Comparative Outcomes of Gross Total Resection vs. Subtotal Resection Plus Radiotherapy for Preventing Craniopharyngioma Recurrence: A Meta-Analysis of the Endoscopic Endonasal Approach
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Meta-Analysis
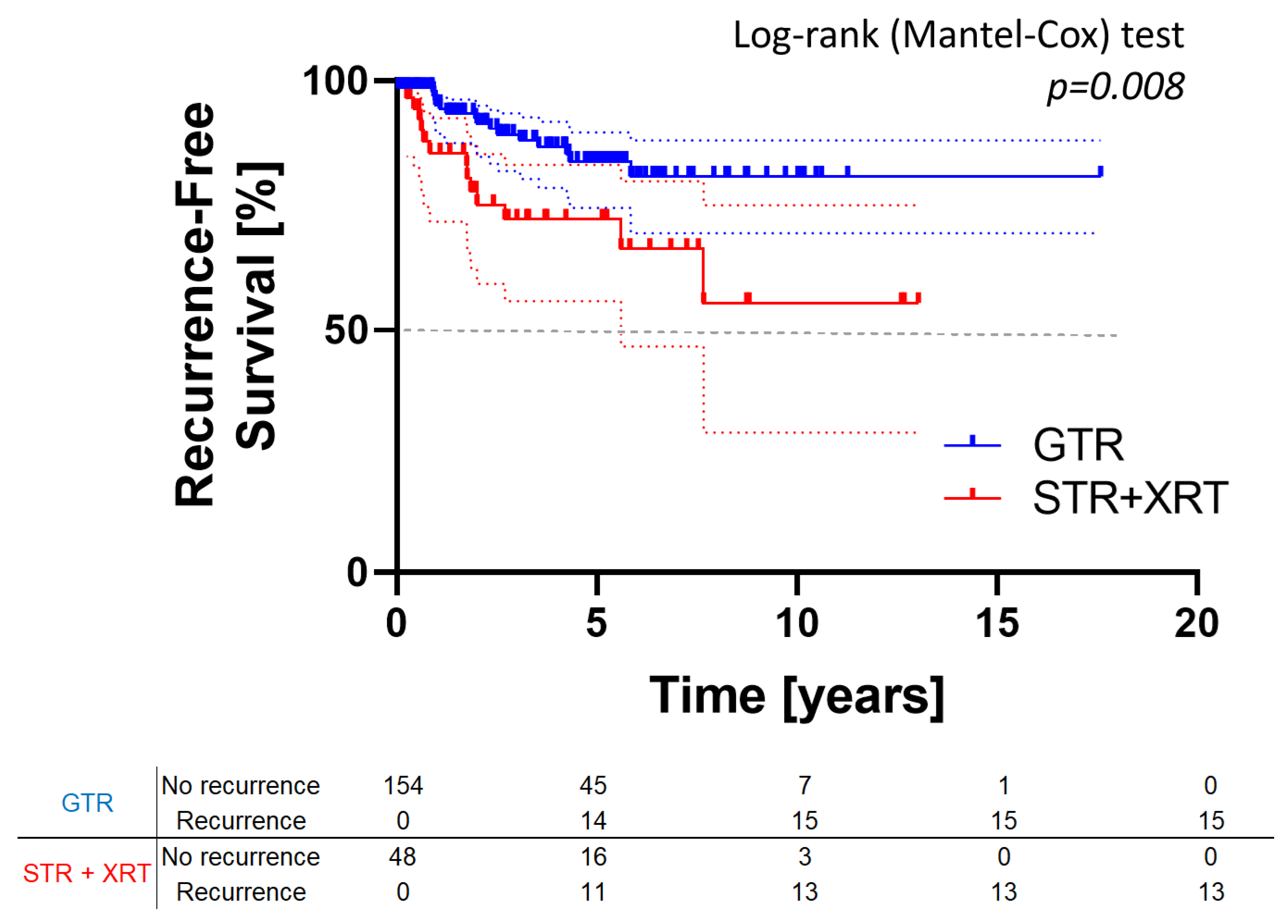
3.2. Survival Analysis
4. Discussion
Study Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CI | confidence interval |
| CSF | cerebrospinal fluid |
| EEA | endoscopic endonasal approach |
| GTR | gross total resection |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| OR | odds ratio |
| P | progression |
| PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| QoL | quality of life |
| R | recurrence |
| XRT | radiation therapy |
| STR | subtotal resection |
References
- Park, H.J.; Dho, Y.S.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Park, C.K.; Kim, Y.H. Recurrence Rate and Prognostic Factors for the Adult Craniopharyngiomas in Long-Term Follow-Up. World Neurosurg. 2020, 133, e211–e217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serbis, A.; Tsinopoulou, V.R.; Papadopoulou, A.; Kolanis, S.; Sakellari, E.I.; Margaritis, K.; Litou, E.; Ntouma, S.; Giza, S.; Kotanidou, E.P.; et al. Predictive Factors for Pediatric Craniopharyngioma Recurrence: An Extensive Narrative Review. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šteňo, J.; Bízik, I.; Šteňo, A.; Matejčík, V. Recurrent Craniopharyngiomas in Children and Adults: Long-Term Recurrence Rate and Management. Acta Neurochir. 2014, 156, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuny, T.; Reynaud, R.; Raverot, G.; Coutant, R.; Chanson, P.; Kariyawasam, D.; Poitou, C.; Thomas-Teinturier, C.; Baussart, B.; Samara-Boustani, D.; et al. Diagnosis and Management of Children and Adult Craniopharyngiomas: A French Endocrine Society/French Society for Paediatric Endocrinology & Diabetes Consensus Statement. Ann. Endocrinol. 2025, 86, 101631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piloni, M.; Gagliardi, F.; Bailo, M.; Losa, M.; Boari, N.; Spina, A.; Mortini, P. Craniopharyngioma in Pediatrics and Adults. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2023, 1405, 299–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossu, G.; Ramsay, D.S.C.; Daniel, R.T.; El Cadhi, A.; Kerherve, L.; Morlaix, E.; Houidi, S.A.; Millot-Piccoli, C.; Chapon, R.; Le Van, T.; et al. Update on Neoadjuvant and Adjuvant BRAF Inhibitors in Papillary Craniopharyngioma: A Systematic Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brastianos, P.K.; Shankar, G.M.; Gill, C.M.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Nayyar, N.; Panka, D.J.; Sullivan, R.J.; Frederick, D.T.; Abedalthagafi, M.; Jones, P.S.; et al. Dramatic Response of BRAF V600E Mutant Papillary Craniopharyngioma to Targeted Therapy. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108, djv310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brastianos, P.K.; Twohy, E.; Geyer, S.; Gerstner, E.R.; Kaufmann, T.J.; Tabrizi, S.; Kabat, B.; Thierauf, J.; Ruff, M.W.; Bota, D.A.; et al. BRAF–MEK Inhibition in Newly Diagnosed Papillary Craniopharyngiomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Akutsu, H.; Takano, S.; Kino, H.; Ishikawa, E.; Tanaka, S.; Miyamoto, H.; Sakamoto, N.; Hattori, K.; Sakata-Yanagimoto, M.; et al. Clinical and Biological Significance of Adamantinomatous Craniopharyngioma with CTNNB1 Mutation. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 131, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Deng, J.; Tang, X.; Liu, F.; Huang, J.; Chen, H.; Liang, R.; Zan, X.; et al. Characterization of Novel CTNNB1 Mutation in Craniopharyngioma by Whole-Genome Sequencing. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apps, J.R.; Stache, C.; Gonzalez-Meljem, J.M.; Gutteridge, A.; Chalker, J.; Jacques, T.S.; Forshew, T.; Hölsken, A.; Martinez-Barbera, J.P. CTNNB1 Mutations Are Clonal in Adamantinomatous Craniopharyngioma. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2020, 46, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, G.; Yuan, X.; Yuan, J.; Krumtally, N.A.; Li, Y.; Feng, C.; Liu, Q.; Peng, Z.; Li, X.; Ding, X. Pituitary Stalk Management during the Microsurgery of Craniopharyngiomas. Exp. Ther. Med. 2014, 7, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobeff, E.J.; Mathios, D.; Mistry, A.A.; Dobri, G.A.; Souweidane, M.M.; Anand, V.K.; Tabaee, A.; Kacker, A.; Greenfield, J.P.; Schwartz, T.H. Predictors of Extent of Resection and Recurrence Following Endoscopic Endonasal Resection of Craniopharyngioma. J. Neurosurg. 2023, 139, 1235–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, S.; Hide, T.; Shinojima, N. Surgical Outcomes of Endoscopic Endonasal Skull Base Surgery of Craniopharyngiomas Evaluated According to the Degree of Hypothalamic Extension. World Neurosurg. 2017, 100, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.S.; Thamboo, A.; Quon, J.; Nayak, J.V.; Hwang, P.H.; Edwards, M.; Patel, Z.M. Outcomes After Endoscopic Endonasal Resection of Craniopharyngiomas in the Pediatric Population. World Neurosurg. 2017, 108, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.R.; Kshettry, V.R.; Farrell, C.J.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, Y.H.; Bin Won, T.; Han, D.H.; Do, H.; Nyguist, G.; Rosen, M.; et al. Clinical Outcome After Extended Endoscopic Endonasal Resection of Craniopharyngiomas: Two-Institution Experience. World Neurosurg. 2017, 103, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apra, C.; Enachescu, C.; Lapras, V.; Raverot, G.; Jouanneau, E. Is Gross Total Resection Reasonable in Adults with Craniopharyngiomas with Hypothalamic Involvement? World Neurosurg. 2019, 129, e803–e811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutourousiou, M.; Gardner, P.A.; Fernandez-Miranda, J.C.; Tyler-Kabara, E.C.; Wang, E.W.; Snyderman, C.H. Endoscopic Endonasal Surgery for Craniopharyngiomas: Surgical Outcome in 64 Patients. J. Neurosurg. 2013, 119, 1194–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turel, M.K.; Tsermoulas, G.; Gonen, L.; Klironomos, G.; Almeida, J.P.; Zadeh, G.; Gentili, F. Management and Outcome of Recurrent Adult Craniopharyngiomas: An Analysis of 42 Cases with Long-Term Follow-Up. Neurosurg. Focus 2016, 41, E11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Fukuhara, N.; Yamaguchi-Okada, M.; Nishioka, H.; Takeshita, A.; Takeuchi, Y.; Inoshita, N.; Ito, J. Therapeutic Outcomes of Transsphenoidal Surgery in Pediatric Patients with Craniopharyngiomas: A Single-Center Study. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2018, 21, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dho, Y.-S.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Se, Y.-B.B.; Han, D.H.; Kim, J.H.; Park, C.-K.K.; Wang, K.-C.C.; Kim, D.G. Endoscopic Endonasal Approach for Craniopharyngioma: The Importance of the Relationship between Pituitary Stalk and Tumor. J. Neurosurg. 2018, 129, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, P.J.; Buch, V.P.; Douglas, J.E.; Parasher, A.K.; Lerner, D.K.; Alexander, E.; Workman, A.D.; Palmer, J.N.; Lang, S.S.; Kennedy, B.C.; et al. Endoscopic Endonasal Resection versus Open Surgery for Pediatric Craniopharyngioma: Comparison of Outcomes and Complications. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2019, 24, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, T.; Kamada, K.; Izumo, T.; Nagata, I. Indication and Limitations of Endoscopic Extended Transsphenoidal Surgery for Craniopharyngioma. Neurol. Med. Chir. 2014, 54, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javadpour, M.; Amoo, M.; Crimmins, D.; Caird, J.; Daly, P.; Pears, J.; Owens, C.; Capra, M.; Cody, D. Endoscopic Extended Transsphenoidal Surgery for Newly Diagnosed Paediatric Craniopharyngiomas. Child’s Nerv. Syst. 2021, 37, 1547–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.O.; Shafiq, I.; Mesfin, F.B. Craniopharyngioma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Tampa, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Ma, Z.; He, W.; Shou, X.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Qiao, N.; Zhou, X.; Cao, X.; et al. Impact of Pituitary Stalk Preservation on Tumor Recurrence/Progression and Surgically Induced Endocrinopathy After Endoscopic Endonasal Resection of Suprasellar Craniopharyngiomas. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 753944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Fan, Y.; Cen, B. Effect of Preserving the Pituitary Stalk during Resection of Craniopharyngioma in Children on the Diabetes Insipidus and Relapse Rates and Long-Term Outcomes. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2017, 28, e591–e595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.Y.; Jung, S.; Moon, K.S.; Kim, I.Y.; Kang, S.S.; Kim, J.H. Endocrinological Outcomes of Pediatric Craniopharyngiomas with Anatomical Pituitary Stalk Preservation: Preliminary Study. Pediatr. Neurosurg. 2010, 46, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, T.Y.; Jung, S.; Choi, J.E.; Moon, K.S.; Kim, I.Y.; Kang, S.S. Adult Craniopharyngiomas: Surgical Results with a Special Focus on Endocrinological Outcomes and Recurrence According to Pituitary Stalk Preservation: Clinical Article. J. Neurosurg. 2009, 111, 572–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, M.; Takayasu, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Saito, K.; Sugita, K. Bifrontal Basal Interhemispheric Approach to Craniopharyngioma Resection with or without Division of the Anterior Communicating Artery. J. Neurosurg. 1996, 84, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goudie, C.; Cullinan, N.; Villani, A.; Mathews, N.; van Engelen, K.; Malkin, D.; Irwin, M.S.; Foulkes, W.D. Retrospective Evaluation of a Decision-support Algorithm (MIPOGG) for Genetic Referrals for Children with Neuroblastic Tumors. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, 3517–3527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bobeff, E.J.; Mathios, D.; Longo, D.; Estin, J.; Joshua, S.; Tabaee, A.; Kacker, A.; Anand, V.K.; Schwartz, T.H. Reuse of Nasoseptal Flaps for Endoscopic Endonasal Skull Base Reconstruction. J. Neurol. Surg. Part B Skull Base 2023, 85, 517–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karavitaki, N.; Brufani, C.; Warner, J.T.; Adams, C.B.T.; Richards, P.; Ansorge, O.; Shine, B.; Turner, H.E.; Wass, J.A.H. Craniopharyngiomas in Children and Adults: Systematic Analysis of 121 Cases with Long-Term Follow-Up. Clin. Endocrinol. 2005, 62, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, H.L. Craniopharyngioma. Endocr. Rev. 2014, 35, 513–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yi, X.; Wang, H.; Zhao, H. An Analysis of Related Factors of Surgical Results for Patients with Craniopharyngiomas. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2012, 114, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bobeff, E.J.; Szmyd, B.M.; Shen, M.; Jaskólski, D.J.; Schwartz, T.H. The Impact of Pituitary Stalk Sacrifice on Recurrence and Endocrine Dysfunction During Craniopharyngioma Surgery: A Systematic Review of the Literature. World Neurosurg. 2025, 196, 123769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Author and Year | Children/Adults | Follow-Up [Years] | Patients | Recurrence | Recurrence After GTR | Recurrence After STR and XRT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bobeff, 2023 | Mixed | 4.8 (IQR 1.3–7) | 95 | 16 (17%) | 13% | 38% |
| Apra, 2019 | Adults | STR: 5.3 (2.1–9.9) GTR: 3.7 (1.7–9.9) | 20 | 2 (10%) | 0 | 33% |
| Madsen, 2019 | Children | 2 | 26 | 3 (12%) | 8% | 50% |
| Yamada, 2018 | Children | 7.8 (range 1.3–25.6) | 61 | 7 (11%) | 12% | 0 |
| Dho, 2018 | Adults | 2.6 | 63 | 2 (3%) | 3% | 0 |
| Yano, 2017 | Mixed | 3.3 (IQR 1.7–5.8) | 9 | 3 (33%) | 29% | 50% |
| Park, 2017 | Mixed | 2.9 (range 0.1–9.6) | 72 | 8 (11%) | 9% | 17% |
| Patel, 2017 | Children | 4.7 (range 0.1–7.5) | 15 | 2 (13%) | 7% | 100% |
| Turel, 2016 | Adult | 8.6 ± 7.1 | 26 | 7 (27%) | 0 | 32% |
| Matsuo, 2014 | NS | 3.2 (range 0.5–6.5) | 11 | 1 (9%) | 0 | 100% |
| Koutourousiou, 2013 | Mixed | 3.2 (range 0.1–11.3) | 33 | 9 (27%) | 25% | 33% |
| TOTAL | Mixed | Mean/median 2–8.6 | 431 | 60 (14%) | 10% | 30% |
| GTR | STR Plus XRT | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Children | N | 41 | 17 |
| Follow-up [years] | 2.8 (IQR: 0.9–5.0) | 2.7 (IQR: 0.7–4.2) | |
| Recurrence | 2/41 (4.9%) | 7/17 (41.2%) | |
| Adults | N | 113 | 31 |
| Follow-up [years] | 2.6 (IQR: 0.9–5.2) | 3 (IQR: 1.2–5.5) | |
| Recurrence | 13/113 (11.5%) | 6/31 (19.4%) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bobeff, E.J.; Szmyd, B.; Młynarski, W.; Jouanneau, E.; Apra, C.; Shen, M.; Patel, Z.M.; Jaskólski, D.J.; Schwartz, T.H. Comparative Outcomes of Gross Total Resection vs. Subtotal Resection Plus Radiotherapy for Preventing Craniopharyngioma Recurrence: A Meta-Analysis of the Endoscopic Endonasal Approach. Cancers 2025, 17, 2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152516
Bobeff EJ, Szmyd B, Młynarski W, Jouanneau E, Apra C, Shen M, Patel ZM, Jaskólski DJ, Schwartz TH. Comparative Outcomes of Gross Total Resection vs. Subtotal Resection Plus Radiotherapy for Preventing Craniopharyngioma Recurrence: A Meta-Analysis of the Endoscopic Endonasal Approach. Cancers. 2025; 17(15):2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152516
Chicago/Turabian StyleBobeff, Ernest J., Bartosz Szmyd, Wojciech Młynarski, Emmanuel Jouanneau, Caroline Apra, Ming Shen, Zara M. Patel, Dariusz J. Jaskólski, and Theodore H. Schwartz. 2025. "Comparative Outcomes of Gross Total Resection vs. Subtotal Resection Plus Radiotherapy for Preventing Craniopharyngioma Recurrence: A Meta-Analysis of the Endoscopic Endonasal Approach" Cancers 17, no. 15: 2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152516
APA StyleBobeff, E. J., Szmyd, B., Młynarski, W., Jouanneau, E., Apra, C., Shen, M., Patel, Z. M., Jaskólski, D. J., & Schwartz, T. H. (2025). Comparative Outcomes of Gross Total Resection vs. Subtotal Resection Plus Radiotherapy for Preventing Craniopharyngioma Recurrence: A Meta-Analysis of the Endoscopic Endonasal Approach. Cancers, 17(15), 2516. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152516








