The Kinase Inhibitor GNF-7 Is Synthetically Lethal in Topoisomerase 1-Deficient Ewing Sarcoma
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Genome-Scale CRISPR-Cas9 Knockout (GeCKO) Library Screen
2.3. Lentiviral Infection
2.4. Protein Isolation and Western Blotting
2.5. Cell Confluence Assays
2.6. Synergy Assay
2.7. Cell Doubling Time
2.8. Exome Sequencing
2.9. RNA Sequencing
2.10. RNA-Seq and Exome-Seq Data Analysis
2.11. Quantitative High-Throughput Combination Screening (qHTCS)
2.12. Capillary Immunoassays
2.13. Cell Proliferation and Apoptosis Induction Assays
2.14. Cell Cycle Analysis
2.15. Fluorescent Cell Cycle Reporter Assay
2.16. In Situ Kinase Selectivity Profiling (KiNativ™)
2.17. siRNA Kinome Screen
2.18. Immunofluorescence Staining and Microscopy
2.19. Immunohistochemistry and H&E Staining
2.20. Animal Models
2.21. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
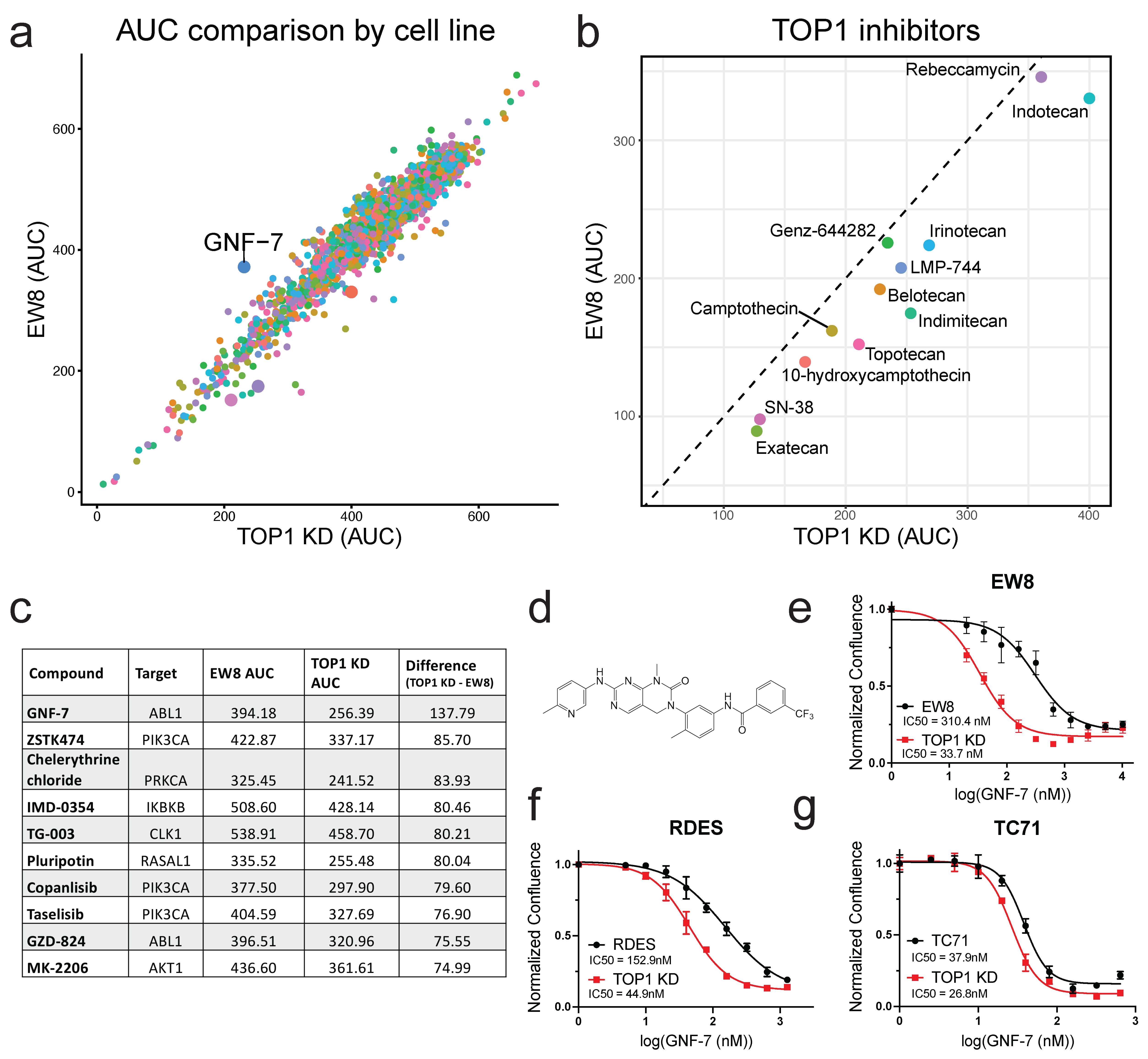
3.1. TOP1 Knockdown Confers Resistance to TOP1 Inhibitors in ES Cells
3.2. Small-Molecule Screening Identifies GNF-7 as Having Increased Potency in TOP1-Deficient Cells
3.3. GNF-7 Increases G1 Arrest and Inhibits the EWS/FLI1 Gene Signature
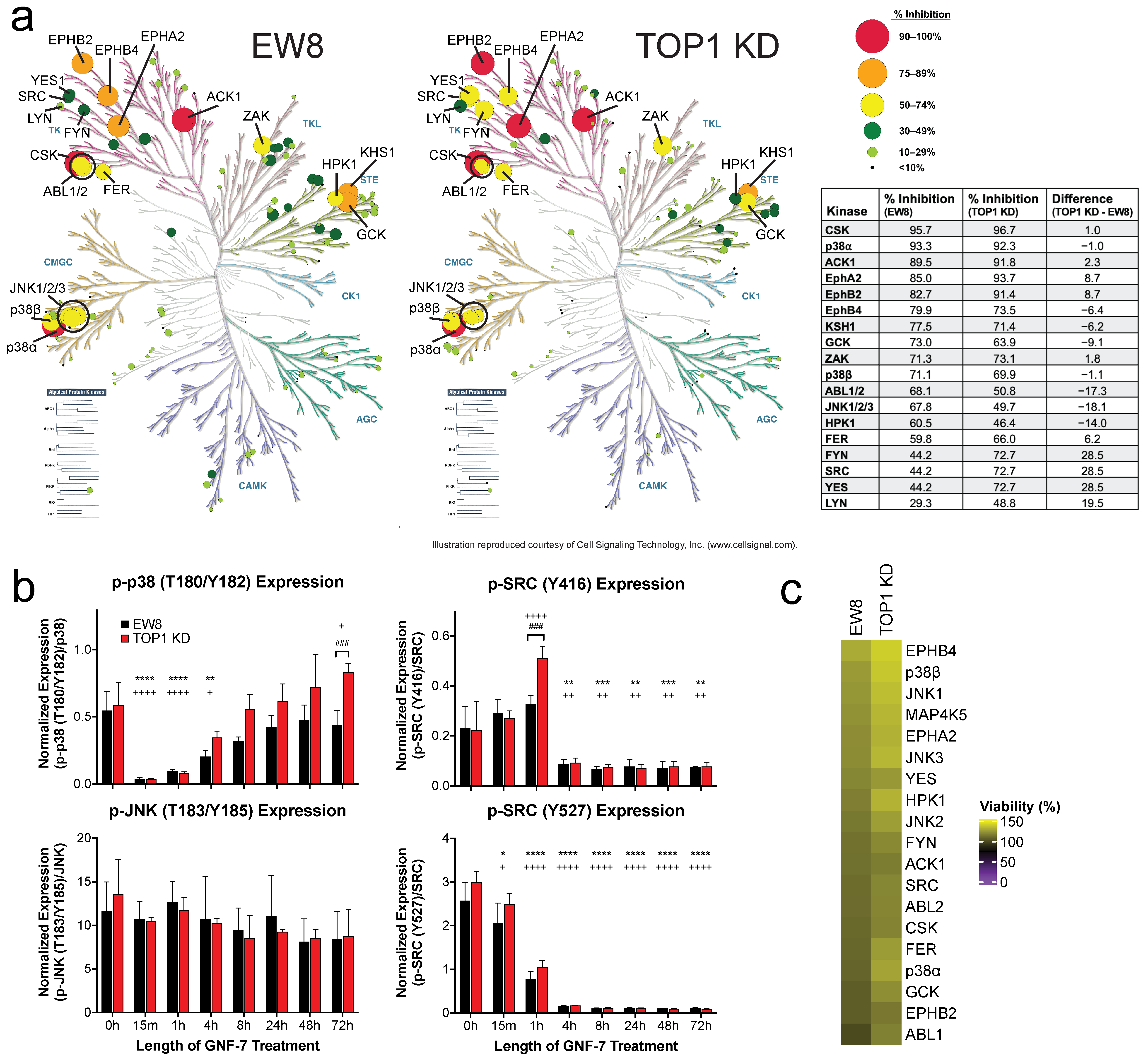
3.4. GNF-7 Inhibits Multiple Kinases
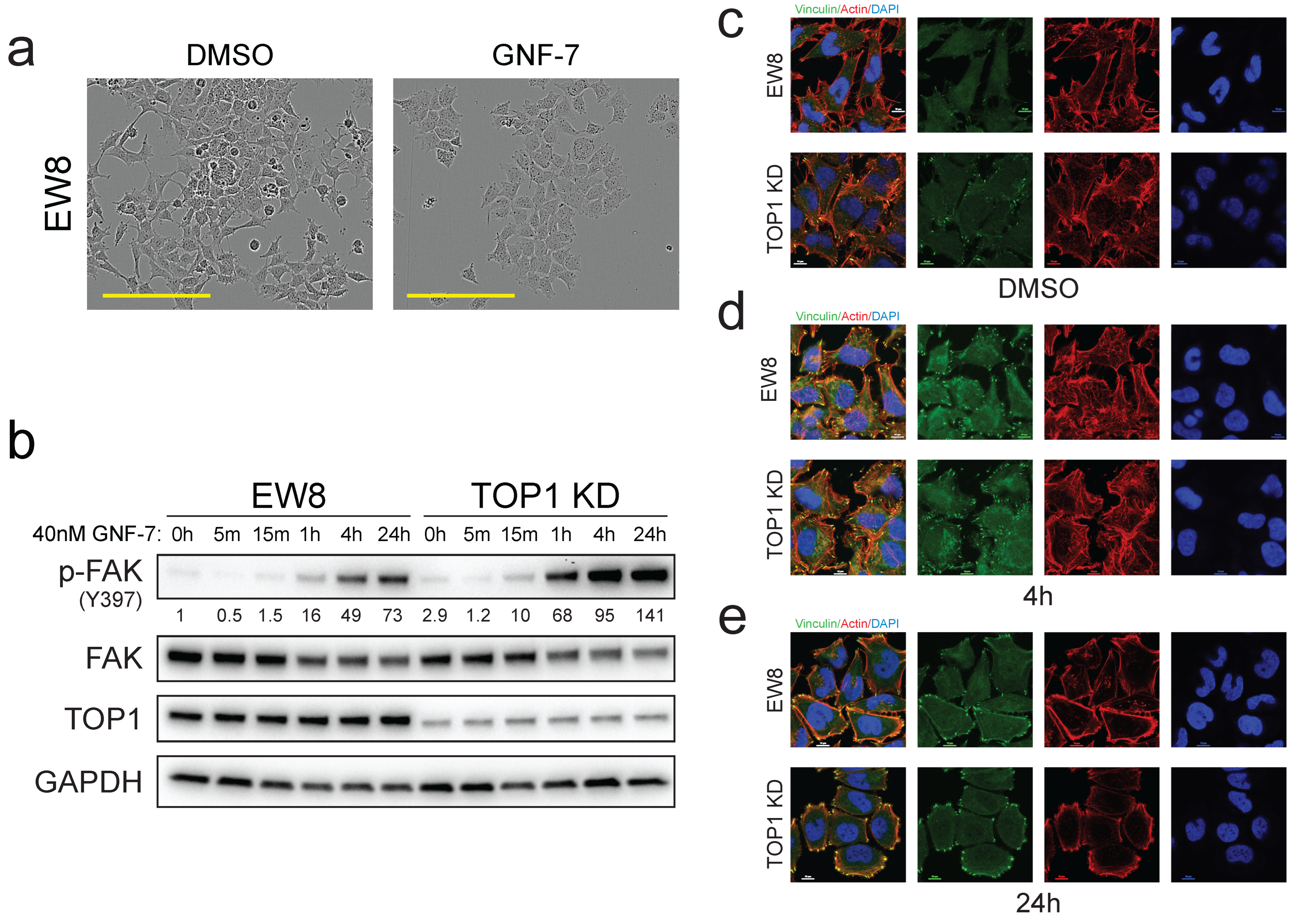
3.5. GNF-7 Induces FAK Activation and Focal Adhesion Formation
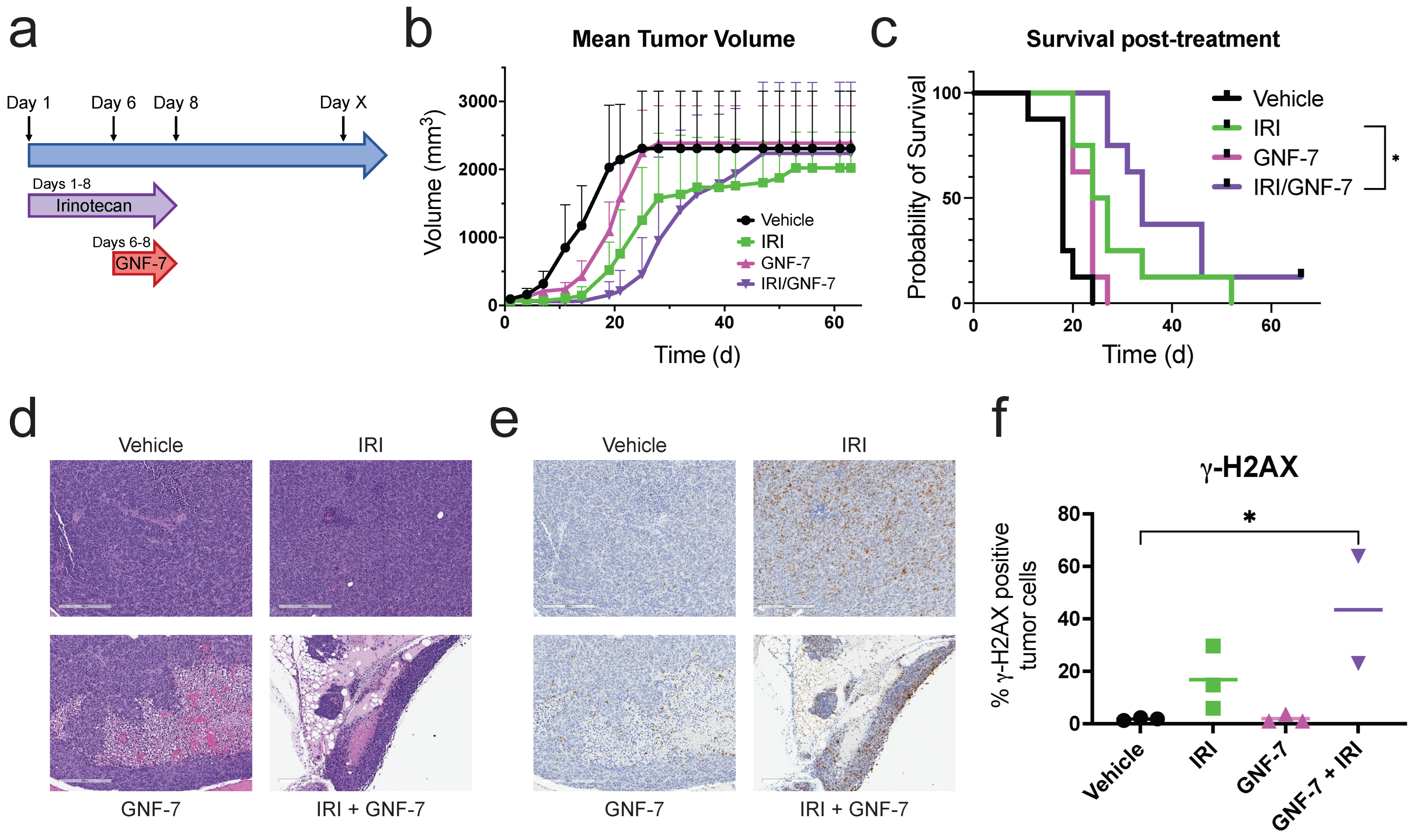
3.6. Combination Treatment of GNF-7 and a TOP1 Inhibitor Extends Survival In Vivo
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kolb, E.A.; Kushner, B.H.; Gorlick, R.; Laverdiere, C.; Healey, J.H.; LaQuaglia, M.P.; Huvos, A.G.; Qin, J.; Vu, H.T.; Wexler, L.; et al. Long-term event-free survival after intensive chemotherapy for Ewing’s family of tumors in children and young adults. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 3423–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, M.; Ranft, A.; Paulussen, M.; Bolling, T.; Vieth, V.; Bielack, S.; Gortitz, I.; Braun-Munzinger, G.; Hardes, J.; Jurgens, H.; et al. Risk of recurrence and survival after relapse in patients with Ewing sarcoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2011, 57, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Dietz, M.S.; Riedel, R.F.; Dhir, A.; Borinstein, S.C.; Isakoff, M.S.; Aye, J.M.; Rainusso, N.; Armstrong, A.E.; DuBois, S.G.; et al. Consensus recommendations for systemic therapies in the management of relapsed Ewing sarcoma: A report from the National Ewing Sarcoma Tumor Board. Cancer 2024, 130, 4028–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommier, Y.; Pourquier, P.; Fan, Y.; Strumberg, D. Mechanism of action of eukaryotic DNA topoisomerase I and drugs targeted to the enzyme. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1400, 83–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pommier, Y.; Redon, C.; Rao, V.A.; Seiler, J.A.; Sordet, O.; Takemura, H.; Antony, S.; Meng, L.; Liao, Z.; Kohlhagen, G.; et al. Repair of and checkpoint response to topoisomerase I-mediated DNA damage. Mutat. Res. 2003, 532, 173–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiang, Y.-H.; Liu, L.F. Identification of Mammalian DNA Topoisomerase I as an Intracellular Target of the Anticancer Drug Camptothecin. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 1722–1726. [Google Scholar]
- Wright, C.M.; van der Merwe, M.; DeBrot, A.H.; Bjornsti, M.A. DNA topoisomerase I domain interactions impact enzyme activity and sensitivity to camptothecin. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 12068–12078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.C.; Xiao, B.Y.; Lin, G.H. Irinotecan plus temozolomide in relapsed Ewing sarcoma: An integrated analysis of retrospective studies. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.Y.; Yu, C.; Potmesil, M.; Wall, M.E.; Wani, M.C.; Liu, L.F. Camptothecin Overcomes MDR1-mediated Resistance in Human KB Carcinoma Cells. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 6039–6044. [Google Scholar]
- Kawabata, S.; Oka, M.; Shiozawa, K.; Tsukamoto, K.; Nakatomi, K.; Soda, H.; Fukuda, M.; Ikegami, Y.; Sugahara, K.; Yamada, Y.; et al. Breast Cancer Resistance Protein Directly Confers SN-38 Resistance of Lung Cancer Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 280, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsurutani, J.; Nitta, T.; Hirashima, T.; Komiya, T.; Uejima, H.; Tada, H.; Syunichi, N.; Tohda, A.; Fukuoka, M.; Nakagawa, K. Point mutations in the topoisomerase I gene in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with irinotecan. Lung Cancer 2002, 35, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelman, R.O.; Wu, B.; Barnes, H.; Medford, A.; Norden, B.; Putur, A.; Bitman, E.; Thant, W.; Liu, T.; Weipert, C.; et al. TOP1 Mutations and Cross-Resistance to Antibody–Drug Conjugates in Patients with Metastatic Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2025, 31, 1966–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, N.F.; Agama, K.; Roy, A.; Smith, D.H.; Pfister, T.D.; Rømer, M.U.; Zhang, H.-L.; Doroshow, J.H.; Knudsen, B.R.; Stenvang, J.; et al. Characterization of DNA topoisomerase I in three SN-38 resistant human colon cancer cell lines reveals a new pair of resistance-associated mutations. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woessner, R.D.; Eng, W.K.; Hofmann, G.A.; Rieman, D.J.; McCabe, F.L.; Hertzberg, R.P.; Mattern, M.R.; Tan, K.B.; Johnson, R.K. Camptothecin hyper-resistant P388 cells: Drug-dependent reduction in topoisomerase I content. Oncol. Res. 1992, 4, 481–488. [Google Scholar]
- Yanase, K.; Sugimoto, Y.; Tsukahara, S.; Oh-hara, T.; Andoh, T.; Tsuruo, T. Identification and Characterization of a Deletion Mutant of DNA Topoisomerase I mRNA in a Camptothecin-resistant Subline of Human Colon Carcinoma. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 2000, 91, 551–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, R.; Slade, D.L.; Fujimori, A.; Pommier, Y.; Harker, W.G. Altered topoisomerase I expression in two subclones of human CEM leukemia selected for resistance to camptothecin. Oncol. Res. 1995, 7, 83–95. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Z.; Robey, R.W.; Guirouilh-Barbat, J.; To, K.K.W.; Polgar, O.; Bates, S.E.; Pommier, Y. Reduced Expression of DNA Topoisomerase I in SF295 Human Glioblastoma Cells Selected for Resistance to Homocamptothecin and Diflomotecan. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 490–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.G.; Ren, P.; Adrian, F.; Sun, F.; Lee, H.S.; Wang, X.; Ding, Q.; Zhang, G.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. A Type-II Kinase Inhibitor Capable of Inhibiting the T315I “Gatekeeper” Mutant of Bcr-Abl. J. Med. Chem. 2010, 53, 5439–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orth, M.F.; Surdez, D.; Faehling, T.; Ehlers, A.C.; Marchetto, A.; Grossetete, S.; Volckmann, R.; Zwijnenburg, D.A.; Gerke, J.S.; Zaidi, S.; et al. Systematic multi-omics cell line profiling uncovers principles of Ewing sarcoma fusion oncogene-mediated gene regulation. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 111761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, J.; Konermann, S.; Gootenberg, J.S.; Abudayyeh, O.O.; Platt, R.J.; Brigham, M.D.; Sanjana, N.E.; Zhang, F. Genome-scale CRISPR-Cas9 knockout and transcriptional activation screening. Nat. Protoc. 2017, 12, 828–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjana, N.E.; Shalem, O.; Zhang, F. Improved vectors and genome-wide libraries for CRISPR screening. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 783–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Xu, H.; Xiao, T.; Cong, L.; Love, M.I.; Zhang, F.; Irizarry, R.A.; Liu, J.S.; Brown, M.; Liu, X.S. MAGeCK enables robust identification of essential genes from genome-scale CRISPR/Cas9 knockout screens. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ianevski, A.; Giri, A.K.; Aittokallio, T. SynergyFinder 2.0: Visual analytics of multi-drug combination synergies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, W488–W493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Tamayo, P.; Mootha, V.K.; Mukherjee, S.; Ebert, B.L.; Gillette, M.A.; Paulovich, A.; Pomeroy, S.L.; Golub, T.R.; Lander, E.S.; et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: A knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15545–15550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang da, W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.L.; Wilson, K.M.; Ceribelli, M.; Stanton, B.Z.; Woo, P.J.; Kreimer, S.; Qin, E.Y.; Zhang, X.; Lennon, J.; Nagaraja, S.; et al. Therapeutic strategies for diffuse midline glioma from high-throughput combination drug screening. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaaw0064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathews Griner, L.A.; Guha, R.; Shinn, P.; Young, R.M.; Keller, J.M.; Liu, D.; Goldlust, I.S.; Yasgar, A.; McKnight, C.; Boxer, M.B.; et al. High-throughput combinatorial screening identifies drugs that cooperate with ibrutinib to kill activated B-cell–like diffuse large B-cell lymphoma cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2349–2354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, S.; Fang, L.; McGowen, K.; Yin, J.; Bowman, J.; Ku, A.T.; Alilin, A.N.; Corey, E.; Roudier, M.P.; True, L.D.; et al. Tumor-derived biomarkers predict efficacy of B7H3 antibody-drug conjugate treatment in metastatic prostate cancer models. J. Clin. Investig. 2023, 133, e162148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patricelli, M.P.; Szardenings, A.K.; Liyanage, M.; Nomanbhoy, T.K.; Wu, M.; Weissig, H.; Aban, A.; Chun, D.; Tanner, S.; Kozarich, J.W. Functional Interrogation of the Kinome Using Nucleotide Acyl Phosphates. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, S.; Turk, S.; Volkamer, A.; Rippmann, F.; Fulle, S. KinMap: A web-based tool for interactive navigation through human kinome data. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mootha, V.K.; Lindgren, C.M.; Eriksson, K.-F.; Subramanian, A.; Sihag, S.; Lehar, J.; Puigserver, P.; Carlsson, E.; Ridderstråle, M.; Laurila, E.; et al. PGC-1α-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2003, 34, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houghton, P.J.; Stewart, C.F.; Cheshire, P.J.; Richmond, L.B.; Kirstein, M.N.; Poquette, C.A.; Tan, M.; Friedman, H.S.; Brent, T.P. Antitumor activity of temozolomide combined with irinotecan is partly independent of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase and mismatch repair phenotypes in xenograft models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 4110–4118. [Google Scholar]
- Gongora, C.; Vezzio-Vie, N.; Tuduri, S.; Denis, V.; Causse, A.; Auzanneau, C.; Collod-Beroud, G.; Coquelle, A.; Pasero, P.; Pourquier, P.; et al. New Topoisomerase I mutations are associated with resistance to camptothecin. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.D.; Li, T.K.; Rodriguez-Bauman, A.; Rubin, E.H.; Liu, L.F. Ubiquitin/26S proteasome-mediated degradation of topoisomerase I as a resistance mechanism to camptothecin in tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 5926–5932. [Google Scholar]
- Bates, S.E.; Medina-Perez, W.Y.; Kohlhagen, G.; Antony, S.; Nadjem, T.; Robey, R.W.; Pommier, Y. ABCG2 mediates differential resistance to SN-38 (7-ethyl-10-hydroxycamptothecin) and homocamptothecins. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 310, 836–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsherniak, A.; Vazquez, F.; Montgomery, P.G.; Weir, B.A.; Kryukov, G.; Cowley, G.S.; Gill, S.; Harrington, W.F.; Pantel, S.; Krill-Burger, J.M.; et al. Defining a Cancer Dependency Map. Cell 2017, 170, 564–576.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinestel, K.; Trautmann, M.; Jansen, E.P.; Dirksen, U.; Rehkamper, J.; Mikesch, J.H.; Gerke, J.S.; Orth, M.F.; Sannino, G.; Arteaga, M.F.; et al. Focal adhesion kinase confers pro-migratory and antiapoptotic properties and is a potential therapeutic target in Ewing sarcoma. Mol. Oncol. 2020, 14, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, K.; Bruce, B.; Hewitt, S.; Thomas, D.; Khanna, C.; Helman, L.J. Ezrin mediates growth and survival in Ewing’s sarcoma through the AKT/mTOR, but not the MAPK, signaling pathway. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2006, 23, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonami, A.; Sattler, M.; Weisberg, E.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Patricelli, M.P.; Christie, A.L.; Saur, A.M.; Kohl, N.E.; Kung, A.L.; et al. Identification of novel therapeutic targets in acute leukemias with NRAS mutations using a pharmacologic approach. Blood 2015, 125, 3133–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Hu, L.; Shi, S.-N.; Chen, X.; Zhuang, C.; Zhang, W.; Jitkaew, S.; Pang, X.; Yu, J.; Tan, Y.-X.; et al. The Bcr-Abl inhibitor GNF-7 inhibits necroptosis and ameliorates acute kidney injury by targeting RIPK1 and RIPK3 kinases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 113947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.-H.; Shin, I.; Kim, N.; Nam, Y.; Sim, T. The first small molecules capable of strongly suppressing proliferation of cancer cells harboring BRAF class I/II/III mutations. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 532, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.; Shin, I.; Lee, J.; Jeon, E.; Kim, Y.; Ryu, S.; Ju, E.; Cho, W.; Sim, T. Novel and Potent Small Molecules against Melanoma Harboring BRAF Class I/II/III Mutants for Overcoming Drug Resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkizan, H.V.; Uversky, V.N.; Toretsky, J.A. Oncogenic partnerships: EWS-FLI1 protein interactions initiate key pathways of Ewing’s sarcoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 4077–4083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolotti, A.; Melot, T.; Acker, J.; Vigneron, M.; Delattre, O.; Tora, L. EWS, but not EWS-FLI-1, is associated with both TFIID and RNA polymerase II: Interactions between two members of the TET family, EWS and hTAFII68, and subunits of TFIID and RNA polymerase II complexes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 1489–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, X.; Pan, X.; Wang, D.; Zhuang, X.; Luo, J.; Yu, R.; Ding, K. Hybrid pyrimidine alkynyls inhibit the clinically resistance related Bcr-Abl(T315I) mutant. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 3458–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Shin, I.; Ju, E.; Choi, S.; Hur, W.; Kim, H.; Hong, E.; Kim, N.D.; Choi, H.G.; Gray, N.S.; et al. First SAR Study for Overriding NRAS Mutant Driven Acute Myeloid Leukemia. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 8353–8373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crompton, B.D.; Carlton, A.L.; Thorner, A.R.; Christie, A.L.; Du, J.; Calicchio, M.L.; Rivera, M.N.; Fleming, M.D.; Kohl, N.E.; Kung, A.L.; et al. High-throughput tyrosine kinase activity profiling identifies FAK as a candidate therapeutic target in Ewing sarcoma. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 2873–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bierbaumer, L.; Katschnig, A.M.; Radic-Sarikas, B.; Kauer, M.O.; Petro, J.A.; Hogler, S.; Gurnhofer, E.; Pedot, G.; Schafer, B.W.; Schwentner, R.; et al. YAP/TAZ inhibition reduces metastatic potential of Ewing sarcoma cells. Oncogenesis 2021, 10, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sayers, C.M.; Carter, M.B.; Lei, H.; Mendoza, A.; Shema, S.; Zhang, X.; Wilson, K.; Chen, L.; Klumpp-Thomas, C.; Thomas, C.J.; et al. The Kinase Inhibitor GNF-7 Is Synthetically Lethal in Topoisomerase 1-Deficient Ewing Sarcoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 2475. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152475
Sayers CM, Carter MB, Lei H, Mendoza A, Shema S, Zhang X, Wilson K, Chen L, Klumpp-Thomas C, Thomas CJ, et al. The Kinase Inhibitor GNF-7 Is Synthetically Lethal in Topoisomerase 1-Deficient Ewing Sarcoma. Cancers. 2025; 17(15):2475. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152475
Chicago/Turabian StyleSayers, Carly M., Morgan B. Carter, Haiyan Lei, Arnulfo Mendoza, Steven Shema, Xiaohu Zhang, Kelli Wilson, Lu Chen, Carleen Klumpp-Thomas, Craig J. Thomas, and et al. 2025. "The Kinase Inhibitor GNF-7 Is Synthetically Lethal in Topoisomerase 1-Deficient Ewing Sarcoma" Cancers 17, no. 15: 2475. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152475
APA StyleSayers, C. M., Carter, M. B., Lei, H., Mendoza, A., Shema, S., Zhang, X., Wilson, K., Chen, L., Klumpp-Thomas, C., Thomas, C. J., Heske, C. M., & Shern, J. F. (2025). The Kinase Inhibitor GNF-7 Is Synthetically Lethal in Topoisomerase 1-Deficient Ewing Sarcoma. Cancers, 17(15), 2475. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers17152475





