Carboxypeptidase A4: A Biomarker for Cancer Aggressiveness and Drug Resistance
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. CPA4: History and Protein Structure
3. CPA4 and Cancer
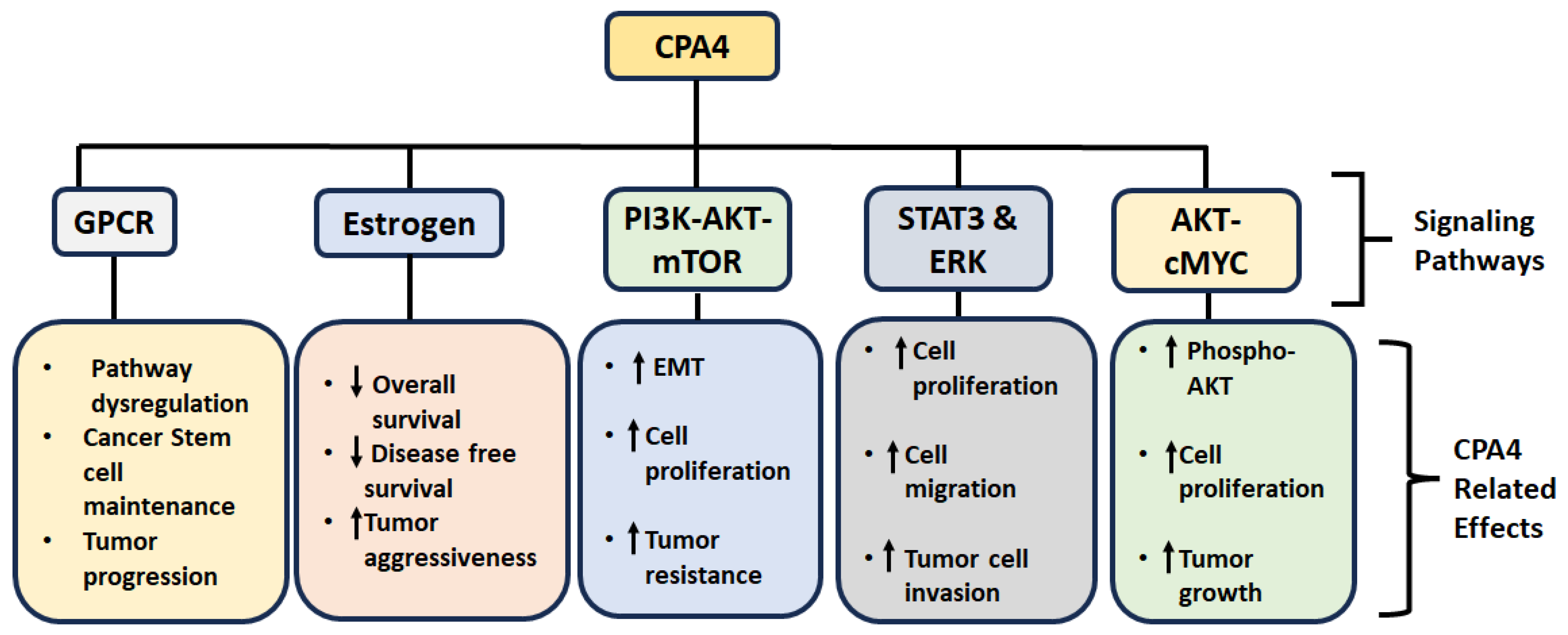
4. CPA4 and Signal Transduction
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| APC | Anaplastic thyroid cancer |
| ccRCC | Clear cell renal cell carcinoma |
| ceRNA | Competing endogenous RNA |
| CM | Conditioned media |
| CP | Carboxypeptidase |
| CPA | Carboxypeptidase A |
| CPB | Carboxypeptidase B |
| CPE | Carboxypeptidase E |
| CPN | Carboxypeptidase N |
| CPA4 | Carboxypeptidase A 4 |
| EMT | Epithelial--mesenchymal transition |
| ESCC | Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma |
| GPCR | G-protein coupled receptor |
| HDAC | Histone deacetylase |
| HMEpC | Human mammary epithelial cells |
| NaBu | Sodium butyrate |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung cancer |
| PC | Pancreatic cancer |
| SCCHN | Squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| TIME | Tumor immune microenvironment |
| TNBC | Triple negative breast cancer |
References
- Rawlings, N.D.; Barrett, A.J. Peptidases. In eLS; Elsevier Inc: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gomis-Rüth, F.X. Structure and mechanism of metallocarboxypeptidases. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 43, 319–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arolas, J.L.; Vendrell, J.; Aviles, F.X.; Fricker, L.D. Metallocarboxypeptidases: Emerging drug targets in biomedicine. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 349–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vendrell, J.; Querol, E.; Avilés, F.X. Metallocarboxypeptidases and their protein inhibitors. Structure, function and biomedical properties. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Protein Struct. Mol. Enzymol. 2000, 1477, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skidgel, R.A.; Erdös, E.G. Cellular carboxypeptidases. Immunol. Rev. 1998, 161, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breddam, K. Serine carboxypeptidases. A review. Carlsberg Res. Commun. 1986, 51, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Reed, C.P.; Zhang, J.-S.; Shridhar, V.; Wang, L.; Smith, D.I. Carboxypeptidase A3 (CPA3): A Novel Gene Highly Induced by Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors during Differentiation of Prostate Epithelial Cancer Cells1. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 2981–2988. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, S.; Segura, S.; Vendrell, J.; Aviles, F.X.; Lanoue, E.; Day, R.; Feng, Y.; Fricker, L.D. Identification and characterization of three members of the human metallocarboxypeptidase gene family. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 14954–14964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fricker, L. Carboxypeptidases. In xPharm: The Comprehensive Pharmacology Reference; Enna, S.J., Bylund, D.B., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Tanco, S.; Zhang, X.; Morano, C.; Avilés, F.X.; Lorenzo, J.; Fricker, L.D. Characterization of the substrate specificity of human carboxypeptidase A4 and implications for a role in extracellular peptide processing. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 18385–18396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, P.L.; Cheng, I.; Liu, X.; Cicek, M.S.; Carroll, P.R.; Casey, G.; Witte, J.S. Carboxypeptidase 4 gene variants and early-onset intermediate-to-high risk prostate cancer. BMC Cancer 2009, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallarès, I.; Bonet, R.; García-Castellanos, R.; Ventura, S.; Avilés, F.X.; Vendrell, J.; Gomis-Rüth, F.X. Structure of human carboxypeptidase A4 with its endogenous protein inhibitor, latexin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3978–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hass, G.M.; Nau, H.; Biemann, K.; Grahn, D.T.; Ericsson, L.H.; Neurath, H. The amino acid sequence of a carboxypeptidase inhibitor from potatoes. Biochemistry 1975, 14, 1334–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverter, D.; Vendrell, J.; Canals, F.; Horstmann, J.; Avilés, F.X.; Fritz, H.; Sommerhoff, C.P. A carboxypeptidase inhibitor from the medical leech Hirudo medicinalis. Isolation, sequence analysis, cDNA cloning, recombinant expression, and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 32927–32933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanglas, L.; Aviles, F.X.; Huber, R.; Gomis-Rüth, F.X.; Arolas, J.L. Mammalian metallopeptidase inhibition at the defense barrier of Ascaris parasite. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1743–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Covaleda, G.; del Rivero, M.A.; Chávez, M.A.; Avilés, F.X.; Reverter, D. Crystal structure of novel metallocarboxypeptidase inhibitor from marine mollusk Nerita versicolor in complex with human carboxypeptidase A4. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 9250–9258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomis-Rüth, F.X.; Botelho, T.O.; Bode, W. A standard orientation for metallopeptidases. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Proteins Proteom. 2012, 1824, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentley, L.; Nakabayashi, K.; Monk, D.; Beechey, C.; Peters, J.; Birjandi, Z.; Khayat, F.E.; Patel, M.; Preece, M.A.; Stanier, P.; et al. The imprinted region on human chromosome 7q32 extends to the carboxypeptidase A gene cluster: An imprinted candidate for Silver-Russell syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 2003, 40, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kayashima, T.; Yamasaki, K.; Yamada, T.; Sakai, H.; Miwa, N.; Ohta, T.; Yoshiura, K.; Matsumoto, N.; Nakane, Y.; Kanetake, H.; et al. The novel imprinted carboxypeptidase A4 gene (CPA4) in the 7q32 imprinting domain. Hum. Genet. 2003, 112, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagakawa, O.; Ogasawara, M.; Murata, J.; Fuse, H.; Saiki, I. Effect of prostatic neuropeptides on migration of prostate cancer cell lines. Int. J. Urol. 2001, 8, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Burnett, J.; Guo, C.; Xie, Y.; Pan, J.; Yang, Z.; Ran, Y.; Sun, D. CPA4 is a promising diagnostic serum biomarker for pancreatic cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2016, 6, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, R.; Zang, H.; Pei, W.; Sun, T. CPA4 Promotes EMT in Pancreatic Cancer via Stimulating PI3K-AKT-mTOR Signaling. Onco Targets Ther. 2020, 13, 8567–8580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.A.; Phang, W.M.; Gopinath, S.C.; Hashim, O.H.; Kiew, L.V.; Chen, Y. Revealing Glycoproteins in the Secretome of MCF-7 Human Breast Cancer Cells. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 453289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Niu, Y.; Song, P.; Liu, Y.; Burnett, J.; Yang, Z.; Sun, D.; Ran, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Carboxypeptidase A4 negatively correlates with p53 expression and regulates the stemness of breast cancer cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 1753–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, T.; Katayama, A.; Yokobori, T.; Yamane, A.; Fujii, T.; Obayashi, S.; Kurozumi, S.; Kawabata-Iwakawa, R.; Gombodorj, N.; Nishiyama, M.; et al. Carboxypeptidase A4 accumulation is associated with an aggressive phenotype and poor prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liang, H.; Fang, H.; Xiao, J.; Yang, C.; Zhou, Z.; Feng, J.; Chen, C. Angiopoietin-1 promotes triple-negative breast cancer cell proliferation by upregulating carboxypeptidase A4. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2023, 55, 1487–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bademler, S.; Ucuncu, M.Z.; Tilgen Vatansever, C.; Serilmez, M.; Ertin, H.; Karanlık, H. Diagnostic and Prognostic Significance of Carboxypeptidase A4 (CPA4) in Breast Cancer. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Burnett, J.; Pan, J.; Yang, Z.; Ran, Y.; Myers, I.; Sun, D. CPA4 is a Novel Diagnostic and Prognostic Marker for Human Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Cancer 2016, 7, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, J.; Becker, A.C.; Dhamija, S.; Seiler, J.; Abdelkarim, M.; Sharma, Y.; Behr, J.; Meng, C.; Ludwig, C.; Kuster, B.; et al. Systematic analysis of migration factors by MigExpress identifies essential cell migration control genes in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2021, 15, 1797–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Su, L.; Cai, M.; Yao, B.; Xiao, S.; He, Q.; Xu, L.; Yang, L.; Zhao, C.; Wan, T.; et al. Downregulation of CPA4 inhibits non small-cell lung cancer growth by suppressing the AKT/c-MYC pathway. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 2026–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zhang, H.; Lu, J. Identification of potential microRNAs and their targets in promoting gefitinib resistance by integrative network analysis. J. Thorac. Dis. 2019, 11, 5535–5546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.M.; Lin, P.M.; Lin, H.C.; Lai, C.C.; Yang, C.H.; Lin, S.F.; Yang, M.Y. Altered Expression of Imprinted Genes in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Anticancer. Res. 2016, 36, 2251–2258. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Cao, J.; Guo, C.; Burnett, J.; Yang, Z.; Ran, Y.; Sun, D. Associations of carboxypeptidase 4 with ALDH1A1 expression and their prognostic value in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis. Esophagus 2017, 30, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Guo, C.; Yuan, H.; Burnett, J.; Pan, J.; Yang, Z.; Ran, Y.; Myers, I.; Sun, D. Overexpression of carboxypeptidase A4 (CPA4) is associated with poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 5071–5075. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, X.; Liu, D.; Song, D.; Fan, J.; Dai, G.; Yang, L. Knockdown of carboxypeptidase A4 (CPA4) inhibits gastric cancer cell progression via cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2022, 13, 2823–2831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Guo, C.; Burnett, J.; Yang, Z.; Ran, Y.; Sun, D. Serum carboxypeptidaseA4 levels predict liver metastasis in colorectal carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 78688–78697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Guo, C.; Burnett, J.; Pan, J.; Yang, Z.; Ran, Y.; Sun, D. Association between expression of Carboxypeptidase 4 and stem cell markers and their clinical significance in liver cancer development. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Hao, C.; Wang, H.; Shang, H.; Li, Z. Carboxypeptidase A4 promotes proliferation and stem cell characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2019, 100, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, T.; Lv, H.; Wang, K.; Wang, Z.; Wang, L.; Wu, S.; Zhao, L. CPA4 overexpression correlates with poor prognosis and tumor progression in endometrial cancer. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2025, 30, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ding, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, M.; Wang, J.; Kou, Z.; Liu, S.; Jiang, B.; Hou, S. CPA4 as a biomarker promotes the proliferation, migration and metastasis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2024, 28, e18165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.S.; Jeon, M.J.; Doolittle, W.K.L.; Song, D.E.; Kim, K.; Kim, W.B.; Kim, W.G. Macrophage-Induced Carboxypeptidase A4 Promotes the Progression of Anaplastic Thyroid Cancer. Thyroid 2024, 34, 1150–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, H.; Fu, L.; Xu, T. Investigating the Underlying Mechanisms of Circular RNAs and Their Application in Clinical Research of Cervical Cancer. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 653051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shell, S.; Park, S.M.; Radjabi, A.R.; Schickel, R.; Kistner, E.O.; Jewell, D.A.; Feig, C.; Lengyel, E.; Peter, M.E. Let-7 expression defines two differentiation stages of cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11400–11405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Qin, C.; Zhang, C.; Su, J.; Xiao, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Xiao, K.; Liu, Q. circCPA4 acts as a prognostic factor and regulates the proliferation and metastasis of glioma. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 6658–6665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Xue, M.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, X. Circular RNA circ-CPA4/let-7 miRNA/PD-L1 axis regulates cell growth, stemness, drug resistance and immune evasion in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Lei, Y.; Chen, N.; Guo, G.; Xiang, X.; Huang, Y. circRNA-CPA4 Regulates Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer via the miR-1183/PDPK1 Axis. Biochem. Genet. 2024, 62, 4087–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, Y.; Moon, R.; Roh, H.; Chang, S.; Lee, S.; Park, H. HIF-1α-Dependent Induction of Carboxypeptidase A4 and Carboxypeptidase E in Hypoxic Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells. Mol. Cells 2020, 43, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso del Rivero, M.; Reytor, M.L.; Trejo, S.A.; Chávez, M.A.; Avilés, F.X.; Reverter, D. A noncanonical mechanism of carboxypeptidase inhibition revealed by the crystal structure of the Tri-Kunitz SmCI in complex with human CPA4. Structure 2013, 21, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| SNPs | Location | Allele Change |
|---|---|---|
| rs901799 | 5′ | C > A |
| rs3807344 | intron | A > G |
| rs1569132 | intron | A > G |
| rs1038628 | intron | G > T |
| rs2171492 | exon | A > G |
| rs1488009 | intron | G > T |
| Cancer Type | Amplification | mRNA High | Mutation | Deep Deletion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cervical SCC | 0 (0%) | 10/18 (55.56%) | 0/18 (0%) | 0/18 (0%) |
| SCCHN | 1/43 (2.33% | 21/43 (48.84%) | 0/43 (0%) | 0/43 (0%) |
| Ovarian | 0/23 (0%) | 11/23 (47.83%) | 0/23 (0%) | 0/23 (0%) |
| Renal | 12/32 (37.5%) | 0/32 (0%) | 0/32 (0%) | 0/32 (0%) |
| Pancreatic | 23/81 (28.4%) | 0/81 (0%) | 0/81 (0%) | 0/81 (0%) |
| Melanoma | 22/107 (20.56%) | 0/107 (0%) | 1/107 (0.93%) | 0/107 (0%) |
| Leiomyosarcoma | 2/15 (13.33%) | 1/15 (6.67%) | 0/15 (0%) | 0/15 (0%) |
| Bladder SCC | 0/23 (0%) | 3/23 (13.04%) | 0/23 (0%) | 0/23 (0%) |
| Glioblastoma | 6/39 (15.38%) | 0/39 (0%) | 0/39 (0%) | 0/39 (0%) |
| Lung SCC | 4/47 (8.51%) | 2/47 (4.26%) | 1/47 (2.13%) | 0/47 (0%) |
| Breast | 4/34 (11.76%) | 0/34 (0%) | 1/34 (2.94%) | 0/34 (0%) |
| Serous Ovarian | 11/100 (11%) | 1/100 (1%) | 0/100 (0%) | 0/100 (0%) |
| Stomach Adenocarcinoma | 2/17 (11.76%) | 0/17 (0%) | 0/17 (0%) | 0/17 (0%) |
| Uterine | 1/20 (5%) | 1/20 (5%) | 0/20 (0%) | 0/20 (0%) |
| Chromophobe Renal | 4/43 (9.3%) | 0/43 (0%) | 0/43 (0%) | 0/43 (0%) |
| Esophageal | 8/97 (8.25%) | 0/97 (0%) | 0/97 (0%) | 1/97 (1.03%) |
| Papillary Stomach Adenocarcinoma | 2/22 (9.09%) | 0/22 (0%) | 0/22 (0%) | 0/22 (0%) |
| Colorectal | 4/44 (9.09%) | 0/44 (0%) | 0/44 (0%) | 0/44 (0%) |
| Medulloblastoma | 7/93 (7.53%) | 0/93 (0%) | 1/93 (1.93%) | 0/93 (0%) |
| Osteosarcoma | 3/35 (8.57%) | 0/35 (0%) | 0/35 (0%) | 0/35 (0%) |
| Uterine | 2/24 (8.33%) | 0/24 (0%) | 0/24 (0%) | 0/24 (0%) |
| Cholangiocarcinoma | 2/26 (7.69%) | 0/26 (0%) | 0/26 (0%) | 0/26 (0%) |
| Anaplastic Medulloblastoma | 2/27 (7.41%) | 0/27 (0%) | 0/27 (0%) | 0/27 (0%) |
| ccRCC | 4/111 (3.6%) | 4/111 (3.6%) | 0/111 (0%) | 0/111 (0%) |
| Burkit Lymphoma | 1/17 (5.88%) | 0/17 (0%) | 0/17 (0%) | 0/17 (0%) |
| Oligodendroglioma | 1/18 (5.56%) | 0/18 (0%) | 0/18 (0%) | 0/18 (0%) |
| Liposarcoma | 1/19 (5.26%) | 0/19 (0%) | 0/19 (0%) | 0/19 (0%) |
| HCC | 13/306 (4.25%) | 1/306 (0.33%) | 1/306 (0.33%) | 1/306 (0.33%) |
| Signaling Pathway | CPA4 Role | Key Findings (Reference) |
|---|---|---|
| GPCR Signaling | Associated with GPCR binding genes | CPA4 expression correlates with GPCR-related functions in cancer stem cell biology [40] |
| Estrogen Signaling | Correlated with hormone-responsive tumors | Overexpressed in endometrial cancer; implicated in ER-positive cancer processes [26,40] |
| PI3K-AKT-mTOR | Activates pathway components | Enhances EMT, drug resistance, and proliferation in pancreatic and cardiac tissues [23] |
| AKT–cMYC | Promotes AKT phosphorylation and c-MYC expression | Drives proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in NSCLC [31] |
| STAT3 and ERK | Activates both STAT3 and ERK | Enhances migration, invasion, and proliferation in thyroid cancer [42] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adeluola, A.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Amin, A.R.M.R. Carboxypeptidase A4: A Biomarker for Cancer Aggressiveness and Drug Resistance. Cancers 2025, 17, 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152566
Adeluola AA, Hossain MS, Amin ARMR. Carboxypeptidase A4: A Biomarker for Cancer Aggressiveness and Drug Resistance. Cancers. 2025; 17(15):2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152566
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdeluola, Adeoluwa A., Md. Sameer Hossain, and A. R. M. Ruhul Amin. 2025. "Carboxypeptidase A4: A Biomarker for Cancer Aggressiveness and Drug Resistance" Cancers 17, no. 15: 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152566
APA StyleAdeluola, A. A., Hossain, M. S., & Amin, A. R. M. R. (2025). Carboxypeptidase A4: A Biomarker for Cancer Aggressiveness and Drug Resistance. Cancers, 17(15), 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152566







