Biomarkers in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Immunohistochemical Validation Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Systematic Review Search Strategy
2.2. Study Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Study Selection and Data Extraction
2.4. Quality Assessment
2.5. Quantitative Analysis
2.6. Immunohistochemistry Validation Cohort
2.7. Tissue Preparation
2.8. Immunohistochemistry
2.9. Image Analysis
2.10. Analysis of Publicly Available Gene Expression Data
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Systematic Review
3.2. Cohort Demographics
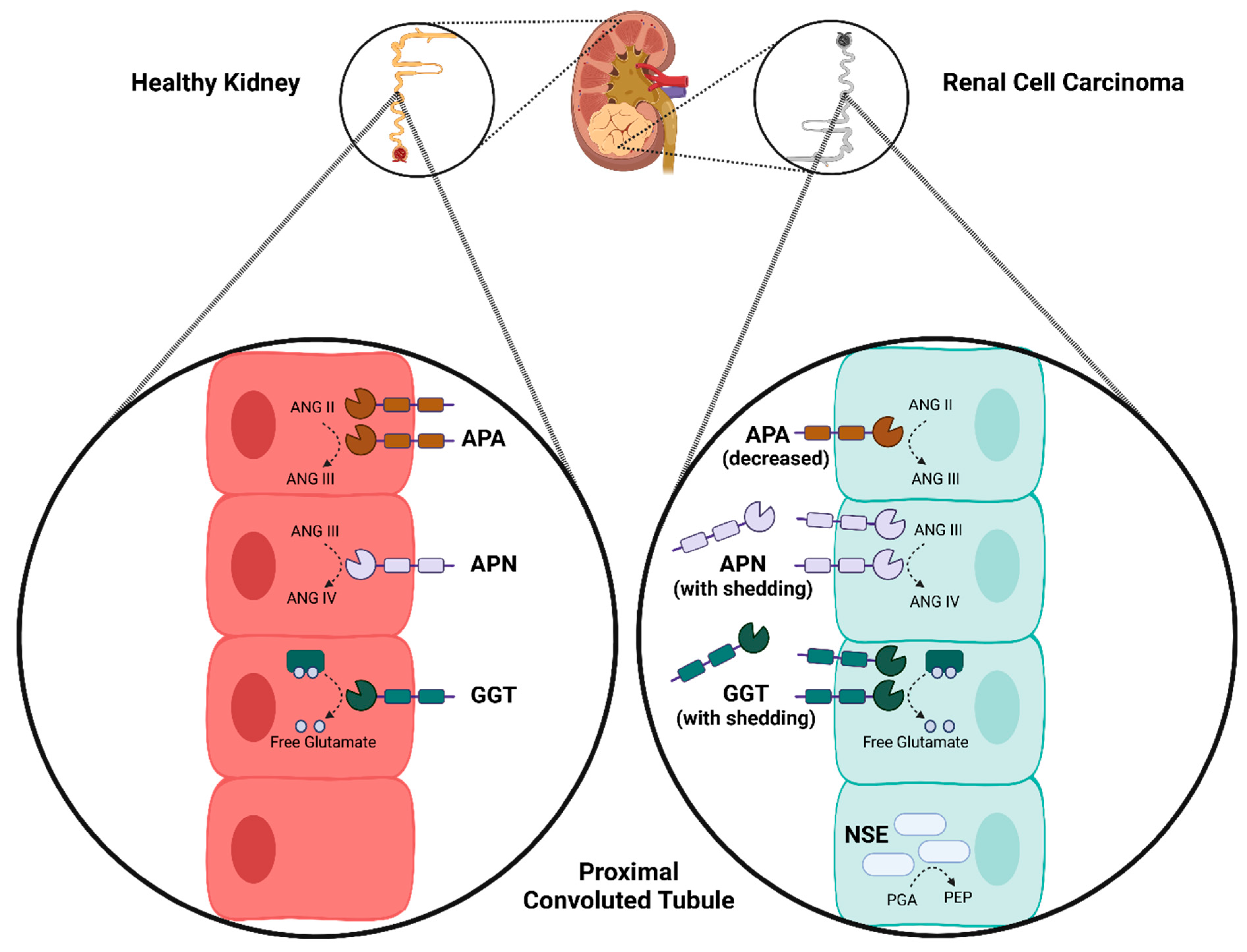
3.3. Immunohistochemistry
3.4. Semi-Quantitative Image Analysis
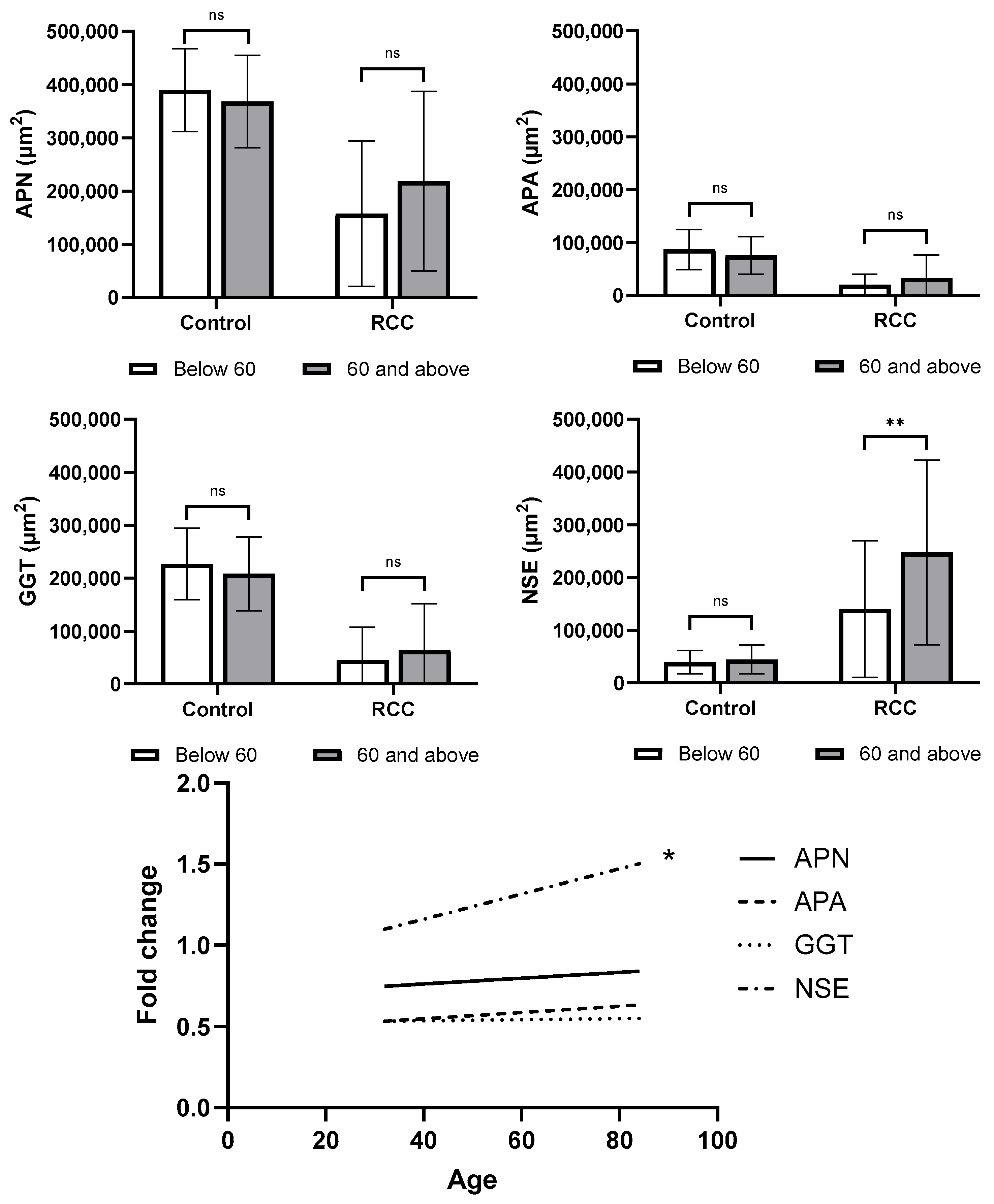
3.5. Quantitative Image Analysis
3.6. Exploratory Correlations with Clinical Data
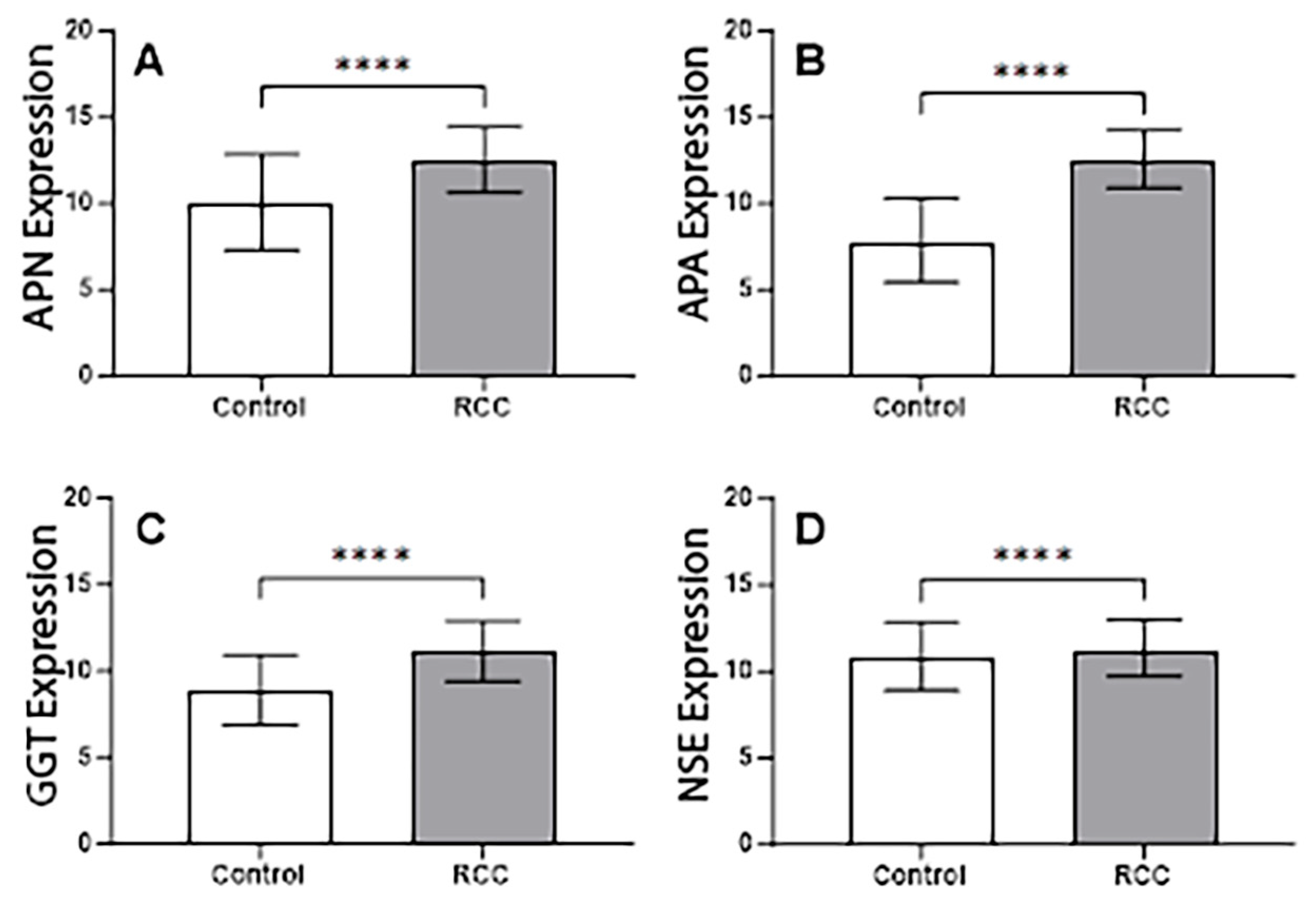
3.7. Gene Expression Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ngo, T.C.; Wood, C.G.; Karam, J.A. Biomarkers of renal cell carcinoma. Urol. Oncol. 2014, 32, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cirillo, L.; Innocenti, S.; Becherucci, F. Global epidemiology of kidney cancer. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2024, 39, 920–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Cancer Data in Australia. Available online: https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/cancer/cancer-data-in-australia/contents/overview (accessed on 1 August 2025).
- Mihara, S.; Kuroda, K.; Yoshioka, R.; Koyama, W. Early detection of renal cell carcinoma by ultrasonographic screening—Based on the results of 13 years screening in Japan. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1999, 25, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cairns, P. Renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2011, 9, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musaddaq, B.; Musaddaq, T.; Gupta, A.; Ilyas, S.; von Stempel, C. Renal Cell Carcinoma: The Evolving Role of Imaging in the 21st Century. Semin. Ultrasound CT MR 2020, 41, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohlberg, E.M.; Metzner, T.J.; Leppert, J.T. The harms of overdiagnosis and overtreatment in patients with small renal masses: A mini-review. Eur. Urol. Focus 2019, 5, 943–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuch, B.; Pantuck, A.J.; Bernhard, J.C.; Morris, M.A.; Master, V.; Scott, A.M.; van Praet, C.; Aksoy, T.; Önal, B.; Bailly, C.; et al. [89Zr] Zr-girentuximab for PET–CT imaging of clear-cell renal cell carcinoma: A prospective, open-label, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2024, 25, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, R.J.; Del Vecchio, S.J.; Ng, K.L.; Owens, E.P.; Coombes, J.S.; Morais, C.; Francis, R.S.; Wood, S.T.; Gobe, G.C. The Correlates of Kidney Dysfunction–Tumour Nephrectomy Database (CKD-TUNED) Study: Protocol for a prospective observational study. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 18, 3281–3285. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, R.J.; Kalma, B.; Del Vecchio, S.J.; Aliano, D.N.; Ng, K.L.; Dimeski, G.; Ma, L.; Guard, D.; Bertram, J.F.; Morais, C.; et al. Chronic kidney cortical damage is associated with baseline kidney function and albuminuria in patients managed with radical nephrectomy for kidney tumours. Pathology 2019, 51, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finstad, C.L.; Cordon-Cardo, C.; Bander, N.H.; Whitmore, W.F.; Melamed, M.R.; Old, L.J. Specificity analysis of mouse monoclonal antibodies defining cell surface antigens of human renal cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1985, 82, 2955–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ino, K.; Nagasaka, T.; Okamoto, T.; Uehara, C.; Nakazato, H.; Nakashima, N.; Mizutani, S. Expression of aminopeptidase A in human gestational choriocarcinoma cell lines and tissues. Placenta 2000, 21, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, C.; Lin, Y.L.; Li, F. Structural insights into central hypertension regulation by human aminopeptidase A. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 25638–25645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanus, D.M.; Bogenrieder, T.; Papandreou, C.N.; Finstad, C.L.; Lee, A.; Vlamis, V.A.; Motzer, R.J.; Bander, N.H.; Albino, A.P.; Reuter, V.E. Aminopeptidase A expression and enzymatic activity in primary human renal cancers. Int. J. Oncol. 1998, 13, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Look, A.; Ashmun, R.; Shapiro, L.; Peiper, S. Human myeloid plasma membrane glycoprotein CD13 (gp150) is identical to aminopeptidase N. J. Clin. Investig. 1989, 83, 1299–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensbergen, V.Y.; Broxterman, H.; Hanemaaijer, R.; Jorna, A.; Van Lent, N.; Verheul, H.; Pinedo, H.; Hoekman, K. Soluble aminopeptidase N/CD13 in malignant and nonmalignant effusions and intratumoral fluid. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 3747–3754. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.; Zhou, D.; Rini, J. The X-ray crystal structure of human aminopeptidase N reveals a novel dimer and the basis for peptide processing. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 36804–36813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasqualini, R.; Koivunen, E.; Kain, R.; Lahdenranta, J.; Sakamoto, M.; Stryhn, A.; Ashmun, R.; Shapiro, L.; Arap, W. Aminopeptidase N is a receptor for tumor-homing peptides and a target for inhibiting angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 722. [Google Scholar]
- Wetmore, L.A.; Gerard, C.; Drazen, J.M. Human lung expresses unique gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase transcripts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 7461–7465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castonguay, R.; Halim, D.; Morin, M.; Furtos, A.; Lherbet, C.; Bonneil, E.; Thibault, P.; Keillor, J.W. Kinetic characterization and identification of the acylation and glycosylation sites of recombinant human γ-glutamyltranspeptidase. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 12253–12262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, S.; West, M.B.; Cook, P.F.; Hanigan, M. Gamma-glutamyl compounds: Substrate specificity of gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase enzymes. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 414, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, J.B.; West, M.B.; Cook, P.F.; Hanigan, M. A novel, species-specific class of uncompetitive inhibitors of γ-glutamyl transpeptidase. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 9059–9065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bansal, A.; Sanchez, D.J.; Nimgaonkar, V.; Sanchez, D.; Riscal, R.; Skuli, N.; Simon, M.C. Gamma-glutamyltransferase 1 promotes clear cell renal cell carcinoma initiation and progression. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 1881–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofbauer, S.L.; Stangl, K.I.; De Martino, M.; Lucca, I.; Haitel, A.; Shariat, S.F.; Klatte, T. Pretherapeutic gamma-glutamyltransferase is an independent prognostic factor for patients with renal cell carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1526–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemura, K.; Yuasa, T.; Inamura, K.; Amori, G.; Koga, F.; Board, P.G.; Yonese, J. Impact of serum γ-glutamyltransferase on overall survival in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma in the era of targeted therapy. Target. Oncol. 2020, 15, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isgrò, M.A.; Bottoni, P.; Scatena, R. Neuron-specific enolase as a biomarker: Biochemical and clinical aspects. In Advances in Cancer Biomarkers; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 125–143. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, D.S.; Choi, Y.P.; Kang, S.; Gao, M.Q.; Kim, B.; Park, H.R.; Choi, Y.D.; Lim, J.B.; Na, H.J.; Kim, H.K.; et al. Panel of candidate biomarkers for renal cell carcinoma. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3710–3719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasmuson, T.; Grankvist, K.; Roos, G.; Ljungberg, B. Neuroendocrine differentiation in renal cell carcinoma: Evaluation of chromogranin A and neuron-specific enolase. Acta Oncol. 1999, 38, 623–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.Y.; Su, T.; Shi, W.Q.; Fang, J.W.; Zhang, M.Y.; Xu, Q.H.; Liang, R.B.; Ge, Q.M.; Li, B.; Shao, Y. Neuron-Specific Enolase and Hemoglobin as Risk Factors of Intraocular Metastasis in Patients with Renal Cell Carcinoma. Dis. Markers 2022, 2022, 2883029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, K.U.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, H.K. Association of serum gamma-glutamyltransferase and alanine aminotransferase activities with risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus independent of fatty liver. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2009, 25, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Biomarker | Studies (n) | Quality Score (Range) | ccRCC (n, %) | pRCC (n, %) | chRCC (n, %) | RO (n, %) | Malignant (n, %) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11β-HSD2 | 1 | 5 | 2/75 (2.6) | 0/14 (0) | 19/20 (95) | 14/14 (100) | 21/109 (19) |
| AEG-1 | 1 | 5 | 41/86 (47) | - | - | - | 53/102 (52) |
| AMACR | 3 | 3–5 | 10/11 (91) | 10/10 (100) | 4/11 (36) | 19/33 (58) | 36/80 (45) |
| Aminopeptidase A/CD249 | 1 | 3 | 33/34 (97) | - | 1/4 (25) | 0/4 (0) | 35/40 (88) |
| AMY-1a | 1 | 5 | 0/60 (0) | 0/40 (0) | 7/54 (13) | 75/75 (100) | 7/154 (4.5) |
| Arrestin-1 | 1 | 6 | 8/17 (47) | 4/6 (67) | 5/6 (83) | 9/10 (90) | 17/29 (59) |
| BAP-1 | 1 | 4 | 169/187 (90) | 61/61 (100) | 17/17 (100) | 34/34 (100) | 247/265 (93) |
| Bax | 1 | 4 | - | - | 10/10 (100) | 10/10 (100) | 10/10 (100) |
| β-catenin | 2 | 5 | 40/41 (98) | - | 1/1 (100) | - | 55/56 (98) |
| Bcl-2 | 1 | 4 | - | - | 28/28 (100) | 33/33 (100) | 28/28 (100) |
| CA-IX | 3 | 3–5 | 61/67 (91) | 8/10 (80) | 1/3 (33) | 23/42 (55) | 123/141 (87) |
| Cathepsin | 1 | 6 | 43/150 (29) | - | - | - | 43/150 (29) |
| Cav-1 | 2 | 4 | 29/32 (91) | 1/20 (5.0) | 20/36 (56) | 1/27 (3.7) | 61/103 (59) |
| CD3 | 2 | 4 | 19/19 (100) | - | 3/3 (100) | - | 49/49 (100) |
| CD4 | 2 | 4 | 16/17 (94) | - | 3/3 (100) | - | 43/47 (91) |
| CD8 | 2 | 4 | 17/19 (89) | - | 3/3 (100) | - | 42/49 (86) |
| CD9 | 1 | 6 | 31/66 (47) | 13/13 (100) | 5/5 (100) | 2/2 (100) | 50/88 (57) |
| CD10 | 5 | 1–4 | 60/80 (75) | 16/27 (59) | 10/50 (20) | 9/56 (16) | 95/171 (56) |
| CD11 | 2 | 4–5 | 19/19 (100) | - | 3/3 (100) | - | 43/57 (75) |
| CD13/APN | 1 | 5 | 33/34 (97) | - | 0/4 (0) | 0/4 (0) | 34/40 (85) |
| CD14 | 1 | 4 | 19/19 (100) | - | 3/3 (100) | - | 48/48 (100) |
| CD15/LeuM-1 | 1 | 3 | - | - | 1/21 (4.8) | - | 1/21 (4.8) |
| CD26/DP-4 | 1 | 5 | 34/34 (100) | 2/4 (50) | 4/4 (100) | 1/2 (50) | 40/42 (95) |
| CD31/PECAM-1 | 2 | 4 | 50/50 (100) | 8/8 (100) | 5/5 (100) | - | 67/67 (100) |
| CD44-6v | 1 | 5 | 14/68 (21) | - | 6/11 (55) | 0/8 (0) | 23/92 (25) |
| CD44-9v | 1 | 5 | 8/68 (12) | - | 10/11 (91) | 0/8 (0) | 20/92 (22) |
| CD44s | 1 | 5 | 22/68 (32) | - | 10/11 (91) | 0/8 (0) | 36/92 (39) |
| CD56/NCAM | 3 | 4–6 | 26/63 (41) | 10/21 (48) | 3/8 (38) | 9/9 (100) | 40/95 (42) |
| CD73 | 1 | 4 | 81/157 (52) | - | - | - | 81/157 (52) |
| CD105 | 1 | 4 | - | - | - | - | 39/45 (87) |
| CD117/c-KIT | 8 | 3–6 | 20/988 (2.0) | 14/221 (6.3) | 188/216 (87) | 123/139 (88) | 225/1470 (15) |
| CD147/EMMPRIN | 1 | 5 | 313/322 (97) | 36/42 (86) | 22/22 (100) | 8/8 (100) | 371/386 (96) |
| Chromogranin A | 1 | 6 | 0/34 (0) | 0/9 (0) | 0/2 (0) | - | 0/45 (0) |
| CK (pan) | 1 | 5 | 117/125 (94) | 20/20 (100) | 22/22 (100) | 62/66 (94) | 159/167 (95) |
| CK2a | 1 | 6 | 80/105 (76) | 18/27 (67) | 7/8 (88) | 12/13 (92) | 107/142 (75) |
| CK7 | 11 | 1–6 | 38/287 (13) | 56/76 (74) | 97/119 (82) | 80/176 (45) | 236/532 (44) |
| CK8 | 3 | 1–5 | 40/156 (26) | 24/37 (67) | 44/64 (69) | 45/74 (61) | 109/257 (42) |
| CK8-18L | 1 | 5 | 143/155 (92) | 35/58 (92) | 58/64 (91) | 94/95 (99) | 250/271 (92) |
| CK18 | 4 | 1–5 | 143/155 (92) | 35/38 (92) | 58/64 (91) | 94/95 (99) | 250/271 (92) |
| CK19 | 3 | 1–5 | 37/155 (24) | 32/36 (89) | 24/64 (38) | 32/72 (44) | 93/255 (36) |
| CK20 | 1 | 1 | 2/30 (6.7) | 1/16 (6.3) | 3/21 (14) | 0/8 (0) | 6/68 (8.8) |
| Cks | 1 | 5 | 82/384 (21) | 8/81 (9.9) | 0/17 (0) | - | 90/482 (19) |
| Claudin-7 | 1 | 4 | 0/33 (0) | 4/19 (21) | 4/6 (67) | 2/6 (33) | 8/58 (14) |
| Clusterin | 1 | 6 | - | - | - | - | 65/67 (97) |
| Dcr-3 | 1 | 6 | 39/464 (8.4) | 6/48 (13) | 2/25 (8) | - | 52/560 (9.3) |
| Desmin | 1 | 5 | - | - | - | - | 4/30 (13) |
| DNMT-1 | 1 | 6 | 50/89 (56) | - | - | - | 56/111 (50) |
| E-cadherin | 3 | 3–5 | 18/154 (12) | 3/20 (15) | 15/56 (95) | 16/16 (100) | 77/233 (33) |
| EpCAM | 1 | 5 | 131/318 (41) | - | - | - | 131/318 (41) |
| EPO | 1 | 6 | 33/34 (97) | 0/9 (0) | 0/2 (0) | - | 33/45 (73) |
| ERa36 | 1 | 4 | 27/67 (40) | 4/6 (67) | 14/19 (74) | - | 48/99 (48) |
| Erg | 1 | 3 | 87/184 (47) | 11/14 (79) | 3/13 (23) | 3/3 (100) | 101/211 (48) |
| Estrogen Rec. | 1 | 5 | - | - | - | - | 0/29 (0) |
| EZH2 | 1 | 6 | 334/422 (79) | 48/55 (87) | 12/23 (52) | - | 411/520 (79) |
| Fas | 1 | 5 | 18/20 (90) | 11/11 (100) | 17/20 (85) | - | 46/51 (90) |
| FasL | 1 | 5 | 20/20 (100) | 11/11 (100) | 20/20 (100) | - | 51/51 (100) |
| FGFR-1 | 1 | 5 | 14/16 (88) | 10/12 (83) | 5/5 (100) | 9/9 (100) | 29/33 (88) |
| FGFR-2 | 1 | 6 | - | 49/214 (23) | - | - | 49/214 (23) |
| FXYD-2 | 1 | 6 | 2/15 (13) | 0/11 (0) | 26/27 (96) | 5/30 (17) | 28/53 (53) |
| Galectin-1 | 1 | 8 | 87/91 (96) | - | - | - | 170/182 (93) |
| GATA-3 | 2 | 2–4 | 1/116 (0.9) | 0/53 (0) | 2/33 (6.1) | 9/47 (19) | 6/241 (2.5) |
| GGT | 1 | 5 | 34/34 (100) | - | 0/4 (0) | 1/4 (25) | 35/40 (88) |
| GLTSCR-2 | 1 | 5 | 46/75 (61) | - | - | - | 127/159 (80) |
| Glucocorticoid Receptor | 1 | 6 | 97/147 (66) | 6/23 (26) | 1/17 (5.9) | 2/14 (14) | 104/187 (56) |
| GPC-3 | 1 | 4 | 27/502 (5.4) | 16/62 (26) | 32/40 (80) | 12/21 (57) | 75/604 (12) |
| HER-2 | 1 | 6 | - | - | - | - | 7/42 (17) |
| HLA-I | 2 | 4–5 | 74/120 (62) | - | - | - | 107/162 (66) |
| HLA-II | 1 | 7 | 8/12 (67) | 2/10 (20) | 3/7 (43) | 1/5 (20) | 13/29 (45) |
| HLA-B,C | 1 | 7 | 12/12 (100) | 10/10 (100) | 3/7 (43) | 5/5 (100) | 29/33 (88) |
| HLA-G | 1 | 7 | 7/12 (58) | 0/10 (0) | 0/7 (0) | 0/5 (0) | 7/33 (21) |
| HMGB-1 | 1 | 5 | - | - | - | - | 71/80 (89) |
| Hsp-27 | 1 | 5 | 16/19 (84) | 0/2 (0) | 1/3 (33) | 0/1 (0) | 17/24 (71) |
| IFN-γ | 1 | 6 | 16/60 (27) | - | - | - | 16/60 (27) |
| KL-1 | 1 | 2 | - | - | 15/21 (71) | 86/103 (83) | 15/21 (71) |
| Ksp-cadherin | 2 | 5–6 | 20/161 (12) | 13/71 (18) | 18/67 (27) | 28/74 (28) | 51/302 (17) |
| LRAT | 1 | 4 | 13/13 (100) | 7/7 (100) | 6/6 (100) | 4/4 (100) | 27/27 (100) |
| Lysozyme | 1 | 2 | - | - | 6/21 (29) | 10/103 (9.7) | 6/21 (29) |
| MAGE-A3/4 | 1 | 4 | - | - | 7/18 (39) | 15/17 (88) | 7/18 (39) |
| MIA | 1 | 3 | - | - | - | 23/24 (96) | 14/14 (100) |
| Mineralocorticoid Receptor | 1 | 3 | 0/75 (0) | 14/14 (100) | 9/10 (90) | 13/14 (93) | 23/108 (21) |
| MOC-31 | 1 | 4 | 8/10 (80) | - | 22/23 (96) | 2/8 (25) | 36/48 (75) |
| MSH-2 | 1 | 3 | 53/129 (41) | - | - | - | 53/129 (41) |
| MUC-1 | 7 | 1–6 | 215/325 (66) | 58/82 (71) | 110/115 (96) | 142/164 (87) | 400/551 (73) |
| N-cadherin | 2 | 2–3 | 8/19 (42) | - | 2/37 (5.4) | 0/16 (0) | 10/56 (18) |
| NDUFA4L2 | 1 | 5 | 70/86 (81) | - | - | - | 70/86 (81) |
| NEP | 1 | 5 | 33/34 (97) | - | 1/4 (25) | 0/4 (0) | 34/40 (85) |
| NPM | 1 | 4 | 18/40 (45) | 5/7 (71) | 0/8 (0) | 9/9 (100) | 27/61 (44) |
| NSE | 1 | 6 | 33/34 (97) | - | 0/9 (0) | 0/2 (0) | 33/43 (77) |
| NY-ESO-1 | 1 | 4 | - | - | 6/18 (33) | 15/17 (88) | 6/18 (33) |
| OSCAR | 1 | 3 | - | - | - | 22/22 (100) | 13/13 (100) |
| p27Kip1 | 2 | 4–5 | 263/524 (50) | 20/81 (25) | 3/17 (18) | - | 286/622 (46) |
| p53 | 3 | 3–7 | 17/52 (33) | 5/10 (50) | 24/39 (62) | 30/42 (71) | 46/101 (45) |
| PAX-2 | 1 | 6 | 29/30 (97) | 17/30 (57) | 10/30 (33) | 27/30 (90) | 56/90 (62) |
| PAX-8 | 2 | 2–4 | 89/104 (86) | 19/21 (90) | 9/11 (81) | 20/21 (95) | 124/145 (86) |
| Paxillin | 1 | 4 | 1/65 (1.5) | 1/14 (7.1) | 6/6 (100) | 2/2 (100) | 9/89 (10) |
| PBMR-1 | 2 | 4–8 | 210/506 (42) | 85/103 (83) | 22/39 (56) | 34/42 (81) | 332/671 (49) |
| PD-L1 | 1 | 3 | - | 5/50 (10) | 2/36 (5.6) | 4/13 (31) | 7/86 (8.1) |
| p-Glycoprotein | 1 | 4 | 30/75 (40) | - | - | - | 30/75 (40) |
| Progesterone Receptor | 2 | 3–5 | 3/11 (27) | 3/10 (30) | 3/11 (27) | 6/9 (67) | 9/61 (15) |
| pSTAT-3 | 1 | 5 | 25/42 (60) | 4/7 (57) | 8/32 (25) | 4/15 (27) | 37/81 (46) |
| RAGE | 1 | 5 | - | - | - | - | 72/80 (90) |
| RASSF1A | 1 | 6 | 33/60 (55) | - | - | - | 33/60 (55) |
| RECK | 1 | 5 | 31/322 (9.6) | 20/43 (47) | 12/22 (55) | 7/8 (88) | 63/387 (16) |
| Recoverin | 1 | 4 | - | - | - | 11/12 (92) | 26/38 (68) |
| RET | 1 | 5 | 0/18 (0) | 34/66 (52) | 4/10 (40) | 4/4 (100) | 49/107 (46) |
| RON | 2 | 3–4 | 53/82 (65) | 38/38 (100) | 65/75 (87) | 84/86 (98) | 156/195 (80) |
| S100A1 | 2 | 3–5 | 30/41 (73) | 34/36 (94) | 6/61 (9.8) | 41/44 (93) | 79/147 (54) |
| SCF | 1 | 5 | 40/40 (100) | 25/25 (100) | 19/19 (100) | 27/27 (100) | 84/84 (100) |
| Secretagogin | 1 | 4 | 35/94 (37) | 0/37 (0) | 0/24 (0) | 0/30 (0) | 35/155 (23) |
| Skp-2 | 1 | 5 | 68/384 (18) | 3/81 (3.7) | 0/17 (0) | - | 71/482 (15) |
| Synaptophysin | 1 | 6 | 2/34 (5.9) | 0/9 (0) | 0/2 (0) | - | 2/45 (4.4) |
| TFE-3 | 1 | 5 | 4/25 (16) | 0/6 (0) | 1/9 (11) | - | 5/40 (12.5) |
| TFE-B | 1 | 5 | 0/25 (0) | 0/6 (0) | 0/9 (0) | 0/1 (0) | 0/40 (0) |
| TFF-1 (pS2) | 1 | 4 | 15/60 (25) | - | - | - | 15/50 (25) |
| THP | 1 | 3 | - | - | 0/21 (0) | - | 0/21 (0) |
| TPI-1 | 1 | 5 | 18/19 (95) | 1/2 (50) | 0/3 (0) | 0/1 (0) | 19/24 (79) |
| uPA | 1 | 6 | 3/17 (18) | - | - | - | 3/18 (17) |
| uPAR | 1 | 6 | 14/17 (82) | - | - | - | 15/18 (83) |
| VEGF | 1 | 4 | 25/31 (84) | 6/8 (75) | 1/2 (50) | - | 34/44 (77) |
| VHL | 1 | 8 | 77/317 (24) | 13/40 (33) | 4/22 (18) | 4/8 (50) | 102/400 (26) |
| Vimentin | 5 | 1–6 | 96/132 (73) | 52/62 (84) | 3/102 (2.9) | 39/174 (22) | 167/313 (53) |
| VLA-4 | 1 | 4 | 19/19 (100) | - | 3/3 (100) | - | 23/23 (100) |
| Control | ccRCC | |
|---|---|---|
| Aminopeptidase A (APA) | ||
| Strong | 65 (89.0%) | 11 (15.1%) |
| Weak | 8 (11.0%) | 55 (75.3%) |
| No Stain | 0 (0%) | 7 (9.6%) |
| Aminopeptidase N (APN) | ||
| Strong | 73 (100%) | 35 (47.9%) |
| Weak | 0 (0%) | 27 (37.0%) |
| No Stain | 0 (0%) | 11 (15.1%) |
| Gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) | ||
| Strong | 69 (94.5%) | 8 (11.0%) |
| Weak | 4 (5.5%) | 52 (71.2%) |
| No Stain | 0 (0%) | 13 (17.8%) |
| Neuron-specific enolase (NSE) | ||
| Strong | 0 (0%) | 31 (42.5%) |
| Weak | 57 (78.1%) | 33 (45.2%) |
| No Stain | 16 (21.9%) | 9 (12.3%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Berezowski, B.; Boothe, R., Jr.; Chaplin, B.; Del Vecchio, S.J.; Fares, Z.; Humphries, T.L.R.; Ng, K.L.; Noonan, T.; Samaratunga, H.; Urquhart, A.; et al. Biomarkers in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Immunohistochemical Validation Study. Cancers 2025, 17, 2588. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152588
Berezowski B, Boothe R Jr., Chaplin B, Del Vecchio SJ, Fares Z, Humphries TLR, Ng KL, Noonan T, Samaratunga H, Urquhart A, et al. Biomarkers in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Immunohistochemical Validation Study. Cancers. 2025; 17(15):2588. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152588
Chicago/Turabian StyleBerezowski, Brett, Robert Boothe, Jr., Billy Chaplin, Sharon J. Del Vecchio, Zakariya Fares, Tyrone L. R. Humphries, Keng Lim Ng, Taylor Noonan, Hemamali Samaratunga, Aaron Urquhart, and et al. 2025. "Biomarkers in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Immunohistochemical Validation Study" Cancers 17, no. 15: 2588. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152588
APA StyleBerezowski, B., Boothe, R., Jr., Chaplin, B., Del Vecchio, S. J., Fares, Z., Humphries, T. L. R., Ng, K. L., Noonan, T., Samaratunga, H., Urquhart, A., Vesey, D. A., Wood, S. T., Gobe, G. C., & Ellis, R. J. (2025). Biomarkers in Renal Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Immunohistochemical Validation Study. Cancers, 17(15), 2588. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152588






