NRG Oncology Liver Proton SBRT and Hypofractionated Radiation Therapy: Current Treatment Technical Assessment and Practice Patterns
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
3. Proton Therapy Using SBRT and Hypofractionation for Liver Cancer Treatment
3.1. Survey Response Overview
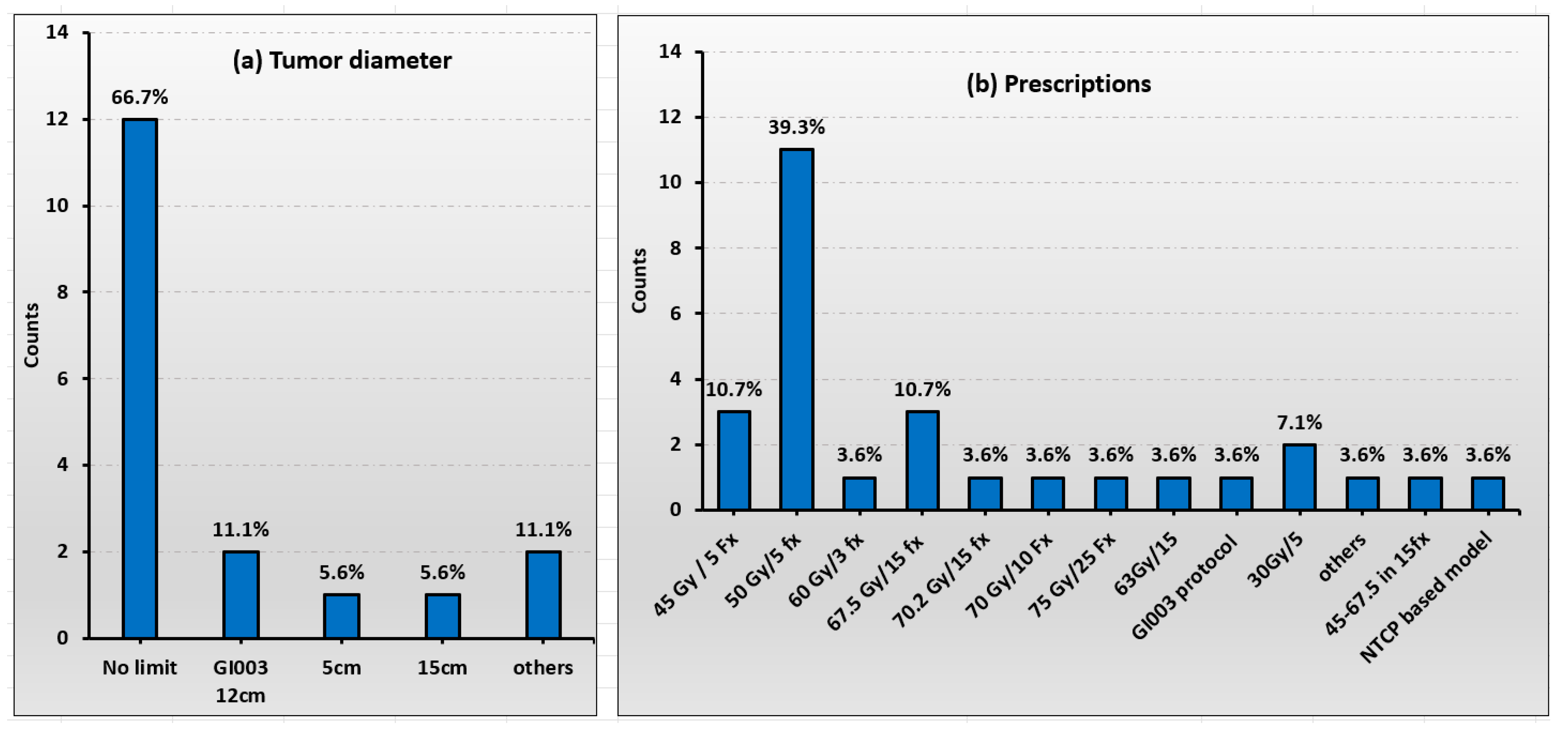
3.2. Patient Selection
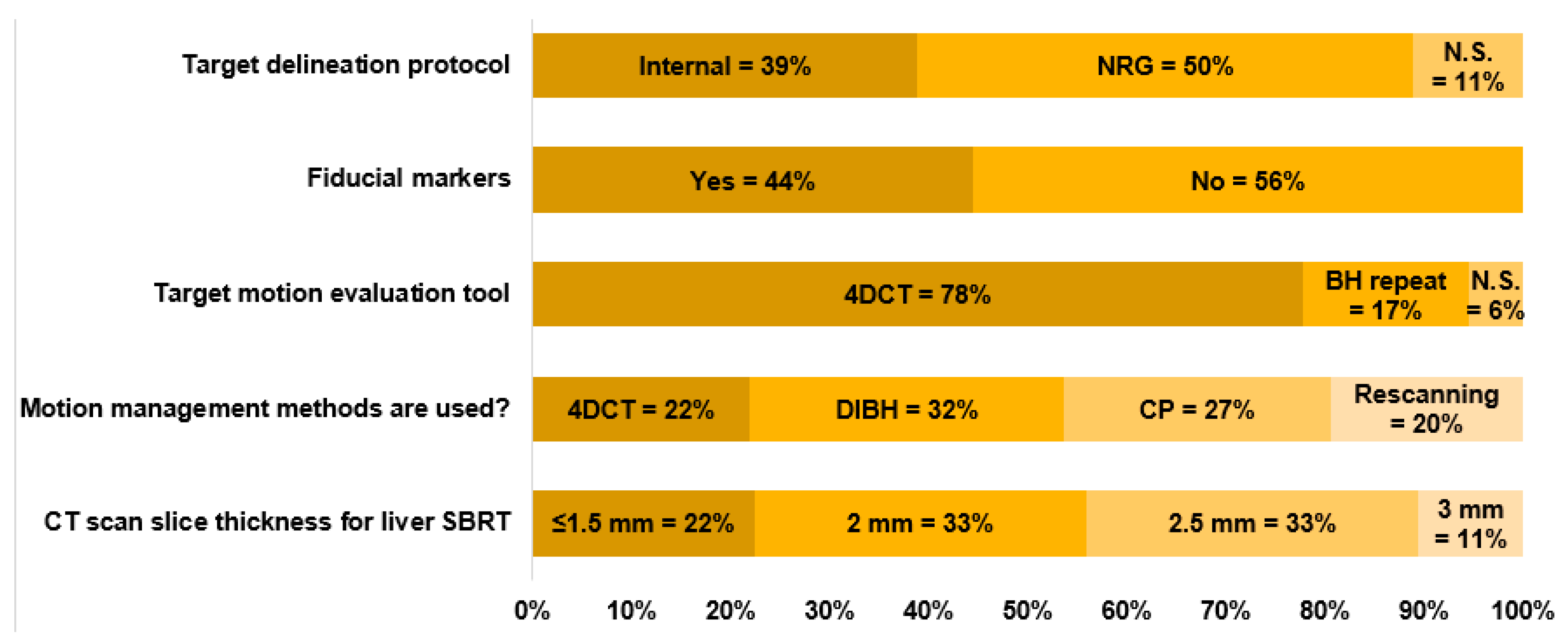
3.3. Simulation and Motion Management
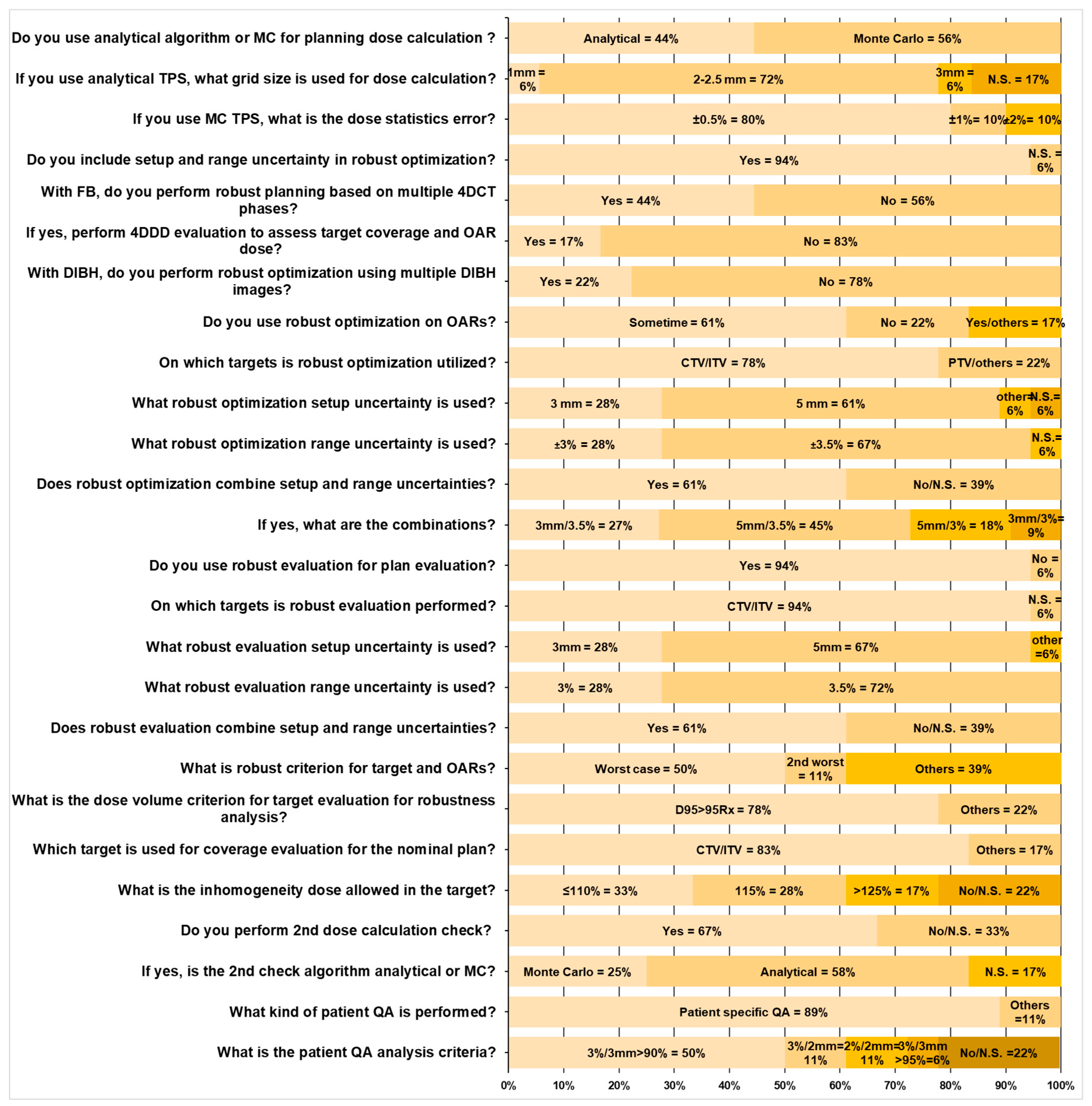
3.4. Treatment Planning and Quality Assurance (QA)
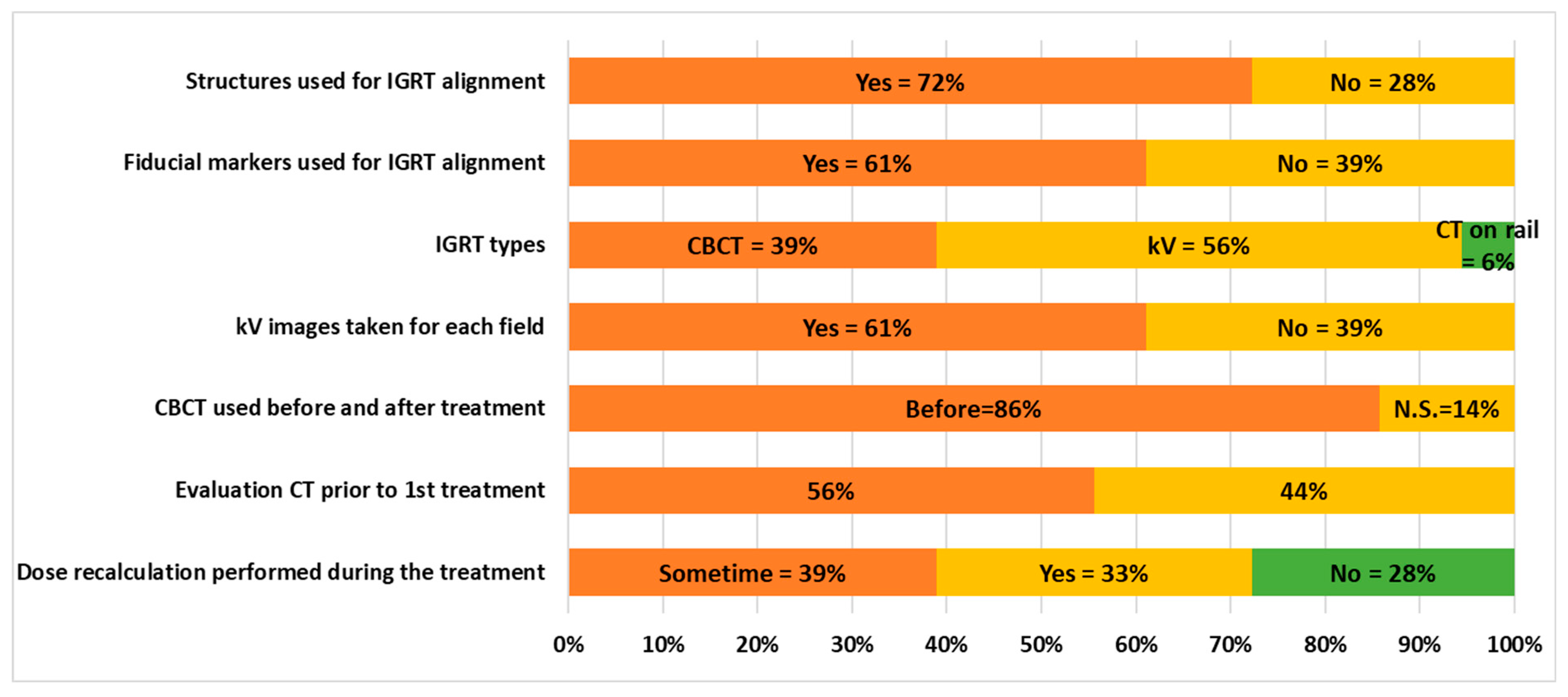
3.5. Delivery and IGRT Procedures
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Roberts, H.J.; Wo, J.Y. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for primary liver tumors: An effective liver-directed therapy in the toolbox. Cancer 2022, 128, 956–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, J.; Dawson, L.A. Hepatocellular carcinoma radiation therapy: Review of evidence and future opportunities. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 87, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aitken, K.L.; Hawkins, M.A. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for liver metastases. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 27, 307–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusthoven, K.E.; Kavanagh, B.D.; Cardenes, H.; Stieber, V.W.; Burri, S.H.; Feigenberg, S.J.; Chidel, M.A.; Pugh, T.J.; Franklin, W.; Kane, M.; et al. Multi-institutionalphase I/II trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for liver metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1572–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodman, B.D.; Mannina, E.M.; Althouse, S.K.; Maluccio, M.A.; Cárdenes, H.R. Longterm safety and efficacy of stereotactic body radiation therapy for hepatic oligometastases. Pract. Radiat. Oncol. 2016, 6, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bujold, A.; Massey, C.A.; Kim, J.J.; Brierley, J.; Cho, C.; Wong, R.K.S.; Dinniwell, R.E.; Kassam, Z.; Ringash, J.; Cummings, B.; et al. Sequential phase I and II trials of stereotactic body radiotherapy for locally advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavizadeh, N.; Waller, J.G.; Fain, R.; Chen, Y.; Degnin, C.R.; Elliott, D.A.; Mullins, B.T.; Patel, I.A.; Dyer, B.A.; Fakhoury, K.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Accelerated Hypofractionation and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients With Varying Degrees of Hepatic Impairment. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2018, 100, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohri, N.; Tomé, W.A.; Méndez Romero, A.; Miften, M.; Ten Haken, R.K.; Dawson, L.A.; Grimm, J.; Yorke, E.; Jackson, A. Local Control After Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Liver Tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 110, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, S.; Barry, A.; Hawkins, M.A. Hypofractionation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma—The Effect of Fractionation Size. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 34, e195–e209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobeissi, J.M.; Hilal, L.; Simone, C.B., 2nd; Lin, H.; Crane, C.H.; Hajj, C. Proton Therapy in the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, M.; Krause, M.; Overgaard, J.; Debus, J.; Bentzen, S.M.; Daartz, J.; Richter, C.; Zips, D.; Bortfeld, T. Radiation oncology in the era of precision medicine. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 234–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill-Kayser, C.E.; Tochner, Z.; Li, Y.; Kurtz, G.; Lustig, R.A.; James, P.; Balamuth, N.; Womer, R.; Mattei, P.; Grupp, S.; et al. Outcomes after proton therapy for treatment of pediatric high-risk neuroblastoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 104, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, B.C.; Mitra, N.; Harton, J.G.; Xiao, Y.; Wojcieszynski, A.P.; Gabriel, P.E.; Zhong, H.; Geng, H.; Doucette, A.; Wei, J.; et al. Comparative effectiveness of proton vs photon therapy as part of concurrent chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, V.; Lin, S.H.; Simone, C.B., 2nd; Mehta, M.P. Clinical outcomes and toxicities of proton radiotherapy for gastrointestinal neoplasms: A systematic review. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2016, 7, 644–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Simone, C.B.; Mishra, M.V. Quality of life and patient-reported outcomes following proton radiation therapy: A systematic review. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, S.; Abel, S.; Verma, V.; Webster, P.; Arscott, W.T.; Wegner, R.E.; Kirichenko, A.; Simone, C.B., II. Proton beam therapy versus stereotactic body radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: Practice patterns, outcomes, and the effect of biologically effective dose escalation. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2019, 10, 999–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanford, N.N.; Pursley, J.; Noe, B.; Yeap, B.Y.; Goyal, L.; Clark, J.W.; Allen, J.N.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Ryan, D.P.; Ferrone, C.R.; et al. Protons versus Photons for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Liver Decompensation and Overall Survival. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2019, 105, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Kang, M.; Wang, Y.; Higgins, K.A.; Simone, C.B.; Patel, P.; McDonald, M.W.; Lin, L.; Bohannon, D. Proton liver stereotactic body radiation therapy: Treatment techniques and dosimetry feasibility from a single institution. J. Radiosurgery SBRT 2023, 9, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Bush, D.A.; Kayali, Z.; Grove, R.; Slater, J.D. The safety and efficacy of high-dose proton beam radiotherapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase 2 prospective trial. Cancer 2011, 117, 3053–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukumitsu, N.; Sugahara, S.; Nakayama, H.; Fukuda, K.; Mizumoto, M.; Abei, M.; Shoda, J.; Thono, E.; Tsuboi, K.; Tokuuye, K. A prospective study of hypofractionated proton beam therapy for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2009, 74, 831–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.I.; Sufficool, D.C.; Hsueh, C.T.; Wroe, A.J.; Patyal, B.; Reeves, M.E.; Slater, J.D.; Yang, G.Y. A phase I trial of Proton stereotactic body radiation therapy for liver metastases. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2019, 10, 112–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, T.S.; Wo, J.Y.; Yeap, B.Y.; Ben-Josef, E.; McDonnell, E.I.; Blaszkowsky, L.S.; Kwak, E.L.; Allen, J.N.; Clark, J.W.; Goyal, L.; et al. Multi-Institutional Phase II Study of High-Dose Hypofractionated Proton Beam Therapy in Patients With Localized, Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NRG-GI003, ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT03186898 (accessed on 1 October 2024).
- Li, H.; Dong, L.; Bert, C.; Chang, J.; Flampouri, S.; Jee, K.W.; Lin, L.; Moyers, M.; Mori, S.; Rottmann, J.; et al. AAPM Task Group Report 290: Respiratory motion management for particle therapy. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, e50–e81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Kang, M.; Huang, S.; Solberg, T.D.; Mayer, R.; Thomas, A.; Teo, B.K.; McDonough, J.E.; Simone, C.B., 2nd; Lin, L. A study of the beam-specific interplay effect in proton pencil beam scanning delivery in lung cancer. Acta Oncol. 2017, 56, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Choi, J.I.; Souris, K.; Zhou, J.; Yu, G.; Shepherd, A.F.; Ohri, N.; Lazarev, S.; Lin, L.; Lin, H.; et al. Advances in treatment planning and management for the safety and accuracy of lung stereotactic body radiation therapy using proton pencil beam scanning: Simulation, planning, quality assurance, and delivery recommendations. J. Radiosurgery SBRT 2023, 9, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Sabouri, P.; Molitoris, J.; Ranjbar, M.; Moreau, J.; Simone, C.B.; Mohindra, P.; Langen, K.; Mossahebi, S. Dosimetric Evaluation and Reproducibility of Breath-hold Plans in Intensity Modulated Proton Therapy: An Initial Clinical Experience. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2023, 9, 101392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Souris, K.; Kang, M.; Glick, A.; Lin, H.; Huang, S.; Stützer, K.; Janssens, G.; Sterpin, E.; Lee, J.A.; et al. Evaluation of motion mitigation using abdominal compression in the clinical implementation of pencil beam scanning proton therapy of liver tumors. Med. Phys. 2017, 44, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.W.; Sharpe, M.B.; Jaffray, D.A.; Kini, V.R.; Robertson, J.M.; Stromberg, J.S.; Martinez, A.A. The use of active breathing control (ABC) to reduce margin for breathing motion. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1999, 44, 911–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keall, P.J.; Mageras, G.S.; Balter, J.M.; Emery, R.S.; Forster, K.M.; Jiang, S.B.; Kapatoes, J.M.; Low, D.A.; Murphy, M.J.; Murray, B.R.; et al. The management of respiratory motion in radiation oncology report of AAPM Task Group 76. Med. Phys. 2006, 33, 3874–3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Zhang, W.; Su, Y.; Liu, P.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, G.; Song, Y. Optical Surface Management System for Patient Positioning in Interfractional Breast Cancer Radiotherapy. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 6415497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Zhang, X.D. A Review of the Robust Optimization Process and Advances with Monte Carlo in the Proton Therapy Management of Head and Neck Tumors. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2021, 8, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barten, D.L.J.; Tol, J.P.; Dahele, M. Comparison of organ-at-risk sparing and plan robustness for spot-scanning proton therapy and volumetric modulated arc photon therapy in head-and-neck cancer. Med. Phys. 2015, 42, 6589–6598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casiraghi, M.; Albertini, F.; Lomax, A.J. Advantages and limitations of the “worst case scenario” approach in IMPT treatment planning. Phys. Med. Biol. 2013, 58, 1323–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stützer, K.; Lin, A.; Kirk, M.; Lin, L. Superiority in Robustness of Multifield Optimization Over Single-Field Optimization for Pencil-Beam Proton Therapy for Oropharynx Carcinoma: An Enhanced Robustness Analysis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2017, 99, 738–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Taylor, P.A.; Shen, J.; Saini, J.; Kang, M.; Simone, C.B.; Bradley, J.D.; Li, Z.; Xiao, Y. NRG Oncology Survey of Monte Carlo Dose Calculation Use in US Proton Therapy Centers. Int. J. Part. Ther. 2021, 8, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Lin, L.; Kang, M.; Solberg, T.D.; Mertens, T.; Baeumer, C.; Ainsley, C.G.; McDonough, J.E. Use of a novel two-dimensional ionization chamber array for pencil beam scanning proton therapy beam quality assurance. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2015, 16, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Cessac, R.; Pang, D. Commissioning and beam characterization of the first gantrymounted accelerator pencil beam scanning proton system. Med. Phys. 2020, 47, 3496–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arjomandy, B.; Taylor, P.; Ainsley, C.; Safai, S.; Sahoo, N.; Pankuch, M.; Farr, J.B.; Park, S.Y.; Klein, E.; Flanz, J.; et al. AAPM task group 224: Comprehensive proton therapy machine quality assurance. Med. Phys. 2019, 46, e678–e705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.R.; Li, Y.; Mackin, D.; Li, H.; Poenisch, F.; Lee, A.K.; Mahajan, A.; Frank, S.J.; Gillin, M.T.; Sahoo, N.; et al. Towards Effective and Efficient Patient-Specific Quality Assurance for Spot Scanning Proton Therapy. Cancers 2015, 7, 631–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, T.; Inaniwa, T.; Hara, Y.; Mizushima, K.; Shirai, T.; Noda, K. Patient-specific QA and delivery verification of scanned ion beam at NIRS-HIMAC. Med. Phys. 2013, 40, 121707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Sahoo, N.; Poenisch, F.; Suzuki, K.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Lee, A.K.; Gillin, M.T.; Zhu, X.R. Use of treatment log files in spot scanning proton therapy as part of patient-specific quality assurance. Med. Phys. 2013, 40, 021703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simone, C.B.; Lin, L. Proton SBRT is ready to move past uncertainties and towards improved clinical outcomes. J. Radiosurgery SBRT 2023, 9, 3–6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Wei, S.; Lin, H.; Shi, C.; Xiong, W.; Chen, C.C.; Huang, S.; Press, R.H.; Hasan, S.; Chhabra, A.M.; Choi, J.I.; et al. Use of single-energy proton pencil beam scanning Bragg peak for intensity-modulated proton therapy FLASH treatment planning in liver-hypofractionated radiation therapy. Med. Phys. 2022, 49, 6560–6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Lin, H.; Choi, J.I.; Press, R.H.; Lazarev, S.; Kabarriti, R.; Hajj, C.; Hasan, S.; Chhabra, A.M.; Simone, C.B., 2nd; et al. FLASH Radiotherapy Using Single-Energy Proton PBS Transmission Beams for Hypofractionation Liver Cancer: Dose and Dose Rate Quantification. Front. Oncol. 2022, 11, 813063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, N.; Kang, M.; Liu, R.; Charyyev, S.; Wahl, N.; Liu, W.; Zhou, J.; Higgins, K.A.; Simone, C.B., 2nd; Bradley, J.D.; et al. A Novel Inverse Algorithm To Solve the Integrated Optimization of Dose, Dose Rate, and Linear Energy Transfer of Proton FLASH Therapy With Sparse Filters. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2024, 119, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veiga, C.; Janssens, G.; Teng, C.-L.; Baudier, T.; Hotoiu, L.; McClelland, J.R.; Royle, G.; Lin, L.; Yin, L.; Metz, J.; et al. First Clinical Investigation of Cone Beam Computed Tomography and Deformable Registration for Adaptive Proton Therapy for Lung Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 95, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Yin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kirk, M.; Song, G.; Ahn, P.H.; Lin, A.; Gee, J.; Dolney, D.; Solberg, T.D.; et al. Quantitative assessment of anatomical change using a virtual proton depth radiograph for adaptive head and neck proton therapy. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2016, 17, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Hasan, S.; Press, R.H.; Yu, F.; Abdo, M.; Xiong, W.; Choi, J.I.; Simone, C.B.; Lin, H. Using patient-specific bolus for pencil beam scanning proton treatment of periorbital disease. J. Appl. Clin. Med. Phys. 2021, 22, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuong, M.D.; Lee, P.; Low, D.A.; Kim, J.; Mittauer, K.E.; Bassetti, M.F.; Glide-Hurst, C.K.; Raldow, A.C.; Yang, Y.; Portelance, L.; et al. Stereotactic MR-guided on-table adaptive radiation therapy (SMART) for borderline resectable and locally advanced pancreatic cancer: A multi-center, open-label phase 2 study. Radiother. Oncol. 2024, 191, 110064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keall, P.J.; Glide-Hurst, C.K.; Cao, M.; Lee, P.; Murray, B.; Raaymakers, B.W.; Tree, A.; van der Heide, U.A. ICRU REPORT 97: MRI-Guided Radiation Therapy Using MRI-Linear Accelerators. J. ICRU 2022, 22, 1–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, L.; Kashani, R.; Robinson, C.; Curcuru, A.; DeWees, T.; Bradley, J.; Green, O.; Michalski, J.; Mutic, S.; Parikh, P.; et al. Phase I trial of stereotactic MR-guided online adaptive radiation therapy (SMART) for the treatment of oligometastatic or unresectable primary malignancies of the abdomen. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 126, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henke, L.E.; Olsen, J.R.; Contreras, J.A.; Curcuru, A.; DeWees, T.A.; Green, O.L.; Michalski, J.; Mutic, S.; Roach, M.C.; Bradley, J.D.; et al. Stereotactic MR-Guided Online Adaptive Radiation Therapy (SMART) for Ultracentral Thorax Malignancies: Results of a Phase 1 Trial. Adv. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 4, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Chuong, M.D.; Clark, M.A.; Henke, L.E.; Kishan, A.U.; Portelance, L.; Parikh, P.J.; Bassetti, M.F.; Nagar, H.; Rosenberg, S.A.; Mehta, M.P.; et al. Patterns of utilization and clinical adoption of 0.35 Tesla MR-guided radiation therapy in the United States—Understanding the transition to adaptive, ultra-hypofractionated treatments. Clin. Transl. Radiat. Oncol. 2022, 38, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Oncoray Launches World’s First Whole-Body Mri-Guided Proton Therapy System. Available online: https://physicsworld.com/a/oncoray-launches-worlds-first-whole-body-mri-guided-proton-therapy-system/ (accessed on 1 May 2024).
- Bookbinder, A.; Krieger, M.; Lansonneur, P.; Magliari, A.; Zhao, X.; Choi, J.I.; Simone, C.B.; Lin, H.; Folkerts, M.; Kang, M. Implementation of a novel pencil beam scanning Bragg peak FLASH technique to a commercial treatment planning system. Med. Phys. 2025, 120, e103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, T.; Selvaraj, B.; Shen, J.; Wei, S.; Cheng, C.; Gao, H.; Poulsen, P.R.; Li, H.; Diffenderfer, E.; et al. Advancing Proton FLASH Radiation Therapy: Innovations, Techniques, and Clinical Potentials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, M.; Wei, S.; Choi, J.I.; Lin, H.; Simone, C.B. A Universal Range Shifter and Range Compensator Can Enable Proton Pencil Beam Scanning Single-Energy Bragg Peak FLASH-RT Treatment Using Current Commercially Available Proton Systems. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2022, 113, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillie, L.; Lazarev, S.; Simone, C.B.; Sisk, M. Geospatial Disparities in Access to Proton Therapy in the Continental United States. Cancer Investig. 2021, 39, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Vendors | Count | Rate | Techniques | Count | Rate | TPS | Count | Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IBA | 8 | 44% | PBS | 14 | 74% | RayStation | 10 | 56% |
| Mevion | 4 | 22% | Passive Scatter | 4 | 21% | Eclipse | 6 | 33% |
| Varian | 2 | 11% | Uniform scanning | 1 | 5% | Others | 2 | 11% |
| Hitachi | 3 | 17% | ||||||
| Optivus | 1 | 6% | ||||||
| Total | 18 | 19 * | 18 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, M.; Taylor, P.A.; Shen, J.; Zhou, J.; Saini, J.; Hong, T.S.; Higgins, K.; Liu, W.; Xiao, Y.; Simone, C.B., II; et al. NRG Oncology Liver Proton SBRT and Hypofractionated Radiation Therapy: Current Treatment Technical Assessment and Practice Patterns. Cancers 2025, 17, 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142369
Kang M, Taylor PA, Shen J, Zhou J, Saini J, Hong TS, Higgins K, Liu W, Xiao Y, Simone CB II, et al. NRG Oncology Liver Proton SBRT and Hypofractionated Radiation Therapy: Current Treatment Technical Assessment and Practice Patterns. Cancers. 2025; 17(14):2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142369
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Minglei, Paige A. Taylor, Jiajian Shen, Jun Zhou, Jatinder Saini, Theodore S. Hong, Kristin Higgins, Wei Liu, Ying Xiao, Charles B. Simone, II, and et al. 2025. "NRG Oncology Liver Proton SBRT and Hypofractionated Radiation Therapy: Current Treatment Technical Assessment and Practice Patterns" Cancers 17, no. 14: 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142369
APA StyleKang, M., Taylor, P. A., Shen, J., Zhou, J., Saini, J., Hong, T. S., Higgins, K., Liu, W., Xiao, Y., Simone, C. B., II, & Lin, L. (2025). NRG Oncology Liver Proton SBRT and Hypofractionated Radiation Therapy: Current Treatment Technical Assessment and Practice Patterns. Cancers, 17(14), 2369. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17142369









