A Decision-Making Method for Photon/Proton Selection for Nasopharyngeal Cancer Based on Dose Prediction and NTCP
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patient Selection and Plan
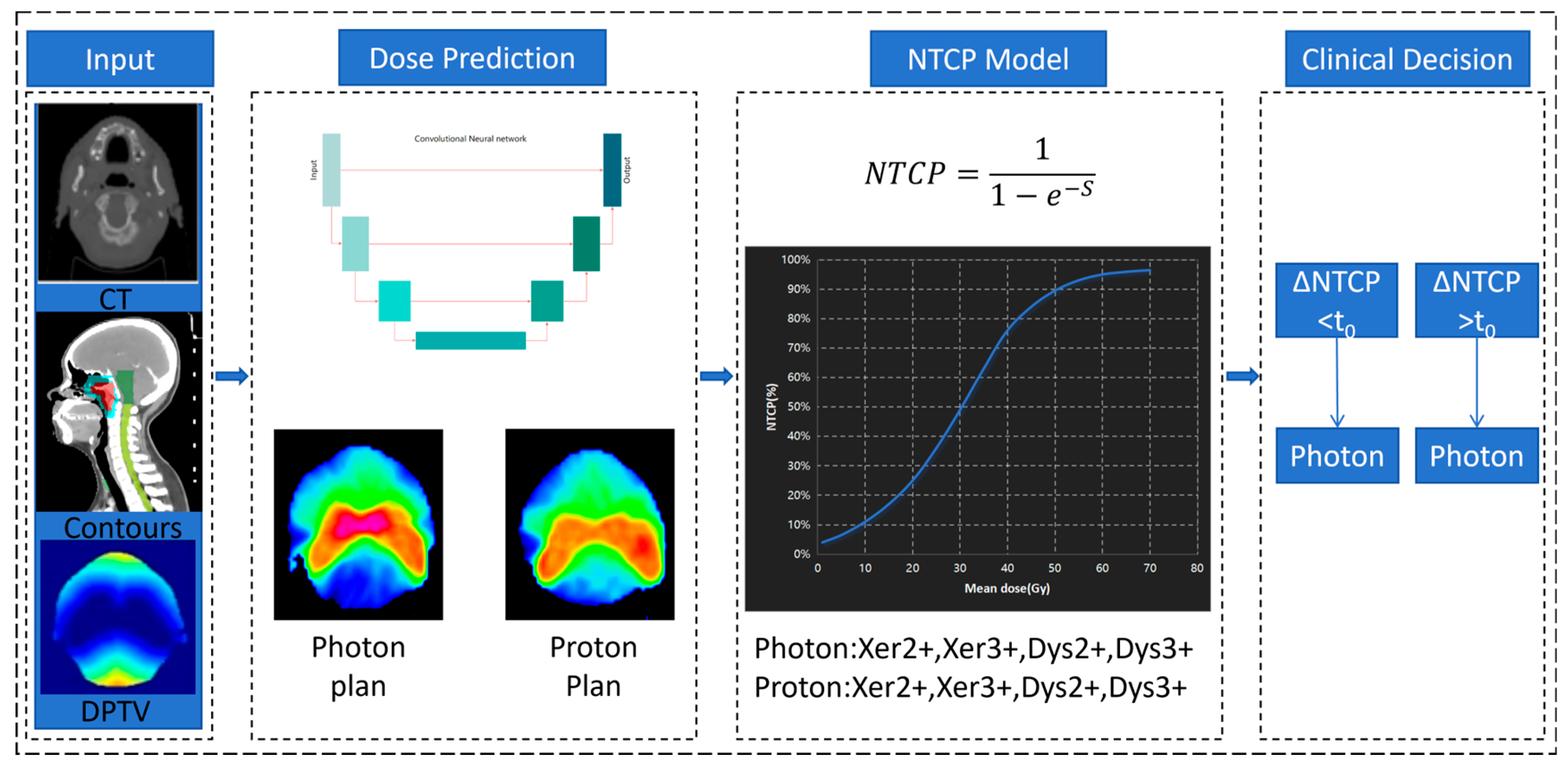
2.2. Workflow of Decision-Making Method
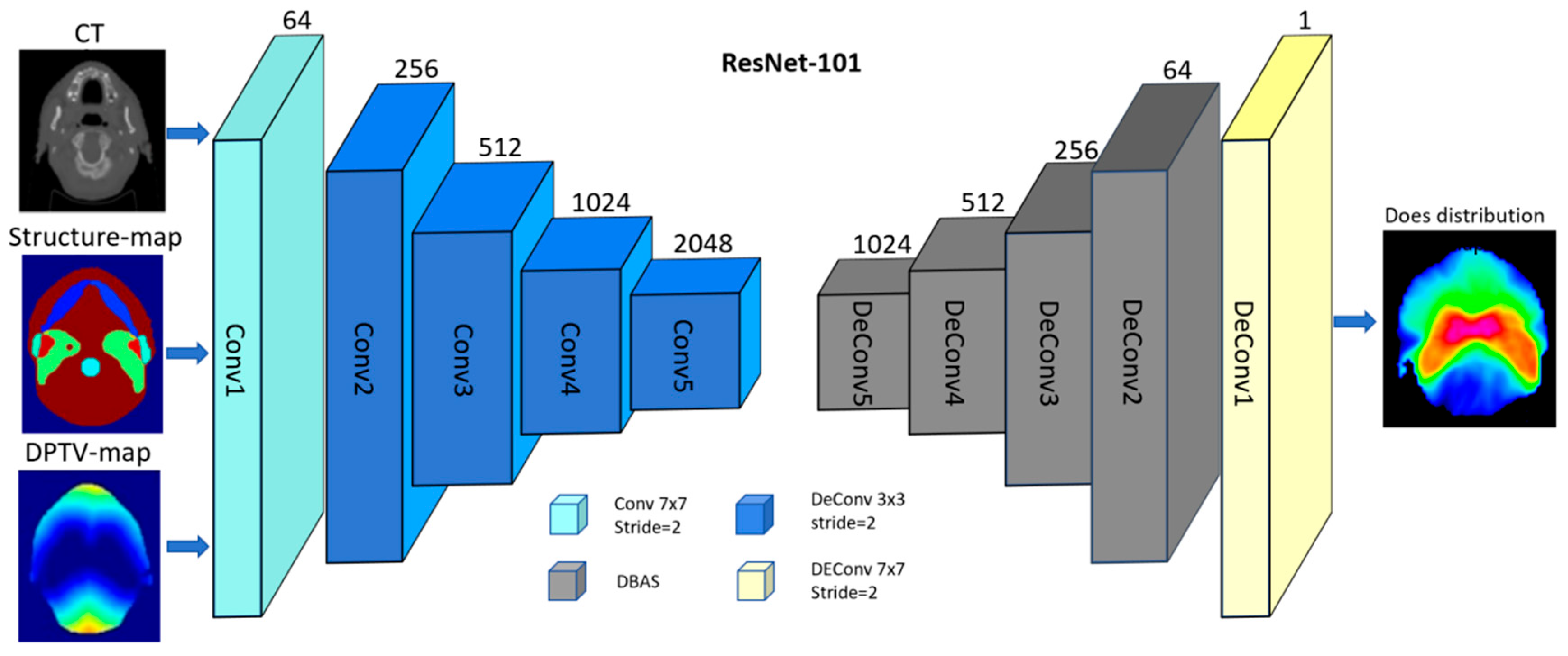
2.3. Deep Learning-Based Dose Prediction Method
2.4. NTCP Modeling
2.5. Decision-Making
2.6. Performance Evaluation
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
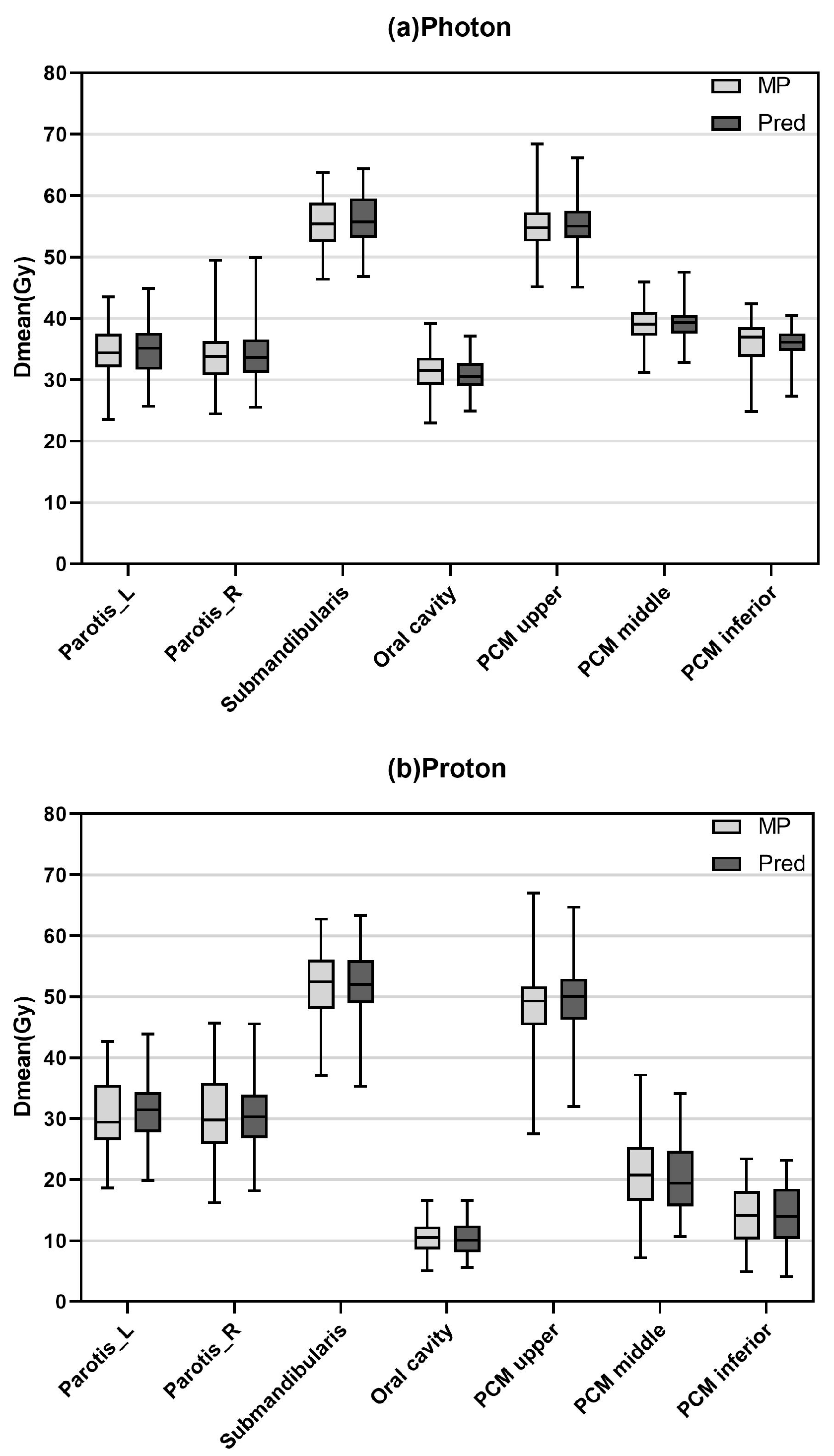
3.1. Dose Prediction Accuracy
3.2. NTCP Modeling Accuracy
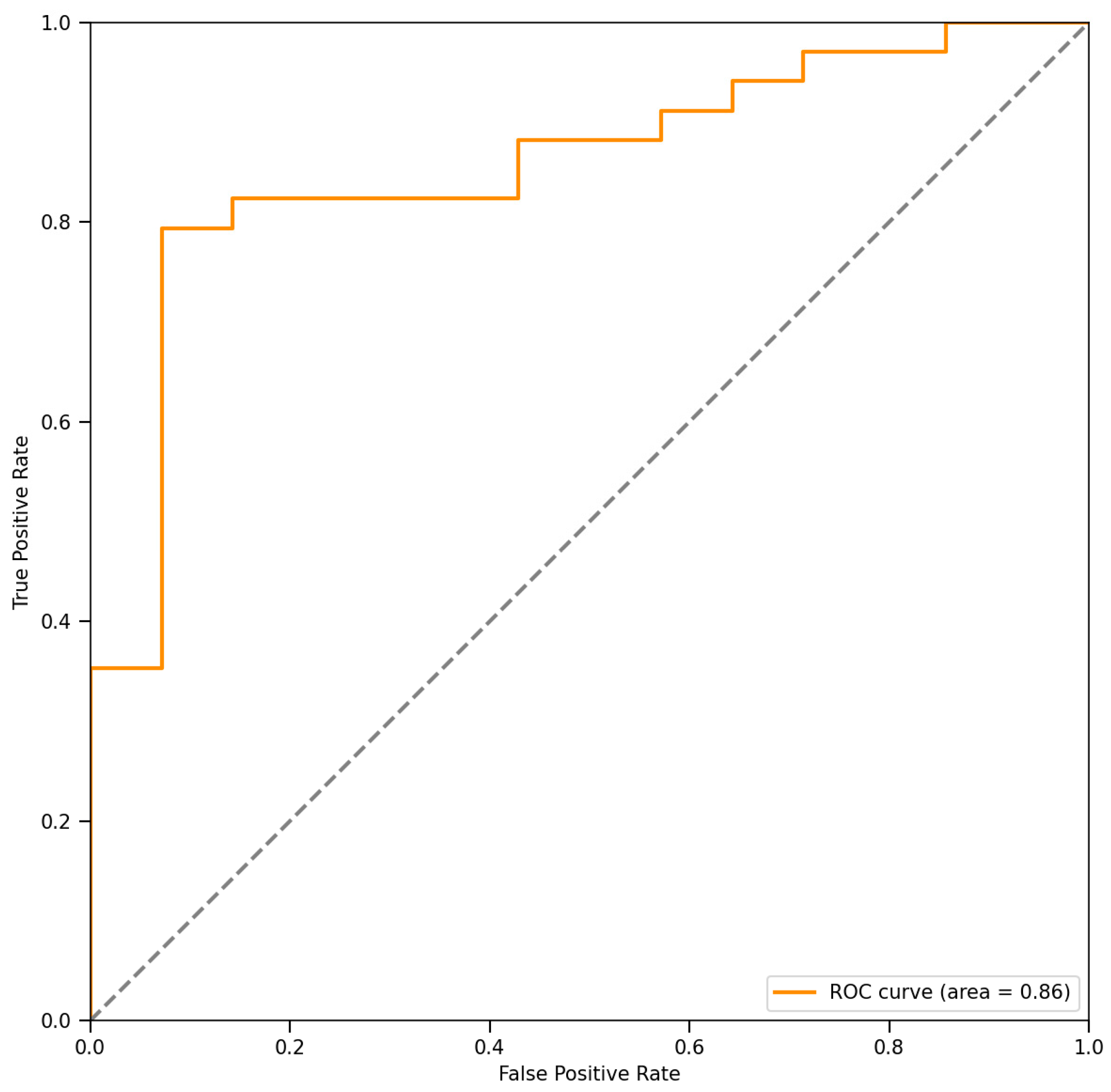
3.3. Decision-Making Accuracy
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| XT | photon therapy |
| PT | proton therapy |
| NIPP | Netherlands’s National Indication Protocol Proton therapy |
| NCC | convolutional neural network |
| DL | deep learning |
| NTCP | normal tissue complication probability |
| RT | radiation therapy |
| IMRT | intensity-modulated radiation therapy |
| VMAT | volumetric modulated arc therapy |
| IMPT | intensity-modulated proton therapy |
| OAR | organs at risk |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| NPC | nasopharyngeal carcinoma |
| TPS | treatment planning system |
| PMC U | pharyngeal constrictor muscles upper |
| PMC M | pharyngeal constrictor muscles middle |
| PMC I | pharyngeal constrictor muscles inferior |
| DPTV | contours and distance map |
| COM | combined model |
| PL | parotid left |
| PR | parotid right |
| OC | oral cavity |
| MP | manual plan |
| MAE | mean absolute error |
| Dmean | mean dose |
| AUC | area under curve |
| ROC | operating characteristic curve |
| Xer2+ | xerostomia ≥ grade 2 |
| Xer3+ | xerostomia ≥ grade 3 |
| Dys2+ | dysphagia ≥ grade 2 |
| Dys3+ | dysphagia ≥ grade 3 |
References
- Tang, L.L.; Chen, W.Q.; Xue, W.Q.; He, Y.Q.; Zheng, R.S.; Zeng, Y.X.; Jia, W.H. Global trends in incidence and mortality of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2016, 374, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busson, P. Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Keys for Translational Medicine and Biology. In Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 778, pp. 7–8. [Google Scholar]
- Scandurra, D.; Meijer, T.W.; Free, J.; van den Hoek, J.G.; Kelder, L.; Oldehinkel, E.; Steenbakkers, R.J.; Both, S.; Langendijk, J.A. Evaluation of robustly optimised intensity modulated proton therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 168, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Riaz, N.; Cheng, S.K.; Lu, J.J.; Lee, N.Y. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A review. J. Radiat. Oncol. 2012, 1, 129–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.T.; Corry, J.; Langendijk, J.A.; Lee, A.W.M.; Mäkitie, A.; Mendenhall, W.M.; Rinaldo, A.; Rodrigo, J.P.; Saba, N.F.; Smee, R.; et al. Current management of stage IV nasopharyngeal carcinoma without distant metastasis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2020, 85, 101995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langendijk, J.A.; Doornaert, P.; Verdonck-de Leeuw, I.M.; Leemans, C.R.; Aaronson, N.K.; Slotman, B.J. Impact of late treatment-related toxicity on quality of life among patients with head and neck cancer treated with radiotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 3770–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Han, F.; Xiao, W.; Xiang, Y.; Lu, L.; Deng, X.; Cui, N.; Zhao, C. Analysis of late toxicity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with intensity modulated radiation therapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.L.; Chien, C.Y.; Tsai, W.L.; Liao, K.C.; Chou, S.Y.; Lin, H.C.; Dean Luo, S.; Lee, T.F.; Lee, C.H.; Fang, F.M. Long-term late toxicities and quality of life for survivors of nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with intensity-modulated radiotherapy versus non-intensity-modulated radiotherapy. Head Neck 2016, 38 (Suppl. 1), E1026–E1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.R.; Liu, Y.T.; Jiang, N.; Fan, Y.X.; Wen, J.; Huang, S.F.; Guo, W.J.; Bian, X.H.; Wang, F.J.; Li, F.; et al. Ten-year survival outcomes for patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma receiving intensity-modulated radiotherapy: An analysis of 614 patients from a single center. Oral Oncol. 2017, 69, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Au, K.H.; Ngan, R.K.C.; Ng, A.W.Y.; Poon, D.M.C.; Ng, W.T.; Yuen, K.T.; Lee, V.H.F.; Tung, S.Y.; Chan, A.T.C.; Sze, H.C.K.; et al. Treatment outcomes of nasopharyngeal carcinoma in modern era after intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT) in Hong Kong: A report of 3328 patients (HKNPCSG 1301 study). Oral Oncol. 2018, 77, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langendijk, J.A.; Lambin, P.; De Ruysscher, D.; Widder, J.; Bos, M.; Verheij, M. Selection of patients for radiotherapy with protons aiming at reduction of side effects: The model-based approach. Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 107, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minatogawa, H.; Yasuda, K.; Dekura, Y.; Takao, S.; Matsuura, T.; Yoshimura, T.; Suzuki, R.; Yokota, I.; Fujima, N.; Onimaru, R.; et al. Potential benefits of adaptive intensity-modulated proton therapy in nasopharyngeal carcinomas. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2021, 22, 174–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vai, A.; Molinelli, S.; Rossi, E.; Iacovelli, N.A.; Magro, G.; Cavallo, A.; Pignoli, E.; Rancati, T.; Mirandola, A.; Russo, S.; et al. Proton Radiation Therapy for Nasopharyngeal Cancer Patients: Dosimetric and NTCP Evaluation Supporting Clinical Decision. Cancers 2022, 14, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landelijk Platform Protonentherapie (LPPT). Landelijk Indicatie Protocol Protonentherapie Hoofdhals Versie 2.2; Landelijk Platform Protonentherapie (LPPT): Almere, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Mirandola, A.; Russo, S.; Bonora, M.; Vischioni, B.; Camarda, A.M.; Ingargiola, R.; Molinelli, S.; Ronchi, S.; Rossi, E.; Vai, A.; et al. A Patient Selection Approach Based on NTCP Models and DVH Parameters for Definitive Proton Therapy in Locally Advanced Sinonasal Cancer Patients. Cancers 2022, 14, 2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tambas, M.; van der Laan, H.P.; van der Schaaf, A.; Steenbakkers, R.J.H.M.; Langendijk, J.A. A Decision Support Tool to Optimize Selection of Head and Neck Cancer Patients for Proton Therapy. Cancers 2022, 14, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teoh, S.; Fiorini, F.; George, B.; Vallis, K.A.; Van den Heuvel, F. Proton vs photon: A model-based approach to patient selection for reduction of cardiac toxicity in locally advanced lung cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2020, 152, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stick, L.B.; Jensen, M.F.; Bentzen, S.M.; Kamby, C.; Lundgaard, A.Y.; Maraldo, M.V.; Offersen, B.V.; Yu, J.; Vogelius, I.R. Radiation-Induced Toxicity Risks in Photon Versus Proton Therapy for Synchronous Bilateral Breast Cancer. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2022, 8, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draguet, C.; Barragán-Montero, A.M.; Vera, M.C.; Thomas, M.; Populaire, P.; Defraene, G.; Haustermans, K.; Lee, J.A.; Sterpin, E. Automated clinical decision support system with deep learning dose prediction and NTCP models to evaluate treatment complications in patients with esophageal cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2022, 176, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeuwenberg, A.M.; Reitsma, J.B.; Van den Bosch, L.G.L.J.; Hoogland, J.; van der Schaaf, A.; Hoebers, F.J.P.; Wijers, O.B.; Langendijk, J.A.; Moons, K.G.M.; Schuit, E. The relation between prediction model performance measures and patient selection outcomes for proton therapy in head and neck cancer. Radiother. Oncol. 2023, 179, 109449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, J.; Yang, B.; Chen, D.; Men, K.; Dai, J. Combining distance and anatomical information for deep-learning based dose distribution predictions for nasopharyngeal cancer radiotherapy planning. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1041769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Men, K.; Li, Y.; Yi, J.; Dai, J. A feasibility study on an automated method to generate patient-specific dose distributions for radiotherapy using deep learning. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huet-Dastarac, M.; Michiels, S.; Rivas, S.T.; Ozan, H.; Sterpin, E.; Lee, J.A.; Barragan-Montero, A. Patient selection for proton therapy using Normal Tissue Complication Probability with deep learning dose prediction for oropharyngeal cancer. Med. Phys. 2023, 50, 6201–6214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirlepesov, F.; Wilson, L.; Moskvin, V.P.; Breuer, A.; Parkins, F.; Lucas, J.T., Jr.; Merchant, T.E.; Faught, A.M. Three-dimensional dose and LETD prediction in proton therapy using artificial neural networks. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 7417–7427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Structure | Dosimetric Parameter | Per Protocol |
|---|---|---|
| Target | ||
| PGTV74 | V73.92 Gy [%] | ≥95 |
| PGTV70 | V69.96 Gy [%] | ≥95 |
| PTV60 | V60.06 Gy [%] | ≥95 |
| OAR | ||
| Spinal Cord PRV | Dmax [Gy] | ≤40 |
| Brain stem PRV | Dmax [Gy] | ≤40 |
| Lens L | Dmax [Gy] | ≤9 |
| Lens R | Dmax [Gy] | ≤9 |
| Optic Nerve L | Dmax [Gy] | ≤66 |
| Optic Nerve R | Dmax [Gy] | ≤66 |
| Optic Chiasm | Dmax [Gy] | ≤66 |
| Parotid L | V30 Gy [%] | ≤50 |
| Parotid R | V30 Gy [%] | ≤50 |
| Larynx | Dmax [Gy] | ≤40 |
| Trachea | Dmax [Gy] | ≤40 |
| Parotid_L (%) | Parotid_R (%) | Submandibularis (%) | Oral Cavity (%) | PCM U (%) | PCM M (%) | PCM I (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAE | |||||||
| Photon | 4.49 ± 1.54 | 4.63 ± 1.48 | 3.00 ± 0.82 | 3.91 ± 1.62 | 3.19 ± 0.81 | 2.77 ± 1.21 | 3.50 ± 1.68 |
| Proton | 4.22 ± 1.23 | 4.15 ± 1.67 | 3.95 ± 1.50 | 2.78 ± 1.00 | 4.28 ± 1.09 | 4.62 ± 2.59 | 3.88 ± 1.92 |
| ME | |||||||
| Photon | 0.0060 ± 0.0044 | 0.0068 ± 0.0042 | 0.0094 ± 0.0022 | −0.0024 ± 0.0045 | 0.0008 ± 0.0025 | 0.0047 ± 0.0035 | −0.0003 ± 0.0049 |
| Proton | 0.0056 ± 0.0052 | 0.0051 ± 0.0052 | 0.0007 ± 0.0044 | −0.0071 ± 0.0029 | 0.0062 ± 0.0040 | −0.0009 ± 0.0069 | −0.0065 ± 0.0049 |
| Mean NTCP (%) | p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MP | Prediction | |||
| Xer2+ | XT | 46.98 ± 2.44 | 47.38 ± 2.32 | 0.003 |
| PT | 43.72 ± 3.53 | 44.05 ± 3.10 | 0.082 | |
| Xer3+ | XT | 13.46 ± 0.97 | 13.61 ± 0.93 | 0.003 |
| PT | 12.22 ± 1.32 | 12.33 ± 1.16 | 0.109 | |
| Dys2+ | XT | 17.00 ± 2.76 | 16.83 ± 2.33 | 0.303 |
| PT | 5.87 ± 1.59 | 5.82 ± 1.42 | 0.426 | |
| Dys3+ | XT | 3.87 ± 0.96 | 3.80 ± 0.75 | 0.305 |
| PT | 0.63 ± 0.30 | 0.60 ± 0.25 | 0.056 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, G.; Chen, X.; Ding, J.; Shen, L.; Li, M.; Yi, J.; Dai, J. A Decision-Making Method for Photon/Proton Selection for Nasopharyngeal Cancer Based on Dose Prediction and NTCP. Cancers 2025, 17, 2620. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162620
Li G, Chen X, Ding J, Shen L, Li M, Yi J, Dai J. A Decision-Making Method for Photon/Proton Selection for Nasopharyngeal Cancer Based on Dose Prediction and NTCP. Cancers. 2025; 17(16):2620. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162620
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Guiyuan, Xinyuan Chen, Jialin Ding, Linyi Shen, Mengyang Li, Junlin Yi, and Jianrong Dai. 2025. "A Decision-Making Method for Photon/Proton Selection for Nasopharyngeal Cancer Based on Dose Prediction and NTCP" Cancers 17, no. 16: 2620. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162620
APA StyleLi, G., Chen, X., Ding, J., Shen, L., Li, M., Yi, J., & Dai, J. (2025). A Decision-Making Method for Photon/Proton Selection for Nasopharyngeal Cancer Based on Dose Prediction and NTCP. Cancers, 17(16), 2620. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17162620





