, C.; Sierra, J. Early clinical impact of iron overload in stem cell transplantation. A prospective study. Ann. Hematol. 2007, 86, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, M.; Morgades, M.; Vives, S.; Ferrà, C.; Oriol, A.; Sancho, J.M.; Xicoy, B.; Moreno, M.; Magallón, L.; Ribera, J.M. Usefulness and safety of oral cryotherapy in the prevention of oral mucositis after conditioning regimens with high-dose melphalan for autologous stem cell transplantation for lymphoma and myeloma. Eur. J. Haematol. 2014, 93, 487–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blijlevens, N.; Schwenkglenks, M.; Bacon, P.; D’Addio, A.; Einsele, H.; Maertens, J.; Niederwieser, D.; Rabitsch, W.; Roosaar, A.; Ruutu, T.; et al. Prospective Oral Mucositis Audit: Oral Mucositis in Patients Receiving High-Dose Melphalan or BEAM Conditioning Chemotherapy—European Blood and Marrow Transplantation Mucositis Advisory Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1519–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.K.; Sborov, D.W.; Lamprecht, M.; Li, J.; Wang, J.; Hade, E.M.; Gao, Y.; Tackett, K.; Williams, N.; Benson, D.M.; et al. Associations of High-Dose Melphalan Pharmacokinetics and Outcomes in the Setting of a Randomized Cryotherapy Trial. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 102, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.K.; Hong, S.Y.; Jeon, S.J.; Namgung, H.W.; Lee, E.; Lee, E.; Bang, S.M. Efficacy of parenteral glutamine supplementation in adult hematopoietic stem cell transplantation patients. Blood Res. 2019, 54, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebri, E.; Kiss, A.; Tóth, F.; Hortobágyi, T. Female sex as an independent prognostic factor in the development of oral mucositis during autologous peripheral stem cell transplantation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gori, E.; Arpinati, M.; Bonifazi, F.; Errico, A.; Mega, A.; Alberani, F.; Sabbi, V.; Costazza, G.; Leanza, S.; Borrelli, C.; et al. Cryotherapy in the prevention of oral mucositis in patients receiving low-dose methotrexate following myeloablative allogeneic stem cell transplantation: A prospective randomized study of the Gruppo Italiano Trapianto di Midollo Osseo nurses group. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2007, 39, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grazziutti, M.L.; Dong, L.; Miceli, M.H.; Krishna, S.G.; Kiwan, E.; Syed, N.; Fassas, A.; van Rhee, F.; Klaus, H.; Barlogie, B.; et al. Oral mucositis in myeloma patients undergoing melphalan-based autologous stem cell transplantation: Incidence, risk factors and a severity predictive model. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2006, 38, 501–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Park, H.K.; Park, S.; Lee, A.; Lee, Y.H.; Shin, D.Y.; Koh, Y.; Choi, J.Y.; Yoon, S.S.; Choi, Y.; et al. Strong association between herpes simplex virus-1 and chemotherapy-induced oral mucositis in patients with hematologic malignancies. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2020, 35, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwazaki, H.; Matsushita, T.; Sugita, J.; Shigematsu, A.; Kasashi, K.; Yamazaki, Y.; Kanehira, T.; Kondo, T.; Endo, T.; Tanaka, J.; et al. A comparison of oral mucositis in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation between conventional and reduced-intensity regimens. Support. Care Cancer 2012, 20, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Wada, H.; Yamasaki, R.; Ishihara, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Ashizawa, M.; Sato, M.; Machishima, T.; Terasako, K.; Kimura, S.I.; et al. Low-dose acyclovir prophylaxis for the prevention of herpes simplex virus disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2013, 15, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laheij, A.M.; de Soet, J.J.; von dem Borne, P.A.; Kuijper, E.J.; Kraneveld, E.A.; van Loveren, C.; Raber-Durlacher, J.E. Oral bacteria and yeasts in relationship to oral ulcerations in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients. Support. Care Cancer 2012, 20, 3231–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.E.; Lim, J.Y.; Ryu, D.B.; Kim, T.W.; Jeon, Y.W.; Yoon, J.H.; Cho, B.S.; Eom, K.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, H.J.; et al. Circulating CD3+CD4+CD161+ Cells Are Associated with Early Complications after Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation in Multiple Myeloma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 5097325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.; Hong, J.; Shin, D.Y.; Koh, Y.; Yoon, S.S.; Kim, P.J.; Kim, H.G.; Kim, I.; Park, H.K.; Choi, Y. Association of HSV-1 and Reduced Oral Bacteriota Diversity with Chemotherapy-Induced Oral Mucositis in Patients Undergoing Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legert, K.G.; Tsilingaridis, G.; Remberger, M.; Ringdèn, O.; Heimdahl, A.; Yucel-Lindberg, T.; Dahllöf, G. The relationship between oral mucositis and levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in serum and in gingival crevicular fluid in allogeneic stem cell recipients. Support. Care Cancer 2015, 23, 1749–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garming Legert, K.; Ringdén, O.; Remberger, M.; Törlén, J.; Mattsson, J.; Dahllöf, G. Oral mucositis after tacrolimus/sirolimus or cyclosporine/methotrexate as graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis. Oral Dis. 2021, 27, 1217–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, C.E.; Trotman, J.; Tiley, C.; Presgrave, P.; Joshua, D.; Kerridge, I.; Kwan, Y.L.; Gurney, H.; McLachlan, A.J.; Earl, J.W.; et al. High melphalan exposure is associated with improved overall survival in myeloma patients receiving high dose melphalan and autologous transplantation. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 82, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.T.; Shayani, S.; Palmer, J.; Dagis, A.; Forman, S.J.; Epstein, J.; Spielberger, R. Palifermin for prevention of oral mucositis in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: A single-institution retrospective evaluation. Support. Care Cancer 2015, 23, 3141–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, V.; Porcher, R.; Fernandes, J.F.; Filion, A.; Bittencourt, H.; Silva, W.; Vilela, G.; Zanette, D.L.; Ferry, C.; Larghero, J.; et al. Association of drug metabolism gene polymorphisms with toxicities, graft-versus-host disease and survival after HLA-identical sibling hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for patients with leukemia. Leukemia 2009, 23, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salvador, P.T. Factors influencing the incidence and severity of oral mucositis in patients undergoing autologous stem cell transplantation. Can. Oncol. Nurs. J. 2005, 15, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shouval, R.; Kouniavski, E.; Fein, J.; Danylesko, I.; Shem-Tov, N.; Geva, M.; Yerushalmi, R.; Shimoni, A.; Nagler, A. Risk factors and implications of oral mucositis in recipients of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Eur. J. Haematol. 2019, 103, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugita, J.; Matsushita, T.; Kashiwazaki, H.; Kosugi, M.; Takahashi, S.; Wakasa, K.; Shiratori, S.; Ibata, M.; Shono, Y.; Shigematsu, A.; et al. Efficacy of folinic acid in preventing oral mucositis in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients receiving MTX as prophylaxis for GVHD. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012, 47, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeh, M.; Kargar, M.; Mansouri, A.; Kamranzadeh, H.; Gholami, K.; Heidari, K.; Hajibabaei, M. Factors Affecting the Incidence and Severity of Oral Mucositis Following Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Res. 2018, 12, 142–152. [Google Scholar]
- Amiri Khosroshahi, R.; Barkhordar, M.; Talebi, S.; Imani, H.; Sadeghi, E.; Mousavi, S.A.; Mohammadi, H. The impact of malnutrition on mortality and complications of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with acute leukemia. Clin. Nutr. 2023, 42, 2520–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursu, S.G.; Maples, S.; Williams, K.J.; Patrus, G.; Samhouri, Y.; Fazal, S.; Mewawalla, P.; Sadashiv, S. The Impact of Renal Impairment in Multiple Myeloma Patients Undergoing Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation With Melphalan Conditioning. J. Hematol. 2023, 12, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savaş, E.M.; Yegin, Z.A.; Kök, M.İ.; Karayel, H.T.; Özkurt, Z.N.; Bozer, M.N.; Çamoğlu, M.; Gülbahar, Ö. Hypomagnesemia May Predict Better Survival and Reduced Nonrelapse Mortality in Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Recipients. Transplant. Proc. 2024, 56, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.P.; Tan, S.M.; Lee, C.S.; Law, K.B.; Lim, Y.A.L.; Rajasuriar, R. Prospective longitudinal analysis of clinical and immunological risk factors associated with oral and gastrointestinal mucositis following autologous stem cell transplant in adults. Support. Care Cancer 2023, 31, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garming-Legert, K.; Tour, G.; Sugars, R.; von Bahr, L.; Davies, L.C.; Le Blanc, K. Enhanced Oral Healing Following Local Mesenchymal Stromal Cell Therapy. Oral Oncol. 2015, 51, e97–e99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oku, S.; Futatsuki, T.; Imamura, Y.; Hikita, H.; Inada, A.; Mizutani, S.; Mori, Y.; Kashiwazaki, H. Protective effect of cryotherapy against oral mucositis among allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients using melphalan-based conditioning. Support. Care Cancer 2023, 31, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lachance, S.; Bourguignon, A.; Boisjoly, J.A.; Bouchard, P.; Ahmad, I.; Bambace, N.; Bernard, L.; Cohen, S.; Delisle, J.S.; Fleury, I.; et al. Impact of Implementing a Bendamustine-Based Conditioning Regimen on Outcomes of Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation in Lymphoma while Novel Cellular Therapies Emerge. Transplant. Cell Ther. 2023, 29, 34.e1–34.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dandoy, C.E.; Kim, S.; Chen, M.; Ahn, K.W.; Ardura, M.I.; Brown, V.; Chhabra, S.; Diaz, M.A.; Dvorak, C.; Farhadfar, N.; et al. Incidence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Patients Who Develop Mucosal Barrier Injury-Laboratory Confirmed Bloodstream Infections in the First 100 Days After Allogeneic Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e1918668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satheeshkumar, P.S.; Mohan, M.P. Association and risk factors of healthcare-associated infection and burden of illness among chemotherapy-induced ulcerative mucositis patients. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin, M.G.; Bektas, H.; Özer, Z. The effect of cryotherapy on oral mucositis management in patients undergoing stem cell transplantation: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Nurs. Pract. 2023, 29, e13102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, B.K. Current approaches to prevent and treat GVHD after allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program. 2018, 2018, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, K.; Jandial, A.; Kumar, A.; Lad, D.; Prakash, G.; Khadwal, A.; Malhotra, P. Methotrexate and Mucositis: A Merry-Go-Round for Oncologists. Indian J. Med. Paediatr. Oncol. 2019, 40, 150–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waszczuk-Gajda, A.; Lewandowski, Z.; Drozd-Sokołowska, J.; Boguradzki, P.; Dybko, J.; Wróbel, T.; Basak, G.W.; Jurczyszyn, A.; Mądry, K.; Snarski, E.; et al. Autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in dialysis-dependent multiple myeloma patients-DAUTOS Study of the Polish Myeloma Study Group. Eur. J. Haematol. 2018, 101, 475–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majhail, N.S.; Farnia, S.H.; Carpenter, P.A.; Champlin, R.E.; Crawford, S.; Marks, D.I.; Omel, J.L.; Orchard, P.J.; Palmer, J.; Saber, W.; et al. Indications for Autologous and Allogeneic Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Guidelines from the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015, 21, 1863–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.D.; Verweij, J.; Rowinsky, E.K.; Donehower, R.C.; Schellens, J.H.; Grochow, L.B.; Sparreboom, A. Role of body surface area in dosing of investigational anticancer agents in adults, 1991–2001. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 1883–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazana, I.; Floro, L.; Christmas, T.; Shah, S.; Bramham, K.; Cuthill, K.; Bassett, P.; Schey, S.; Kazmi, M.; Potter, V.; et al. Autologous stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma patients with chronic kidney disease: A safe and effective option. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2022, 57, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gröber, U.; Schmidt, J.; Kisters, K. Magnesium in Prevention and Therapy. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8199–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philibert, D.; Desmeules, S.; Filion, A.; Poirier, M.; Agharazii, M. Incidence and severity of early electrolyte abnormalities following autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2008, 23, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakshith, H.T.; Lohita, S.; Rebello, A.P.; Goudanavar, P.S.; Raghavendra Naveen, N. Sex differences in drug effects and/or toxicity in oncology. Curr. Res. Pharmacol. Drug Discov. 2023, 4, 100152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliver, S.C. Sex steroids as inflammatory regulators. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2010, 120, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Reference, Year | Country | Study Design | Clinical Setting | Patient Population | Oral Mucositis Grading | Infectious Complication |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Annaissie et al., 2004 [26] | USA | Prospective cohort | University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences in Little Rock | Cancer patients undergoing HSCT (n = 190) | Not stated | RSV + with complications |
| Deveci et al., 2022 [27] | Turkey | Retrospective cohort | Medstar Antalya Hospital | Autologous and allogeneic HSCT recipients with hematologic malignancy (n = 210) | Not stated | Typhlitis |
| Lavallee et al., 2016 [28] | Canada | Case-control | A single hospital in Montreal | Allogeneic HSCT recipients with hematologic malignancy (n = 760) | NCI-CTCAE version 3.0 | Clostridium difficile + blood culture |
| Mikulska et al., 2010 [29] | Italy | Case-control | HSCT Unit of San Martino Hospital in Genoa | Allogeneic HSCT recipients with hematologic malignancy (n = 306) | WHO OM grading | Enterococcus bacteremia |
| Santos et al., 2012 [30] | Brazil | Cross-sectional | University Hospital, Universidade Federal de Juiz de Fora (UFJF) | Autologous HSCT recipients with hematologic malignancy (n = 112) | Not stated | Infection with + blood culture |
| Study | Study Design | Intervention or Exposure | Comparison | Clinical Setting | Patients | Oral Mucositis Grading | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Altes et al., 2007 [31] | Prospective cohort | Iron overload (above 75th percentile for ferritin and transferrin saturation) | Below the 75th percentile for ferritin and transferrin saturation | Not stated | HSCT recipients (n = 81) | NCI-CTCAE version 2.0 | OM (grades 0–4), bacteremia, and fever |
| Batlle et al., 2014 [32] | Retrospective cohort | Cryotherapy | No cryotherapy | Single center | MM, NHL, or HL patients who underwent autologous HSCT with HDM conditioning (n = 134) | WHO OM grading | OM (grades 1–2 and 3–4) incidence and duration |
| Blijlevens et al., 2008 [33] | Prospective cohort | HDM conditioning | BEAM conditioning | Twenty-five centers across 13 European countries | MM and NHL patients (n = 214) | WHO OM grading | OM and severe OM (grades 3–4) duration and incidence |
| Cho et al., 2017 [34] | RCT | 6 h of cryotherapy | 2 h of cryotherapy | The Ohio State University, Ohio | Autologous HSCT recipients with MM (n = 146) | WHO OM grading | OM (grades 0–1 and 2–3) |
| Cho et al., 2019 [35] | Retrospective cohort | Glutamine-supplemented total parenteral nutrition | Non-glutamine-supplemented total parenteral nutrition | Seoul National University Bundang Hospital | HSCT recipients (n = 91) | Not stated | Weight change, infections, complications (mucositis, neutropenia, GVHD), and 100-day mortality |
| Coleman et al., 2015 [18] | Retrospective cohort | Total therapy treatment protocols | Non-total therapy treatment protocols | Myeloma Institute for Research and Treatment, Arkansas | Caucasian MM patients treated with autologous HSCT and HDM (n = 972) | CTCAE version 4.0 | OM (grades 0–1 and 2–4 |
| Gebri et al., 2020 [36] | Retrospective cohort | Lymphoma (NHL and HL) diagnosis | MM diagnosis | Hematopoietic Transplantation Centre of the Clinical Centre of the University of Debrecen, Hungary | Autologous HSCT recipients with hematological malignancies (n = 192) | WHO OM grading scale | OM (grades 0–1 and 2–4) |
| Gori et al., 2007 [37] | RCT | Cryotherapy | No cryotherapy | Institute of Hematology and Medical Oncology at the University of Bologna | Allogeneic HSCT patients undergoing MAC and MTX-containing GVHD prophylaxis (n = 130) | WHO OM grading | Severe OM (grades 3–4) incidence |
| Grazziutti et al., 2006 [38] | Retrospective cohort | 200 mg melphalan dose | 140 mg melphalan dose | Myeloma Institute for Research and Treatment, Arkansas | HDM and autologous HSCT recipients with MM (n = 381) | NCI-CTCAE version 2.0 | OM and severe OM (grades 3–4) incidence |
| Hong et al., 2020 [39] | Prospective cohort | Presence of HSV-1/2 or Candida | Absence of HSV-1/2 or Candida | Seoul National University School of Dentistry | Patients with hematological malignancies receiving intensive chemotherapy or HSCT (n = 80) | WHO OM grading and NCI-CTCAE version 3.0 | OM incidence (grades 1–4), subjective discomfort |
| Kashiwazaki et al., 2012 [40] | Retrospective cohort | RIC (FLUBU, FLUMEL) | Standard regimen (TBI, CY, with or without VP-16) | Stem Cell Transplantation Center of Hokkaido University Hospital | HSCT recipients (n = 130) | NCI-CTCAE version 3.0 | OM incidence (grades 0–2 and 3–4) |
| Kawamura et al., 2013 [41] | Retrospective cohort | 1000 mg acyclovir | 200 mg acyclovir | Saitama Medical Center, Jichi Medical University | HSV-positive allogeneic HSCT recipients (n = 93) | Bearman scoring system | OM (grades 0–1 and 2–4) and HSV disease |
| Laheij et al., 2012 [42] | Prospective cohort | Presence of bacterial and Candida species | No presence of bacterial and Candida species | Leiden University Medical Center | HSCT patients with hematological malignancies (n = 49) | WHO OM grading | Ulcerative OM (grades 2–4) incidence |
| Lee et al., 2018 [43] | Prospective cohort | CD161 + T cells > 3.72% | CD161 + T cells ≤ 3.72% | One hospital in Korea | Autologous HSCT recipients with MM (n = 108) | NCI-CTC | OM (grades 1–2 and 3–4), infection, and cytomegalovirus reactivation |
| Lee et al., 2020 [44] | Prospective cohort | Autologous HSCT patients | Healthy volunteers | Seoul National University School of Dentistry | Adults who received oral examination (n = 61) | NCI-CTCAE version 3.0 and OM assessment scale | OM incidence (grades 0–4), HSV-1 detection, Candida detection, bacterial diversity |
| Legert et al., 2015 [45] | Prospective cohort | MAC (BUCY or CYTBI) | RIC (FLUBU, FLUCY, FLUTBI, FLUCYTBI, or CY) | Karolinska University Hospital, Huddinge, Sweden | Patients scheduled for HSCT (n = 77) | WHO OM grading | OM (grades 1–2 and 3–4) and serum and gingival crevicular fluid cytokine levels |
| Legert et al., 2021 [46] | RCT | Tacrolimus/Sirolimus | Cyclosporine/Methotrexate (standard regimen) | Two centers in Stockholm, Sweden, and Turku, Finland | Patients scheduled to receive allogeneic HSCT (n = 215) | OM assessment scale and WHO OM grading scale | NIH grade II-IV GVHD, OM (grades 0–1 and 2–4) |
| Nath et al., 2016 [47] | Prospective cohort | High melphalan dose (≥12.84 mg/hr) | Low melphalan dose (<12.84 mg/hr) | Six hospitals in the Autologous Working Party of BMT Network NSW, Australia | Autologous HSCT and HDM (n = 114) | NCI-CTCAE version 3.0 | Severe OM (grades 3–4), time to progression, progression-free survival, and overall survival |
| Nguyen et al., 2015 [48] | Retrospective cohort | Palifermin | Historical control (no palifermin instituted) | City of Hope National Medical Center | Allogeneic HSCT recipients with hematological malignancies conditioned with full TBI and etoposide (n = 129) | NCI-CTCAE version 2.0 | OM (grades 1–2 and 3–4) incidence |
| Rocha et al., 2009 [49] | Retrospective cohort | Presence of genetic polymorphisms | Absence of genetic polymorphisms | Hospital Saint Louis | Allogeneic HSCT recipients with leukemia (n = 107) | Research grading system | OM, hemorrhagic cystitis, liver toxicity, veno-occlusive disease, GVHD, and mortality |
| Salvador et al., 2005 [50] | Retrospective cohort | Primary prevention (before symptomatic OM) | Secondary prevention (after symptomatic OM) | University hospital in southern Ontario, Canada | Autologous HSCT recipients with MM, HL, or NHL (n = 140) | WHO OM grading | OM (grades 0–1 and 2–4) onset, incidence, and duration |
| Shouval et al., 2019 [51] | Retrospective cohort | MAC (BEAM, BUCY, CYTBI, FLUBU4, THIOFLUBU3) | RIC (FLAMZA, FLUBU2, FLUCYTBI, THIOFLUBU2) and Reduced Toxicity Conditioning (fludarabine and treosulfan) | Chaim Sheba Medical Center in Tel-Hashomer, Israel | Allogeneic HSCT recipients with hematological malignancies (n = 115) | CTCAE version 4.0 | OM (grades 0–1 and 2–4) |
| Sugita et al., 2012 [52] | Retrospective cohort | Folinic acid (administered to high-risk patients) | No folinic acid | Hokkaido University Hospital, Japan | Allogeneic HSCT and MTX recipients (n = 141) | NCI-CTCAE version 3.0 | OM (grades 1–2 and 3–4) incidence |
| Valeh et al., 2018 [53] | Prospective cohort | Allogeneic HSCT | Autologous HSCT | Hematology-Oncology and Stem Cell Transplantation Research Centre, Shariati Hospital, Tehran University of Medical Sciences | HSCT recipients (n = 173) | WHO OM grading | OM (grades 1–2 and 3–4) incidence and duration |
| Ursu et al., 2023 [55] | Retrospective cohort | Chronic kidney disease (Creatinine clearance less than 60 mL/min) | No chronic kidney disease (creatinine clearance greater than 60 mL/min) | Allegheny Health Network Cancer Institute | MM, who underwent autologous HSCT (n = 124) | NCI-CTCAE version 5.0 | OM (grades 3 or 4) incidence |
| Khosroshahi et al., 2023 [54] | Prospective cohort | Presence of malnutrition based on GLIM criteria | Absence of malnutrition based on GLIM criteria | Hematology Center of Shariati Hospital in Tehran, Iran | Allogeneic HSCT recipients (n = 98) | WHO OM grading | OM (grades 2–4) incidence |
| Saori Oku et al., 2023 [59] | Retrospective cohort | Oral cryotherapy | No oral cryotherapy | Kyushu University Hospital, Japan | Allogeneic HSCT recipients (n = 78) | NCI-CTCAE version 3.0 | OM (grades 1–3) incidence and duration |
| Wong et al., 2022 [57] | Prospective cohort | Presence of increasing inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β) in saliva and plasma | Absence of inflammatory cytokines in saliva and plasma | Ampang Hospital, Malaysia | Autologous HSCT recipients (n = 142) | WHO OM grading | OM (grades 1–4) incidence and duration |
| Lachance et al., 2023 [60] | Retrospective cohort | Bendamustine-based conditioning regimen | Carmustine-based conditioning regimen | Maisonneuve-Rosemont Hospital in Montreal, Quebec, Canada | Autologous HSCT recipients (n = 227) | Not stated | OM (grades 1–4) incidence |
| Merve Savaş et al., 2024 [56] | Retrospective cohort | Hypomagenesmia | Normal magnesium levels | Gazi University, Department of Hematology, Ankara, Turkey | Allogeneic HSCT recipients (n = 340) | NCI-CTCAE version 4.0 | OM (grades 1–4) incidence |
| Variable | Study | Risk Estimate for OM |
|---|---|---|
| Baseline patient characteristics | ||
| Age | Kashiwazaki et al., 2012 [40] | Age < 40 years: OR = 5.6 [1.9–16.5] |
| Sex | Garming Legert et al., 2021 [46] Gebri et al., 2020 [36] Lee et al., 2018 [43] Valeh et al., 2018 [53] Hong et al., 2020 [39] Ursu et al., 2023 [55] | Female sex: OR = 2.50 [1.15–5.42] Female sex: OR = 2.301 [1.124–4.714] Female sex: RR = 6.39 [1.74–29.71] Female sex: OR = 2.33 Female sex: OR = 0.221 [0.093–0.52] Female sex: OR = 4.2 [1.1–16.4] |
| HSV-1 presence | Hong et al., 2020 [39] Lee et al., 2020 [43] | OR = 7.660 [2.762–21.242] OR = 3.668 [1.512–8.895] |
| Renal function | Nath et al., 2016 [47] Lee et al., 2018 [43] Salvador et al., 2005 [50] Grazziutti et al., 2006 [38] Ursu et al., 2023 [55] | Beta-2 microglobulin: HR = 1.257 [1.035–1.528] GFR: RR = 0.98 [0.97–1.00] Peak Cr: Beta coefficient = 0.0283 Serum Cr: OR = 1.581 [1.080–2.313] CKD: OR = 8.2 [1.4–47.2] |
| Functional status | Blijlevens et al., 2008 [33] | ECOG performance: OR = 1.8 [1.1–2.8] |
| Immune status | Lee et al., 2018 [43] | Presence of CD3+CD4+CD161+ cells: RR = 0.19 [0.04–0.73] |
| Nutritional status | Khosroshahi et al., 2023 [54] | Presence of malnutrition based on GLIM criteria: OR = 1.39 [0.45–4.27] |
| Genetics | Rocha et al., 2009 [49] Coleman et al., 2015 [18] | CYP2B6*4 polymorphism: OR = 3.03 [1.37–6.73] CPEB1/LINC00692 (3p24.2) rs1426765 AA genotype: OR = 0.45 [0.32–0.65] FBN2 (5q23-q31) rs10072361 AA genotype: OR = 1.80 [1.29–2.51] FBN2 (5q23-q31) rs10072361 AG genotype: OR = 6.42 [2.16–19.07] FBN2 (5q23-q31) rs10072361 GG genotype: OR = 3.56 [1.18–10.81] ALDH1A1 (9q21.13) rs1469167 AA genotype: OR = 0.36 [0.22–0.58] DMTRA1/FLJ35282 (9p21.3) rs62572481 CC genotype: OR = 0.32 [0.18–0.58] DMTRA1/FLJ35282 (9p21.3) rs62572531 TT genotype: OR = 3.26 [1.81–5.84] MMP13 (11q22.3) rs1940228 AA genotype: OR = 0.27 [0.13–0.56] MMP13 (11q22.3) rs948695 AA genotype: OR = 0.25 [0.12–0.49] JPH3 (16q24.3) rs4843257 AA genotype: OR = 1.55 [1.08–2.21] JPH3 (16q24.3) rs4843257 AG genotype: OR = 2.56 [1.70–3.84] JPH3 (16q24.3) rs4843257 GG genotype: OR = 1.66 [1.17–2.34] DHRS7C (17p13.1) rs11078818 AG genotype: OR = 2.58 [1.11–5.98] DHRS7C (17p13.1) rs11078818 GG genotype: OR = 1.88 [1.37–2.60] CEP192 (18p11.21) rs12606033 GG genotype: OR = 1.97 [1.41–2.77] |
| Laboratory results | ||
| Ferritin level | Altes et al., 2007 [31] | RR = 3.4 [1.1–10] |
| Duration of neutropenia | Kashiwazaki et al., 2012 [40] Sugita et al., 2012 [52] Gebri et al., 2020 [36] | OR = 12.4 [1.4–109] OR = 4.78 [1.77–13.90] OR = 1.492 [1.228–1.813] |
| Oral microbiota | Laheij et al., 2012 [42] | Presence of P. gingivalis (non-keratinized mucosal involvement): beta coefficient = 3.36 Presence of C. kefyr (non-keratinized mucosal involvement): beta coefficient = 2.01 Load of P. gingivalis (non-keratinized mucosal involvement): beta coefficient = 1.37 Load of C. kefyr (non-keratinized mucosal involvement): beta coefficient = 2.056 Percentage of P. gingivalis (non-keratinized mucosal involvement): beta coefficient = 1.372 Percentage of P. micra (non-keratinized mucosal involvement): beta coefficient = 0.00 Percentage of F. nucleatum (non-keratinized mucosal involvement): beta coefficient = 1.58 Percentage of T. denticola (non-keratinized mucosal involvement): beta coefficient = 0.87 Percentage of C. glabrata (non-keratinized mucosal involvement): beta coefficient = 3.49 Presence of P. gingivalis (keratinized mucosal involvement): beta coefficient = 4.38 Presence of P. micra (keratinized mucosal involvement): beta coefficient = 0.46 Load of P. gingivalis (keratinized mucosal involvement): beta coefficient = 0.75 Load of C. kefyr (keratinized mucosal involvement): beta coefficient = 1.83 |
| Serum magnesium level | Merve Savaş et al., 2024 [56] | Serum magnesium less than 1.33 mg/dL: HR = 0.380 [0.161–0.896] |
| Inflammatory cytokines in saliva and plasma | Wong et al., 2022 [57] | Increase in plasma IL-6 by 10 pg/mL: OR = 1.01 [1.001–1.004] Increase in saliva IL-6 by 100 pg/mL: OR = 1.003 [1.001–1.004] Reduction in plasma TNF-⍺ by 10 pg/mL: OR = 0.91 [0.85–0.99] |
| Cancer treatment and conditioning regimens | ||
| Chemotherapy | Salvador et al., 2005 [50] Batlle et al., 2014 [32] | NHL regimen vs. HL regimen: beta coefficient = 1.4712 ≥2 treatment lines before HSCT: OR = 3.103 [1.035–9.300] |
| HSCT modality | Cho et al., 2019 [35] | Autologous HSCT: beta coefficient = 0.38 |
| Conditioning regimen | Blijlevens et al., 2008 [33] Cho et al., 2017 [34] Grazziutti et al., 2006 [38] Nath et al., 2016 [47] Batlle et al., 2014 [32] Gori et al., 2007 [37] Cho et al., 2019 [35] Kawamura et al., 2013 [41] Garming Legert et al., 2015 [45] Garming Legert et al., 2021 [46] Shouval et al., 2019 [51] Saori Oku et al., 2023 [59] Wong et al., 2022 [57] Lachance et al., 2022 [60] | HDM: OR = 2.6 [1.6–4.4] High dose carmustine: OR = 1.9 [1.3–2.6] HDM: RR = 1.21 [1.04–1.41] HDM: OR = 1.595 [1.065–2.389] HDM: HR = 1.213 [1.064–1.382] Use of BEAM: OR = 3.633 [1.181–11.176] TBI: RR = 3.2 [1.4–7.6] MAC: Beta coefficient = 1.11 [0.295–4.18] MAC: OR = 7.22 [2.66–19.50] MAC: OR = 1.37 [1.03–1.82] Reduced intensity conditioning: OR = 0.18 [0.06–0.56] Reduced intensity conditioning: RR = 0.04 [0.01–0.17] HDM: OR = 3.82 [1.085–13.46] BEAM or busulphan based regimen: OR = 9.2 [1.16–72.9] Bendamustine based conditioning regimen: HR = 2.946 [1.19–7.27] |
| Methotrexate use | Nguyen et al., 2015 [48] Shouval et al., 2019 [51] Saori Oku et al., 2023 [59] | OR = 3.21 [1.38–7.46] RR = 3.53 [ 1.15–10.81] OR = 7.61 [2.41–23.97] |
| OM prophylaxis | ||
| Folinic acid | Sugita et al., 2012 [52] Gori et al., 2007 [37] | Use of folinic acid: OR = 0.13 [0.04–0.73] Lack of folinic acid: RR = 2.6 [1.2–5.7] |
| Cryotherapy | Batlle et al., 2014 [32] | Lack of cryotherapy: OR = 8.345 [3.342–20.837] |
| Prophylaxis | Valeh et al., 2018 [53] Salvador et al., 2005 [50] | Use of prophylaxis: OR = 0.47 Primary prevention vs. secondary prevention: Beta coefficient = 0.9356 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eichhorn, S.; Rudin, L.; Ramasamy, C.; Varsani, R.; Padhi, P.; Nassour, N.; Meleveedu, K.; Epstein, J.B.; Semegran, B.; Pili, R.; et al. Elevated Likelihood of Infectious Complications Related to Oral Mucositis After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Outcomes and Risk Factors. Cancers 2025, 17, 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162657
Eichhorn S, Rudin L, Ramasamy C, Varsani R, Padhi P, Nassour N, Meleveedu K, Epstein JB, Semegran B, Pili R, et al. Elevated Likelihood of Infectious Complications Related to Oral Mucositis After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Outcomes and Risk Factors. Cancers. 2025; 17(16):2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162657
Chicago/Turabian StyleEichhorn, Susan, Lauryn Rudin, Chidambaram Ramasamy, Ridham Varsani, Parikshit Padhi, Nour Nassour, Kapil Meleveedu, Joel B. Epstein, Benjamin Semegran, Roberto Pili, and et al. 2025. "Elevated Likelihood of Infectious Complications Related to Oral Mucositis After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Outcomes and Risk Factors" Cancers 17, no. 16: 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162657
APA StyleEichhorn, S., Rudin, L., Ramasamy, C., Varsani, R., Padhi, P., Nassour, N., Meleveedu, K., Epstein, J. B., Semegran, B., Pili, R., & Satheeshkumar, P. S. (2025). Elevated Likelihood of Infectious Complications Related to Oral Mucositis After Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Outcomes and Risk Factors. Cancers, 17(16), 2657. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162657