Integrating Clinical and Imaging Markers for Survival Prediction in Advanced NSCLC Treated with EGFR-TKIs
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design, Participants, and Data Collection
2.2. Data Management and Confidentiality
2.3. Statistical Analysis
2.4. Study Variables and Predictors
2.5. Missing Data Handling
2.6. Derivation of the Survival Model
2.7. Discrimination and Calibration
2.8. Internal Validation
2.9. Model Presentation
3. Results
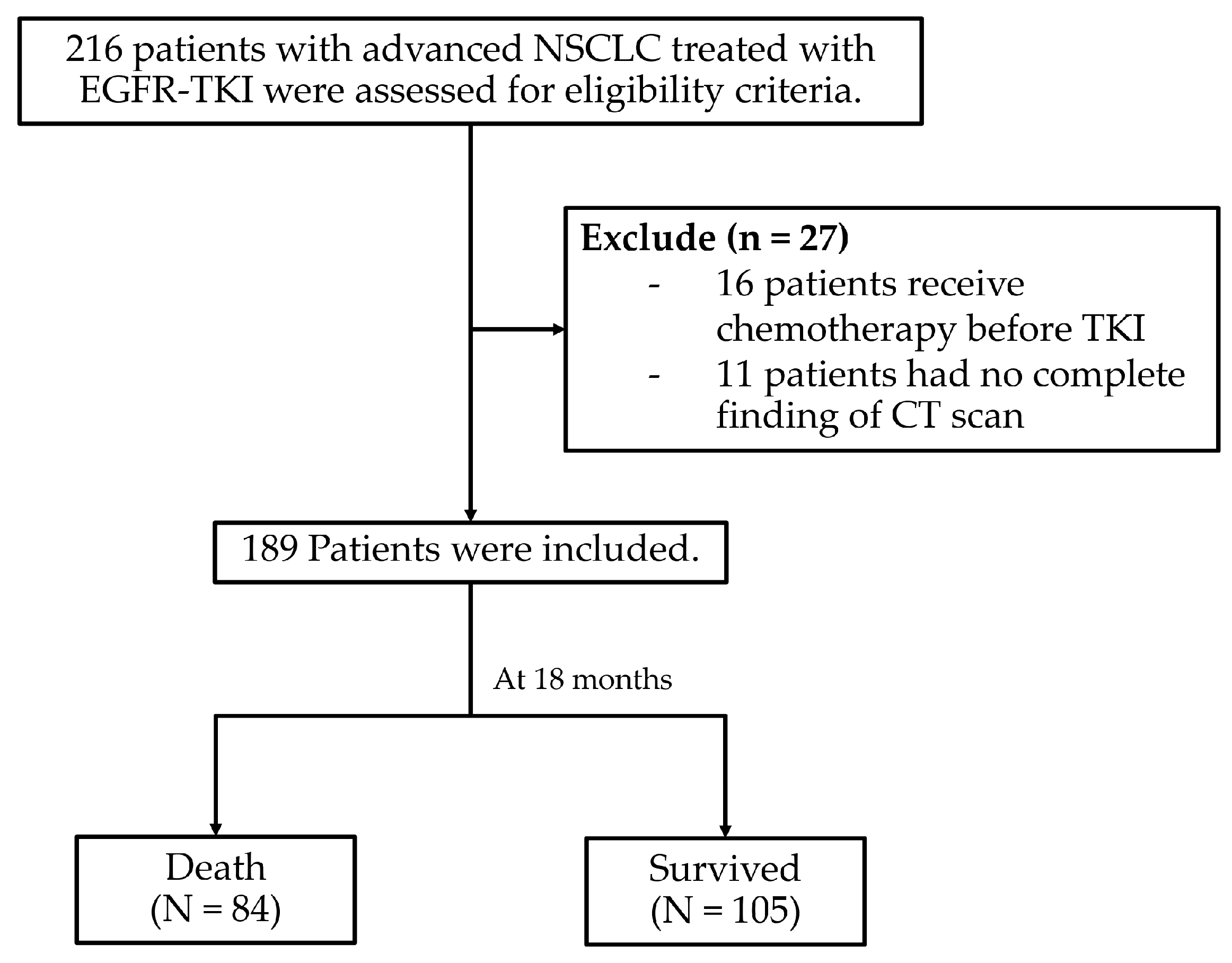
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Survival Rate of Patients
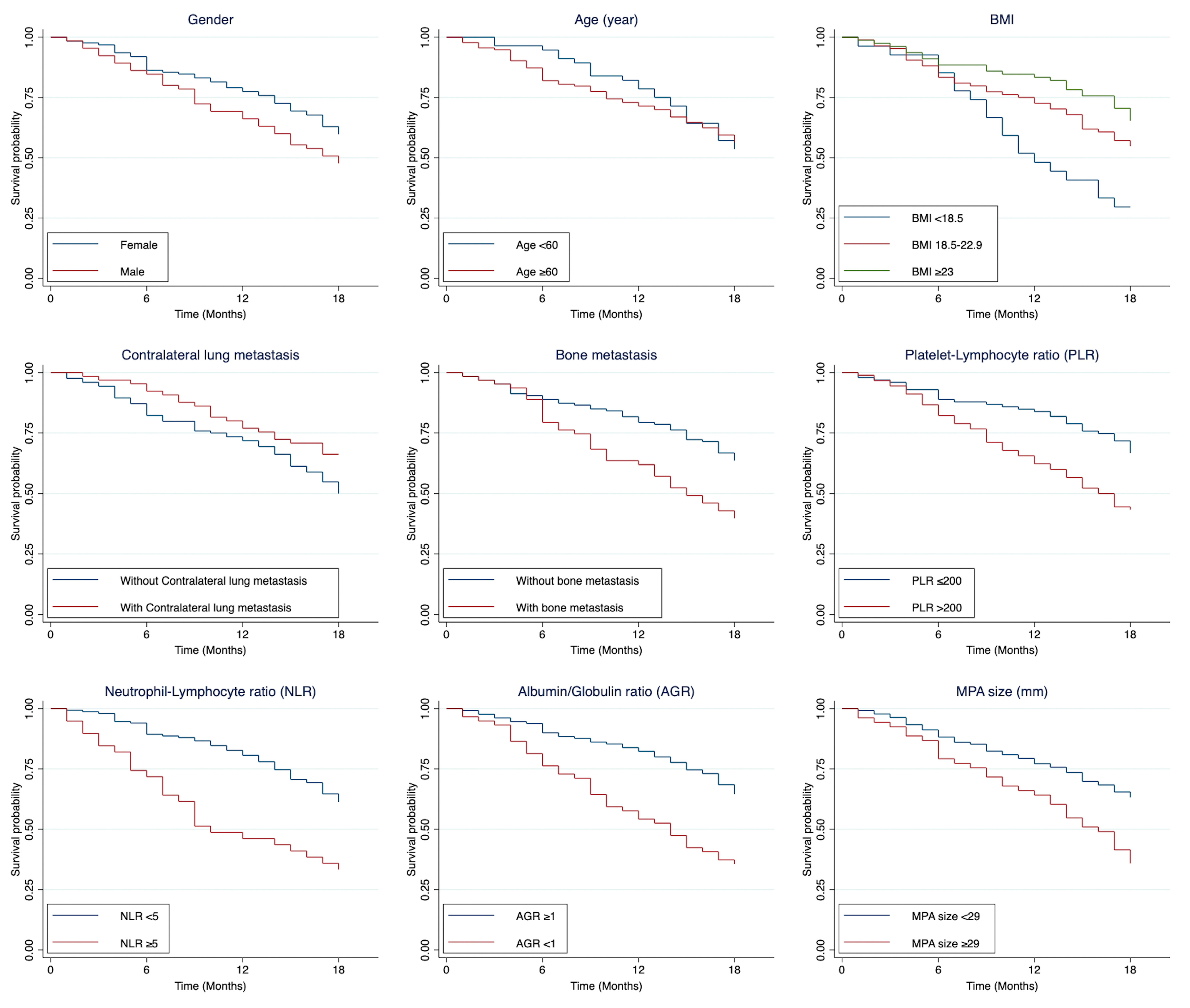
3.3. Predictors Associated with 18-Month Mortality
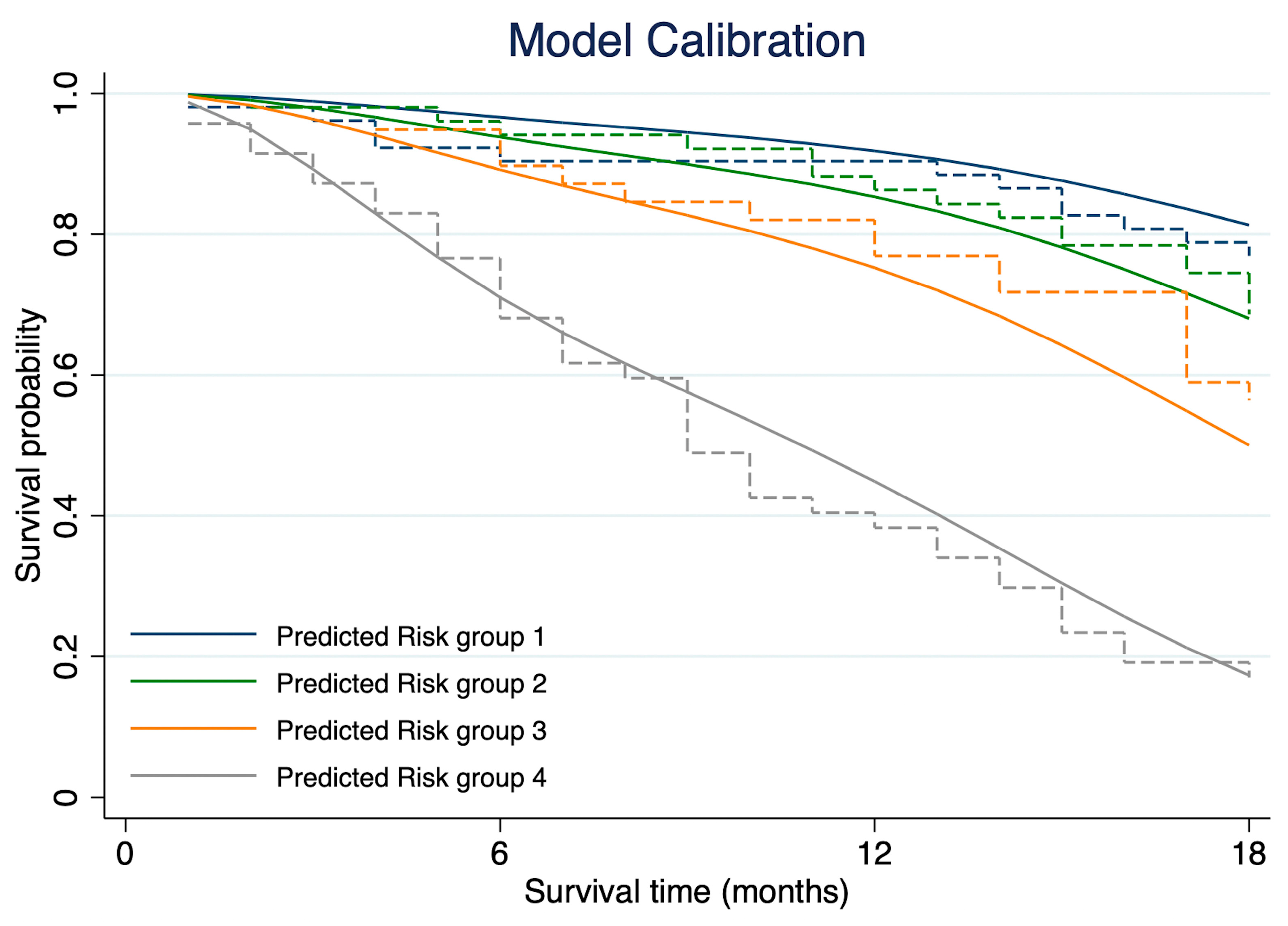
3.4. Model Discrimination and Calibration
3.5. Internal Validation
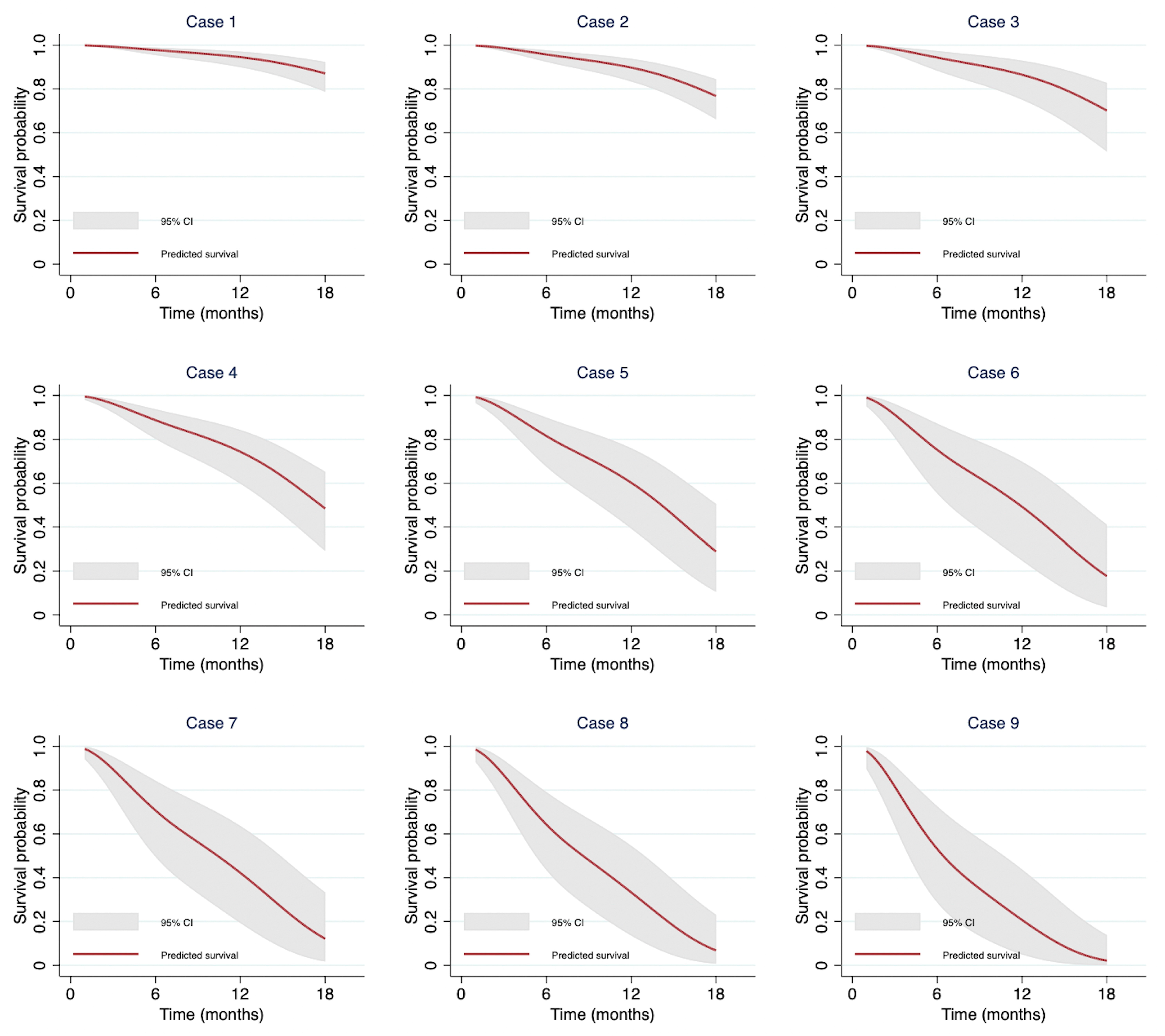
3.6. Demonstration of Individual Predictions from the Model
4. Discussion
Limitation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| NSCLC | non-small cell lung cancer |
| TKIs | tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
| OS | overall survival |
| PS | performance status |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| NLR | neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| COPD | chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| DFS | disease-free survival |
| CT | computed tomography |
| CAC | coronary artery calcium |
| PA/Ao | pulmonary artery-to-aorta |
| ECOG-PS | Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status |
| CBC | complete blood count |
| Cr | creatinine |
| LFT | liver function test |
| PLR | platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio |
| AGR | albumin-to-globulin ratio |
| BMI | body mass index |
| MPA | main pulmonary artery |
| AO | aorta |
| PACS | Picture Archiving and Communication System |
| PHI | protected health information |
| SD | standard deviation |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| HR | hazard ratio |
| kNN | k-nearest neighbor |
| RP | Royston–Parmar |
| AIC | Akaike Information Criterion |
| BIC | Bayesian Information Criterion |
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reungwetwattana, T.; Oranratnachai, S.; Puataweepong, P.; Tangsujaritvijit, V.; Cherntanomwong, P. Lung Cancer in Thailand. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2020, 15, 1714–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Planchard, D.; Popat, S.; Kerr, K.; Novello, S.; Smit, E.F.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Mok, T.S.; Reck, M.; Van Schil, P.E.; Hellmann, M.D.; et al. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, iv192–iv237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvayrac, O.; Pradines, A.; Pons, E.; Mazières, J.; Guibert, N. Molecular biomarkers for lung adenocarcinoma. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1601734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos, E.; Feld, E.; Horn, L. Driven by Mutations: The Predictive Value of Mutation Subtype in EGFR-Mutated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 612–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ettinger, D.S.; Wood, D.E.; Aisner, D.L.; Akerley, W.; Bauman, J.R.; Bharat, A.; Bruno, D.S.; Chang, J.Y.; Chirieac, L.R.; D’Amico, T.A.; et al. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, Version 3.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2022, 20, 497–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall Survival with Osimertinib in Untreated, EGFR-Mutated Advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukauichai, S.; Maneenil, K.; Supavavej, A.; Paul, V.; Benjawongsathien, D.; Chantharakhit, C.; Neesanun, S.; Chayangsu, C.; Bowornkitiwong, T.; Sukaraphat, N. EGFR Mutation-positive Lung Cancer in Real-world Treatment Outcomes: A Multicenter Study from Thailand. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Care 2022, 7, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Xu, L.; Li, Z.; Hu, X.; Liu, J.; Teng, Y.; Jin, B.; Zhao, M.; Shi, J.; Guo, T.; et al. A Clinical Prognostic Score to Predict Survival of Advanced or Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Patients Receiving First-Line Chemotherapy: A Retrospective Analysis. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 8264–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Ma, Y.; Wei, S.; Liang, X. A Low Albumin-to-Globulin Ratio Predicts a Poor Prognosis in Patients with Metastatic Non-small-cell Lung Cancer. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 621592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogura, Y.; Kataoka, N.; Kunimatsu, Y.; Tachibana, Y.; Sugimoto, T.; Tani, N.; Sato, I.; Hirose, K.; Kato, D.; Takeda, T. Predictors of survival among Japanese patients receiving first-line chemoimmunotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.K.; Wu, Y.L.; Ding, P.N.; Lord, S.J.; Inoue, A.; Zhou, C.; Mitsudomi, T.; Rosell, R.; Pavlakis, N.; Links, M.; et al. Impact of Specific Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutations and Clinical Characteristics on Outcomes After Treatment with EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Versus Chemotherapy in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1958–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.H.; Lin, D.; Xu, L.; Wang, Q.; Hu, H.H.; Xu, H.P.; He, Z.Y. The association between clinical prognostic factors and epidermal growth factor receptor-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI) efficacy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients: A retrospective assessment of 94 cases with EGFR mutations. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 3412–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.H.; Guan, W.J.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.Q.; Zhu, Y.N.; Chen, R.C.; Zhang, G.J. Impact of COPD and emphysema on survival of patients with lung cancer: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Respirology 2016, 21, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Shen, Y.; Tan, L.; Li, W. Prognostic Value of Sarcopenia in Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Chest 2019, 156, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, I.; Marquardt, J.P.; Mercaldo, N.D.; Bourgouin, P.P.; Wrobel, M.M.; Mrah, S.; Sharp, G.C.; Khandekar, M.J.; Willers, H.; Keane, F.K.; et al. Utility of Noncancerous Chest CT Features for Predicting Overall Survival and Noncancer Death in Patients With Stage I Lung Cancer Treated With Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2022, 219, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, L.; Guerini Rocco, E.; Spitaleri, G.; Raimondi, S.; Attili, I.; Ranghiero, A.; Cammarata, G.; Minotti, M.; Lo Presti, G.; De Piano, F.; et al. Association between Contrast-Enhanced Computed Tomography Radiomic Features, Genomic Alterations and Prognosis in Advanced Lung Adenocarcinoma Patients. Cancers 2023, 15, 4553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Lu, B.; Yang, X.; Lan, D.; Lin, S.; Zhou, Z.; Li, K.; Deng, D.; Peng, P.; Zeng, Z.; et al. Prognostic analysis and risk stratification of lung adenocarcinoma undergoing EGFR-TKI therapy with time-serial CT-based radiomics signature. Eur. Radiol. 2023, 33, 825–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowarik, A.; Templ, M. Imputation with the R Package VIM. J. Stat. Softw. 2016, 74, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbour, K.C.; Riely, G.J. Systemic Therapy for Locally Advanced and Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Review. JAMA 2019, 322, 764–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, K.; Hagiwara, K. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation and personalized therapy in advanced nonsmall cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Target. Oncol. 2013, 8, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Y.L.; Chen, G.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Ren, S.; et al. Final overall survival results from a randomised, phase III study of erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment of EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802). Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 1877–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocco, D.; Della Gravara, L.; Ragone, A.; Sapio, L.; Naviglio, S.; Gridelli, C. Prognostic Factors in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Immunotherapy. Cancers 2023, 15, 4684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Chen, X.; Qin, N.; Su, D.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Jin, M.; Wang, J. The prognostic role of EGFR-TKIs for patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evcil, F.Y.; Önal, Ö.; Özkan, E.E. The Effect of Body Mass Index on Survival in Lung Cancer. Nutr. Cancer 2023, 75, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepshelovich, D.; Xu, W.; Lu, L.; Fares, A.; Yang, P.; Christiani, D.; Zhang, J.; Shiraishi, K.; Ryan, B.M.; Chen, C.; et al. Body Mass Index (BMI), BMI Change, and Overall Survival in Patients With SCLC and NSCLC: A Pooled Analysis of the International Lung Cancer Consortium. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2019, 14, 1594–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, K.; Christiansen, C.F.; Jacobsen, J.B.; Nørgaard, M.; Sørensen, H.T. Bone metastasis, skeletal-related events, and mortality in lung cancer patients: A Danish population-based cohort study. Lung Cancer 2014, 86, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, H.; Yamada, K.; Sugiura, T.; Hida, T.; Mitsudomi, T. Predictors of survival in patients with bone metastasis of lung cancer. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2008, 466, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, B.J.; Devarakonda, S.; Govindan, R. Bone metastases in non-small cell lung cancer: A narrative review. J. Thorac. Dis. 2022, 14, 1696–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cedrés, S.; Torrejon, D.; Martínez, A.; Martinez, P.; Navarro, A.; Zamora, E.; Mulet-Margalef, N.; Felip, E. Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) as an indicator of poor prognosis in stage IV non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2012, 14, 864–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, N.K.; Rouhani, S.J.; Bestvina, C.M.; Ritz, E.M.; Gilmore, B.A.; Tarhoni, I.; Borgia, J.A.; Batus, M.; Bonomi, P.D.; Fidler, M.J. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Is a Predictive Biomarker in Patients with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Mutated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) Treated with Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI) Therapy. Cancers 2021, 13, 1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Che, G. Prognostic Value of Pretreatment Albumin to Globulin Ratio in Lung Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Nutr. Cancer 2021, 73, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duran, A.O.; Inanc, M.; Karaca, H.; Dogan, I.; Berk, V.; Bozkurt, O.; Ozaslan, E.; Ucar, M.; Eroglu, C.; Ozkan, M. Albumin-globulin ratio for prediction of long-term mortality in lung adenocarcinoma patients. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 6449–6453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, S.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, P.; Che, G. The prognostic value of serum albumin-globulin ratio in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective study. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 3545–3554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Kim, S.H.; Han, J.Y.; Kim, H.T.; Yun, T.; Lee, J.S. Early neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio reduction as a surrogate marker of prognosis in never smokers with advanced lung adenocarcinoma receiving gefitinib or standard chemotherapy as first-line therapy. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 138, 2009–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratanawatkul, P.; Oh, A.; Richards, J.C.; Swigris, J.J. Performance of pulmonary artery dimensions measured on high-resolution computed tomography scan for identifying pulmonary hypertension. ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 00232–02019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Lin, L.; Liu, X. Elevated Pulmonary Artery Systolic Pressure is Associated with Poor Survival of Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 6363–6371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florescu, M.; Hasan, B.; Seymour, L.; Ding, K.; Shepherd, F.A. A Clinical Prognostic Index for Patients Treated with Erlotinib in National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group Study BR.21. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2008, 3, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Bai, H.; Wang, Z.; Daun, J.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; Chang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, J. Establishment of prognostic nomograms for predicting the progression free survival of EGFR-sensitizing mutation, advanced lung cancer patients treated with EGFR-TKIs. Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keam, B.; Kim, D.W.; Park, J.H.; Lee, J.O.; Kim, T.M.; Lee, S.H.; Chung, D.H.; Heo, D.S. Nomogram Predicting Clinical Outcomes in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Patients Treated with Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 46, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafri, S.H.; Shi, R.; Mills, G. Advance lung cancer inflammation index (ALI) at diagnosis is a prognostic marker in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A retrospective review. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.S.; Shin, A.Y.; Yeo, C.D.; Kim, S.K.; Park, C.K.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.W. Significance of Glasgow Prognostic Scores in NSCLC Patients Treated With Immunotherapy After Platinum-based Cytotoxic Chemotherapy. In Vivo 2021, 35, 3423–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kos, M.; Hocazade, C.; Kos, F.T.; Uncu, D.; Karakaş, E.; Dogan, M.; Yildirim Gökay, N.; Zengin, N. Association between blood urea nitrogen/albumin ratio and prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Acta Medica Mediterr. 2015, 31, 219–223. [Google Scholar]
| Clinical Characteristics | Results | Missing N, (%) | Hazard Ratio * (95% CI) | 6-Month Survival, % (95% CI) | 12-Month Survival, % (95% CI) | 18-Month Survival, % (95% CI) | p-Value ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years), mean (SD) | 64.81 (10.76) | 0 | 1.00 (0.98–1.02) | - | - | - | 0.809 |
| Age group, N (%) | 0 | ||||||
| Age < 60 years | 56 (29.63) | - | Reference | 94.64 (84.30–98.24) | 78.57 (65.36–87.22) | 53.57 (39.75–65.55) | 0.997 |
| Age ≥ 60 years | 133 (70.37) | - | 1.00 (0.63–1.59) | 81.95 (74.30–87.52) | 71.43 (62.93–78.31) | 56.39 (47.54–64.32) | |
| Male, N (%) | 65 (34.39) | 0 | 1.46 (0.95–2.26) | 84.62 (73.29–91.41) | 66.15 (53.29–76.24) | 47.69 (35.20–59.16) | 0.080 |
| BMI (kg/m2), mean (SD) | 22.38 (4.05) | 0 | 0.90 (0.85–0.96) | - | - | - | 0.001 |
| BMI group, N (%) | 0 | ||||||
| <18.5 | 27 (14.29) | - | 1.95 (1.12–3.39) | 85.19 (65.20–94.17) | 48.15 (28.69–65.19) | 29.63 (14.06–47.03) | 0.001 |
| 18.5–22.9 | 84 (44.44) | - | Reference | 83.33 (73.49–89.77) | 72.62 (61.74–80.88) | 54.76 (43.54–64.66) | |
| ≥23 | 78 (41.27) | - | 0.69 (0.42–1.12) | 88.46 (79.00–93.82) | 83.33 (73.04–89.96) | 65.38 (53.72–74.79) | |
| ECOG-PS, N (%) | 0 | ||||||
| 0–1 | 183 (96.83) | - | Reference | 85.79 (79.84–90.10) | 74.32 (67.34–80.03) | 55.74 (48.24–62.58) | 0.641 |
| 2–3 | 6 (3.17) | 1.31 (0.41–4.15) | 83.33 (27.31–97.47) | 50.00 (11.09–80.37) | 50.00 (11.09–80.37) | ||
| Smoking, N (%) | 0 | ||||||
| Never | 119 (62.96) | - | Reference | 86.55 (78.99–91.54) | 75.63 (66.87–82.38) | 58.82 (49.44–67.05) | 0.196 |
| Yes | 70 (37.04) | - | 1.32 (0.86–2.04) | 84.29 (73.42–90.97) | 70.00 (57.79–79.29) | 50.00 (37.84–61.00) | |
| Comorbid disease, N (%) | 107 (56.61) | 0 | 0.72 (0.47–1.11) | 83.18 (74.64–89.05) | 77.57 (68.43–84.36) | 60.75 (50.84–69.27) | 0.131 |
| COPD | 6 (3.17) | - | 1.86 (0.68–5.10) | 66.67 (19.46–90.44) | 66.67 (19.46–90.44) | 33.33 (4.61–67.56) | 0.208 |
| Hypertension | 82 (43.39) | - | 0.74 (0.47–1.15) | 82.93 (72.88–89.51) | 76.83 (66.11–84.54) | 62.20 (50.79–71.69) | 0.169 |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 31 (16.40) | - | 1.06 (0.60–1.89) | 80.65 (61.91–90.80) | 70.97 (51.62–83.71) | 54.84 (35.97–70.26) | 0.833 |
| Other cancers | 9 (4.76) | - | 0.41 (0.10–1.67) | 88.89 (43.30–98.36) | 88.89 (43.30–98.36) | 77.78 (36.48–93.93) | 0.191 |
| TKI, N (%) | 0 | ||||||
| Gefitinib | 91 (48.15) | - | Reference | 84.62 (75.41–90.59) | 73.63 (63.29–81.47) | 54.95 (44.17–64.47) | 0.540 |
| Erlotinib | 81 (42.86) | - | 0.99 (0.63–1.54) | 85.19 (75.39–91.30) | 70.37 (59.14–79.05) | 54.32 (42.89–64.41) | |
| Afatinib | 7 (3.70) | - | 1.10 (0.39–3.06) | 100 (NA) | 85.71 (33.41–97.86) | 42.86 (9.78–73.44) | |
| Osimertinib | 10 (5.29) | - | 0.37 (0.09–1.54) | 90.00 (47.30–98.53) | 90.00 (47.30–98.53) | 80.00 (40.87–94.59) | |
| Characteristics of cancer | |||||||
| Staging of NSCLC, N (%) | 0 | ||||||
| Locally advanced | 3 (1.59) | - | Reference | 100 (NA) | 100 (NA) | 66.67 (5.41–94.52) | 0.569 |
| Advanced | 186 (98.41) | - | 1.74 (0.24–12.53) | 85.48 (79.55–89.81) | 73.12 (66.13–78.90) | 55.38 (47.94–62.18) | |
| Site of metastasis, N (%) | 0 | ||||||
| Multiple sites | 62 (32.80) | - | 0.93 (0.59–1.47) | 90.32 (79.72–95.53) | 74.19 (61.38–83.32) | 56.45 (43.25–67.70) | 0.761 |
| Contralateral lung | 65 (34.39) | - | 0.61 (0.37–1.00) | 92.31 (82.50–96.72) | 76.92 (64.67–85.39) | 66.15 (53.29–76.24) | 0.044 |
| Brain | 33 (17.46) | - | 1.31 (0.77–2.23) | 78.79 (60.59–89.27) | 66.67 (47.94–79.96) | 48.48 (30.83–64.06) | 0.308 |
| Bone | 63 (33.33) | - | 2.03 (1.32–3.12) | 79.37 (67.13–87.46) | 61.90 (48.76–72.60) | 39.68 (27.67–51.43) | <0.001 |
| Liver | 17 (8.99) | - | 0.55 (0.22–1.35) | 100 (NA) | 94.12 (65.02–99.15) | 70.59 (43.15–86.56) | 0.175 |
| Adrenal | 9 (4.76) | - | 1.54 (0.67–3.54) | 88.89 (43.30–98.36) | 66.67 (28.17–87.83) | 33.33 (7.83–62.26) | 0.295 |
| Pleural | 82 (43.39) | - | 0.98 (0.63–1.51) | 85.37 (75.67–91.41) | 73.17 (62.18–81.44) | 56.10 (44.71–66.03) | 0.918 |
| Pericardial | 4 (2.12) | - | 1.81 (0.57–5.75) | 100 (NA) | 75.00 (12.79–96.05) | 25.00 (0.89–66.53) | 0.299 |
| Laboratory Characteristics | Results | Missing, N (%) | Hazard Ratio * (95% CI) | 6-Month Survival, % (95% CI) | 12-Month Survival, % (95% CI) | 18-Month Survival, % (95% CI) | p-Value ** |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hemoglobin (g/dL), mean (SD) | 12.01 (1.76) | 2 (1.06) | 0.78 (0.69–0.90) | - | - | - | <0.001 |
| WBC (cells/mm3), mean (SD) | 8099.68 (2722.25) | 2 (1.06) | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | - | - | - | 0.548 |
| PMN (%), mean (SD) | 66.84 (10.70) | 2 (1.06) | 1.04 (1.02–1.06) | - | - | - | <0.001 |
| Lymphocyte (%), mean (SD) | 23.43 (11.21) | 2 (1.06) | 0.95 (0.93–0.98) | - | - | - | <0.001 |
| PLT (×103 cells/mm3), mean (SD) | 329.91 (112.31) | 2 (1.06) | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | - | - | - | 0.166 |
| PLR (plt/lymph ratio), med (IQR) | 194.92 (135.14–279.14) | 2 (1.06) | 1.00 (1.00–1.00) | - | - | - | <0.001 |
| PLR group, N (%) | 2 (1.06) | ||||||
| PLR ≤ 200 | 97 (51.87) | - | Reference | 89.69 (81.69–94.32) | 84.54 (75.67–90.37) | 67.01 (56.70–75.39) | <0.001 |
| PLR > 200 | 90 (48.13) | - | 2.14 (1.37–3.33) | 82.22 (72.63–88.71) | 62.22 (51.37–71.32) | 43.33 (32.95–53.24) | |
| NLR (neu/lymph ratio), med (IQR) | 3.05 (2.00–4.62) | 2 (1.06) | 1.07 (1.03–1.10) | - | - | - | <0.001 |
| NLR group, N (%) | 2 (1.06) | ||||||
| NLR < 5 | 148 (79.14) | - | Reference | 89.86 (83.75–93.76) | 81.08 (73.79–86.53) | 61.49 (53.15–68.78) | <0.001 |
| NLR ≥ 5 | 39 (20.86) | - | 2.55 (1.60–4.06) | 71.79 (54.88–83.28) | 46.15 (30.16–60.73) | 33.33 (19.29–48.02) | |
| Bun (mg/dL), med (IQR) | 11.00 (9–14) | 54 (28.57) | 0.97 (0.92–1.02) | - | - | - | 0.175 |
| Cr, med (IQR) | 0.75 (0.62–0.91) | 4 (2.12) | 0.27 (0.10–0.75) | - | - | - | 0.012 |
| BUN/Alb ratio, med (IQR) | 2.41 (0–3.40) | 10 (5.29) | 1.05 (0.94–1.17) | - | - | - | 0.429 |
| Albumin, mean (SD) | 3.92 (1.68) | 10 (5.29) | 0.34 (0.24–0.48) | - | - | - | <0.001 |
| AGR (alb/glob ratio), mean (SD) | 1.13 (0.44) | 16 (8.47) | 0.16 (0.07–0.41) | - | - | - | <0.001 |
| AGR group, N (%) | 16 (8.42) | ||||||
| AGR ≥ 1 | 118 (68.21) | - | Reference | 91.53 (84.82–95.35) | 83.045 (74.97–88.71) | 67.80 (58.55–75.41) | <0.001 |
| AGR < 1 | 55 (31.79) | - | 2.57 (1.62–4.10) | 78.18 (64.79–86.97) | 54.55 (40.56–66.56) | 38.18 (25.53–50.71) | |
| CT finding characteristics | |||||||
| Emphysema | 20 (10.58) | 0 | 1.36 (0.72–2.56) | 90.00 (65.60–97.40) | 70.00 (45.05–85.25) | 45.00 (23.11–64.71) | 0.334 |
| MPA size (mm), mean (SD) | 26.03 (3.93) | 0 | 1.09 (1.04–1.15) | - | - | - | 0.001 |
| MPA group, N (%) | 0 | ||||||
| MPA < 29 (mm) | 137 (72.11) | - | Reference | 88.24 (81.52–92.62) | 77.21 (69.20–83.38) | 63.24 (54.54–70.71) | <0.001 |
| MPA ≥ 29 (mm) | 53 (28.04) | - | 2.08 (1.34–3.21) | 79.25 (65.66–87.93) | 64.15 (49.73–75.42) | 35.85 (6.59–48.57) | |
| AO size (mm), mean (SD) | 31.05 (4.10) | 0 | 1.05 (1.00–1.11) | - | - | - | 0.054 |
| MPA to AO ratio, mean (SD) | 0.84 (0.12) | 0 | 3.63 (0.71–18.54) | - | - | - | 0.121 |
| Predictors | Full Model | Reduced Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | p Value | HR | 95% CI | p Value | |
| BMI group | ||||||
| <18.5 | 1.35 | 0.75–2.45 | 0.320 | 1.34 | 0.76–2.38 | 0.313 |
| 18.5–22.9 | 1.00 | Reference | NA | 1.00 | Reference | NA |
| ≥23 | 0.58 | 0.34–0.99 | 0.045 | 0.52 | 0.31–0.88 | 0.015 |
| Contralateral lung metastasis | ||||||
| No | 1.00 | Reference | NA | Not include | ||
| Yes | 0.63 | 0.38–1.40 | 0.071 | |||
| Bone metastasis | ||||||
| No | 1.00 | Reference | NA | 1.00 | Reference | NA |
| Yes | 1.93 | 1.21–3.05 | 0.005 | 2.08 | 1.34–3.25 | 0.001 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 0.93 | 0.80–1.07 | 0.310 | Not include | ||
| PMN (%) | 1.01 | 0.98–1.04 | 0.535 | Not include | ||
| PLR group | ||||||
| PLR ≤ 200 | 1.00 | Reference | NA | Not include | ||
| PLR > 200 | 1.03 | 0.61–1.73 | 0.908 | |||
| NLR group | ||||||
| NLR < 5 | 1.00 | Reference | NA | 1.00 | Reference | NA |
| NLR ≥ 5 | 1.66 | 0.83–3.31 | 0.148 | 2.25 | 1.39–3.64 | 0.001 |
| Cr | 0.59 | 0.24–1.40 | 0.230 | Not include | ||
| AGR group | ||||||
| AGR ≥ 1 | 1.00 | Reference | NA | 1.00 | Reference | NA |
| AGR < 1 | 1.96 | 1.21–3.16 | 0.006 | 2.17 | 1.40–3.35 | <0.001 |
| MPA group | ||||||
| MPA < 29 (mm) | 1.00 | Reference | NA | 1.00 | Reference | NA |
| MPA ≥ 29 (mm) | 2.57 | 1.60–4.14 | <0.001 | 2.74 | 1.72–4.36 | <0.001 |
| Input Predictors | Model Estimation of Survival Probability (%, 95% CI) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | BMI Groups | Bone Metastasis | NLR > 5 | AGR < 1 | MPA ≥ 29 | 6 Months | 12 Months | 18 Months |
| 1 | ≥23 | No | No | No | No | 97.76 (95.43–98.90) | 94.51 (89.90–97.05) | 87.09 (78.68–92.34) |
| 2 | 18.5–22.9 | No | No | No | No | 95.75 (92.36–97.65) | 89.75 (83.37–93.77) | 76.76 (66.07–84.47) |
| 3 | <18.5 | No | No | No | No | 94.34 (88.30–97.31) | 86.49 (75.07–92.92) | 70.11 (51.35–82.77) |
| 4 | 18.5–22.9 | No | No | No | Yes | 88.78 (80.23–93.77) | 74.35 (59.78–84.30) | 48.43 (29.17–65.27) |
| 5 | 18.5–22.9 | Yes | Yes | No | No | 81.57 (67.55–89.96) | 60.22 (39.25–75.96) | 28.92 (10.49–50.52) |
| 6 | <18.5 | No | Yes | Yes | No | 75.24 (55.34–87.22) | 49.26 (24.76–69.82) | 17.69 (3.43–41.06) |
| 7 | <18.5 | No | No | Yes | Yes | 70.74 (49.57–84.30) | 42.23 (19.32–63.64) | 12.14 (1.75–33.35) |
| 8 | 18.5–22.9 | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | 64.31 (43.53–79.12) | 33.32 (13.60–54.59) | 6.80 (0.72–23.10) |
| 9 | ≥23 | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | 53.15 (28.66–72.63) | 20.73 (4.98–43.79) | 2.13 (0.6–13.85) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ketpueak, T.; Losuriya, P.; Kanthawang, T.; Prakaikietikul, P.; Lumkul, L.; Phinyo, P.; Tajarernmuang, P. Integrating Clinical and Imaging Markers for Survival Prediction in Advanced NSCLC Treated with EGFR-TKIs. Cancers 2025, 17, 2565. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152565
Ketpueak T, Losuriya P, Kanthawang T, Prakaikietikul P, Lumkul L, Phinyo P, Tajarernmuang P. Integrating Clinical and Imaging Markers for Survival Prediction in Advanced NSCLC Treated with EGFR-TKIs. Cancers. 2025; 17(15):2565. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152565
Chicago/Turabian StyleKetpueak, Thanika, Phumiphat Losuriya, Thanat Kanthawang, Pakorn Prakaikietikul, Lalita Lumkul, Phichayut Phinyo, and Pattraporn Tajarernmuang. 2025. "Integrating Clinical and Imaging Markers for Survival Prediction in Advanced NSCLC Treated with EGFR-TKIs" Cancers 17, no. 15: 2565. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152565
APA StyleKetpueak, T., Losuriya, P., Kanthawang, T., Prakaikietikul, P., Lumkul, L., Phinyo, P., & Tajarernmuang, P. (2025). Integrating Clinical and Imaging Markers for Survival Prediction in Advanced NSCLC Treated with EGFR-TKIs. Cancers, 17(15), 2565. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152565






