Advances in Bidirectional Therapy for Peritoneal Metastases: A Systematic Review of Pressurized Intraperitoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (PIPAC) Combined with Systemic Chemotherapy
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background and Evolving Role of PIPAC
1.2. Rationale for Bidirectional Chemotherapy
1.3. Operational Definition of Bidirectional Chemotherapy
2. Methods
2.1. Protocol and Study Registration
2.2. Literature Search
2.3. Study Selection
2.4. Data Extraction
- Study characteristics: Author, year, country, design, sample size, proportion receiving bidirectional therapy.
- Patient demographics: Age, sex, primary tumor origin, prior chemotherapy.
- Intervention details: PIPAC drugs and dosages, systemic regimens, treatment intervals.
- Outcomes: Overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), pathological response (e.g., PRGS), radiological response (e.g., RECIST criteria), quality of life (e.g., EORTC QLQ-C30, EQ-5D), and adverse events (Clavien–Dindo, CTCAE).
2.5. Methodological Quality Assessment
2.6. Data Synthesis
- Study characteristics (design, demographics, prior treatment).
- PIPAC and systemic chemotherapy regimens.
- Survival and tumor response outcomes.
- Quality of life measures and longitudinal scores.
- Adverse event rates (Clavien–Dindo, CTCAE) and treatment discontinuation.
3. Results
3.1. Study Selection
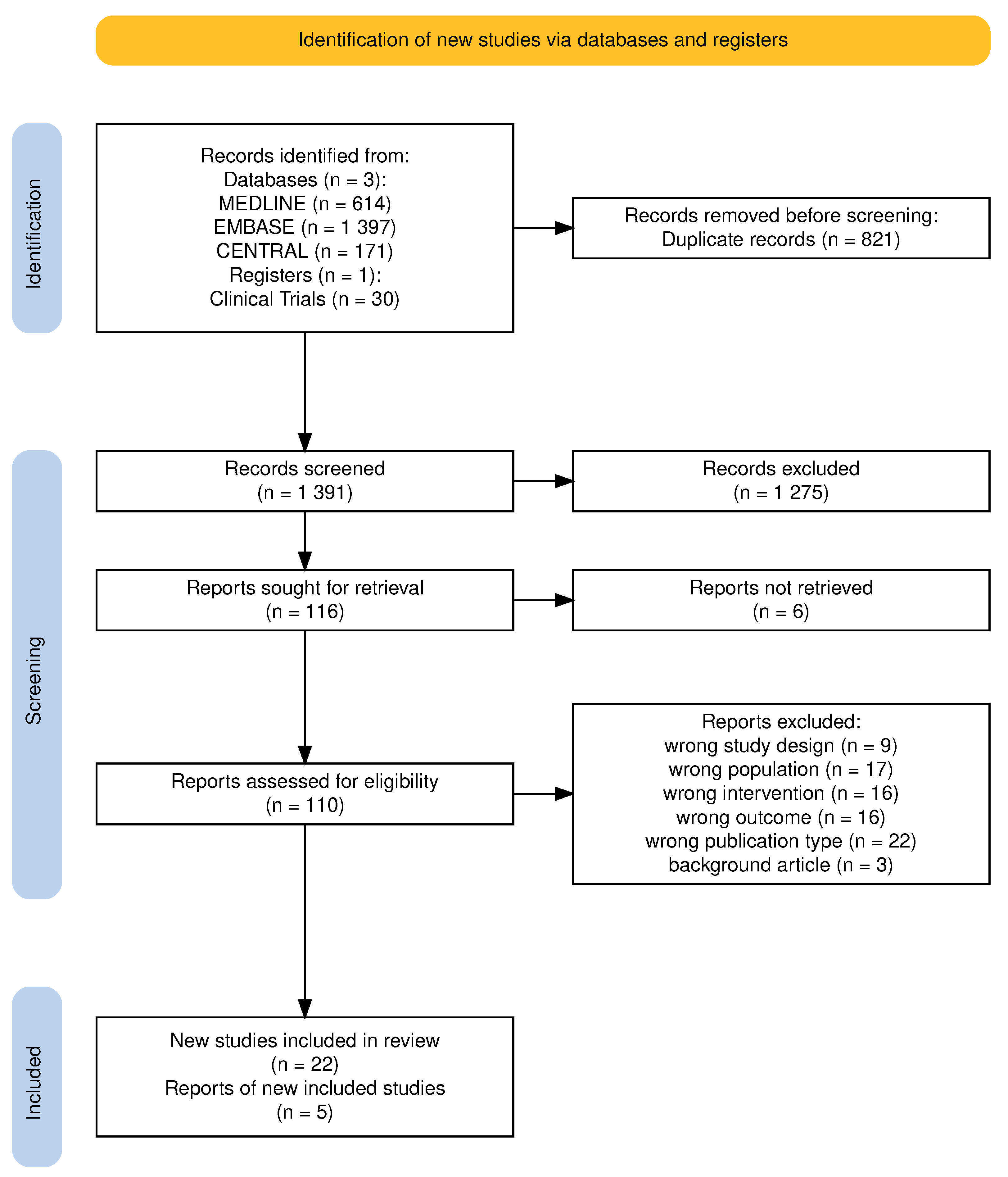
3.1.1. Study Flow
3.1.2. Excluded Studies
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Patient Characteristics
3.4. Treatment Regimens
- Oxaliplatin (92 mg/m2), mainly for colorectal and appendiceal cancers; or
- Cisplatin (7.5 mg/m2) combined with doxorubicin (1.5 mg/m2), commonly used in gastric, ovarian, and other peritoneal surface malignancies.
- FOLFOX, FOLFIRI, FOLFOXIRI, XELOX in gastrointestinal tumors.
- FLOT in advanced gastric cancer.
- Platinum-based doublets in ovarian and mesothelial malignancies.
- Occasional use of targeted therapies (e.g., bevacizumab, EGFR inhibitors) and immune checkpoint inhibitors.
3.5. Survival and Tumor Response
3.6. Safety and Treatment-Related Toxicity
3.7. Forthcoming Bidirectional PIPAC Trials
| Trial (Author & Year) | Country * | Design | Tumor/Eligibility | Intervention | N | Outcomes | Status | Est. Completion |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dumont et al., 2025 [46] | FRA | PRO; II randomized; multicentric | CRC/PCI > 15; ECOG 0–2 | FOLFIRI/FIRINOX ± PIPAC Oxaliplatin | 114 | Prim: PFS; Sec: OS, ORR, safety, QoL, PK, biomarkers | Not yet recruiting | August 2029 § |
| Di Giorgio et al., 2024 [47] | ITA | PRO; II; Single-arm; open label; monocentric | PC-PM; ECOG 0–1 | IV Nab-Pac Gem + PIPAC Nab-Pac | 38 | Prim: RR (RECIST); Sec: safety (CTCAE, CD), PRGS, PFS, OS, QoL, PK, biomarkers | Recruiting | July 2025 † |
| Casella et al., 2022 [49] | ITA | PRO; III randomized; open label; multicentric | Oligometastatic GC-PM; PCI ≤ 6; ECOG 0–1 | FOLFOX ± PIPAC (Cis + Dox) | 98 | Prim: R0 resectability; Sec: OS, PFS, histology (PRGS/TRG), QoL, AEs, cost-effectiveness | Recruiting | April 2028 ‡ |
| Luksta et al., 2023 [48] | LTU | PRO; II; Single-arm, open label; multicentric | GC-PM; ECOG 0–1; 1L FOLFOX | 3 × PIPAC (Cis + Dox) + 6 × FOLFOX | 37 | Prim: RR (RECIST); Sec: procedural metrics, PCI/PRGS, ascites, safety, QoL, PFS, OS | Recruiting | — |
| Sgarbura et al., 2019 [50,51] | FRA | PRO; II; randomized; open label; multicentric | Mid/low RC; ≥2 MRI-risk; ECOG 0–2 | Cis + Pem ± PIPAC (Cis + Dox) | 66 | Prim: OS; Sec: PFS, safety, compliance, feasibility, conversion to resectability, histological response, QoL | Completed | December 2024 |
| Eveno et al., 2018 [52] | FRA | PRO; II; randomized; open label; multicentric | GC-PM; PCI > 8; WHO 0–1 | PIPAC (Cis + Dox) ± IV chemo | 94 | Prim: PFS; Sec: OS, safety, QoL, morbidity, secondary resectability | NR | — |
3.8. Methodological Quality Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quénet, F.; Elias, D.; Roca, L.; Goéré, D.; Ghouti, L.; Pocard, M.; Facy, O.; Arvieux, C.; Lorimier, G.; Pezet, D.; et al. Cytoreductive surgery plus hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy versus cytoreductive surgery alone for colorectal peritoneal metastases (PRODIGE 7): A multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 256–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rijken, A.; Lurvink, R.J.; Luyer, M.D.P.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.P.; van Erning, F.N.; van Sandick, J.W.; de Hingh, I.H.J.T. The Burden of Peritoneal Metastases from Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review on the Incidence, Risk Factors and Survival. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breusa, S.; Zilio, S.; Catania, G.; Bakrin, N.; Kryza, D.; Lollo, G. Localized chemotherapy approaches and advanced drug delivery strategies: A step forward in the treatment of peritoneal carcinomatosis from ovarian cancer. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1125868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minicozzi, P.; Cassetti, T.; Vener, C.; Sant, M. Analysis of incidence, mortality and survival for pancreatic and biliary tract cancers across Europe, with assessment of influence of revised European age standardisation on estimates. Cancer Epidemiol. 2018, 55, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solass, W.; Kerb, R.; Mürdter, T.; Giger-Pabst, U.; Strumberg, D.; Tempfer, C.; Zieren, J.; Schwab, M.; Reymond, M.A. Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy of Peritoneal Carcinomatosis Using Pressurized Aerosol as an Alternative to Liquid Solution: First Evidence for Efficacy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 21, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, E.; Harkins, P.; Fenn, S.; Khan, F.; McCormack, O.; Mulsow, J.; Shields, C. Pressurised intraperitoneal aerosolised chemotherapy (PIPAC) for peritoneal malignancy, a systematic review of its occupational safety. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2025, 51, 110312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempfer, C.B.; Winnekendonk, G.; Solass, W.; Horvat, R.; Giger-Pabst, U.; Zieren, J.; Rezniczek, G.A.; Reymond, M.A. Pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy in women with recurrent ovarian cancer: A phase 2 study. Gynecol. Oncol. 2015, 137, 223–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadiradze, G.; Giger-Pabst, U.; Zieren, J.; Strumberg, D.; Solass, W.; Reymond, M.A. Pressurized Intraperitoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (PIPAC) with Low-Dose Cisplatin and Doxorubicin in Gastric Peritoneal Metastasis. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2016, 20, 367–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Giorgio, A.; Abatini, C.; Attalla El Halabieh, M.; Vita, E.; Vizzielli, G.; Gallotta, V.; Pacelli, F.; Rotolo, S. From palliation to cure: PIPAC for peritoneal malignancies. Minerva Medica 2019, 110, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Yang, Z.; Li, R.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. Pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer with peritoneal metastases: A comprehensive meta-analysis of feasibility, efficacy, and safety. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2025, 13, goaf040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kepenekian, V.; Péron, J.; You, B.; Bonnefoy, I.; Villeneuve, L.; Alyami, M.; Bakrin, N.; Rousset, P.; Benzerdjeb, N.; Glehen, O. Non-resectable Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma Treated with Pressurized Intraperitoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (PIPAC) Plus Systemic Chemotherapy Could Lead to Secondary Complete Cytoreductive Surgery: A Cohort Study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 29, 2104–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graversen, M.; Detlefsen, S.; Fristrup, C.; Pfeiffer, P.; Mortensen, M.B. Adjuvant Pressurized IntraPeritoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (PIPAC) in resected high-risk colon cancer patients—Study protocol for the PIPAC-OPC3 Trial. A prospective, controlled phase 2 Study. Pleura Peritoneum 2018, 3, 20180107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giorgio, A.; Macrì, A.; Ferracci, F.; Robella, M.; Visaloco, M.; De Manzoni, G.; Sammartino, P.; Sommariva, A.; Biacchi, D.; Roviello, F.; et al. 10 Years of Pressurized Intraperitoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (PIPAC): A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cancers 2023, 15, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploug, M.; Graversen, M.; Pfeiffer, P.; Mortensen, M.B. Bidirectional treatment of peritoneal metastasis with Pressurized IntraPeritoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (PIPAC) and systemic chemotherapy: A systematic review. BMC Cancer 2020, 20, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacquet, P.; Sugarbaker, P.H. Peritoneal-plasma barrier. In Peritoneal Carcinomatosis: Principles of Management; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1996; pp. 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bree, E.; Michelakis, D.; Stamatiou, D.; Romanos, J.; Zoras, O. Pharmacological principles of intraperitoneal and bidirectional chemotherapy. Pleura Peritoneum 2017, 2, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugarbaker, P.H. Bidirectional chemotherapy long-term as a treatment strategy for peritoneal metastases. Transl. Cancer Res. 2024, 13, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst. Rev. 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 3166-1; Codes for the Representation of Names of Countries and Their Subdivisions—Part 1: Country Codes. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/72482.html (accessed on 31 July 2025).
- Slim, K.; Nini, E.; Forestier, D.; Kwiatkowski, F.; Panis, Y.; Chipponi, J. Methodological index for non-randomized studies (MINORS): Development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J. Surg. 2003, 73, 712–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffone, A.; Pellecchia, G.; Pregnolato, S.; Raimondo, D.; Travaglino, A.; Neola, D.; Driul, L.; Scambia, G.; Arcieri, M.; Vastarella, M.G.; et al. Impact of optimal secondary cytoreductive surgery on survival outcomes in women with recurrent endometrial carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Gynecol. Obstet. 2025, 170, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreve, M.; Vos, C.; Vahl, A.; de Vries, J.; Kum, S.; de Borst, G.; Ünlü, u. Venous Arterialisation for Salvage of Critically Ischaemic Limbs: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2017, 53, 387–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddaway, N.R.; Page, M.J.; Pritchard, C.C.; McGuinness, L.A. PRISMA2020: An R package and Shiny app for producing PRISMA 2020-compliant flow diagrams, with interactivity for optimised digital transparency and Open Synthesis. Campbell Syst. Rev. 2022, 18, e1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reymond, M.; Demtroeder, C.; Solass, W.; Winnekendonk, G.; Tempfer, C. Electrostatic precipitation Pressurized IntraPeritoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (ePIPAC): First in-human application. Pleura Peritoneum 2016, 1, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kryh-Jensen, C.G.; Fristrup, C.W.; Ainsworth, A.P.; Detlefsen, S.; Mortensen, M.B.; Pfeiffer, P.; Tarpgaard, L.S.; Graversen, M. What is long-term survival in patients with peritoneal metastasis from gastric, pancreatic, or colorectal cancer? A study of patients treated with systemic chemotherapy and pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy (PIPAC). Pleura Peritoneum 2023, 8, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebert, M.; Alyami, M.; Mercier, F.; Gallice, C.; Villeneuve, L.; Laplace, N.; Passot, G.; Bakrin, N.; Glehen, O.; Kepenekian, V. Pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy (PIPAC) in association with systemic chemotherapy and bevacizumab, evaluation of safety and feasibility. A single center comparative study. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundar, R.; Chia, D.; Zhao, J.; Lee, A.; Kim, G.; Tan, H.; Pang, A.; Shabbir, A.; Willaert, W.; Ma, H.; et al. Phase I PIANO trial—PIPAC-oxaliplatin and systemic nivolumab combination for gastric cancer peritoneal metastases: Clinical and translational outcomes. ESMO Open 2024, 9, 103681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van de Vlasakker, V.C.J.; Rauwerdink, P.; Rovers, K.P.B.; Wassenaar, E.C.; Creemers, G.J.; Los, M.; Burger, J.W.A.; Nienhuijs, S.W.; Kranenburg, O.; Wiezer, M.J.; et al. Patient-reported outcomes during first-line palliative systemic therapy alternated with pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy for unresectable colorectal peritoneal metastases: A single-arm phase II trial (CRC-PIPAC-II). Surg. Endosc. 2024, 38, 6566–6576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, F.; Bencivenga, M.; Brancato, G.; Torroni, L.; Ridolfi, C.; Puccio, C.; Alloggio, M.; Meloni, F.; Fusario, D.; Marrelli, D.; et al. Bidirectional Approach with PIPAC and Systemic Chemotherapy for Patients with Synchronous Gastric Cancer Peritoneal Metastases (GCPM). Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 30, 5733–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyle, P.; Perry, K.; Moutadjer, A.; Gilfillan, N.; Webb, R.; Basak, D.; Ziprin, P.; Blunt, D.; Burn, J.; Van Ree, K.; et al. UK trial of pressurised intraperitoneal aerosolised chemotherapy (PIPAC) with oxaliplatin for colorectal cancer peritoneal metastases (NCT03868228). Pleura Peritoneum 2023, 8, 157–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raoof, M.; Whelan, R.L.; Sullivan, K.M.; Ruel, C.; Frankel, P.H.; Cole, S.E.; Tinsley, R.; Eng, M.; Fakih, M.; Chao, J.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Oxaliplatin Pressurized Intraperitoneal Aerosolized Chemotherapy (PIPAC) in Colorectal and Appendiceal Cancer with Peritoneal Metastases: Results of a Multicenter Phase I Trial in the USA. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2023, 30, 7814–7824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyami, M.; Bonnot, P.E.; Mercier, F.; Laplace, N.; Villeneuve, L.; Passot, G.; Bakrin, N.; Kepenekian, V.; Glehen, O. Pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy (PIPAC) for unresectable peritoneal metastasis from gastric cancer. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 47, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldbrügge, L.; Gronau, F.; Brandl, A.; Auer, T.A.; Oeff, A.; Thuss-Patience, P.; Pratschke, J.; Rau, B. Systemic Chemotherapy Including Ramucirumab in Combination With Pressurized Intra-Peritoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy Is a Safe Treatment Option for Peritoneal Metastasis of Gastric Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 610572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Giorgio, A.; Schena, C.A.; El Halabieh, M.A.; Abatini, C.; Vita, E.; Strippoli, A.; Inzani, F.; Rodolfino, E.; Romanò, B.; Pacelli, F.; et al. Systemic chemotherapy and pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy (PIPAC): A bidirectional approach for gastric cancer peritoneal metastasis. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 34, 270–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gockel, I.; Jansen-Winkeln, B.; Haase, L.; Niebisch, S.; Moulla, Y.; Lyros, O.; Lordick, F.; Schierle, K.; Wittekind, C.; Thieme, R. Pressurized IntraPeritoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (PIPAC) in patients with peritoneal metastasized colorectal, appendiceal and small bowel cancer. Tumori J. 2019, 106, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkenstein, T.A.; Blechert, A.; Biedermann, R.; Malzahn, U.; Königsrainer, A.; Königsrainer, I. First Clinical Data of Pressurized Intraperitoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (PIPAC) as Salvage Therapy for Peritoneal Metastatic Biliary Tract Cancer. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larbre, V.; Alyami, M.; Mercier, F.; Vantard, N.; Bonnefoy, I.; Opsomer, M.A.; Villeneuve, L.; Bakrin, N.; Rioufol, C.; Glehen, O.; et al. No Renal Toxicity After Repeated Treatment with Pressurized Intraperitoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (PIPAC) in Patients with Unresectable Peritoneal Metastasis. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 6869–6875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyami, M.; Gagniere, J.; Sgarbura, O.; Cabelguenne, D.; Villeneuve, L.; Pezet, D.; Quenet, F.; Glehen, O.; Bakrin, N.; Passot, G. Multicentric initial experience with the use of the pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy (PIPAC) in the management of unresectable peritoneal carcinomatosis. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 43, 2178–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira Farinha, H.; Grass, F.; Kefleyesus, A.; Achtari, C.; Romain, B.; Montemurro, M.; Demartines, N.; Hübner, M. Impact of Pressurized Intraperitoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy on Quality of Life and Symptoms in Patients with Peritoneal Carcinomatosis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2017, 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilal, Z.; Rezniczek, G.A.; Klenke, R.; Dogan, A.; Tempfer, C.B. Nutritional status, cachexia, and anorexia in women with peritoneal metastasis and intraperitoneal chemotherapy: A longitudinal analysis. J. Gynecol. Oncol. 2017, 28, e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosrawipour, T.; Khosrawipour, V.; Giger-Pabst, U. Pressurized Intra Peritoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy in patients suffering from peritoneal carcinomatosis of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demtröder, C.; Solass, W.; Zieren, J.; Strumberg, D.; Giger-Pabst, U.; Reymond, M. Pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy with oxaliplatin in colorectal peritoneal metastasis. Color. Dis. 2016, 18, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khomyakov, V.; Ryabov, A.; Ivanov, A.; Bolotina, L.; Utkina, A.; Volchenko, N.; Kaprin, A. Bidirectional chemotherapy in gastric cancer with peritoneal metastasis combining intravenous XELOX with intraperitoneal chemotherapy with low-dose cisplatin and Doxorubicin administered as a pressurized aerosol: An open-label, Phase-2 study (PIPAC-GA2). Pleura Peritoneum 2016, 1, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robella, M.; Vaira, M.; De Simone, M. Safety and feasibility of pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy (PIPAC) associated with systemic chemotherapy: An innovative approach to treat peritoneal carcinomatosis. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 14, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Systemic Antitumor Treatment with or Without Pressurized Intraperitoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy for Colon Peritoneal Metastases (PIPOX02); Identifier NCT06681038; National Library of Medicine (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2024; [About 12 Screens]. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT06681038 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Di Giorgio, A.; Ferracci, F.; Bagalà, C.; Carbone, C.; Salvatore, L.; Strippoli, A.; Attalla El Halabieh, M.; Abatini, C.; Alfieri, S.; Pacelli, F.; et al. Combined Nabpaclitaxel pressurized intraPeritoneal aerosol chemotherapy with systemic Nabpaclitaxel-Gemcitabine chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer peritoneal metastases: Protocol of single-arm, open-label, phase II trial (Nab-PIPAC trial). Pleura Peritoneum 2024, 9, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luksta, M.; Bausys, A.; Bickaite, K.; Rackauskas, R.; Paskonis, M.; Luksaite-Lukste, R.; Ranceva, A.; Stulpinas, R.; Brasiuniene, B.; Baltruskeviciene, E.; et al. Pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy (PIPAC) with cisplatin and doxorubicin in combination with FOLFOX chemotherapy as a first-line treatment for gastric cancer patients with peritoneal metastases: Single-arm phase II study. BMC Cancer 2023, 23, 1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casella, F.; Bencivenga, M.; Rosati, R.; Fumagalli, U.R.; Marrelli, D.; Pacelli, F.; Macrì, A.; Donini, A.; Torroni, L.; Pavarana, M.; et al. Pressurized intraperitoneal aerosol chemotherapy (PIPAC) in multimodal therapy for patients with oligometastatic peritoneal gastric cancer: A randomized multicenter phase III trial PIPAC VEROne. Pleura Peritoneum 2022, 7, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sgarbura, O.; Gourgou, S.; Tosi, D.; Bakrin, N.; Bouazza, N.; Delaine, S.; De Forges, H.; Pocard, M.; Quénet, F. MESOTIP: Phase II multicenter randomized trial evaluating the association of PIPAC and systemic chemotherapy vs. systemic chemotherapy alone as 1st-line treatment of malignant peritoneal mesothelioma. Pleura Peritoneum 2019, 4, 20190010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Rectal Surgery Evaluation Trial (RESET); Identifier NCT03574493; National Library of Medicine (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2025; [about 5 screens]. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03574493 (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- Eveno, C.; Jouvin, I.; Pocard, M. PIPAC EstoK 01: Pressurized IntraPeritoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy with cisplatin and doxorubicin (PIPAC C/D) in gastric peritoneal metastasis: A randomized and multicenter phase II study. Pleura Peritoneum 2018, 3, 20180116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Author & Year | Country * | Design ** | Duration *** | Patients n | Bidirectional n (%) | Sex M (%) | Age † | Malignancies ‡ | Prev. Chemo n (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sundar et al., 2024 [28] | SGP & BEL | PRO I | Jun 20–Nov 22 | 18 | 18 (100%) | 7 (39%) | 65 a [52.5–70.75] | GC | 18 (100%) |
| van de Vlasakker et al., 2024 [29] | NLD | PRO II | Feb 20–Aug 22 | 20 | 20 (100%) | 10 (50%) | 57.5 a (41–70) | CRC, AC | 0 (0%) |
| Casella et al., 2023 [30] | ITA | RETRO | Oct 19–Apr 22 | 42 | 42 (100%) | 15 (36%) | 60.5 a (49–68) | GC | NR |
| Kryh-Jensen et al., 2023 [26] | DNK | RETRO | Jan 16–Feb 23 | 108 | 49 (45%) | 53 (49%) | GC 64 a; PC 61 a; CRC 69 a | GC, PC, CRC | 107 (99%) |
| Kyle et al., 2023 [31] | GBR | PRO | Jan 19–Jan 22 | 5 | 5 (100%) | 2 (40%) | 44 a (34–66) | CRC | 5 (100%) |
| Raoof et al., 2023 [32] | USA | PRO I | Aug 20–Jan 22 | 12 | 12 (100%) | 7 (58%) | 60 a (29–75) | AC, CRC | 12 (100%) |
| Alyami et al., 2021 [33] | FRA | RETRO | NR–Jan 18 | 42 | 42 (100%) | 20 (48%) | 51.5 a (32–74.7) | GC | 42 (100%) |
| Feldbruegge et al., 2021 [34] | DEU | RETRO | Mar 17–May 20 | 50 | 50 (100%) | 28 (56%) | 58 a (31–76) | GC | 50 (100%) |
| Kepenekian et al., 2021 [11] | FRA | RETRO | Jan 16–May 20 | 26 | 26 (100%) | 14 (54%) | 64 a [56–69] | DMPM | 9 (35%) |
| Siebert et al., 2021 [27] | FRA | RETRO | Dec 15–Mar 18 | 134 | 134 (100%) | 60 (45%) | 59.3 a (25–78) | GC, CRC, OC | 134 (100%) |
| Di Giorgio et al., 2020 [35] | ITA | RETRO | Sep 17–Sep 19 | 28 | 26 (93%) | 12 (43%) | 50 a (38–79) | GC | 28 (100%) |
| Gockel et al., 2020 [36] | DEU | PRO | Nov 15–Feb 18 | 13 | 13 (100%) | 6 (46%) | 61 a (49–77) | CRC, AC, small bowel | 12 (66%) |
| Falkenstein et al., 2018 [37] | DEU | RETRO | Feb 13–Jan 17 | 13 | 3 (23%) | 8 (61%) | 58 b [37–75] | HPB | 7 (54%) |
| Larbre et al., 2018 [38] | FRA | RETRO | Dec 15–Sep 17 | 43 | 39 (91%) | 19 (44%) | 59.8 b (33–77.9) | GC, OC, DMPM, PMP | 39 (91%) |
| Alyami et al., 2017 [39] | FRA | RETRO | Dec 15–Dec 16 | 73 | 64 (88%) | 31 (42%) | 57.1 a (32.3–77.9) | GC, CRC, OC, DMPM, PMP | 64 (88%) |
| Farinha et al., 2017 [40] | CHE | RETRO | Jan 15–Apr 16 | 42 | 1 (2%) | 8 (19%) | 66 a (59–73) | GYN, DIG | NR |
| Hilal et al., 2017 [41] | DEU | PRO | Apr 14–May 16 | 84 | 6 (7%) | 0 (0%) | 60.4 b ± 12.2 | GYN | 84 (100%) |
| Khosrawipour et al., 2017 [42] | DEU | RETRO | Jun 15–Jun 17 | 20 | 6 (30%) | 15 (75%) | 60.6 b (49–69) | PC | 20 (100%) |
| Demtroeder et al., 2016 [43] | DEU | RETRO | Oct 12–Feb 14 | 17 | 11 (65%) | 10 (59%) | 59 b ± 12 | CRC | 16 (94%) |
| Khomyakov et al., 2016 [44] | RUS | PRO II | Aug 13–Jul 16 | 31 | 31 (100%) | 9 (29%) | 52 b | GC | 7 (23%) |
| Reymond et al., 2016 [25] | DEU | RETRO | Jul 14–Oct 15 | 3 | 1 (33%) | 1 (33%) | 66.3 b (59–72) | PC, GBC | 3 (100%) |
| Robella et al., 2016 [45] | ITA | RETRO | Jun 15–Feb 16 | 14 | 13 (93%) | NR | (18–78) | GC, CRC, OC, DMPM, PMP | 14 (100%) |
| Total [Mode] | [DEU] | [R: 15 (68%)] | — | 1010 | 742 (73%) | 314 M: 453 F | — | [GC] | 671 (66%) |
| Author & Year | PIPAC Drug (Dose mg/m2) | Systemic Regimen * | Median Interval Between PIPACs | Median PIPAC n ** | Total PIPAC n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sundar et al., 2024 [28] | OXA (90) | Nivolumab | 6 wks | 1 [1–3] | 32 |
| van de Vlasakker et al., 2024 [29] | OXA (92) | CapOX/FOLFOX/ FOLFIRI/ FOLFOXIRI + BEVA | 1–4 wks post SC | NR | 52; NR e |
| Casella et al., 2023 [30] | CDDP + DXR (7.5/1.5 → 10.5/2.1) | FLOT/FOLFOX | 6 wks | NR | 74 |
| Kryh-Jensen et al., 2023 [26] | OXA (NR) | NR | 4–7 wks | 3 (1–9) | NR; NR e |
| Kyle et al., 2023 [31] | OXA (92) | NR | 8 wks | 2 (1–4) | 10 |
| Raoof et al., 2023 [32] | OXA (90) | FU + LV | 6 wks | 2 (1–3) | 26 |
| Alyami et al., 2021 [33] | CDDP + DXR (7.5/1.5) | XELOX | 6 wks | 3 (1–12) | 163 |
| Feldbrügge et al., 2021 [34] | CDDP + DXR (7.5/1.5) | NR ± Ramucirumab | 20 d (7–41) | NR | 90 |
| Kepenekian et al., 2021 [11] | CDDP + DXR (7.5/1.5) | CDDP + MTA/GEM | 6–8 wks | 3 [1–3] (1–15) | 79 |
| Siebert et al., 2021 [27] | CDDP + DXR (7.5/1.5)/OXA (92) | NR ± BEVA | 6 wks | 3 | 397 |
| Di Giorgio et al., 2020 [35] | CDDP + DXR (1.5/7.5) | ECF/mFOLFOX/5-FU/FOLFIRI/PTX | 6–8 wks (2 wks post-SC) | NR | 46 |
| Gockel et al., 2020 [36] | CDDP + DXR (7.5/1.5) | FOLFOX + BEVA/ antiEGFR/FOLFIRI/ Cap+antiEGFR | 6 wks | 2 (1–6) | 26 |
| Falkenstein et al., 2018 [37] | CDDP + DXR (7.5/1.5) | NR | 6 wks | NR | 17 |
| Larbre et al., 2018 [38] | CDDP + DXR (7.5/1.5) | NR | 6 wks | 3 (3–9) | 175 |
| Alyami et al., 2017 [39] | CDDP + DXR (7.5/1.5) OXA (92)/MMC (1.5) | NR | 6–8 wks | 2 (1–6) | 164 |
| Farinha et al., 2017 [40] | CDDP + DXR (7.5/1.5) | NR | 6 wks | 2 (1–4) | 91 |
| Hilal et al., 2017 [41] | CDDP + DXR (7.5/1.5) | NR | 4–6 wks | NR | NR |
| Khosrawipour et al., 2017 [42] | CDDP + DXR (7.5/1.5) | GEM + Nab-PTX/FOLFIRINOX/ GEM | 6 wks | NR | 41 |
| Demtröder et al., 2016 [43] | OXA (92) | NR | 6 wks | 3 (1–6) | 48 |
| Khomyakov et al., 2016 [44] | CDDP/DXR (7.5/1.5) | XELOX | 6 wks | NR | 56 |
| Reymond et al., 2016 [25] | CDDP/DXR (7.5/1.5) | CDDP + GEM | 6 wks | 2 (2–6) | 10; 4 e |
| Robella et al., 2016 [45] | CDDP + DXR (7.5/1.5)/OXA (92) | Various SC | 6 wks | 3 (2–4) | 40 |
| Author & Year | Follow-Up (mo) | OS (mo) | PFS (mo) | RR * | PRGS | PCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sundar et al., 2024 [28] | 20.8 | 6.0 (2.4–18.4) p | 1.8 (1.6–6.0) p | 7%; SD 57% | 1–2 in 66.7% 2; 100% 3 | 20 [12.3–30]; Δ −5/−7 at 2,3 |
| van de Vlasakker et al., 2024 [29] | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 27 (15–38)–NR |
| Casella et al., 2023 [30] | NR | 19.6 (14–24) d; 10.5 (7–13) p | NR | NR | 1: 37.1%; 2: 31.0%; 3: 21.4% 2; 1: 2.4%; 2: 2.4%; 3: 9.5% 3 | 16 [8–26]–NR |
| Kryh-Jensen et al., 2023 [26] | NR | GC 7.8; PC 10.0; CRC 16.0 p | NR | NR | GC ↓ 61%; PC ↓ 59%; CRC ↓ 69% | NR |
| Kyle et al., 2023 [31] | 11.6 | 11.6 (4.7–3.6) p; 25.0 (7.2–42.2) d | 6.0 (0.5–25.1) p | NR | NR | 25 (20–32)–NR |
| Raoof et al., 2023 [32] | 5.4 | 12.0 [4.3–NR] p | 2.9 [1.4–6.6] p | SD 50%; PD 50% | ↓42%; SD 17%; ↑ 42% | 28 [19–32]; ↓ 50%; ↑ 50% |
| Alyami et al., 2021 [33] | NR | 19.1 p | NR | NR | NR | 17 (1–39)–NR |
| Feldbrügge et al., 2021 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 19 (1–39)–NR |
| Kepenekian et al., 2021 [11] | 29.6 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 15% | median pre 3.0 (2.2–4.0); median post 2.0 (2.0–3.0) | pre 27 (20–34); post 25 (20–39) |
| Siebert et al., 2021 [27] | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 18 (0–39)–NR |
| Di Giorgio et al., 2020 [35] | NR | 12.3 (11.7–17.4) d | NR | NR | CR (1) 7.7%; PR (2–3) 53.8%; SD (4) 38.5% | 20 ± 9.9; ↑ 76.9%; SD 7.7%; ↓ 15.4% |
| Gockel et al., 2020 [36] | NR | 10.1 (1–16.3) p | NR | NR | NR | 14 (2–27)–71% Stable |
| Falkenstein et al., 2018 [37] | NR | 2.8 (95% CI = 2.0–3.7) p | NR | NR | TRG0: 20%; TRG1-2: 40%; TRG3: 40% | 20 [8–27]–NR |
| Larbre et al., 2018 [38] | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 17 (5–39)–NR |
| Alyami et al., 2017 [39] | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 19 (1–39) 1–16 (1–39) 2–15 (2–31) 3 |
| Farinha et al., 2017 [40] | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 10 (5–17)–NR |
| Hilal et al., 2017 [41] | 2.4 (0.3–21.7) | NR | NR | NR | NR | 18.9 ± 11.2–NR |
| Khosrawipour et al., 2017 [42] | 10.0 | 8.5 (95% CI = 8.5–11.9) p | NR | NR | TRG1: 15%; TRG3: 25%; TRG4: 10% | 26.6 (1–39)–NR |
| Demtroeder et al., 2016 [43] | 22.0 ± 4 | 15.7 p | NR | NR | TRG0: 11.7%; TRG1-2: 6%; TRG3: 24%; TRG4: 41.2% | 16 ± 10–NR |
| Khomyakov et al., 2016 [44] | 13.0 | 13.0 p | NR | NR | 1: 27%; 2: 33%; 3–4 40% | 16 (6–34)–NR |
| Reymond et al., 2016 [25] | NR | 11.7 (11.1–22) d; 9.1 (8.6–18) p | NR | PR 66%; SD 33% | 1: 67%; 2: 33% | 3 (3–17)–NR |
| Robella et al., 2016 [45] | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 17 (12–21)–NR |
| Author & Year | Follow-Up (mo) | OS (mo) | PFS (mo) | RR * | PRGS | PCI |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gastric Cancer (GC) | ||||||
| Sundar 2024 [28] | 20.8 | 6.0 (2.4–18.4) p | 1.8 (1.6–6.0) p | 7%; SD 57% | 1–2 in 66.7% 2; 100% 3 | 20 [12.3–30]; Δ−5/−7 2,3 |
| Casella 2023 [30] | NR | 19.6 (14–24) d; 10.5 (7–13) p | NR | NR | 1 37.1%; 2 31.0%; 3 21.4% 2;1 2.4%; 2 2.4%; 3 9.5% 3 | 16 [8–26] |
| Alyami 2021 [33] | NR | 19.1 p | NR | NR | NR | 17 (1–39) |
| Di Giorgio 2020 [35] | NR | 12.3 (11.7–17.4) d | NR | NR | CR 7.7%; PR 53.8%; SD 38.5% | 20 ± 9.9; ↑ 76.9%; SD 7.7%; ↓ 15.4% |
| Khomyakov 2016 [44] | 13.0 | 13.0 p | NR | NR | 1 27%; 2 33%; 3–4 40% | 16 (6–34) |
| Kryh-Jensen 2023 [26] § | NR | 7.8 p | NR | NR | ↓ 61% | NR |
| Colorectal Cancer (CRC) | ||||||
| Kyle 2023 [31] | 11.6 | 11.6 (4.7–36) p; 25.0 (7.2–42.2) d | 6.0 (0.5–25.1) p | NR | NR | 25 (20–32) |
| Demtrøder 2016 [43] | 22.0 ± 4 | 15.7 p | NR | NR | TRG0 11.7%; TRG1-2 6%; TRG3 24%; TRG4 41.2% | 16 ± 10 |
| Kryh-Jensen 2023 [26] § | NR | 16.0 p | NR | NR | ↓ 69% | NR |
| Pancreatic Cancer (PC) | ||||||
| Kryh-Jensen 2023 [26] § | NR | 10.0 p | NR | NR | ↓ 59% | NR |
| Khosrawipour 2017 [42] | 10.0 | 8.5 (95% CI 8.5–11.9) p | NR | NR | TRG1 15%; TRG3 25%; TRG4 10% | 26.6 (1–39) |
| Diffuse Malignant Peritoneal Mesothelioma (DMPM) | ||||||
| Kepenekian 2021 [11] | 29.6 | 12.0 | 12.0 | 15% | Pre 3.0 (2.2–4.0);Post 2.0 (2.0–3.0) | Pre 27 (20–34);Post 25 (20–39) |
| Hepato-pancreato-biliary (HPB)† | ||||||
| Falkenstein 2018 [37] | NR | 2.8 (95% CI 2.0–3.7) p | NR | NR | TRG0 20%; TRG1-2 40%; TRG3 40% | 20 [8–27] |
| Author & Year | Surgical (CD) | Medical (CTCAE) | Key Other AEs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sundar et al., 2024 [28] | NR | G3: 50%; G4: 16.7%; G5: 11% | Pain; nausea/vomiting; weight loss; fatigue; etc. |
| van de Vlasakker et al., 2024 [29] | 0% | NR | Mild GI symptoms |
| Casella et al., 2023 [30] | CD > 3a: 0% | G3/G4: 2% | NR |
| Kryh-Jensen et al., 2023 [26] | NR | NR | NR |
| Kyle et al., 2023 [31] | NR | G3: 20% | G1/G2: pain; nausea; constipation |
| Raoof et al., 2023 [32] | 0% | G1: 58%; G2: 33%; G3: 17% | Pain; constipation; nausea/vomiting |
| Alyami et al., 2021 [33] | NR | G1–4: 6.1%; G3–4: 3.1%; G5: 4.7% | NR |
| Feldbrügge et al., 2021 [34] | CD ≤ 4: 11%; CD 3–4: 6% | NR | SSI |
| Kepenekian et al., 2021 [11] | NR | G1/G2: 10%; G3/G4: 3% | NR |
| Siebert et al., 2021 [27] | NR | >G3: 3.5%; mortality (30 d): 1.5% | Bowel obstruction; allergy |
| Di Giorgio et al., 2020 [35] | CD ≥ 3: 2% | G1–2: 22%; G3–4: 4%; G5 (30 d): 4% | NR |
| Gockel et al., 2020 [36] | 0% | NR | 6 non-access |
| Falkenstein et al., 2018 [37] | NR | G1: 41.4%; G2: 35.3%; G3–5: 0% | NR |
| Larbre et al., 2018 [38] | NR | NR | NR |
| Alyami et al., 2017 [39] | NR | G3–4: 9.7%; G5 (30d): 6.8% | Bowel obstruction; SSI |
| Farinha et al., 2017 [40] | NR | NR | Fatigue; GI symptoms |
| Hilal et al., 2017 [41] | NR | NR | NR |
| Khosrawipour et al., 2017 [42] | NR | G1: 34%; G2: 2.4%; G3–4: 0%; G5: 2.4% | NR |
| Demtröder et al., 2016 [43] | 0% | G1: 71%; G3: 23%; G4–5: 0% | Nausea/vomiting; renal/liver toxicity G1 |
| Khomyakov et al., 2016 [44] | NR | G2: 6.4%; G3: 3.2%; G4–5: 0% | NR |
| Reymond et al., 2016 [25] | NR | G1: 66%; G2: 33% | Pain |
| Robella et al., 2016 [45] | 0% | G1: 46%; G2: 62% | Pain; nausea |
| Author & Year | I1 | I2 | I3 | I4 | I5 | I6 | I7 | I8 | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sundar et al., 2024 [28] | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 13 |
| van de Vlasakker et al., 2024 [29] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 12 |
| Casella et al., 2023 [30] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 13 |
| Kryh-Jensen et al., 2023 [26] | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 12 |
| Kyle et al., 2023 [31] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 14 |
| Raoof et al., 2023 [32] | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 13 |
| Alyami et al., 2021 [33] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 13 |
| Feldbrügge et al., 2021 [34] | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 11 |
| Kepenekian et al., 2021 [11] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 13 |
| Di Giorgio et al., 2020 [35] | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 11 |
| Gockel et al., 2020 [36] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 13 |
| Falkenstein et al., 2018 [37] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 13 |
| Larbre et al., 2018 [38] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 13 |
| Alyami et al., 2017 [39] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 13 |
| Farinha et al., 2017 [40] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 13 |
| Hilal et al., 2017 [41] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 11 |
| Khosrawipour et al., 2017 [42] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 13 |
| Demtröder et al., 2016 [43] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 13 |
| Khomyakov et al., 2016 [44] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 11 |
| Reymond et al., 2016 [25] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 13 |
| Robella et al., 2016 [45] | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 13 |
| Author & Year | I1 | I2 | I3 | I4 | I5 | I6 | I7 | I8 | I9 | I10 | I11 | I12 | Overall |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Siebert et al., 2021 [27] | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 14 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Robella, M.; Vitturini, M.; Di Giorgio, A.; Aulicino, M.; Hubner, M.; Koumantakis, E.; Borghi, F.; Catania, P.; Cinquegrana, A.; Berchialla, P. Advances in Bidirectional Therapy for Peritoneal Metastases: A Systematic Review of Pressurized Intraperitoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (PIPAC) Combined with Systemic Chemotherapy. Cancers 2025, 17, 2580. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152580
Robella M, Vitturini M, Di Giorgio A, Aulicino M, Hubner M, Koumantakis E, Borghi F, Catania P, Cinquegrana A, Berchialla P. Advances in Bidirectional Therapy for Peritoneal Metastases: A Systematic Review of Pressurized Intraperitoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (PIPAC) Combined with Systemic Chemotherapy. Cancers. 2025; 17(15):2580. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152580
Chicago/Turabian StyleRobella, Manuela, Marco Vitturini, Andrea Di Giorgio, Matteo Aulicino, Martin Hubner, Emanuele Koumantakis, Felice Borghi, Paolo Catania, Armando Cinquegrana, and Paola Berchialla. 2025. "Advances in Bidirectional Therapy for Peritoneal Metastases: A Systematic Review of Pressurized Intraperitoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (PIPAC) Combined with Systemic Chemotherapy" Cancers 17, no. 15: 2580. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152580
APA StyleRobella, M., Vitturini, M., Di Giorgio, A., Aulicino, M., Hubner, M., Koumantakis, E., Borghi, F., Catania, P., Cinquegrana, A., & Berchialla, P. (2025). Advances in Bidirectional Therapy for Peritoneal Metastases: A Systematic Review of Pressurized Intraperitoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (PIPAC) Combined with Systemic Chemotherapy. Cancers, 17(15), 2580. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152580









